Propagation of hydrangea
Studying how indoor hydrangea reproduces, do not forget about varietal characteristics. There are varieties that reproduce in only one way. Nevertheless, the vast majority of subspecies can be propagated:
By dividing the root system. The procedure is performed at the time of transplantation. Delenki must have a growing point and a powerful root. For successful completion of the work, it is necessary to shorten the roots and shoots. Full rooting of the divisions occurs by autumn, and the next year the plant blooms. When dividing the bush, all the properties of the mother plant are preserved.
Seeds. This method is performed in the winter. Seeds are sown in February in a composition of turf, garden soil and humus, taken in equal quantities. It is necessary to sow hydrangea superficially, cover the crops with plastic wrap. Greenhouses are ventilated and sprayed daily. At the first emergence of seedlings, the crops are opened and moved to a bright place. As soon as the hydrangea forms 2-3 leaves, it is dived into separate pots with a diameter of 5-7 cm.
Cuttings. For the implementation of the technique, cut off root cuttings 8 cm long with 3 internodes in February. The leaves are shortened by 2/3, and the bottom is cut off altogether. Places of cuts are treated with special preparations for the formation of a root system and planted in a substrate of sand and peat. The planted specimens are kept at a temperature of 20 degrees in the brightest place. The rooting period lasts 3-4 weeks.
Cuttings
For grafting you need to prepare:
- sterile secateurs;
- the drug Kornevin;
- planting substrate (clean sand or infertile soil);
- small low pot;
- shelter (cellophane, cut plastic bottle, etc.);
- a spray bottle with warm water;
- turmeric or charcoal powder for processing slices.
Step-by-step process of grafting:
Cut off the selected green stalk.
Carefully cut off the chosen twig
We make a cut under the lower kidney.
Cut off the stalk under the lower bud
We also cut off part of the branch above the upper bud.
Cut off the top above the upper kidney
Cut off the excess lower leaves.
The lower leaves of the cuttings are now useless
Cut the remaining leaves by about half to reduce water evaporation
Leaves should be trimmed by about half.
We dip the lower cut into Kornevin and place the lower part of the cutting slightly at an angle into a dry substrate by 1.5–2 cm. If you are planting several cuttings, the leaves should not touch the soil and each other.
We stick the cutting into the substrate
We moisten the substrate abundantly from a spray bottle with warm water.
Wet the substrate abundantly with water
Powder the slices with turmeric or charcoal, cover the cuttings and put them in a shady, cool place for a month.
Cover the cuttings to preserve moisture
- it is necessary to check the condition of the substrate 1-2 times a week and spray it so that it does not dry out;
- the optimum temperature for rooting is 18–25 ° C;
- a month and a half after rooting, the cuttings are planted in a more nutritious mixture (one per pot). Can be planted in regular hydrangea soil;
- for winter, cuttings are prepared for rest, like ordinary hydrangeas;
- in the spring, fertilize or spray the cuttings with nitrogen fertilizer for better growth until June 1 time per week;
- in May of the following year, after planting, the cutting can be cut by 2/3 for better branching.
Given the short lifespan, they propagate while the mother plant has not died out. Three methods are used for reproduction.
When carrying out autumn pruning, long cuttings are not thrown away. They are good for rooting. The most acceptable length of the process is 8 - 10 cm. It should have 2 - 3 buds.Before planting, the base of the cutting is treated with a growth stimulant, the lower leaves are cut off, and the upper ones are shortened. The stems are planted in peat under a jar, providing high humidity and good lighting. When new leaves begin to appear on the stem, the jar is removed daily for 2 hours, and with the arrival of spring, they are removed altogether.
An adult specimen at 3-4 years of age is suitable for this method. During the transplant, it is divided into several parts.
It is important not to damage the delicate roots, otherwise new plants will grow poorly. After transplanting, all specimens are watered with "Kornevin"
This method is the easiest and gives good results.
You can grow a flower from a bag of seeds.
The container is covered with glass
It is important that the soil is constantly moist. If it dries up, the seeds will not germinate.
When the first shoots appear on the surface, the glass is removed. Youngsters dive when real leaves appear.
Tips for choosing materials
The materials for the foundation will depend on the functionality, labor intensity, and cost of the foundation. Consider all types of foundations that are suitable for a polycarbonate greenhouse:
-
The foundation-frame is made of a bar, which is connected at the corners end-to-end or "in a paw" and placed on a sand-crushed stone pillow (filled into a depression from the removed fertile layer) and waterproofing. Pros: It's quick and easy. Cons: even with a good antiseptic and hydrophobic impregnation, it is short-lived.
-
Monolithic "tape" - is poured into the formwork on the sand-crushed stone drainage mixture either on the ground with the fertile layer removed (unburied foundation), or in a shallow trench (shallow), waterproofing is attached on top. Ready-made concrete or self-mixed cement mortar is used. The most versatile and quickest base in construction: it can be used on almost any soil. But it hardens for a long time.
-
A prefabricated "tape" of blocks connected with a solution is laid on a sand-crushed stone drainage mixture either on the ground with a fertile layer removed (unburied foundation), or in a shallow trench (shallow), waterproofing is attached on top. It is quickly constructed and relatively inexpensive: the price depends on the type of blocks - expanded clay and cinder blocks are cheaper, foam and aerated concrete blocks are more expensive. It is used for all soils.
-
The prefabricated "tape" made of bricks is more difficult to lay. Such a foundation will cost more than a block foundation. He needs a screed (concrete base), which complicates the process and lengthens the construction time. But it is beautiful and does not need plastering. Waterproofing is placed on top... It is laid in any soil.
-
A shallow columnar foundation of blocks connected with mortar is erected quickly. It will be inexpensive. But under it you need to dig a large number of identical neat marked pits. The blocks are placed in pits on the drainage mixture and connected with a grillage (for a greenhouse, a wooden grillage from a bar will be enough). Waterproofing is placed on top. It is used in almost all soils, but it is preferable for marshy and quicksands.
-
A shallow columnar foundation made of bricks on mortar is similar to the same block, but more expensive, and its installation is technically more difficult.
-
An unsubmerged columnar foundation made of concrete blocks is the easiest to manufacture from the above: blocks one by one or two / four (connected with mortar) are laid on a sand-crushed stone mixture on the ground with a fertile layer removed, or simply on the ground, connected with a grillage or strapping. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is used for hard soils.
-
A pile foundation made of pipes (metal and asbestos-cement) needs to be connected with a strong grillage, which complicates its construction. The number of supports and pits is much greater here. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is preferable to use on marshy soils and quicksands.
-
A prefabricated strip foundation made of heavy concrete slabs connected with mortar can be installed quickly, but only with the help of heavy machinery. If it is shallow, then the walls of the greenhouse will have to be additionally insulated. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is used for all soils.
-
Metal screw piles are reliable but expensive. When screwing them in, skills and special devices are needed. Such a foundation needs a serious, strong grillage. If it is made of metal, it will cost even more, and welding will be required for installation. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is preferable to apply on marshy soils and quicksands.
-
A monolithic slab is the most labor-intensive and material-intensive foundation. For a shallow slab, a large pit is dug, and for an unburied slab, a fertile layer is removed. A sand-crushed stone pillow is made, reinforcement is laid. Waterproofing is laid on top. It is applied on any soil. Cons: completely covers the layer of the earth. The fashion for a monolith came from the West - there in greenhouses they always arrange a floor and capital shelves.
For a small polycarbonate greenhouse, it is better to choose a shallow monolithic strip foundation. It is easier to dig a shallow trench on the markings than deep separate pits for concrete "pillars". If you plan to use the greenhouse in winter, then it is advisable to insulate the foundation.
The following materials will be required:
Varieties of wooden frames
As already noted, the tree allows you to make a structure of any size and shape, so the variety of wooden greenhouses is amazing. Among them there are some options that combine functionality and ease of construction.

These include:
- Frame with a gable roof. The most popular and simplest option. It looks like a rectangle and a roof with a slope of no more than 30 °. Film and glass are suitable for their shelter. It is not profitable to use polycarbonate, as a lot of residues are obtained.
- Arched type. This design is the most efficient in terms of heating (there is no stagnation of air in the corners), which means that it is easier to maintain the optimal temperature. It is best to use polycarbonate to cover it.
- Shed roof. This type of construction is most suitable as a wall structure, which allows for good thermal insulation. Its installation is very simple, since the base is attached to the capital structure. Any material can be used for cover.
- Ball construction. It is difficult to mount a round structure, since there are many details and joints. But on the other hand, such a structure is well lit, it is easy to heat it. The frame can be covered with foil or polycarbonate.
- Meatlider design. The frame has a shape similar to a simple gable greenhouse, but its slopes do not close in the ridge and have a different angle of inclination.
How to build your greenhouse for polycarbonate
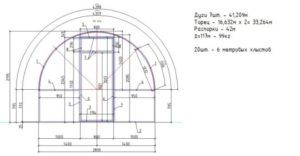 Drawing of an arched polycarbonate greenhouse
Drawing of an arched polycarbonate greenhouse
Film and glass can be used as covering materials for your greenhouse. The main disadvantage of the film is its fragility. This coating will have to be changed annually. Glass significantly increases the weight of the structure. Therefore, polycarbonate is most often used - a light material that is much stronger and cheaper than glass.
At the preparatory stage, it is necessary to draw up drawings of the greenhouse and study the diagram. On their basis, calculations of the amount of building materials are made, and then the structure is erected.
For the construction of a greenhouse, a site is prepared for the foundation. Their greenhouses with a timber frame are installed on a concrete or wooden base. Along the perimeter of the future building, strapping is performed with a beam of 120x20 mm thick. Wooden beams are pre-treated with an antiseptic solution and bitumen mastic. A frame is erected on the prepared base.
Frame preparation
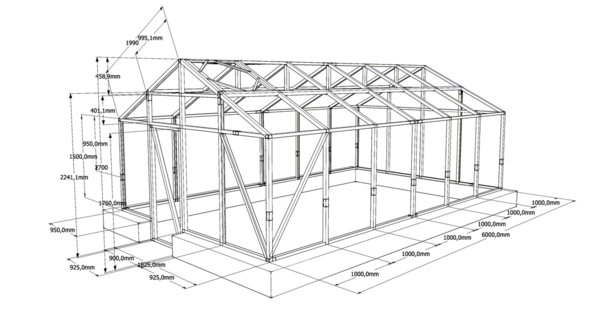
 Greenhouse frame structures
Greenhouse frame structures
To make a greenhouse for polycarbonate, you will need to prepare wooden blocks with a size of 450x450 mm. In the considered option, the size of the greenhouse will be 8x2.8 meters. To increase the strength of the structure, you need to ensure that the distance between the posts does not exceed 1 meter. The best option is 0.7 m.
All elements of their structure are fastened to each other with metal corners and self-tapping screws. The bars are hammered into the ground, strapping strips are attached to them. The use of metal plates will allow you to ensure a tight fit of the joints at the frame of your greenhouse.
A sheet of polycarbonate is thrown over the roof, secured with self-tapping screws and washers. Each sheet is overlapped. The end parts are closed with a plastic corner, the edges are treated with a sealant.
After laying and fixing all the sheets, their greenhouse made of wood, created by the hands of an amateur master, is treated with an antiseptic solution and painted.
Assembling the belt-type structure
Before installing the structure, do the following:
- Decide on a place. A flat, sunny area without strong drafts is ideal for setting up a greenhouse.
- Design the size and type of structure. Draw up a drawing. The dimensions of the foundation frame from a bar directly depend on this.
- Level the pads.
- Make the markup for future installation. To help - pegs and strings. Mark the corners with hammered stakes. Place a few more along the thread between them, with an interval of 10-20 cm. Duplicate the markings along the width of the future trench.
Now start digging the ditch. The thickness is 7-8 cm, the depth is 5 cm more than the section of the bar. Fill the bottom with a layer of sand or gravel. Then cover the bottom and walls with roofing felt. Place the pre-sized pieces of wood. Connect them to each other by the method "in a paw" or "in half a tree". To do this, you must first make suitable cuts at the ends.

Fasten the timber with galvanized corners, self-tapping screws from the same material (with dowels), dowels, or drive directly into the ground using pieces of reinforcement. The fastening of the components must be rigid and durable. Therefore, it is recommended to tighten two bolts and self-tapping screws in one unit. Use washers.
An alternative solution is the construction of a columnar foundation. It has fewer advantages, but it is the fastest to install such a support. The stages of preparation are the same. Instead of a trench around the perimeter, several points are dug for future posts.
Depth - about 0.5 m. Width - 50 mm more than the cross-section of the timber. A wooden frame is installed on the resulting posts. It is made in the same way. Fastening - corners, anchor bolts or galvanized screws.
Arrangement of beds

Arrangement of beds My greenhouse came out raised above the ground by as much as 30 cm, the height of the beds from the flooring is 20 cm, and the finishing floor covering is arranged 10 cm above ground level. Thus, I saved the beds in the greenhouse from the bay with melt water in the spring. Whoever does not have such a problem, then I do not see the need to raise the greenhouse, and the floors can be made on the ground.
Albeit inconvenient, it is possible to step over a high threshold. But rolling the cart through such a threshold will be problematic. And I decided, at the entrance to the greenhouse, to build a ramp.
The passage was marked with a bar. I dug a trench, leveled its floor and walls. Then I laid the required layer of sand cushion (in my case, it turned out to be 7 cm). And already on top of the pillow I laid out road geotextiles with a density of 120-150 g / m2. And only then he laid the paving slabs 50 by 50 cm. The main thing is not to add sand under the tiles and not to neglect the use of dense geotextiles. Otherwise, sneaky ants will settle in the sand under the tiles.
The arrangement of the beds, so that it does not sag under the influence of the soil, I made from fastened beams with a section of 100 by 50 mm and 100 by 150 mm.In my opinion, this turned out to be the most correct solution, since with the help of the beams I managed to create an angular connection in the form of a thorn-fork. For a strong connection of the harness to the curb, I cut out the grooves in the frontal beam.
The adjoining parts of the curb beams abundantly missed with bituminous mastic and connected with ruffled nails, hammering them in at an angle. The upper and the edges of the beams directed into the passage were scribbled, and chamfered from the sharp corners.
Having adjusted the bars, I took them off again to smear the back grooves and edges with bitumen mastic. I covered the tiles in the aisle with foil. Having smeared the previously untreated strapping places with mastic, he laid the curb in its place - a passage of 80 cm was formed.
I scattered the earth extracted from the passage outside the foundation. Made the slope more steep on the north side. Here I will plant ground cover plants - thyme, mint, carnation, etc. On the south side, a gentle slope with a width of about 1.3-1.4 m - garden strawberries will be planted here. I made a narrow hollow along the foundation in the ground - sedimentary water will accumulate in it. This water will partially penetrate into the greenhouse to the beds.
Useful information
 Hydrangea in a pot. Photo
Hydrangea in a pot. Photo
Possessing a positive, light energy, the flower spreads calm serenity. From the position of Feng Shui, it has many useful properties:
- extinguishes mutual hostility, softens conflict in communication;
- at home normalizes family relations, helps to achieve mutual understanding;
- contemplation of hydrangea relieves mental fatigue after an incident or stress, helping to calm down;
- a flowering plant relieves of bad mood, negativity of others, bad thoughts.
Did you manage to grow Hortense?
While trying it Yes, it was very easy!
Installation of a greenhouse structure
Any greenhouse has a foundation. In modern models, this is a horizontally located profile pipe. It, like the rest of the metal structure, must be covered with an anti-corrosion compound. Installation on a foundation from a bar of any type is carried out using self-tapping screws or screws. They should be in every corner.

The number of perimeter connection points is determined by the size of the building and the opinion of the assembler. Minimum - half a meter, maximum - 1 m. It is advisable to adhere to an equal step. Also, during installation, it is better not to connect the timber to the strapping near the places of its connection with the vertical elements of the frame. Then assemble the main part of the greenhouse, with glass or polycarbonate sheathing.
If you are performing the installation of an aluminum profile structure on your own, use the following tips:
- pre-drill holes for fasteners;
- first bait the self-tapping screws, then align the strapping using the construction level and only after that tighten the attachment points;
Such precautions are not necessary for steel structures. Press the profile by hand and use the anchor bolts to fix the foundation into the pre-drilled holes
Often, when installing such greenhouses at the corners, tees for guides are used. But all the same, it is better to bait the fasteners first and only then fasten them.
For a greenhouse structure made of wood, it is convenient to use a reinforcing fixation of the foundation from a bar in the ground. The metal pins will be the anchor for the building. They will connect the parts of the support and provide reliable fixation when installing the above-ground part. In addition to bars, polymer arcs are easily attached to the pins.
Installing a greenhouse on a log base is a budget solution for private households. In small dimensions, such a foundation will cope with the dimensions of a structure made of any material. If desired, the support can be simply disassembled and moved to a new place.
3 Small greenhouses and greenhouses made of polycarbonate
Lightweight greenhouse and greenhouse structures do not require solid support.Using buildings, the weight of which does not exceed 50 kg, seasonally, summer residents often move them annually, changing the place of planting of heat-loving vegetables.
Creating solid foundations for such structures makes sense:
- if the periodic transfer of greenhouses from place to place is not expected;
- if you want to make buildings more durable;
- to simplify the operation of structures;
- due to ease of use if vegetables are supposed to be grown in high beds.

For light buildings, columnar and point foundations and their variations are suitable. When preparing a site for the construction of a foundation from pillars or piles, it is necessary to clear the site, determine the size of the future foundation. For greenhouses and greenhouses up to 2 meters, it is enough to prepare 4-6 pits for supports: 4 in the corners and, if desired, one in the center of each long side.
DIY greenhouse designs
Many summer residents and villagers purchase ready-made greenhouses produced by factories and cooperatives. Their wide variety allows you to choose the design of the desired parameters. But if a greenhouse is made from a bar with their own hands, then the owners feel pride in the work, and the greenhouse comes out exactly of the configuration that is needed in a particular case. This building is much cheaper than the purchased one.
Before starting the construction of a greenhouse, everything is well thought out. The site is measured and the location of the structure is selected. They draw a sketch and carry out drawings, which indicate the exact dimensions of the building. This is necessary to calculate the amount of material.
The greenhouse can be made of PVC pipes, polycarbonate, window frames, boards, beams, etc. But most often a wooden beam is chosen for these works.
For a greenhouse with a frame, this material has several advantages:
- it is readily available, that is, it can be purchased everywhere, and its cost is low;
- there is no need to look for high quality material;
- the wood must be properly dried and free from defects;
- no special skills are required to assemble the frame;
- the material is non-toxic and environmentally friendly;
- the construction is durable, and its service life is at least 5 years.
It is worth noting that the tree, in addition to its positive characteristics, has some disadvantages. Among the "disadvantages" of greenhouses made of beams are:
- to protect the frame from decay, it is necessary to treat it with a special compound;
- if it is necessary to move the structure or dismantle it, then this will not be easy to do;
- the environment negatively affects the tree (bad weather, microorganisms, moisture, insects, etc.);
- in comparison with metal structures, such structures are easily flammable.
In addition to the shape, material and dimensions, one of the important points in the construction of a greenhouse is its location. After all, the convenience of use, the ripening of vegetables, fruits and other plantings largely depends on this.
There are some factors that need to be taken into account when choosing a greenhouse location:
- illumination is one of the main conditions for raising yields;
- relief of the site - it is better to build a building on a hill;
- protection from wind gusts - the installation is carried out near the fence;
- distance to the water source (if a centralized irrigation system is not equipped);
- soil composition.
Most often, the greenhouse is located away from tall buildings or trees. Natural light should constantly fall on the greenhouse throughout the day. Since it is difficult to install a structure on a hilly surface, a flat area is chosen under the greenhouse or a hilly one is leveled. If a greenhouse made of wood is unstable, then with a slight wind it can deform or collapse.
It should not be cool inside the greenhouse, and so that the cold does not penetrate inside, a fence is installed around it or a low shrub is planted. Heat loss is reduced by slightly reinforcing the roof.If the body is overlapped with glass or film, then an additional layer of the same material is used.
First, they are determined with these parameters, since you should not overdo it. After all, completely different conditions are needed for each variety of vegetables. For example, tomatoes and cucumbers cannot be grown in the same building, since the latter require high humidity, and tomatoes cannot tolerate it. Therefore, two different structures are often built for them, which will be more useful than one large one.
The optimal size of such a structure is considered to be 3 x 6 meters. You can build a structure with other dimensions, for example, 6 x 20 or 5 x 4, it all depends on the size of the site itself and the requests of the owners. These dimensions are relevant if the greenhouse is rectangular.
Many summer residents do not want to have a greenhouse of a standard shape. Therefore, the owners of the site have structures of different configurations. If this is a geo-dome, then its dimensions are determined by measuring the diameter of the structure. To make it convenient to work in a greenhouse, its height should be 2.5 meters. A taller structure will not retain heat and is unstable. If you want to make a gable roof, then the height of the greenhouse should not be more than 2 meters.

Greenhouse in the form of a geo-dome or semicircle
Typical configurations include semicircular and arched. They are practical and are not affected by gusts of wind. Snow does not accumulate on the roof, and the design is pleasing to the eye. This shape is easy to make from aluminum or plastic arches, but not from wooden beams.
Types of wooden greenhouses
Modern designs of greenhouses made of wood differ in shape, type of covering material and rate of penetration into the ground. The choice of a building depends on its purpose and future dimensions. Wooden structures are heavy and therefore require a solid foundation.
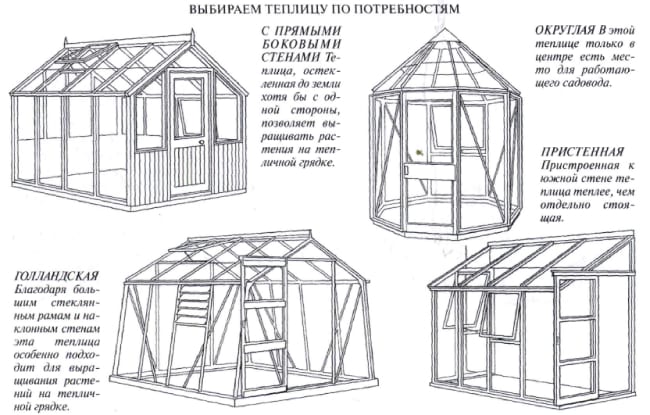 Types of greenhouses by shape and needs
Types of greenhouses by shape and needs
By form
Based on the configuration of the roof, walls, there are several types of greenhouses with a wooden frame. More about them:
- Shed. One side of the building is the wall of the capital building. The advantages are compactness, availability (requires few consumables), the ability to supply heat from home. There are also disadvantages: limited area, illumination.
- Gable. A greenhouse with straight sides looks like a house. The design is practical and versatile. Snow does not linger on it, so it does not load the frame. The downside of the structure is the large heat loss through the north side. To increase the area for planting crops, choose a gable greenhouse "Dutch" with inclined walls.
- Tent. Assembling the structure is difficult due to the many mating corners and parts. The advantage is good illumination throughout the day. Racks or curly beds will help to rationally use the space.
- Tunnel. Made from arched arches. The design is suitable for tall and short crops, is easy to maintain, is wind-resistant and contributes to an even distribution of light. Due to the absence of corners, it is easy to cover it. The main drawback is the complexity of the assembly.
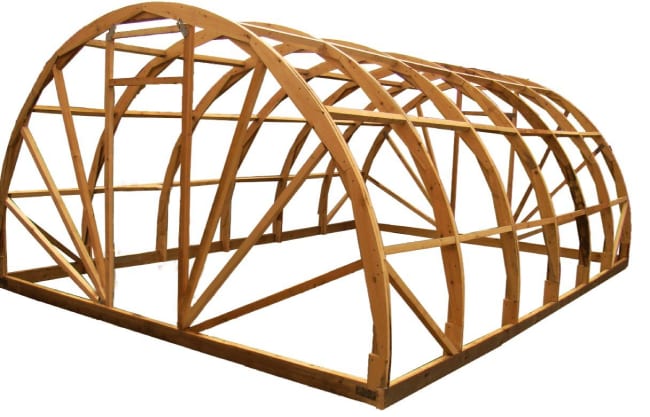 Tunnel greenhouses
Tunnel greenhouses
By covering material
The warmth for the rapid growth of plants is stored inside the structure due to the covering material. There are three main types of coating used for a wooden greenhouse:
- Film. The most affordable and lightweight material that does not put pressure on the wood. For rafters and struts of the structure, use beams of medium size, for example, 5x5 cm - but it is better to make the base from a more durable material. The service life of the film is short - about one season. It will be dismantled for the winter. the film coating will not withstand heavy pouring rains and snow.
- Polycarbonate. A durable material with good light transmission, an acceptable cost, but it is more difficult to install it than a film.Polycarbonate is not susceptible to moisture, is more flexible than glass, resistant to impacts and has good thermal insulation properties due to closed cells. There is a choice of colors. Cons of the material: has insufficient abrasion resistance (easily scratched) and shrinks or expands under the influence of low and high temperatures.
-
Glass. Expensive material. It transmits the sun's rays well, is durable and is not demanding to care for. The disadvantages are fragility and high weight, so a strong wooden frame and a reliable foundation are needed under the glass.
By burrowing into the ground
A greenhouse from a bar can be above ground and buried. The last type of building is called a "thermos". It can go 2-3 m underground. In a thermos greenhouse, light and heat-loving plants can be grown all year round. The thermal effect inside the structure reduces the cost of maintaining the required temperature in the "thermos" to a minimum. Advantages:
- High productivity. In a "thermos" the percentage of the yield obtained can be 2-3 times higher than in a conventional greenhouse.
- High thermal insulation performance. Allow to save heat and energy resources.
- Uniform distribution of light and heat due to the use of polycarbonate.
- High resistance to adverse external factors, i.e. to temperature extremes, strong winds and precipitation.
- The ability to grow a variety of crops, including exotic ones, due to the special microclimate.
 Ground greenhouse made of wood
Ground greenhouse made of wood
The main disadvantages of the "thermos" are significant financial costs and the complexity of construction. The greenhouse should be buried in the soil at the level of soil freezing. The foundation is completely sheathed with heat-insulating material, and the above-ground part is covered with a translucent double coating. With high-quality construction, the greenhouse will stand for more than 3-4 years.
A detailed diagram of a greenhouse from a bar with your own hands
Timber framed greenhouses are considered classic contractions and were popular even before modern designs. She is so popular because her device does not require expensive materials. The most common model is a greenhouse with a gable roof.
Doors are always installed in the end walls; half walls can be made from the simplest boards. This type of greenhouse is installed on a strip foundation. The lower parts of the structure are very thoroughly impregnated with an antiseptic, it is advisable to do this in several layers, and are installed only after complete drying. When working, it is always necessary to use a building level. To simplify the work, it is recommended to prepare the boards in advance to use them as props.
All parts must be connected at the same angle. Wall panels must be fastened from completely dried material. The frames are built independently, both under the panels at the bottom of the walls and the glass part of the structure. It is advisable to start fixing the panels on the end walls with ordinary nails with small heads. Larger panels can be installed for side pieces than for end pieces. All panels must be fastened between the uprights. After that, all wooden elements must be thoroughly impregnated with an antiseptic solution.
Polycarbonate panels can be used for the side walls. You can use ready-made drawings for work.
Polycarbonate greenhouse foundation - photo and step-by-step instructions
We will arrange a strip foundation for a greenhouse, size 3 * 6 m, with a high brick base and insulation around the perimeter.
Making a drawing
Before building a greenhouse, you should choose a project or make a drawing with your own hands, indicating the dimensions and main structural units. It also determines the materials, their quantity, the main stages of work. It is better to use a typical project and adapt it to your own conditions.
Typical Ergonomic Greenhouse Design
Choosing a place
The choice of location depends on the individual characteristics of the site. It is better to build a greenhouse from the southern and maximum windless side, behind the house. We clear the site from debris, tree roots, weeds. We fence off the perimeter with pegs, pull the rope, check the geometry. The diagonals must be equal. We remove the upper, soft layer of soil.
Foundation device
We dig a trench 800 mm deep around the perimeter. Align the bottom. We cover with roofing material for 2 layers, you can lay geotextiles. We fill in crushed stone, sandstone, layers of 100-200 mm, ram the pillow.
We install the reinforcing frame. There will be two horizontal belts, two parallel rods in each, vertical bundles every 300-500 mm. The reinforcement is corrugated, with a cross section of 8-12 mm. We put pebbles, 50 mm high, or stands on the bottom.
We put 2 lower horizontal rods, the distance between them is 200 mm, we lay smooth thin rods perpendicular to better preserve the shape of the frame. At the corners, we bend the reinforcement to the adjacent side, we go in 500 mm or more. Also, on the other hand, a double overlap is obtained to strengthen the structure. We drive in vertical rods, we tie the parts with wire. We mount the upper horizontal belt in the same way.
How to knit reinforcement correctly
The distance between the horizontal belts depends on the height of the greenhouse foundation. If the tape is 400 mm high, then there should be a distance of 300 mm between the upper and lower rods, +50 mm per concrete layer on each side. The width is calculated in the same way, if the overall dimension is 300 mm, then the frame is 200 mm. Remember, the height must be greater than the width of the tape.
We install formwork in the trench, it can be knocked-down boards from a board, moisture-resistant plywood, plastic durable panels. For the correct geometry, we make a bundle along the top of the sheathing with bars, and on the outside we install spacers, they will hold the structure when poured with concrete.
For your information: In order to preserve heat in the greenhouse as much as possible, to protect the structure from harmful influences, the height of the foundation should be calculated in such a way that it rises 1/3 above ground level.
The tape should be poured in at the same time, so that seams and cold bridges do not form. The proportions of the solution for the foundation for the greenhouse: cement (binder) - 1 part, sand - 3 parts, crushed stone, fraction up to 40 mm (preferably 10-20 mm) 4-5 parts, water 4-5 parts, until the consistency of thick sour cream. First, dry components are thoroughly mixed, then water is added.
In the photo, how to properly fill the base for a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands
Pour the mixture into the crate, ram it, remove the air. Bubbles in the hardened concrete will cause destruction. The solution must be hardened, until it is fully formed - 4 weeks, only then the foundation must be loaded.
We remove the formwork, glue the sides with roofing material or coat it with bitumen mastic for 2 layers, attach foam sheets on top, you can order insulation - PPU spraying. From above we close the sheets with 2 layers of roofing material, overlap seams of 100-200 mm, seal with tape, weld with a blowtorch. Backfilling the soil. For horizontal waterproofing, roofing material is laid on top of the foundation under the greenhouse.
How to install a polycarbonate greenhouse on a foundation
On fresh concrete in the center of the tape, in the corners and every meter, it is recommended to install and release reinforcement for metal structures or special corners with welded anchors to the outside, for fixing the bars, the greenhouse frame will be attached to them. If the mortgages were not provided for in the process of pouring the foundation for the greenhouse, then the frame can be fixed with anchor bolts.
Method of fastening the frame to the foundation
The installation of a polycarbonate greenhouse on the foundation has another important stage: in order to avoid drafts, ice, freezing, the gap formed when the base of the greenhouse adjoins the foundation is sealed with elastic sealants, a gasket with rubber edges is placed in the gap
This is especially important if the structure is insulated and it is planned to grow crops in it all year round. When equipping a winter greenhouse, do not forget about additional lighting and heating
