Regulatory requirements
The construction of a shallow foundation tape under a one-story house is possible even on a cushion of sand and gravel, this helps to save money and speed up work without any risk. But such work can only be done on certain soils:
- not inclined to heaving;
- completely dry;
- characterized by uniform freezing.
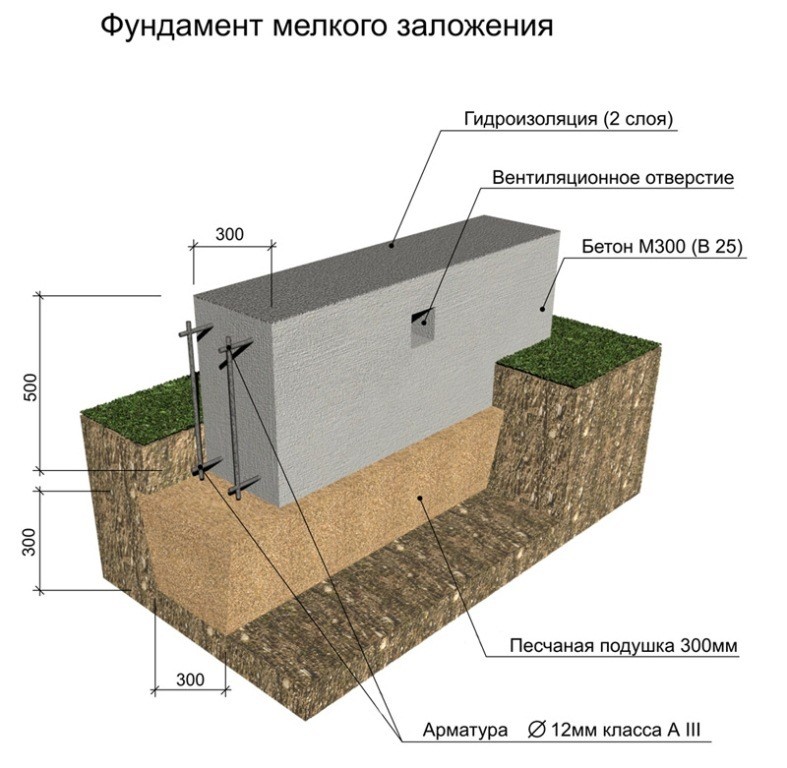
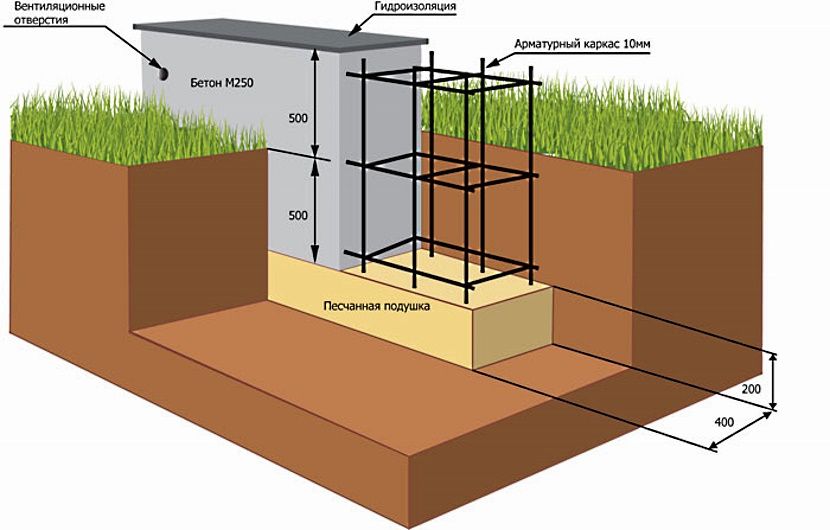
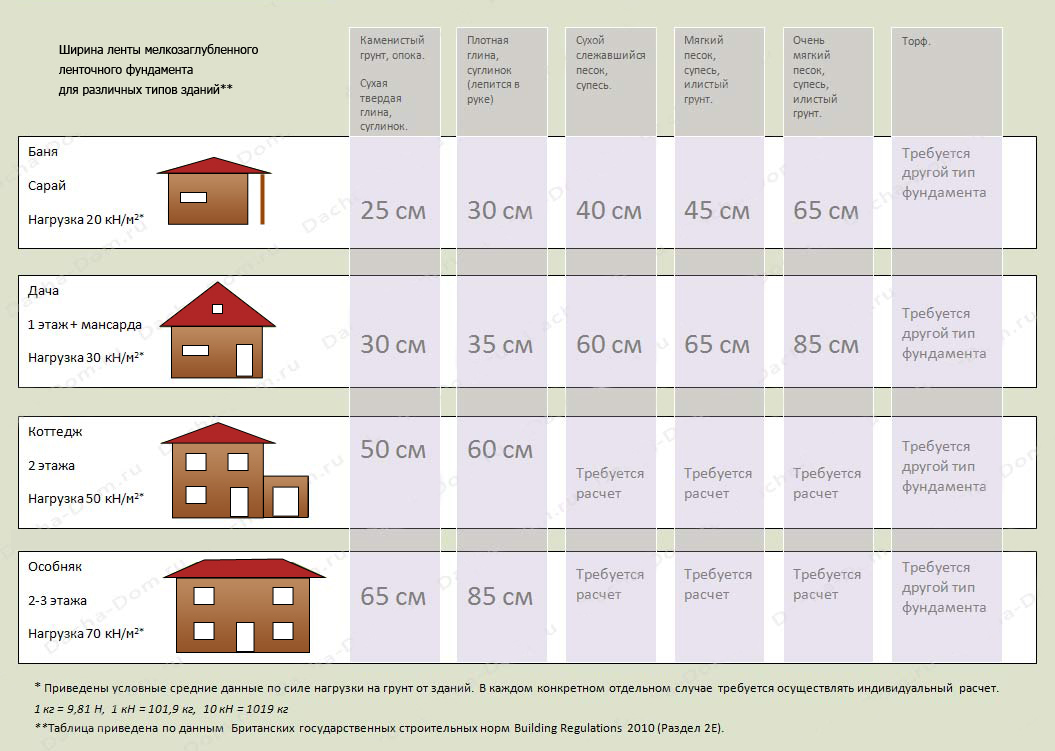
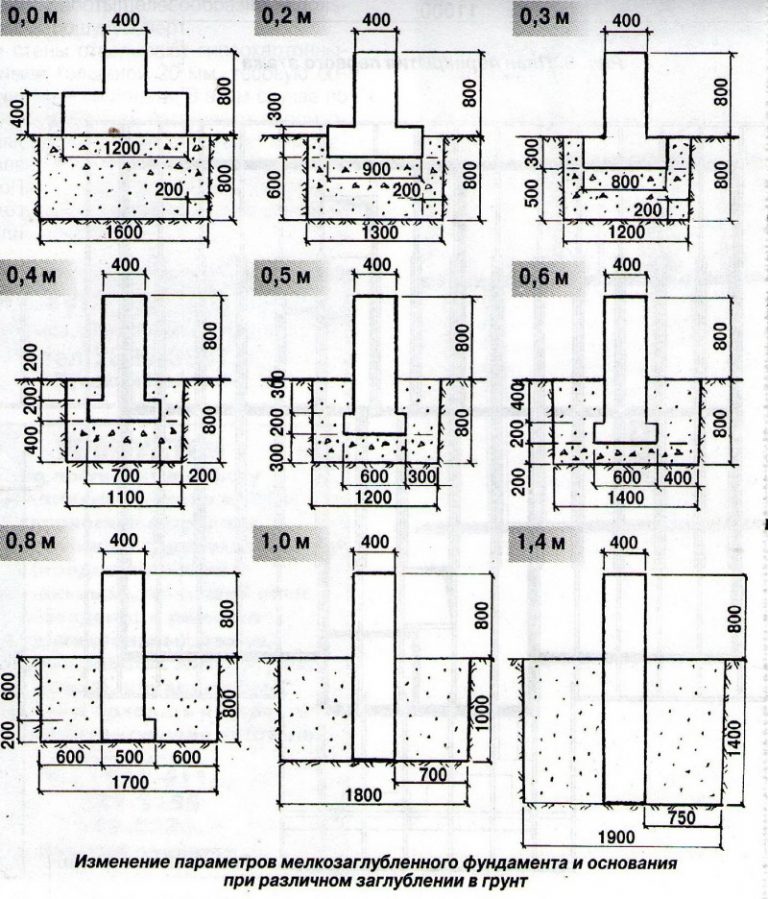
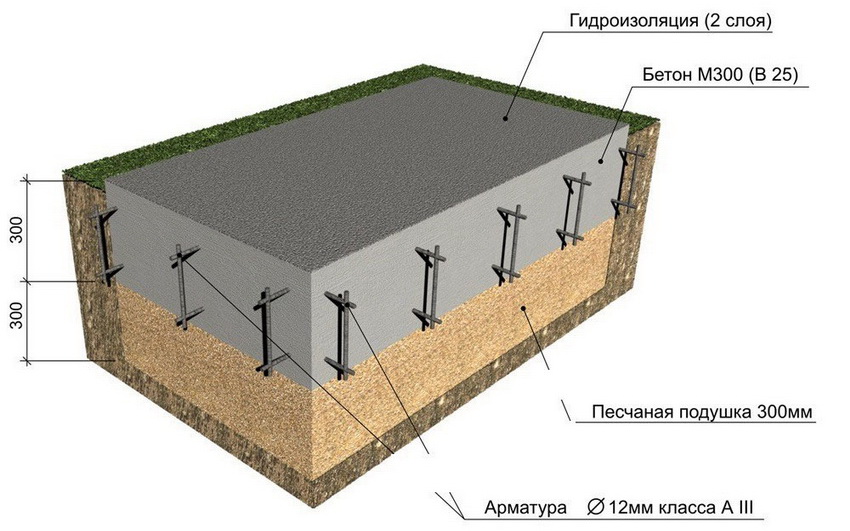
A reinforced concrete tape with a shallow deepening under a small private house is made 0.3-0.5 m wide underground, the height of the basement is at least 0.3 m.For the greatest accuracy, work begins with a marking, then trenches are dug, the walls of which should be vertically even ... The shallow laying makes it possible to do with trenches with a depth of 0.5 and a width of 0.6 to 0.8 m. When the excavations are dug and leveled, a sand cushion of 200-400 mm is made. It is supposed to be rammed, since the denser the base, the less the subsidence of the whole house will be over time.
Sand is filled in layers, 150 mm each, it must be moistened before tamping. For the highest mechanical strength, gravel is poured from above with watering with liquid concrete.
To form the formwork, boards with a thickness of 2 cm sanded on one side are used.Instead of them, you can take more:
- slate in the form of flat sheets;
- sheet metal;
- plywood.
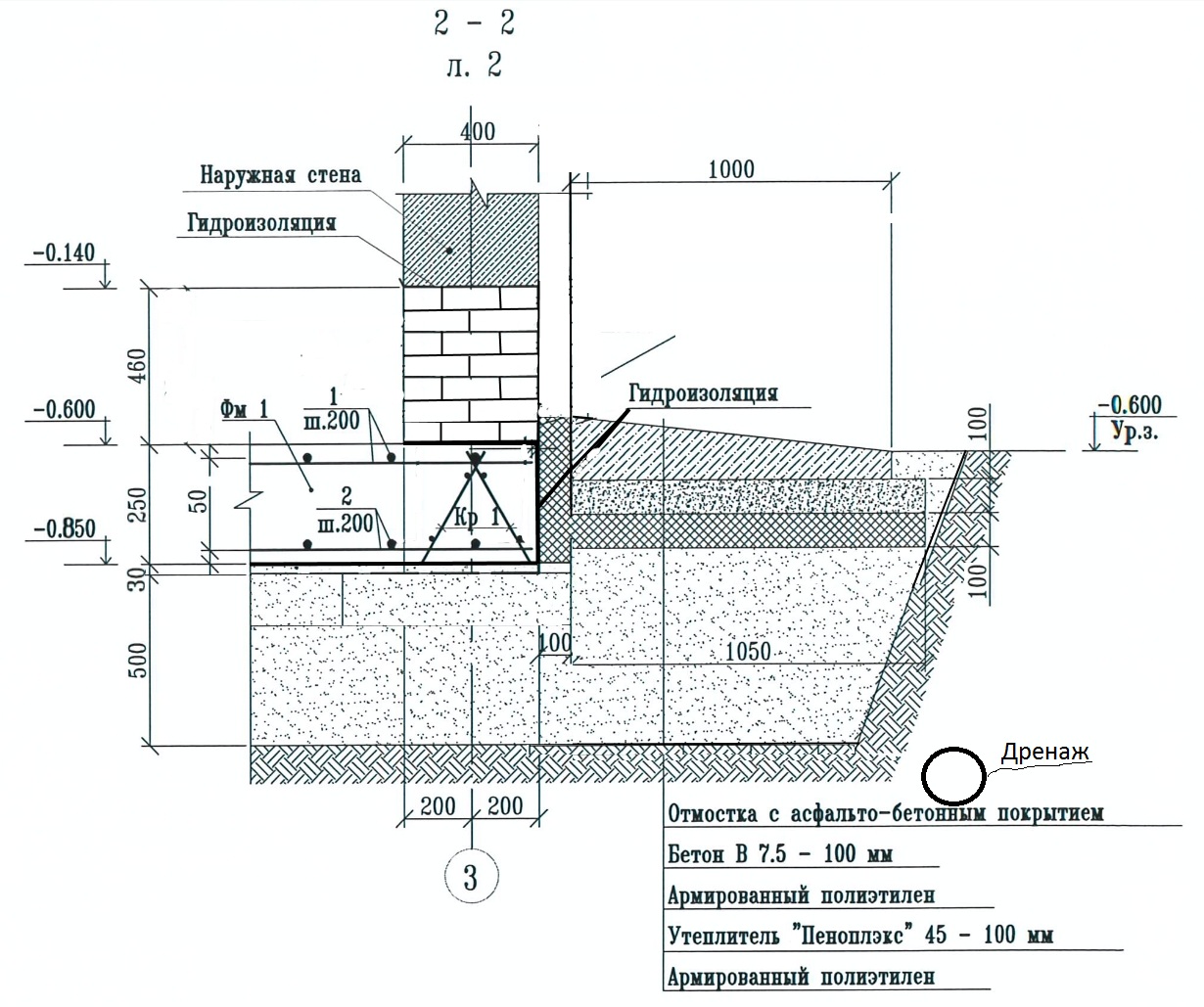
The reinforcement of the formwork is carried out using spacers and support stakes, it must be verified vertically and horizontally. From the inside, the structure is laid with a dense waterproofing material. In order for the required thickness of this material to be less, the depth of the bookmark should be selected, focusing on the level and movement of groundwater.
The foundation in the form of a tape for a two-story brick house is laid in a pit filled with 0.3 m of sand. Since the house will have to be equipped with bathrooms, it is recommended to add a cement and sand screed up to 0.1 m thick over the water and sewer pipes.
Waterproofing is placed on the hardened screed, but a heat-insulating layer is not always needed. Then comes the frame, created from the reinforcing steel network, then the formwork. Only then can the tape be poured as such. The sole of the base under the house must necessarily go 200-250 mm deeper than the freezing line. Houses made of foam blocks are lighter than brick buildings of similar size.
But this does not automatically mean that you can lay the foundation closer to the surface. We will have to analyze all the parameters that characterize the geological structure of the site
In addition, the severity of the floors, furniture products provided by the project, and the snow load that may be present on the roof even for a short period are taken into account. Among the different options for bookmarks in depth, you should choose the one that you can only afford, for material reasons
The soil in different areas freezes by 100-180 cm, and in most cases, they choose a laying of up to 150 cm.
It should be borne in mind that even when using geological prospecting information and SNiP norms in calculations, it allows you to find only the minimum required values.
Trenches are thought out and dug out immediately with a reserve for all the necessary layers of bedding, screeds and additional structures. A relatively light house on a ground that is not prone to heaving is allowed to be placed on a base 600 mm deep, made in the format of a floating tape. Such a structure must be carefully calculated, only this allows one to avoid destruction during movements of soil masses.
A tape for aerated concrete should be calculated no less carefully than for a brick or other heavy material.The lightness of aboveground structures is deceiving; without careful calculations of the strength and bearing capacity of the support, they will turn out to be unreliable. The foundation project should be prepared with maximum buoyancy. For heavier wall materials, it is insignificant, but lightweight aerated concrete blocks are easily pushed out of the soil.
If, nevertheless, the choice is made in favor of the filler support, when calculating, they are guided primarily by:
- the mass of the walls and the pressure exerted by them by 1 linear meter. m;
- the mass of all floors;
- the severity of roofing materials and underlying structures.
Construction of brick houses
 The technology is simple, reliable, does not require any special equipment, except for lifts, however, it is complex in execution and rather laborious
The technology is simple, reliable, does not require any special equipment, except for lifts, however, it is complex in execution and rather laborious
The technology of building from bricks became known for a long time, even before our era, people built dwellings from burnt pieces of clay, giving them almost the correct size. The technology is simple, reliable, does not require any special equipment, except for lifts, however, it is complex in execution and rather laborious. At the same time, brick construction is impossible without the experience, knowledge and application of the labor of highly qualified workers. Minimal errors in masonry will lead to irreparable loss of appearance, therefore, brick construction of a multi-storey building should either be carried out under constant supervision, or only by the hands of professionals.
Today there are 2 types of bricks used:
- Ceramic piece product has strength, heat resistance, seismic resistance, moisture resistance. At the same time, the brick is easy to manufacture.
- Silicate is made from a mixture of lime and sand, has a cheaper price and its characteristics are more modest: it does not tolerate moisture, high-temperature conditions.
 A strong, solid and well-recessed foundation is required, since the brickwork is massive
A strong, solid and well-recessed foundation is required, since the brickwork is massive
Stages of building a brick house:
- Foundation. A strong, solid and well-buried foundation is required, since the brickwork is massive.
- Foundation waterproofing.
- The first row of masonry on a "dry" basis, then the following rows of masonry are made, and the choice of the option for installing bricks is carried out depending on the features of the project, the height of the house and the customer's preferences;
- Reinforcing elements of the masonry or "bundle" must be present in every 2-4 row;
- Interfloor floors are laid using a slab method;
- Each subsequent floor is laid out, like the first, one should not forget about the bundle and strengthening of the wall panels.
- Building insulation and waterproofing;
- The roof is mounted rough, mostly flat. Finishing roofing is done only after the structure has shrunk.
- Installation of windows, doors.
- Final finishing works.
Brick construction of a multi-storey building has a lot of nuances: from the choice of the type of masonry to the variability of the bond. However, despite the difficulties, the numerous advantages of the final result atone for all the technological inconveniences:
- Highest thermal performance;
- The best soundproofing performance;
- Maintaining a comfortable microclimate inside the house;
- Variability of building formats;
- Undemanding facade finishing due to the good aesthetic appearance of exposed bricks.
There are several disadvantages:
- Obligatory use of qualified labor;
- High price bar for construction works;
- Slow construction of the house;
- Time requirement for shrinkage;
- Limited number of storeys of buildings;
- Mandatory availability of a large warehouse for material at the construction site.
Dependence on the level of groundwater
Another factor, the definition of which will help determine what depth of foundation is needed for your structure, is the level of groundwater. If the site you have chosen for construction is too high, and the soil is heaving, then this is not the best option for construction.This combination promises increased expenses and non-standard solutions in the design of a building. Additional waterproofing will most likely be required for the supporting structure. Therefore, it is best not to stop your choice on such sites. Be sure to find out this information before starting the construction of the building. This can be done without any surveying. Interview the owners of the plots in the neighborhood, visit the real estate agencies, or contact the firms that study and test the soil in the area. There are also a number of soil types on which neither winter soil freezing nor the height of groundwater rise have a significant effect. These types of soil are, for example, semi-rock and rock.
What should it be?
The main task of the foundation is to evenly take on the loads of a brick house and distribute them evenly on the ground so that the latter does not sell through in any one area
Therefore, it does not matter which of the three types will be used as the basis for a brick structure. Is it tape, slab, or columnar
The main question is which foundation is better for a brick building, taking into account the following indicators:
- type of soil at the construction site;
- the level of soil freezing;
- groundwater level;
- the size of the house, and accordingly its weight;
- relief of a suburban area.
It is these parameters that will form the basis for calculating the foundation for a brick house. Of course, the main parameter is still the type of soil and the weight of the building. Because the type of soil on a building site indicates its bearing capacity. For example, if these are soft moving soils, then slabs or pillars are used to build the foundation. If the soil is strong, then it is better than a tape, a structure cannot be found.
At the same time, in slab structures, the main bearing function is performed by the thickness of the foundation, in strip structures, the width of the foundation, in columnar sections of piles and their depth. It should be borne in mind that the approach to the foundation for a two-story brick house is not the same as for a one-story one. An increase in the mass of a building requires an increase in the size of the base for it. Therefore, this must be taken into account at the stage of calculations.
But it must be noted that laying the foundation for a one-story brick house is no different from this procedure associated with the construction of a multi-storey building. That is, the technology is no different. The differences are only in the greater volume of work carried out. And the sequence of construction operations, the types of materials used are the same.
And yet, the question of whether the foundation is being laid well or whether there are claims to it requires a thorough analysis. Therefore, we will consider all types of foundation structures that can be used for a brick house.
How to calculate?
The depth of occurrence, mentioned in various sources and special literature, is by no means the depth of the trench being torn off. By this term, experts understand the gap that separates the soil surface from the lowest plane of the foundation. A tape without deepening is used extremely rarely, since its bearing capacity is extremely low. The minimum deepening is more common than deep, but at the same time it is capricious. We'll have to calculate the action of the soil heaving forces.
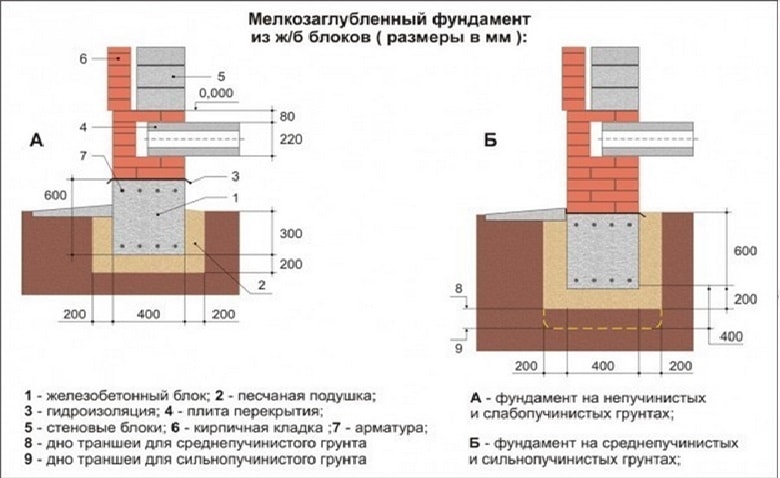
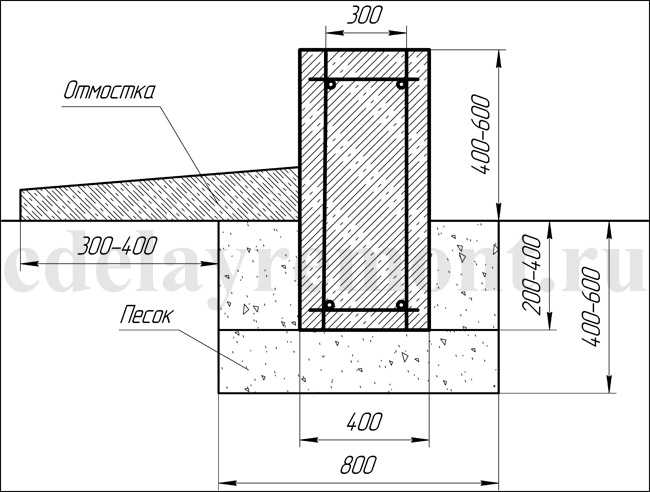
The depth of laying cannot be less than 50% of the depth of soil freezing. If the level of the ground liquid is high, a depth of 100-200 mm is usually made under the freezing line. An exception is made for rocky soils, gravel or coarse-grained sand. In swampy soil, on peat and similar substrates, the tape will have to be laid below the problematic layers. Sometimes only a trench is enough to a solid mass filled with sand; but such a decision can only be made by trained professionals.
Insulation of the foundation and adjacent soil will help to significantly reduce the required excavation. The organization of high-quality drainage has an important role, it helps to protect against freezing. The sand cushion should be placed both under the belt itself and to the side of it. The best way to solve the problem is a combined approach - a combination of a pillow, insulation and drainage structures.
The midpoint of the bookmark changes depending on whether the house is heated or not, whether it is planned to make a basement. For unheated buildings, a 10% burial reserve is sufficient, and if the building is to be heated, 30% is needed.
Digging a pit for a simple concrete tape placed under sheds, poultry houses and small outbuildings can be from 0.5 to 1 m deep. For most of such structures, except for the most massive, 80 cm is enough. But a residential building, even a relatively small (one-story) one, should be fixed lower, its root is 2 meters. However, the differences are not limited to this. In residential construction, the tape is supposed to be reinforced, which immediately increases its width.
The formwork necessarily contains a lattice made of reinforcing bar. A bundle of rods is achieved through the use of a knitting wire. Strength after pouring is achieved in 28 - 42 days on average. Walls can only be placed on the hardened tape. When building a house with a basement, the trench technique is not suitable, a foundation pit becomes mandatory. If you plan to build a two-story and higher dwelling, you will have to use standard blocks of increased strength; their height is certainly taken into account.
Calculation recommendations
 In case of mass development, the calculation of the depth is carried out by specialists in design institutes. More often, with individual self-development, the question arises: how to calculate the foundation for a garage, a bathhouse or a one-story cottage?
In case of mass development, the calculation of the depth is carried out by specialists in design institutes. More often, with individual self-development, the question arises: how to calculate the foundation for a garage, a bathhouse or a one-story cottage?
After obtaining all the necessary data about the soil and the weight of the building, the final calculation is performed and the depth of the foundation is determined.
The depth, being within the same limits, will nevertheless always be different. On the same site, the foundation for a one-story or two-story brick house will differ significantly.
Each calculation is purely individual. If it is not possible to contact a specialist, you can enter the data into an online calculator and find out the recommended dimensions, adjusted for the freezing depth. For more information on calculations, see this helpful video:
 But there are a few general guidelines to follow:
But there are a few general guidelines to follow:
- Any foundation is laid below the level of soil freezing by 10%. If the freezing value is set at 70 cm, then the depth of the pit under the base should be 77 cm.
- For loose soils in temperate climates, it is better to use a strip base with a depth of 0.5 to 1 m.
- In the northern regions with slightly weeping soils, a base is made deeply up to 2 m deep.
- In swampy areas or on clay, a slab would be an ideal option, and the depth of burial can reach 2.5 m, which makes it possible to make a basement.
The basic rule when calculating the foundation: a competent and reliable foundation is the key to a long service life of the building. It is worth noting that too much in the building is also fraught with consequences, as well as savings. A pit dug below the required level will not give the house more reliability, but will increase the consumption of materials and the area that will be negatively affected by soil and groundwater.
Construction stages
The preparation of the building foundation is carried out in several stages.
Marking the territory for the foundation
In accordance with the plan of the house, the area is marked. All waste, plants, uprooted shrubs and trees were removed. It is advisable to remove about 10 cm of the topsoil.
With the help of pegs and tensioned ropes, the boundaries of the house and all load-bearing internal walls are marked.It should be checked that the angle between the walls is strictly 90º, unless the structure involves complex wall configurations.
Trench
In this case, the trench is used for convenient piling. It is dug to a depth of no more than 40 cm and a width, which allows you to easily mount wooden formwork and dig pile holes.
Once construction is complete, the trench can be buried as the concrete belt acting as a sander does not need to lie on the ground. Sand can be poured under the belt to the desired height.
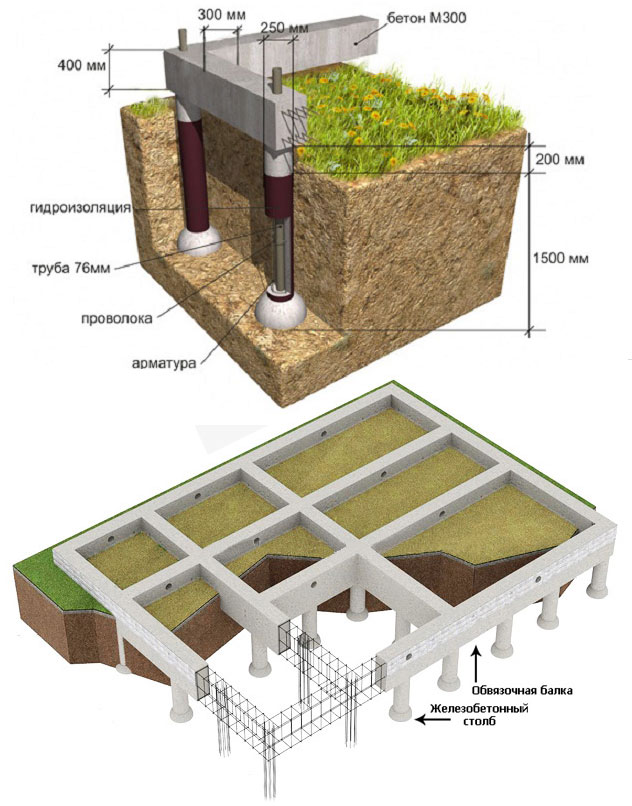
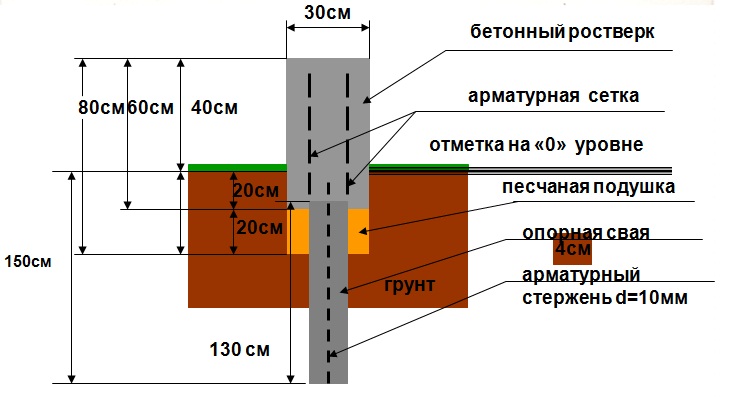
Where to dig in the pillars?
The number, diameter and depth of piles should be determined at the design stage. Supports are installed in the corners of the building, under the load-bearing walls, in the corners where these walls are connected and where heavy equipment is to be installed.
If, for example, it is necessary to install a stove, chimney, etc., then in this case, reinforcement of the foundation may be required. In this case, it makes sense to install piles at the corners of the reinforced pile.
To save concrete, you can increase the area of the pile post on the ground due to its wider base. This means that the diameter and weight of the pile does not increase, and the load on the ground is reduced due to the wider supporting surface. This can be done with a special drill. TISE.
Watch out guys! For the record, drill. TISE Differs from the conventional mounted plow, which allows a larger cavity to be created in the desired part of the excavation under the tine. At the bottom of the bottom, the sand is filled with a layer of gravel about 10 cm thick, possibly gravel.
Formwork
Before concreting, the formwork must be made and the pile hole must be reinforced. The formwork can be used as formwork for slabs, plywood, metal, special slabs, workshop panels, etc. The formwork can also be used as pile formwork. The holes are sealed with 2 layers of roll to roll to roll to roll to roll to roll to roll material.
The pile formwork can be an asbestos-cement pipe, which then remains in the ground. Rubber, pipes are inserted into the pile hole to the end. Inside, the reinforcement forms a reinforcing cage with a diameter of 12-16 mm.
The ends of the reinforcement should protrude 15-25 cm beyond the ends of the pipe, since they are connected to the reinforcement base of the foundation strip.
Pouring with concrete
The hole is ready for concreting. First, a layer 20 cm thick is poured and the roofing pipe is raised so that the mortar can spread over the entire base of the pile and form a bearing load "shoe".
During the casting process, air inclusions can form, which can significantly reduce the strength of the entire structure. To eliminate voids, it is better to take care of an underwater vibrator in advance.
After concreting all the piles, the sheet pile is formed.
The mooring part of the foundation is not intended for contact with the ground, its task is to transfer the load to the piles. After concreting the piles, the formwork should be backfilled with sand, a sealing layer of material should be laid, reinforced and reinforcement should be attached to the beams protruding from the flooded piles and filled with mortar.
Watch the video below for more information on how to create your own columnar feed:
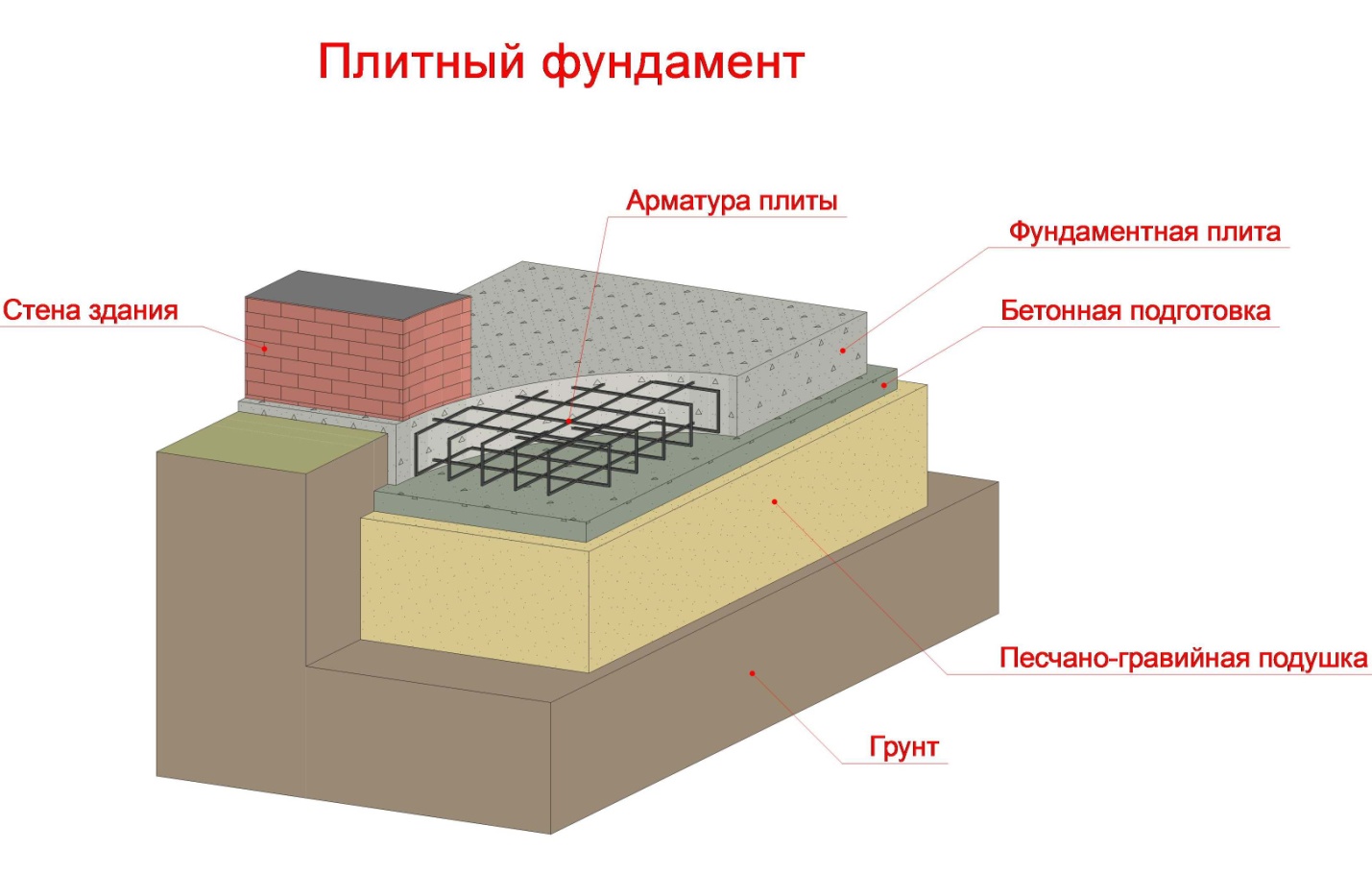
Plate
 Slab foundation can be mounted on any kind of soil
Slab foundation can be mounted on any kind of soil
Like the tape, the monolithic slab can be buried or not. In the first case, the slab is poured into the pit and has high ribs. The main disadvantage of such a device is its high cost. But this is the only type of foundation that has no restrictions on the type of soil.
How to calculate the depth of laying, and what should be the slab? The heaving of the soil does not affect the state of the structure on such a basis, therefore this distance is determined based on the operational requirements for the building.For more information on building the foundation, see this video:
The summary table shows the types of foundations, soil types and the mass of the structure
| Foundation type | Soil type | Heaving | Freezing depth | Building type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Columnar | sand of coarse and medium fraction, coarse, gristly | suitable for heaving soils | small-sized, light | |
| Pile | except for rocks | suitable for non-porous soils | the device is allowed with a large freezing depth | any, without an underground floor |
| Tape | sand of coarse and medium fraction, coarse, gristly | suitable for heaving soils | lungs | |
| Monolithic slab | without Borders | suitable for heaving soils | any heavy |
The most common mistakes
We have already said how to properly lay the foundation for a house. We also talked about the mistakes that are encountered, but according to existing experience, each of them must be named again. This approach helps to avoid them during construction work.
- The first mistake is that the features of the soil and the depth of its freezing were not taken into account. Potential consequences: Cracks in your home, reduced lifespan.
- The second mistake is significant savings on building materials. As much as you would like to build a budget house, it is still not recommended to save on the quality of building materials. All this will lead to the rapid destruction of your home. In order to avoid this mistake, it is necessary to correctly calculate the cost of the entire project, find materials from a domestic manufacturer, similar in quality to foreign ones.
- The third and final mistake is poor-quality construction work. Here you can list the incorrect, inaccurate marking of the corners of the pit, non-observance of the temperature regime when the concrete solidifies, the withdrawal of water under the concrete - all this will definitely lead to a distortion of the base of the house, which means to its destruction.
All these stages of construction work, all possible mistakes must be carefully studied in order to build a high-quality foundation for a private house. Each of the stages has its own individual characteristics, which are not indicated by us, but which you may encounter during construction work.
In conclusion, I would like to give one simple but very important advice. If you decide to build a house on your own: from the construction of the foundation to finishing work, do not rush to get to work. Read the necessary literature, ask for advice from friends-builders, seek help from friends who may have already gone through this. "Filter" information: by throwing away all unnecessary, eliminate the gaps that remain. Draw up a rough plan of action and a finished project for your building. Only now can you start working. Remember, you will take a lot of physical and psychological strength, but the result will definitely please you. You built this house yourself!
Calculation of the sole area
An important place in the design of the base for future construction is occupied by the calculation of the area of the sole. This stage of work is carried out according to the formula shown in the figure below.
The value obtained as a result of the calculations is the approximate total area of the base of the foundation, necessary in order not to literally push the soil under load. If we are talking about the construction of the most expensive - a slab foundation (in the article on the calculation of reinforcement you will appreciate how "economical" this solution is), then you can completely avoid these calculations, because it is enough to fill the slab under the entire area of the house, and such a sole will be enough to prevent all surprises that the soil presents.
Each type of soil, depending on the depth, density and porosity, has its own load resistance. It goes without saying that soil layers at great depths as a result of natural compaction are characterized by high values of resistance.So, if you plan to build a foundation to a depth of less than 1.5 m, then the calculated soil resistance will take on a slightly different value. In this case, it will be calculated according to the formula: R = 0.005R0 (100 + h / 3), where R0 is the tabular value of the design resistance, h is the depth of the foundation relative to the zero mark, see. In turn, a lot depends on groundwater, because increased soil moisture reduces its resistance to load.
Naturally, with an independent calculation, you will have to tinker with calculating the load from the structure being erected, which will be on the layers of soil under the base of the foundation. This includes:
- the total load from the structure, including the approximate one - from the foundation (data from the table presented in the figure below are used);
- load from objects that will be placed in the building (fireplaces, furniture, people);
- weight of seasonal snow loads. For the middle lane, it is taken equal to 100 kg per sq. m of roof, for the south - 50 kg, for the north - 190 kg.
The value of the basement foot area obtained as a result of calculations is used when drawing up the foundation project: choosing the width of the tape (for a strip monolithic base) or the support area (for columnar, pile types of foundations). Consider a specific example of calculation for a 6 × 8 m stone house. How the reinforcement for the foundation is selected will be discussed in a separate article.
An example of a foundation calculation
Suppose we are building a two-storey stone house 6 × 8 m, the design of which includes one internal load-bearing wall. The mass of the house, taking into account all the loads, turned out to be equal to 160,000 kg. The soil is wet clay (design resistance - 6 kg / cm²). Condition factor - 1. Reliability factor - 1.2. We substitute all the values in the formula for calculating the area of the sole:
S = 1.2 × 160,000 / (1 × 6) = 32,000 cm² = 3.2 m²
For strip foundations: with a total strip length of approximately (6 + 8) × 2 + 6 (inner wall) = 34 m, the minimum strip width is 3.2 / 34 = 0.1 m. This is the minimum value!
If we consider the foundation for a light wooden house, provided that the minimum foot area is equal to 1 m2, then for the construction of a pile foundation (the base area of each pile is taken to be 0.07 m2, provided that the lower part of the pile is 0.3 m in diameter ) would need:
1 / 0.07 = 15 piles
Sheathing and reinforcement
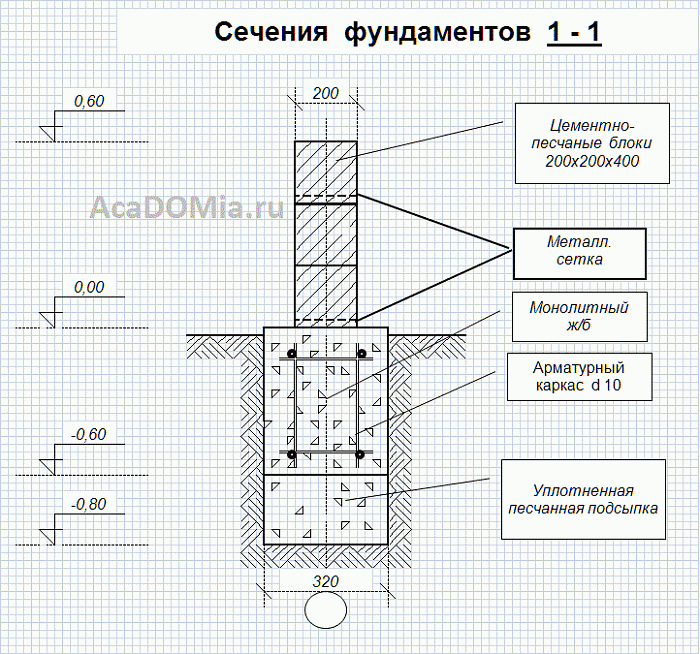
The lathing is, although a preparatory stage of work, it is extremely important. The concrete will fit in the shape of the crate, therefore, when installing it, it is necessary to accurately measure, align the geometric dimensions and, most importantly, observe the same height level at all points. Ideally, this can be done simply with a laser level, but in its absence, you will have to arm yourself with an ordinary water level, a plumb line, a tape measure, several running meters of twine and a long straight rail.
Wood corners are pre-installed in the corners of the future house. Starting from one of the corners, the rope is pulled to the next. And then all the corners are strictly oriented perpendicular to the ground, at the same level along the plane and observing a right angle between each. After marking, the length of the diagonals is checked (they must be strictly the same). The crate itself is mounted from boards, slate or corrugated board.
Reinforcing reinforcement, metal or composite, is mounted inside the crate. A volumetric lattice is built from the bars with the help of knitting wire or welding with a step depending on the required concrete strength. Usually the side of the square is 500mm. It will be preferable to refrain from welding, in the place of welding seams there are foci of corrosion, which over time deteriorates the strength characteristics of concrete.
It is better to cover the lathing boards from the inside with plastic wrap so that they can be reused.
Sometimes builders forget about technological holes in the foundation, which is unacceptable.After all, it is easier to do the right thing right away than to spend time fixing the flaws.
The holes in the facade have several purposes:
- air ducts, to ensure ventilation in the summer, if there is no ventilation in the underground, mold begins to form, and the fungus can begin to spread throughout the building;
- heating and water supply outputs.
Punching holes in hardened concrete up to a meter thick is difficult and thankless, therefore it is much easier to install plastic pipes of the appropriate diameter in the formwork. Ventilation openings in winter are closed with special plugs
When designing a water supply system, it is important to understand that in winter the water in the pipes can freeze and destroy the pipe itself, therefore, electrical heating must be laid or the pipes must pass below the freezing level
Perimeter base
A strip foundation is a foundation that is laid along the entire perimeter of future walls. On such a foundation, walls of brick, concrete, adobe can be erected. This basis is ideal for multi-storey buildings, as it is designed for heavy walls. The height of the foundation for a two-story house is calculated based on:
- the level of soil freezing,
- how deep the groundwater goes
- soil composition.
As a rule, this is from 0.8 to 1.6 meters, depending on the bearing soil within the freezing range.
The strip foundation for a two-story house has several varieties:
-
Rubble - which is made from rubble masonry. If the depth is not more than 55 -60 cm, then the strip foundation is laid out to the entire depth of the ditch. If more, then sand is poured in layers of 10-15 cm, moistened with water and compacted. The height of such a "pillow" is no more than half of the entire height of the base.
- Brick - when laying the first layer of brick or stone, you must first pour a concrete mixture, 3-5 cm thick, and lay a brick on it. Tamp and make sure that there are no voids, otherwise it can lead to settlement of the structure.
- The rubble concrete version of the belt base is a very strong and durable base. The instruction for bookmarking this type looks like this:
- At a depth of up to a meter and vertical walls, the first thing to do is tamp down, the bottom of the ditch is compacted.
- The construction mixture is poured (concrete with a layer thickness of 5 cm).
- It is filled with stone chips, bricks, crushed stone, etc. layers (layer 15-20 cm).
- Liquid concrete mortar (5 cm) is poured and compacted tightly.
- Next, the next layer.
If the depth is more than one meter, and the width is greater than the width of the base sole, formwork technology from wooden panels or planks is used. The formwork is removed two to three weeks after the end of the work.
-
Sandy - used for the construction of one-story houses, small in size. In this case, the width of the foundation is calculated simply. 10-15 cm is added to the planned wall thickness. A ditch is dug to a depth of a dense layer of soil, after which coarse sand is poured in layers of 10-15 cm, each layer is moistened and compacted. Before reaching the upper edge of the trench 25-30 cm, crushed stone is laid out on the sand, also in layers of 10-15 cm and poured with concrete or cement-clay mixture, compacted, compared with the surface of the earth. Then brickwork is displayed in 2-3 rows above the ground surface. Waterproofing is done and the basement is removed.
- Slit. Also used in the construction of low-rise buildings. It is quite a budget option, unlike when formwork is underway. Another plus is the dense placement of concrete using vibration compaction, which gives a tight adhesion to the side surfaces of the ditch.
A slab foundation is a type of strip foundation, that is, a shallow strip foundation with rigid spatial reinforcement not along the perimeter, but along the entire bearing plane.The construction of such a base is quite costly and is justified only for low-rise buildings or the construction of buildings of non-standard shapes on the so-called "floating" soils.
Another nuance is the fact that strip foundations are used when an internal cellar is set up in the house.
This type of foundation is durable, reliable, but material-intensive, which, of course, is costly. But when it comes to a two-story building on the basis, it is better not to save. Because it can come out as in the saying "The miser pays twice."
Soil, exposure to frost and proximity of water to the surface
It is necessary to dwell in more detail on the characteristics of the soil and the depth of passage of groundwater, as well as the influence on the basis of the process of freezing and thawing of the soil.
In order to determine the calculations, what should be the thickness of the foundation, the depth of the ditch under it, the type of foundation for the house, you should carefully consider what soils lie on the future construction site.
There are three groups into which soils are subdivided:
- The soil, consisting of loam and fine sandy soils, is heaving.
- Hard and rocky soils are non-porous.
- Coarse soil, coarse gravelly sand - slightly loose.
This gradation should be taken into account, since the factor of change in the volume of the soil under the influence of different climatic manifestations (frost, heat, moisture) affects the foundation. If this parameter is ignored, the house may “float” or “go cracked”.
The next factor, seriously, affecting the strength of the foundation is soil freezing. Again, the type of soil on the construction site is very important, since its porosity and looseness determines how much it is exposed to low temperatures or high in combination with groundwater close to the surface.
And finally, the effect of moisture. From how deeply or close to the surface of the earth the underground waters pass sometimes whether construction is possible at all. Moreover, when it comes to a two-story building.
The close location of waters to the surface in combination with heaving soils calls into question the construction of a house. The best thing would be to search for a new site, because even with a very high-quality foundation with non-standard solutions (as a way out of this situation), the house will “float” with all the consequences - cracks on the walls, deformation, the constant need to strengthen the foundation, etc.