Bricklaying technique
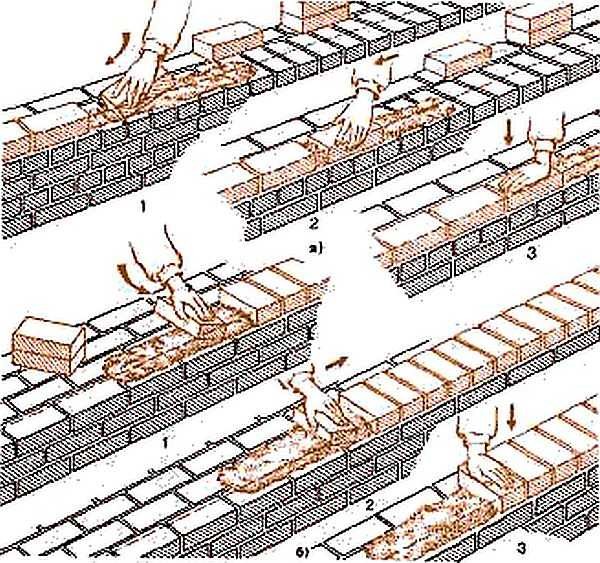
Stir the solution before use, as heavy particles can sink down and water rise up. The mixed solution is placed in buckets and transferred to the masonry site, where it is distributed. Immediately put a strip of mortar - bed - for one row. Under the butt row, the bed width is 200-220 mm, for the spoon row - 80-100 mm. If the seam is completely filled, about 10-15 mm recede from the edge, the height of the mortar is 20-25 mm, which, when laying, provides a seam of 10-12 mm. Before installing the brick, the mortar is leveled with a trowel.
There are three techniques for masonry. On a hard, low-plasticity solution, the "press-on" technique is used. In this case, the seams are completely filled. If the solution is plastic, use the "injected" technique.
Bricklaying technique "interspersed"
As already mentioned, this method of laying bricks is used with a plastic mortar. It should be flexible, easy to apply and displace. This is achieved by adding additives. You can spread the mortar immediately on the entire surface of the wall: additives allow you to extend the time before the start of setting.
The bed is laid with a thickness of about 20 mm, an indent of about 15-20 mm remains from the edge. This indentation avoids squeezing the mortar onto the front surface, but at the same time the edges of the seams often remain unfilled. This significantly reduces the strength of the wall, therefore, in regions with seismic activity, laying verst rows (external and internal) by this method is prohibited.
When laying a spoon row, take a brick, holding it with a slight slope. Approaching the already laid one, at a distance of 8-10 cm, they begin to scoop up the solution with the edge (poke). When joining, it turns out that the seam is already partially filled. The brick is pressed down a little (settles), pressing it to the bed. The surplus is removed with a trowel and sent either to a bucket or to a wall.
Bricklaying technique "adherent"
With this technique, it often happens that the vertical seams are only partially filled. Therefore, this method is also called "wasteland". They are filled in when laying the bed for the next row. If the technique is not yet very worked out, it is better to fill the seams before laying the next row: the voids reduce the strength and thermal insulation characteristics.
When laying the butt row, everything is exactly the same, only the solution is raked up with a spoon edge. The zabutka is laid, like the stitching rows, and then pressed with the palm of the hand. It is necessary to ensure that all stones are at the same level. This is done using a building level, and the verticality of the wall is checked with a plumb line every 3-4 rows.
Technique "press-on"
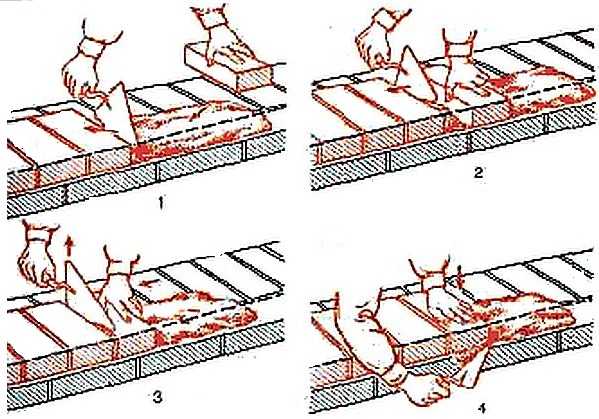
When working with hollow bricks, as a rule, hard mortars are used. In this case, a brick is used with the "press-on" technique. In this case, you also have to work with a trowel.
The bed is laid at a distance of 10 mm from the edge, the thickness is still about 20 mm. Since such a composition stretches badly, it is raked to the edge of the laid brick with the edge of the tool. They take a brick with their left hand and press it against the trowel, while pulling it up. At the same time, they continue to press with a brick, achieving the required seam thickness (10-12 mm).
End-to-end technique
Excess mortar is picked up with a trowel. Having laid several fragments, take a level, checking the horizontal line, by tapping the handle of the trowel, straightening the position. The solution squeezed out at the same time is selected. It turns out dense masonry, but the process takes longer: more movement is required.
Insertion with undercut
An average method in terms of productivity is the butt-in with undercutting of the seams. With this method, the bed is laid out close to the edge (10 mm), as when laying it in a press, and the masonry technique is in place: they grabbed the mortar with a brick, put it down, pressed it down, removed the excess. If the wall is not subsequently planned to be finished with anything, after several rows it is necessary to take a jointing - a special tool and give the seams the required shape (convex, concave, flat).
As you can see, this is a kind of symbiosis. To make it more convenient to work, the solution is also made with "intermediate" plasticity.If it is too liquid, it will flow down the wall, leaving streaks, therefore it needs to be kneaded a little denser than when laying in a sprinkle.
Making masonry in one and a half and two bricks
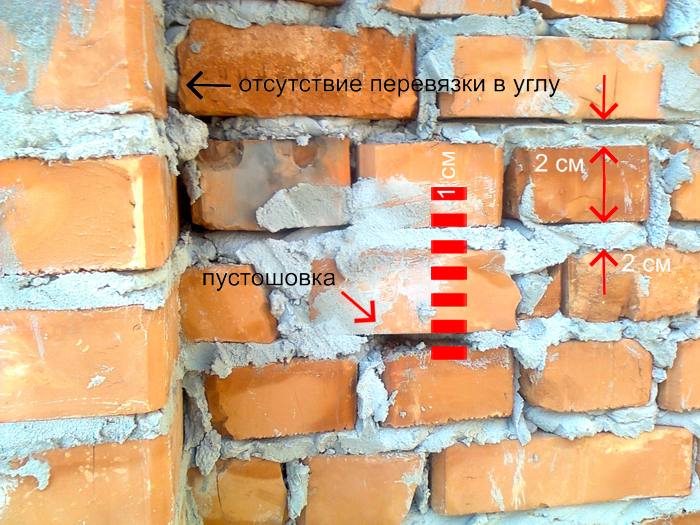
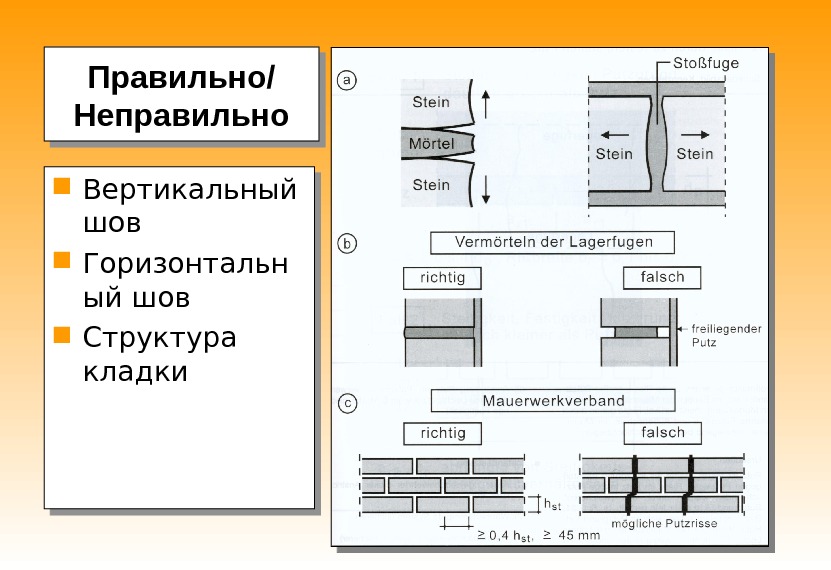
 The basic principle of high-quality construction is the precise ligation of the vertical seam that connects the entire structure
The basic principle of high-quality construction is the precise ligation of the vertical seam that connects the entire structure
Brickwork is done according to certain rules. The basic principle of high-quality construction is the precise ligation of the vertical seam that connects the entire structure. The essence of the dressing is to correctly distribute the load and increase the strength of the structure. Bandaging can be done in three ways:
- transverse seam, preventing the connection of the displacement of bricks throughout the structure;
- ligation of the vertical seam;
- longitudinal seam, which prevents delamination and displacement of the building material, distributes an even load.
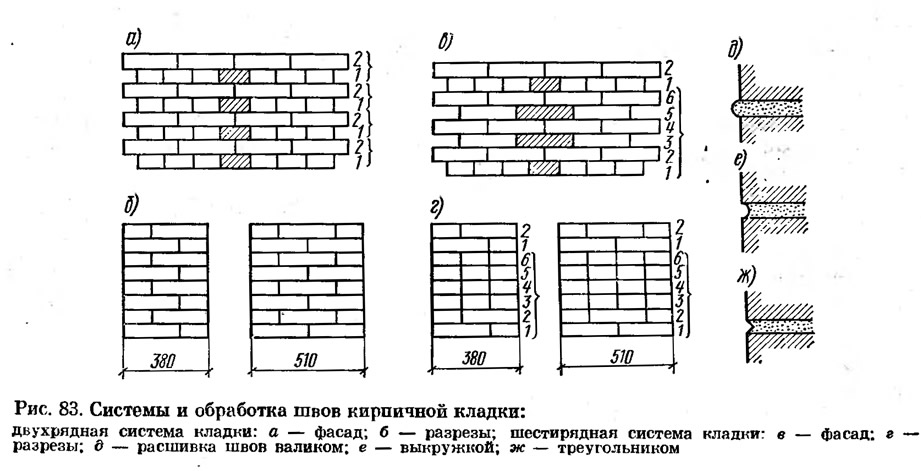
Brick walls are laid out in two ways: multi-row or single-row. For a single-row type, it is characteristic to lay out the row outward with the spoon side, and the second row is laid out outward with the butt-side surface. As a result, it turns out that each transverse seam is shifted by ¼ of the building material, and the longitudinal seam by 0.5.
The multi-row type is characterized by alternation through several spoonfuls.
Construction in one and a half products. The thickness of the walls of a brick house can be 380 mm. This masonry method is quite common and is called one and a half bricks. The product begins to be laid out from the corners, the first bricks are placed perpendicularly. The first row is laid out using a construction cord, which is fixed at the height of the first and second bricks. We place the poking surface on the outer side, and place the inner side with the spoon part. The next row is laid out opposite to the first, thus, a mirror reflection is obtained. The thickness of the wall, arranged in one and a half bricks, is able to withstand the load of the roof and floors between floors. The peculiarity of this method is that the vertical seam does not coincide, it is completely covered by the surface of other bricks.
Two-piece construction. The method of laying in 2 bricks or 500 mm is performed in places with strong temperature changes. Such a thickness of brick walls does not require the use of insulation materials. The quality of the structure directly depends on the durability of the structure and its thermal insulation.
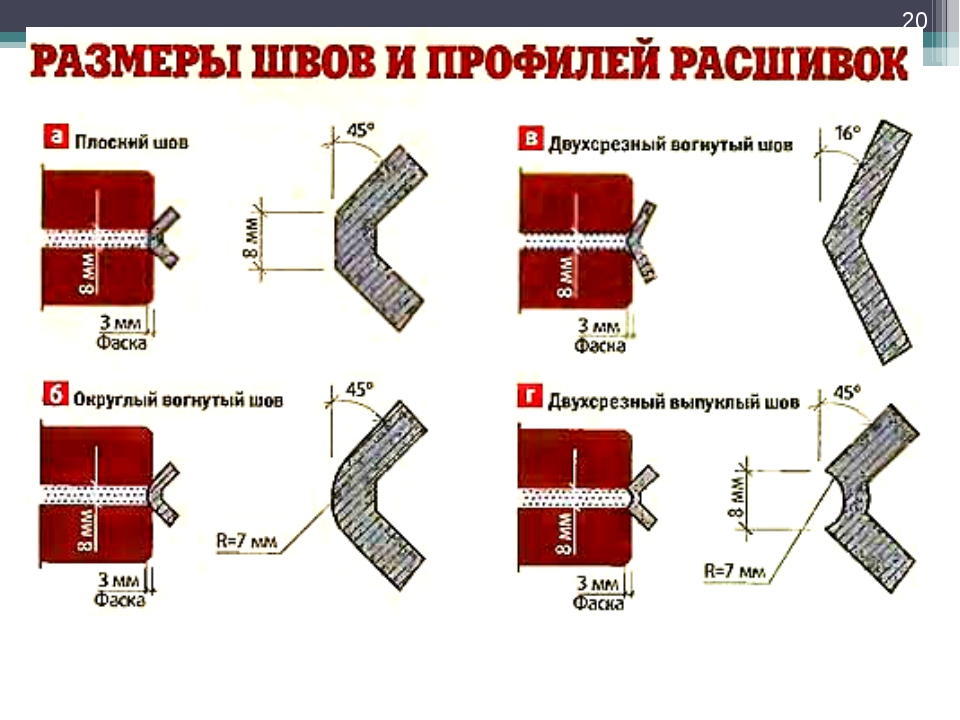
Joining options
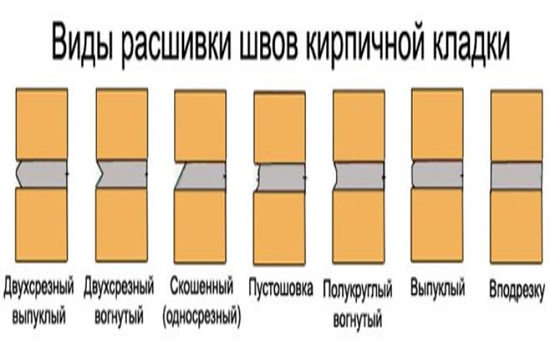
Joining gives the structure a finished look and is carried out at the end of the masonry. This work is painstaking and requires accuracy from a specialist.
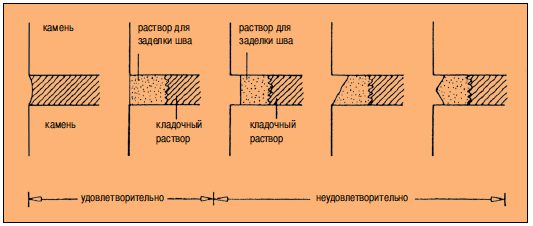
The jointing serves to protect mortar and brick from moisture penetration through existing cracks and irregularities. For better adhesion, special components are added to the solution. The seam between the bricks, the size of which meets the standards, is sewn with a special tool. Its use allows you to more clearly and accurately carry out the work.
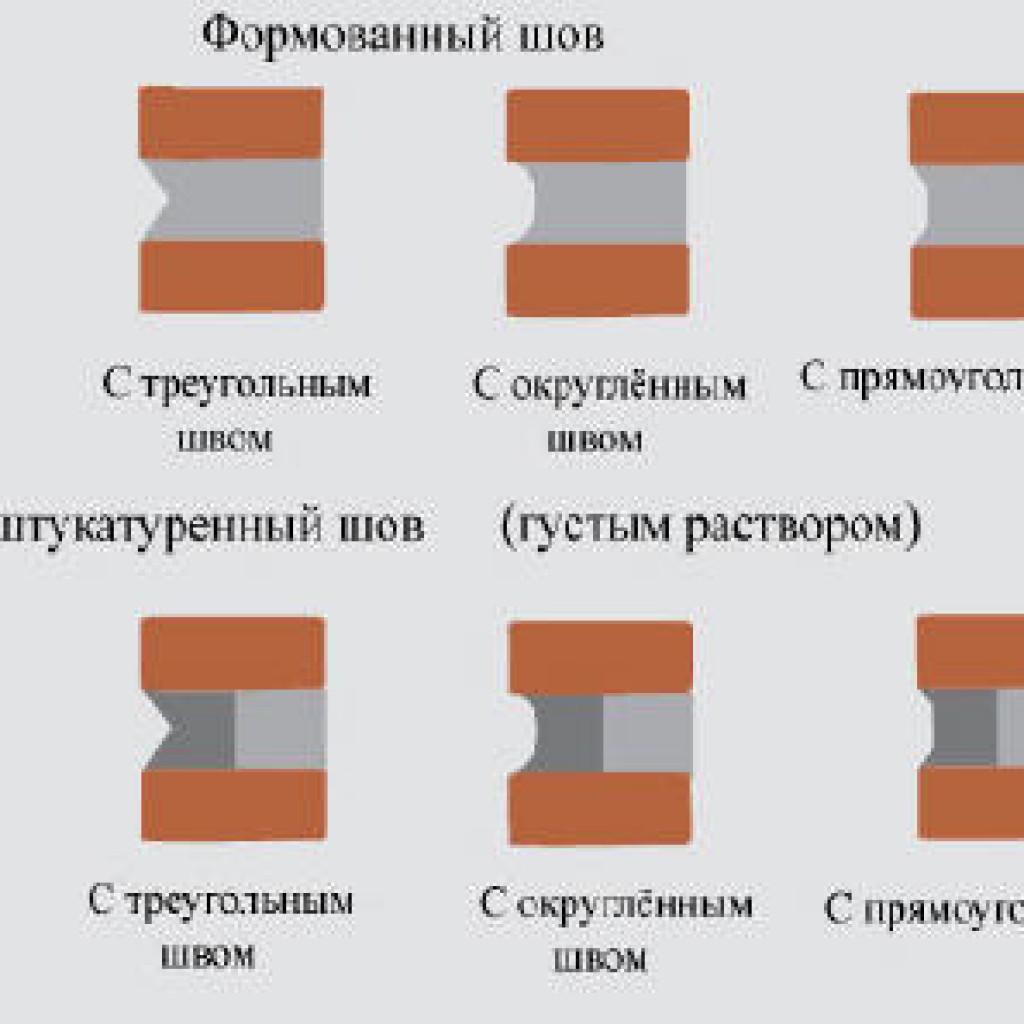
There are several types of joining:
- Convex and concave
- Undercut
- Pustoshovka
- Single cut
- Double-cut concave and double-cut convex.
The joining of the front side of the wall has its own differences. Depending on the design, the seam is made complete or incomplete, with a depression of up to 15 mm. Incomplete seam contributes to better plastering of the surface.
The convex shape of the seam protects the masonry from the effects of precipitation. If the climate is drier, the seam is made more concave.
The original is considered to be the joining made in black or white. Its contrast with brick makes the exterior of the building more attractive.
With the help of masonry joining, the facades of old houses, with unplastered brick walls, are renewed. To do this, first deepen the existing joints by 2-3 mm and apply new mastic. With careful work, the masonry will look like freshly laid. Deepening in the old mortar is done with a chisel.
Features of brick walls
Brick, especially solid brick, has only one drawback.These are its low thermal performance indicators, worse than which are only similar characteristics of reinforced concrete.
If the wall is one and a half bricks (38 cm) and can withstand heavy loads, then large frosts become a problem for it. Nevertheless, winter temperatures of -30 degrees are the norm for most regions of our country. How to make it warm in a brick house?
To keep the walls warm
Given the rather low coefficient of thermal insulation of solid bricks, in order to achieve heat, the walls from it would have to be laid out with a thickness of 64 cm.Of course, these are unnecessary costs - and not only on the walls, but also on the foundation, therefore the construction of solid masonry with a thickness exceeding 38 cm is considered economically impractical.
Hollow wall brick
So:
- There are many ways to get out of the situation. For this purpose, a hollow (slotted) brick was invented, so that it was possible to reduce the weight of the masonry, and, accordingly, to reduce the load on the foundation of the building. Technologies are also used that make it possible to facilitate masonry with the use of solid bricks.
- This is the maintenance of masonry with widened seams, with the formation of longitudinal voids and wells, filled with effective insulation. In addition, for the construction of brick walls, masonry and plaster solutions are used, which are usually called warm. Due to the content of perlite sand, their thermal insulation coefficient is several times lower than that of a conventional solution.
Warm masonry mortar
- The undoubted advantages of brick houses is the fact that the air temperature in their premises fluctuates very slightly. The thing is that the masonry not only warms up slowly, but also slowly cools down, and the thicker the wall, the longer the heat will remain.
- However, in country houses and country houses, in which no one constantly lives, heating brick walls requires much more fuel consumption than just maintaining a comfortable microclimate. Temperature changes contribute to the formation of condensation on the outer and inner surfaces of the walls, which is fraught with the appearance of mold and efflorescence, leading to the gradual destruction of the masonry.

Cladding of brick walls in an intermittently heated house
Best of all in such cases, when the walls are sheathed with wood from the inside. Depending on the status of the house, it can be clapboard, planken, plywood or OSB sheets, wood or MDF panels.
Drywall is also excellent, since it also has good thermal insulation qualities. Well, outside it is desirable to revet them according to the system of insulated ventilated facades - approximately as shown in the photo above.
Some useful information
Low-rise buildings can be built from any type of brick. In addition to ordinary clay, these are also silicate and hyper-pressed bricks, which, however, have some limitations.
Despite their strength, which, in principle, is not inferior to the strength of ceramic bricks, these products are not used for the construction of basement walls and strip foundations. In rooms with high humidity, the surface of such masonry must be protected.
Walls erected from silicate bricks
If the inner brick wall is load-bearing, then it cannot in any way have a thickness less than one brick. It can be built from both solid and hollow bricks. There are also norms for laying walls and pillars. The size of the wall cannot be less than 250 * 610 mm in cross section. The cross-section of the pillar laid out of bricks must be at least 380 * 380 mm.
Living room with brick wall
- When starting construction, it would be nice to know in advance what options for interior decoration and interior design will be used in it. And partitions can help with this.For their construction, you can use not a worker, but a front brick, which will allow you to use such an interior design option as a brick wall in the living room, dining room, or in the bedroom at no extra cost.
- A decorative wall made from the side of the facade for insulation, or just as a cladding, also looks incredibly beautiful. Here, of course, nothing can compare with clinker bricks. In appearance, it is good in itself, and if we take into account also the various variations of its front finish, then with a competent approach to the choice of color and texture, the facade of the house will look just like a picture.
Clinker cladding on the facade
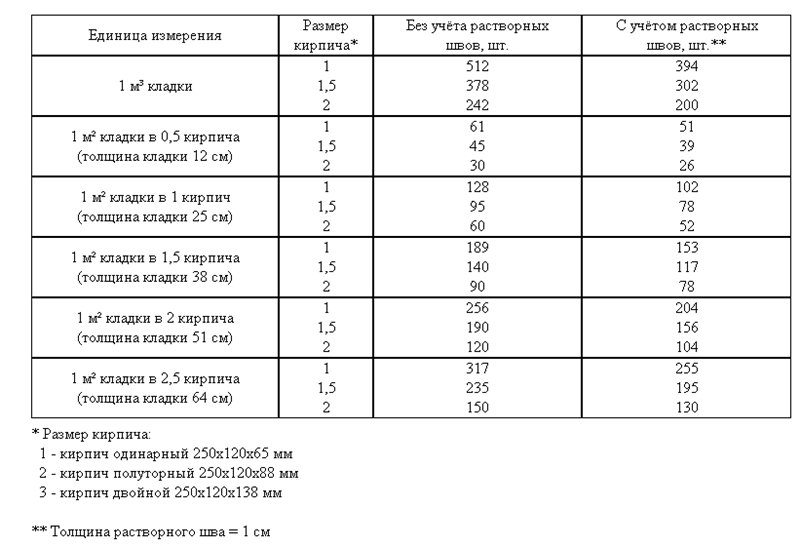
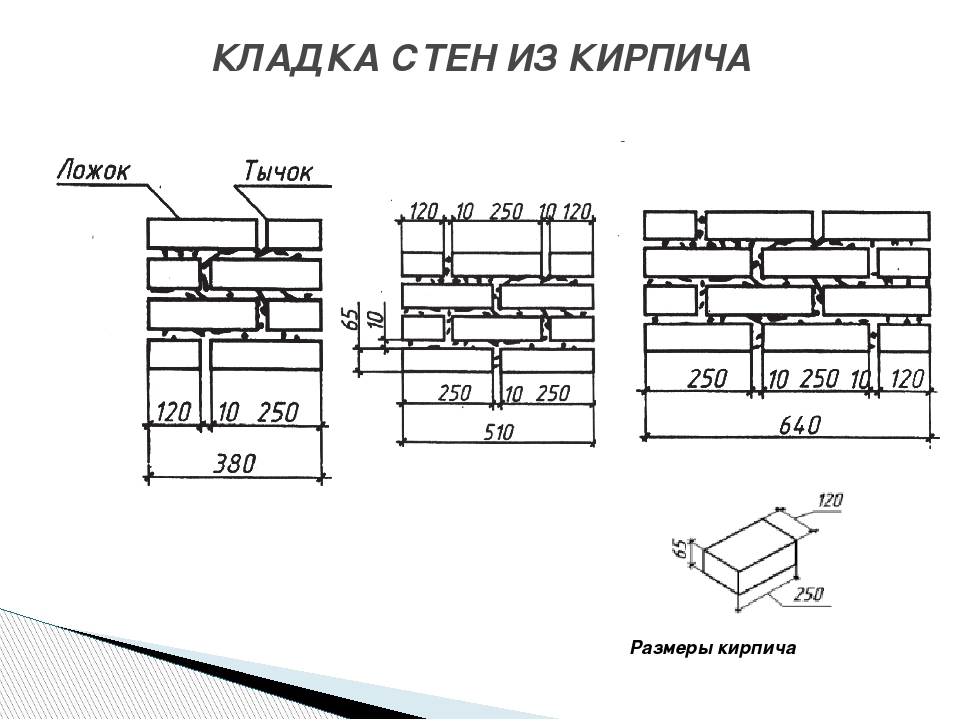
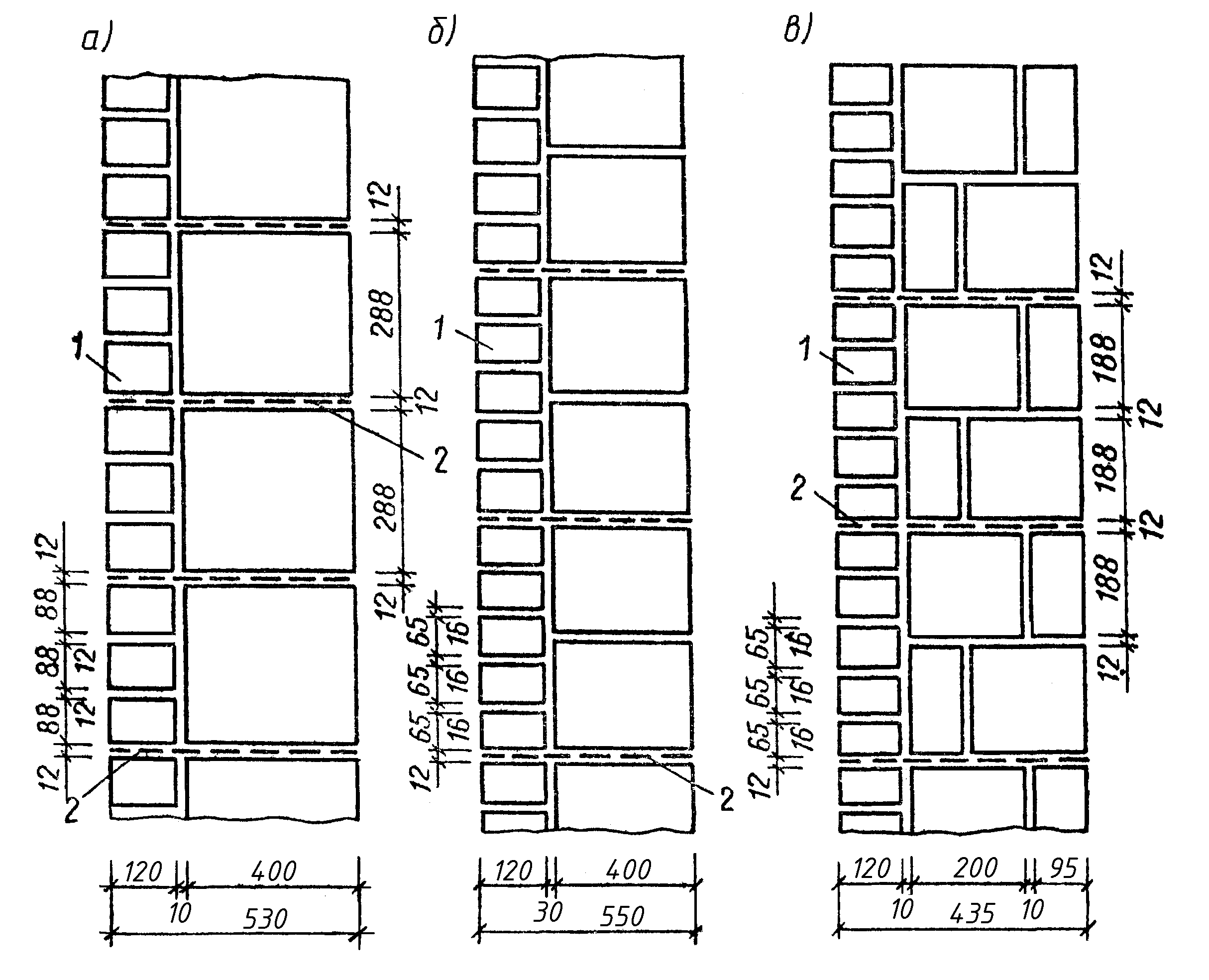
Dimensions of brickwork
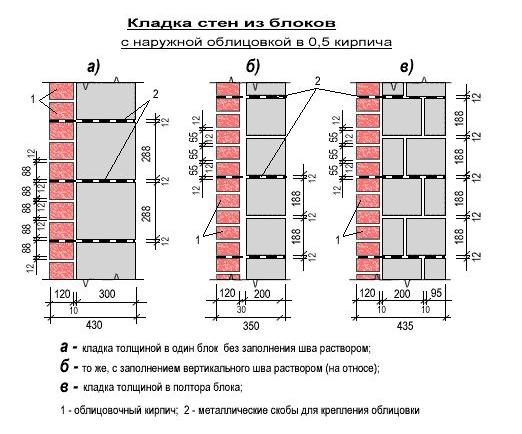
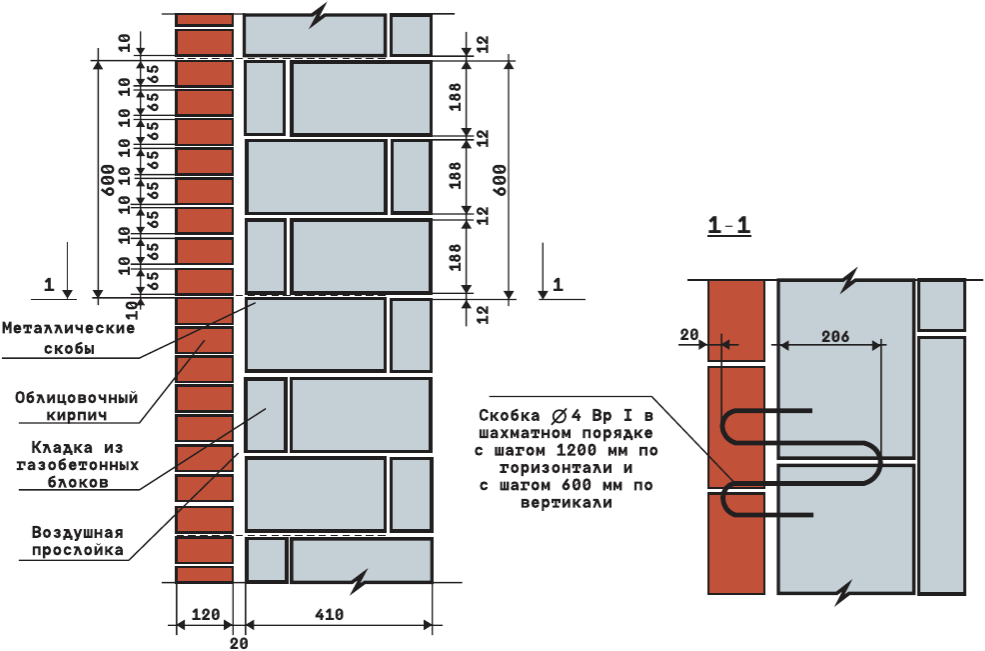
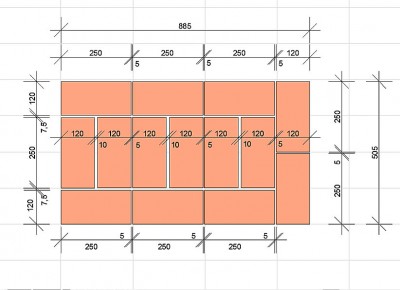
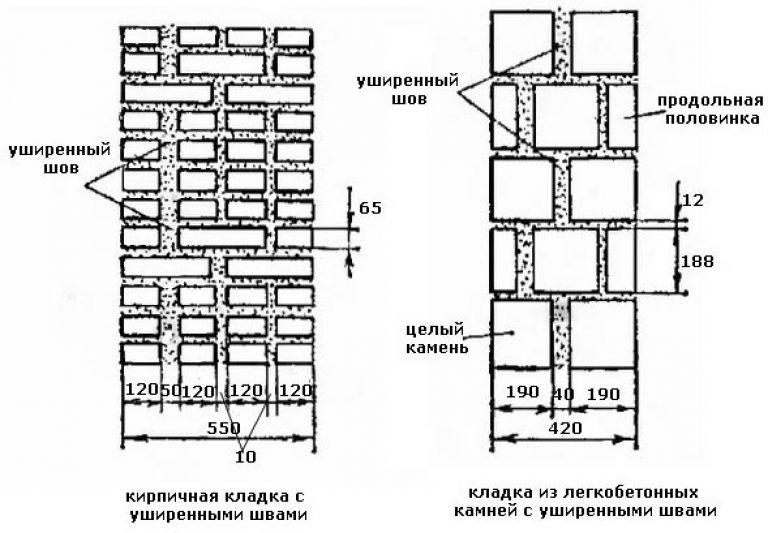
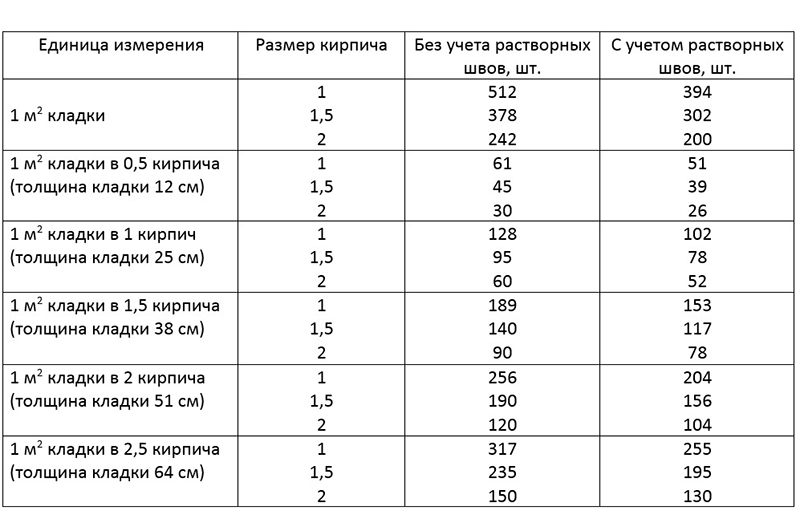
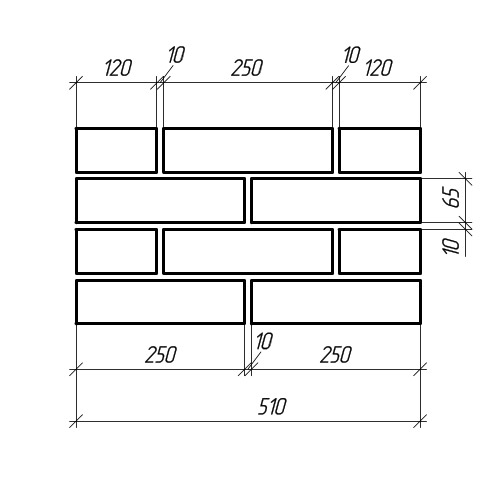
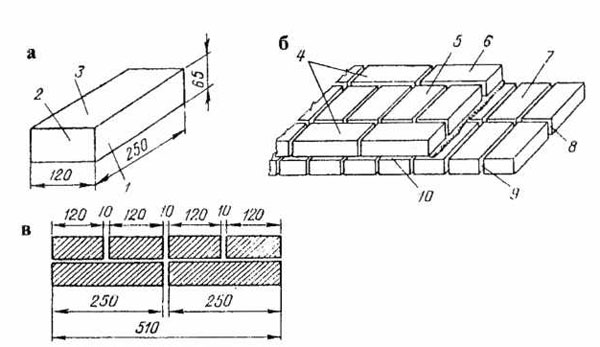
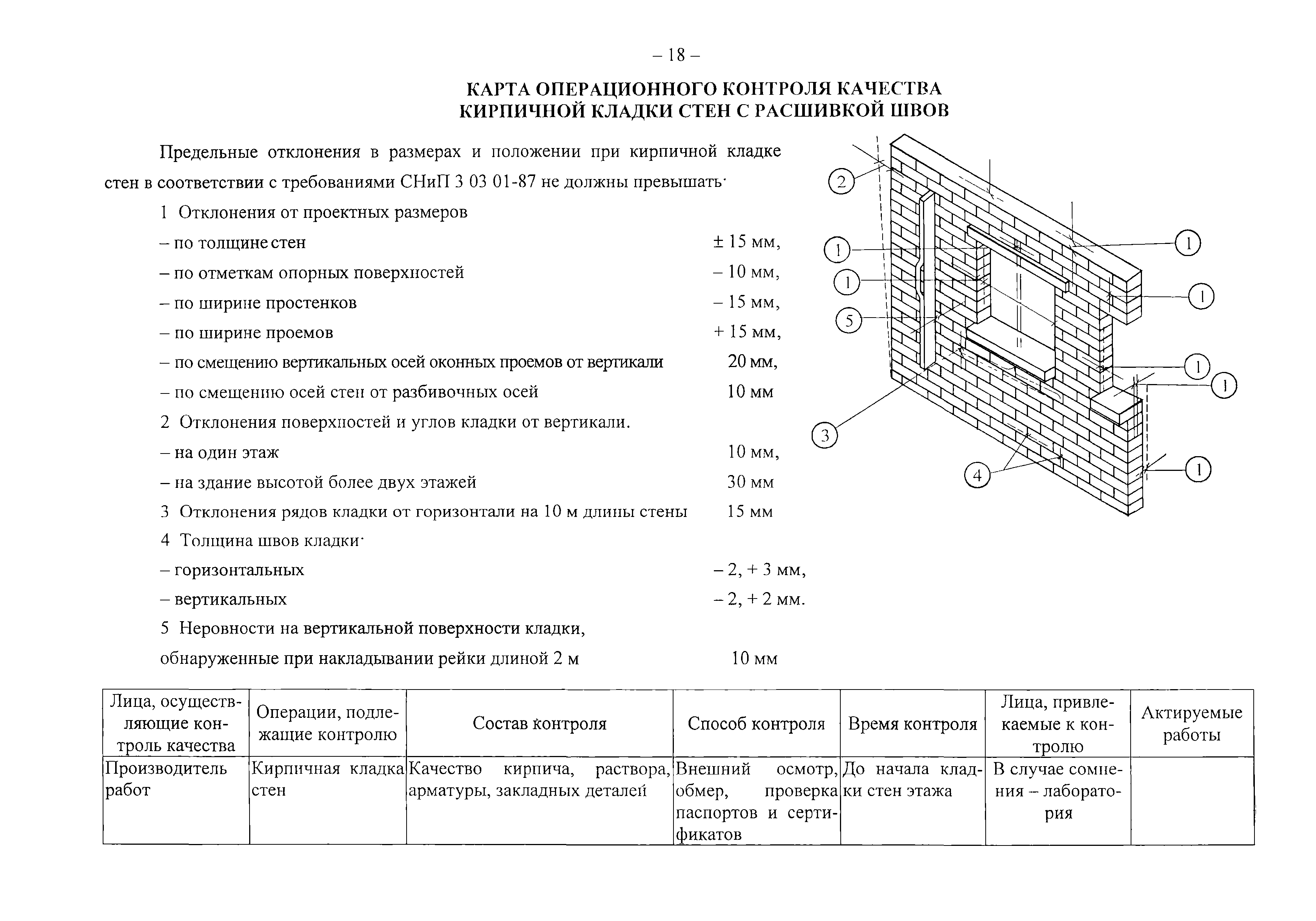
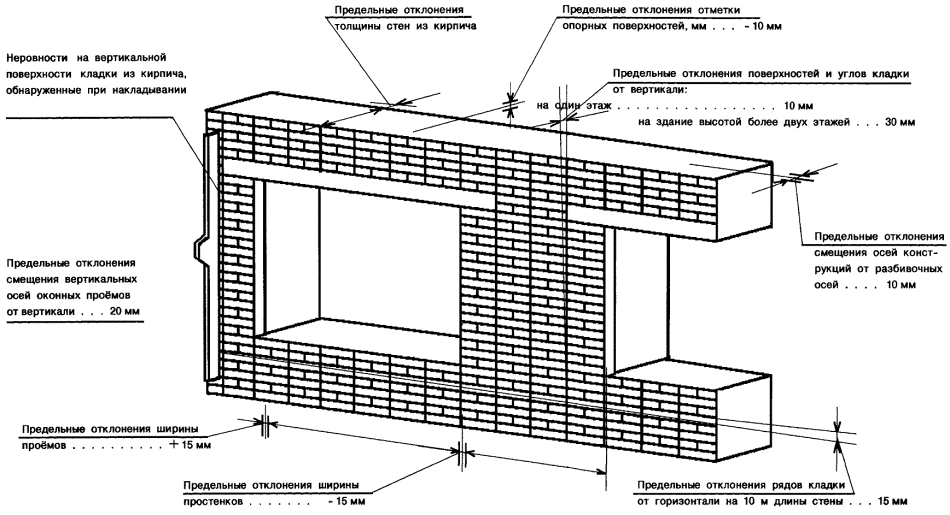
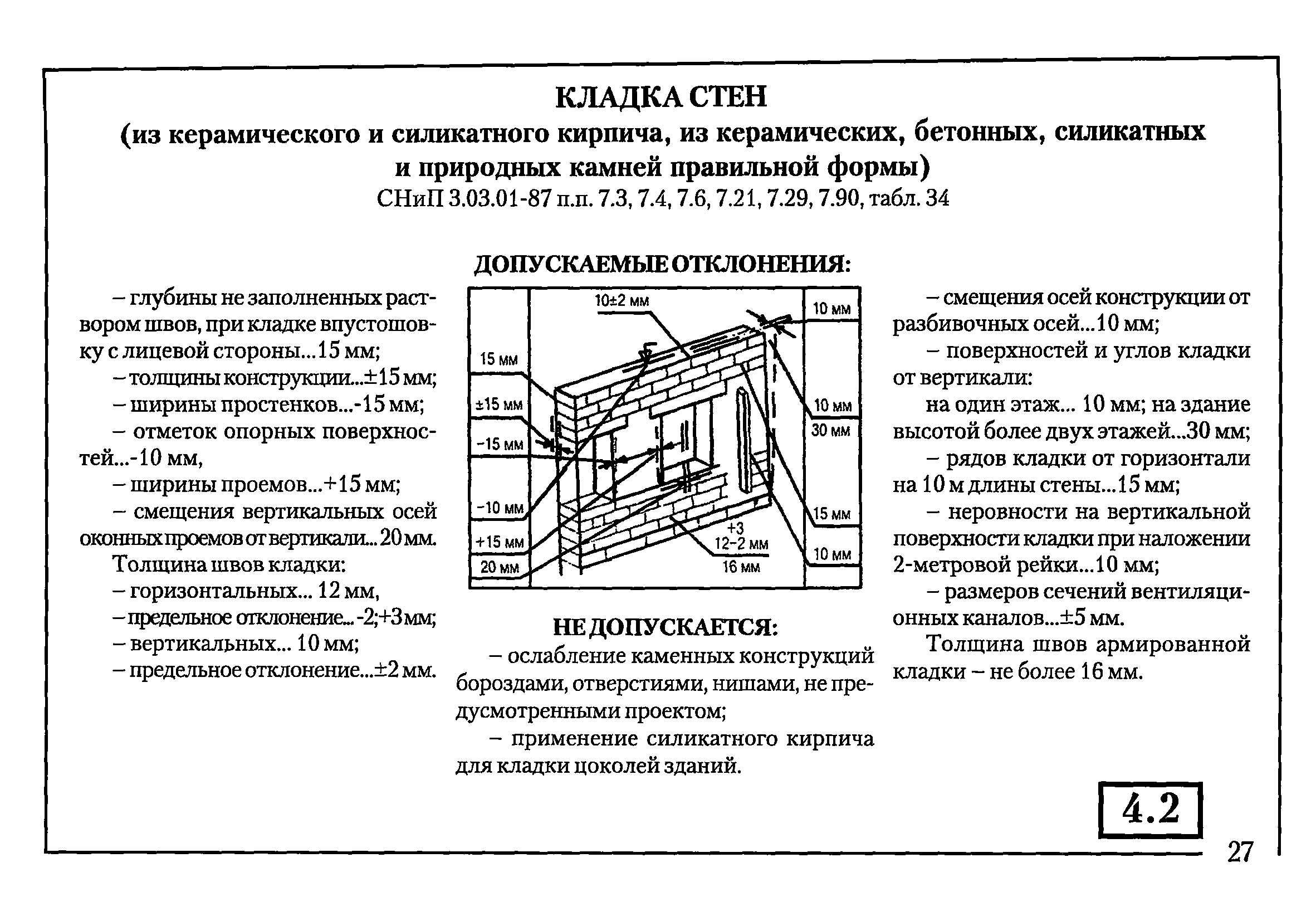
Standardization of masonry dressing systems and brick sizes contributes to the standardization of masonry sizes. In the case of masonry walls without insulation or air spaces, the dimensions of the walls correspond to the modular dimensions of the brick edges and the normalized thicknesses of the masonry joints. When designing the dimensions of brick columns, walls and wall thicknesses, it is customary to consider the width of the vertical masonry joint equal to 10 mm (in practice, 8-12 mm). In this case, two bricks laid with a poke make up a masonry section equal to the length of a brick laid with a spoon (120 mm + 10 mm + 120 mm = 250 mm).
Consequently, the dimensions of the brickwork in the plan can be 120, 250, 380, 510, 640, 770, 900, 1030 mm and more. There are also exceptions. Sometimes, brick partitions are made by laying bricks on the edge. In this case, the thickness of the partition is not 120, but 65 mm. Another exception is the aforementioned wall construction with an air gap or insulation. In this case, the dimensions of the brick wall depend on the thickness of the insulation or the void. The section thickness is made up of the modular size of the structural part of the wall, a facing layer with a thickness of 120 mm and the estimated thickness of the insulation.
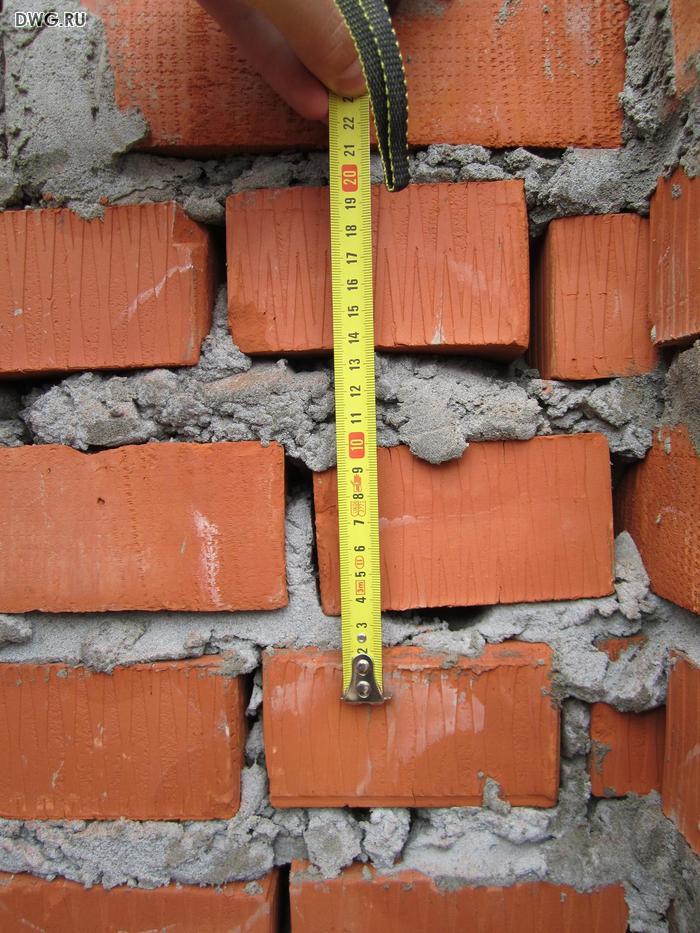
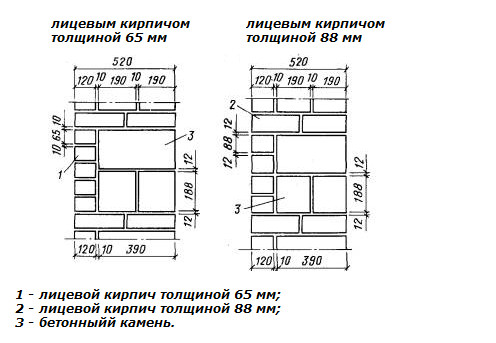
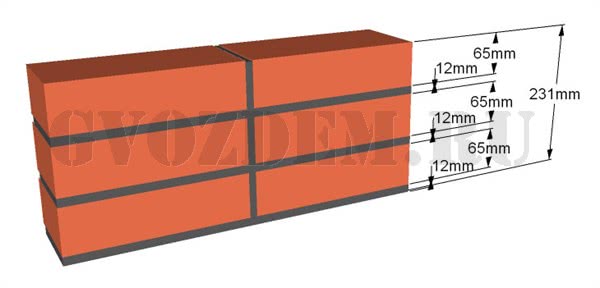
We figured out the dimensions of the brickwork in the plan. The vertical dimensions of the masonry are subject to the same laws, but with one caveat. In construction, two brick standards have been adopted. An ordinary brick is 65 mm high. There is also a thickened one with a height of 88 mm. When designing the heights of structures, the size of the brickwork seam between the horizontal rows is taken - 12 mm. In practice, 10-15 mm is allowed. When performing reinforced brickwork and when electrically heating the masonry, grids or electrodes are placed in the horizontal seams. Therefore, the size of the joints in winter brickwork is at least 12 mm. We get the height of walls, piers and columns from ordinary bricks - 77, 154, 231, 308, 385, 462 and further through 77 mm. For thickened (one-and-a-half) bricks - 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 and further every 100 mm. At the same time, 13 rows of standard bricks correspond to 10 rows of one and a half (1000 mm).
The dimensions of the brickwork openings are set depending on the installed window or door frames. Today, mass construction is focused on individual planning. Therefore, partitions and openings in them are erected after the sale of the apartment (house), taking into account the wishes of the owner. If, however, the size of the box is known in advance, the opening is made 20 mm larger. This guarantees high-quality installation of the frame (box) in the opening with subsequent sealing.
When performing masonry plans based on architectural drawings, it is necessary to bring the sketch dimensions to the constructive ones, taking into account the dimensions of the brick. In order not to calculate each time, the designer uses a table of brickwork sizes.
Rows (for vertical dimensions)
Vertical dimensions for standard bricks, mm
Vertical dimensions for thick bricks, mm
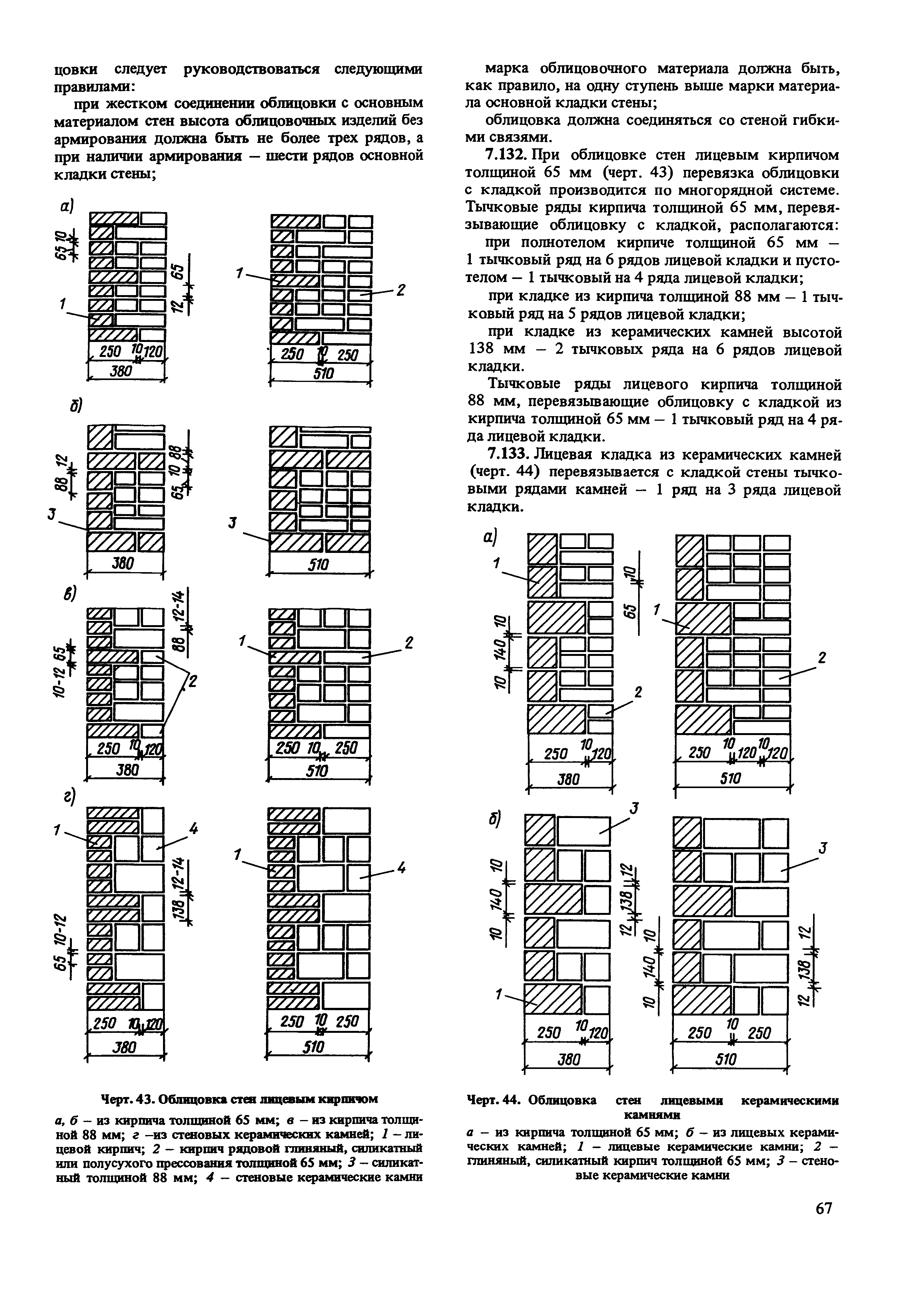
Recommendations for laying different types of bricks
Load-bearing walls and basement areas subject to frequent moisture influences are erected from solid ceramic bricks, most often of a single format. The optimal scheme in this case is considered to be a two-row one, it ensures an even distribution of weight loads, the total thickness is 25 cm. The products are recommended to be mounted after a thorough check of the evenness and waterproofing of the base and a visual inspection for damage. To eliminate errors, the first row is first placed without solution, in dry form, all non-formatted blocks are removed.
The thickness of the lowest layer can reach 20 mm, all subsequent ones are laid taking into account the design data. To make vertical seams, a little composition is applied to the butt side of the brick, after which it is slightly pressed against the previously installed blocks. Excess mixture in the longitudinal direction is immediately removed with a trowel, smooth movement from bottom to top
When performing horizontal rows, this is not recommended because of the risk of smearing the DSP on the surface, which is especially important when working with facing bricks. A special template helps to achieve uniform thickness without overspending, in the absence of experience it is used not only in the longitudinal, but also in the transverse direction
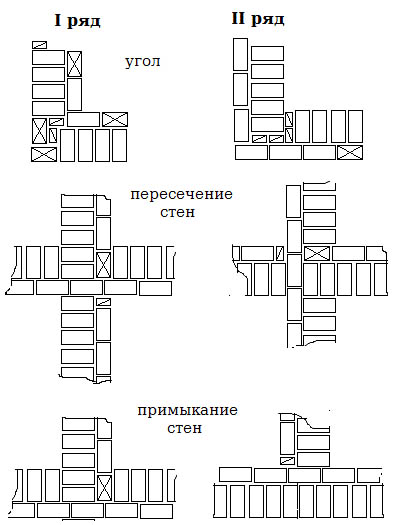
The construction of any structures begins from the corner, followed by the fixing of the order - a special bar for level control. Walls to be plastered or insulated are erected with wasteland - by sinking the mortar into the depth of 10-15 mm from the front side of the brickwork.
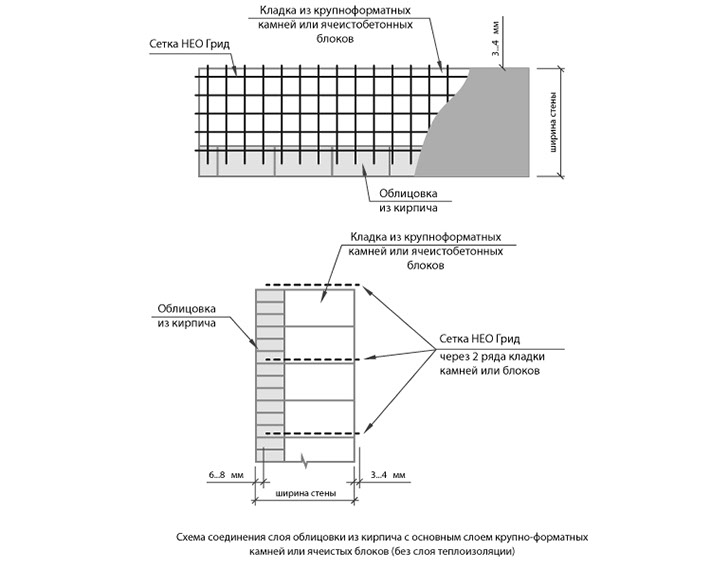
Multi-row heat-insulating systems are erected from porous ceramics with a fairly good strength grade. The general requirements for joint thickness and evenness remain unchanged, but due to the presence of voids, one should be prepared for an increase in mortar consumption. Changes also concern its composition, in order to exclude cold bridges in a standard DSP mixed in a ratio of 1: 3, additives that reduce thermal conductivity are introduced: expanded clay crumbs, foam glass and their analogs. The scheme in multi-row structures becomes more complicated, if in doubt in their abilities, the work is entrusted to specialists.
Ceramic and pressed sand-lime bricks, by analogy with the others, begin to be laid from the corner, with a careful level check and each row being dry. But due to the high requirements for decorativeness, the type of seam changes, it becomes concave or convex, grouting is carried out immediately. The second type is more often chosen when facing facades, such a jointing enhances the moisture resistance of the walls.
The nuances include the laying of small ventilation holes in the vertical seams, as a rule, on every 4th row. In the course of work, the front surface is protected from splashing solution, accidentally falling drops are removed with a dry cloth before they begin to set. The requirements for masonry and grouting mixtures depend on the degree of water saturation: ordinary ceramic varieties are wetted before installation, clinker ones are mounted dry, but only on special compounds with a minimum content of salt-drawing substances.
The value of the dressing during the erection of the structure
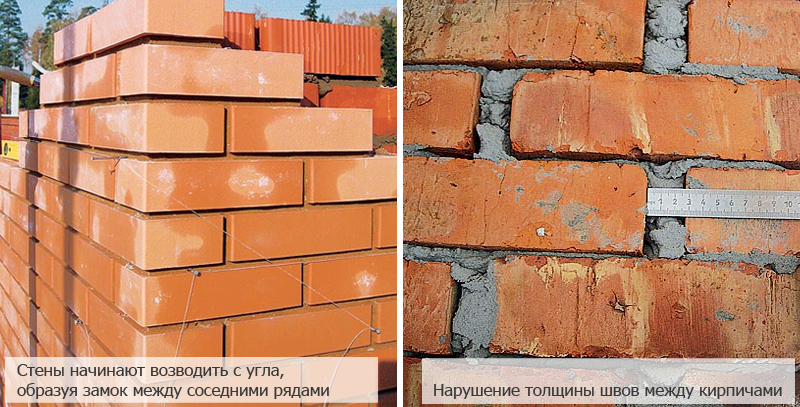
The safety of a building structure depends on its correct construction. Normal laying is carried out with the long side of the material, this method is called spoons, with the short side and across the wall - poking. The construction begins with the removal of the corners a few bricks higher than the usual structure. The layer formed between the masonry gets better, and the excess is removed until the mortar has hardened. Then jointing is carried out.
Main rules:
- When erecting a building, it is necessary to check the laying of the corners with a square at least twice over the course of 1 m of masonry.
- Check the horizontality of the rows (by the rule and the level), and the verticality of the surface of the corners (by the rule with the plumb line).
- It is better to align the arisen with the next row.
- The thickness of the mortar between the material should be measured every 5-6 rows.
What is joining for?
Now let's take a closer look at why this grout and trimming of seams in a brick house is needed, because many buildings stand for years and no one does anything with them.
- As we have already said, this has a beneficial effect on the aesthetic side of the house. For example, you can easily hide the difference in shade when the solution is mixed gradually over several days.
- Grouting brickwork joints reduces the amount of moisture that enters the joints, destroying the cementitious base.This allows you to extend the life of the entire house, postponing repair work into the distant future. If you do not know, then the price of brick wall restoration, when cracks and collapses appear, are very, very "unpleasant".
- Correct jointing also allows you to increase the insulating properties of brick walls, because it is the seams that are the main source of heat loss.
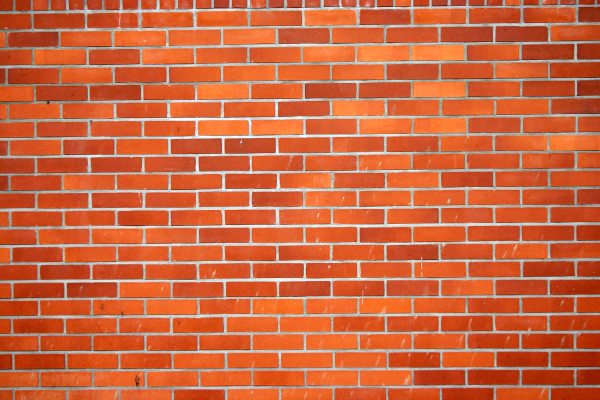

Wall after jointing - the seam is monochromatic, the bricks stand out clearly
Where is the jointing used?
Interestingly, both building bricks and double silicate brick M 150 are suitable for grouting (also suitable for decorative facing bricks).
The main thing is that the wall should not be plastered, because the jointing is an analogue of the finishing material, it is only applied to a certain part of the surface.
- It can be used for street walls, which is the most common option.
- It is also useful for interior work, when you need to add color to a decorative surface.
- The jointing can also be used for walls that are built from natural (natural) stone.
- You can embroider the masonry at any stage: directly when the walls are cocked, or after the house is built and shrinks. There is one fundamental difference - with joint joining and masonry, it is easier to remove excess mortar, which has not yet had time to dry. On a ready-made house, this must be done with effort, because the cement mortar is quite durable.
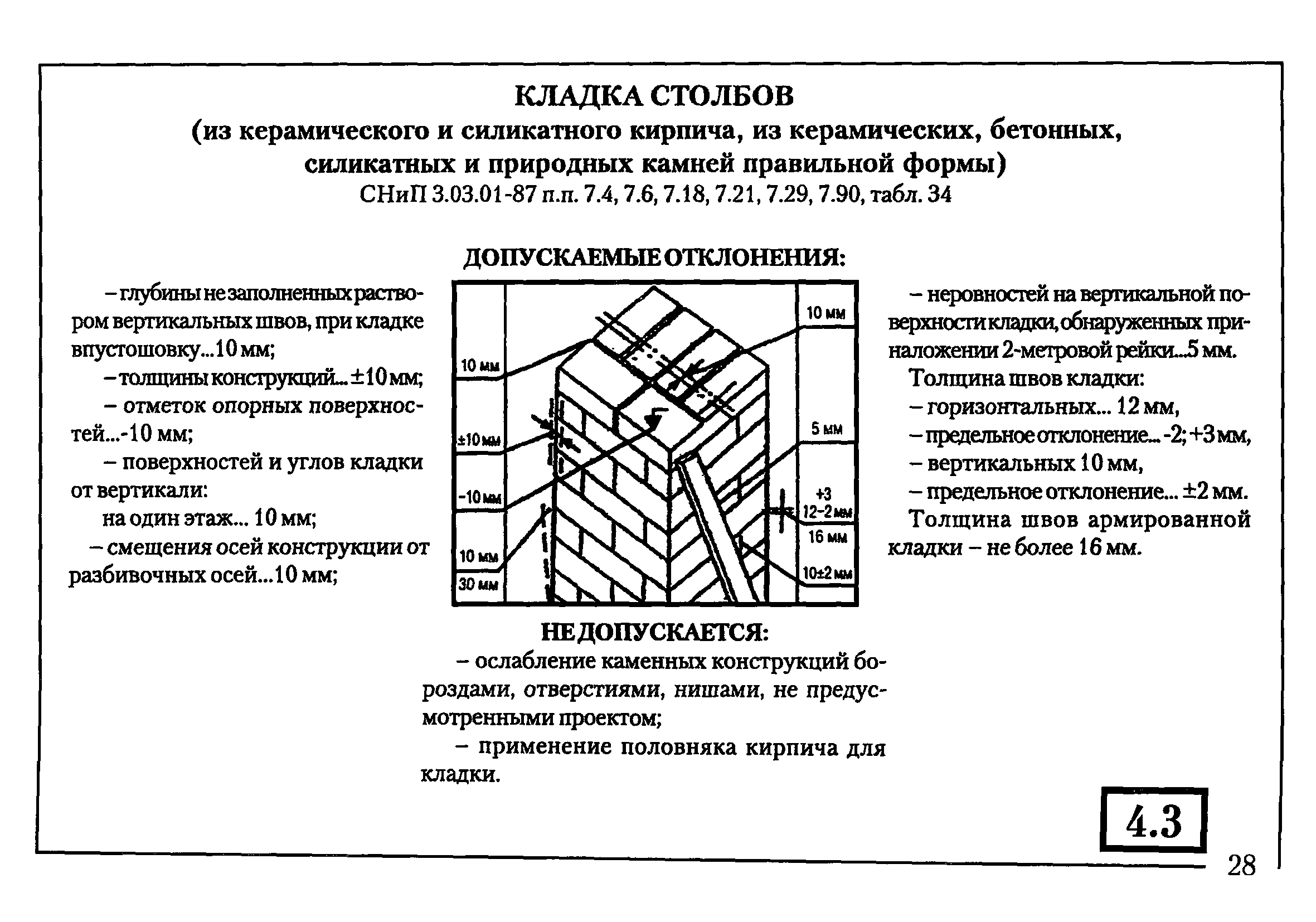
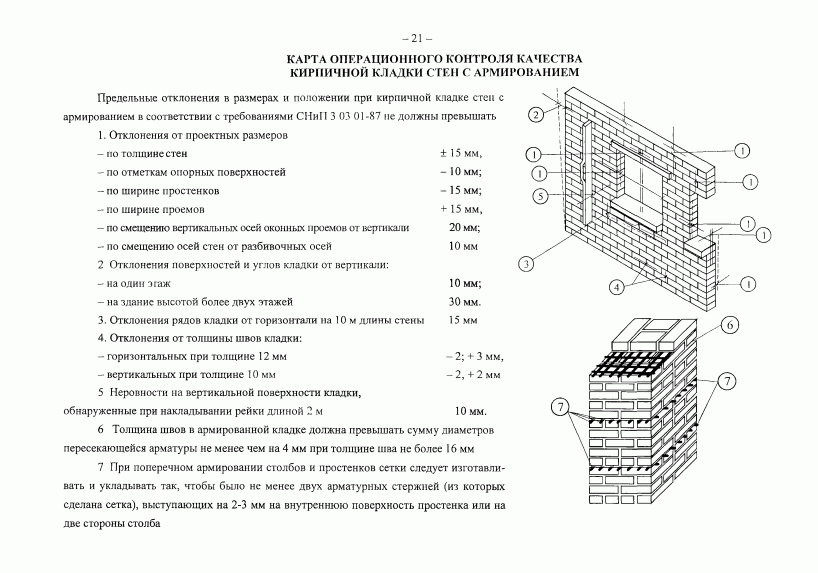
Factors affecting seam size
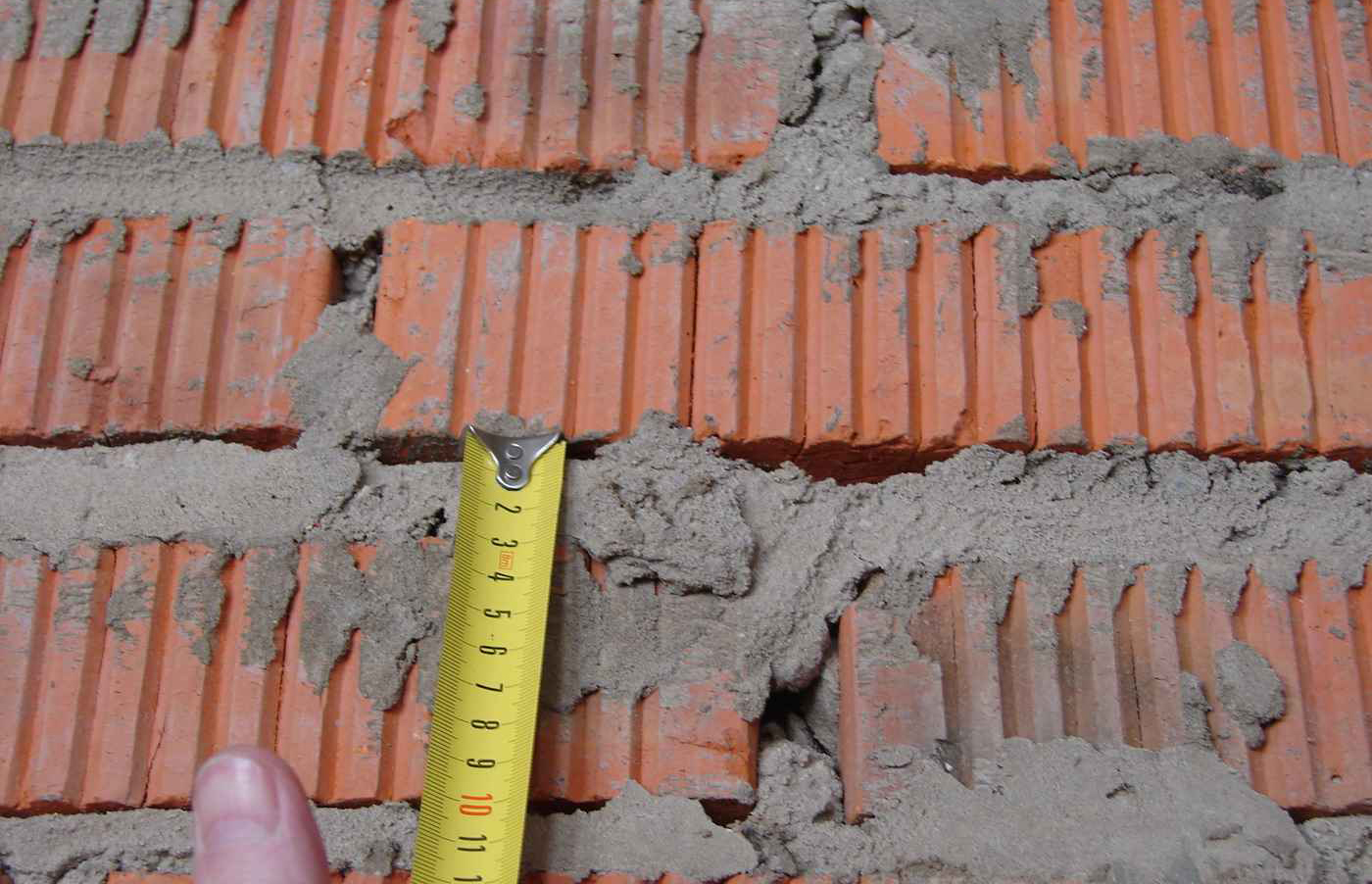
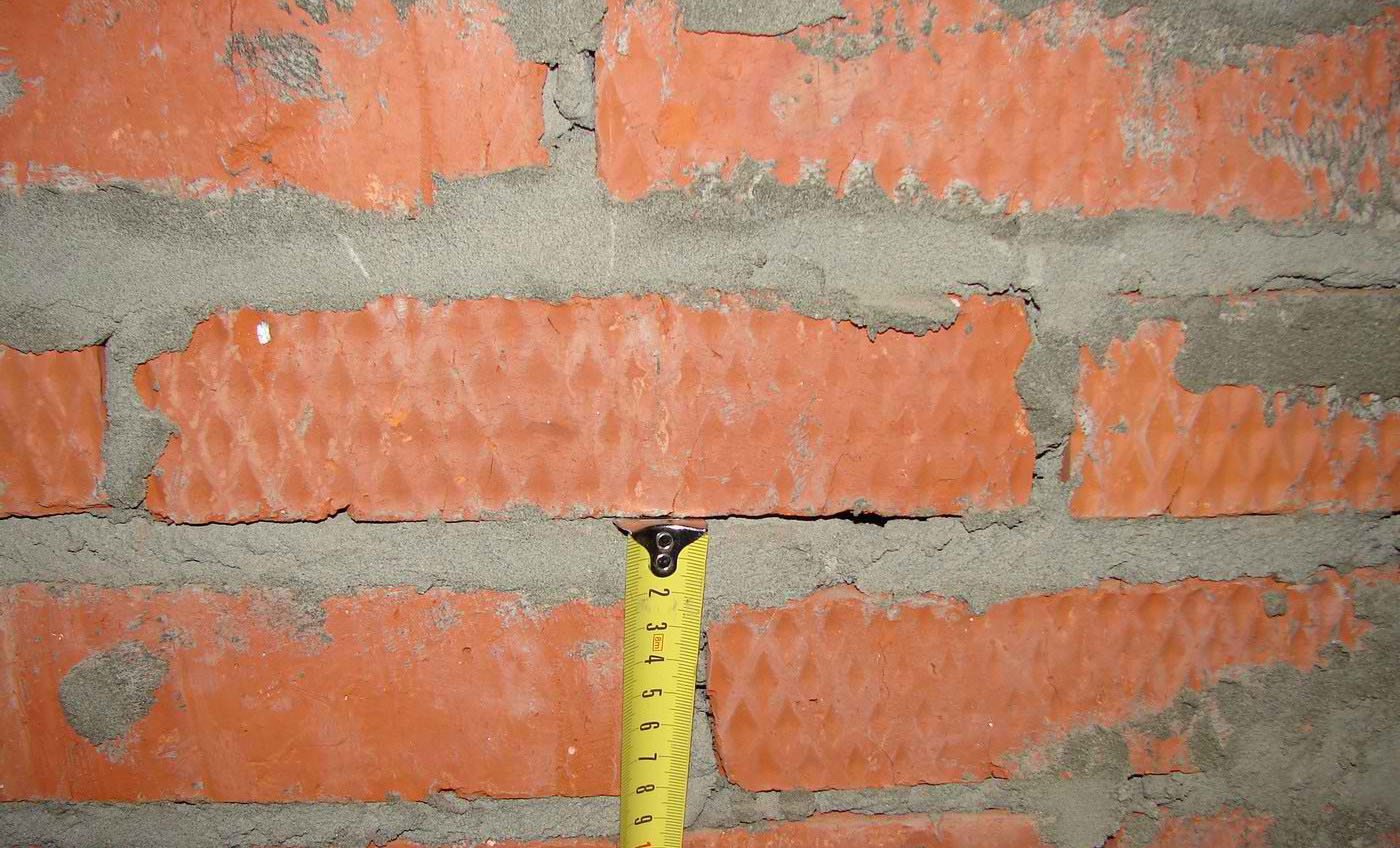
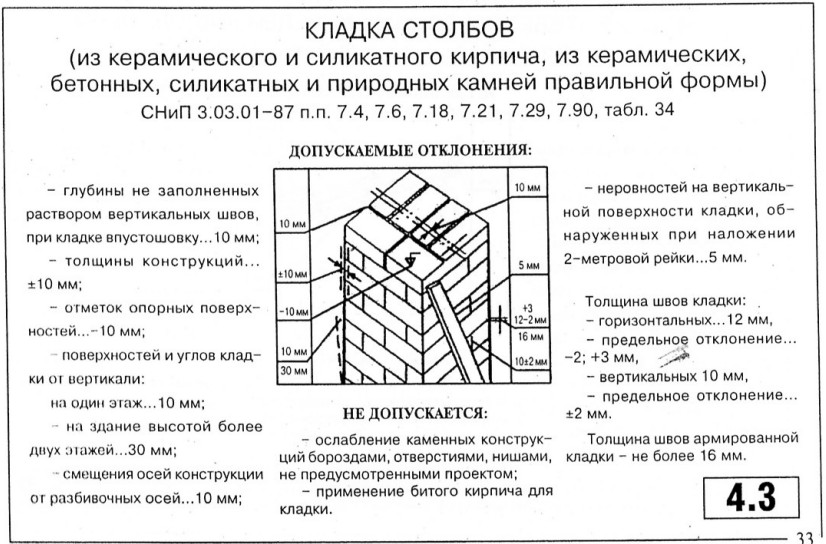
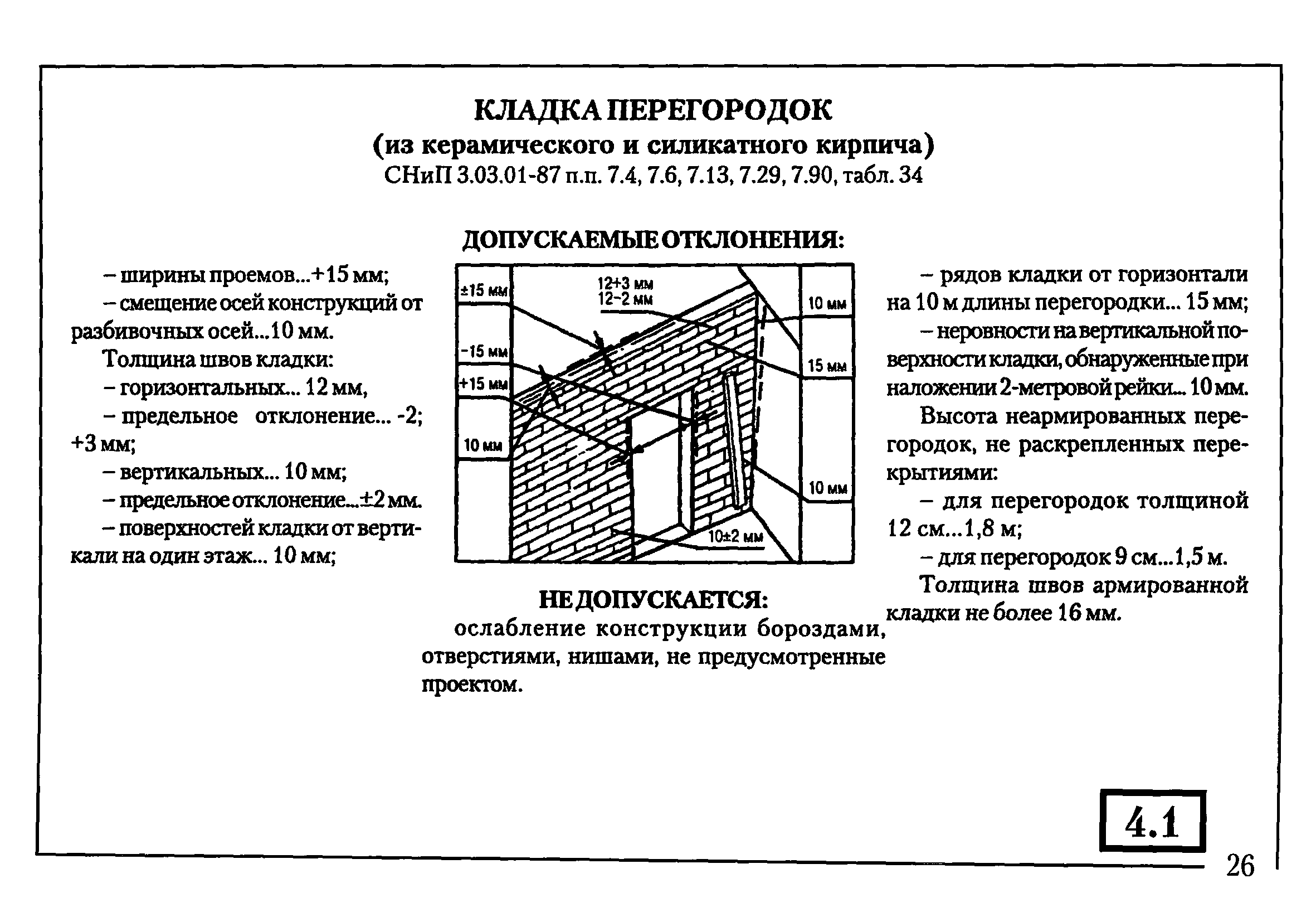
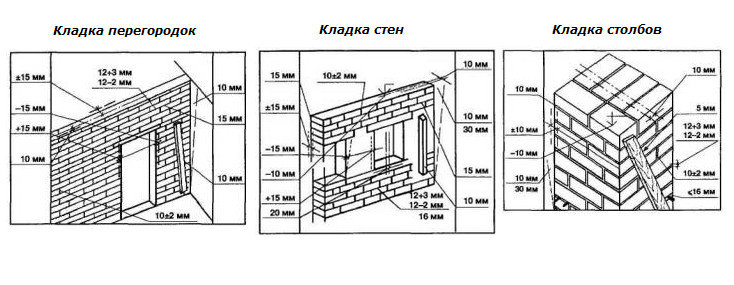
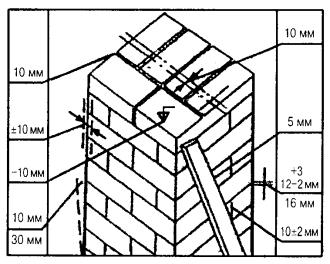
When erecting walls, adhere to the established average thickness of horizontal joints of 10 mm. This value varies by 1-2 millimeters in one direction and the other. More specific indicators of the thickness of the joints between bricks are determined in the approved building design and are strictly controlled.
Most bricklayers make a horizontal joint 12 mm thick and a transverse joint 10 mm thick.
Valid values are:
- in longitudinal rows 10-15 mm;
- in vertical rows 8-12 mm.
The reason for the decrease in strength is the uneven withdrawal of water from the solution.

The uniformity and thickness of the masonry joints depend on:
- The professionalism of the builders. It is better to entrust the work to specialized teams of bricklayers.
- The hardness of the solution. If a cement-sand composition of a thick consistency is used, a mortar thickness of up to 12 mm is allowed. When using plastic adhesives, this parameter can be 8-10 mm.
- Conditions of work. In winter, brick laying is carried out with the use of anti-frost additives or heating of structures. The size of the seam is best kept to a minimum, since at low temperatures the masonry is made more monolithic.
- The shape and size of the material. Brick, as the most common building material, is characterized by uneven surface and uneven dimensions, especially when using its cheap types. When erecting walls, experienced bricklayers adjust the width of the joint between the bricks to 2 mm, depending on the design data.
The accuracy of the brickwork also depends on the proportion of voids in the products, the frost resistance of the mortar and the grade of cement used.
The thickness of the mortar between the bricks is influenced by the consistency of the masonry composition. A properly prepared mixture fills all irregularities and voids, but only up to a certain thickness. If it is exceeded, the layer simply creeps along the sides, without filling the roughness, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of the masonry.
SNiP requirements
All building stones that are used in the construction of structures must be selected in accordance with the standards for various types of building materials, which also determines SNiP. Brick that is used for outdoor masonry must have a rectangular shape and clear edges. Each building stone is visually inspected by a master before laying.
It is also important to properly prepare the solution, which should have a mobility of no more than 7 cm.To ensure such parameters, it may be necessary to add various components to the cement mixture, including plasticizers, lime and chemical additives.
These components are introduced depending on the requirements of the manufacturer.
In winter, it is recommended to keep the temperature of the solution not lower than +25 degrees. If conditions do not allow adhering to such a temperature, then it is necessary to add plasticizers to the solution.
Also SNiP determines that it is prohibited to use building stones that do not have appropriate certificates, especially when erecting residential buildings.
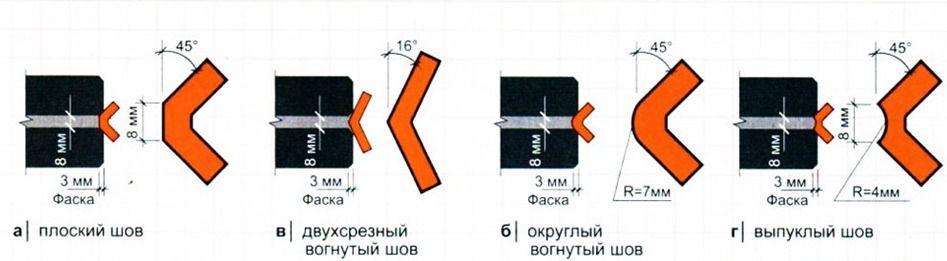
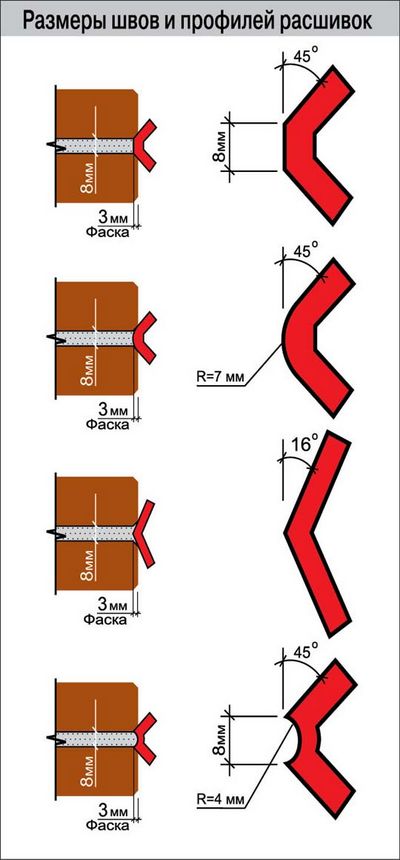
Masonry joint thickness
Needless to say, ceramic bricks are one of the most demanded building materials. Brick production technology, as well as various types of brickwork, have been known since time immemorial. How long a brick-built building will last depends not only on its quality, but also on the quality of the mortar, laying technology, the skill of the bricklayer and the thickness of the joints in the brickwork.
Although one of the parameters of the durability of a structure is the frost resistance of the brick (the ability to withstand a certain number of complete freeze and thaw cycles), corrected for the climatic coefficient, an incorrect joint thickness can completely destroy the entire calculation system.
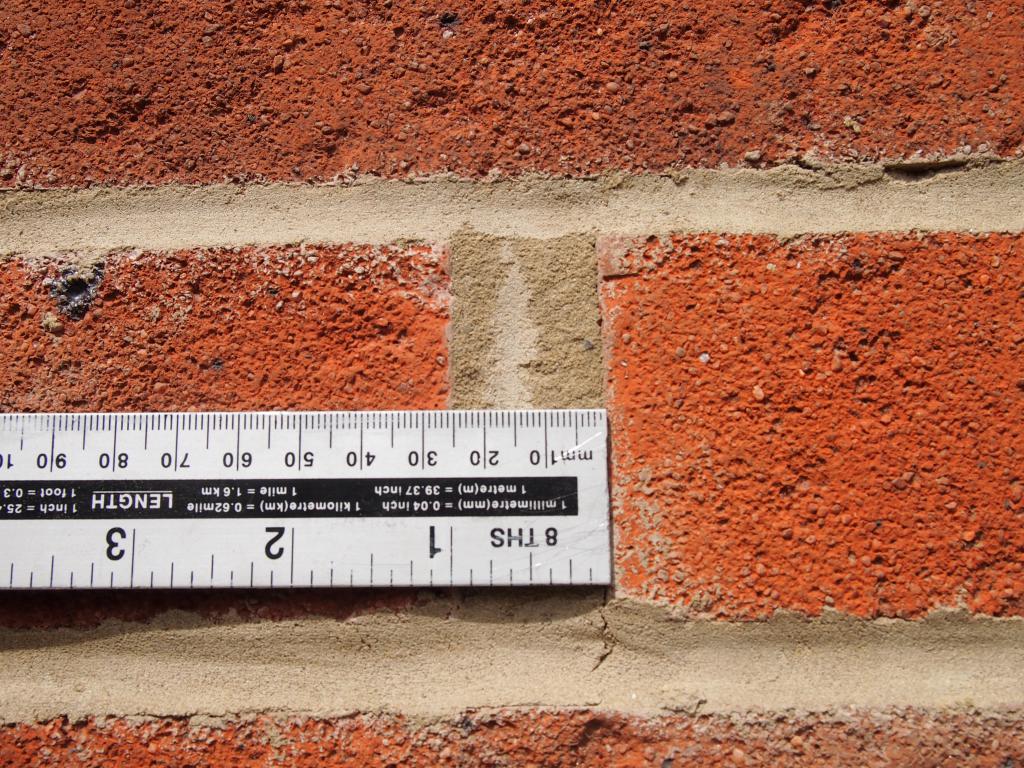
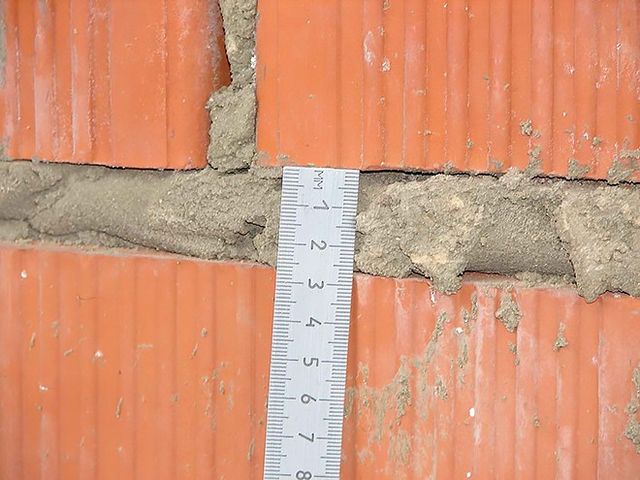
For masonry, the thickness of the horizontal joints should be 12 mm. In some cases, the minimum joint thickness is 10 mm, the maximum joint width is 15 mm.
The vertical seam should be 10 mm. The smallest possible vertical seam is 8 mm. The maximum width of the vertical seam is 15 mm. In any construction project, the thickness of the seams must be indicated. Without this indicator, it is very difficult to make a correct estimate for the construction of an object, since it is difficult to calculate the amount of cement, sand and even the amount of bricks. As soon as the bricklayer reduces the thickness of the joints by a couple of millimeters, the total amount of bricks may increase. As soon as the bricklayer increases the size of the joint, the strength of the building decreases.
The greater the thickness of the brickwork joint, the more difficult it is to achieve a uniform joint density between the bricks. Brick due to uneven density may experience additional bending and shear stresses. Thick seams in masonry lead to greater deformation. Therefore, for a certain type of masonry, the designers set a certain seam thickness. In addition to the types of masonry, the thickness of the joints is influenced by the climatic conditions in which the building will be used.
In addition, the thickness of the joints may vary depending on the weather conditions in which the brick is being laid. The thickness of the joint is especially important when the brick is laid in frosty conditions. With an increase in the thickness of the seam, until the setting of the solution occurs, moisture that is inside the solution can crystallize.
Simply put, the water in the solution will simply freeze. And as soon as the temperature rises, the ice will again turn into water, but instead of a strong seam, a kind of free-flowing substance will already be obtained. Therefore, the thickness of the seam of the brickwork when working in frosty weather should be as low as possible. In addition, various fillers are added to the solution, which play the role of antifreeze.
The thickness of the seams, with the right approach to technology, must be checked. To do this, measure the width of several rows of masonry (usually 5-6 rows). The resulting size is divided by the number of rows, the size of the bricks is subtracted, and the remaining figure is divided by the number of seams. The resulting average figure should not go beyond the limits prescribed in the building design.
In some cases, the seams may be as small as 5 millimeters thick. Usually this is a responsible refractory brick masonry, which is used in furnaces with a huge temperature.
Gas silicate, gas silicate blocks, aerated concrete, aerated concrete, autoclaved aerated concrete.All these names refer to the same building material - autoclaved aerated concrete.
Brick laying for jointing is used when no finishing materials will be applied to the surface of the brickwork, but the surface should look visually finished.
The characteristics of the building directly depend on the quality of the brickwork. In particular, the strength, thermal insulation and durability of the building as a whole depend on the quality of the masonry.
Vladimir Posts: 1
Average seam size Reply # 1 date: 10.24.2013 at 05:53:48
With your specified calculation of the average seam thickness, even abnormal seams can pass. Example: between six rows of bricks, the thickness of the seams measured at each seam is 8,19,23,7 - not a single seam complies with SNiP. We count according to your scheme: we measure 6 rows from brick to brick - 465, subtract the size of the brick - for example 65.465 - 65 * 6 = 75 divided by the number of seams - 5, 75/5 = 15, which is quite consistent with SNiP. Those. non-standard seams with this calculation turn out to be within the framework of SNiP.
Fields marked * required. HTML tags are disabled.
House exterior wall thickness
In terms of the load-bearing part, the thickness of the outer wall of an individual house of 25 cm will cope with its task completely, but solid brick, in addition to its excellent qualities, has its drawbacks. One of the disadvantages is good thermal conductivity. In short, if you build a house with insufficient external brick thickness and without additional insulation, then at negative temperatures in winter the walls in the house will start to get wet.
What to do in this case?
Increasing the wall thickness of an individual building
If you try to increase the thickness of the wall, it turns out that it should be 0.64 m., I.e. 2.5 bricks based on the maximum winter temperature of -30 ° C. Considering that the specific gravity of brickwork is very large, a massive foundation for a house is needed under such a wall, which would withstand such a load, and this is a huge cost, and the brick itself is not the cheapest building material.
Using hollow brick for brick wall
In the masonry, you can use the so-called hollow brick, which will reduce the thickness of the wall of an individual structure due to voids, with the help of which its thermal conductivity will decrease.
Using insulation inside the wall of an individual house
The use of additional material for insulation inside a brick wall is ideal in this case, which is very popular and has a lot of advantages. Today, the construction of walls of a brick house without insulation is not advisable, and is practically not used in modern construction.
The cake of such a wall looks like this:
The outer part of the wall is 0.5 bricks thick, i.e. 12 cm. - insulation, the thickness and type of which is selected taking into account climatic conditions. - the inner part of the wall, to ensure the bearing capacity, from bricks 25 cm thick or blocks.
The choice of this method of erecting brick walls of an individual house will solve several problems at once:
Reducing foundation costs - reducing brick costs - increasing the area of the house, by reducing the thickness of the wall
Anyway, living in an individual brick house is a pleasure. Such a house will never lose its popularity, because, with a properly laid foundation, such a house will stand for "eternity".
Greetings to all readers! What should be the thickness of the brick exterior walls - the topic of today's article. The most commonly used small stone walls are brick walls. This is due to the fact that the use of bricks solves the issues of creating buildings and structures of almost any architectural form.
Starting to carry out a project, the design firm calculates all structural elements - including the calculation of the thickness of the brick exterior walls.
The walls in the building have different functions:
-
If the walls are only a building envelope
- in this case, they must meet the thermal insulation requirements in order to ensure a constant temperature and humidity microclimate, as well as have sound insulating qualities. -
Load-bearing walls
must be distinguished by the necessary strength and stability, but also as enclosing, have heat-shielding properties. In addition, based on the purpose of the building, its class, the thickness of the bearing walls must correspond to the technical indicators of its durability and fire resistance.
The size of the joint between bricks
The correct choice of the brickwork method describes the strength and quality of the object being built, the consumption in, as well as the cost and duration of the construction work.
An important role in ensuring the properties of the structure under construction is played by the brick ligation itself.

The fact is that such masonry implies the presence of vertical and horizontal joints, which are filled with cement. It acts as a connecting component that connects individual blocks to each other into a single structure.
Proportions
Preparation of mortar for brickwork implies compliance with certain proportions in each specific case.
This ratio of the initial components depends on the number of storeys of the structure being built, the type of structure being built, the composition and type of soil, as well as some other parameters.
Traditionally, the ratio of cement and sand is, and in some cases, this ratio can reach, depending on the construction features of the structure under construction and the brand of the cement itself.
Water takes up approximately 0.8 parts to one part dry cement.
2. The hardness of the solution and the chosen design. When placed in the press, thick, durable cement-sand consistencies are used, the thickness of the seam is very likely - 12 mm.
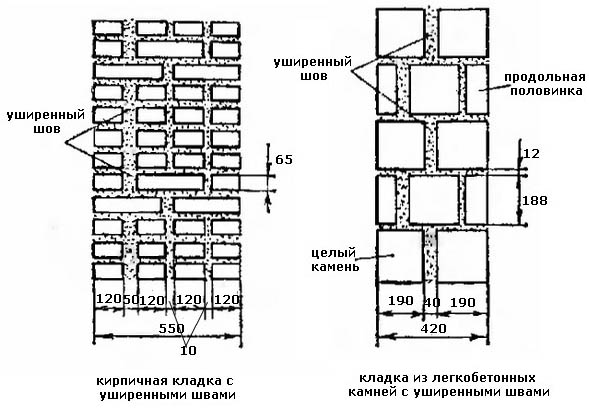
When using the most watery and plastic compounds (flush and with undercut), the products should be laid as closely as possible. The distance between adjacent elements in this case does not exceed mm.
The thickness of the lowest layer can be up to 20 mm, all the following are laid taking into account the design data. To make vertical seams, little composition is applied to the butt side of the brick, after which it is slightly pressed against the previously installed blocks.
After checking the level and carefully adjusting (if necessary), the elements cannot be moved until the start of setting, after a couple of rows it is recommended to take a break.
In the case of the release of the last rows of bricks, the vertical seam is moved apart or shifted by 2 mm in one direction or another.
At the same time, 13 rows of ordinary brick corresponds to 10 rows of one and a half (mm).
Gas silicate, gas silicate blocks, aerated concrete, aerated concrete, autoclaved aerated concrete.
All these names refer to the same building - autoclaved aerated concrete.
On the practical side, the greater the thickness of the joint between the bricks, the more difficult it is to achieve the uniformity and density of the solution between the blocks. Wide seams can contribute to unnecessary deformation. Each certain type of masonry corresponds to a certain mortar thickness. The climatic conditions in which the operation of the structure under construction is planned are also taken into account when determining such an indicator as the thickness of the joints between individual blocks.
There are many examples when it is required to maintain the thickness of the joints in strictly defined parameters in order to ensure the required strength of the masonry.