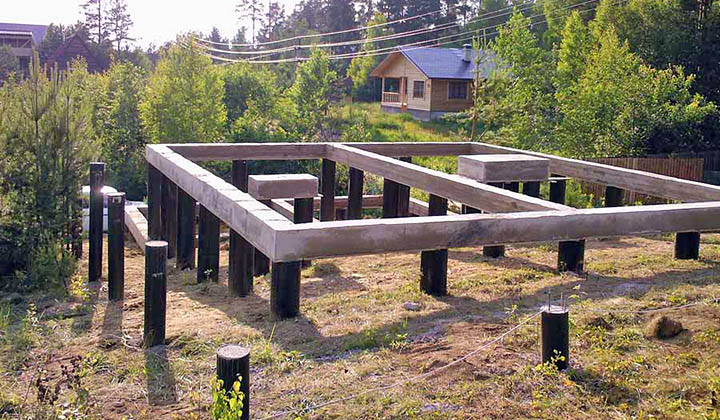
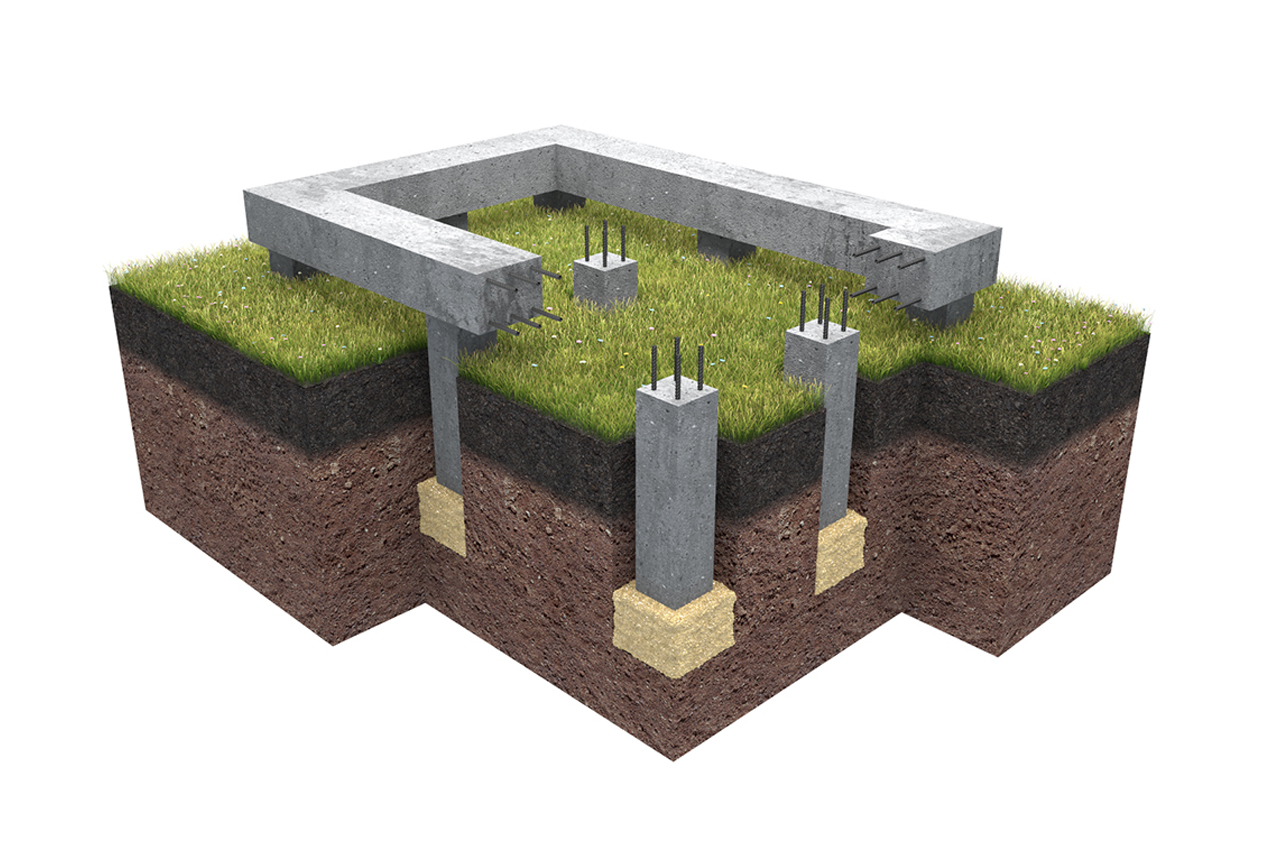
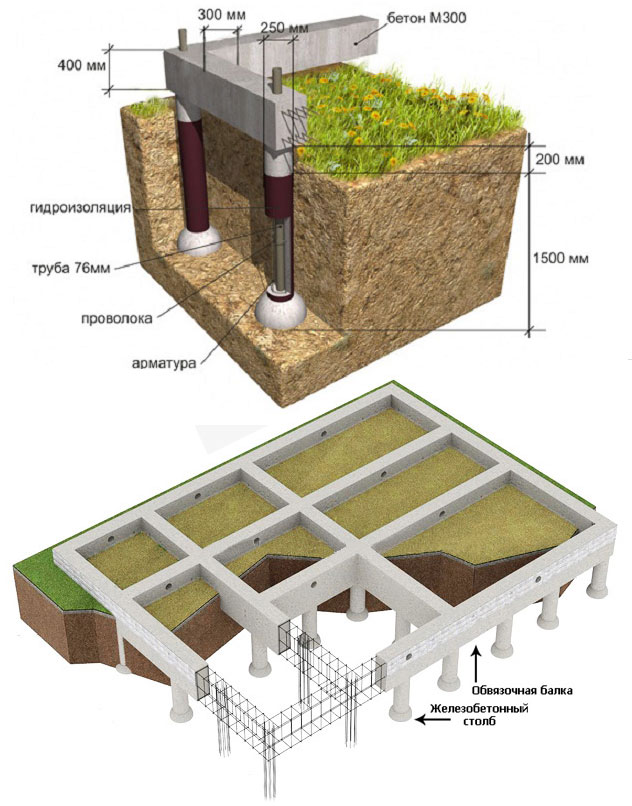
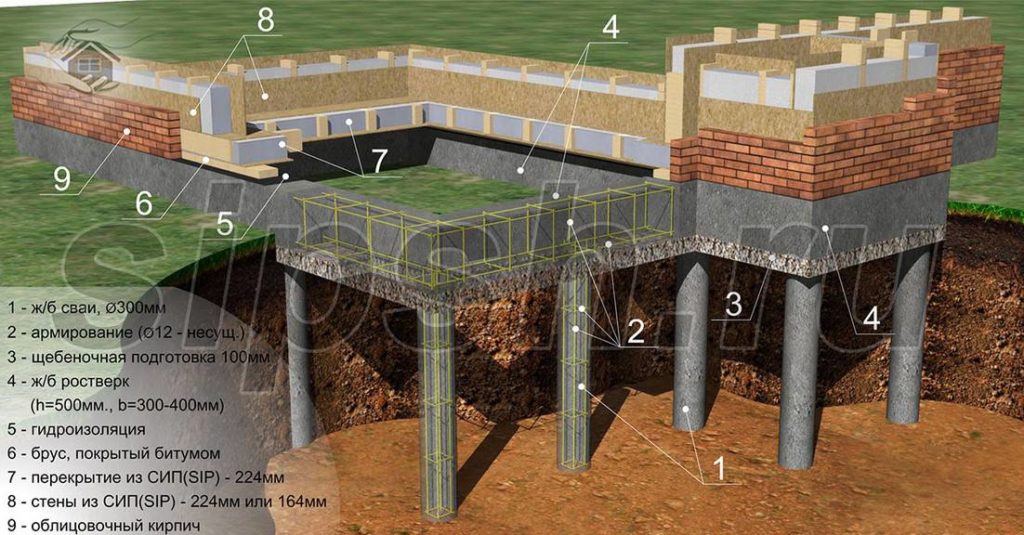
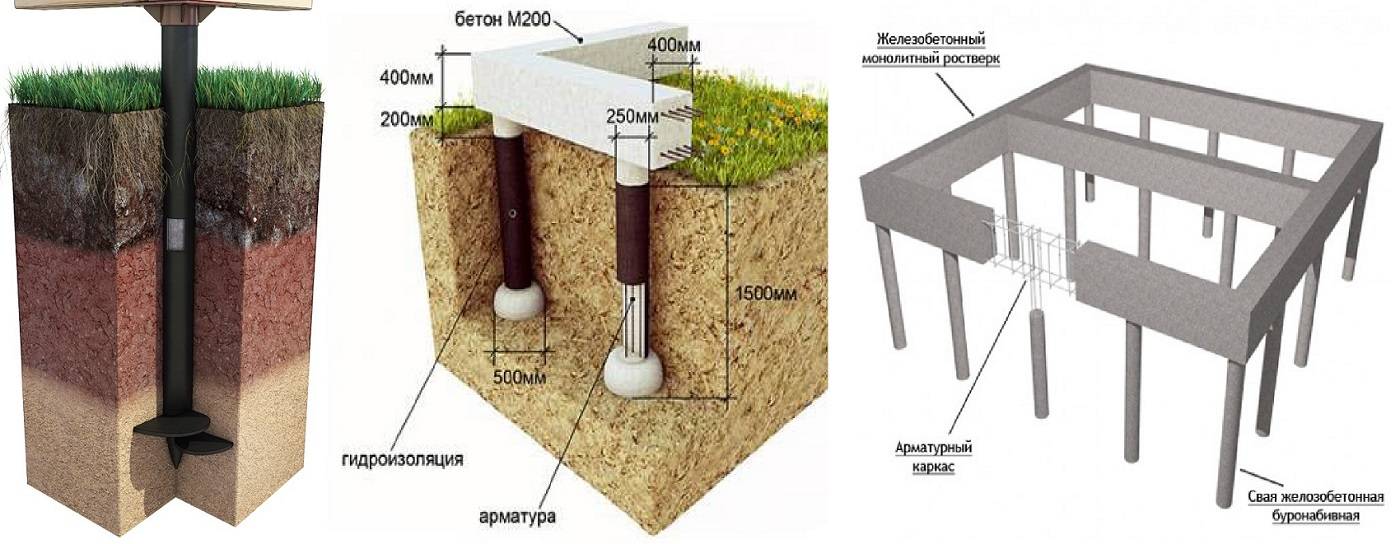
What is a pile-grillage foundation
A pile foundation is probably imagined by everyone: it is a certain number of piles buried in the ground to the level of the bearing layer or below the freezing level. In its pure form, this type of foundation is rarely used. This is due to the peculiar design, which does not allow redistributing the load from the house between the piles. Therefore, the pile foundation is mainly made for log houses from logs or beams, sometimes - for frame buildings. These types of building materials, due to their characteristics, redistribute the load themselves. They are poorly compatible with houses made of other materials.
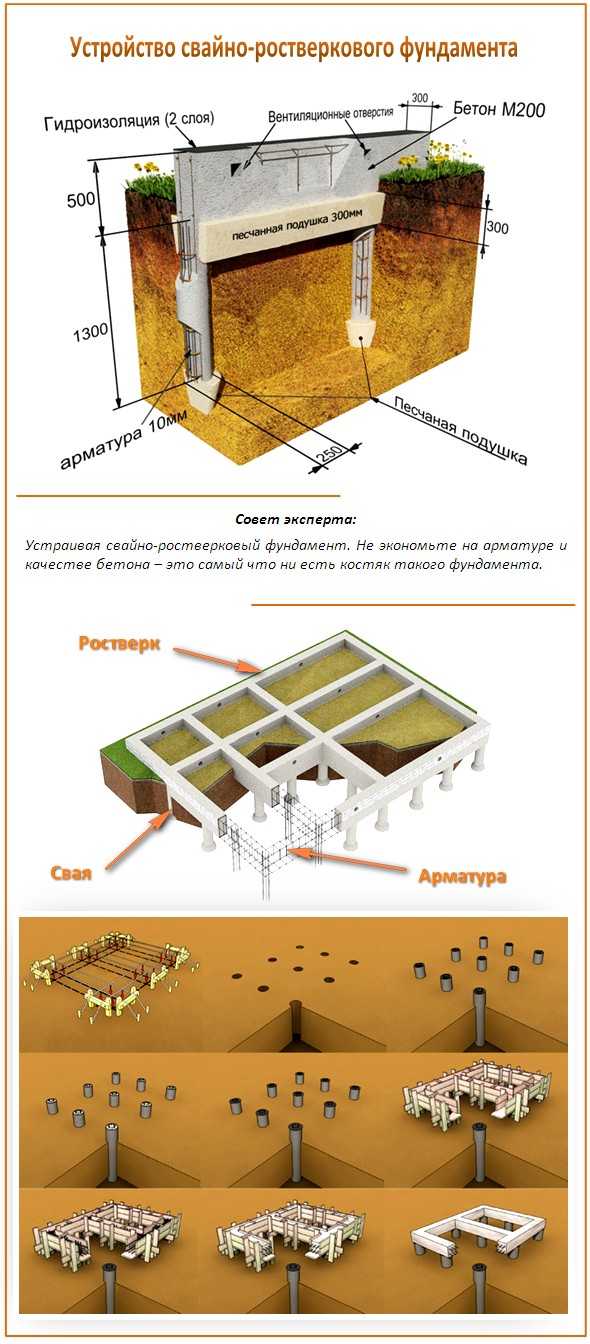
But their improved form - a pile foundation with a grillage - is devoid of many drawbacks and can be used both for brick and block buildings. In them, all the supports are tied with a tape made of metal or reinforced concrete (concrete) into a single structure. This tape is called the grillage.
It looks like a pile-grillage foundation taken out of the ground
A grillage is a part of the foundation that unites the pile heads and serves as a support for the walls. It is the grillage that accepts, and due to the closed structure, redistributes the load, transferring it to the piles. It can be metal, wood, concrete or reinforced concrete. By the type of execution, concrete (reinforced concrete) grillages are low and high.
Distinguish between pile foundations with a high and low grillage
The high grillage is above ground level. Most often it is made of metal - channels of large cross-section or square metal pipes. They also make such a grillage from concrete, but its structure is more complicated: you have to figure out how to pour the tape at a distance from the ground.
How does the grillage work and what does it give
Any house in different parts will give a different load: decoration, furniture, sanitary ware, other things are unevenly placed. Consequently, the load from different parts of it will be different. The grillage takes on these uneven loads and redistributes them. The “leveled” load is already transferred to the piles.
What is the difference between pile and pile-grillage foundations (to increase the size of the picture, right-click on it)
Why is this good? The fact that with the same loading of piles, there is less chance that they will shrink unevenly. And uneven shrinkage, as you know, leads to cracks in the foundation and walls. Therefore, the pile-grillage foundation is more stable. Although the main drawback of pile foundations remains: we cannot know what kind of soil is under each of the piles. Therefore, it is unrealistic to predict their behavior. That is why architects are not very fond of them: it is impossible to guarantee the long-term operation of the house.
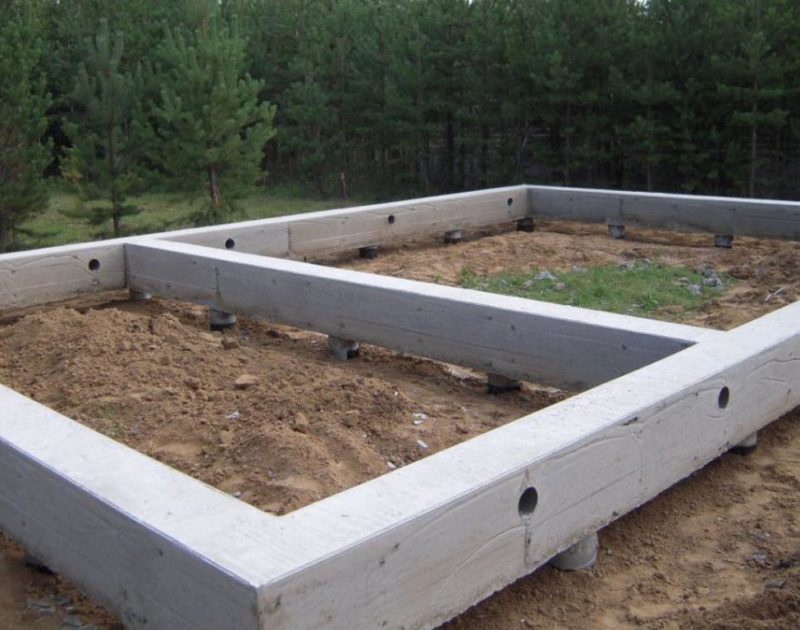
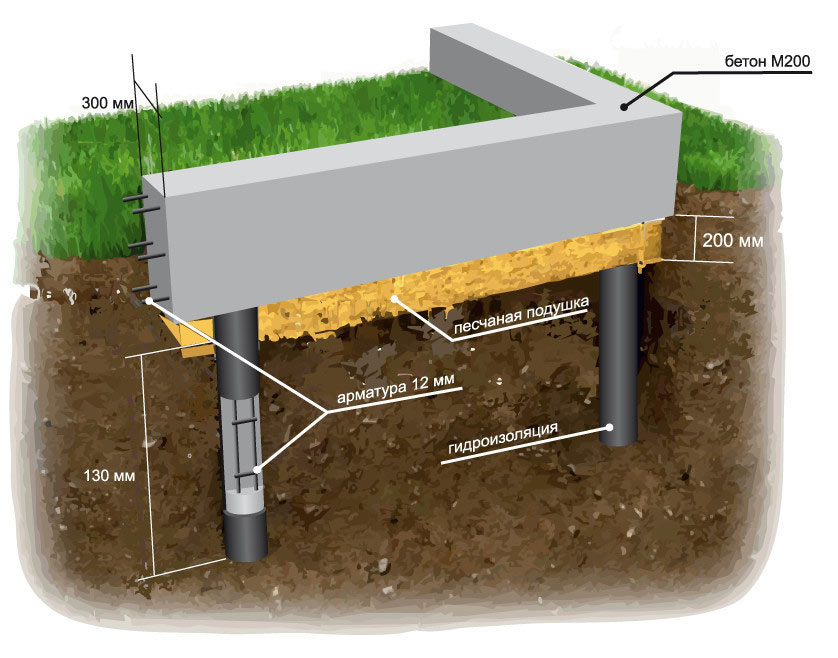
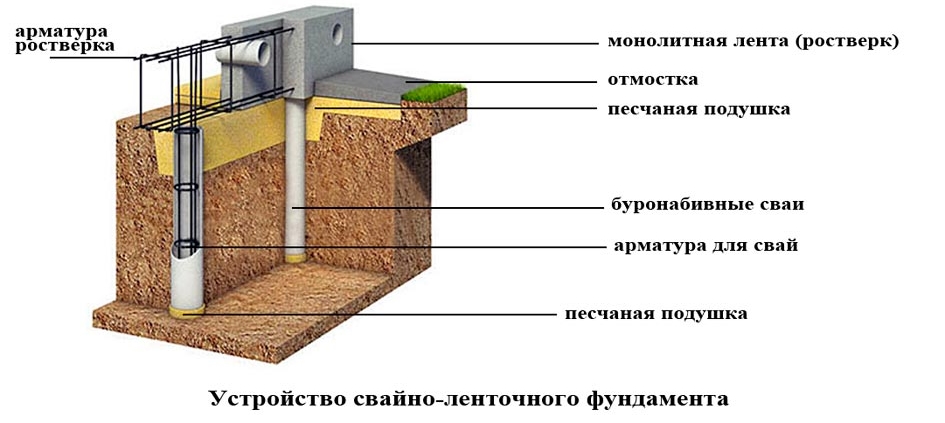
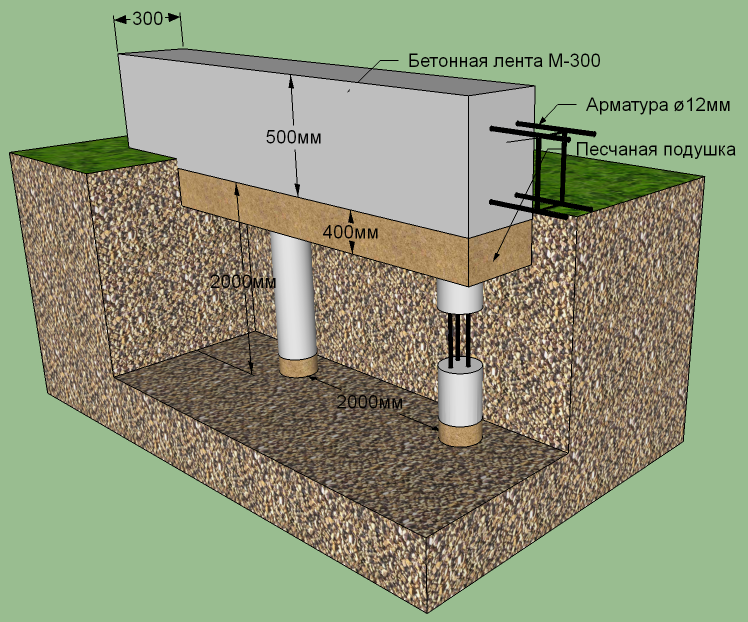
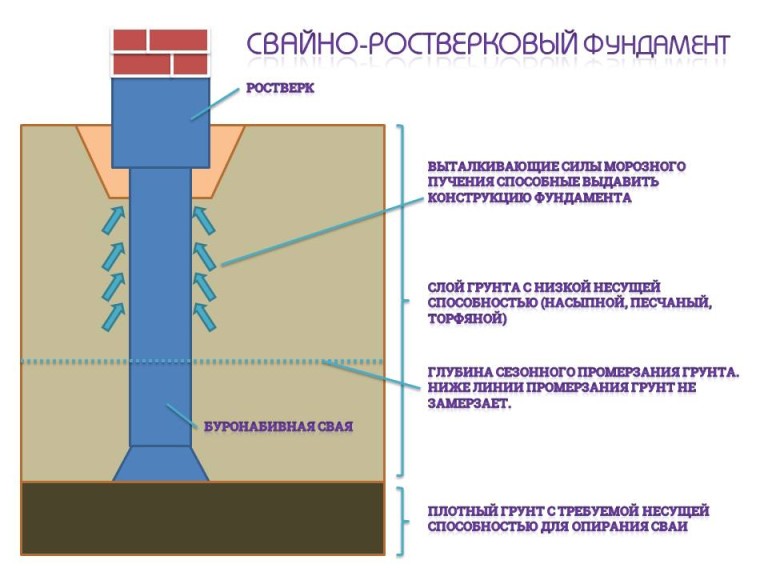
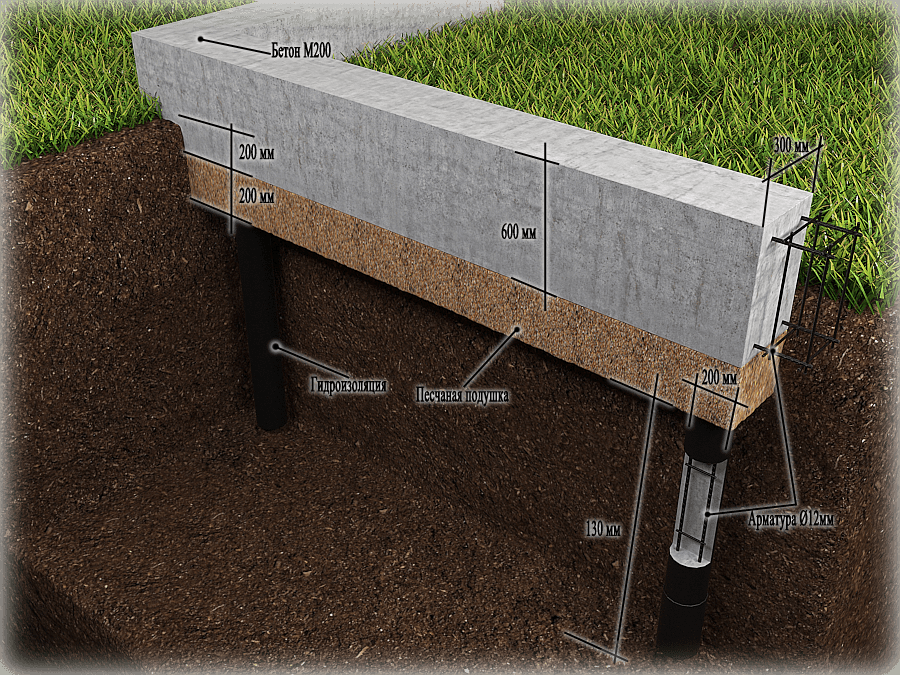
Strip foundation on piles
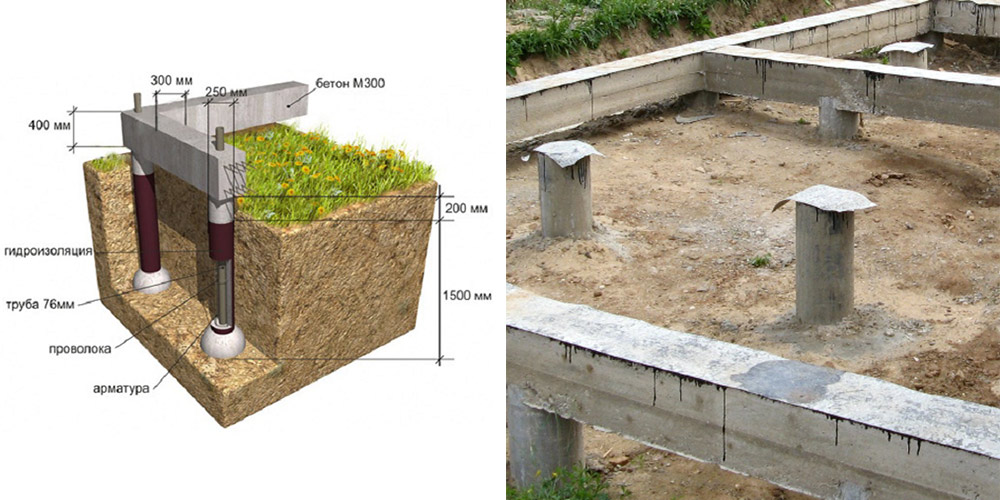
Low grillages are more predictable in this regard. They usually start below ground level and are cast from reinforced (or not depending on the project) concrete. Moreover, the reinforcement of the piles is connected with the reinforcement of the grillage.
In this case, the grillage is a shallow strip foundation and it is made using the same technology. It differs in that it has a rigid connection with the piles, which significantly increases the reliability and stability of the structure. Such foundations are also called tape-based on piles or pile-tape. This design is almost ideal: it combines the advantages of the pile and strip foundations, largely compensating for their shortcomings.
The device of the pile-strip foundation (to increase the size of the picture, click on it with the right mouse button)
How does he work? The load from the house is transferred to the belt. Due to the presence of longitudinal reinforcement, it is redistributed over the entire area.Since the tape also rests on the ground, part of the load is transferred to it, the rest falls on the piles. In this case, the load and shrinkage are uniform: they are "aligned" by the tape.
In winter, when heaving forces begin to act on the foundation, all the advantages of the pile-strip foundation are manifested. If the house stands on heaving soils, their depth is below the freezing level, it is very difficult to imagine the conditions under which the house will be flexible or it will give uneven shrinkage.
When heaving forces act on the tape, the "heels" of the piles, and they themselves, do not allow the soil to move the foundation. Therefore, strip-pile foundations are an excellent choice on highly heaving soils. At the same time, the costs are much higher than in the construction of a conventional pile foundation, but much lower than in the construction of a tape below the freezing depth.
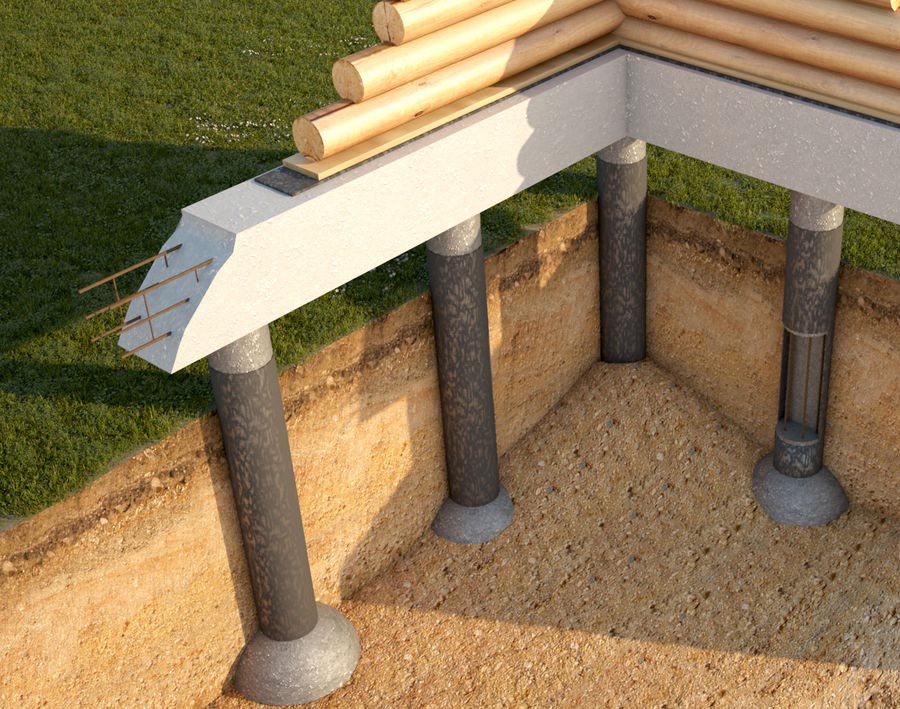
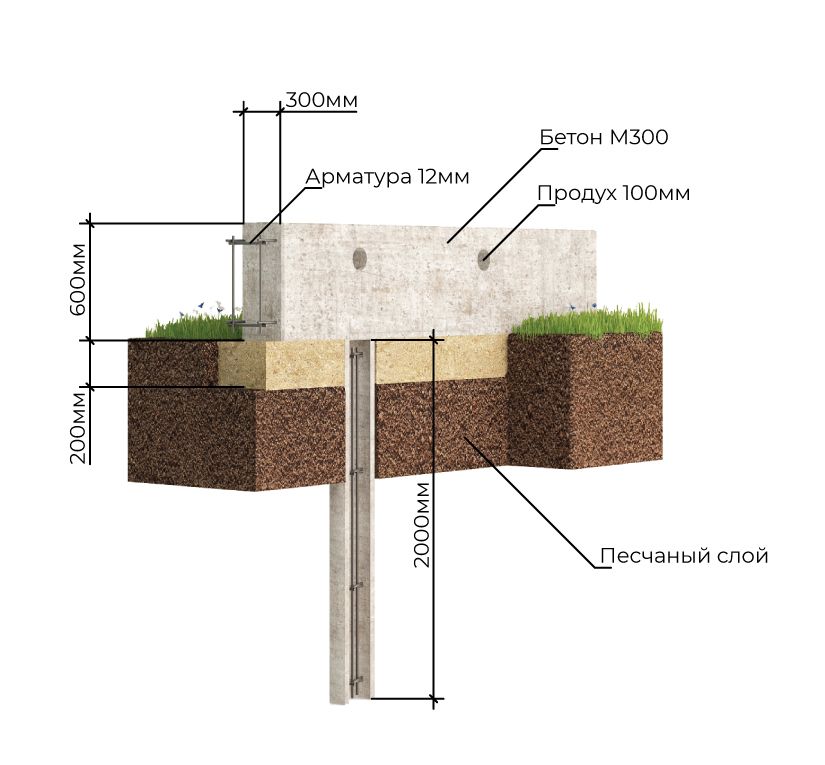
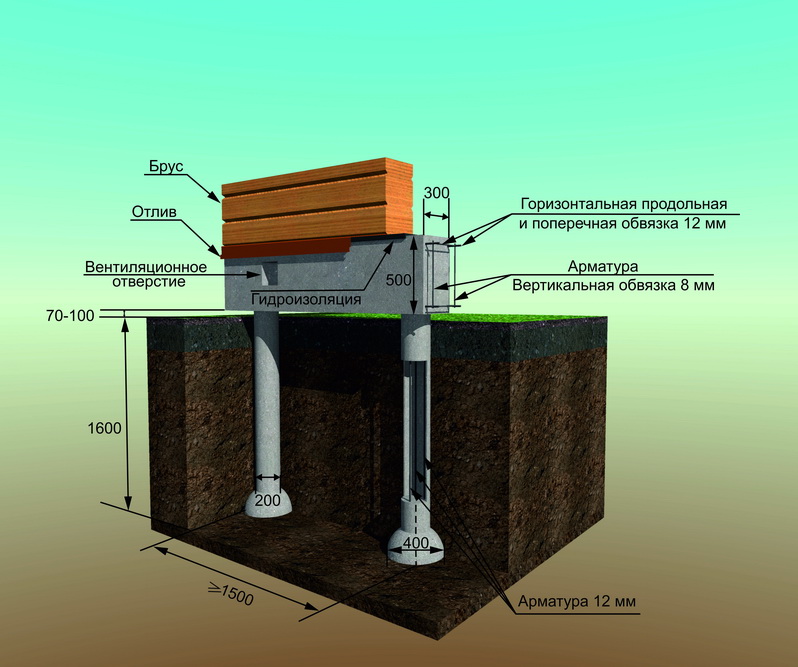
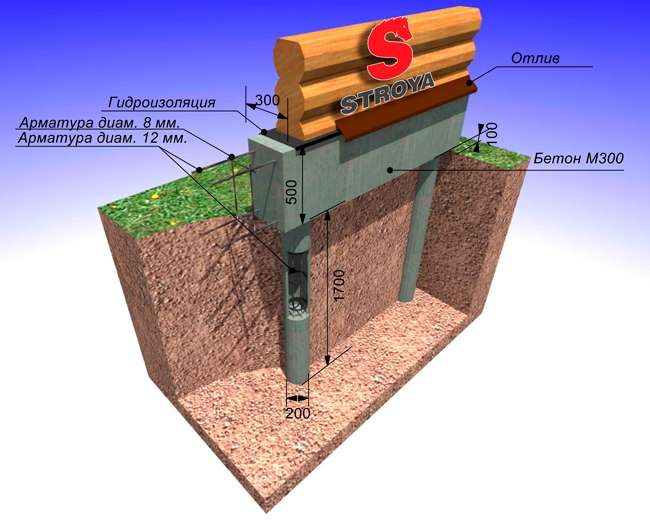
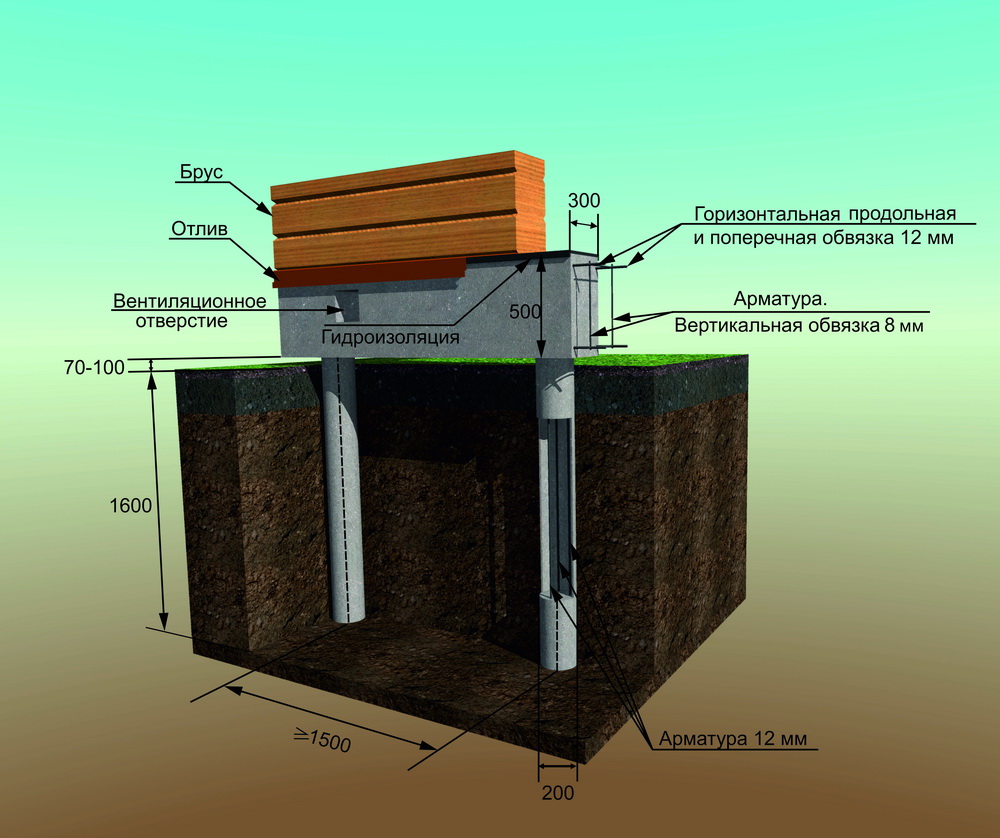
Pile foundation with a high grillage
A high grillage is a beam that unites the heads of the piles and redistributes the load on them from the structures located above, while its base is located above the ground surface.
The greater the distance between the piles, the larger the cross-section of the used beam should be.
A beam, a log, a channel, an I-beam, a corner (section beams) can be used as a beam.
Tying the pile-screw foundation with a bar or log
The strapping beam (Fig. 1) is used in the construction of wooden, frame structures.
Picture 1
Bar section:
-
150x150 with a step between piles of 2500-2700 mm;
-
200x200 mm with a step between piles of 3000 mm.
Attachment to the head is carried out on a hairpin.
The waterproofing device is not critical, since metal does not absorb moisture like concrete. However, since condensation can form on metal surfaces, it is still recommended to install a waterproofing pad between the support platform (head) and the wooden structure.
Log (Fig. 2). This material is resistant to bending, as the wood retains its integrity. A rounded log gives a greater deflection in relation to an untreated one, since in this case the integrity of the solid layers of wood is violated.
Picture 2
The first crown of a log structure is allowed to be laid directly on the head. If the foundation is made of concrete, then it should be made of oak or larch, as this will increase the service life of the structure. In the case of a pile-screw base, these measures can be abandoned if the height of the grillage is at least 500 mm from the ground level.
Strapping with a bar / log is the most economical and quickly implemented type of connection. To prevent the strapping from deforming, the piles must be located at the same level. Otherwise, the alignment is carried out by partially cutting the bar / log.
Docking of a bar / log (Fig. 3). To connect in proportion to each of the bars, cuts are made from above and below, the bar / log is folded at right angles. Joints should be treated with special solutions that protect against moisture, laid with jute.
Figure 3
The use of antiseptics for timber / logs is mandatory only for concrete substrates. When building a foundation from screw piles, this procedure is advisory, but only if the height of the grillage is at least 500 mm from the ground level.
Tying the pile-screw foundation with a channel or I-beam
The constructive solution of the metal grillage is determined depending on the loads on the foundation SNiP II-23-81 * "Steel structures", SP 53-102-2004 "General rules for the design of steel structures".
The strapping is carried out both manually and with the involvement of special equipment (depending on the standard size of the channel / I-beam).
Channel (Fig. 4 - 7). Fits flat or on the edge. The rib option works better for deflection, but due to the resulting torsional moment, in this case it is better to use a welded channel.
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
If the channel is laid flat (with shelves down), then with a pile pitch of more than 2000 mm, it bends even under its own weight, therefore, when choosing this option, the distance between the piles should be designed no more than 2000 mm.
I-beam (Fig. 8). It is used for the reconstruction of foundations.
Figure 8
In both cases (channel or I-beam), the connection of structural elements is welded.
Sufficient thickness of long products (from 5 mm), as well as the susceptibility of this part of the structure only to atmospheric corrosion, will ensure that its service life meets the requirements of GOST 27751-2014 “Interstate Standard. Reliability of building structures and foundations. Basic Provisions ”, even without additional anti-corrosion protection. Nevertheless, after the completion of welded work, the structure (at least for reasons of aesthetics) should be treated with an anti-corrosion compound.
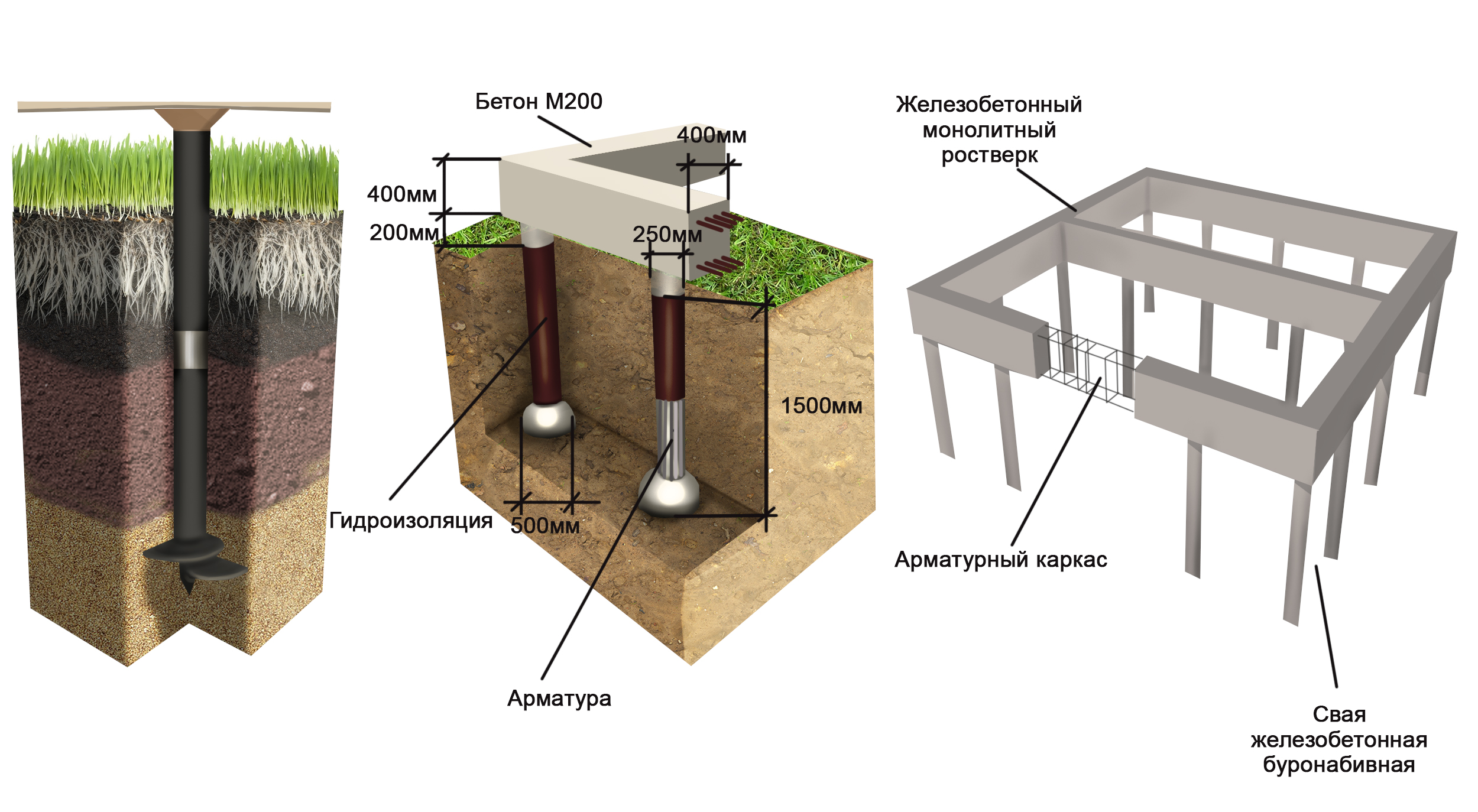
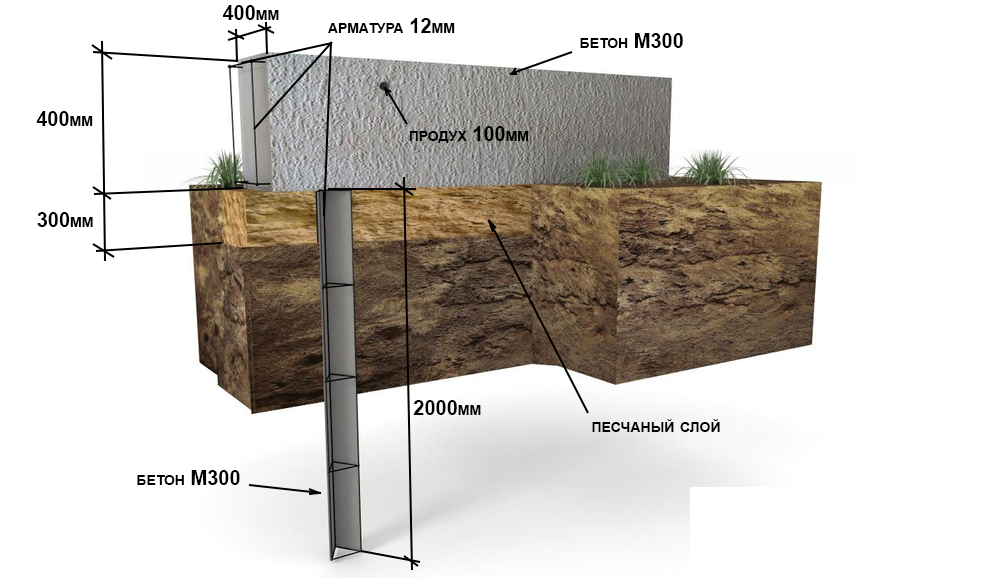
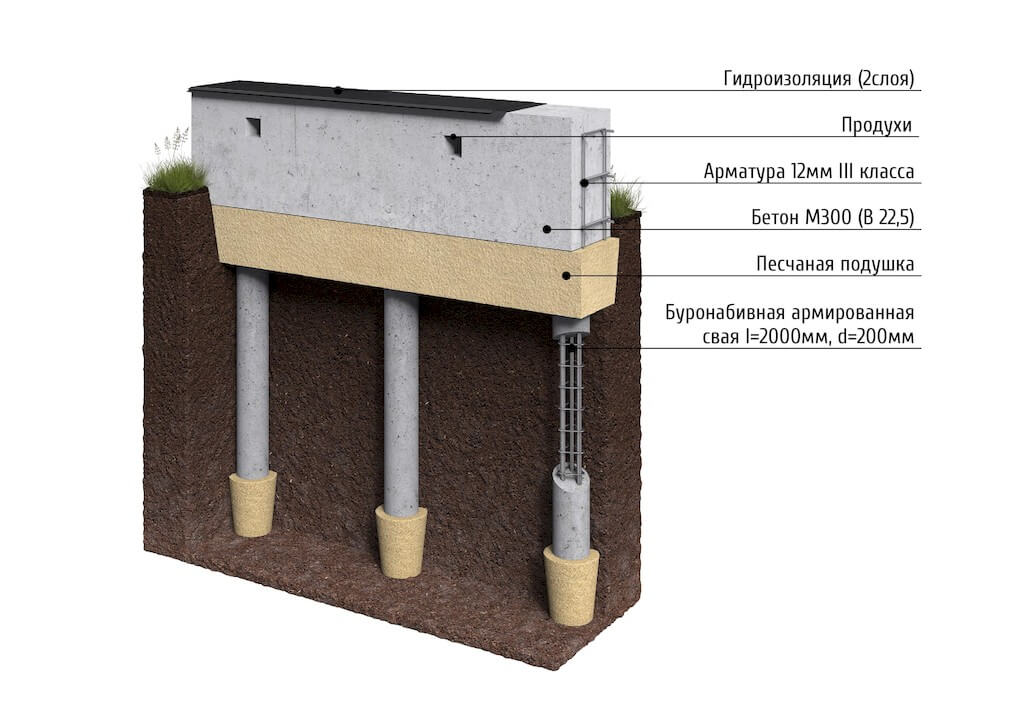
DIY pile-grillage foundation using bored technology
Drilling
Before starting work on the construction of the foundation using bored technology, it is necessary to break down the area for drilling. The placement of piles on the plan and on the ground begins from the corners of the house, then at the places where the perimeter and load-bearing walls meet.
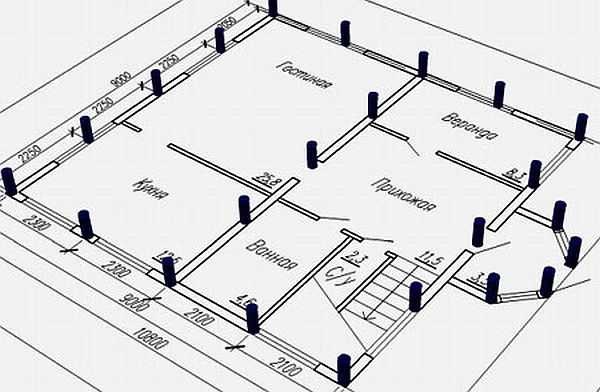
Design scheme of pile placement
For drilling wells for the installation of bored piles, a special technique is used - yamobur - with a vertical drilling auger. The formwork is lowered into the resulting well. If the pile has a circular cross-section, then the role of formwork can be played by roofing material folded in several layers or galvanized steel. Also, for formwork, you can use wooden panels to form piles of rectangular cross-section.
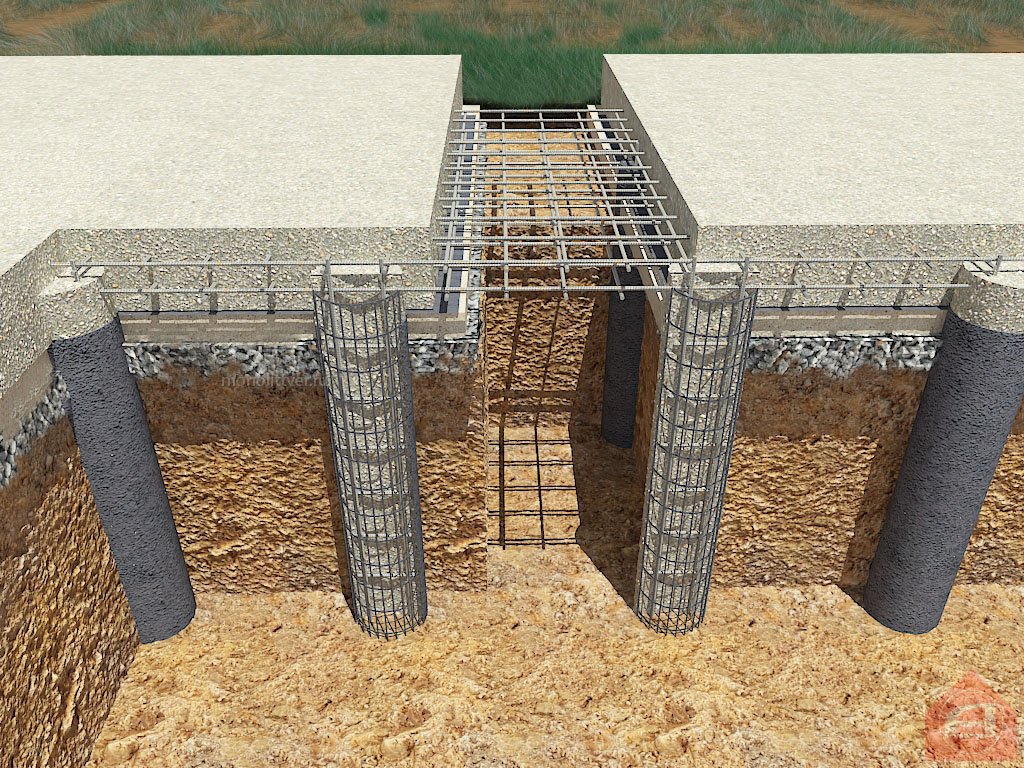
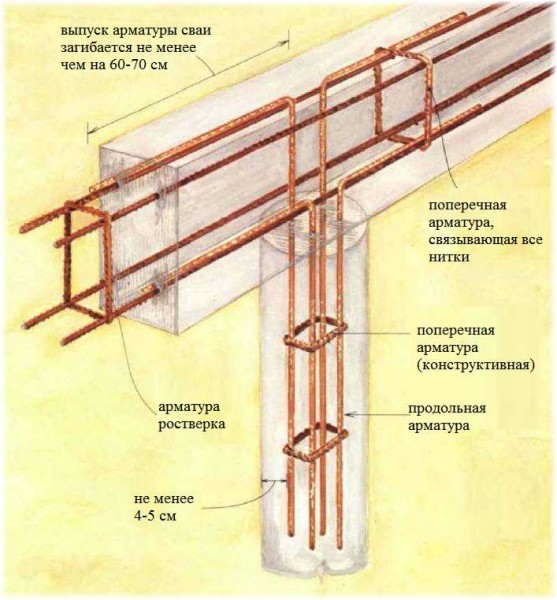
After drilling and installation of the formwork, a reinforcing cage is installed in the shaft.
Reinforcement cage
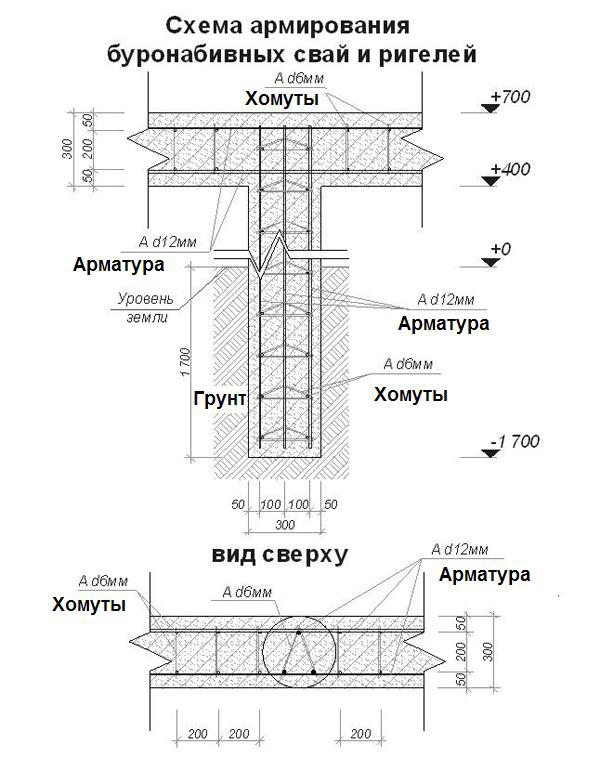
The reinforcement cage is manufactured at the construction site from twisted reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm. To do this, measure 3 - 4 rods with a length exceeding the depth of the well by 60-70 cm. Subsequently, these "tails" will be linked to the reinforced frame of the grillage.
Reinforcing rods are formed in the form of a tri-quadrangle with such a size that there is a gap of 4-5 cm to the walls of the formwork. The rods are tied with transverse reinforcement of a smooth profile with a diameter smaller than the main rods.
Pouring with concrete
In the case of a small volume, concrete for pile filling is prepared directly on site using concrete mixers.
Having filled the pile with concrete, it must be vibrated in order to exclude shrinkage and the formation of voids in the body of the structure. This process will achieve uniformity and the required strength. During the initial setting of the concrete in the structure, which is 4-5 days, the frames are prepared for the grillage.
After pouring all the piles, the grillage is installed. In the case of a high grillage, a lower formwork platform is prepared. The lower support of the formwork can be sand, if the height does not exceed 30 cm, or wooden shields that rest on the edges of the piles. From below, the formwork is reinforced with additional supports.

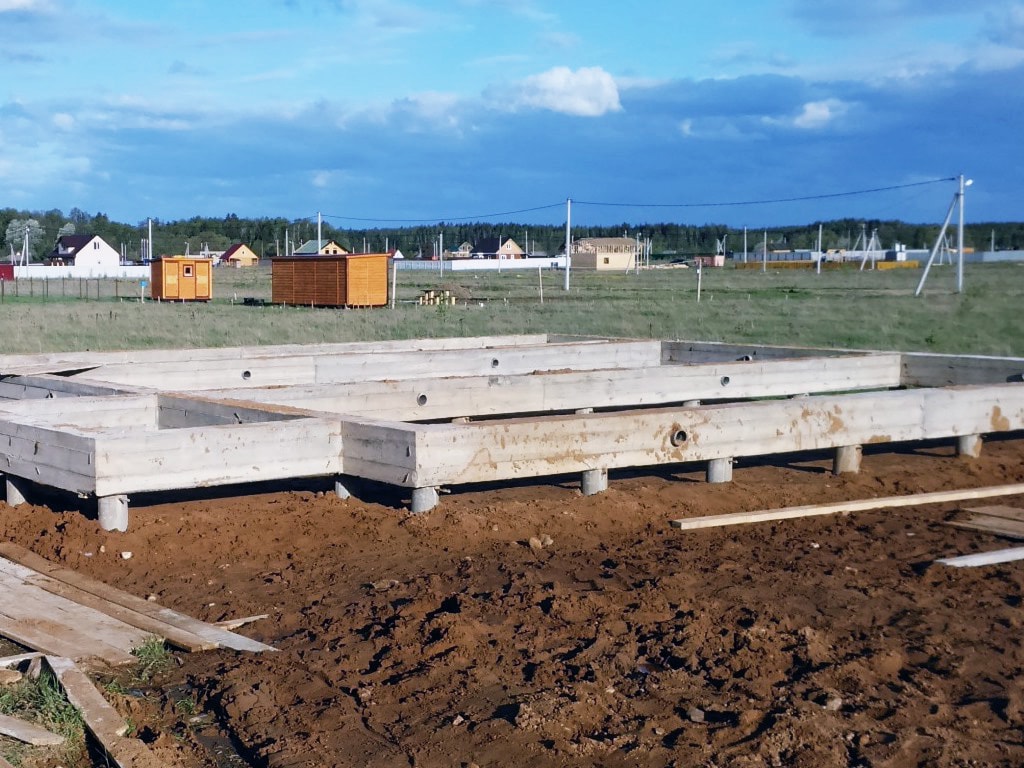
View of the pile foundation before installing the formwork and grillage frame
After the bottom of the grillage is formed, the grillage frame is mounted, which is connected to the pile frame. The side walls of the formwork are installed and then the concrete is poured.
If the concrete is poured at a temperature of +20 and above, the formwork can be removed after 4 days. If work is performed with an ambient temperature not higher than +10, then a pause of 14 days is required.

The formwork is ready for pouring concrete
Materials used
The design features of buildings and the magnitude of the loads obtained dictate the use of materials for creating grillages:
- reinforced concrete;
- wood;
- metal.
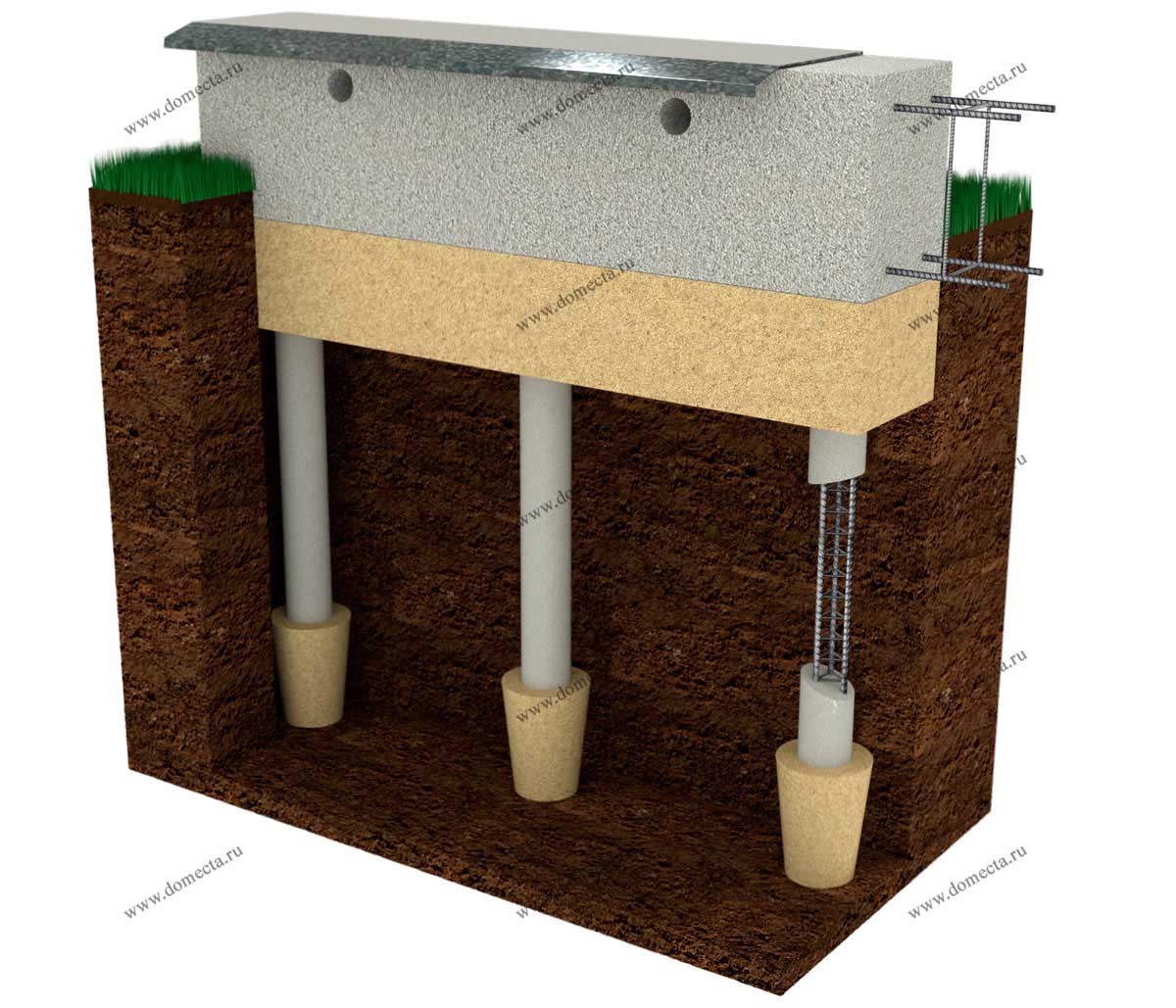
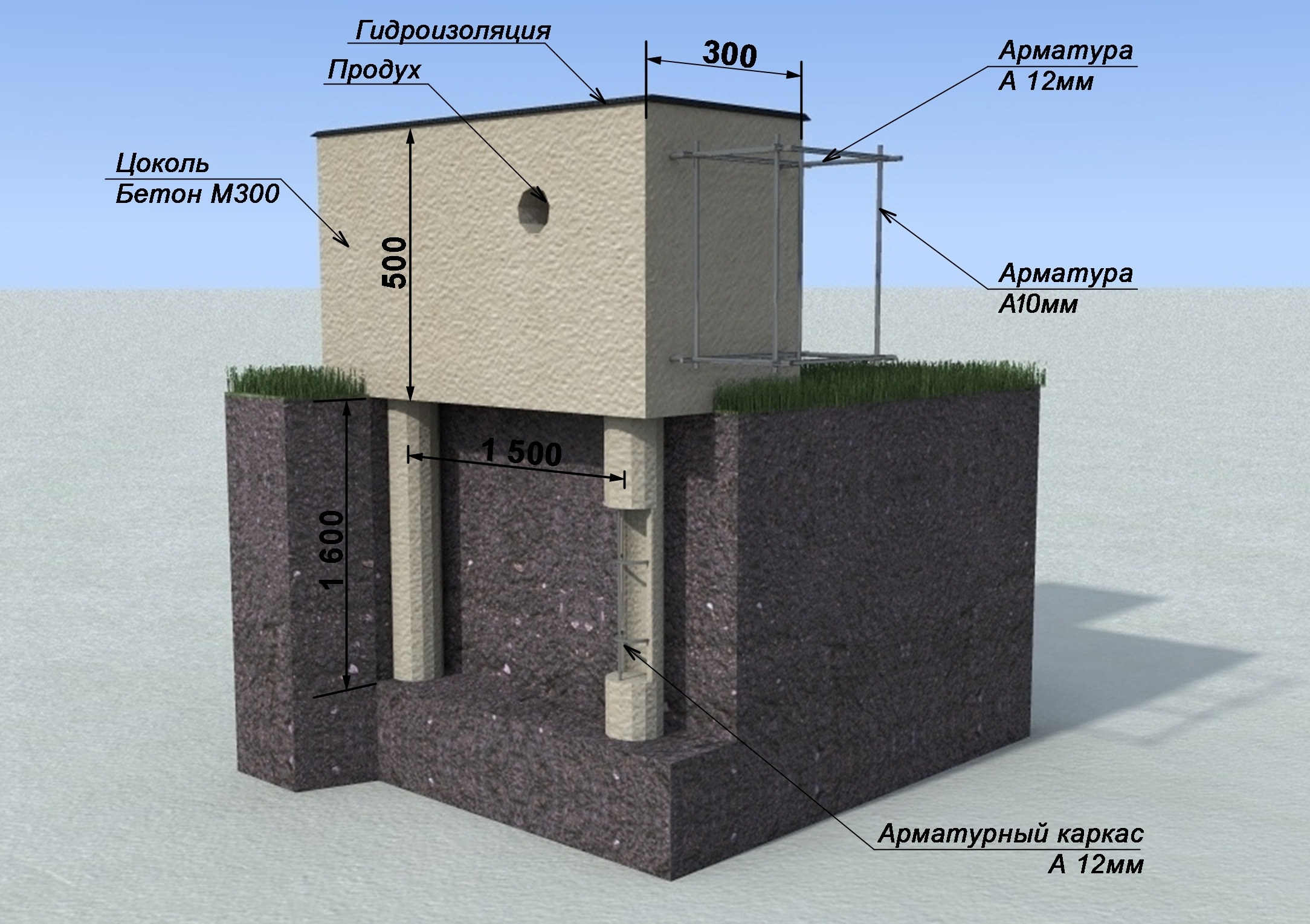
Pile foundations with monolithic grillages
Reinforced concrete belt has high stability, rigidity, reliability, durability and can withstand high loads. These qualities have become the reason for the widespread use of pile grillage with monolithic overlap. The structure consists of iron reinforcement, which increases the strength characteristics of the foundation, and concrete. Strengthening of a monolithic grillage on piles can be performed with hotel rods fastened into a flat frame or volumetric skeletons.

Hanging type reinforced concrete grillage
Concrete grillages are similar in structure to reinforced concrete belts, the only difference is the lack of reinforcement in the structure of the former. The entire load is laid down and distributed by concrete. The heads of the foundation piles must be recessed by 100 mm in the concrete of the grillage. Such belts are used only in the construction of one-story buildings.
Lumber constructions
The wooden structure is mainly used in the construction of lumber houses. Laying a wooden grillage on a columnar foundation is carried out on a special waterproofing pad made of roofing felts or roofing felt. Also, in order to exclude premature damage to wood, the structure should be treated with special bioprotective impregnations. The fixing of the timber to the piles is carried out by means of brackets or bolts.

Wooden grillage structure
There are two options for the device of a lumber belt:
- When constructing the foundation of a building, a single or double deck is created from pre-processed logs, which is installed on a planned rubble platform. This option was previously used for the construction of small lumber buildings;
- The grillage is fastened from a bar on a columnar foundation. However, the structure does not have high strength, since wood is not the most reliable building material, therefore it is most often used to create sheds and arbors.
Video: device grillage for a wooden house
Metal belt for foundation
The metal lathing is made of channel, I-beam or square profile and has high strength and rigidity. As a rule, this design is used when constructing screw-pile foundations for one-story houses. The channel is installed on the heads of the supports and fixed by means of a welding joint.

Metal grillage on concrete columns
A metal belt is used mainly in a hanging version. However, in recent years, such structures have been used very rarely, since, due to the severity of the material, the involvement of lifting special equipment is required, which is economically unprofitable. In addition, the metal is subject to the risk of corrosive processes.
It's interesting: How make the formwork for foundation: consider the points
What piles to use
It is recommended to install pile-grillage foundations in the following cases:
When unstable and weakly bearing soils go to a sufficiently large depth. These are karst, forest, peat soils, quicksands, plant and fertile soils of great thickness (more than 1.4-1.5 meters). In this case, the load must be transferred to dense soils located below with normal bearing capacity. It is not always possible to get to the bottom of them, and if it is possible, then the foundation turns out to be too expensive. Therefore, transferring the load with piles is the best choice.
In areas with large elevation differences. In this case, it is often much cheaper to use piles of different heights than to carry out work on leveling the ground or pouring a deep tape that can compensate for the height difference.
One of the types of pile-growth foundation - with TISE piles
With a high level of groundwater. Pile foundations are the only ones for which the level of groundwater does not matter
It is important that there is a load-bearing soil under the heel. The level of the location of the waters affects only the type of grillage: if the water is close to the surface, the grillage is made high, if it lies deep, it can be made low.
When building in hard ground
In this case, small amounts of land work (in comparison with strip or slab foundations) have a positive effect.
If you decide to build a house using frame technology. To make a tape for it is a waste of money: it will turn out to be too large a margin of safety, which, in this case, is useless.In this case, a pile or pile-grillage foundation is the best choice.
With a large building mass (more than 350 tons). Then it turns out that tape or plate must be very massive and therefore expensive. In this case, the pile-grillage foundation is often cheaper.
Sometimes it's even simpler: they start from the lowest cost. But you always need to remember that any type of pile foundation is less reliable than slab and strip. And all because we cannot know exactly what kind of soil is under each of the piles. That is why, when calculating the parameters, an increased safety margin is laid in the design. Not 1.2, as is commonly believed, but 1.4. And still, no one can guarantee anything.
Any piles can be used in pile-grillage foundations. They are chosen based on the soil, the planned load of the house. Piles are made of metal, concrete, sometimes wood. They can be round or square. They also differ in the installation method:
-
Driving. They are installed without drilling or digging. Usually - they are hammered, that's why they are called so. They are rarely used in private construction: special equipment is required.
Driven reinforced concrete piles are used more often in the construction of multi-storey buildings
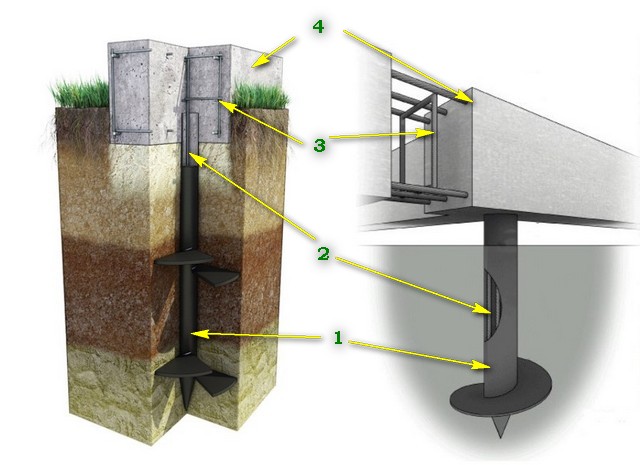
- Bored. First, a well is drilled in the ground, then the formwork is installed and fixed in it. It contains reinforcement that increases the strength characteristics. Then the whole structure is poured with concrete.
- Reinforced concrete drilling. In this case, wells are also drilled, but ready-made reinforced concrete piles are installed (hammered, but with less effort) in them.
-
Screw. These are metal piles, pointed at the end and having helical blades that cut the soil. At great depths, special equipment is required, small ones, up to 2-3 meters long, can be installed manually.
One of the types of piles is screw. They can be used with grillages from different materials for different houses (to increase the size of the picture, right-click on it)
In private construction, bored piles are most often used. They are especially popular in the construction of summer cottages or baths. They can also be used in the construction of small houses. But if summer cottages and baths can be done without calculation, then when building a house it is very desirable to order a project.
Different piles are in shape: square or triangular cross-section, round filled and round hollow, sometimes complex shapes are developed specifically for the project. By the way the piles transfer the load to the ground, they are:
- hanging;
-
piles-racks.
What is the difference between piles by type of work (to increase the size of the picture, right-click on it)
Rack piles, on the contrary, transfer most of the load through the tip. In this case, the side walls are undeveloped and smooth, and it makes sense to expand at the end of the pile. One of the types of this type is TISE piles. They have a cylindrical extension at the bottom, which is why they transfer the load over a large area. Also, the heel prevents the heaving forces from raising the foundation.
How to choose the right piles for your foundation
The correct choice of piles is based on the following factors:
- Price.
- Installation speed.
- Reliability and durability.
Considering all the advantages and disadvantages of the above grounds for arrangement, having weighed all the pros and cons, you need to make your best choice.
In private low-rise construction, screw piles have recently been used more often.
In addition to the fact that screw piles are used to equip traditional grillages, some of their types are used to strengthen slab and tape bases.
Tubular structures with welded or cast ends make it possible to carry out construction where it is very difficult to do it:
- In the swamp.
- On the water.
- On the slope.
And all this without planning the building plot.The very essence of the technology is to make the minimum tangential load on such a support.
Optimal pile design for low-rise construction:
- Frame. Seamless pipe with a wall of 4-4.5 mm made of St3 steel. The 30XMA steel structure has a longer resource - the wall in this case is from 6 to 10 millimeters.
- Blades. They are welded to the body or made in the form of a functionally finished tip - cast or welded, which is also welded to the body.
Whatever the design, it is multifunctional. The choice of the screw support should be based on the SNiP - building codes and regulations (latest edition of 2011)
Support types:
- Narrow-lobed. In fact, this is an analogue of the same self-tapping screw, that is, a multi-turn support. The tip is cast, welded to the body. It is used for dense soil and permafrost.
- Broad-lobed. For light buildings.
- Multi-bladed. For better support. They are intended for three-level buildings with an attic.
Most individual developers do not even suspect what the range of applications for these supports is:
- Baths.
- Cottages.
- Fences.
- Gazebos.
- Greenhouses.
- Advertising constructions.
- Power transmission poles.
- Temporary buildings. Here there is the possibility of dismantling and transferring to another place.
- Fences.
- Bridges and moorings.
This is not a complete list of where you can use the screw mounts.
Expert opinion
Sergey Yurievich
Construction of houses, outbuildings, terraces and verandas
Ask a Question
The final and correct choice is carried out using the detailed instructions of SNiP.
In order to increase the reliability and durability of the screw pile, it is necessary to apply a special anti-corrosion coating to it.
Of the most significant drawbacks, it is worth highlighting the following: the need to equip a false basement and careful isolation of communications under the house.
The advantages clearly outweigh the disadvantages, and in addition to the above advantages, you need to add the following:
- Quick delivery of the object.
- Small amount of earthworks.
- Suitability for building any plot of land.
- Maintainability.
- All-season building.
Expert opinion
Sergey Yurievich
Construction of houses, outbuildings, terraces and verandas
Ask a Question
The correct distance between the supports during design is the key to many years of operation of such a foundation.
In addition, it is worth paying special attention to the quality of products - economical technologies will not add reliability to the design.
Pile types
There are different pile designs:
- Rack piles. Vertical supports in close contact with solid soil layers. Provide maximum stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Hanging piles. They are held by the frictional force between the side walls and the ground, as well as by the compacted soil pad under the tip. They do not have support on solid layers. Strength is provided due to the contact area - the longer the pile, the more securely it is installed. Capable of precipitating suddenly due to subsurface changes in hydrogeology.
By type of dive, there are:
- Driving. They are immersed in the ground using special mechanisms. They have maximum bearing capacity and stability, but they pose a considerable danger when immersed for all buildings located nearby.
- Injection molded. These piles are reinforced concrete castings made directly on site. Reinforcement is installed in the drilled well and concrete is poured, obtaining a strong vertical rod. Convenient for self-production.
- Screw. A specific type of piles driven into the ground by screwing (like a screw). Allows self-installation, does not require preliminary preparation or excavation.
The material for piles can be:
- Wood. Traditional material, but today wooden piles have practically disappeared from the stage, giving way to more durable and convenient types.
- Metal.Apart from screw piles, special designs are not produced. Use massive pieces of a channel, rail, I-beam, etc. The disadvantage of metal piles is electrochemical corrosion, from which it is almost impossible to protect them.
- Reinforced concrete. Driven and rammed piles are made of it, obtaining strong and load-resistant supports. It is the most common material, resistant to all loads and almost 3 times more durable than metal piles.
The choice of the type of piles is determined by the technical requirements and construction conditions. Most often, driven or bored reinforced concrete rods are used.
Making a base using pillars
We figured out the installation of the grillage for the pile foundation, and now let's start creating the bearing plane for the columnar base.
Materials and tools
We stock up on the following set:
- "Bayonet" and "selection";
- drill;
- pickaxe;
- tape measure;
- stakes;
- chemicals to prevent vegetation growth;
- OSB board, plywood or edged board for the manufacture of formwork;
- reinforcing cage;
- concrete mortar;
- geotextile;
- sand;
- rubble;
- polyethylene;
- bituminous mastic.
Installation process
We carry out the following work:
- we clean the area intended for the future structure from vegetation;
- we water the working area with chemicals to prevent the growth of vegetation;
- we mark the site - we drive in the pegs and pull the rope between them;
- digging holes for pillars;
- we fill the sand into the pits;
- pour water on a sandy pillow (10-15 cm high), ram it well;
- we put geotextiles on the sand;
- we fill the canvas with rubble;
- we make formwork - we form panels and boxes;
- we lower the boxes into the pit;
- cover the formwork system with polyethylene;
- we knit the reinforcement;
- we lower the frame into the hole for the post;
- we form pillars - pour concrete in layers;
- we process a layer of concrete with a shovel or vibrator;
- take a technical break;
- we process the surface of the pillars with bituminous mastic;
- we mount the formwork between the supports, make a sand bed, fill in a concrete solution, which is reinforced with reinforcement;
- we make a technical break so that the concrete hardens;
- we produce hydro and thermal insulation.
Anecdote is not the topic: - Ah! How great your coffee smells!
- Come in! Do not be shy! Sniff your health!
So what can you say? The grillage is an object that, despite its simplicity, plays a very important role in the “life” of every building. Do not be lazy, give a welcoming and cozy home or bathhouse a future without destruction! Patience and good luck to you! Bye!
Quote of Wisdom: Keeping your secret is wise, but waiting for others to keep it is foolish (Samuel Johnson).