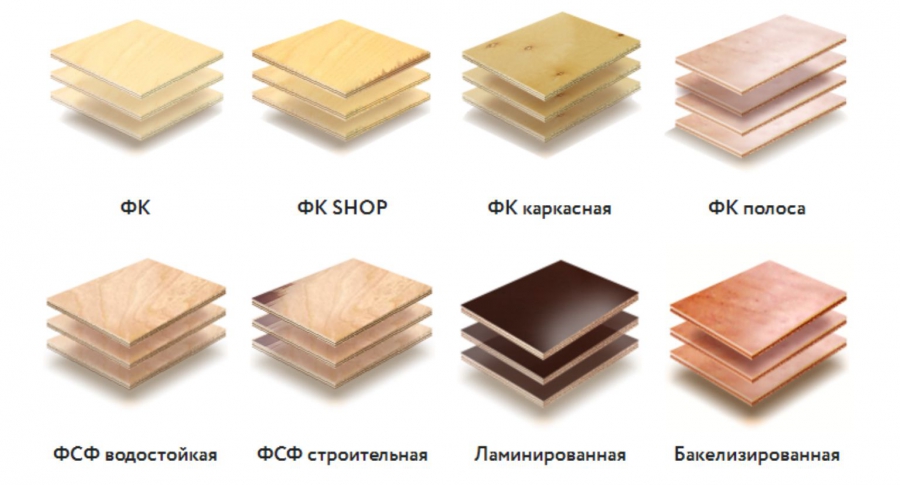
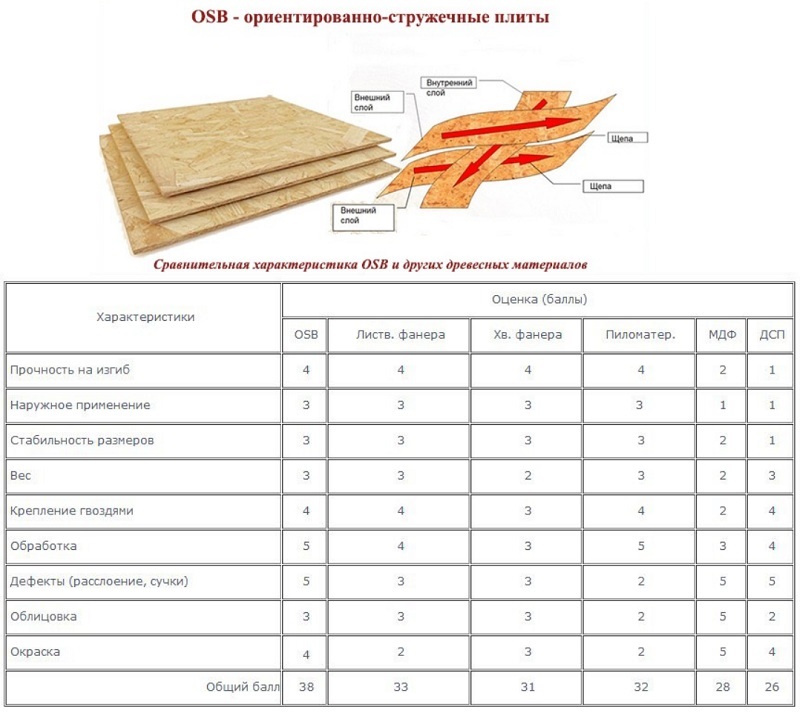
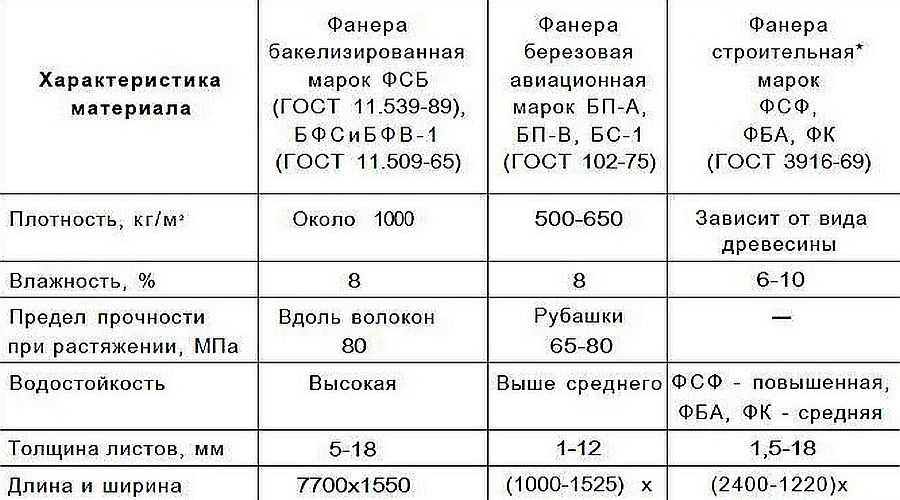
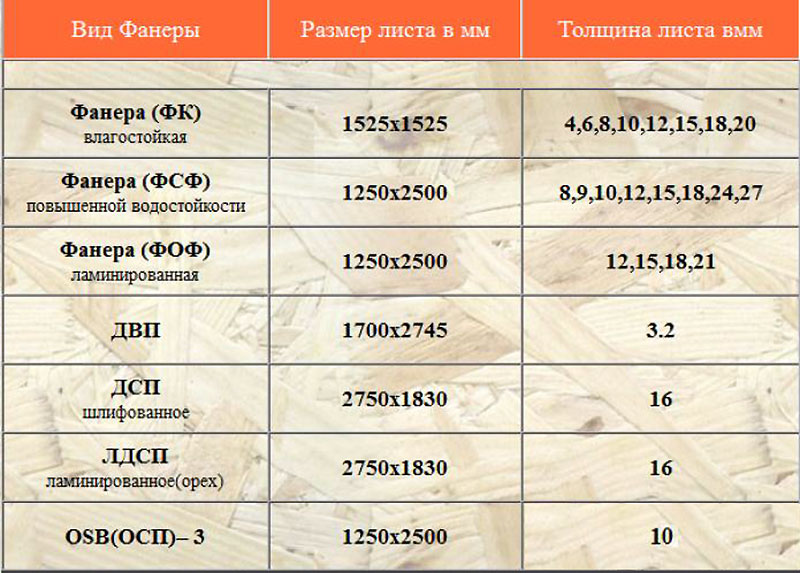
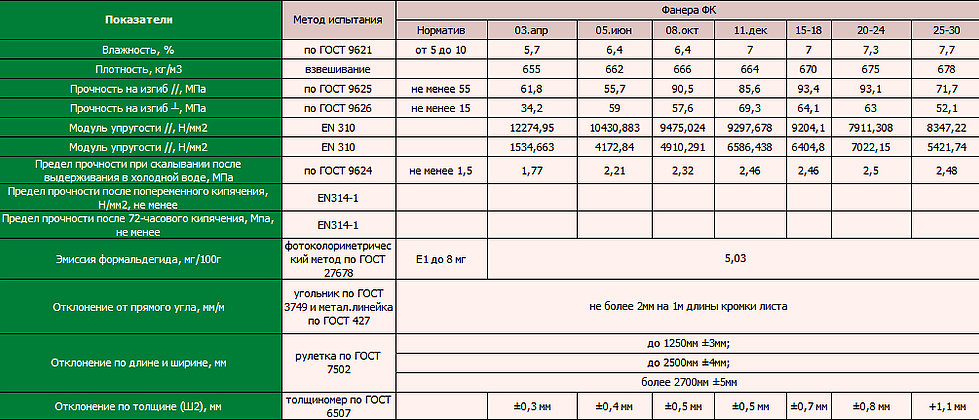
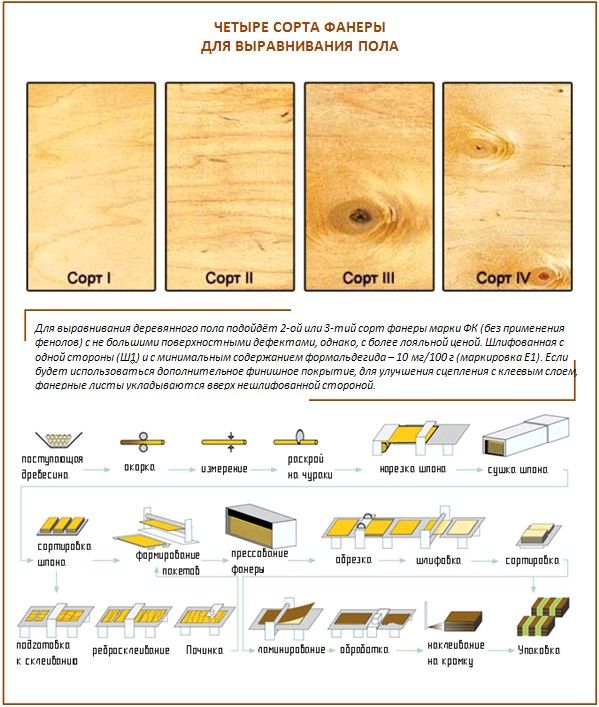
Separations and nuances
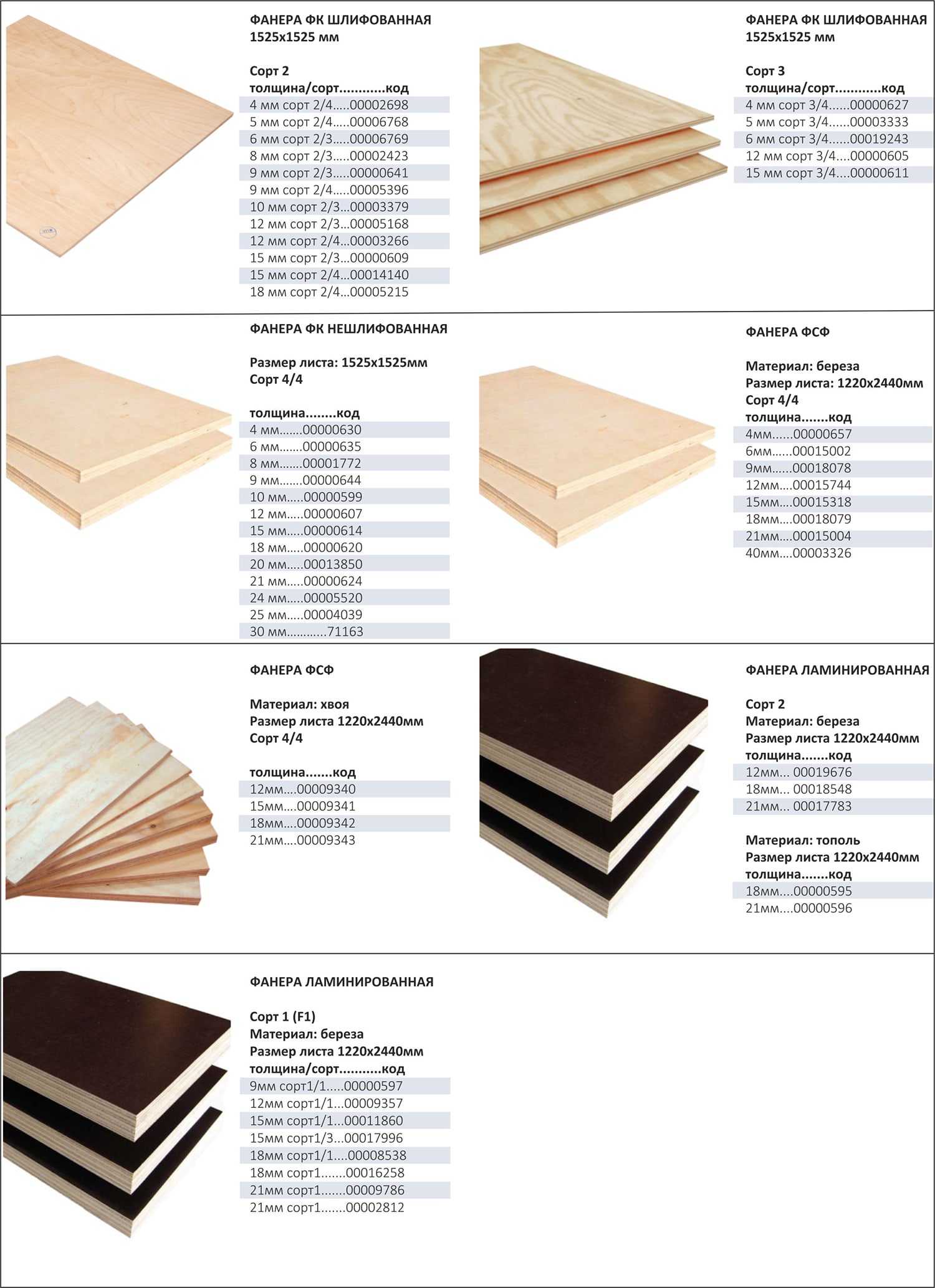
Plywood FC is divided into grades:
Plywood grades table.
- 1 grade. Plywood with this grade marking has an ideal surface to be varnished. At the same time, the defects of the top veneer along the length should not exceed 20 cm, and such defects as chipped edges, lack of veneer on one of the sides of the sheet should not be more than 3 quantitatively. And if any, the dimensions should be minimal.
- 2 varieties. Such FC plywood has several defects and possible production damage. Cracks not exceeding 20 cm in size and the presence of inserts from other wood are allowed. Defects of the outer veneer layer, such as scratches and dents, should be no more than 5% of the total area of the plywood sheet. At the same time, the wood itself, from which veneer for grade 2 plywood is made, may have knots of various colors and holes associated with their loss as a result of processing in production.
- 3 varieties. On such plywood, flaws in the amount of 9 pieces of such a nature as knots (accrete, healthy), wormholes with a diameter of 6 mm are permissible. During production, glue can seep onto the edge or joints of veneer sheets by 5% of the total area of the sheet. The width of the edge defect associated with a shortage of veneer should not exceed 20 cm, as well as the overlap.
- 4 varieties. This plywood is of the lowest production quality. The number of knots, both dropped out and present, is not limited. In addition, the standards do not impose restrictions on wormholes, the diameter of which does not exceed 40 mm. Due to such a low quality of plywood of 4 grades, it is used for the production of containers and for other rough construction work.
Table of properties of FC plywood.
In addition to the division into grades, FC plywood can be divided according to the degree of processing of the outer surface into unpolished, sanded on one side, sanded on both sides. This division is indicated in the marking of the sheet with the designations NSh, Sh1, Sh2, respectively. A description of all the characteristics of plywood must be attached in the documentation that is located with the seller of this product. The buyer has the right to demand it.
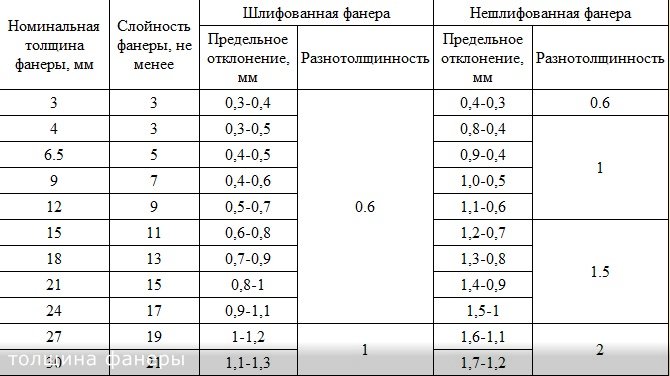
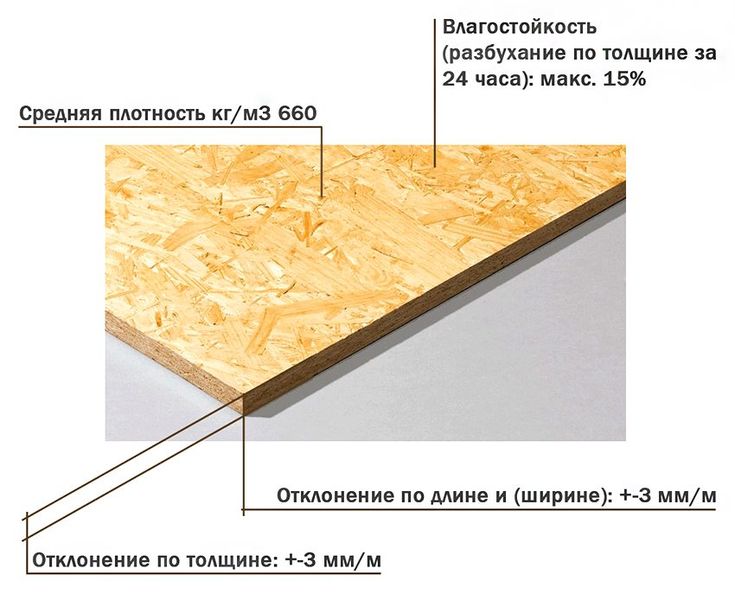
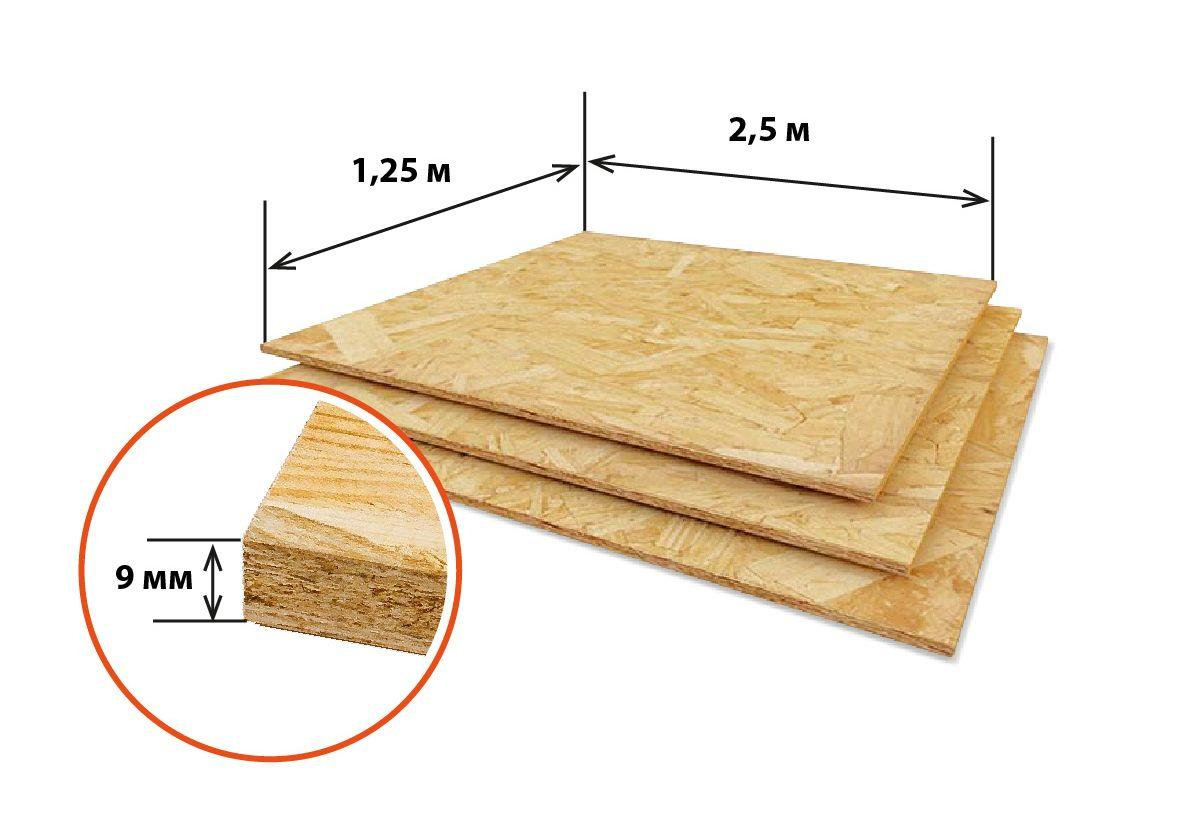
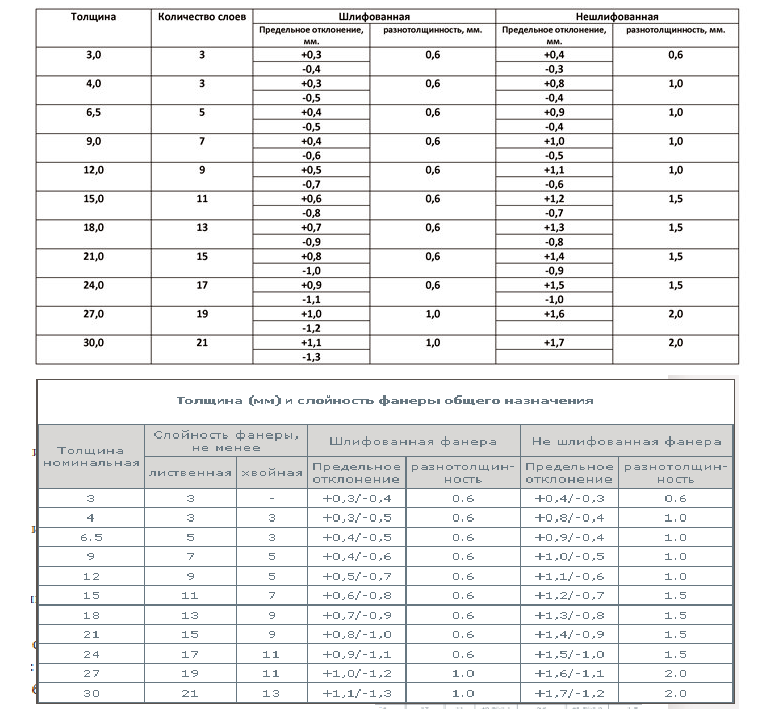
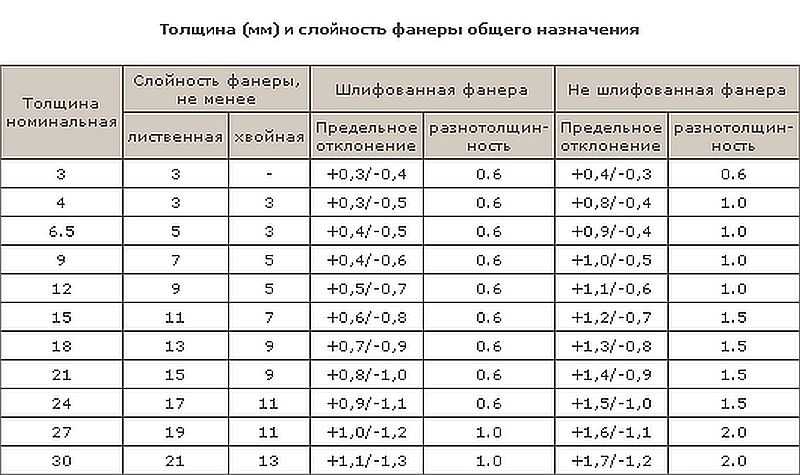
The thickness of the plywood sheet ranges from 3 mm to 30 mm. This characteristic is determined by the number of veneer layers glued. In the production of plywood, an odd number of veneer sheets are glued together. That is, if the thickness of the sheet is 3 mm, then 3 layers of veneer were glued together to make it. 30 mm plywood is 21 layers and is the most durable.
Dependence of durability on transverse bending stress for FC plywood of various layering.
The wood species of the central plywood layer, on which the veneer is subsequently glued, may differ from each other. But this does not in the least affect the characteristics of the plywood sheet as a whole. If more than 2 sheets are used in the production of plywood, and their wood fibers are at right angles to each other, then the result is facing plywood.
Most often, birch wood is used as a starting material for the production of FC plywood.
However, the use of conifers is permissible. Plywood made from birch or pine can be distinguished by eye by the texture and color of the outer veneer.
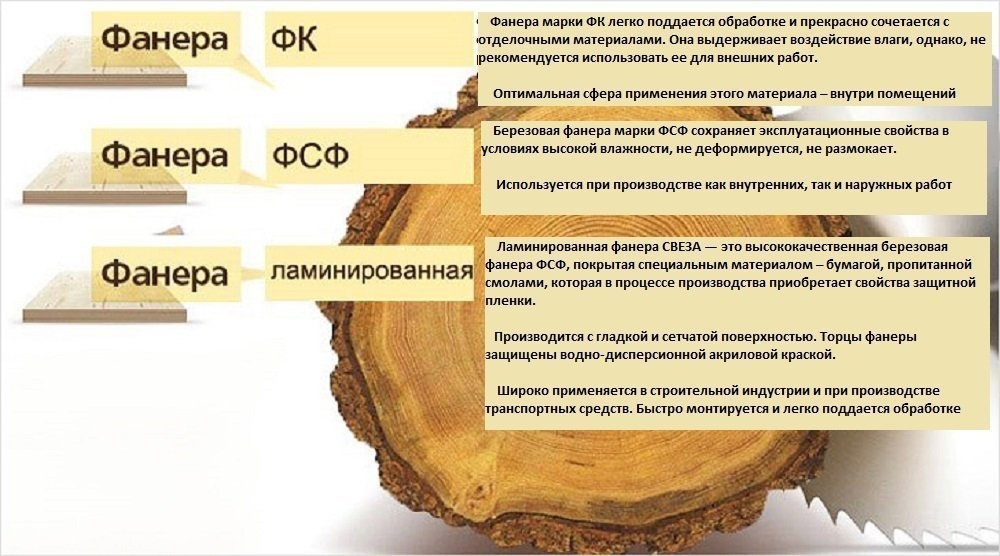
Plywood brand FC
FK plywood is moisture resistant, made of veneer treated with a compound based on urea resins, which are readily soluble in water (photo). Therefore, this type of plywood is not particularly moisture resistant, although it is declared moisture resistant.
FK plywood made in accordance with GOST does not emit harmful compounds of phenol and formaldehyde, therefore it can be used inside residential premises.
Several types of FK plywood are made:
- Coniferous - made of coniferous veneer;
- Birch - made of hardwood veneer;
Several varieties are produced, the most expensive of which is elite. To reduce the cost of material, manufacturers often produce sheets with one side of a higher grade. The so-called front side of a plywood sheet can be of one type, and the back side of another.
Application of plywood FC
Moisture-resistant plywood of the FK brand is used:
- in construction, for interior wall cladding;
- to create inexpensive furniture;
- as a basis for laying laminate or laminate boards; base for the floor;
- to create various types of temporary architectural structures.

Which plywood to choose?
Softwood and hardwood plywood have their own advantages and disadvantages. Coniferous in comparison with birch is much cheaper and lighter in weight. Coniferous plywood has fewer veneer layers than birch plywood. Because of this, the strength, elasticity and wear resistance of the material are inferior to plywood from sheet wood species.
Coniferous veneer is impregnated with natural resins, so it is less susceptible to various molds. The appearance of birch veneer is less textured, light, coniferous veneer is darker and more interesting in design (photo).
Definitely, if you need a more durable structure, it is better to use grades of hardwood plywood, in this case, birch, if you need a relatively inexpensive and environmentally friendly material - softwood veneer plywood. Birch, coniferous plywood is a practical and convenient building material.
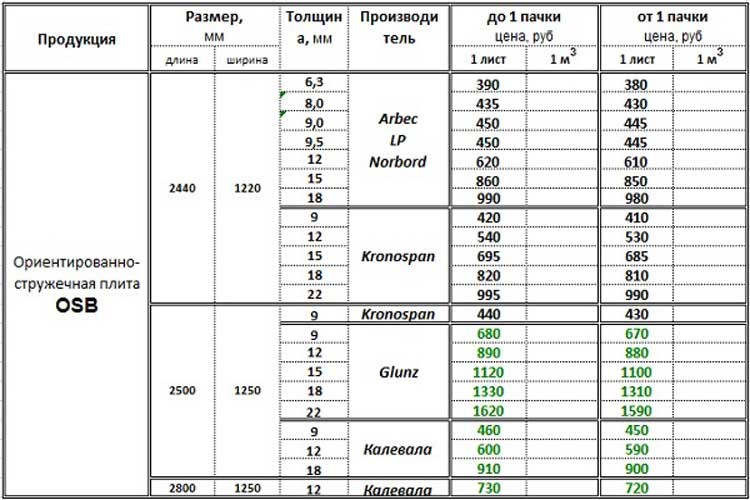
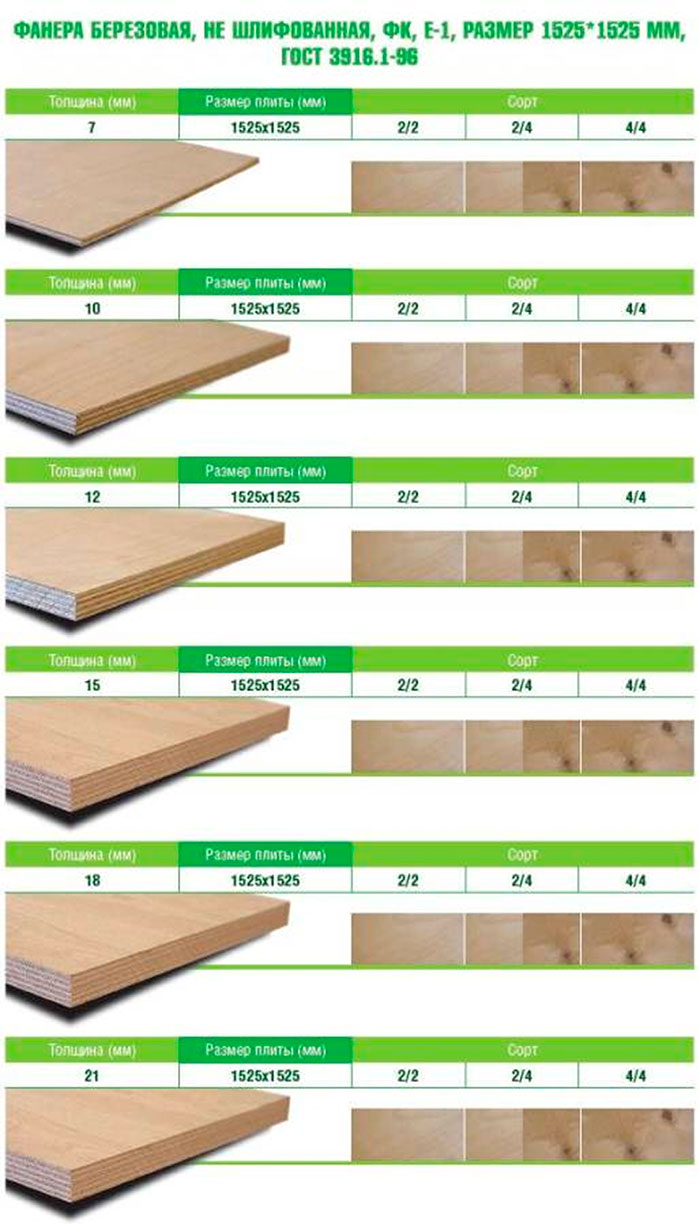
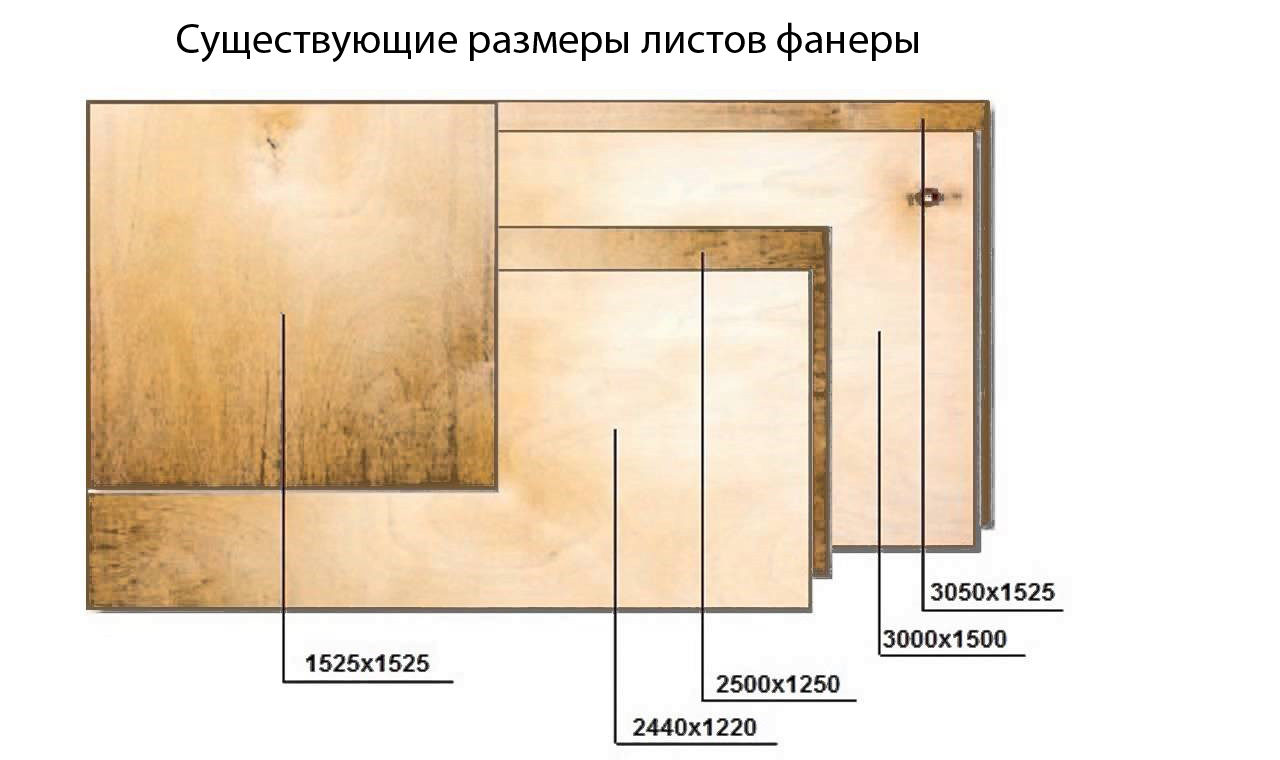
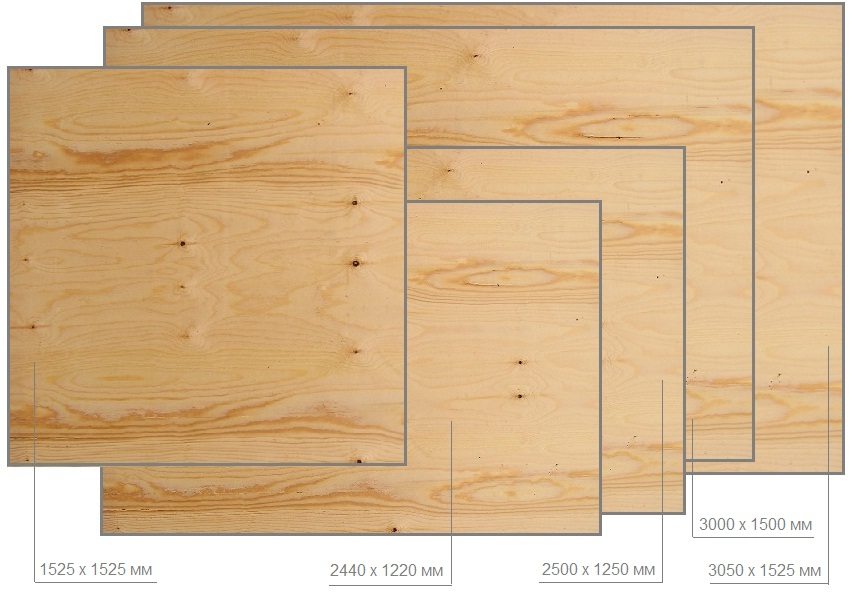
Plywood: sheet dimensions, thickness
Sheet material of various sizes may be more convenient for different jobs. And plywood is no exception. It is produced in different sizes, which are usually divided into standard and not. Standard ones are spelled out in GOST (GOST 3916.1-96), non-standard ones are produced on order - for large companies or those formats that are more in demand in retail. Usually a plywood sheet looks like a rectangle, but it can also be in the form of a square.
There are plywood sheets rectangular and square
Standard plywood sizes
In general, different types of plywood are described by different GOSTs (GOST 2707, GOST 20907, GOST 102-75, GOST 3916.1-96) and they contain different mesh sizes.
The standard dimensions may vary in different codes.
The most common small-format plywood sheets have the following standard sizes:
- 1220 * 1220 mm;
- 1525 * 1220 mm;
- 1525 * 1525 mm.
Small sheets of plywood are good because you can work with them without helpers. But a large number of seams is not good.
According to GOST 3916.1-96, it is allowed to produce plywood of non-standard length by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
Plywood dimensions according to GOST 3916.1-96
In theory, combinations from the above list can be any. In practice, there are much fewer of them.
Large format
In some cases, it is more convenient to use large plywood sheets - the joints become much smaller. The most commonly used large-format plywood of the following sizes:
- 1830 * 1525 mm;
- 3050 * 1525 mm
- 3000 * 1500mm;
- 2500 * 1250 mm;
- 2440 * 1220 mm.
Plywood: dimensions and thickness are standardized by a large number of standards
No one has brought order to the standards, so theoretically you can find almost any size from those that fit into one of them. So, for example, according to GOST 102-75:
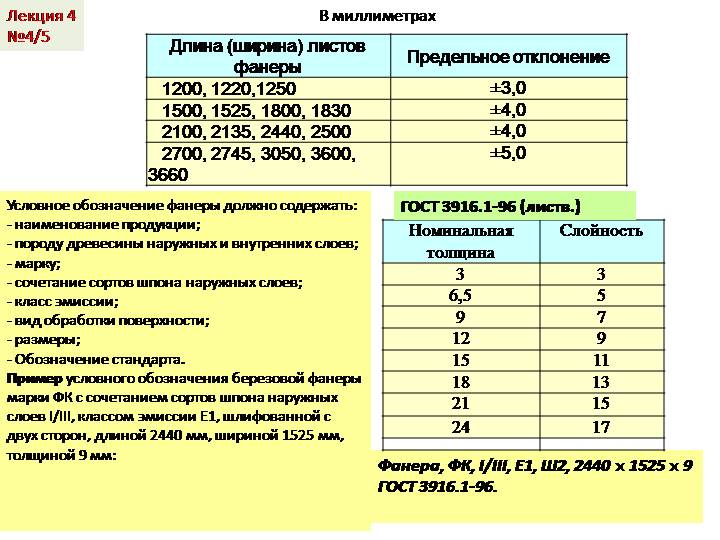
- The length of the plywood sheet can be from 1000 mm to 1525 mm. The length increment is 25 mm.
- The width can be from 800 mm to 1525 mm with the same gradation step - 25 mm.
Moreover, the maximum deviation in length and width is 4 mm. The thickness of plywood can be from 1 mm, but this is a rare "aviation" grade. Plain comes in thicknesses from 3 mm to 30 mm, but can be found up to 40 mm.The permissible error in dimensions in thickness is 0.5 mm.
There are standards governing the size of softwood and hardwood plywood
If you study the later standard 3916.1-96, it indicates a different grid of plywood sizes with a specific listing of possible values (see the table above).
Thickness
With the thickness of plywood, the picture is about the same: if you wish, you can find from 1 mm to 40 mm thick. The possibility is not excluded that there are thicker options. But most often there are slabs with a thickness of 6 mm to 27 mm.
Thickness of hardwood and coniferous plywood, layering and permissible deviations for sanded and non-sanded boards
By the way, it is interesting that in any of the standards the maximum permissible deviation is prescribed - 0.5 mm
Which, taking into account the not always large figure, is not so small. And this deviation can significantly complicate the installation of the material on the floor.
The difference has to be corrected with thin pads, or, if it is small, grind off at the joints with a grinder.
Main dimensions
The veneered layers from which the plywood is made are bonded with various adhesives and cured under a press until they are fully adhered. Lay these layers on top of each other so that the direction of the wood fibers in the previous layer does not coincide with the direction of the next layer. This method improves the strength of the material to bending and other mechanical damage. The minimum number of veneered layers in a plywood sheet is made at least 3 - in this case, the size of the sheet thickness is marked as 3 mm. The largest number of them is 21 sheets, but the thickness of the finished material can be in the range of 30-40 mm.
The dimensions of plywood may differ in width and length, each of these parameters is measured in millimeters. According to their size range, plywood sheets can be large, for example, 2000x3000 or 2000x3500 mm, and small, for example, squares 1220x1220 mm. The indicator of the standard size of the thickness of the material directly depends on the number of veneered sheets glued together. The thicker the plate or sheet, the stronger this material is.
Standard
Small errors in the dimensional parameters of the plywood sheet are also regulated by the state standard. GOST, adopted in our country, allows the manufacture of these woodworking products in any size, at the request of the consumer.
The most common dimensions for plywood are 1220 and 1525 mm. The length of the product can be limited to 1525 or 2440 mm. Such parameters are in demand among consumers, since they are easier to use during operation, and they can be transported by low-tonnage vehicles. Plywood materials with large format or non-standard parameters are 3500 or 3660 mm long and 1500 or 1525 mm wide. Sheet materials with a similar cut are often used for finishing work when decorating large premises or for production needs.
Non-standard
Small format wood panels are also popular. On sale you can see products with the following dimensions: 1220 by 1220, 1220 by 1525 or 1525 by 1525 mm. This minimal cutting is convenient in that 1 person can handle a sheet of plywood without the involvement of third-party assistants. On the other hand, cladding with such sheets results in too many joint seams, which sometimes is not a good solution.
With a large format, sheets are most often in demand, the sizes of which are: 1525x1830, 1220x2440, 2500x1250, 1500x3000 or 1525x3050 mm. Such product parameters are not found in every manufacturer - someone produces only a part of the listed formats or is guided by their own dimensional standards.
If we start from the standards of GOST, adopted in 1975, then the dimensions of the sheet material are as follows:
- the length of the sheet is made from 1000 to 1525 mm, the interval of increasing the dimension is 25 mm;
- the width of the sheet is made from 800 to 1525 mm, the interval of increasing the dimension is also 25 mm.
Due to the fact that plywood is not subject to particularly precise requirements for compliance with dimensions, typical values may deviate from the requirements of the standard up to 0.5-4 mm in length and width, and 0.5 mm in terms of thickness.
Veneer for plywood production
Veneer is the main element of plywood, which is thin sheets of wood with a thickness of 0.1 mm to 8 mm. To understand the peculiarities of plywood, you need to tell in more detail about the veneer from which it is made.
Normative base
Veneer production is regulated by the following regulations:
- GOST 99-96 "Peeled veneer"
- GOST 2977-82. "Sliced veneer"
- GOST 99-89. "Rotary cut veneer" (obsolete)
There are three main ways to produce veneer:
- Peeling;
- Planing;
- Sawing.
Rotary cut veneer
For the peeling operation, special peeling machines are used. The principle is as follows - a churak (a sawn tree trunk, cleaned of bark) rotates around its own axis, and a special knife of a peeling machine, located parallel to the log, cuts off a thin layer of wood of a given thickness from it. As the block rotates, the knife moves to its center, thereby providing a uniform veneer thickness. For peeling, both coniferous and deciduous wood species can be used:
- Pine;
- Birch;
- Linden;
- beech;
- oak;
- maple;
- ash;
- fir;
- cedar;
- alder;
- aspen;
- spruce
etc.
Sliced veneer
To obtain sliced veneer, the wood surface is cut (planed) on special machines. In this case, the width of the veneer obtained does not exceed the width of the planed bar.
By varying the different angles of the knife relative to the longitudinal axis of the bar, a different pattern and texture can be obtained. Both coniferous and deciduous wood species can be used for planing:
- Pine;
- Birch
- beech;
- oak;
- pear;
- elm;
- chestnut;
- Red tree;
- Linden;
- ash;
- alder;
- maple;
- velvet tree;
- nut
etc.
Sawn veneer
This is the simplest and oldest method, in which a plate with a thickness of 0.5 - 5 mm is simply sawed off from the workpiece. For the manufacture of sawn veneer, both coniferous and deciduous woods are mainly used:
- Pine;
- Birch
- beech;
- oak;
- Linden
etc.
Fine-line veneer
If the above types of veneer production result in a thin sheet of wood, then fine-line veneer is an artificial veneer. It is based on wood, but there is also glue and dyes (about 8%). For its manufacture, a natural veneer from soft wood is taken, soaked in special solutions and dye, after which it is glued and pressed under high pressure into special packs. Subsequently, these pressed bundles are cut into ultra-thin sheets, which are called fine-line veneers.
The resulting veneer has a number of advantages:
- as well as natural veneer it is environmentally friendly;
- has no defects on the surface, unlike traditional 100% veneer;
- any pattern, texture, or just a solid color can be applied on it;
- high - elasticity and flexibility;
- inexpensive types of wood are used for its manufacture, which makes it less expensive compared to traditional 100% veneer;
- moisture resistant, that is, it can be used in rooms with high humidity.
However, there are also disadvantages, namely:
- Low strength (fragility). Due to the use of soft wood, it is subject to deformation under mechanical stress;
- Possible cracking. To increase the strength, the material is coated with varnish, which, under certain influences, can form cracks.
- The presence of artificial components (8% of glue and dyes) in the composition does not allow this material to be classified as 100% ecological.
Fine-line veneer has a wide range of applications.For example, it is widely used in the manufacture of furniture, doors, floor coverings, as well as various decorative materials for creating interior design solutions.
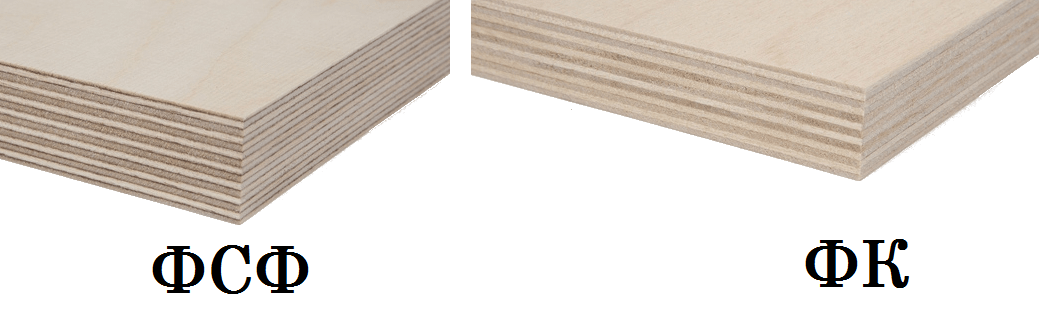
Varieties and labeling
FSF plywood is made from soft or hard tree species, they can be both deciduous and coniferous. It can be longitudinal or transverse, have 3, 5 or more layers (three, five and multi-layer, respectively). These gradations can be combined by manufacturers in various proportions.
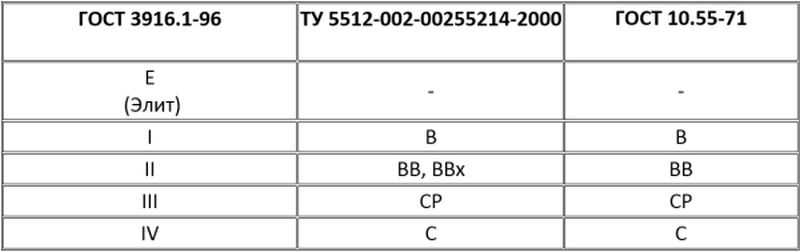
Building material can have different grades:
- grade I is characterized by the greatest damage - the total length of defects on 1 sheet should not exceed 20 cm;
- Grade II - the length of the cracks is up to 15 cm, the presence of an adhesive composition is permissible on the surface of the products (no more than 2% of the plank area);
- III grade - openings from knots, falling out knots, wormholes are permissible for it;
- Grade IV implies the presence of various manufacturing defects (an unlimited number of wormholes up to 4 cm in diameter, intergrown and non-intergrown knots), such products are considered to be of the lowest quality.
They are characterized by minimal deviations in the structure of wood. Wormholes, knots and holes from them, streaks and other defects are not allowed.
To determine the main parameters of a plywood board, manufacturers attach markings to the building material. Let's give an example "pine plywood FSF 2/2 E2 Ш2 1500х3000 х 10 GOST 3916.2-96". The marking says that the presented plywood sheet is made of pine veneer using the FSF technology, with a front and back surface of grade 2, grade 2 of phenolic emission, double-sided grinding, 10 mm thick and 1500x3000 mm in size, manufactured in accordance with the standards of GOST 3916.2-96.
Material advantages and disadvantages
The production method makes plywood strong and resistant to deformation. This is achieved through the presence of multiple layers and special adhesives. Therefore, the following advantages of such plates can be distinguished:
- Resistant to moisture. Waterproof plywood does not deteriorate when exposed to moisture. It does not stick to layers and does not deform.
- Easy to use. The high strength of the material does not interfere with the processing process. Plywood is easily processed using a variety of tools. It is easy to install.
- Compatibility with other building materials. Most often, waterproof plywood is used as an additional material. It easily connects with natural and polymer building materials.
- Wear resistance. Plywood can withstand mechanical stress without compromising its integrity.
- Resistant to temperature extremes.
- Wide scope of use.
- Aesthetics. Plywood externally has an original wood pattern and color.
- Affordable price. Plywood boards are cheaper than solid wood. And you can always save money by choosing a lower grade material.

The only drawback of the material is the presence of harmful substances that make up the glue. It's about formaldehyde. Therefore, it is not recommended to use plywood in residential areas and where there are children or people with allergies.
Plywood classification by purpose
The area of application of plywood (laminated, sanded, moisture resistant and other types) is not limited to construction, due to its properties the material is extremely in demand in various fields.
Ship. Only the highest quality types and grades of moisture-resistant plywood FB (on bakelite glue) are used for finishing shipping facilities, which work perfectly in conditions of high humidity and aggressive environments.
Furniture. The types of plywood used for furniture must be environmentally friendly, wear-resistant and durable. As a rule, combined FC plywood is used for furniture.
Construction. In the construction industry, as a rule, grades 3/4 and 4/4 of birch plywood are used.These types of plywood can be used for floors, walls and other structures as a rough finish.
Aviation. For these purposes, FSF plywood grades are used. This plywood has excellent technical characteristics and is ideal for such demanding and demanding industries as aircraft, ships, railroad cars and automobiles.
Formwork. To create the formwork, FB film-faced plywood is used, which has excellent characteristics in terms of moisture and wear resistance, strength and exposure to an aggressive environment.
Decorative. FK plywood is used for finishing the premises. This type of plywood must have excellent outer layer characteristics (even surface with a textured pattern). Plywood of this type, as a rule, is made from valuable wood species, or from wood of the highest grade.
Automotive. For cars, as a rule, FSF plywood with a laminated or mesh-ribbed surface is used. Plywood has high strength, moisture resistance and durability. It is used for covering all elements of a truck body (walls, floor, doors, ceiling).
The difference between film faced plywood and ordinary
Below are some of the characteristics that have been defined by GOST 2010:
- For the production of laminated plywood boards, plywood of the 1st and 2nd grade of the phenol emission class of the E1 level is used, and at the same time everything meets the strict requirements for the presence of defects on the veneer, the method of gluing and the final density of the material.
- The plywood sheathing can be made from thermosetting plastic or high tenacity plastic film. According to the test conditions, the coating should be unchanged even after 6 hours of boiling, as well as in contact with liquid concrete and an alkaline environment.
A sheet of film faced plywood, in contrast to the bakelite variety, is impregnated with a hot method, and it contains less phenol. As a result, we obtain an elastic and at the same time sufficiently strong material, which has a lacquered protective polymer layer. Film faced plywood with a water-resistant effect is more ductile than bakelite board, which is better than a laminated sample in terms of water resistance, but has an increased sensitivity to abrasion and shock.
To create the coating of the laminated fork, in addition to textured paper and phenol-formaldehyde resin, PVC films and melamine varnishes are used. Although the technical characteristics of melamine and PVC coatings are slightly worse than FFS, they are indispensable when creating a plywood sheet in color. If standard samples have a phenol emission class E1 according to GOST, then a colored PVC sample emit several times less toxic substances.
According to the technical characteristics of film faced plywood and the method of using GOST, the laminated board is used for exterior decoration and in the manufacture of concrete casting molds. If the same plywood sheet is painted, then it can be used for interior work during finishing, as well as for wall cladding in a frame house and as a sublayer for leveling the floor.
It is easy to distinguish standard film faced plywood from painted plywood - it all comes down to color, since the standard version is dark brown, and colored boards are tinted in shades that are lighter than the original.
Moisture-resistant laminated plywood
It can be made, alternating, birch and coniferous veneer. Moisture resistance is the ability not to be exposed to moisture from the environment. The brands of such products are different depending on the brand of glue used:
- Elements are glued with urea formaldehyde, marked with FC, it can be used even inside apartments;
- The veneer is glued with phenol-formaldehyde resin, marked with FSF, it is better to keep it in the fresh air;
- Using bakelite adhesive, it is marked with FBS.The most waterproof, such a building material is allowed to be used even in shipbuilding, aircraft and automobile construction.
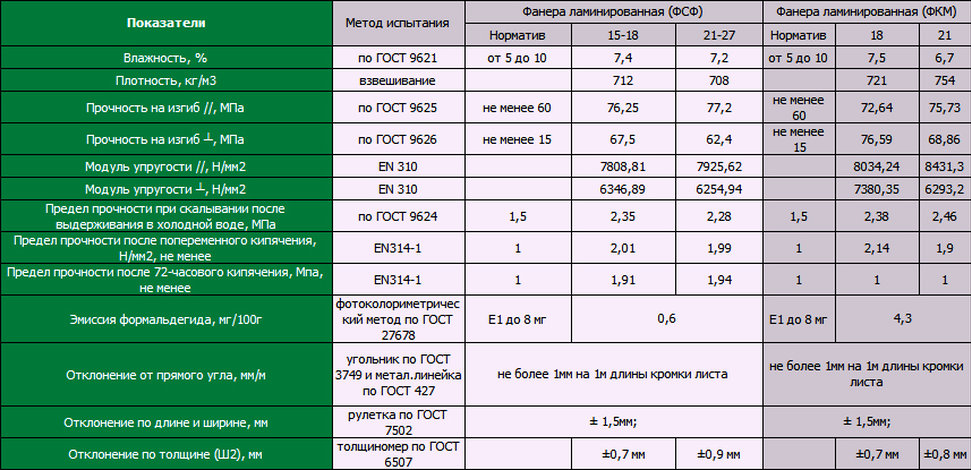
Strength characteristics of laminated sheet
| Parameter name | Value, MPa |
| Maximum shear strength over the adhesive layer after soaking for 24 hours | 1,5 |
| Maximum tensile strength | 40 |
| Maximum static bending strength | 60 |
It is interesting: Garden furniture made of wood: we explain in all details
Varieties
Plywood grades.
According to the degree of moisture resistance, plywood is divided into the following brands:
- FBA;
- FC;
- FSF;
- FOF;
- FB.
The first group is a sheet material glued with albuminocasein natural glue. Among other groups, this plywood has the least resistance to high humidity, but at the same time it is an environmentally friendly product.
The second grade is made from birch veneer. It has an average moisture resistance, so it is usually used for interior finishing work. The main advantages include high environmental safety and non-toxicity. However, at high humidity, its deformation, warping and swelling can occur. The most popular FC sheet format is 152x152 cm.This is a square with a thickness of 2.1 cm.
Plywood of the FSF brand has increased moisture resistance, since moisture resistant glue based on phenolic resins is used in its manufacture. The use of moisture-resistant glue in combination with birch wood gives a great advantage of such plywood over other lumber. The standard sizes of the FSF are 122x244, 125x250, 152x305 and 152x152 cm, with a thickness of 4 to 30 mm. This type of plywood is widely used for exterior construction and finishing works.
Plywood design resistance table.
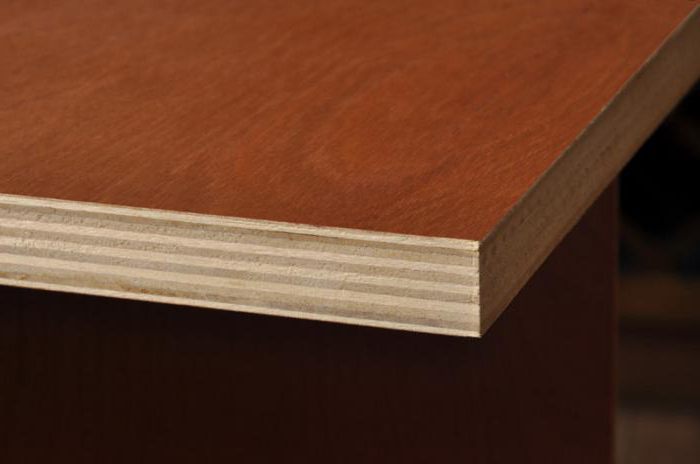
Film faced plywood (FOF) is produced on the basis of the FSF brand. The main purpose of lamination is to give the material increased performance characteristics, including moisture resistant ones, as well as to improve the strength and wear resistance of the material, and to create a decorative effect.
Film faced plywood has the following technical characteristics:
- sheet dimensions: 122x244 and 125x250 cm;
- sheet thickness: from 9 to 40 mm;
- density: 680-700 kg / m3;
- humidity: less than 10%.
Due to its unique characteristics, film faced plywood is used in such areas as:
- construction and finishing works;
- structural work;
- automotive industry;
- car building, etc.
Necessary clearances for plywood mounting.
Bakelized plywood (FB) is the most durable and moisture-resistant brand, which is made with the addition of phenol-formaldehyde resins, which give it these qualities.
The technology of gluing bakelized material involves the use of high pressure, which increases its strength and gives it a special form stability.
Certain grades of FB plywood are successfully used in the aviation industry and shipbuilding.
Bakelized grades can be used even in aggressive environments, in water and in dry climates.
Main characteristics of bakelized plywood:
- leaf length: 150-770 cm;
- width: 120-155 cm;
- thickness: 5-18 mm;
- density: 1200 kg / m3;
- humidity: no more than 8%.
Plywood marking
Plywood, like any other building material, has markings based on its various properties.
The following parameters are used for marking:
- by type of adhesive
- for processing the top layer
- by formaldehyde content
- decorative plywood marking
Let us examine these designations in more detail.
By type of adhesive
The moisture resistance of plywood is determined primarily by the composition of the adhesive. Depending on it, the following brands of plywood are distinguished.
| Designation | Adhesive composition | Moisture resistance | Application |
| FC | Urea adhesive with the addition of formaldehyde resins | Yes | It can be used both indoors and outdoors.belongs to a high class of environmental friendliness. |
| FSF | Phenol formaldehyde adhesive | Yes | It can only be used outdoors, since the binding components are hazardous to health. It is used for the manufacture of film faced plywood, which is used in the construction of external structures. |
| FBA | Albumocasein glue | No | It can be used indoors. |
| FB | Bakelite varnish | Yes | It can be used in any climatic conditions and at maximum humidity. Withstands exposure to sea water. |
| BS | Alcohol-based bakelite glue | Yes | The characteristics are even better than those of "FB". It is often used in aircraft and shipbuilding, therefore it is also called "aviation". |
| BV | Bakelite composition | No | Since water-soluble bakelite is used in the production, there is no moisture resistance of plywood. Nevertheless, plywood is quite durable. |
By processing the top layer
An important parameter of plywood is the quality of the plywood top layer and its processing. A special label has been defined for this parameter.
| Designation | Description |
| Ш1 | The veneer is sanded on only one side of the plywood |
| W2 | Veneer sanded on both sides of the plywood |
| NSh | The veneer of the top layers of plywood is not sanded |
Formaldehyde content
Since formaldehyde is very harmful to human health, the amount contained in plywood is important and affects the environmental friendliness of the material.
| Designation | Formaldehyde content in 100 g of material |
| E1 | does not reach 10 mg |
| E2 | from 10 to 30 mg |
| E3 | from 30 to 60 mg |
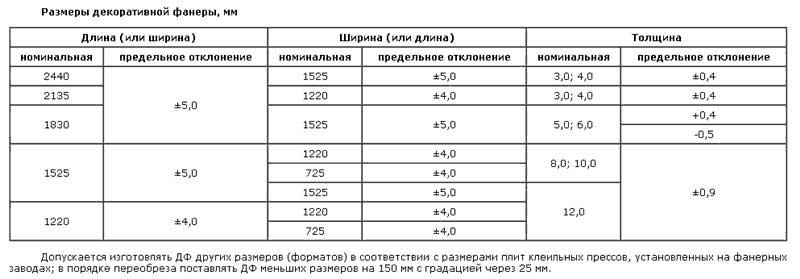
Decorative plywood marking
Decorative plywood (DF) can be faced with various film coatings and paper, which give it a unique appearance and additional enhanced characteristics. The following brands are distinguished.
| Designation | Facing coatings | Resins |
| DF-1 | Transparent, does not hide the texture of natural wood | Urea-melamine-maldehyde |
| DF-2 | Opaque with decorative paper to simulate the texture of precious woods. Any drawing is possible. | |
| DF-3 | Increased water resistance. Transparent, does not hide the texture of natural wood | Melamine-maldehyde |
| DF-4 | Increased water resistance. Opaque with decorative paper that imitates the texture of precious woods. Any drawing is possible. |