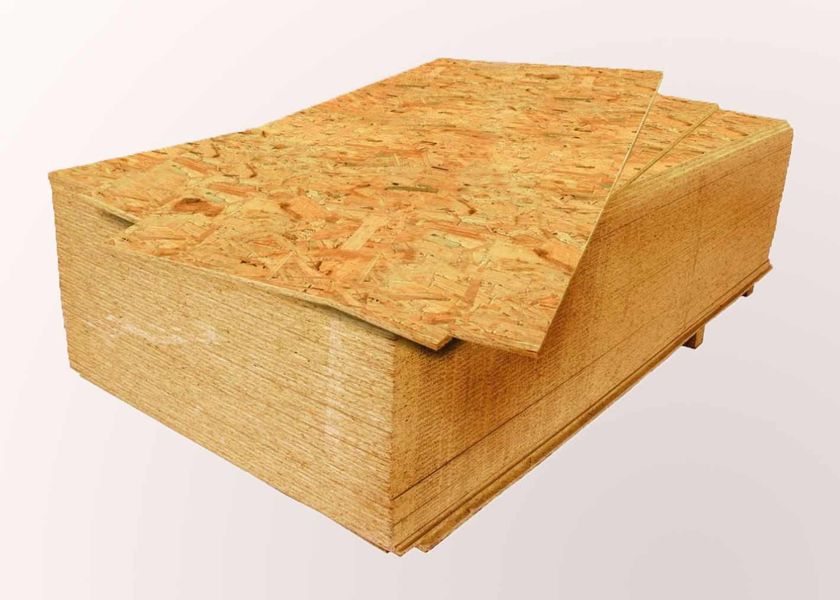
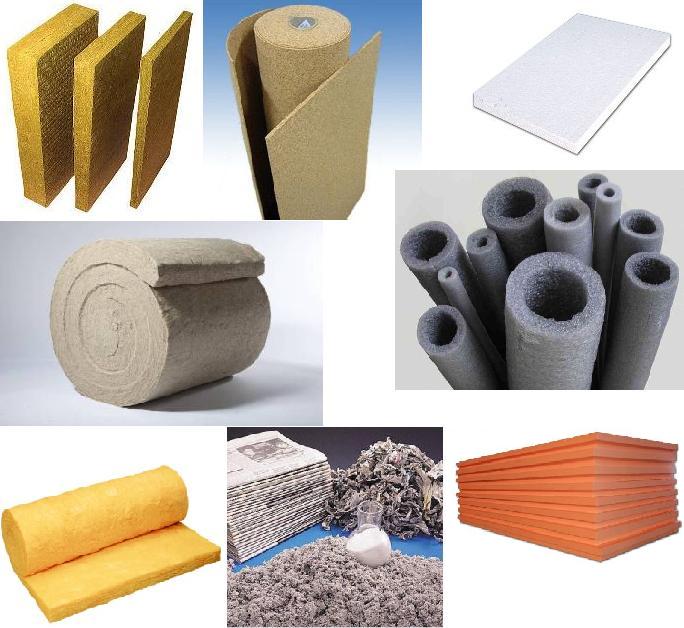
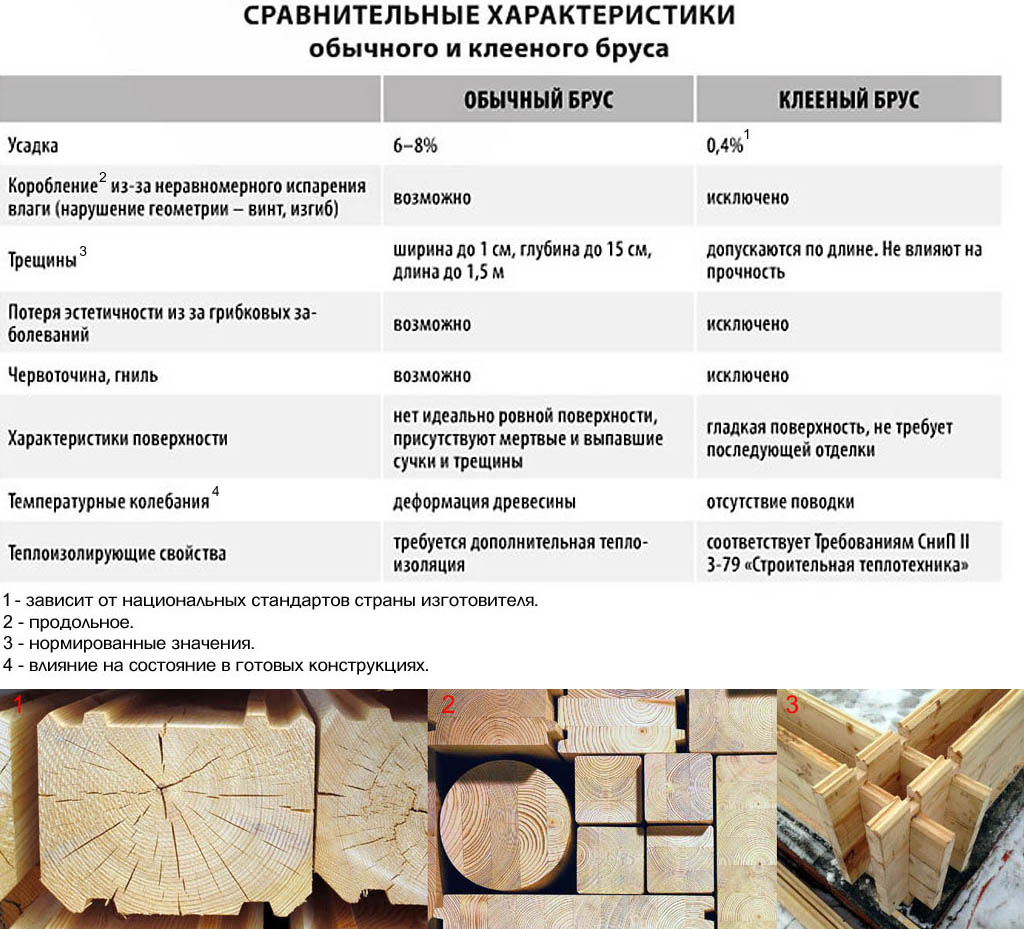
Formaldehyde content in OSB boards and limit norms
According to the European standard EN 717-1, developed by the European Committee for Standardization, oriented strand boards are divided into two classes according to the formaldehyde emission level measured in a climate chamber:
- E1 - up to 0.125 mg / m³;
- E2 - from 0.125 to 1.25 mg / m³.
The former class E3, characterized by a formaldehyde emission level of 1.25 to 2.87 mg / m³, is not used today, and the production of boards corresponding to the E3 class is prohibited in Europe. Currently, the issue of introducing a new class of materials - E1-plus - with a limit value of formaldehyde emission of 0.080 mg / m³ is being actively discussed, which means that it is possible that OSB boards with a new marking will soon appear.
The emission of formaldehyde is directly related to the content of this substance in the material. In accordance with the European standards EN 120 and EN ISO 12460-5, the formaldehyde content (in mg per 100 g of absolutely dry OSB board) for the above classes is:
- E1 - up to 8 mg;
- E2 - 8 to 30 mg
On sale you can find OSB-plates marked E0. This class, characterized by a formaldehyde content of less than 5 mg per 100 grams of dry plate, is not standardized, but sometimes this designation is still used for advertising purposes.
Russian GOST R 56309-2014 assumes the division of all OSB boards into three classes depending on the level of formaldehyde emission:
- E0.5 - up to 0.08 mg / m³;
- E1 - from 0.08 to 0.124 mg / m³;
- E2 - from 0.124 to 1.25 mg / m³.
The formaldehyde content in OSB boards corresponding to these classes is:
- E0.5 - up to 4 mg per 100 grams of dry plate;
- E1 - up to 8 mg;
- E2 - 8 to 30 mg
As you can see, the requirements of modern Russian standards are no different from European ones.
The above figures apply only to OSB, but not to other board materials (plywood, chipboard, MDF, HDF). The production technology of the listed wood-based panels is different, therefore their characteristics (and, consequently, their areas of application) also differ. For example, if for OSB the formaldehyde content of 8 mg per 100 g of dry material is considered the norm, then in the case of chipboard, reducing this figure below 10-14 mg is an impossible task. In general, OSB holds the record among other wood-based panels in terms of their environmental friendliness.
This is due to the fact that OSB does not contain fine shavings and wood dust, and this allows you to reduce the amount of glue used (accordingly, the formaldehyde content in the finished board also decreases). Thus, the question of the health hazard of OSB boards in the context of comparing them with other wood-based materials looks somewhat far-fetched.
Chips for making OSB.
Chipboard shavings.
However, back to the numbers. Now we know everything about the emission of formaldehyde by OSB-plates, manufactured in accordance with the requirements of standards, and about the maximum permissible concentration of formaldehyde in the air of residential premises, it remains to compare these values with each other. Comparing the numbers, you will find that the formaldehyde emission of even the most environmentally friendly OSB board that meets the stringent E1 class requirements is significantly higher than the established sanitary and hygienic standards.
Of course, it is somewhat reassuring to think that uncoated OSB boards should not be used for interior decoration of residential premises, since they are simply not intended for this. Coverings of various kinds insulate the panels, preventing the release of substances harmful to health into the internal environment of the house. In addition, it should be expected that as the age of the house, the level of formaldehyde emissions will gradually decrease (although measurements on real objects have shown that this, as a rule, takes several months).
Over the past two decades, manufacturers have managed to significantly reduce the level of formaldehyde emissions from OSB boards, experts predict a further improvement in the environmental performance of the material. This is achieved primarily by replacing chemically unstable urea-formaldehyde resins with more inert phenol-formaldehyde resins and by introducing fillers into the resin composition that increase their chemical resistance.
Some manufacturers abandoned the use of formaldehyde-containing resins and switched to the production of OSB based on another binder - polymeric methylene diphenyl diisocyanate. However, the transition to formaldehyde-free adhesives is rather a marketing ploy designed to replace formaldehyde, which has discredited itself in the eyes of the general public, with another substance that is no less hazardous to health, but at the same time less known to the ordinary consumer, and therefore does not cause much panic.
Features of various substances
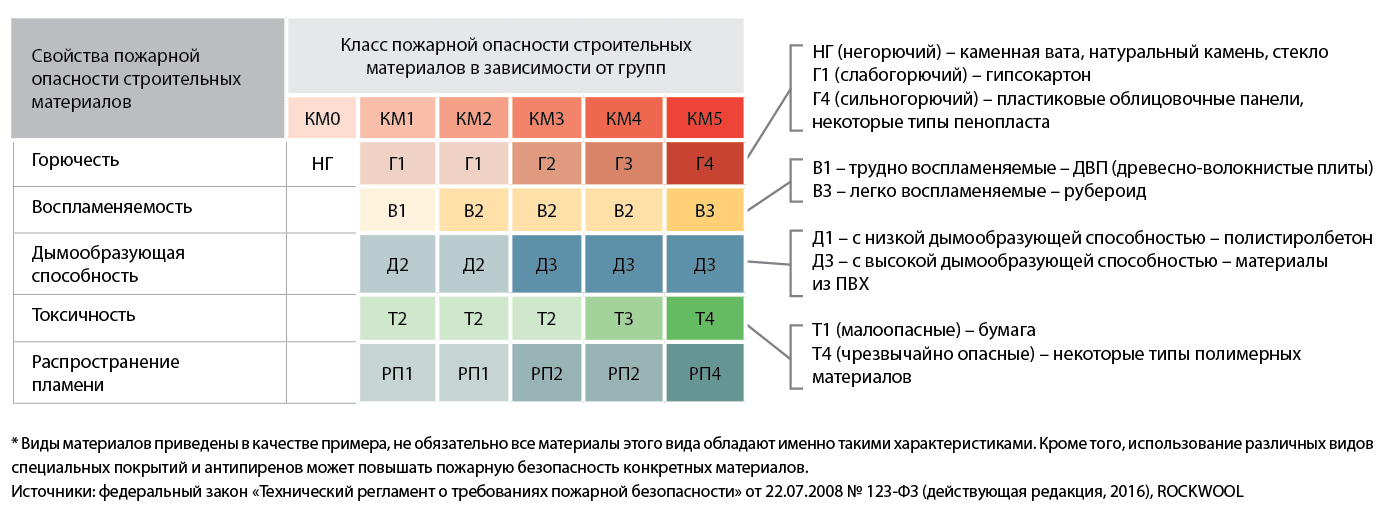
It is known that substances can be in various states of aggregation, which are important to take into account when determining the flammability group. GOST provides a classification based on quantitative indicators
If the substance can burn, before for fire safety, the most optimal flammability group is G1 than G3 or G4.
Flammability is of great importance for finishing, heat-insulating, building materials. On its basis, the class of fire hazard is determined. So, gypsum plasterboard sheets have a flammability group G1, stone wool - NG (not burning), and insulating expanded polystyrene belongs to the flammability group G4, and the use of plaster helps to reduce its fire hazard.

Gaseous substances
Determining the flammability class of gases and liquids, the standards introduce such a concept as the concentration limit. By definition, this is the limiting concentration of a gas in a mixture with an oxidizing agent (air, for example) at which a flame can spread from the point of ignition to any distance.
If such a boundary value does not exist, and the gas cannot spontaneously ignite, then it is called non-combustible.

Liquid
Liquids are called flammable if there is a temperature at which they can ignite. If the liquid ceases to burn in the absence of an external source of heating, then it is called hardly combustible. Non-flammable liquids do not ignite at all in an air atmosphere under normal conditions.

Some liquids (acetone, ether) can flash at 28 ℃ and below. They are classified as especially dangerous. Flammable liquids at 61 ... 66 ℃ and above are classified as flammable (kerosene, white spirit). The tests are carried out in an open and closed crucible.
Solid
In the field of construction, the most relevant is the definition of the flammability group of solid materials. It is preferable to use substances of the flammability group G1 or NG, as the most resistant to ignition.

Selection Tips
A high quality product can only be identified with close inspection. The look of plywood can tell a lot about the performance of a product. Be sure to look at the edge of the sheet, check if the layers are carefully glued. See what color the slice is. For example, the alternation of colored stripes indicates a combination of deciduous and coniferous varieties. The light one indicates the use of deciduous veneer, and the dark one - for coniferous wood.
Many unscrupulous manufacturers sometimes try to deceive consumers - they glue only the outer surface of the panel with high-quality veneer. In this case, the operating parameters practically do not change, only the appearance of the plywood is improved. Such material can only be used for finishing cladding. But for the assembly of furniture and other serious tasks, it is unsuitable.


Common wood defects include:
- pinned or falling out knots;
- cracks;
- sharp shading transitions;
- scratches;
- dents;
- bulges;
- delamination of fibers;
- Wood "patches";
- the presence of rot;
- glue on the edge.
A large number of defects indicate that the manufacturer saved on raw materials, violated the standards for storage and transportation of products, or neglected the standards of the technological process. Such plywood will be short-lived.


Class confirmation
 Samples of materials are tested in laboratories and in open areas according to standard methods separately for non-combustible and combustible building materials.
Samples of materials are tested in laboratories and in open areas according to standard methods separately for non-combustible and combustible building materials.
If the product consists of several layers, the standard provides for checking the flammability of each layer.
Determinations of flammability are carried out on special equipment. If it turns out that one of the components has high flammability, then this status will be assigned to the product as a whole.
The setup for carrying out experimental determinations should be located in a room with room temperature, normal humidity, and no drafts. Bright sunlight or artificial light in the laboratory should not interfere with the reading of the displays.
 Before starting the study of the sample, the device is checked, calibrated, and heated. Then the sample is fixed in the holder of the inner cavity of the oven and the recorders are immediately turned on.
Before starting the study of the sample, the device is checked, calibrated, and heated. Then the sample is fixed in the holder of the inner cavity of the oven and the recorders are immediately turned on.
The main thing is that no more than 5 seconds have passed since the sample was placed. The determination is continued until the temperature balance is reached, at which within 10 minutes the changes do not exceed 2 ° C.
At the end of the procedure, the sample together with the holder is taken out of the oven, cooled in a desiccator, weighed and measured, reckoning them to the flammability group NG, G1, and so on.
Environmental friendliness of plywood products
The plywood production process consists of steaming wood and then peeling it to obtain veneer. (see also Equipment for the production of plywood) The veneer layers obtained in this way are straightened, dried and glued together to form plywood sheets. Since natural wood serves as the material for its manufacture, plywood is initially an absolutely environmentally friendly product.
The degree of environmental friendliness of the finished product is influenced by various impregnations and adhesives, through which individual layers of veneer are formed into a single sheet.
Gluing is a mandatory process, since it is thanks to this technology that the price of pressed plywood is an order of magnitude lower than solid wood, and due to impregnation, it acquires qualities unusual for natural materials - strength, indifference to moisture and wear resistance.  Types of plywood products
Types of plywood products
It follows from this that the main difference between the modifications of plywood sheets depends on what kind of third-party additives were used to make it - the more natural the ingredients are, the more environmentally friendly the final product will be.
Types of eco-friendly wallpaper
As mentioned above, safe wallpapers should be made from natural or non-toxic man-made materials. Depending on the raw materials used in the production, they are divided into several types.
Vegetable
At the moment, wallpaper made of bamboo, reed and other plants is one of the most popular options. Their soft texture makes the room warm and cozy.
The most common are bamboo. In fact, it is a tube-shaped grass that grows very quickly, so cutting it down does not harm flora and fauna. In addition, the material is free of resin and other components. Not only wallpaper is made from bamboo, but also furniture, floor coverings and so on, so with its help you can arrange a completely safe room.
 Combination of two types of bamboo wallpaper
Combination of two types of bamboo wallpaper
Woody
Despite the similarity with the previous type, environmentally friendly wood wallpapers belong to a separate group. In most cases, they are a thin layer of flexible wood that can be rolled up.
There are many options for raw materials for this wallpaper, but each one is natural and environmentally friendly.In addition, such wood is quickly replenished in nature.
Wood always looks rich and noble, so the materials also carry a visual load. As a decoration on the front surface, there can be carving or inlay; in some cases, the wallpaper is painted with natural substances.
 Wood veneer wallpaper
Wood veneer wallpaper
Paper
These wallpapers can be made from parchment, plain or rice paper. The modern market offers a huge range of models, both hand-made and conveyor-made. When choosing, it is necessary to especially carefully study the composition, some unscrupulous manufacturers use unnatural dyes, vinyl, formaldehyde and other harmful substances to reduce costs.
The paper itself must be certified by the Forest Stewardship Council. If it was decided to order foreign-made products, then they must be marked with the FSC inscription with the image of a tree with a checkmark. These documents confirm that the wallpaper was made from raw materials grown in responsibly managed forests, and therefore does not contain harmful substances.
 Comparison of paper wallpaper simplex and duplex
Comparison of paper wallpaper simplex and duplex
Made from recycled materials
These wallpapers are made from recycled paper. These products cannot be called natural, their production is associated with many technological processes, but the result is an environmentally friendly material. In addition, the production of such products reduces the amount of waste and the level of wood extraction.
Textile
Fabric wallpaper can be made entirely of cotton, linen, silk and other fibers, or made using polyester, viscose and other synthetics. In the first case, we are talking about an expensive and completely natural basis. Textile wallpaper made of artificial materials is characterized by lower cost, improved performance, and so on. Both types are absolutely safe for health.
Non-woven
Non-woven fabric is a non-toxic blend of natural and synthetic fibers. Wallpaper breathes well and can be wet cleaned. Ideal for bathrooms, saunas, kitchens and other similar environments.

Fiberglass
Such products contain practically no organic materials. They are made from the same raw materials as ordinary glass, therefore they are chemically inert, due to which they are resistant to detergents and abrasion.
 Glass fiber
Glass fiber
Cork and other coatings
Cork products are paper-based and have anti-static properties. They are harmless and lightweight, so quite often used in the design interior.
Also, you can often find products made from natural or artificial leather. It's a relatively expensive material, but it looks good too.
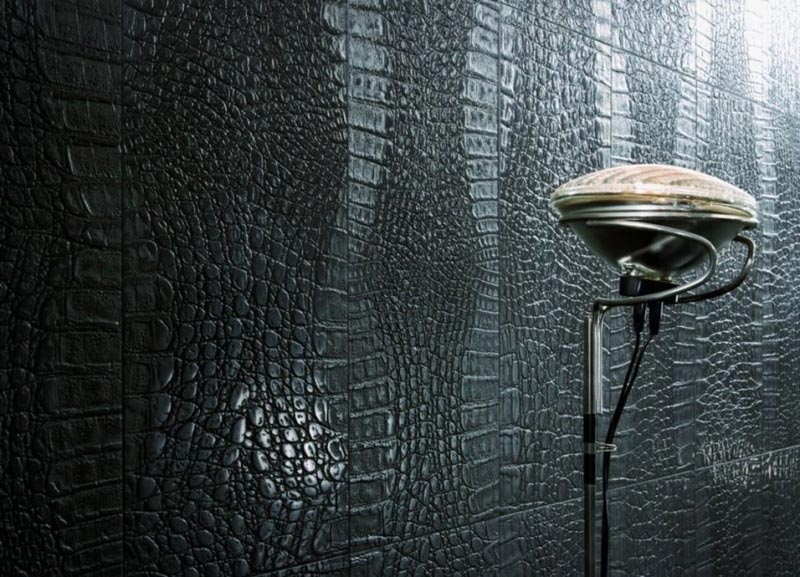 Leather in wall decoration
Leather in wall decoration
There is an opinion that eco-wallpaper should be made only from natural raw materials. This is partially true, but there are also synthetics that are absolutely safe for health and do not cause allergies.
Flammability indicators of some building materials
Here are the parameters of fire resistance of popular construction products:
- all types of gypsum plasterboards, due to the large volume of gypsum, are characterized by high fire resistance, they withstand exposure to an open flame from 20 to 55 minutes, the parameters are determined - G1, T1, D1 and B2, which together allows the use of drywall at objects of any purpose;
- wood is characterized by a high fire hazard, its indicators are G4, RP4, D2, B3 and T3, and the wood burns in both a smoldering mode and an open flame, if this material is used at the facility, even for the manufacture of doors, it must be treated with special compounds ;
- Chipboard belongs to the G4 flammability class, although, unlike wood, it ignites and supports the fire worse - B2, but the combustion products are highly toxic T4, the other parameters are RP4, D2, when used in construction and repair, fire protection treatment is recommended;
- stretch ceilings made of PVC are highly flammable materials, but, undergoing fire-retardant treatment, acquire class G2, the fire hazard of a particular product can be found in the accompanying documentation;
- insulation of the facade with polyurethane foam, expanded polystyrene, polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam is regulated by SNiP21.01.97, here flammability from G1 to G4, flammability from B1 to B3, depending on the design features, for example, the need to ventilate, and the technology implemented;
- mineral roofing materials, such as natural tiles, are non-combustible, onduvill is an organic material that is highly flammable and burns vividly, therefore, its use is limited by the requirements for the general safety of the facility;
- metal sandwich panels with mineral wool insulation - the best option for the construction of facilities with high fire safety requirements, since they are marked with NG, the use of polycarbonate sheets reduces the indicators to G2 and their use is limited;
- all types of linoleum are medium combustible materials, the exception is heterogeneous and homogeneous, they belong to KM2, their other indicators are RP1, B2, T3 and D2, the latter modifications are allowed to be used in medical and educational institutions;
- for objects with high fire safety requirements, special types of laminate have been developed, for example, Parqcolor has the following indicators: G1, RP1, B1, T2 and D2.
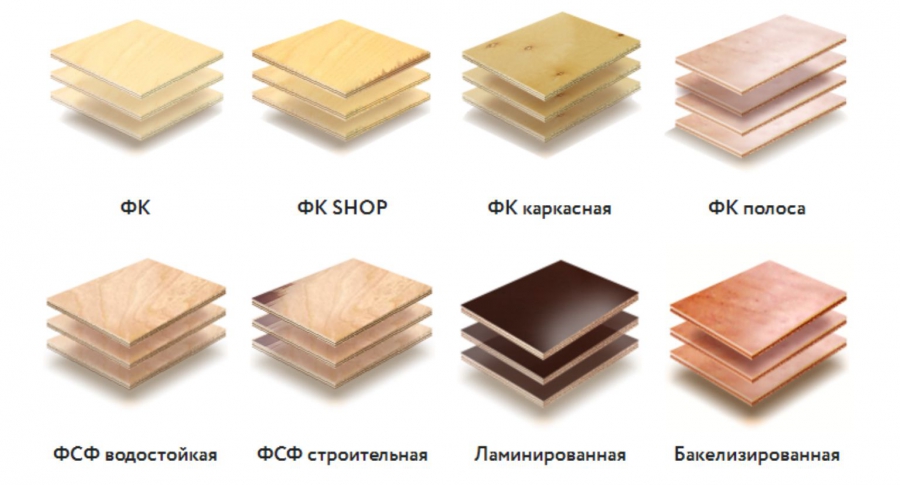
Varieties and brands
There are several common grades of plywood.
- FSF is a material glued with an adhesive based on phenol-formaldehyde resin. It is durable and water resistant. Usually used in the construction industry.
- FC - here the veneered layers are glued with a carbamide compound. Such a material has a slightly lower hygrostability, but to a greater extent meets the requirements of environmental friendliness. It is relevant for interior cladding of structures and furniture production.
- FB - plywood glued with bakelite resins. They increase bending strength by 2-5 times, increase moisture resistance by 60-70%, and give exceptional surface density.
- FBS is the most durable plywood made using alcohol-soluble bakelite resins. The material can withstand prolonged contact even with salt water, therefore, elements of the hull of floating craft are made from it.
- FBV - for gluing veneer sheets, water-soluble resins are used here, so it is 15% less moisture resistant than FBS.
- FBA is the only brand of 100% natural plywood without phenol. In it, veneer slabs are glued together with casein or albumin glue. Such material is absolutely safe for human life and health. Has a low moisture resistance.
The grade classification of the material depends on the quality of the surface. Wood is a material with a heterogeneous structure, cracks or rot are found on it - during peeling, all these flaws pass to the veneer. The GOST contains a list of all possible shortcomings. All varieties have their own possible flaws and their volume. Some deviations are allowed.
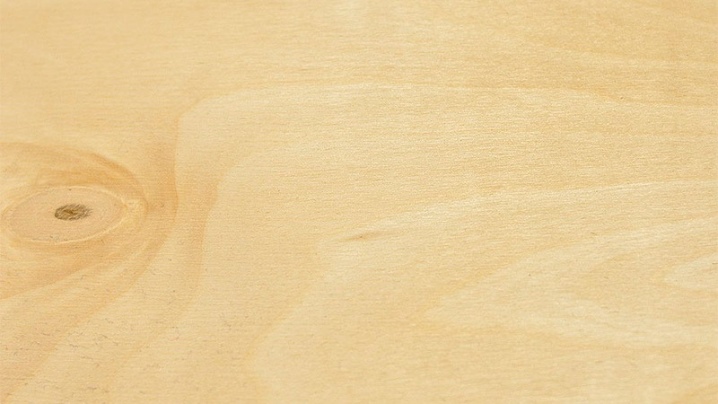
Elite grade E:
- there should be no noticeable defects on the surface;
- on coniferous materials, the presence of single knots is allowed;
- for hardwood there may be minor structural changes in veneer.
Grade 1:
- knots / knot holes;
- single closed cracks of small size;
- pale sprout;
- natural change in shade;
- slight veneer gaps in the inner layers;
- end defects.

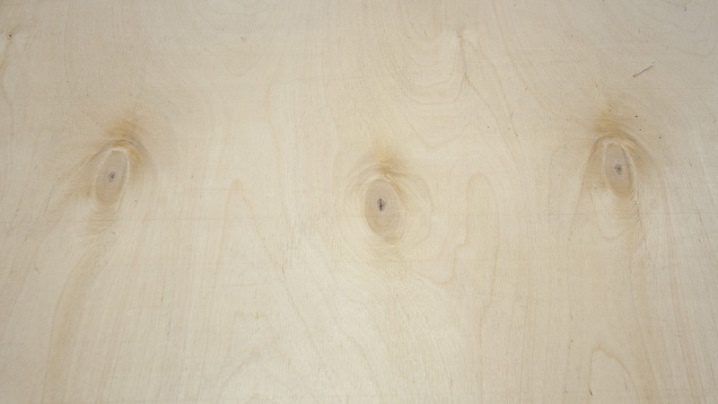
Grade 2:
- knots / wormholes;
- single cracks;
- germinate;
- resin pockets;
- overlapping veneer of the outer layer;
- dents;
- scratches;
- oozing glue.

Grade 3: This grade has the same defects as Grade 2, but in slightly larger quantities.
Grade 4: For this plywood, most of the restrictions have been removed. This is a technical material, low requirements are imposed on it to maintain mechanical characteristics. These types of plywood are mainly used for creativity - modeling and burning.


Application
When using plywood sheets, it is necessary to keep in mind some of the subtleties of its application. Placing flat parts in mutually perpendicular planes, you can achieve the highest strength of the product. The main thing is to correctly redistribute the load on the surface and ensure the fixing of the mount. It is with great difficulty that the nails enter the plywood; they do not hold at the end at all. They are used only as dowels - they are driven into pre-drilled holes. This solution is used under shear loads, since they have little resistance to pulling out.
Screws and self-tapping screws resist pulling out well. However, pre-drilling is usually required to install them. Keep in mind that veneer tears and surface chips often occur during this operation.


Plywood is one of the varieties of furniture and construction material made from wood waste. You should not expect that by purchasing plywood, you will receive a versatile raw material that allows you to create a strong and beautiful structure that is not inferior in density to the Lebanese cedar. But if you use plywood in strict accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations, then this material will serve you for several decades.
In the next video, you will find additional information about the grades of plywood according to GOST.
What is the danger of formaldehyde and what are the standards for its concentration in the air
What is formaldehyde, and is it really that bad for human health, or is it just another horror story of competing marketers?
Formaldehyde (aka formic aldehyde) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor, relatively stable at 80-100 ° C and slowly polymerizing at temperatures below 80 ° C. It has found wide application in various areas of the national economy: in the chemical industry - for the production of plastics and artificial fibers, in the construction industry - for the production of varnishes, paints, polyurethane foam, linoleum, various chipboards (chipboard, OSB, MDF, plywood) and as an antiseptic for wood processing, in the tanning industry - as a tanning agent, in agriculture - as a fumigator during grain storage, etc.
With short-term exposure to high concentrations of formaldehyde vapors (1.2 mg per cubic meter of air), irritation of the upper respiratory tract, skin, mucous membranes of the eyes is observed, the first signs of damage to the central nervous system appear (headaches, dizziness, weakness). Daily exposure to small concentrations of formaldehyde on the human body for a long time is the cause of chronic rhinitis, chronic bronchitis, obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma. In addition, formaldehyde is a carcinogen: with prolonged contact with its vapors, the risk of developing cancerous tumors of the nasopharynx significantly increases.
In accordance with the sanitary and hygienic standards SanPiN 2.1.2.1002–00 and GN 2.1.6.1338–03, approved by Russian legislation, the maximum permissible concentrations of formaldehyde in indoor air are:
- maximum one-time (MPCmr) - 0.05 mg / m³ (exposure 30 minutes),
- average daily (MPCss) - 0.01 mg / m³.
The value of one-time MPC (MPCmr) corresponds to the maximum concentration of a substance in the air, at which there are still no reflex reactions of the human body to contact with this substance. The value of the average daily MPC (MPCss) denotes the concentration limits within which a substance does not cause direct or indirect harm to human health under conditions of constant inhalation for an indefinite period of time. At concentrations of formaldehyde vapors below the MPCss you can not be afraid of the appearance of any pathological changes in the body. The substance has no general toxic, carcinogenic or mutagenic effect at such concentrations.
On the question of terms
 The requirements for ensuring fire safety are regulated by Federal legislation, in the text of Article 13 of which there is a classification according to the degree of danger.
The requirements for ensuring fire safety are regulated by Federal legislation, in the text of Article 13 of which there is a classification according to the degree of danger.
Fire hazard includes all characteristics of materials that describe the possibility of a fire or explosion. The guarantee of the safety of the building is the fire resistance of the structures, the requirements for which are specified in the SNIP.
For the bulk of the population - builders, buyers of materials - terminological nuances are not significant. The main thing is that the structures should not be exposed to fire, they should be resistant to it.
In the price lists of trading companies, in everyday life, the term "fire resistance" is widely used in relation to both structures and materials. The term is convenient for ordinary people.
materials for most consumers is the main safety criterion, determines the choice of construction products.
What to make a ceiling

The most environmentally friendly, versatile and economical option is whitewashing. This time-tested method is still valid. Its result is an aesthetic appearance and the absence of harmful fumes. Lime is used for whitewashing., chalk, water-based paint.
Another option is wallpaper. This is an affordable and environmentally friendly way to decorate the ceiling in a residential area with the right choice of materials. Although there are not so many options for wallpaper for the ceiling in stores, you can still choose something to your taste.

Cork and wood panels are an environmentally friendly and reasonably economical option
It is important to check the safety of the compounds with which the wood has been pretreated.

Fabric stretch ceilings are a rather expensive and rare option for eco-repair. They should not be confused with satin, similar to satin only in appearance. The environmental friendliness of fabric ceilings is relative, since the fabric is artificial, painted with not always safe paint and treated with fire-resistant impregnation.