Cement production
The main element of cement production is clinker.
A clinker is a mixture of natural materials (usually lime and clay) that have been baked at high temperatures in special ovens. The composition of clinker for cement production is usually 75% limestone and 25% clay. Sometimes the clay is replaced by other natural materials - dolomite or trifoil.
In the environment, it is a natural clinker that can be used for direct cement production without firing.
This rock is marl. Due to the low capacity of natural clinkers, its use is very limited, and therefore most Russian cement plants use clinker, which is composed of clay and lime, for the production of cement.
In the production of cement, when grinding clinker, so-called "hydraulic" materials are added - plaster (volume of clinker 3%) or dolomite (volume of clinker 15%).
Component proportions
The components of the concrete mortar are combined in certain proportions. Using the recommended grade M-500, the ratio of cement / sand / crushed stone is 1/3/4. Violation of the ratio of components will significantly reduce the quality of the concrete foundation.
Here are the characteristic disadvantages that arise when the ratio of the ingredients of the solution is inaccurate:
- Excess sand. The dried solution crumbles.
- Excess water. Builders call this "skinny" solution. The mixture hardens slowly, in places it may not grab.
- Lack of water. The mixture sets quickly and cracks when hardened.
- Only 2% underfilling / overflowing water will noticeably deteriorate the quality of the solution.
Preparation of concrete for a pile-rammed foundation
Compared to columnar foundations, only the calculation formula for cylindrical pillars of rammed piles changes. You need to multiply the height by the radius in the square and by the number "Pi" (3.14). Calculation example: multiply the height of 1 m by 0.0625 (radius 0.25 m2) and multiply by 3.14. It turns out 0.19, round up to 0.2 cubic meters. This calculation is for one pile post.
After pouring any foundation, you need to cover it with a protective film against precipitation. On the day of pouring overnight, pour the foundation abundantly with water, otherwise in the morning it may give small cracks, because the top layer dries quickly. For the first week, moisten the foundation every few hours. From the second week, you can once a day.
Ratio of sand and cement for masonry
Depending on the brand of cement, its ratio to sand can be different - from 1 to 3 to 1 to 6. The most popular option is the classic mixture, consisting of one part of cement to three parts of sand. The latter is usually taken from the middle faction. In this case, first, the dry components are kneaded until a homogeneous state, after which water is poured. In the process of mixing, we achieve such a consistency that the mixture does not flow out when the container is tilted by 40 degrees. In this case, the water must be cold (15 degrees) and always clean. Below we present the proportions depending on the brand of cement and other additives:
- Cement-sand mortar with cement grade 500 - 1 part of cement for 3 parts of sand;
- Cement-sand mortar with cement grade 400 - 1 part of cement for 2.5 parts of sand;
- A solution using lime - 1 part of cement (500, 400, 300) for 3, 2.5-4 and 3.5 parts of sand, as well as 2/10, 1.3 / 10 and 2/10 parts of lime, respectively.
In this case, the amount of water is usually 8/10 parts per 1 part of the cement-sand mixture. In the case of a 100 grade solution, 1 part of the latter is taken from ½ to 7/10 parts of water. The last solution is just used to create brick walls. In the case of grade 115, grade 350 cement is usually used with the appropriate consumption of water and sand. Such a solution is ideal for laying bricks within the outer cladding of a building.
Preparing a solution for pouring the foundation - the ratio of sand and cement
The choice of the used proportions of concrete for the foundation is influenced by many factors: soil parameters, expected loads, type of foundation. The basis of the cement slurry is cement, sand, crushed stone or gravel and water, its properties directly depend on the quality and homogeneity of mixing of the components. Changing the regulated ratios is unacceptable, the slightest errors lead to a decrease in the strength of the foundation and, as a result, the risk of destruction of the supporting structures of the building.

Choosing a concrete grade
The main criteria include the geological conditions of the site (relief, level and partial pressure of groundwater on the elements of the foundation, climate, freezing depth), the type of foundation, the presence or absence of a basement, the height of the building and other weight loads. The constraining factor is the budget of work; it is economically inexpedient to use high-quality grades of concrete for the construction of light buildings in summer cottages. The recommended minimum is:
- M400 - for houses over 3 floors.
- М200-М250 - for frame and panel buildings.
- М250-М300 - for buildings made of wooden beams.
- М300 - for low-rise buildings made of expanded clay, gas silicate or cellular blocks.
- М350-М300 - when building from bricks or pouring load-bearing walls from monolithic concrete.
These gradations are relevant for the construction of one- or two-story houses; when adding another floor, it is advisable to choose a higher brand. The same applies to ready-made commercial solutions, especially if purchased from an unverified manufacturer. In general, the minimum permissible strength when concreting the foundations of residential buildings on slightly loose soils is M200; when building on less stable soils, it increases.
Cement proportions for the foundation
Almost all low-rise and most multi-storey buildings in Russia stand on strip or block foundations made of heavy concrete. This is not surprising, given that heavy concrete, due to its plasticity, high bearing capacity and affordable cost, is the preferred material for the construction of foundations for low-rise and multi-storey buildings.

The building structure is the foundation, it is its basis, which takes on the weight: walls, roofs, facade cladding, interior decoration, floor slabs and other structures and elements of a private house, cottage, villa or small country house. Therefore, saving on materials for its construction is unacceptable!
The proportions of cement for the foundation, as well as the proportions of other components of concrete for pouring it, must correspond to the accepted concrete grade. And the accepted concrete grade must correspond to the load on the structure being erected.
Methods for mixing concrete
There are two ways to prepare building concrete with your own hands:
- Mix the solution by hand;
- Use a concrete mixer for mixing.
Manual batching of concrete
- First, pour the required amount of sand into a clean container;
- Strictly observing the proportions, pour cement on top. Mix both fillers well until they are uniform in color;
- Measure out the required amount of water, and add it in small portions to a container with sand and cement, while distributing and stirring the mixture over the entire area. As a result, you should get a gray mass without lumps and visible residues of sand and cement;
- The final stage is adding crushed stone to the resulting solution. Kneading should take place until each pebble is covered with a solution. Add water if necessary to give the concrete the required plasticity.

Of the disadvantages of the manual method, the following can be distinguished:
- Quite a laborious and lengthy process;
- Immediate use of the solution after mixing. Otherwise, the solution may begin to delaminate, which will lead to a deterioration in its quality.
Kneading with a concrete mixer
- Pour a small amount of water into the drum of the concrete mixer, then add cement there and mix well until a gray milk is obtained. From this point on, the drum should rotate continuously;
- Further, according to the calculation of the proportions, proceed to filling the fillers (sand and gravel). Stir for another 2-3 minutes;
- Add a couple more liters of water to the resulting mixture, until a homogeneous consistency is obtained.

Mixing concrete in a concrete mixer
The main advantage of this method of mixing is the possibility of using concrete within an hour after mixing the solution.
Types of concrete foundations
The most basic types of concrete foundations are columnar and tape, but there are other subtypes and varieties of them:
-
Tape. It is installed in the form of a continuous tape, which consists of reinforced concrete, placed under all the load-bearing walls of the structure. The depth of the base of the building is formed depending on the level of soil freezing plus an additional 20 cm.Two subtypes can be used from the indicators of the quality of soils and the climatic zone:
- intermittent;
- continuous.
The material for this type of base is used:
- Booth, which has excellent durability. The material is not affected by low temperatures and flowing groundwater. A buta stone of the same fraction is used. The construction process requires a lot of labor and money, therefore it is used very rarely. The depth of the bookmark does not exceed 70 cm, and its durability is about 150 years.
- Rubble concrete, which includes a combination of cement mortar and filler (crushed stone, small quarry stone, brick fragments). In terms of strength, it has qualities no worse than rubble, but it is much easier to build and more affordable. It is used to build structures made of weighty materials or consisting of several floors.
- Concrete. This type of house base is better known as jellied, because the material is mixed in a concrete mixer, after which the formwork is filled with it. The service life of the material is over 50 years, and its cost is much higher due to the large volumes of cement used. Most often, this option is used in construction for the construction of walls from heavy materials, as well as the construction of country cottages and houses.
- Columnar, which is used for the construction of lightweight structures (for example, baths, garden houses, sheds). This version of the base includes a set of support posts located at the corners of the structure and in places experiencing increased stress. The pillars are formed from pipes, concrete, rubble and reinforced concrete. This foundation is used on solid soils.
- Tape and columnar. It is somewhat cheaper than the strip type of foundation and combines only the best qualities from both types of foundation.
The correct selection of the material and type of foundation allows you to make the structure more solid and durable. There is an opportunity to buy material for the foundation in a ready-made version, in the form of mixtures at industrial enterprises. But it is much better to make the concrete solution yourself, which can significantly save money.
Basic proportions
When preparing solutions, the working measure is the mass or volume fraction of the binder; the most common and convenient ratios include 1: 3: 5 (cement, sand, gravel, respectively). The regulated proportions, depending on the required concrete strength, are:
| The final grade of the solution | Mass fraction, kg | ||
| Cement М400 | Sand | Crushed stone or gravel | |
| M100 | 1 | 4,6 | 7 |
| M150 | 3,5 | 5,7 | |
| M200 | 2,8 | 4,8 | |
| M250 | 2,1 | 3,9 | |
| M300 | 1,9 | 3,7 | |
| M350 | 1,2 | 2,7 | |
| M400 | 1,1 | 2,5 |
The strength of concrete is primarily influenced by the ratio of sand to cement, but in addition to strict control over the proportion of dry components, the amount of water introduced is monitored. When using Portland cement, the W / C proportions are:
| Binder grade | Concrete strength grade | ||||
| 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 400 | |
| M300 | 0,65 | 0,55 | 0,50 | 0,40 | |
| M400 | 0,75 | 0,63 | 0,56 | 0,50 | 0,40 |
| M500 | 0,85 | 0,71 | 0,64 | 0,60 | 0,46 |
| M600 | 0,95 | 0,75 | 0,68 | 0,63 | 0,50 |

When building a foundation on dry soils, it is allowed to introduce lime or clay into the cement mortar, these components increase its plasticity. The recommended proportions when using Portland cement M400 are:
| Received solution grade | Share of cement | Proportion of lime | Proportion of sand |
| M100 | 1 | 0,4 | 4,5 |
| M150 | 0,2 | 3 | |
| M200 | 0,1 | 2,5 |
In private construction, it is inconvenient to determine separately the mass of all the ingredients to be poured; a bucket is usually used as a measuring instrument. In this case, all fillers are pre-weighed dry. The W / C ratio largely depends on the moisture content of the sand, experienced developers introduce no more than 80% of the recommended proportion of water when mixing, and then, if necessary (insufficiently plastic consistency), fill it in portions. Fiber, PAD and other plasticizers are added to the concrete at the very end along with the liquid, their share usually does not exceed 75 g per 1 m3.
Component requirements
To prepare a cement mortar for pouring a foundation, the following are used:
- Fresh Portland cement, ideally the date of issue does not exceed 2 months before the start of concreting. The recommended brand is M400 or M500.
- River sand with particle sizes in the range of 1.2-3.5 mm with silt or clay admixtures not exceeding 5%. It is advised to check its purity (fill with water and track the change in color and sediment), sift, rinse and dry if necessary.
- Pure crushed stone or gravel with a size of fractions from 1 to 8 cm, with a flakiness within 20%. When preparing concrete for the foundation, screenings of hard rocks are used; limestone is not suitable due to its low strength.
- Water: tap water, free of impurities and foreign particles.
- Additives: anti-freeze, plasticizing, reinforcing fiber. The introduction of such impurities is carried out with strict adherence to proportions.
The recommended proportions of cement and sand for masonry mortars are 1: 3 or 1: 2. The first ratio is considered universal, the second is chosen when building foundations on unstable soils. In practice, this means that for one bucket of cement with a grade of at least M400 (M500 at increased loads), 2 or 3 sifted quartz sand and no more than 0.8 parts of water are taken. A properly prepared mixture resembles toothpaste in consistency; to increase workability per 1 m3, 75-100 g of plasticizers (liquid soap or other PAD) are introduced.

How to make a foundation grout?
The process begins with the preparation of components and a concrete mixer, the presence of the latter is mandatory when mixing concrete for underground structures. The amount of building materials is calculated in advance according to the volume of the foundation and is purchased with a small margin
It is extremely important to fill it in one day; when preparing the solution on your own, all components are washed and dried in advance. Then they are poured into buckets into a concrete mixer in the following sequence: part of water → sand and cement → dry additives and fiber (if necessary) → coarse filler → remaining liquid in small portions
After filling in a new ingredient, the drum turns on for 2-3 minutes, no more than 15 minutes later, the finished solution is unloaded.
There is a time-tested method for selecting the correct proportions, chosen in the absence of data on the size of crushed stone. In this case, the bucket is filled with coarse filler, shaken several times and completely covered with water. The resulting volume of water corresponds to the required proportion of sand in the solution.After that, sand is poured into the bucket, again filled with water to determine the proportion of cement. But this approach is considered by some to be complicated and outdated, the more correct is the standard method of recalculating the mass fraction to the volume fraction and pouring the components into a concrete mixer.
Solution components
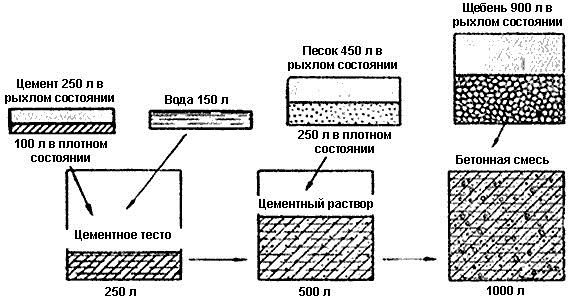
 Cement is a powdered binder that hardens in water and outdoors. Together with large and small aggregates, it ensures the strength and reliability of the structure being erected.
Cement is a powdered binder that hardens in water and outdoors. Together with large and small aggregates, it ensures the strength and reliability of the structure being erected.
Cement is obtained as a result of grinding a mixture of clinker, gypsum and special additives in specified proportions. In turn, clinker is a product from firing limestone with clay and other components, on which the properties and name of cement depend. Depending on the feedstock, the following types of hydraulic binder are distinguished:
- Portland cement:
- slag portland cement;
- pozzolanic;
- lime;
- backfill;
- sulfate resistant and others.
When forming a cement-sand mixture (CPM) in order to obtain concrete of a given strength, it is necessary to take into account the strength grade of Portland cement. The following table shows the strength characteristics of the material for the old and new system:
| Class | Brand | Strength | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | kg / cm 3 | ||
| H 22.5 | M300 | 22,5 | 300 |
| H 32.5 | M400 | 32,5 | 400 |
| H 42.5 | M500 | 42,5 | 500 |
| H 52.5 | M600 | 52,5 | 600 |
In addition, when choosing a material for preparing concrete with the desired characteristics, other properties of cement are also taken into account:
- The fineness of grinding directly affects the strength properties of the concrete mix, especially at the beginning of hardening.
- The density is reflected in the value of the water-cement ratio, and therefore on the water consumption. To reduce it, while obtaining good workability of the mixture, plasticizing additives are used.
- Frost resistance is especially important during construction in winter or in areas with year-round low outdoor temperatures.
- Crack resistance. This indicator is influenced by such a concept as the uniformity of volume expansion during hardening.
Depending on what components the cement is made of, the above qualities vary over a fairly wide range.
The concrete mixture, which, in addition to cement, includes sand, as well as crushed stone or gravel, is formed depending on the purpose of the composition. What proportions of cement, sand and crushed stone should be contained in it is determined in accordance with the recommendations of GOST 27006 - 86 (1989) “Concrete. Rules for the selection of compositions "and GOST 7473 - 94" Concrete mixtures. Technical conditions ".
For concrete mix, sand with a grain size of 1.2-3.5 mm is used.
When choosing this component, pay attention to the purity of the material. In order for the prepared cement-sand mixture to be of high quality, the presence of silt and clay particles in the sand should not exceed 5%
You can check the suitability of the sand for use with water. To do this, you need to pour a small amount of the investigated component into the container, add water and shake the composition. If the liquid is cloudy and contains suspended particles of clay, then the sand is not suitable for preparing concrete.
The composition of the concrete mixture used when pouring the foundation includes crushed stone or gravel of an average fraction. The use of coarse grains will lead to a loss in the strength of the foundation for the construction of the building.
Production of high quality concrete is possible using warm and clean water, without minor impurities (oils, paints).
When preparing a cement-sand mixture, it must be borne in mind that there are no absolutely pure components. In practice, it can be difficult to accurately calculate the proportion of sand, cement for the foundation, especially when pouring the base for individual construction.
Additionally, you need to take into account the factor that over time, the cement for the foundation loses some of its properties.For six months of storage, the material lowers the binding qualities by a third. Accordingly, the grade that characterizes the compressive strength is reduced.
Types of foundations
The basis for the construction of buildings is formed taking into account the load, types of soil, structure. Depending on the type of foundation and its volume, the calculation of the need for materials is performed.
- The strip base is a closed loop made of reinforced concrete, arranged under the load-bearing and internal walls of the building. How to make a tape-type foundation mortar? To calculate the requirements for materials, you must determine the volume of each section and add them. The mixture must be poured continuously, with layer-by-layer compaction and observing the protective layer of the reinforcement.
- The columnar type of base is used for lightweight structures located on dense soils. In practice, a combination of both types of foundation is often used.
- The slab type of foundation is practiced on weak, heaving soils. Made of reinforced concrete. Pouring should be done in one go to prevent delamination of the finished structure. The concrete mixture is distributed evenly with the obligatory compaction with vibrators or bayonet.
- Pile-rammed foundations. The volume of concrete is calculated according to the geometric formula: the cross-sectional area of the well must be multiplied by the depth of the pile and by the number of rods.
After pouring into any type of base, the concrete mixture requires moistening, otherwise the structure may crack due to the rapid drying of the top layer. The first week should be regularly watered and covered with a film or tarp.
DIY foundation concrete
You can use the materials separately or ready-made sand and gravel mixture (proportions in buckets: 1 volume of cement for 5 volumes of the mixture).
Components for 1m 3 of concrete must be mixed in the ratio:
- cement - 300-350 kg;
- crushed stone - 1200 kg;
- sand - 600-700 kg;
- water - 150-180 liters.
Calculation of the amount of cement and sand, crushed stone and water should take into account the properties of materials, their qualitative composition, the value of strength, the presence of impurities (clay particles may be in the sand).
To correctly make a cement mortar for pouring the base, dry components are poured into a concrete mixer, mixed for 2-3 minutes. Then, without stopping to interfere, water is poured in portions. It is better to dissolve the necessary additives in water first. The mixing process should not be long, 5 minutes is enough.
Methods for calculating materials
The concrete recipe for the foundation includes the following components: cement, sand, gravel or crushed stone as aggregates, water. Each component is responsible for quality. In order for the final result to meet regulatory requirements, you need to correctly perform the calculation and determine the required number of components, observing the proportions.
Calculation of components and preparation of concrete for the foundation in buckets is relevant for small volumes of construction work, where 1-4 m 3 of mortar is required. The basis for this calculation is usually the volumetric value of the cement.
What should be the ratio of sand and cement for pouring the foundation
Each component of the concrete mix differs in volumetric weight, therefore, in practice, the following proportions are used: 5 buckets of sand are taken for 2 buckets of cement and 9 are crushed stone or gravel.
The preliminary calculation of ingredients can be done using the online calculator in liters or kilograms. The calculation of emergency situations is carried out taking into account the requirements for concrete and the characteristics of the main materials.
For example, to obtain 1 m³ of concrete grade M200 in the presence of a concrete mixer for 180 liters, cement M400, sand and crushed stone, you will need:
- water - 215 l;
- cement - 233 l;
- rubble - 818 l;
- sand - 389 liters.
Under the given conditions, the calculator will calculate the need for materials for 1 batch and the number of downloads.
When it is necessary to adjust the consumption of raw materials, taking into account the operating conditions of the structure being erected, the type of mixture, the use of a plasticizer, the value of the coefficient of expansion of concrete particles, it is necessary to use the correction table.
General information
The composition of the solution that is used to fill the foundation includes the following components:
- cement;
- sand;
- gravel or other types of crushed stone as filler;
- water;
- various additives such as plasticizers and the like.
The proportions of cement, sand and other constituents of concrete mortar for pouring a foundation depend on the type of material you are using and its properties. Therefore, further we will briefly analyze how to choose high-quality cement and what sand and gravel should be.
Choosing high-quality cement
High-quality cement is the key to the durability and strength of the foundation, so it is worth paying attention to this issue.
It is important to have at least a general idea of the markings on the bags. That is, you need to distinguish and understand what the M300 and M400 are
That is, you need to distinguish and understand what the M300 and M400 are.
So what are the markings?
M - indicates the maximum strength characteristics of the cement.
If M300, then this means that the material is able to withstand pressure and a load of 300 kg per 1 cm.
M600 is called "military" cement because it is used to build various bunkers and other fortifications, but you obviously won't need such cement.
Traditionally, the M300 is used for most construction work.
Depending on this indicator, the ratio of sand and cement, which must be added to the solution, also changes.
In addition, there are such designations CEM I and CEM II. In the first case, there are no additives in the composition of the cement, and in the second, there are and should be indicated which ones and in what quantity.
Advice! For pouring the foundation, it is recommended to choose a material without various impurities and additives.
Types of rubble
Various types of crushed stone are used as filler. They help create a strong and frost-resistant foundation.
There are such types of rubble:
- granite - a stone made of solid rock, is widely used in construction work, there are various fractions;
- limestone - obtained by crushing limestone, mainly used during road works;
- gravel - as a result of crushing a mountain rock or sifting a quarry rock, such crushed stone is obtained, inferior in strength to granite crushed stone;
- slag - waste during foundry processes, has a low price, and therefore enjoys some popularity;
- secondary - construction waste processed into crushed stone, the cheapest and most angry material.
This is general information for thought, let's say. But for pouring the foundation, either granite or gravel crushed stone is best suited. Crushed gravel has a lower strength, but at the same time it is cheaper compared to granite.
Therefore, for pouring the foundation for large buildings, it is better to use more durable granite crushed stone.
Crushed stone fractions
This is another point worth paying attention to.
There are various factions, but the most commonly used are 20x40 or 10x20. The more massive the building, the larger the rubble is recommended to use. That is, the 10x20 fraction is suitable for medium-sized buildings, but 20x40 is required for large buildings.
pay attention to its moisture content, since this factor affects how much water is then needed to dilute the finished solution. The sand should not be so wet that you can make a snowball out of it, let's say.
the sand must be clean, that is, it must not contain various impurities such as gravel, grass, earth, etc.
All these impurities must be removed, so that such poor-quality sand will need to be sieved.
Many experienced builders prefer quarry sand, since many particles in it have sharp edges, which allow them to achieve better adhesion and a stronger mortar in the end.
Giving concrete special properties
If additional requirements and special properties are imposed on the structure to be erected, for example, water resistance or frost resistance, then additives and special concrete of exposure class XD, XF, XM or XA should be used.
To give the concrete solution special properties, various additives are added to it, which can increase and improve certain qualities of the material.
Concrete with high frost resistance requires the addition of an appropriate additive, which increases the level of frost resistance of the concrete base.
The addition of this type of additive ensures that the foundation can withstand a large number of freeze-thaw cycles.
If, in addition to frost, the structure is exposed to salts, additives with high frost resistance and resistance to thawing salts acting on the base are used.
Also, additives are used that can increase the plasticity of the solution. Typically, they are used in formwork mortars with frequently repetitive metal mesh reinforcement. This additive contributes to a better distribution of the mixture along the entire perimeter of the formwork.
They also use additives that increase the degree of stability of the foundation of the structure to erosion by groundwater (waterproof concrete). It is almost impossible to do without them in places where the soil is too saturated with moisture. A solution of a denser consistency is used for buildings with a thickness of 10 to 40 cm so that the depth of water penetration does not exceed 0.6, and for structures with a greater thickness - 0.7.
