How many rows of blocks do you need for a FBS foundation for a brick house?
Sections of the basement walls above ground level that are not in contact with the ground should be sealed with brickwork KORPo 1NF / 100 / 2.0 / 35 / GOST 530-2007 with mortar M 75. 10. Foundation blocks ( series 2.110-1 issue 4 detail 8, 12) or monolithic concrete class. B 10 reinforced with reinforcement A-I with a diameter of 10 mm at the rate of 1 bar per 120 mm of wall thickness with a support of 250 mm (series 2.110-1 release 4 part 9). Place lintels over openings more than 600 mm wide (series 2.110-1 issue 4 detail 11). 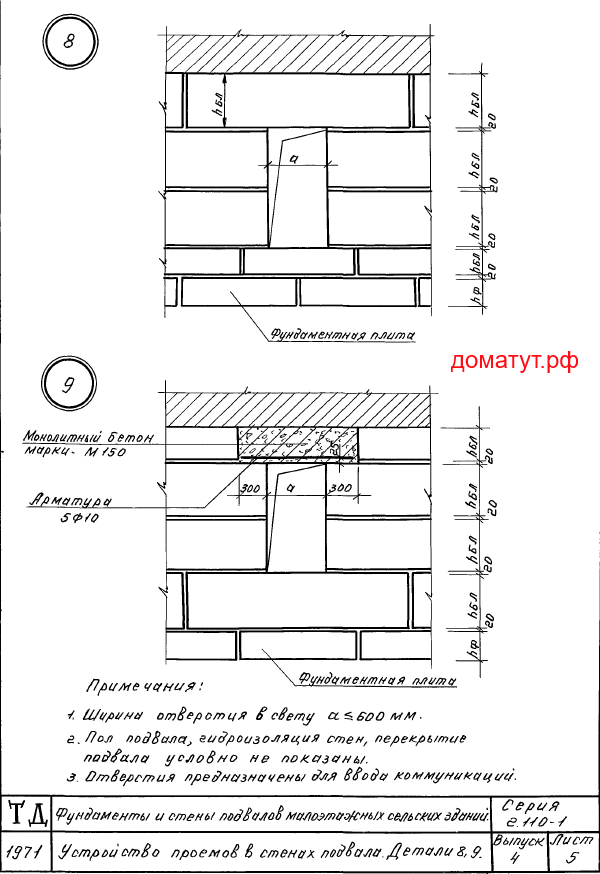
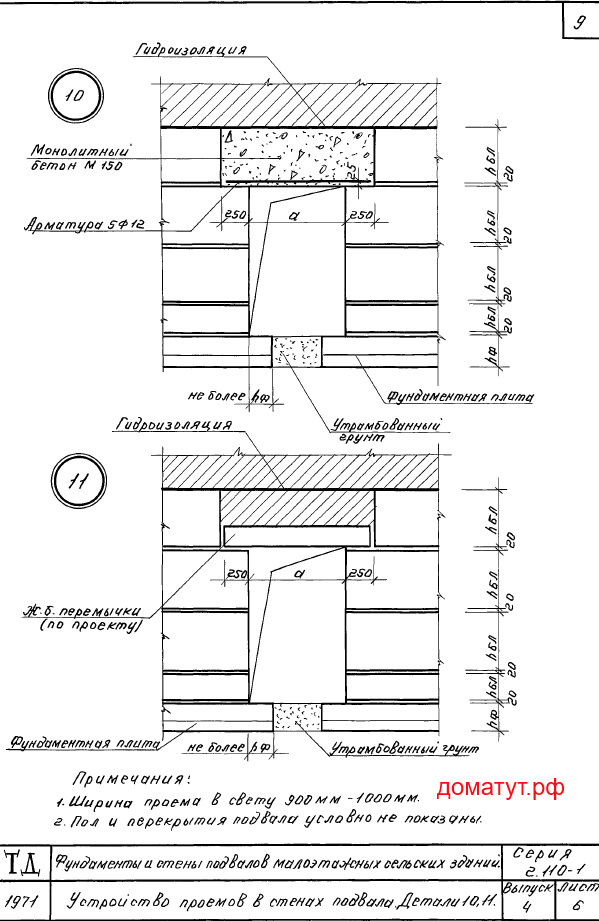 11. After completion of the installation of pipelines of engineering communications, all the holes left for them in the outer and inner walls should be sealed with concrete class. V 7.5, ensuring the tightness of the communications bushings.
11. After completion of the installation of pipelines of engineering communications, all the holes left for them in the outer and inner walls should be sealed with concrete class. V 7.5, ensuring the tightness of the communications bushings.
Block foundation and its application
According to the estimate, a block structure is slightly more expensive than a monolithic tape, but it is erected much faster than it. In terms of their bearing characteristics, they are in many ways similar, the main thing is that the FBS from the side does not have too strong an effect when heaving.
Only the foundation on screw piles can be made faster than the option under consideration. But the latter is often chosen only for light buildings, for the construction of the walls of which SIP panels or lightweight aerated concrete were taken. The block base is more versatile. It's easy to build it yourself. The step-by-step instructions presented above will allow you to complete everything, avoiding possible beginner mistakes.
The main stages of work
The construction of this type of foundation can be easily done independently; no special skills are required for this. The main thing is to follow the construction technology correctly and not to rush.
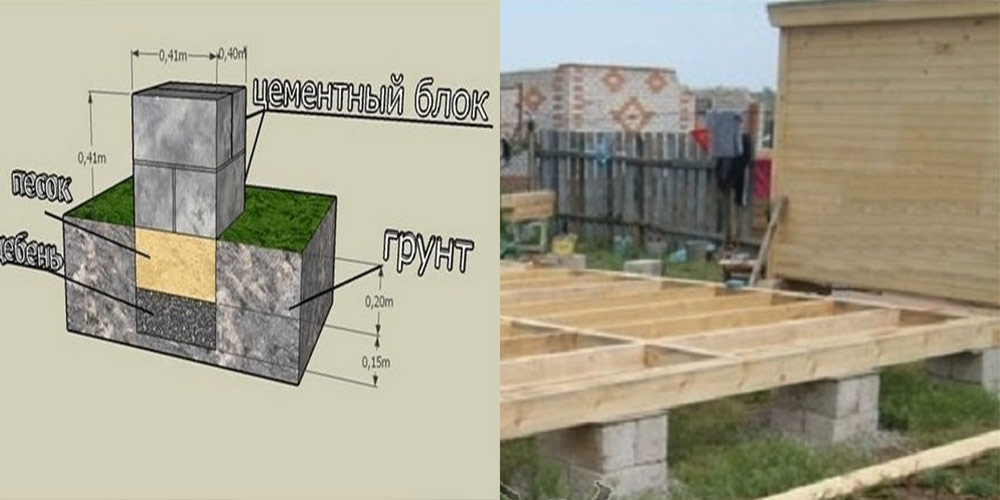
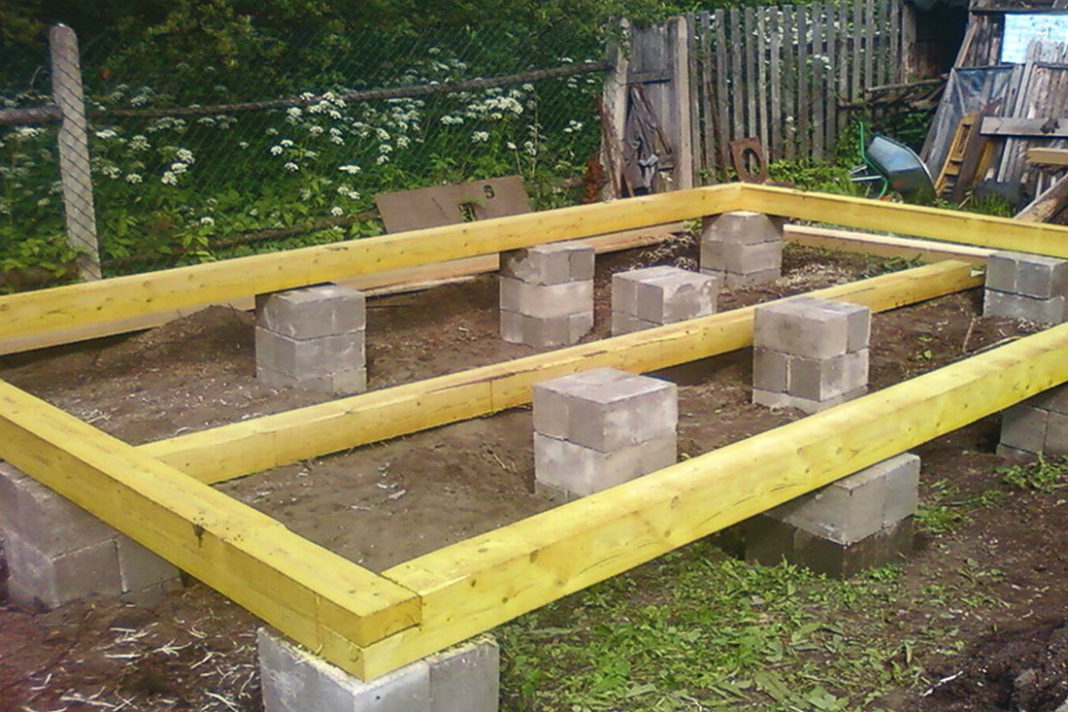
- Preparatory work. First of all, you need to prepare the site itself. To do this, you need to cut off the top layer of the soil, the plants are also all removed. Typically about 30 cm of soil is removed. It is not recommended to leave this under the base. If construction is planned on a clay site, then in addition to everything, you need to put a gravel-sand layer, the thickness of which depends on the characteristics of the soil. In addition to cleaning, the surface of the site must be carefully leveled.
-
Construction plan. It is required to transfer the structure scheme from the drawings to the surface of the earth, using pegs and twine for this. Full compliance with the paper version should be closely monitored, since the reliability and quality of work depends entirely on this.
- Preparing the pits. An excavator can help with this. However, if you do not have the funds, you can also do the job manually with a shovel. Pits should be located along the axes. The strengthening of the pit depends on its size. If the depth is not more than 1 m, then the strengthening process can be missed. Otherwise, you will have to dig a hole with slopes and strengthen it with wooden planks with spacers. The size of the groove is also important. The pit should be 30 cm deeper than the estimated depth of the base under construction. This is necessary in order to be able to make gravel-sand bedding. The width should also be slightly larger so that the cast formwork, as well as the spacers, feel free enough.
- Formwork arrangement. A columnar foundation made of concrete blocks requires good formwork. To do this, you will need a number of boards, which are about 40 mm thick and 150 mm wide. It is possible to use chipboard, steel sheet or moisture resistant plywood, as an alternative to wooden spacers. Planks or other selected material must be placed directly against the concrete.
- Reinforcement of the foundation. This procedure must be carried out in a horizontal direction.For these purposes, A3 rods are used, the diameter of which is about 12-14 mm. For this, horizontal jumpers should be placed at a distance of about 20 cm from each other. As jumpers, you can take a wire with a diameter of about 6 mm. To connect the pillars with the grillage itself through the reinforced frame, you need to position the rods in such a way that the reinforcement rods protrude above the edge of the base at least 10-15 cm.
-
Filling the pillars of the base. The instruction for the construction of this foundation requires pouring the pillars themselves. It is necessary to pour concrete into those pipes that will continue to be in the ground along with the foundation itself. It is necessary to lay concrete in layers. The thickness of each layer should be about 20-30 cm.
- Arrangement of waterproofing pillars. Any foundation needs protection from moisture. For this, long-known materials are suitable, such as hot and cold mastic, glued membranes, as well as ordinary bituminous roofing material. What material you chose is up to you. There are no strict rules here.
- Construction of the grillage itself. This design allows you to make columnar foundation made of blocks more sturdy and reliable. The grillage can be made from reinforced concrete round beams or made monolithic. In the first case, it is necessary to connect the jumpers well enough, using for this trimming the reinforcement, which must be hot-welded to the mounting loops. After that, reinforcement of the formwork itself is required, and then fill everything with concrete, including the reinforcing cage. For these purposes, concrete blocks of the M200 brand are suitable. After that, the concrete must be allowed time to cool down, after which, it is necessary to carry out waterproofing, fill up all the formed sinuses, and at the end, lay the floor slabs.
Column foundation repair
There are times when the already built foundation needs restoration or repair.
Unlike the process of its construction, which is carried out according to strict technology, repairs and reconstruction are strictly individual. This is the only way to achieve an effective result and enjoy the structure for many years.
Often, repairing such a foundation means eliminating the tilt of the pillars themselves. To do this, the house is raised using a special jack, after which the supporting pillars are undermined and then leveled. At the end, they are re-poured with concrete and covered with soil. This procedure is recommended to be repeated after a year, but it is still better not to hope for an ideal result. Therefore, professionals perform the following actions:
- Raise the structure and place it on temporary supports.
- Remove the lopsided posts.
- Dig a trench around the house in which to place a sand cushion.
- Make a reinforcing belt, which is subsequently filled with concrete mortar.
- Allow the foundation to solidify and install the supporting elements on it.
- The house should be lowered onto a new structure. Finally, it is necessary to adjust the doors and windows so that they can be easily opened and closed.
Repair of the foundation requires timely measures to ensure that the structure will serve for many years.
What it is?
Foundation building blocks (FBS) are reinforced concrete, monolithic elements that are manufactured in the factory with strict control of parameters. This ensures their high strength, durability and dimensional stability.
Any type of foundation can be built from these blocks. The classic option is a shallow strip foundation.
Block structures are most suitable for sandy soils. At the same time, due to a certain mobility, the foundation easily tolerates swelling. Do not use the blocks on soft ground where they can sink.
Advantages and disadvantages
The following advantages of FBS can be highlighted:
- increased strength characteristics - monolithic blocks have a strength of the order of 100-200 kg / cm2;
- frost resistance and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles (at least 200 cycles);
- waterproofness;
- incombustibility, fire safety;
- sufficient seismic resistance;
- high speed of installation;
- no need to stop construction for complete solidification of concrete. Even when making an armored belt, a minimum time is required - up to 14 days.
Certain disadvantages of the blocks should also be highlighted:
- transportation costs of large-sized products:
- the need for lifting mechanisms;
- increased requirements for thermal insulation;
- restrictions on use on highly weathered and soft soils.
Disadvantages limit the use of FBS in the construction of large brick or stone houses, but the blocks are quite suitable for the construction of wooden and frame structures.
Varieties of FBS for the foundation, GOST
There are 12 standard sizes of classic FSB on the market:
- The length of the blocks is 9/12/24 dm.
- Width - 3/4/5/6 dm.
- The height of all blocks is 6 dm.
The production of blocks is regulated by GOST, which specifies the type of material, dimensions, design parameters, rules for storage, transportation, installation.
- FBS - solid block of maximum strength;
- FBP - voids are located at the bottom, due to this, the load on the foundation is reduced;
- FBV - solid texture with a cutout for laying communication systems. Relevant for the construction of facilities with numerous engineering systems.
Construction features
This type of foundation is used for those houses in which the construction of a basement is not provided. Its low cost, as well as ease of installation, makes it possible to use it in the construction of small buildings.
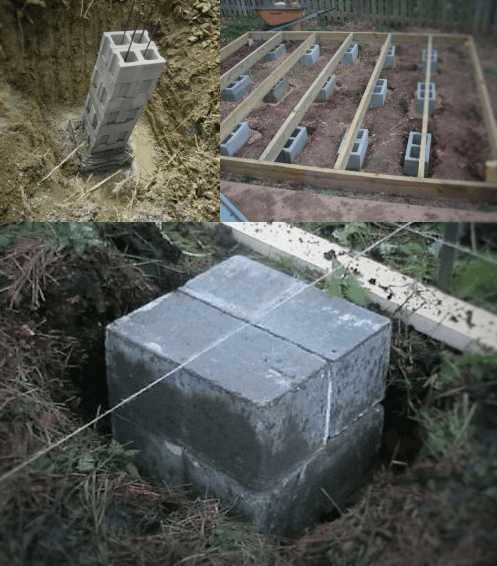
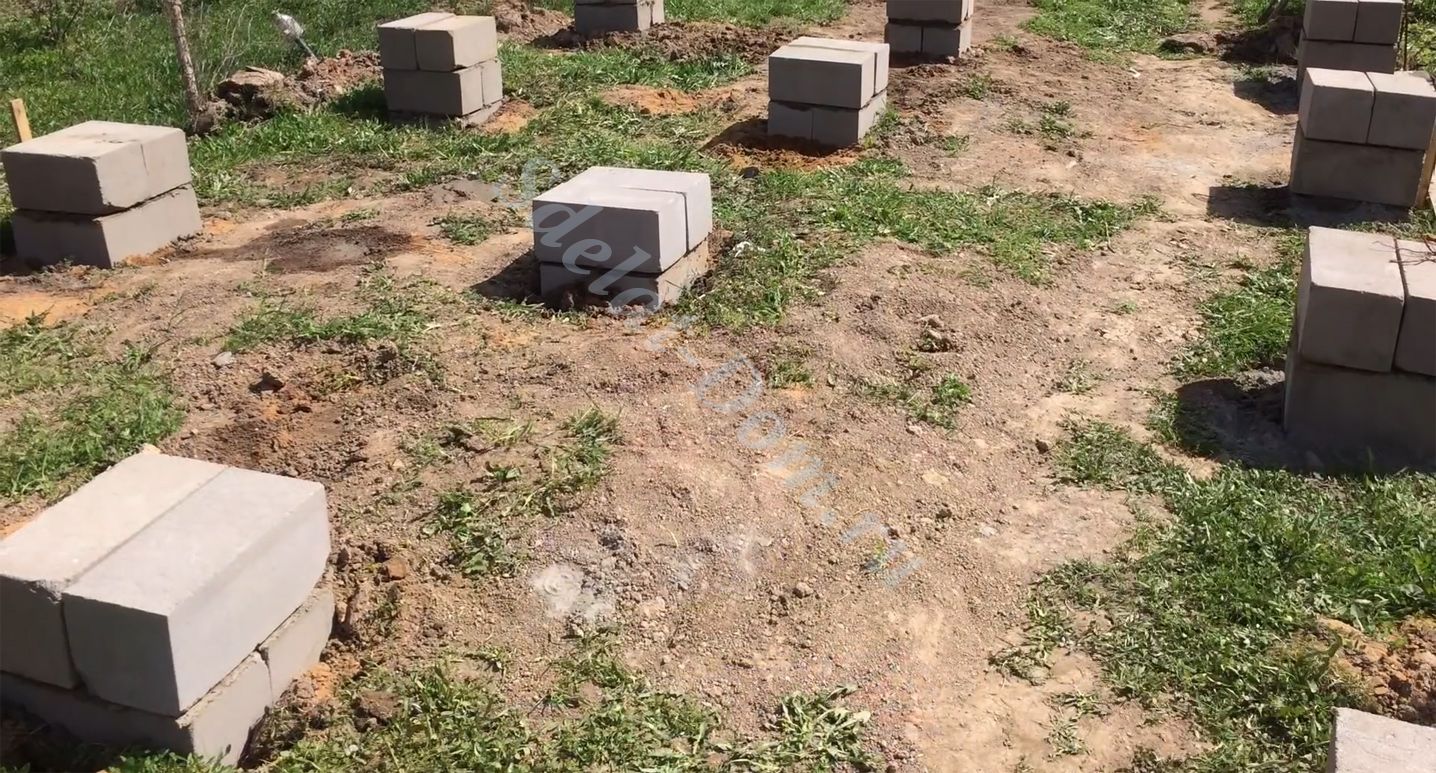
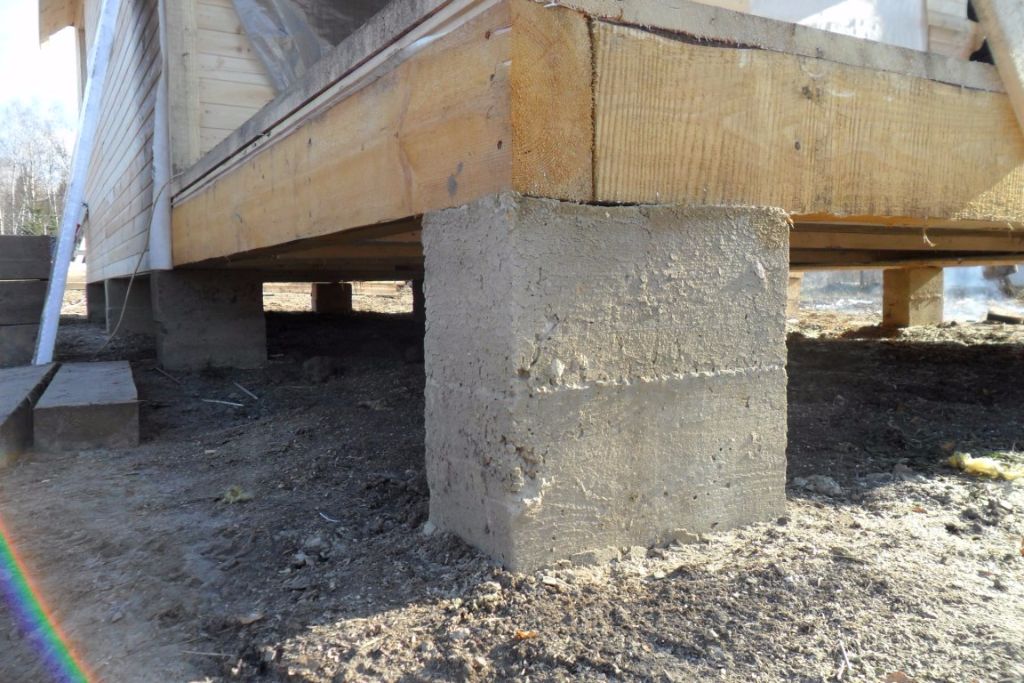
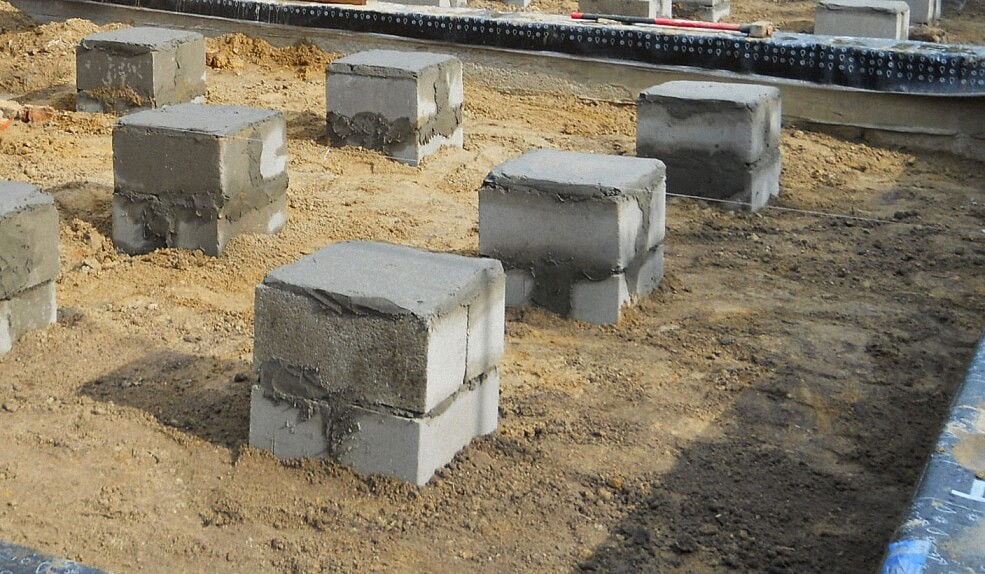
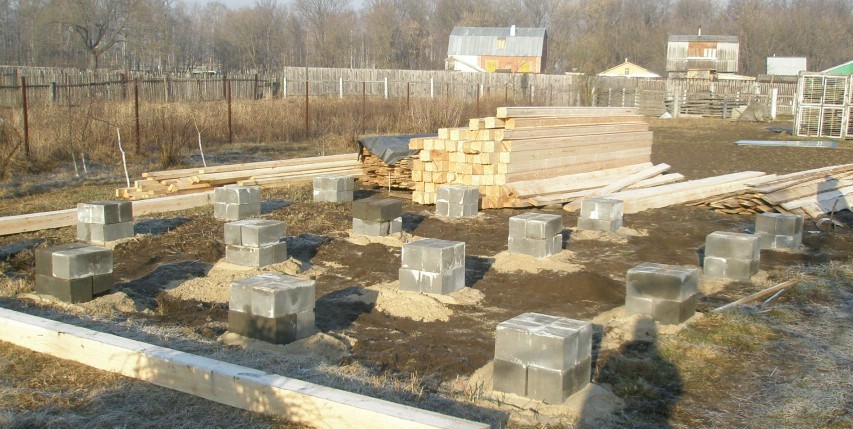
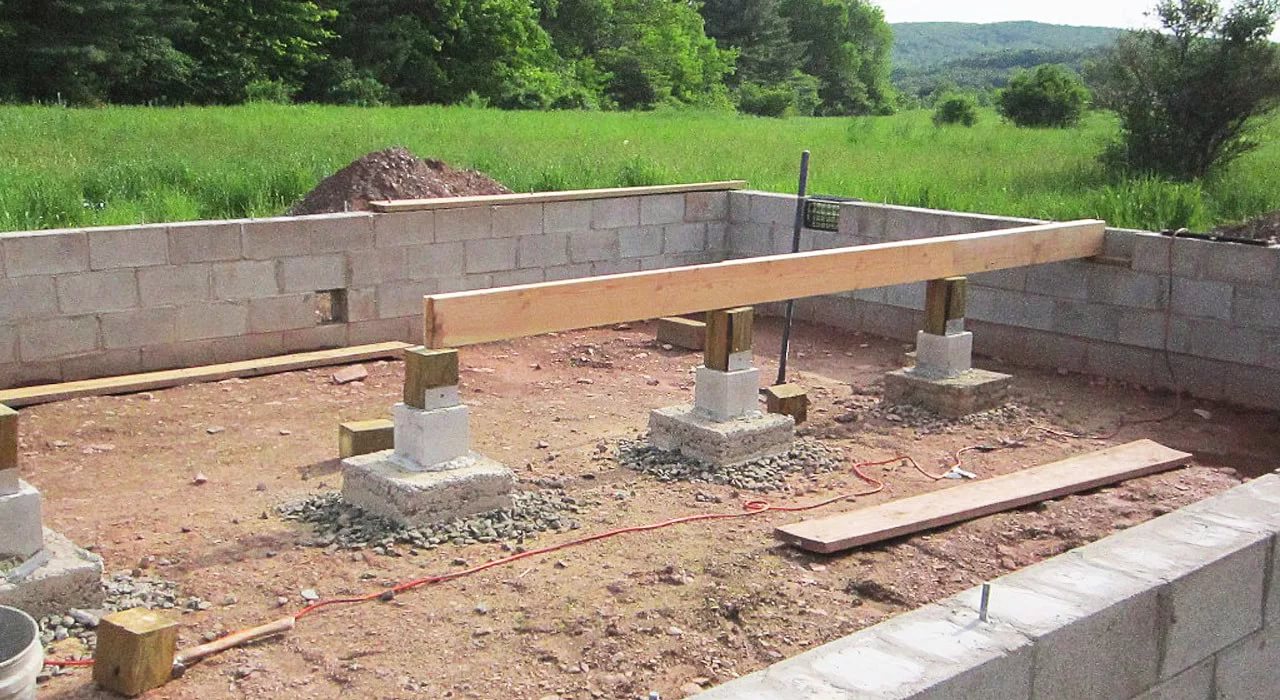
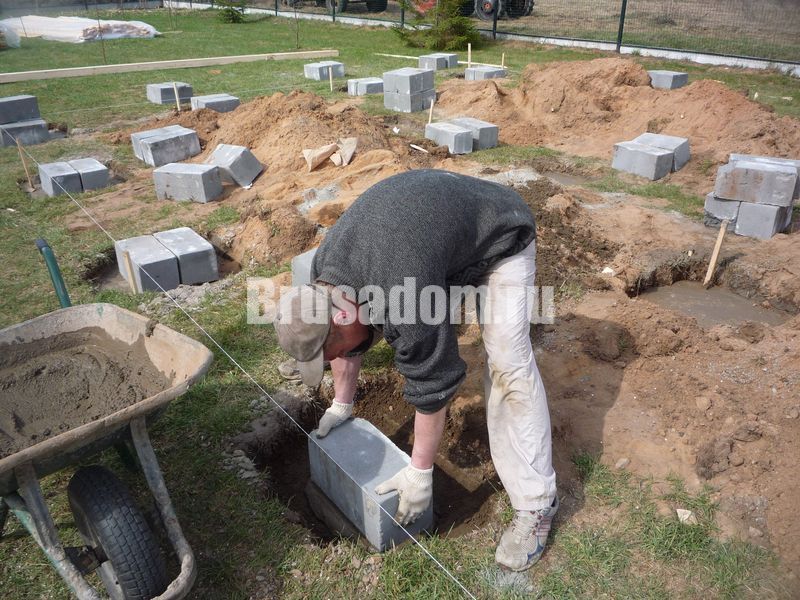
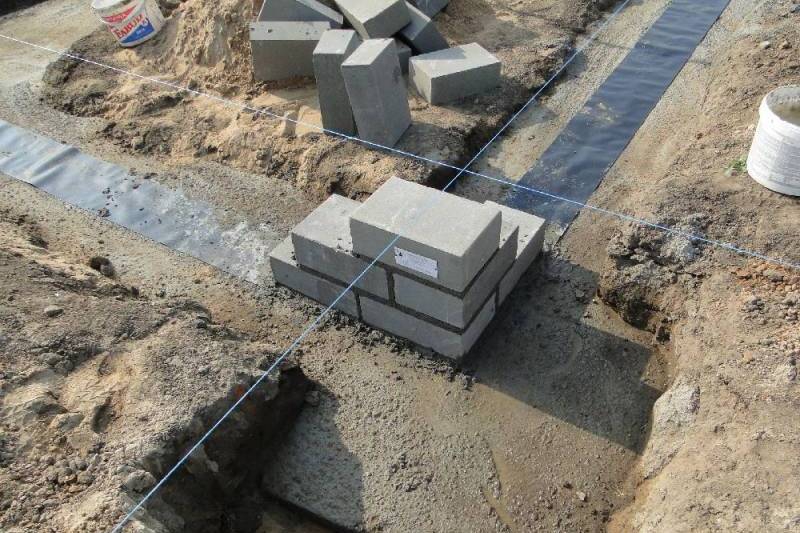
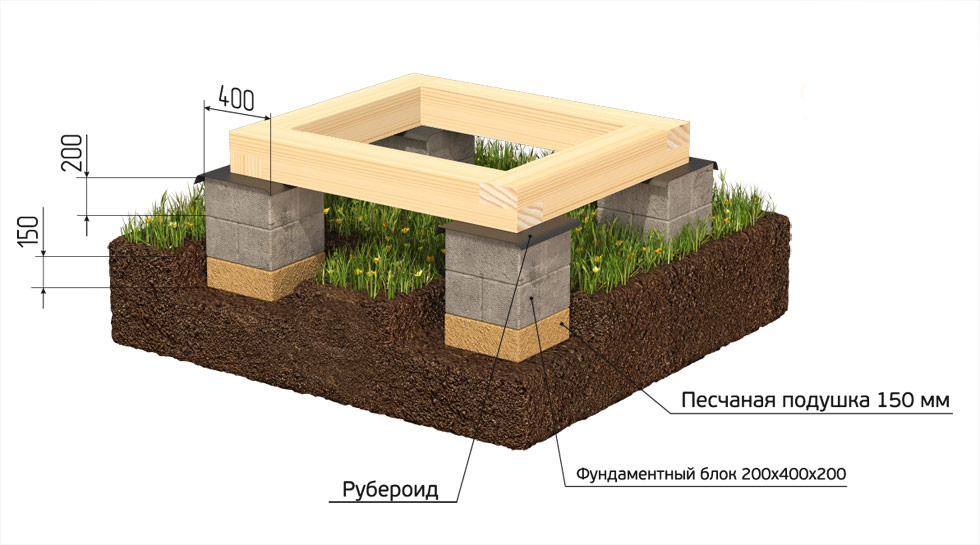
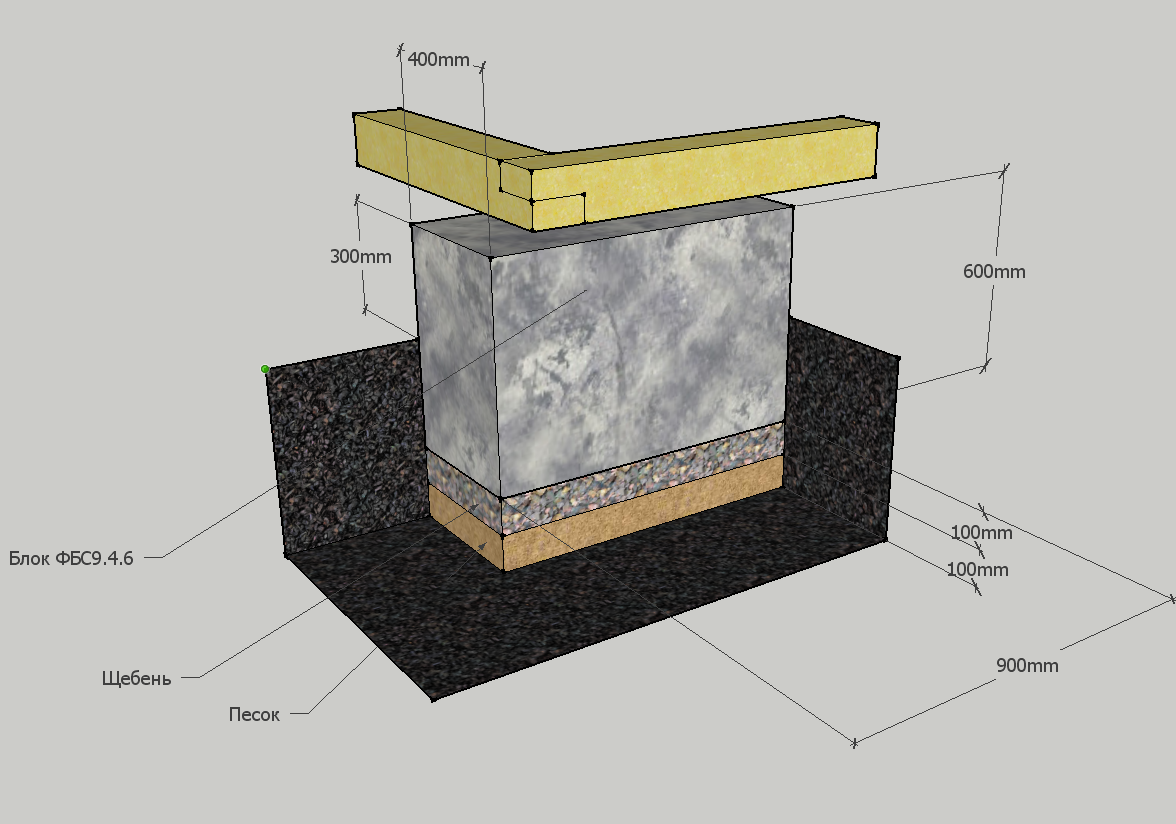
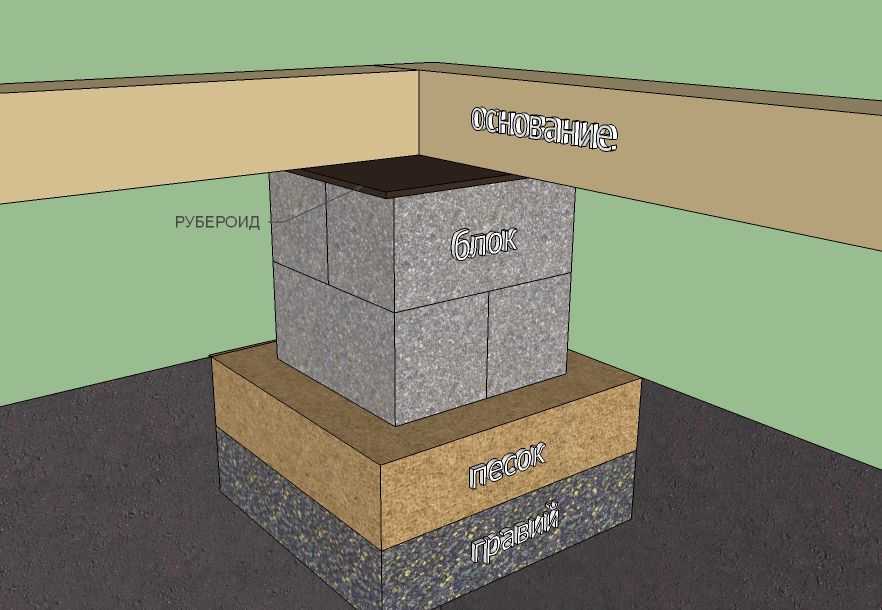
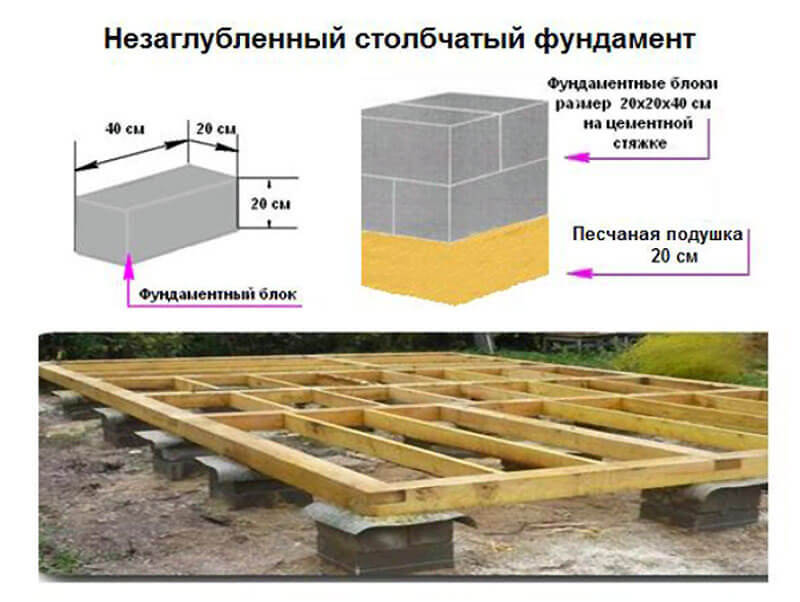
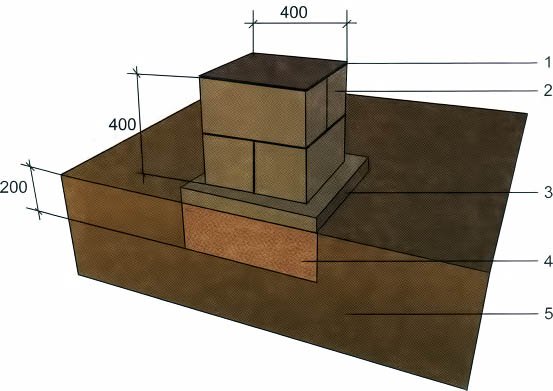
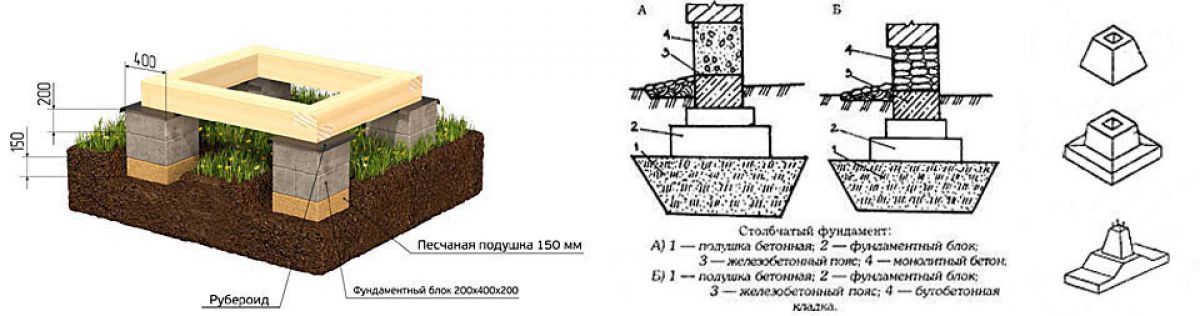
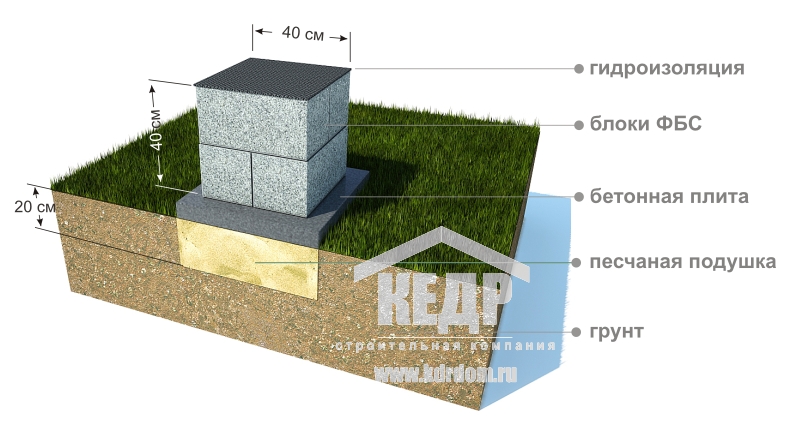
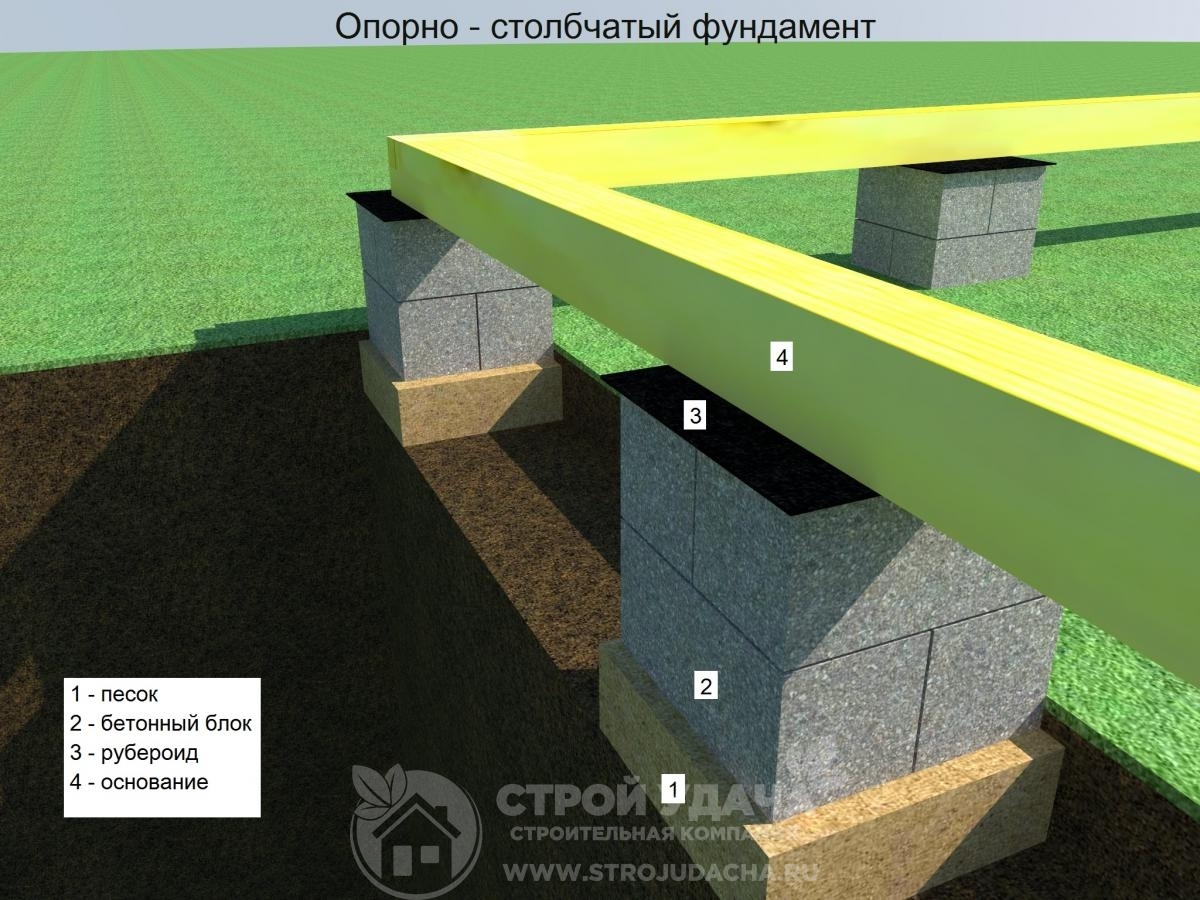
When erecting such a foundation, ready-made blocks made of concrete are taken. Four such blocks are taken on one support. The size of one block is 20x20x40 cm. The number of supports depends entirely on the size of the building, as well as its project.
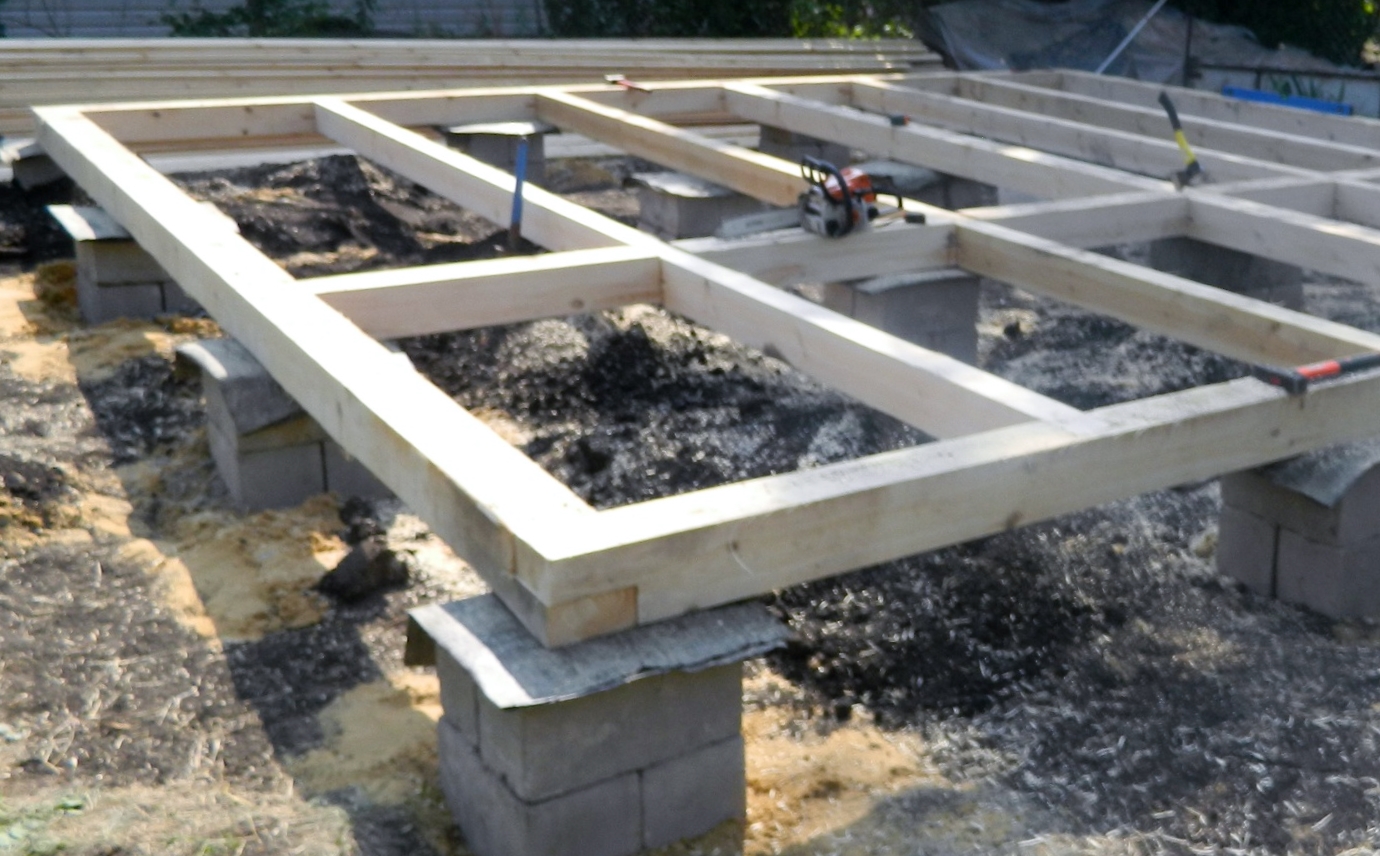
For heavier buildings, it is better to use a columnar foundation of 20x20x40 blocks using a grillage. This will increase stability, eliminate the possibility of its displacement. The grillage is beams, sometimes slabs, which are located on top of the base structure being erected and are used to unload the ground part. The materials for the grillage are reinforced concrete and concrete, less often wood and metal.
Depth and strength of the base
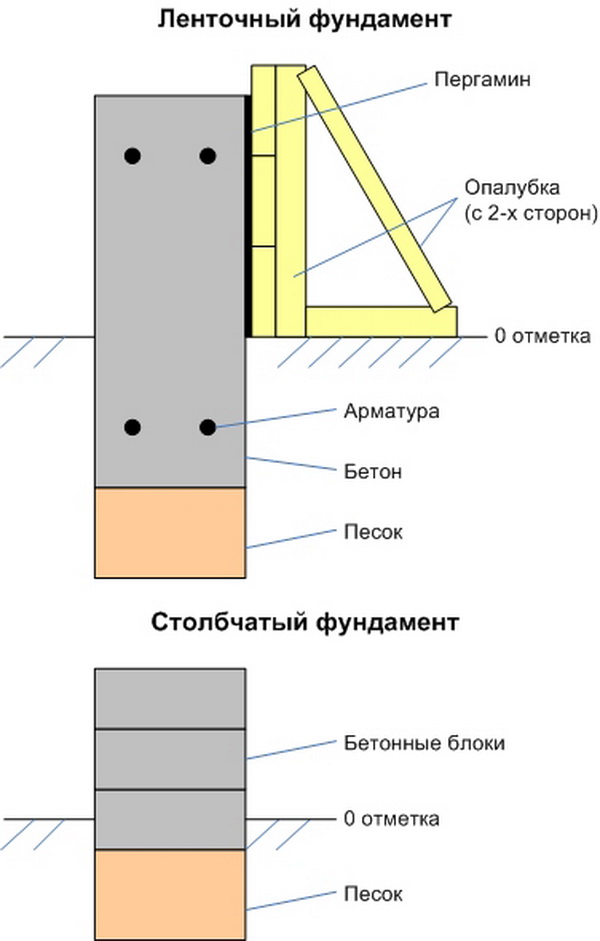
The foundations are subdivided into two types according to the depth:
1. Recessed. Such a base is buried 3-4 meters into the ground and allows you to equip a basement, an operated basement. This design requires the greatest financial investment and labor costs.

This type of foundation can be made both monolithic and block, by choosing a more accessible technology. In comparison with the shallow construction, the recessed tape is characterized by stability and can be used on different types of soils, with the exception of marshy soils.
2. Shallow. An option suitable for the construction of light houses (including logs and squared beams) on stable ground. Not suitable for marshy, sandy and heaving soils. Does not make it possible to equip a basement or basement.
If we compare the strength of a buried strip and block base, the advantage will be on the side of a monolithic structure made of reinforced concrete - the prefabricated structure is not a single whole, and therefore may be vulnerable. Under the strong influence of horizontal ground movements, the integrity of the prefabricated FBS structure is violated due to the displacement of the blocks.
A monolithic base is the best choice when building on complex soils with unstable layers, when building a foundation on a hilly area. On stable soils, the FBS structure will not yield to a monolithic one in terms of reliability and performance, so it makes sense to choose a simpler and cheaper option for construction.

For a shallow tape, a monolith will be the best choice regardless of the characteristics of the soil, since it is the surface layers that are prone to deformation and horizontal displacement. The use of blocks is allowed for light structures of a small size, provided that the soil is stable and the tape is laid in a horizontal section without height differences.
The advantages of a monolithic strip foundation are high strength and reliability. At the same time, FSB bases are easier and faster to install, and also noticeably cheaper, but at the same time they are limited in use.
Pile grillage and shallow foundation
A more complex situation arises when weak, water-saturated soils, prone to frost heaving, lie at the base. It is these conditions that are common in a significant part of the territory of Russia. Despite the sufficient bearing capacity of the strip foundation, it becomes impossible to guarantee the uniformity of the settlement in all its sections. The pushing forces of frost heaving, the effect of groundwater, and the unpredictability of the consolidation of weak soil as a result of loads from the building affect.
In this case, one should strive to compensate for the instability of the base with the rigidity of the supporting structure, on which the walls of aerated concrete are erected. Such possibilities are presented by a solid reinforced concrete slab and a grillage. A variant of a monolithic grillage can be considered a shallow foundation on an artificial foundation.
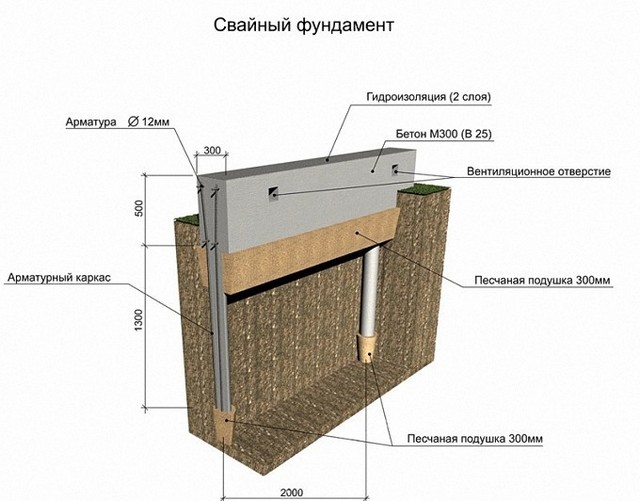
Pile foundation with monolithic reinforced concrete grillage.
The grillage allows you to connect the buried elements of the pile or columnar foundation. It is a monolithic reinforced concrete structure erected at the construction site. Its height can be from 450 to 600 millimeters and even more. The heads of piles or supports are fastened through the outlets of the reinforcement using welding or knitting wire with a grillage frame installed in the formwork.
After pouring a concrete mixture into it, a single monolithic spatial structure appears, which has not only a high bearing capacity, but also a significant resistance to bending moments caused by the difference in the characteristics of the soil under the columnar supports or in the area of the pile surface.
Despite the relative lightness of aerated concrete walls, depending on the characteristics and height of the building, the load on the grillage can be significant, therefore, the dimensions and reinforcement of this structure are best taken on the basis of a calculation performed by a qualified specialist. Having chosen a foundation of this type, you will have to come to terms with the impossibility of arranging a basement in it. It can be challenging to create rooms at ground level, such as a garage. These features of the foundation should be taken into account when choosing or developing the architectural layout of the house.
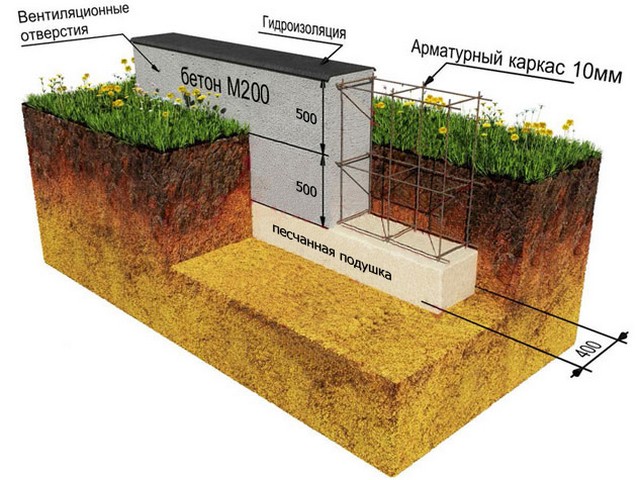
Shallow foundation diagram.
A shallow foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is a monolithic reinforced concrete frame installed on an artificial foundation. Instead of a pile field, a trench is used that reaches the freezing depth mark, filled with non-porous material with a high bearing capacity, for example, medium-sized sand, gravel or crushed stone. The most important condition is careful compaction of the artificial base, preventing its consolidation and settlement in the subsequent period.
The grillage configuration corresponds to the outline of the building walls. As a result, a reinforced concrete frame is obtained, which is located on a solid elastic foundation, unable to deform under the influence of loads. This prevents formation cracks in the walls of lightweight concrete blocks.
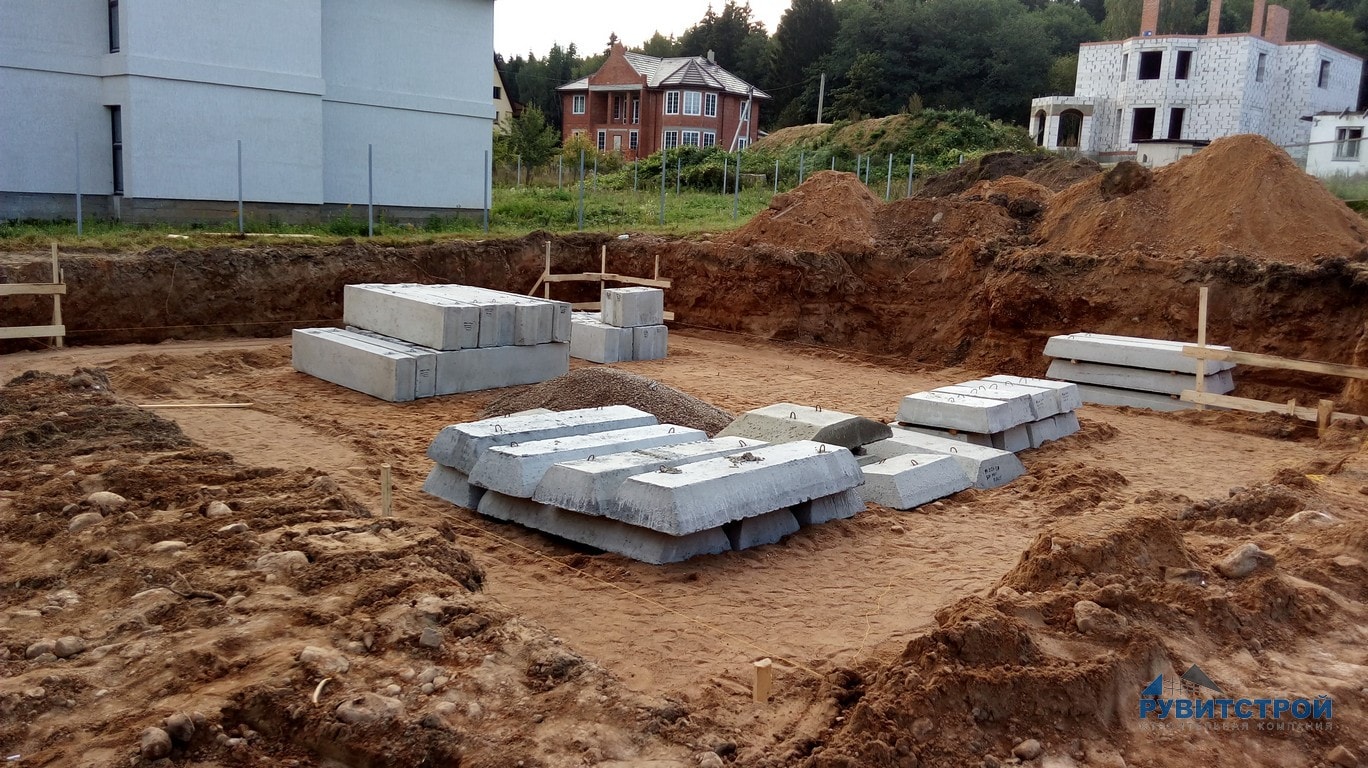
Step-by-step instructions for the construction of a prefabricated foundation from ready-made FBS
Let's consider how to make a foundation from FBS blocks, how to lay blocks correctly and step-by-step instructions for these works.
Step 1
For a house made of blocks, the required number of them is calculated.It is conducted by one of the following options:
- By the required length of straight sections. The length of the segment is divided by the length of the longest block and rounded to the lower whole number. The remaining part is supplemented with additional FBS of shorter length.
- According to the total volume of the prefabricated foundation. Calculate and add up the volume of all straight sections and divide the sum by the volume of the standard FBS.
Round the result to the nearest whole number. The remainder is taken out in the form of gaps between standard blocks, which are filled with either additional FBS or parts split from one of them.
Both methods give an error, which is compensated for by filling the gaps with concrete.
Step 2
Do-it-yourself earthworks during the construction of a foundation from FBS blocks.
The options are:
- A house without a basement. A trench is being dug 200–300 mm wide more than the thickness of the foundation wall. Its bottom is leveled.
- House with a basement. There are two options:
- a pit is dug under the entire basement and a basement box is built from the FBS in it;
- trenches are dug to lay out the foundation blocks and the blocks are mounted in them, while a small amount of earthwork is required. Trench - for the thickness of the block foundation wall and for the additional clearance required for lowering with a crane or manipulator.
Step 3
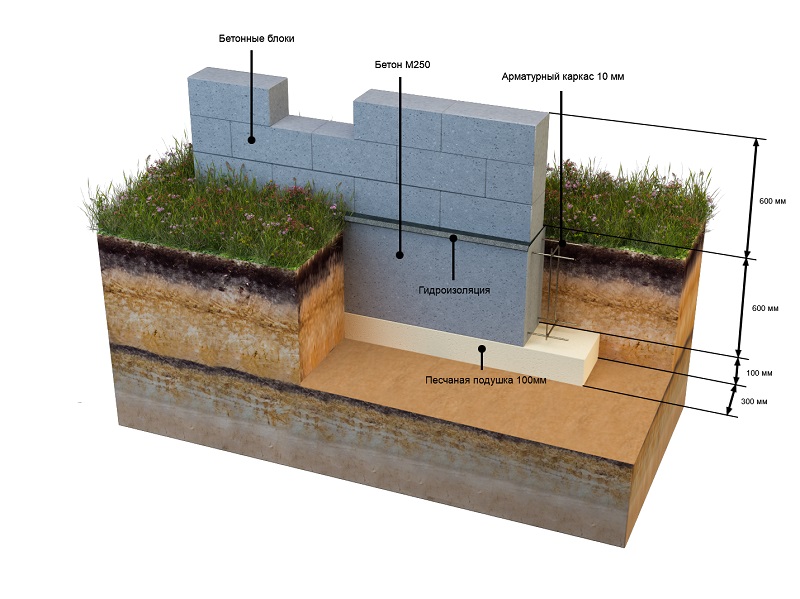
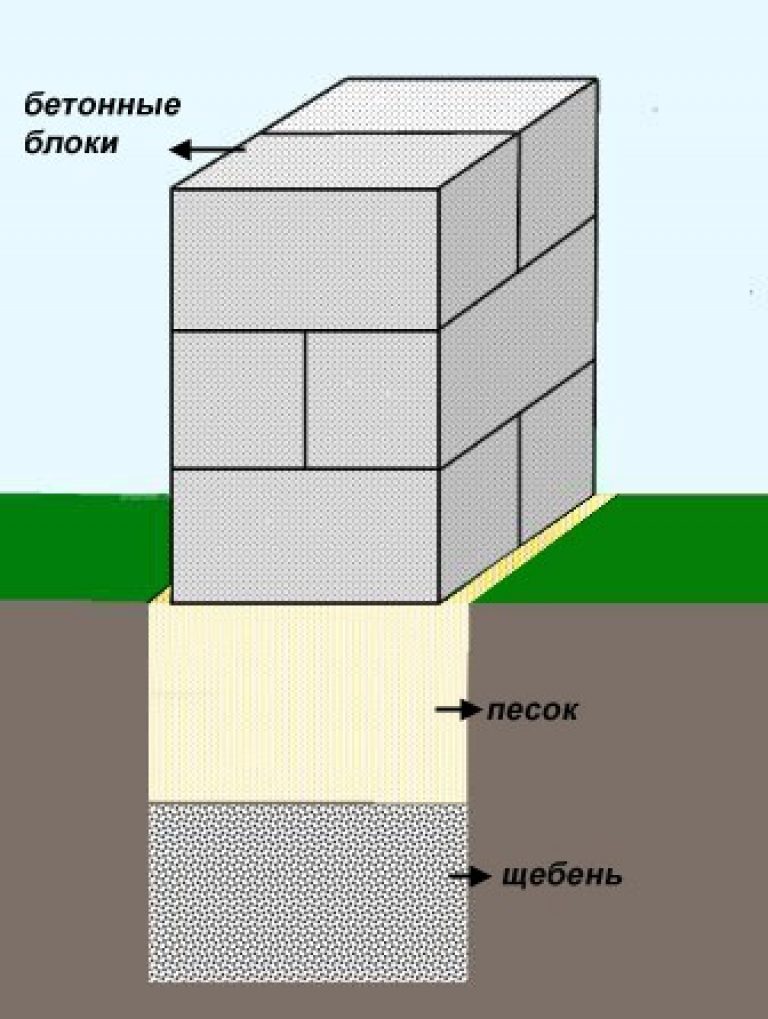
At the bottom of the trench, a sand and gravel cushion is covered with layers.
It is laid under FBS blocks on solid heavy soils that can withstand heavy loads. Thickness is calculated during design. Without a project, it can be made with a thickness of 150 - 250 mm after wetting and tamping or vibrating.
On weak soils, 10–20 mm crushed stone is added to the top layer of the sand cushion. The thickness of the crushed stone layer should be according to the project, usually at least 200 mm. Crushed stone is covered with sand from above and rammed together with it.
The construction of a foundation from FBS blocks in flooded soils requires:
- drainage runoff, which is done, for example, in a sand and gravel bed;
- or laying drainage pipelines around the perimeter of the foundation.
Step 4
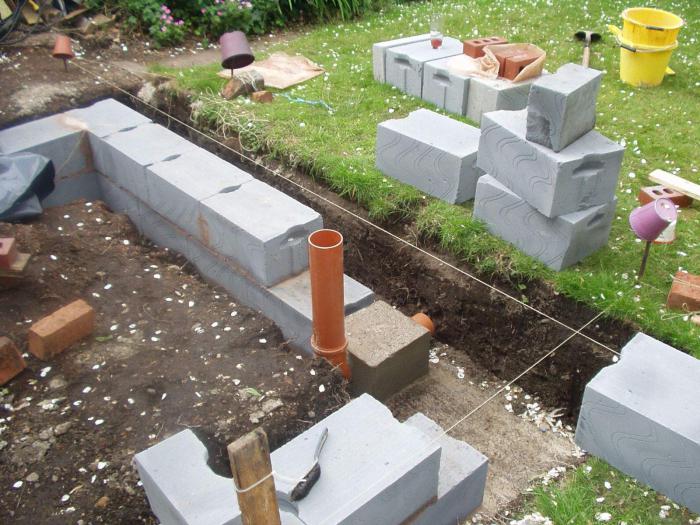
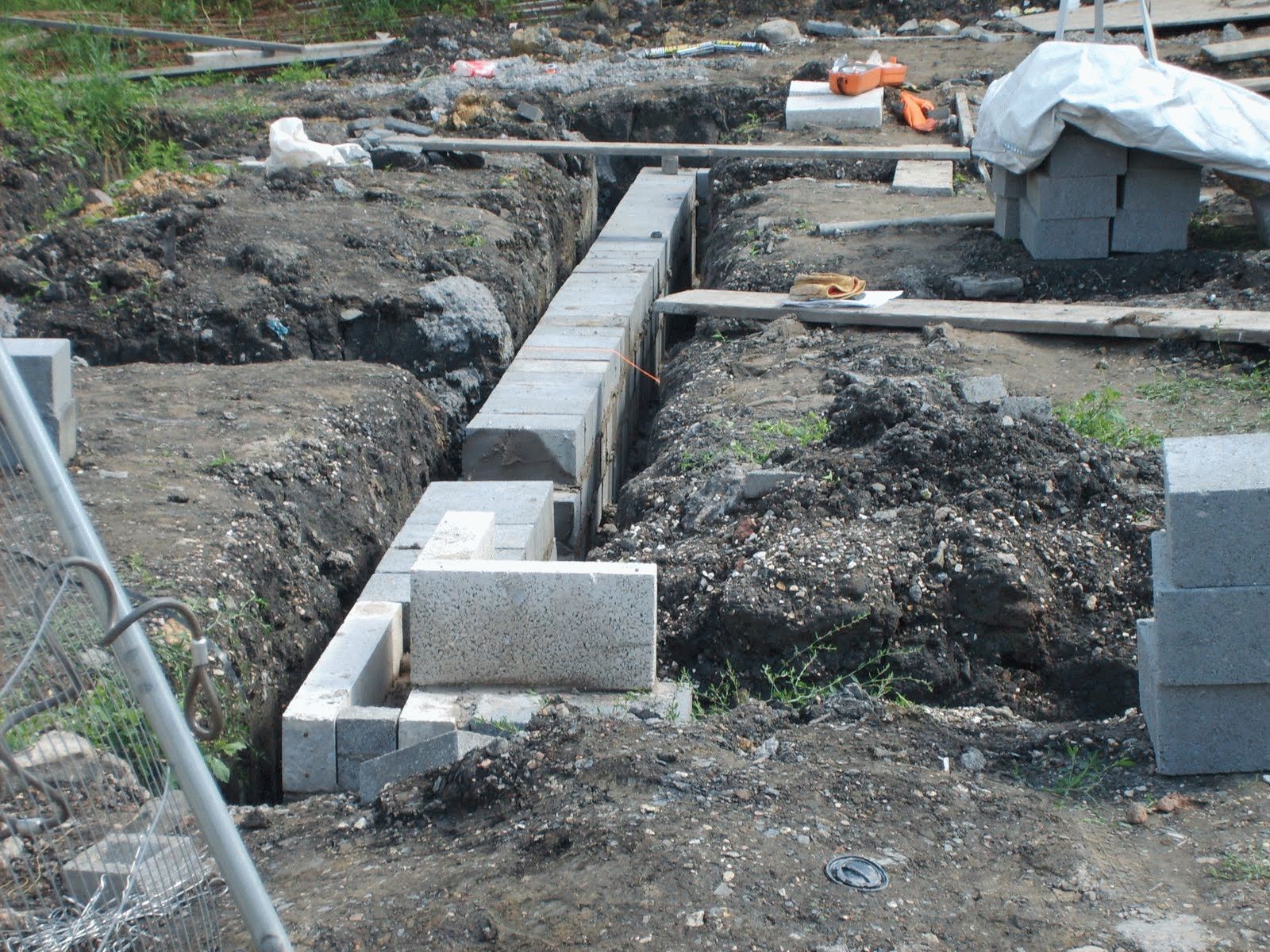
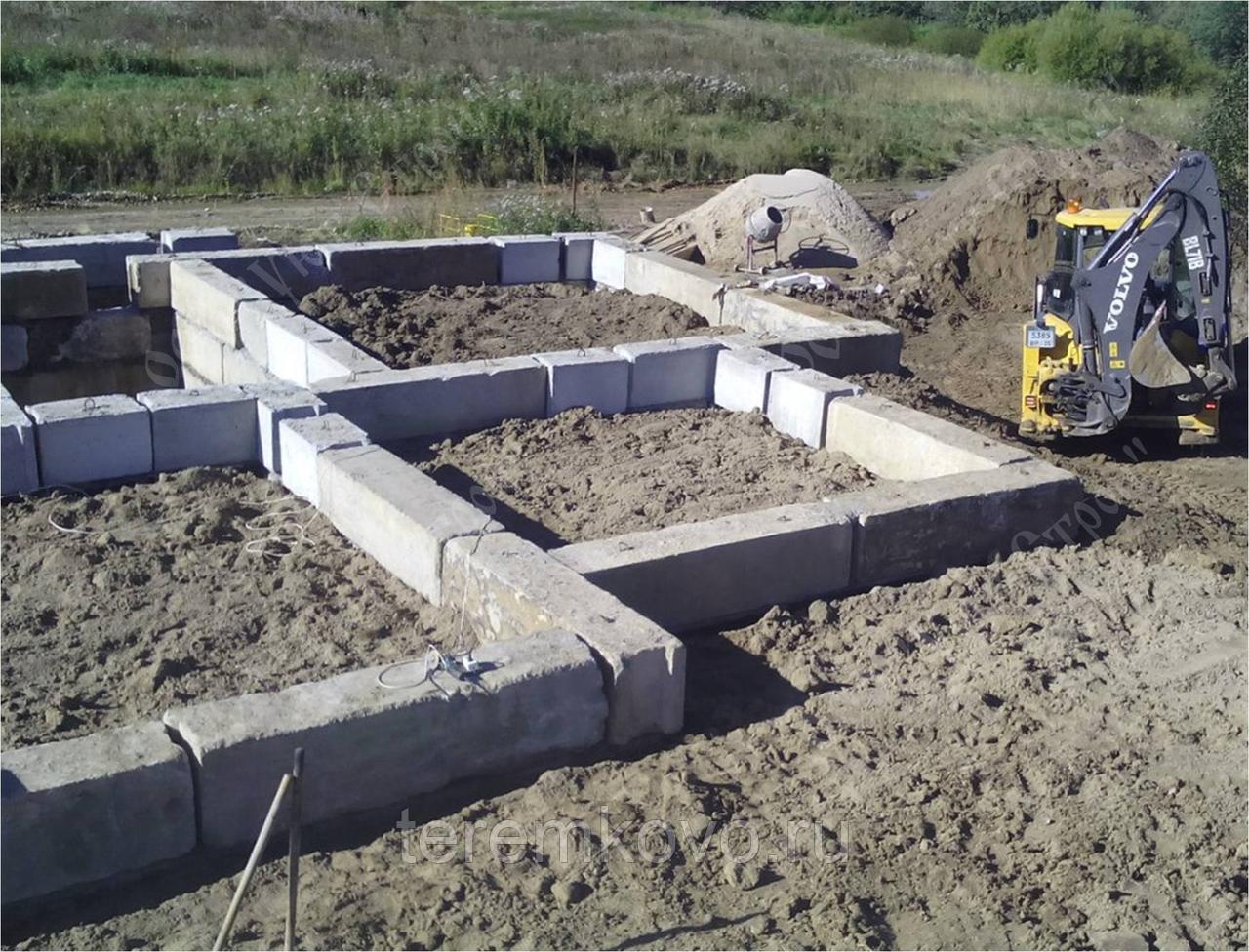
Installation of the FBS foundation or their layout in the trench.
If a reinforced concrete block "cushion" of FL blocks is not used, then FBS are laid out starting from the corners of the building. Typically, a crane of the appropriate lifting capacity is used for this. The gaps are filled with a cement-sand mortar (CPR). Large gaps can be filled with additional blocks or concrete mortar.
How to put FL blocks on the foundation?
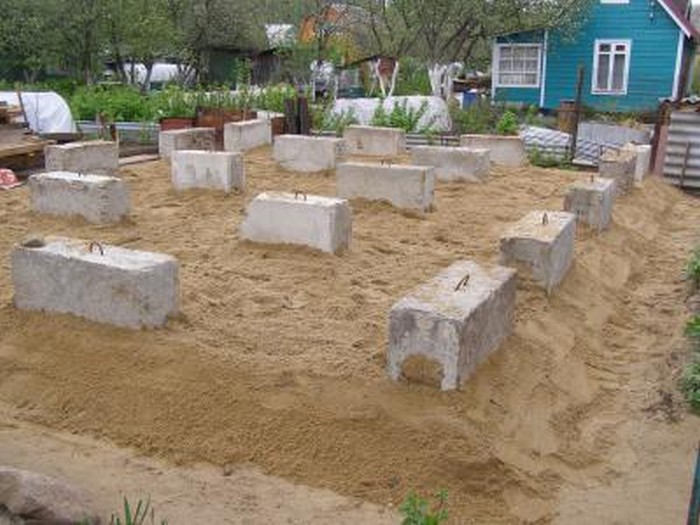
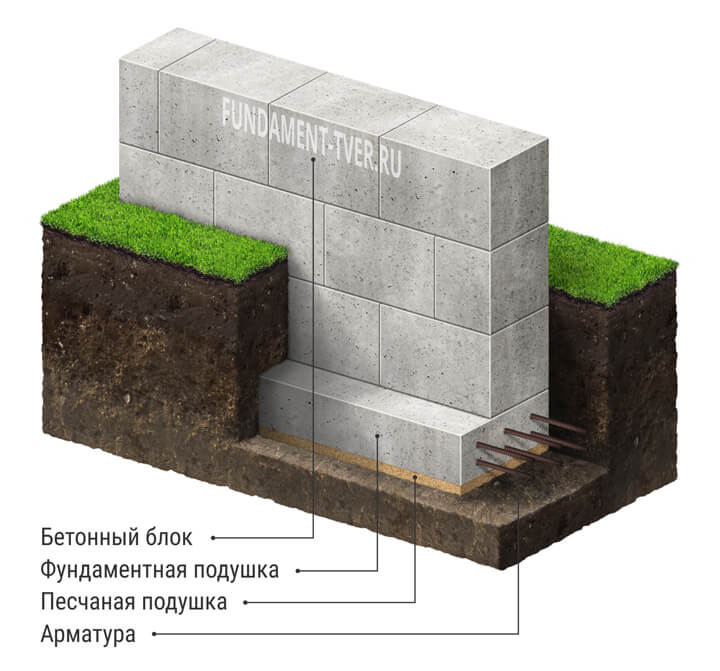
- When using reinforced concrete FL, they are laid in the first row on crushed stone - a sand cushion.
- The foundation FBS is laid in the second and subsequent rows. An example of such a masonry is a staggered brickwork with a half-length overlap. How do I put the first blocks? Installation of foundation blocks starts at the corners. The row is filled from the corners to the middle.
- Installation is performed on the CPR.
Step 5
- The top row is "covered" with a monolithic reinforced concrete belt. Its thickness, type and quality characteristics of concrete, type of reinforcement (steel or composite) and the degree of reinforcement are determined by the foundation design.
- To ensure the vertical bending strength, the belt needs to be reinforced. Reinforcement is prepared in the form of a knitted frame, which is placed in the prepared formwork. When laying, it is required to observe gaps of 30 - 60 mm between the extreme rods of the frame and the plane of the formwork. After the concrete is poured, a protective layer of concrete will form in these gaps.
- To use the concrete solution on frosty days, antifreeze additives must be introduced into it, water must be heated, etc. The poured foundation must be protected from freezing or heated with electricity until the structure gains its acceptance strength.
- When placing concrete in the foundation with your own hands, the top layer of the monolithic belt should be leveled.
Using a strip foundation
The most obvious and common way to reduce the risk of uneven foundation settlement is to reduce the pressure it transfers from the weight of the building to the ground. The relatively low weight and small width of the aerated concrete wall allows in some cases to go this way. For this, it is necessary to know the bearing capacity of the natural foundation, its composition and the regime of soil waters in the building area. The elevation of the foundation is set at a value below the standard depth of soil freezing.
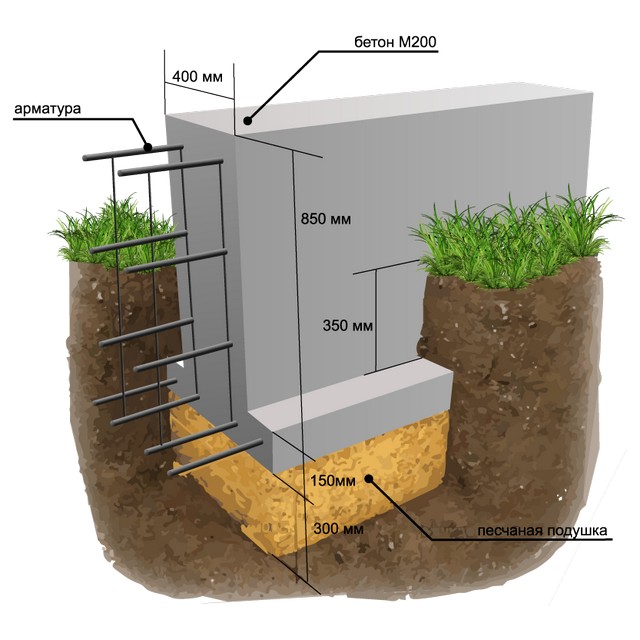
Diagram of the strip foundation device.
Strong soils that are not subject to heaving can serve as a reliable support for the building. To reduce the pressure on the natural foundation, the area of the support cushions or foundation blocks should be increased. To do this, you need to perform calculations based on the collection of loads from the structure and the study of the soil conditions under the building. Perhaps, the broadening of the supporting section of the structure by 0.2-0.3 meters will be enough to obtain the necessary decrease in pressure per square centimeter of soil and ensure a negligible draft.
In the described case, for a house made of aerated concrete blocks, a strip foundation can be used, created from ready-made elements or monolithic concrete, which allows the device in the building of basements. Reinforced belts or ties will serve as an additional guarantee, distributing the arising loads without violating the integrity of the masonry.
Types of foundation blocks
It is recommended to choose it only for areas with dry and low-loamy soils. But in fact, with a competent calculation, you can arrange such a support for any house and on any soil. Reinforced concrete FBS blocks were originally designed to speed up and simplify construction. They are able to withstand considerable loads, you just need to select them correctly.

This is what a block base looks like
On a block foundation, buildings can be erected from all known building materials. There are no restrictions here. But for the same houses from self-supporting insulated wire- panels, distinguished by their light weight, it is better to choose cheaper screw piles. But in general, building rules and regulations are allowed to be placed on the considered base of the wall from bricks, foam blocks, beams and logs. Everything is at the discretion of the owner of the cottage.
Advantages of block columnar supports
Supporting bases of a columnar type have high strength, reliability and durability, it is also worth emphasizing the following advantages of this foundation:
- Efficiency - the foundation of the pillars does not require high costs during the construction, the technology of erection of the pillars does not provide for waterproofing, as well as the digging of continuous trenches, which must be dug out if a strip foundation is being erected, which significantly reduces the cost of work.
- The possibility of construction without the involvement of hired labor and construction mechanisms.
- Use of columnar bases in soils with a wide range of characteristics. The technology of the device of pillars to support buildings provides for construction even in wet soils with insufficient bearing capacity.