Self-calculation
There are five main factors that affect the load-bearing capacity of a pitched roof:
- The angle of inclination of the ramp.
- The type of roofing material.
- The climate in the region where the house is being built.
- The dimensions of the building and the roof.
- Types of materials for thermal insulation cake.

It should be noted that the first two parameters are interconnected. There are certain standards that indicate at what angle of inclination, what kind of roofing material can be used. For example:
- slate or piece shingles - the minimum slope of the slope is 22 °;
- corrugated board - 12 °;
- metal tile - 14 °;
- ondulin - 6 °;
- bituminous tile - 11 °;
- roll materials in three layers - 3-5 °, in two - 15 °.
That is, when calculating a pitched roof, you must first of all decide what kind of roof the roof will have. Based on this, make a decision regarding the slope of the ramp.
As for climatic conditions, here two positions are taken as a basis: snow load and wind load. Both values refer to live loads, since they are not permanent. But they must be taken into account. For this, special formulas are used.
Snow load
Here is its formula:
S = Sg * µ, where Sg is the standard mass of snow cover per 1 m² of the slope plane, µ is a correction factor based on the slope of a pitched roof. For tilt up to 25 °, the coefficient is "1", above this value - "0.7", above 60 °, the coefficient is not taken into account.
Wind load
The formula is:
W = Wo * k, where Wo is the standard in effect in a certain region, k is a correction factor that takes into account the height of the roof above the ground, type of terrain, building site (open or closed).

It should be understood that both loads do not take into account particular situations. For example, a sharp strong gust of wind, which is extremely rare in the building area. Or the monthly amount of snow that fell in one day. Therefore, it is recommended to increase the final value by 15–20% in the process of calculating the rafters and other elements of the pitched roof.
We add that the standard values of snow and wind loads can be found in the public domain on the Internet. They can be graphical or tabular.
Load from roofing material
The two previous loads are categorized as "temporary". But there are so-called constants, which first of all fall into the calculations of the rafters of a pitched roof. In fact, in this structure, the constant load is the roofing material, or rather, its weight, taking into account 1 m2 of the slope surface.
The complexity of calculating this type of load lies in the fact that for some materials, not the actual area is taken into account, but the real (mostly useful). The thing is that most of the roofing materials are laid on the roof lathing with an overlap, which reduces the coverage area, but increases the weight of the products, taking into account the pressure on 1 m2 of the covered surface. In this case, it is imperative to take into account everything with overhangs and cornices, protrusions from the sides.
The minimum slope of a pitched roof: what depends on and how to calculate ↑
Each manufacturer has its own individual requirements for the minimum slope. In addition, a lot depends on the characteristics of the climate of a particular area, in particular, the snow load. For example, the less snow falls, the flatter the roof may be. There is a table of roof slopes, which presents its possible minimum values, in accordance with territorial standards and characteristics of the roofing material.

The roll roof has an upper slope limit of 25 °, although it is recommended that the 15 ° limit is not exceeded in order not to complicate the device.
For slate (asbestos-cement corrugated sheets), a significantly larger slope is required - starting from 25 ° (reinforced profile) or 35 ° (normal). By the way, the overlap of the sheets depends entirely on this value and the greater the slope, the more the overlap will be.
Euroslate is more "loyal" to the steepness of the slope. The minimum slope for it is 6 °. Moreover, for
- 6–10 ° - continuous lathing is required;
- 10-15 ° pitch of boards or construction bars - 45 cm;
- from 15 ° - about 60 cm.
Theoretically, metal tiles can be installed with a slope starting from 10 °. However, practically in the range from 10 ° to 20 °, problems may arise with the sealing of all joints of the sheets. The most acceptable solution would be to use metal tiles for roofs with a slope of more than 20 ° and already the need to provide additional sealing.
Profiled sheeting can be used starting from 5 °. It should be remembered that at 10 ° the overlap must be increased, and a sealing tape must be laid in the joints.
A seam roof with a factory seam or made directly on the construction site is used for foundations with a slope starting from 8 °. With proper sealing of the seam joints, this value can be reduced to 3 °.
Bituminous flexible shingles are used at an angle of inclination not less than 11 °. Up to 18 °, a continuous lining layer is laid, at large values - rolls are rolled only along the outer contour of the slope plane and additional holes are insulated.
Ceramic and concrete tiles are laid starting from 22 °. When installing an additional waterproofing layer under the tiles, the angle can be reduced to 10 °. However, shingles are rarely used for pitched roofs due to their high weight.
How to calculate the slope of the roof: professionals recommend
To measure slopes, professionals recommend using a special protractor designed by M.A.Kozlovsky.
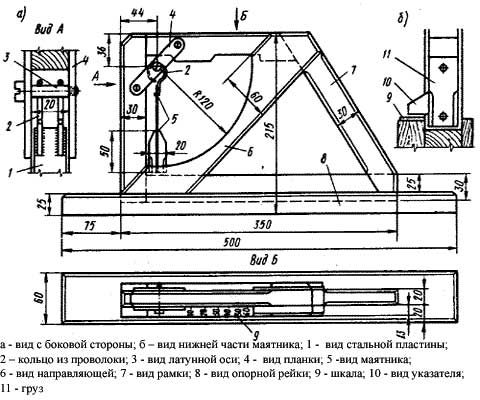
Calculation of the roof slope in percent carried out according to the following scheme.
- The support rail is installed on the lathing perpendicular to the direction of the ridge.
- The side of the frame, where the pendulum is located, is directed to the ridge of the roof structure.
- Under the influence of the weight, the pointer will indicate the slope of the roof in degrees on a semicircular scale. On the vertical axis, you can immediately determine the percentage expression, which is used much more often.
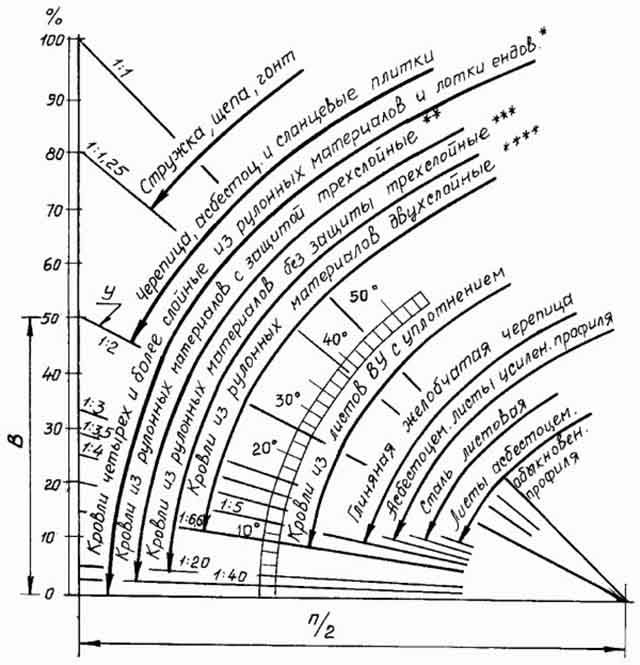
- Roofing materials are divided according to their physical, economic, technical properties into groups, which are shown on the device by arcuate arrows.
- Oblique lines are used to determine the angle of the slope.
- The bold line represents the relationship between the height of the ridge and one part of the position.
Thus, it is possible to determine the minimum angle of inclination recommended for use in a particular group of roofing materials according to the schedule.
2020 .
- Security
-
Roof types
- Attic
- Flat
- Pitched
- Glass
-
Roofing materials
- Keramoplast
- Natural
- Ondulin
- Polycarbonate
- Slate
- Roofing
- Soft roof
- Metal
-
Repair and maintenance
- Types of jobs
- Sealants
- Leakage
-
Rafter system
- Mauerlat
- Lathing
-
Shingles
- Flexible
- Metal tile
- Roofing device
-
Warming and insulation
- Hydro and vapor barrier
- Heat insulating materials
- Warming
- I-beams and channels
-
Roof elements
- Ventilation
- Gutters
- Chimneys
- Ridge
- Stairs
- Low tide
- Snow holders
- Gable
New publications
- Why is Tyvek vapor barrier a good choice?
- Specificity of foil vapor barrier: characteristics, conditions of use, installation
- Mansard roof rafter system: diagrams, device
- How to fix the rafters: fastening to the beams, Mauerlat and other roof elements
- Snow load on the roof: subtleties of calculation during design
2020 Stylish Roof Roof
The images published on our site are taken from open sources. If you are the author of the image, then contact us through the contact form, and we will try to quickly resolve this issue.
Recommendations from the pros!
Bath accessories
DIY gazebo
Concrete fence
Diy potbelly stove
Do-it-yourself veranda
Screw foundation
Country toilet do it yourself
Decorative brick
Stone fence
Pouring the foundation
How to make a fence
Wicket from corrugated board
DIY fireplace
Brick fence
DIY flower beds
Forged gates
Do-it-yourself porch
Bath tub
DIY chicken coop
DIY ladder
Metal gates
Installation of lining
Installation of polycarbonate
Pump for giving
Garage arrangement
Fences for flower beds
Do-it-yourself blind area
Steam room in the bath
Railing for stairs
DIY cellar
Painting the walls
DIY press
Lattices on windows
Rolling gates
Do-it-yourself shed
Alarm for summer cottages
Benches for giving
Fence posts
Floor screed
Solid fuel boilers
DIY greenhouse
Fence installation
House insulation
Attic insulation
Insulation of the foundation
Influence of the type of material on the angle of inclination
An important factor in determining the correct roof position is the choice of decking material. For example, using a soft roof, the inclined angle will be significantly less than when overlapping with slate.
Ondulin and professional flooring
In the first and in the second case, the slope indicator can range from 9 to 25 0.
In addition, the profiled sheet can be used if the roof of the building is at an angle of 5 0. When the slope is more than 10 0, the overlap when laying the material must be increased, and a sealing tape must be applied to the joints.
A prerequisite for the use of these types of materials is the presence of constant air exchange in the under-roof part of the roof.
Slate
For this type of building products, the minimum slope is 20 0, the maximum is 30 0.
It depends on the size of the angle and what the overlap between the sheets will be. The greater the degree, the more each element overlaps with each other.
In the case of wavy slate, if the angle of inclination is within 10 0, then the lathing is made solid. With an indicator above 15 0, the step is from 45 to 60 cm.
Metal tile
When laying at an angle of 10 to 20 0, it is imperative to treat all joints with a sealant. If the indicator is in the range of 20-30 0, there is no such need.
Other types
Flexible shingles are used when the roof slope is 11-18 0.
For a polycarbonate canopy, the minimum slope is considered to be an angle of 30 0, and the optimal indicator is 50 0.
When using sandwich panels for roofing, it is necessary to adhere to a minimum slope of 50. This option is suitable if the surface is made with a continuous span without joints. Otherwise, the angle must be at least 7 0.
Ceramic tiles are used if the roof angle is at least 22 0. But since the material is heavy, it is rarely used for roofing pitched roofs.
What determines the inclination of roof slopes
To determine the steepness of the future roof and calculate the building materials for its construction, the following factors must be taken into account:
- the value of loads from snow cover and wind flows in the region of residence;
- the presence of an exploited attic or a full-fledged attic floor;
- used roofing material.

The dependence here is as follows: with a slight slope (up to 30 °), the volume of the attic space is small due to the low ridge, and the effect of the wind on the structure is minimal. On the other hand, a lot of snow falls on the roof surface, which exerts a static load. Conversely, slopes at a large angle (from 45 °) provide good snow cover and an increase in the size of the attic, but are subject to dynamic wind loads.
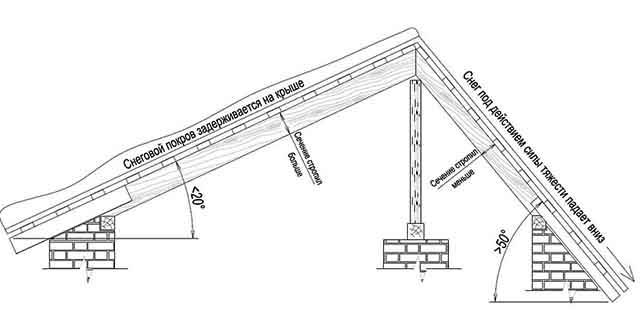
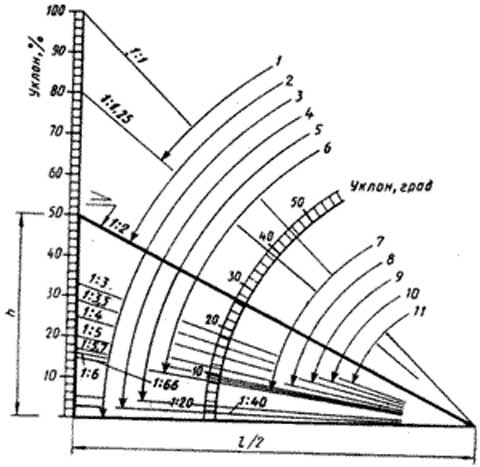
The influence of roofing materials is indirect, since they can be selected depending on the inclination of the slopes. For example, coverings made of standard sheets - slate, metal roofing or corrugated board - cannot be used when the slope is less than 22 °, otherwise water will flow into the attic in case of heavy rain or melting snow.The applicability of certain building materials, depending on the steepness, is shown in the diagram:
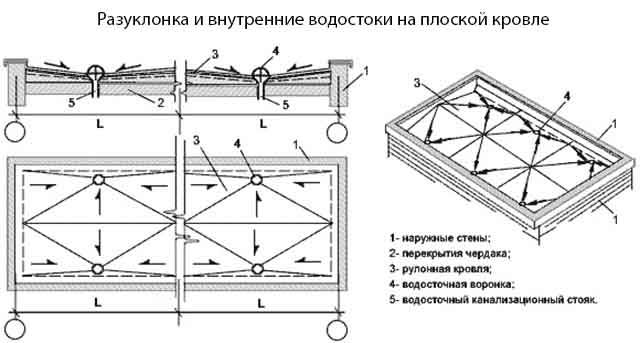
Also, the chosen type of roof - flat or pitched - has a great influence. The first is usually done on reinforced concrete floors and other powerful structures that can withstand the pressure of wet snow. A sloping covering consists of one or several planes, inclined at an angle of 1-3 ° towards external gutters or internal sewer pipes.
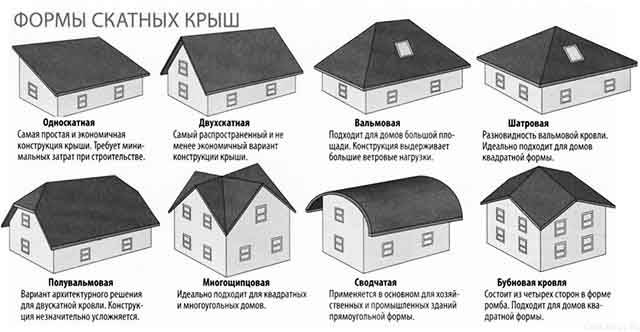
The planes of pitched roofs of private houses are usually oriented outward and are more steep. The angle of inclination depends on the shape of the roof and is in the following ranges:
- single-slope - from 10 to 45 °;
- gable, hip, multi-gable and hip-roof - from 25 to 50 °;
- broken attic - up to 60 °.
All the pros and cons of a pitched roof
Among experienced builders, there are adherents and opponents of this type of building shelter.
In favor of this method, it is worth saying the following:
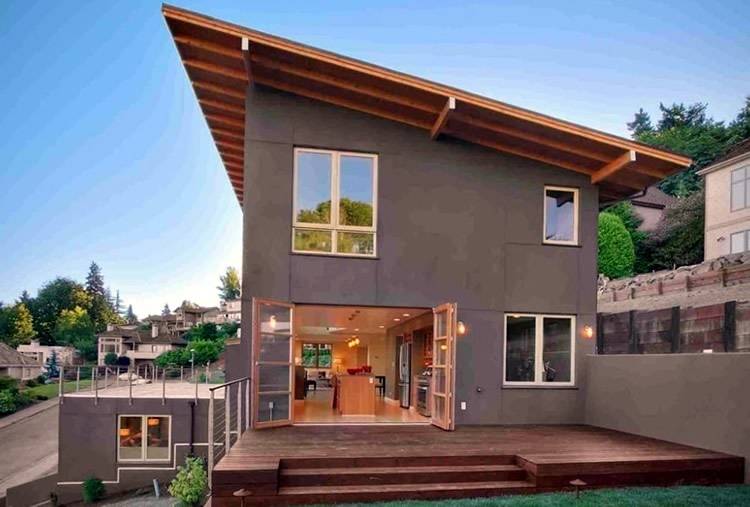

It is worth paying attention to the fact that the roof structure does not allow equipping a cozy attic or attic, which is why some owners refuse this method of flooring the surface of the house. A pitched roof is one of the simplest options for roofing structures, the device of which can be handled without any problems with your own hands.
You just need to study the main features of the technology and do everything in strict accordance with the instructions
A pitched roof is one of the simplest options for roofing structures, the device of which can be handled without any problems with your own hands. You just need to study the main features of the technology and do everything in strict accordance with the instructions.
The design in question is attractive, first of all, in that a large amount of building materials is not needed for its device. Some serious skills and extensive experience are also not needed to do this kind of work. The pitched roof has an extremely simple structure and is perfect for residential and commercial buildings.


It is better if a specialist will deal with the development of the project of a pitched roof. This will greatly simplify the work of the home craftsman. He will only have to do everything in accordance with the instructions and rejoice at the result.
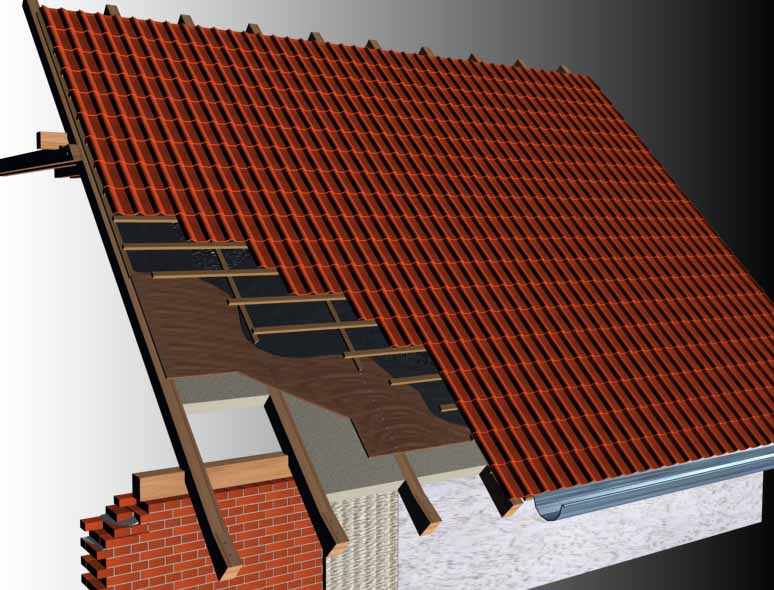
The main material for the manufacture of a shed roof is natural wood. It is used to create battens, beams, rafters and other elements. Slate and its more modern counterpart called ondulin are most often used as a topcoat; tiles and other materials are often used.

Before proceeding with the construction of a gable roof of a house with your own hands, it is necessary to calculate the optimal slope of the roof slope.
As already noted, the main point that you need to focus on at this stage is what kind of finishing roofing material the owner decides to use. For example, metal tiles or the same slate do not delay precipitation in the same way as metal profiles. And all these points must be taken into account at the design and calculation stage of the roofing system.
In the case of using roofing material and other roll roofing materials, a minimum slope of 5-10 degrees can be made. When using slate, it is recommended to increase the slope to 20 degrees. If the roof is covered with tiles, the minimum permissible angle of inclination is 20-30 degrees, but it is better to orientate at least 35 degrees.

In addition to the type of finishing roofing, it is necessary to take into account the main features of the terrain in which the house is built. For example, if the building is located so that the wind can blow on its roof from all sides, the slope of the slope can be reduced.If the house is located among dense plantations of tall trees, it is strongly recommended to equip steeper slopes, because wind power alone is definitely not enough to remove all the snow.
The main advantages of pitched roofs
Despite the fact that not everyone likes the aesthetics of the building over which the pitched roof is mounted (although the question itself is ambiguous), many owners of suburban areas when erecting buildings, and sometimes even a residential building, choose just this option, guided by a number of advantages similar construction.
Single-pitched roofing systems captivate with their clarity, simplicity of calculations and installation
- Materials for a single-pitched rafter system, especially if it is being built over a small outbuilding, will require very little.
- The most "rigid" flat figure is a triangle. It is he who underlies almost any rafter system. In a lean-to system, this triangle is rectangular, which greatly simplifies the calculations, since all geometric relationships are known to everyone who graduated from high school. But this simplicity does not in any way affect the strength and reliability of the entire structure.
- Even if the owner of the site, who is leading independent construction, has never previously encountered the construction of a roof, the installation of a single-pitched rafter system should not cause him excessive difficulties - it is quite understandable, not so complicated. Often, when blocking small outbuildings or other adjoining structures, it is quite possible to do not only without calling a team of specialists, but even without inviting assistants.
- When erecting a roof structure, the speed of work is always important, of course, without loss of quality - you want to protect the structure from the vagaries of the weather as quickly as possible. According to this parameter, the single-pitched roof is definitely the "leader" - there are practically no complex connecting nodes in its design that take a lot of time and require high-precision adjustment.
How significant are the disadvantages of a single-pitched rafter system? Alas, they are, and they also have to be reckoned with:
An attic with a pitched roof is either not assumed at all, or it turns out to be so small that you have to forget about its wide functionality.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, a pitched roof does not imply the presence of a "useful" attic space
- Based on the first point, there are certain difficulties in providing sufficient thermal insulation for the premises located under the pitched roof. Although, of course, this can be corrected - nothing prevents the roof slope itself from being insulated, or placing the insulated attic floor under the rafter system.
- Shed roofs, as a rule, are made with a slight slope, up to 25 ÷ 30 degrees. This has two consequences. Firstly, not all types of roofing are suitable for such conditions. Secondly, the significance of the potential snow load increases sharply, which must be taken into account when calculating the system. But on the other hand, with such slopes, the effect of wind pressure on the roof is significantly reduced, especially if the slope is correctly positioned - to the windward side, in accordance with the prevailing winds in this area of the terrain.
On the network, you can find many projects of residential buildings, in which the main emphasis is placed precisely on the lean-to roof system.
Another drawback, perhaps, can be attributed to very conditional and subjective - this is the appearance of a pitched roof. Lovers of architectural delights may not like it, they say, it greatly simplifies the appearance of the building. One can object to this too. First, the simplicity of the system and the economy of construction often play a decisive role in the construction of auxiliary structures. And threefold - if you look at the overview of projects of residential buildings, then you can find very interesting design options, in which the emphasis is placed on a pitched roof. So, as they say, tastes differ.
Dependence of the height of the roof and the usable area of the attic (attic) on the slope of the roof
A change in the height of the roof, in addition to a change in snow and wind loads on the rafter system, leads to a change in the usable area of the room under the slopes.
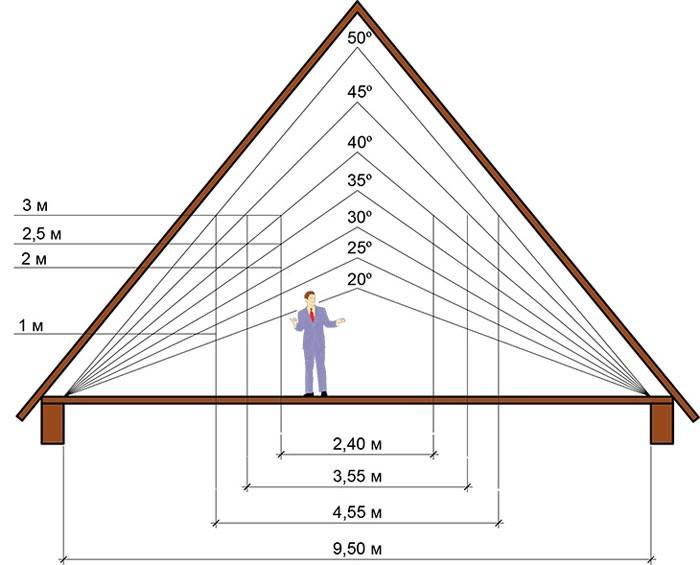
Change in usable area depending on the height of the roof
Since the useful height of the attic is considered to be 2.5 ... 3 m, raising the roof (taking into account the overlap of the attic) to a height of more than 5 m is unprofitable. Taking these parameters into account, for attic rooms, a slope angle of 25 ° is taken (for single-slope and gable buildings). If an attic type of roof is used, its upper part may have a slope of 10 ... 20 degrees, the lower - 50 ... 80.
In this case, the location of the attic room may vary depending on the type of roofing system.
As the illustration shows, more complex outrigger or offset designs provide more usable space. However, the construction is hampered by a large number of calculations for the location of rafters and beams, a changed configuration of the roof as a whole, and problems with the flooring of roofing material.
This also takes into account the use of attic space. So, if it is planned to arrange sleeping places under the "attic" (located between the interfloor overlap and the inclined part of the attic ceiling - Mauerlat) walls, the height of the wall is assumed to be less than if it is supposed to accommodate a workplace or a cabinet of normal height there.
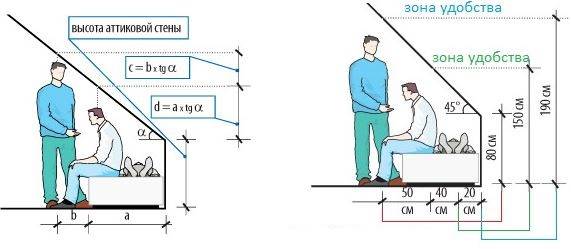
Installation of an attic wall for residential attics
The height of the attic wall for residential attics is taken 60 ... 220 cm:
- 80 ... 130 cm - convenient placement of the bed, skylights above it;
- 130 ... 150 cm - the arrangement of the workplace is acceptable;
- 170 ... 190 cm and more is the normal height of the room, you can walk along the wall.
Thus, by choosing, depending on the configuration of furniture (equipment), the minimum permissible height of the attic wall and the slope of the roof, you can calculate the usable area of the attic with a known ridge height or the size of the "inception" (half the width of the house).
Optimal indicators for calculating the angle of inclination of the roof in one slope
How to calculate the angle of inclination of a pitched roof yourself? Let's start by determining the loads on the future roof, and then, choose the optimal roof slope angle.
1. Calculation of loads on the roof
It is necessary to take into account constant and variable loads. The constant weight of all building materials and equipment (antennas, ventilation, etc.). Variable loads are rainfall, wind and the weight of workers with equipment, if roof repairs are suddenly needed.
I. Snow. If the winter in your area passes almost without snow, then you can safely choose the minimum slope angle. In a snowy winter, a roof at 20-25 degrees experiences snow loads of about 150 kg / m2. In such an area, experts advise making a slope with a slope of 45 degrees in order to ensure a constant and even convergence of snow from the roof. Average winter (center and middle zone of Russia) allows you to choose the optimal slope of 30-35 degrees. However, this figure will depend on the following factor:
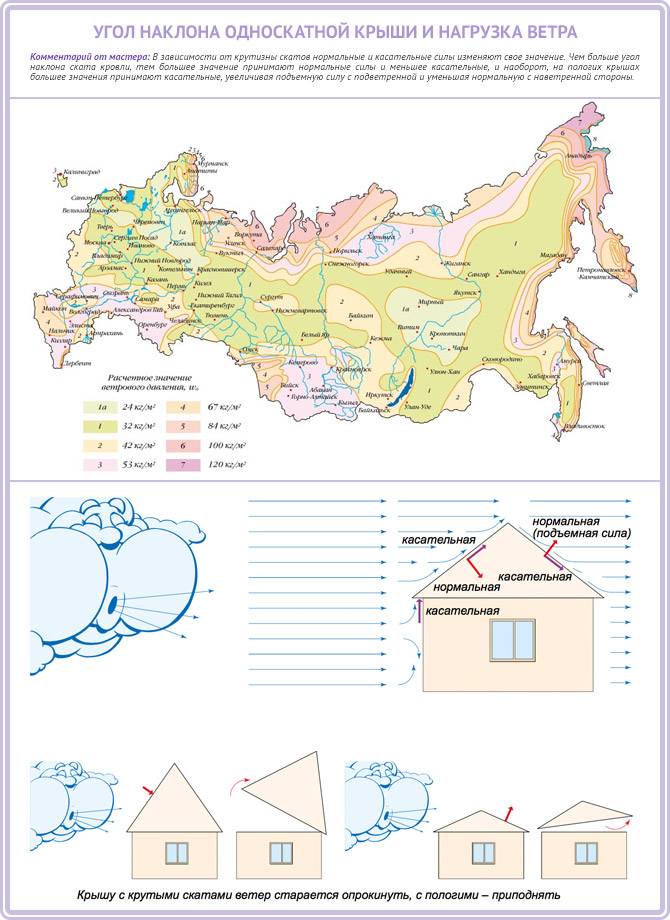
II. Wind. In areas where strong winds prevail, a steeply sloped roof can easily be ripped off. In this case, it is better to position the bottom of the slope towards the wind. To calculate the slope of the roof in windy areas, it is better to use a special map of wind loads:
III. Rain and hail. The force of the falling hail and raindrops also puts pressure on the roof. A steep slope smooths out these loads, protecting the roofing material from damage in regions where bad weather is common.
We conclude: despite the fact that a minimum slope of 10-20 degrees simplifies work and reduces costs, a slope of 35-45 degrees is considered optimal, at which the roof is reliably protected from loads and weather disasters.
2. Determine the optimal slope
Technical and aesthetic characteristics on the side of the steep pitched roof, as the gentle slopes can allow moisture to pass through, trapping snow and debris. However, for outbuildings, garages and small houses, a steep slope is absolutely not necessary, because you can remove snow and dirt manually, and modern sealants will help protect the roof from leaking. So, if we choose:
- Small slope of 3-11 degrees. We need a reinforced rafter system, a continuous sheathing in the form of sheets of moisture-resistant plywood, reliable sealing of joints and a high-quality waterproofing membrane for the roofing material. For such a roof, it is better to choose a soft roofing material, especially if it is a living space;
- Average slope 12-25 degrees. Such a ramp is the best choice for any region of our country. In this case, the joints can not be sealed, but it is better to overlap the roofing material at 20 cm. For this slope, metal tiles, corrugated board, slate, etc. are perfect;
- A steep incline of about 45 degrees. It is chosen for regions with a large amount of precipitation per year. Any solid roofing material is suitable for such a roof.
3. Basic calculations
To provide the desired slope, we need to calculate the length of the rafter leg and the height of the load-bearing wall. We will use the well-known formulas that are used by all builders.
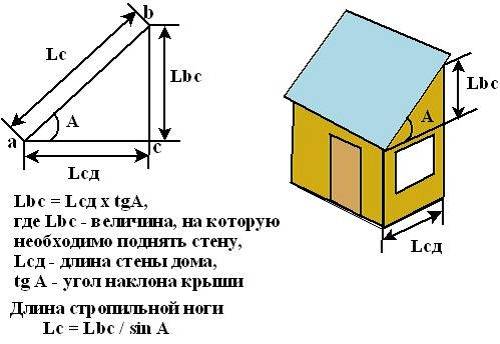
Lbc = Lsd x tgA, where Lbc is the height to which the wall must be raised; Lsd - the length of the house wall (excluding the additional rise for the slope); A - the selected angle of inclination of the roof.
The length of the rafter leg (Lc) is found by the following formula: Lc = Lbc / sinA.
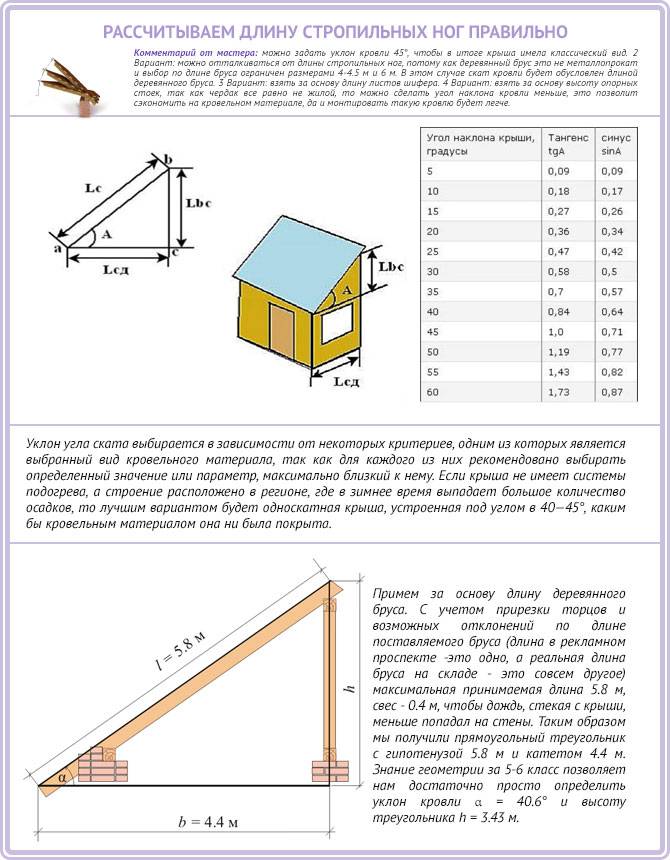
We got the length of the rafters from wall to wall. Also, we need to take into account the rear and front overhangs, which are needed for additional protection from moisture and wind (usually 40-50 cm). So, the final length of the rafter leg will be: (Lc) 3.36 m + 1 m = 4.36 m.
Snow and wind loads
When designing a roof, snow and wind loads on the rafter system are always taken into account. The steeper the slopes, the less snow will linger on them.
To correctly calculate the required structural strength, a correction factor is introduced:
- For roofs with a slope of less than 25 °, a factor of 1 is applied.
- Roof structures with ramps from 25 to 60 ° require a factor of 0.7.
- Roofs made with a slope angle of more than 60 ° do not require the use of a coefficient, since snow practically does not linger on them.
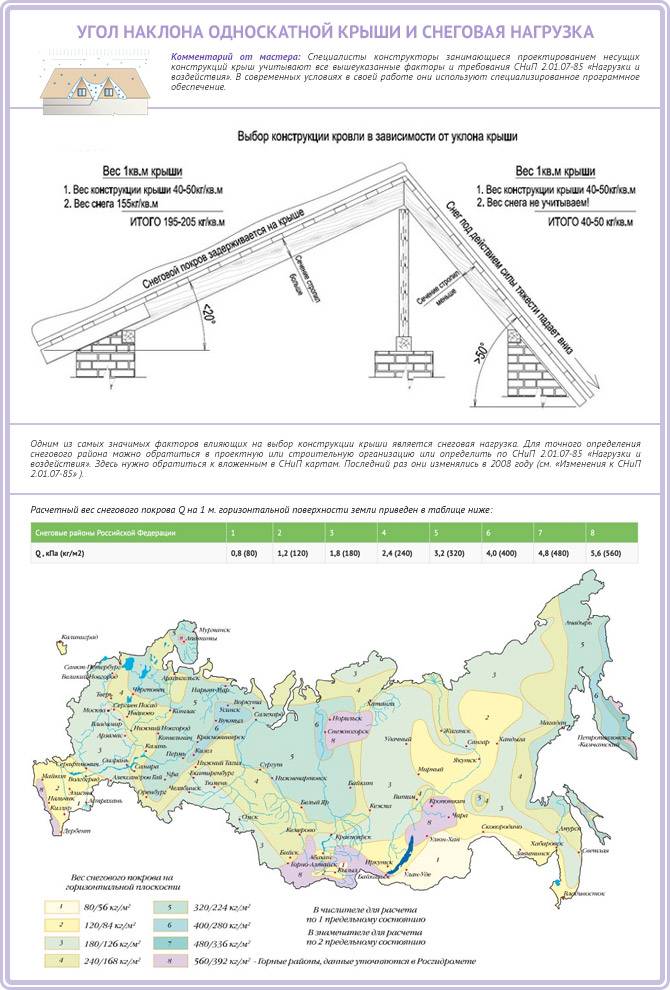
For simplicity of calculations, maps are used in which the average values of snow load in the regions of the Russian Federation are marked.
Calculation examples
The calculation rules are simple: we find our region, determine the snow load, highlighted in our own color, take into account the first value, multiply by the correction factor based on the assumed angle of the roof slope. As an illustrative example, let's calculate the snow load for the roof of a house in Norilsk with a slope angle of 35 °. So, multiply 560 kg / m2 by a factor of 0.7. We get a snow load for a given region and a specific roof structure 392 kg / m2.
To determine wind loads, maps are also used, in which the calculated values of wind loads by region are marked.
In addition, the calculations should take into account:
- The wind rose, and specifically - the location of the house on the ground and in relation to other buildings.
- The height of the building.
By the type of location of the house on the ground, all buildings can be divided into three groups:
- A - buildings located in an open area.
- B - Buildings located in settlements with a wind barrier not higher than 10 m.
- B - buildings located in settlements with a wind barrier from 25 m.
Depending on the location area and the height of the building, when designing the roof, correction factors are introduced taking into account the wind load. All factors influencing the wind load are summarized in a table for easy calculation.
For example: for a one-story house in Norilsk, the wind load will be: 84 kg / m2 multiplied by a factor of 0.5 corresponding to zone "B", which is 42 kg / m2.
In addition, aerodynamic loads affecting the rafter system and roofing material are taken into account. Depending on the direction of the wind, the load is conventionally divided into zones, which imply different correction factors.
Shed roof rafter system.
First of all, the shed roof rafter system depends on the material of the walls and the dimensions of the building.
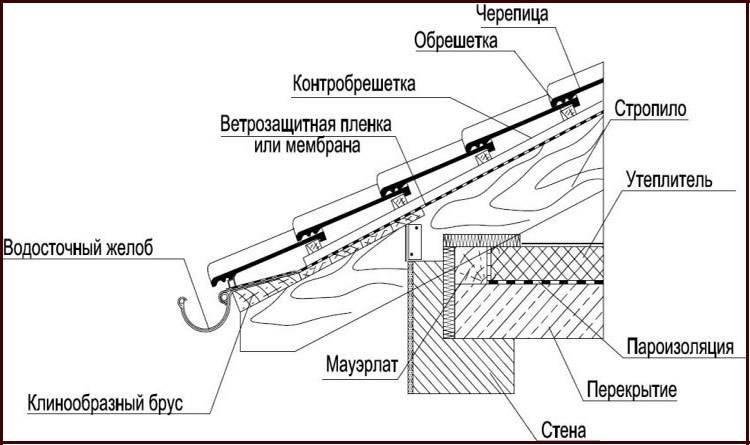
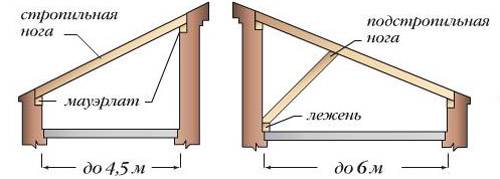
When a gable roof is planned to cover a brick building, then the rafters are installed on the mauerlat - a beam with a section of 100 x 100 or 150 x 150, which is laid on two long walls or, in the case of building a building from logs, on the logs of the upper crown.
The design of the rafter system will be quite simple with a span of up to 4.5 meters, including the Mauerlat, as well as the rafters resting on it.
If the width of the span is up to 6 meters, then a rafter leg will be added to the structure, which rests on the bed and serves to give sufficient bearing capacity to the rafters.
In the construction of the rafter system, it is required to provide for additional fights and racks if the building is planned to be of a larger size.
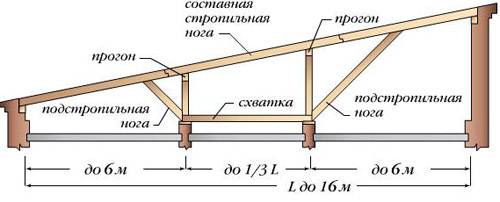
It is possible to carry out the implementation of the rafter system with hanging or inclined rafters, if the frame is made of a bar or rounded logs.

The rafter system with hanging rafters is very often used when constructing gable roofs. You can use the same scheme for the construction of pitched roofs. The essence of the hanging rafters is to support them on horizontal beams that go beyond the perimeter of the structure at the point of support.
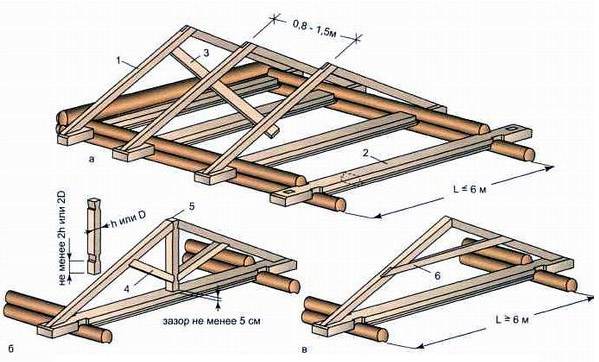
Designations in the figure: a - a system of hanging rafters, b - a rafter system with a headstock and hanging rafters, c - the same, with additional tightening. 1 - rafter leg, 2 - attic floor beam, 3 - wind link, 4 - rafter leg, 5 - headstock, 6 - additional horizontal tightening.
Due to the device of passage through the upper rims of the log house of wooden beams, the use of a system with hanging rafters will somewhat complicate the design. But the forces transmitted from the rafter legs at the same time are more evenly unloaded and do not push against the walls.
How can the material affect the slope of the roof?
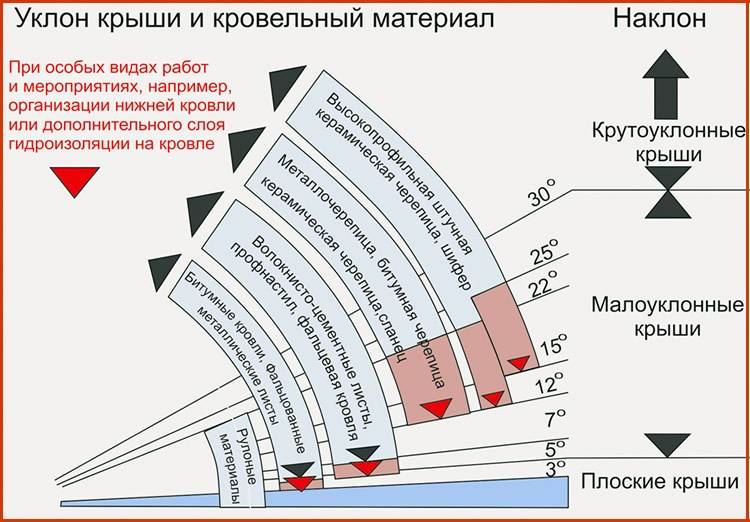
Any roof is a kind of layer cake made of hydro and vapor barrier, insulation, lathing and outer coating... All this is laid on the rafter system at a certain angle, which limits the use of this or that material. Mainly you should be guided by the instructions proposed by the manufacturer, which also relate to the requirements for the slope of the slopes. Roofing materials are rolled, stacked (tiles and slate), sheet, and flexible piece, and for each type there is a minimum roof angle.
For roll coatings, a slope of no more than 15 degrees is considered optimal, provided that the material is laid in 2 layers. If the roof is made of three layers, it should be even more shallow, about 5 degrees, while additional lathing is required to increase the strength in case of an increase in the temporary load (snow, rain). But there is an exception - a membrane covering, which can be used for any roof slope.
Typesetting materials also do not tolerate steep slopes, for the simple reason that they can slide under their own weight at the slightest prerequisite for this, such as a stormy gust of wind. However, the angle cannot be made too small, since in this case the mass of the roofing material will unnecessarily load the supporting structures, that is, rafters, lathing and other elements. The optimal angle is considered to be 22 degrees, sufficient so that moisture can flow freely during rain and not be blown out by the wind under the joints.
With regard to corrugated board and metal tiles, the minimum slope is 12 and 14 degrees, respectively, it is gentle enough for precipitation to flow down from the roof, and at the same time its tightness at the joints is not violated. In a larger direction, the slope can increase without restrictions, however, taking into account the fact that a large roof area has a solid mass. Also, one should not forget about the wind load and high windage of roofs with an angle close to 45 degrees. The optimal slope is about 27-30 degrees.

But for soft tiles, which consist of separate pieces of material of a typical size, the angle of the roof is associated with the density of the sheathing. If the slopes are very gentle, then the distance between the planks should be made as small as possible. This is due to the fact that the snow masses can become an unbearable load for the coating. In the case when the steepness of the slopes is maintained within 30-40 degrees, the lathing step is allowed to be larger, up to 45 centimeters.
Influence of the angle of inclination on the characteristics of the roof
What type of roof is best suited for our climatic conditions? Today there is a wide selection of roof textures and contours. These are two- or four-slope options, tent or any other systems. However, it is the gable roof that is able to combine the optimal set of stability and functionality. Therefore, choosing it for creating a roof dome is the best solution.
How does the wrong slope angle affect the general characteristics of the roof? Incorrectly selected angles of inclination of gable roofs lead to a violation of the strength and durability of the entire system. If the slope angle is too small, water or other foreign formations may penetrate under the plane.
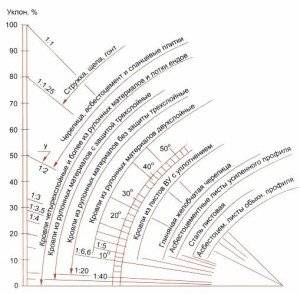
Minimum roof slopes for different types of roofing.
Wringing wind, melt water, snow component - all these criteria are constant risk factors, since they are able to penetrate and fill the most inaccessible places.
Roofs that are too steep can neutralize such factors, but in this case the wind component of the load takes effect.
Snow or water will slide off the roof surface in a natural way, while the roof forms a kind of sail that will take on all the wind load.
I would like to note that it can reach critical values, and this can adversely affect the reliability characteristics of the entire system. Therefore, the optimal angle must be calculated taking into account all critical factors and characteristics of the main covering material.
Roofs with a deviation above 45 ° are considered steep, and with a deviation of 10 ° and below, they are shallow. Therefore, the ideal indicators for gable roofs are average values that vary between 20-35 ° C.
It is these indicators that create good prerequisites for the construction of a roof that is ideal in terms of its qualities.
