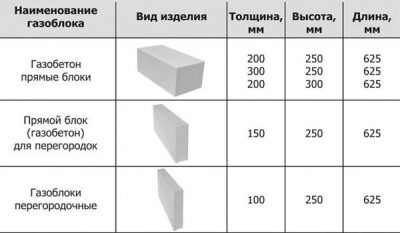
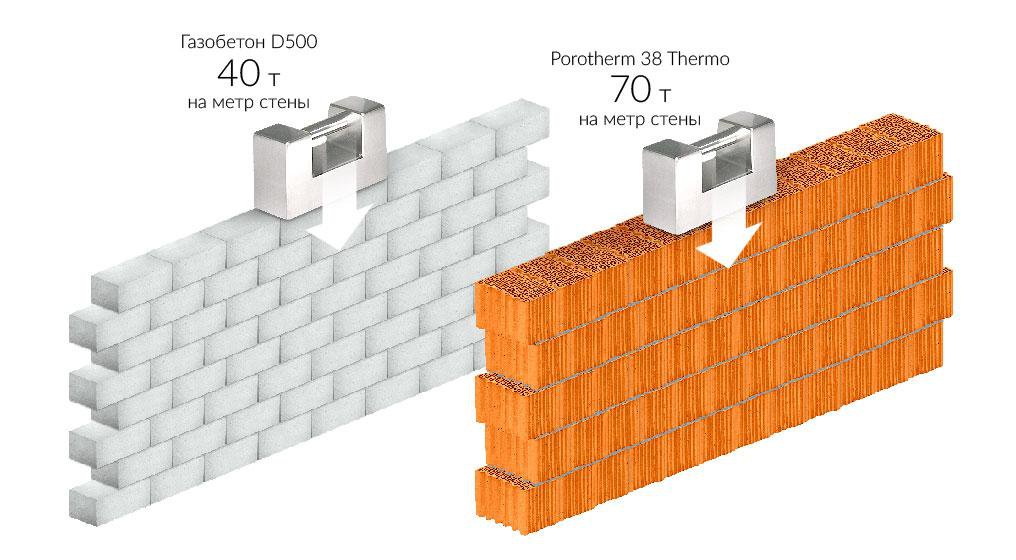
Soundproofing
Airborne noise is propagated by sound waves, which, meeting the enclosing structure (for example, walls or ceilings), are partially reflected, partially absorbed and partially passed through it.
Sound insulation - reducing the sound pressure level when a wave passes through an obstacle. The effectiveness of the enclosing structure is assessed by the airborne sound insulation index Rw (averaged over the range of frequencies most typical for housing - from 100 to 3000 Hz), and overlaps - by the index of reduced impact noise under the overlap Lnw... The more Rw and less Lnw, the better the soundproofing. Both quantities are measured in dB.
The soundproofing ability of the enclosing structure depends both on the material (density, porosity and modulus of elasticity) and on the applied design solution.
Sound absorbing materials have a porous structure. In this case, when a sound wave passes through the thickness of the material, it brings the air trapped in its pores into oscillatory motion, small pores create more resistance to air flow than large ones. The movement of air in them is inhibited, and as a result of friction, part of the mechanical energy of the sound wave turns into heat and it weakens.
The sound absorption property of a material is characterized by its sound absorption coefficient (α), which is the ratio of the absorbed sound energy to the total energy incident on the material.
Sound absorption coefficient of some materials:
|
Building material / construction |
Sound absorption coefficient (α) at a frequency of 1000 Hz |
|
Open window |
1,0 |
|
Autoclaved aerated concrete |
0,2 |
|
Wood |
0,1 |
|
Brick |
0,05 |
|
Concrete |
0,02 |
Fire resistance
The fire hazard of building materials is determined by the following fire-technical characteristics: flammability, flammability, flame spread over the surface, smoke-generating ability and toxicity.
The fire resistance of a building structure is the time from the beginning of the thermal effect on the structure until the moment when it loses its ability to retain its properties.
The indicator of fire resistance is the fire resistance of a structure, which is set by the time (in minutes) of the onset of one or several sequentially normalized for a given structure, signs of limiting states: loss of bearing capacity (R); loss of integrity (E); loss of thermal insulation capacity (I).
Autoclaved aerated concrete is an inorganic material belonging to the category of non-combustible building materials (NG), capable of withstanding one-sided exposure to fire for 3–7 hours and protecting metal structures from direct exposure to fire.
Numerous tests have shown that when the temperature rises to 400 ° C, the strength of autoclaved aerated concrete increases by 85%, with a further increase in temperature to 700 ° C, the strength decreases to its original value. The structure of a building made of autoclaved aerated concrete after a fire remains unchanged, and to eliminate the consequences of a fire, only the renewal of surface coatings and interior decoration is required.
Autoclaved aerated concrete structures meet DIN 4102 fire resistance requirements.
Firewalls (firewalls) made of autoclaved aerated concrete have the following fire resistance limits for different thicknesses:
|
Purpose of the wall |
Firewall thickness |
||
|
100 |
150 |
200 – 400 |
|
|
Fireproof curtain wall |
EI 120 |
EI 240 |
EI 240 |
|
Fireproof load-bearing wall |
– |
REI 120 |
REI 240 |
|
Load-bearing wall inside the fire compartment |
– |
R 120 |
R 240 |
- R is the bearing capacity;
- E - structural integrity;
- I - heat insulating ability.
Monolithic walls made of autoclaved aerated concrete and building structures (in conjunction with metal structures or as cladding) have high fire resistance and, therefore, are ideal for fire walls (firewalls), ventilation and elevator shafts. Due to the low thermal conductivity, the wall made of autoclaved aerated concrete heats up weakly, even when in contact with an open fire, therefore fireplaces and stoves can adjoin such walls, and smoke and ventilation ducts can be laid inside the walls.
We summarize the advantages of autoclaved aerated concrete:
- Low heating rate
- No smoke and no toxic emissions
Regulatory Requirements
The construction of buildings using various concrete of the cellular group, which includes aerated concrete, is regulated by STO number 501-52-01-2007.
If we talk about the main points on the use of aerated concrete, then it should be noted:
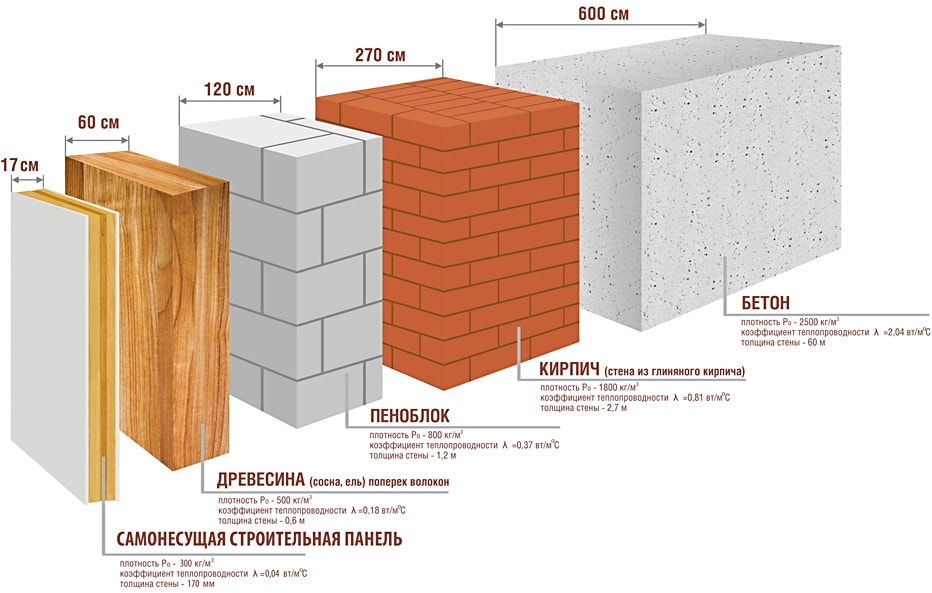
- Limiting the maximum height of buildings. From various categories of aerated concrete, it is possible to create load-bearing walls for buildings, the height of which is up to twenty meters (five floors). If we talk about the height of the walls of the self-supporting category, then it should not be more than nine floors or thirty meters. Foam blocks are used to create load-bearing type walls, the height of which is no more than three floors or ten meters.
- To create self-supporting walls, you need to use blocks of category B 2.5. If we talk about buildings where there are more than three floors, and B 2.0, if the buildings have a height of three floors.
- The normative document regulates the strength of concrete, depending on the number of floors in the building. If it is required to erect external or internal walls of a 5-storey building, then blocks with a strength of at least B 3.5 must be used, and the type of the mortar itself should not be worse than M100. If we talk about three-story buildings, then the class of concrete should be at least B 2.5, and the mortar - M75. And for structures with two floors - B2 and M50.
- This normative document also requires the calculation of the most permissible height of the walls made of the specified concrete only after calculations have been made.
It should be noted that this standard only regulates concrete strength issues, but does not give any explanations at all regarding the thermal insulation of the room. Legal entities must first of all comply with the requirements of regulatory documents. Individuals can use them only as a recommendation or guideline when building a garage, a country house or any other building.
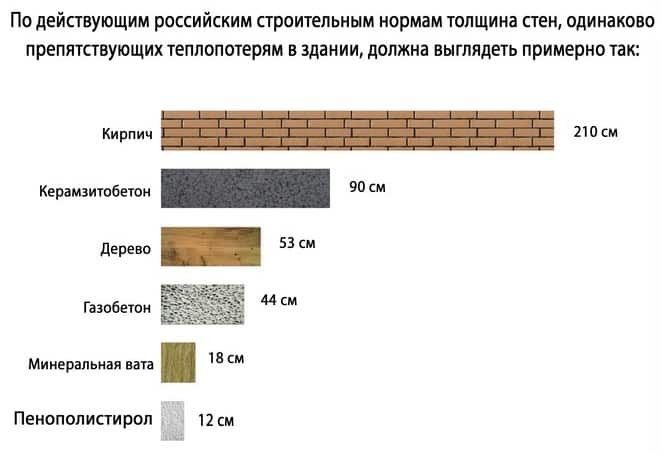
Wall thickness for different regions
It is better for a specialist who knows all the standards and requirements to take into account the peculiarities and nuances to calculate how thick the internal and load-bearing walls should be. Usually, when choosing a thickness, they are guided by the required indicators of heat conservation and strength. Basic calculations relate to load-bearing walls; internal non-load-bearing partitions can be made thinner.
General advice from the masters is as follows: for medium regions (in Moscow and the nearest cities), standard 40 centimeters of thickness are enough, in warm regions they take 30 centimeters as a basis, in cold regions - from 50 centimeters. But these are rather average indicators, it is advisable to focus on the most accurate calculations.
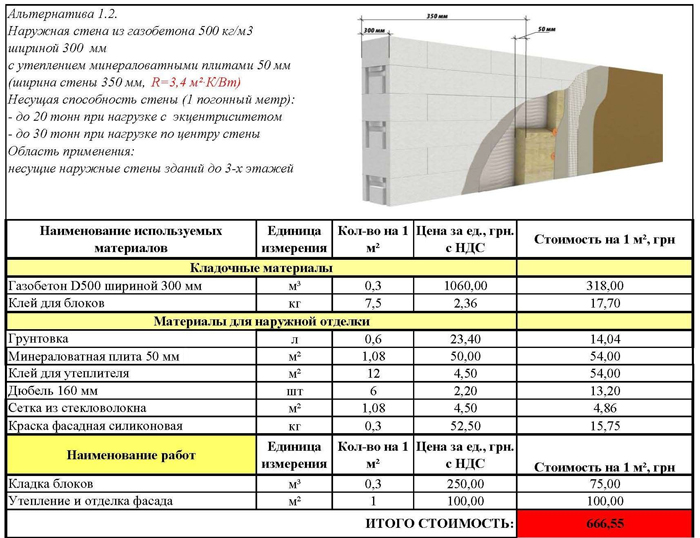
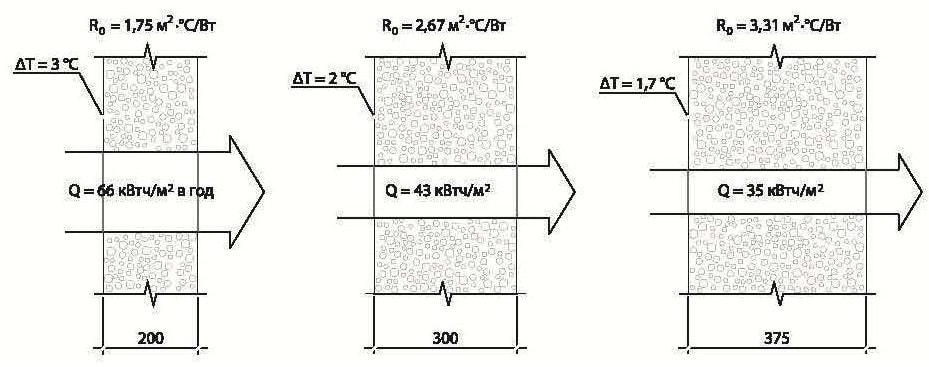
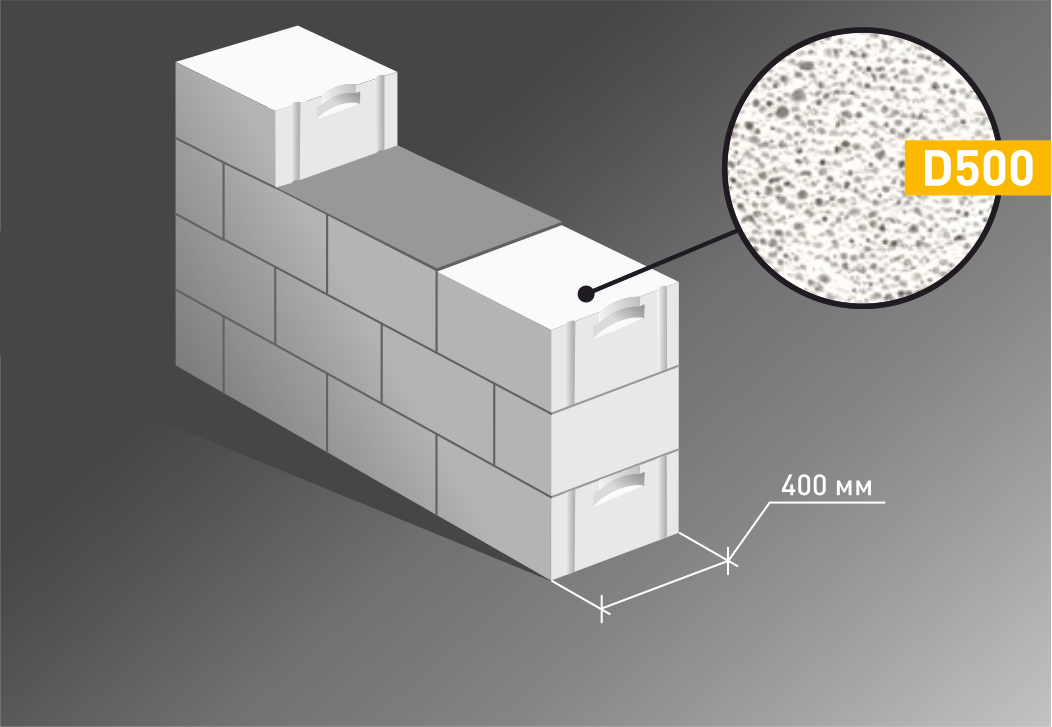
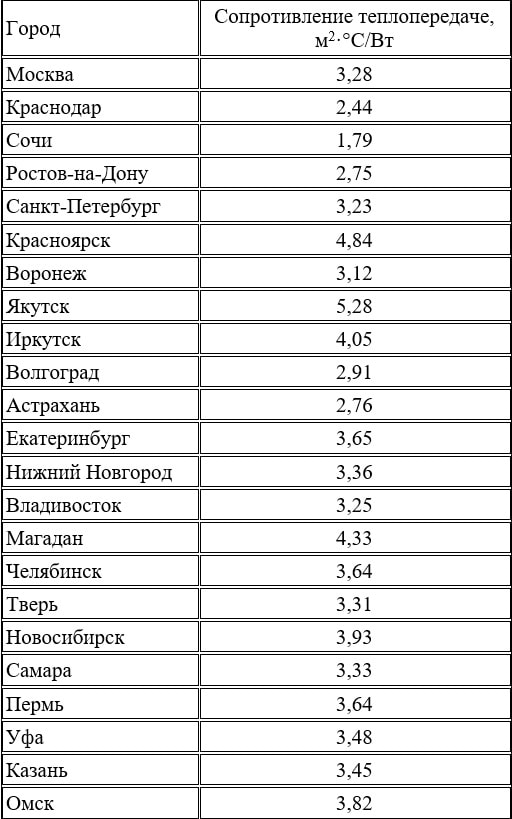
It is customary to take the following data as a basis: for central Russia, the resistance of walls to heat transfer, according to SNiP, should be equal to 3.2 W / m * C. For regions colder, the indicator is higher, respectively, warmer - lower. The required level of thermal protection (indicated in 3.2) is given by the following options: 30 centimeters of wall thickness from D300 blocks, 40 centimeters from D400, 50 centimeters from D500.
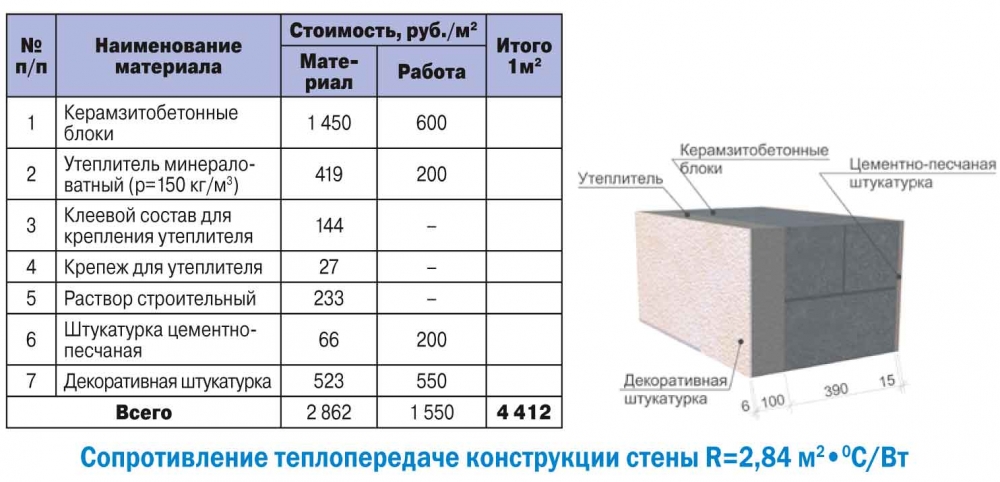
The general indicator of the thermal efficiency of a building is influenced by the thickness of the walls, insulation (not only of walls, but also of ceilings, roofs, floors, armored belts, windows, lintels). The building loses about 30-40% of its heat through insufficiently thick walls. For houses with permanent residence, the optimal choice is the choice of D400 / D500 blocks and wall thickness up to 40-50 centimeters.A country house can be built from D400 blocks with a wall thickness of 25-30 centimeters.
If you plan to insulate the walls, then they can be thinner.
Here it is important to get in the end a proper indicator of thermal protection, based on the values of aerated concrete and the selected insulation (foam plastic, mineral wool, etc.) can act as it. Thus, the cost of insulation increases, but the cost of aerated concrete decreases.
The higher the thermal protection value of the material, the better. Indicators are shown in the table:
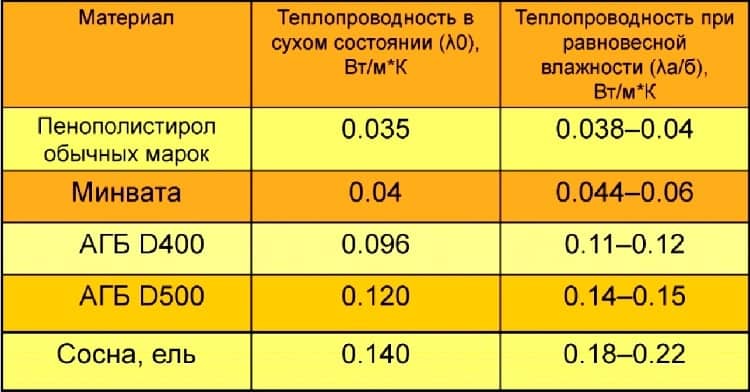
This is a table with coefficients of different brands (the rule works here the lower the better):
To understand the algorithm for performing calculations, you can consider the following example. If you want to build a house in Moscow and the surrounding area, the thermal resistance should be R = 3.28. D500 is used with a thickness of 30 centimeters, insulation is used.
How to find the required parameter:
- The thickness of the aerated concrete wall (0.3 meters) is divided by the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the D500 brand (0.14) - the thermal resistance of the bare wall is R = 0.3 / 0.14 = 2.14 m2 * C / W.
- The resulting indicator must be subtracted from the desired value: 3.28-2.14 = 1.14. This is the thermal resistance of the insulation.
- Mineral wool, for example, has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.04. If you multiply 0.04 by 1.14, you get the desired insulation thickness: 0.04x1.14 = 0.0456 = 45 millimeters = 4.5 centimeters. That is, the thickness of the insulation with walls of 30 centimeters should be about 5 centimeters.
Knowing the standard values, you can easily perform calculations for any brands of aerated concrete blocks and types of insulation.
Calculation of aerated concrete blocks and glue
| ROOM PARAMETERS: | |
| Wall height (m): | |
| External walls: | |
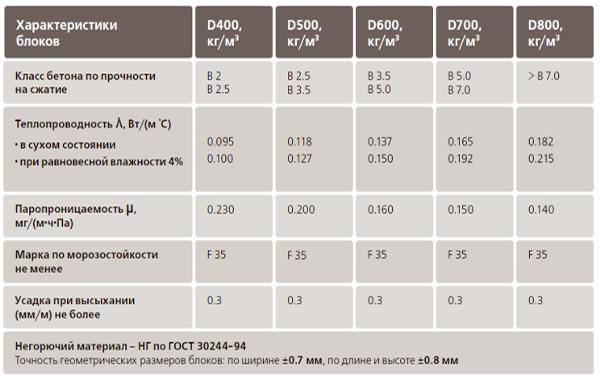
| Density class: | D350D450D500D600D700 |
| Wall length (perimeter) (m): | |
| Wall (block) thickness *: | 100 mm. 150 mm. 200 mm. 250 mm. 300 mm. 375 mm. 400 mm. 500 mm. |
| Area of door and window openings (m2): | |
| PARTITIONS: | |
| Density class: | D600D700 |
| Partition wall length (perimeter): | |
| Partition wall thickness: | 50 mm. 75 mm. 100 mm. 150 mm. 200 mm. |
| Area of door and window openings (m2): | |
| Total for the premises: | |
| APPROXIMATE VOLUME OF BLOCKS: m3 |
|
| VOLUME OF PARTITIONS: m3 |
|
| QTY BAGS OF GLUE **: PCS. |
|
|
* - wall thickness according to the project ** - glue consumption: 25kg per 1m3 of aerated concrete blocks with an adhesive layer thickness of no more than 3mm and a block size of 600x375x250. |
Partition wall thickness
This parameter is selected taking into account certain factors, while the bearing capacity is calculated and the height of the partition is taken into account.
When choosing blocks for such walls, you should pay close attention to the height value:
- if it does not exceed the three-meter mark, then the optimal wall thickness is 10 cm;
- when the altitude value is increased to five meters, it is recommended to use blocks with a thickness of 20 cm.
If you need to get accurate information without performing calculations, you can use the standard values, which take into account the mates with the upper floors and the lengths of the walls being erected.
Particular attention is paid to the following tips:
- when determining the operational load on the inner wall, it becomes possible to choose the optimal materials;
- for load-bearing partitions, it is recommended to use blocks D 500 or D 600, the length of which reaches 62.5 cm, width - varies from 7.5 to 20 cm;
- the construction of conventional partitions implies the use of blocks with a density index of D 350 - 400, which improve the standard parameters of sound insulation;
- the sound insulation index fully depends on the thickness of the block and its density. The higher it is, the better the soundproofing properties of the material.
Related article: How to measure the area of walls in a room
If the length of the partition is eight meters or more, and its height is from four meters, then in order to increase the strength of the entire structure, the frame base is reinforced with a reinforced concrete reinforcing belt. In addition, the required strength of the partition can be achieved with an adhesive composition, with the help of which the masonry is carried out.
The thickness of the load-bearing walls without insulation for permanent residence
determines not only the strength and reliability of the structure, but also the cost of its maintenance. If you save on the thickness of the supporting structures, then this will require additional funds for their insulation and strengthening.Insufficient width will lead to freezing of aerated concrete and large heating bills. In addition, due to the temperature difference, there is a risk of condensation and the development of mold.
Proceeding from this, when choosing the parameters of the future home, you need to be based on factors such as heat and cold levels, air humidity and structural features of the building.
Calculation depending on the region of residence
When planning construction, the average temperature in winter and summer is taken into account
Maximum historical records are not taken into account. Even if the temperature reaches its peak values, it will not last long. In addition, the impact of natural disasters can be compensated for by household appliances: air conditioners, heaters and autonomous systems.
For northern regions, you should choose a wide material with low strength and thermal conductivity. The soil in such areas is characterized by stability and stability. The D300-400 models are the best option.
In places with mobile soil, preference should be given to blocks of high grades, as they must be resistant to shocks and seasonal movements. Depending on the seismic activity, it is advisable to stop at D600-1200 grades.
In addition, it should be remembered that in all cases, aerated concrete wall decoration is necessary. This material is fragile and absorbs moisture well. This expense item is included in any project.
Thermal conductivity
External walls protect the interior of the house from the effects of temperature extremes. At the same time, internal bulkheads also play a role in retaining excess heat and cold.

The blocks themselves are an excellent insulating material that does not need additional insulation. The lower the density of stones, the better they protect the house from external factors. At the same time, a directly proportional decrease in strength is observed. The d400-800 series models are the optimal choice for the construction of residential buildings, which are perfectly adapted for use in all climatic conditions.
An example of calculating thickness for the Moscow region
Large temperature drops are typical for Moscow and the region, which can vary within ± 40 ° C during the year. At the same time, extreme cold and heat can last for weeks. In such conditions, it is necessary to build houses from blocks that are able to withstand such influences. Knowing the value of the thermal conductivity of commercially available materials, you need to choose an equivalent equal to 40 cm with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.1.

Calculation for blocks D400
D400 outdoor units have an average thermal conductivity of 0.10 W / (m × ° C). Based on these indicators, the required thickness of stones should be at least 40 cm. In this case, the supporting structures will be able to protect the interior of the house from extreme temperatures for 10-15 days.
When choosing a product, one should take into account the cold bridges that form at the joints. Even a high-quality polymer solution gives a loss of 10%. Based on this, blocks of 48 cm should be used, followed by finishing with a thin layer of waterproofing. Such a solution will allow construction to be carried out quickly and inexpensively while achieving the proper level of quality and strength.
Calculation for blocks D500
D500 outdoor units have an average thermal conductivity of 0.12 W / (m × ° C). Based on these indicators, the required thickness of the stones should be at least 48 cm. Such a solution provides not only a good level of heat retention, but also the strength of the entire structure, the height of which can be 2 floors.
Since the value of 48 cm is the boundary limit, there is no margin left with this option. The solution is to use warm facade plaster, at least 5 cm thick. This will not only insulate aerated concrete, but also add resistance to temperature changes.
Calculation of the pile foundation
Select the type of grillage:
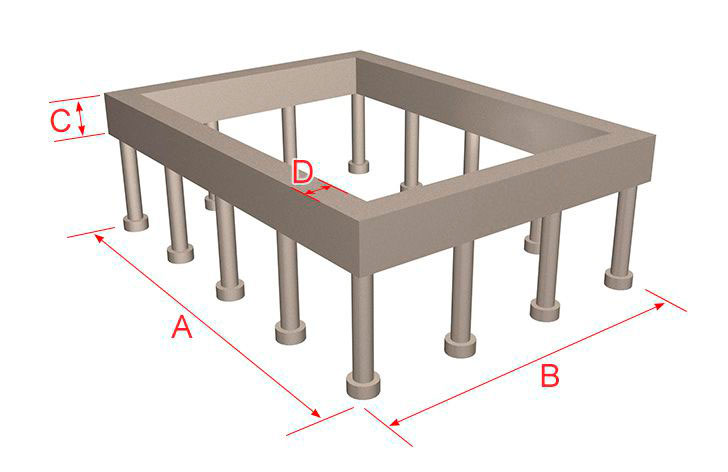
Grillage parameters:
Grillage width A (mm)
Grillage length B (mm)
Grillage height C (mm)
Grillage thickness D (mm)
Concrete grade
M100 (B7.5) M150 (B10) M200 (B15) M250 (B20) M300 (B22.5) M350 (B25) M400 (B30) M450 (B35) M500 (B40) M550 (B45) M600 (B50) M700 ( B55) M800 (B60)
Poles and piles parameters:
Number of poles and piles (pcs)
Column diameter D1 (mm)
Post height H1 (mm)
Post base diameter D2 (mm)
Post base height H2 (mm)
Reinforcement calculation:
Rebar length (m)
Calculation of the grillage formwork:
Board width (mm)
Board length (mm)
Board thickness (mm)
Calculate
Calculation of the thickness of the structure
The thickness of the external aerated concrete walls can, if desired, be calculated by yourself. You should take the standard indicator of the resistance to thermal transfer for a certain area and the thermal conductivity index of the block.
This figure can be calculated by multiplying these indicators by each other. To ensure comfort, the resistance to heat transfer must either be equal to or be greater than the figure of the nominated index, which is calculated by adding the coefficient of the degree-day of the heating period and the coefficient of normal time.

In addition, when the thickness of the aerated concrete wall of the bearing group is determined, the thermal conductivity index of the material is necessarily calculated, which directly depends on the density. The more it will be, the more will be its thermal conductivity.
If we talk about cottage construction, then M500 aerated concrete is most often used here. Such solutions are heat-insulating and structural. Models M600 also have high strength, which have high thermal conductivity, which indicates that they will release a lot of heat from the building.

For thermal insulation, it is excellent to use the M400 option. Here, the ratio of pores to total weight will be higher than 75 percent. This indicates that the material will keep warm well. But its strength will be significantly lower. According to the properties of thermal insulation, the best for creating aerated concrete exterior walls are D300 and D400 aerated concrete grades. Their thickness ranges from 20 to 45 centimeters. Despite these indicators, these materials contain a large number of air pores and little solution, which carries a load.
Aerated concrete of grades D800 and D1000 will be distinguished by the highest strength, but a large wall thickness (from 1 meter or more), necessary in order to retain heat inside the room. As a rule, such brands are used in the construction of trade pavilions and public buildings, as well as structures where there is additional insulation and a large load. But the golden mean, from which you can make interior and exterior walls, will be blocks D500-D600, which are usually used in the construction of cottages, residential buildings, as well as other buildings. They have the best balance in terms of strength and thermal conductivity.




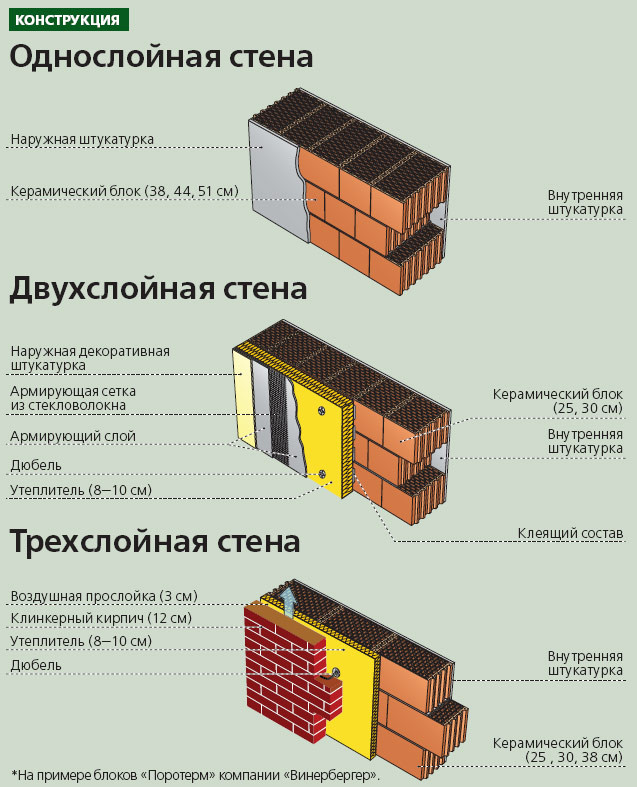
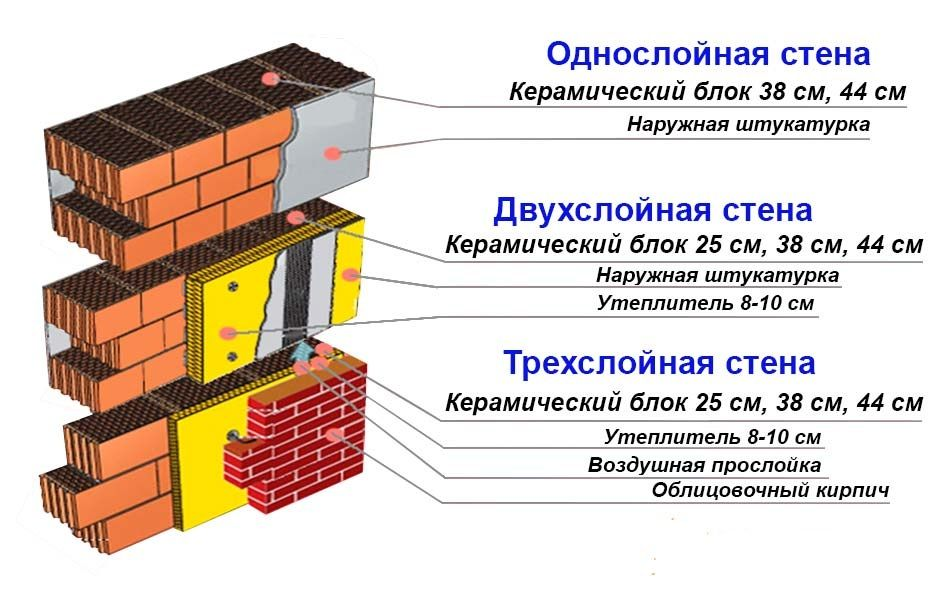
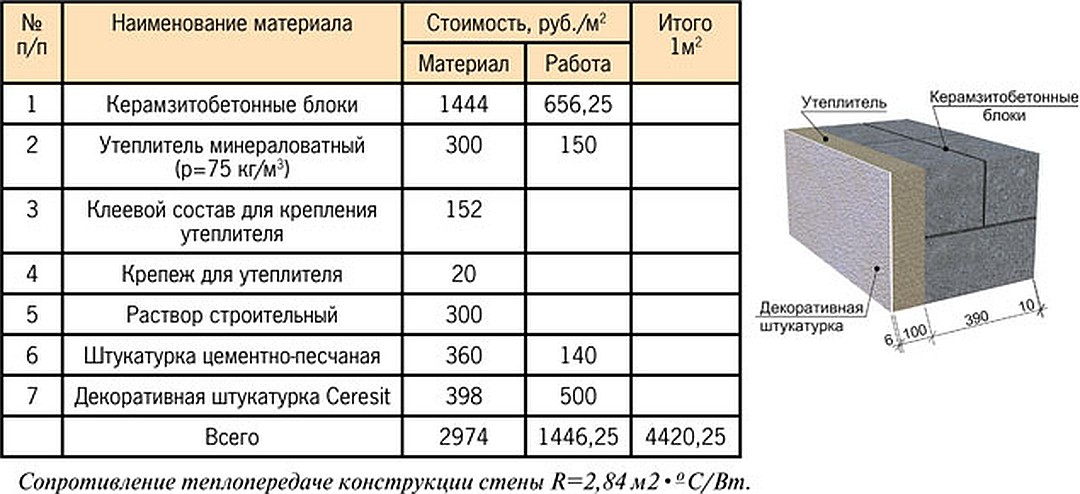
Advantages of Single Layer Exterior Walls
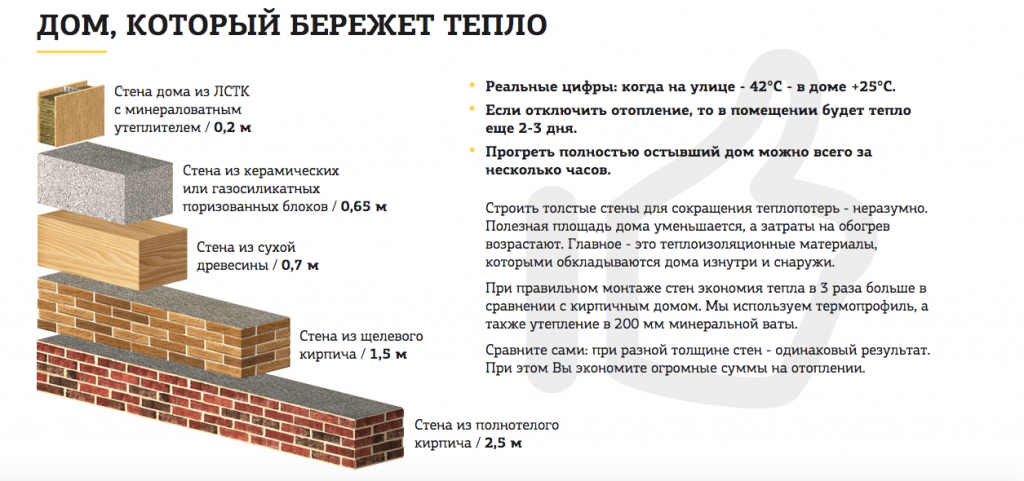
Especially in areas with mild winters, it is cheaper and easier to build a private house with single-layer outer walls made of aerated concrete - gas silicate without additional insulation. These modern building materials make it possible to construct a sufficiently heat-saving single-layer wall of reasonable thickness and necessary strength.
Compared to two- or three-layer walls, The single-layer outer wall construction has the following advantages:
- The total cost of building a house with single-layer external aerated concrete - gas silicate walls up to 40 cm thick, at least does not exceed the cost of building two-layer, and less than three-layer walls. Such walls make it possible to provide high consumer properties of the home and at the same time reduce construction costs in areas with less severe winters.
- Homogeneous construction of single layer stone walls provide greater durability, environmental friendliness, better resistance to mechanical, fire and climatic influences. In the thickness of a single-layer wall, there are no less durable and not resistant to the effects of insulation and polymer films, there are no ventilated gaps, there is no risk of moisture accumulation at the boundary of layers, protection from rodents is not required.
- According to STO 00044807-001-06, for buildings up to 5 floors with outer walls made of autoclaved aerated concrete blocks, the predicted durability is 100 years, the duration of operation before the first major overhaul is 55 years. For comparison, the duration of effective operation of buildings insulated with mineral wool or polystyrene plates before the first major overhaul is 25-35 years. During this period, a complete replacement of the insulation is required.
- Single layer wall least at risk of accidental or deliberate damage.
- Single layer wall is the key to the absence of hidden defects: it is impossible to badly place insulation in it, since the insulation is the masonry material itself; it is impossible to perform a vapor barrier poorly in it, since it does not need a vapor barrier; the entire wall is in front of your eyes and you do not need to worry about the state of the foam or mineral wool hidden in its depths - nothing is hidden in the wall.
- Finishing the facade of a single-layer wall is cheaper and more durable than finishing walls with insulation.
- Single-layer wall masonry is faster , since it is carried out from large-format blocks and does not require additional work on wall insulation.
- For laying single-layer walls, as a rule, blocks with a groove-ridge side surface are used, which makes it possible not to fill the vertical joints of the masonry with mortar. As a result the consumption of masonry mortar is reduced by 30-40% .
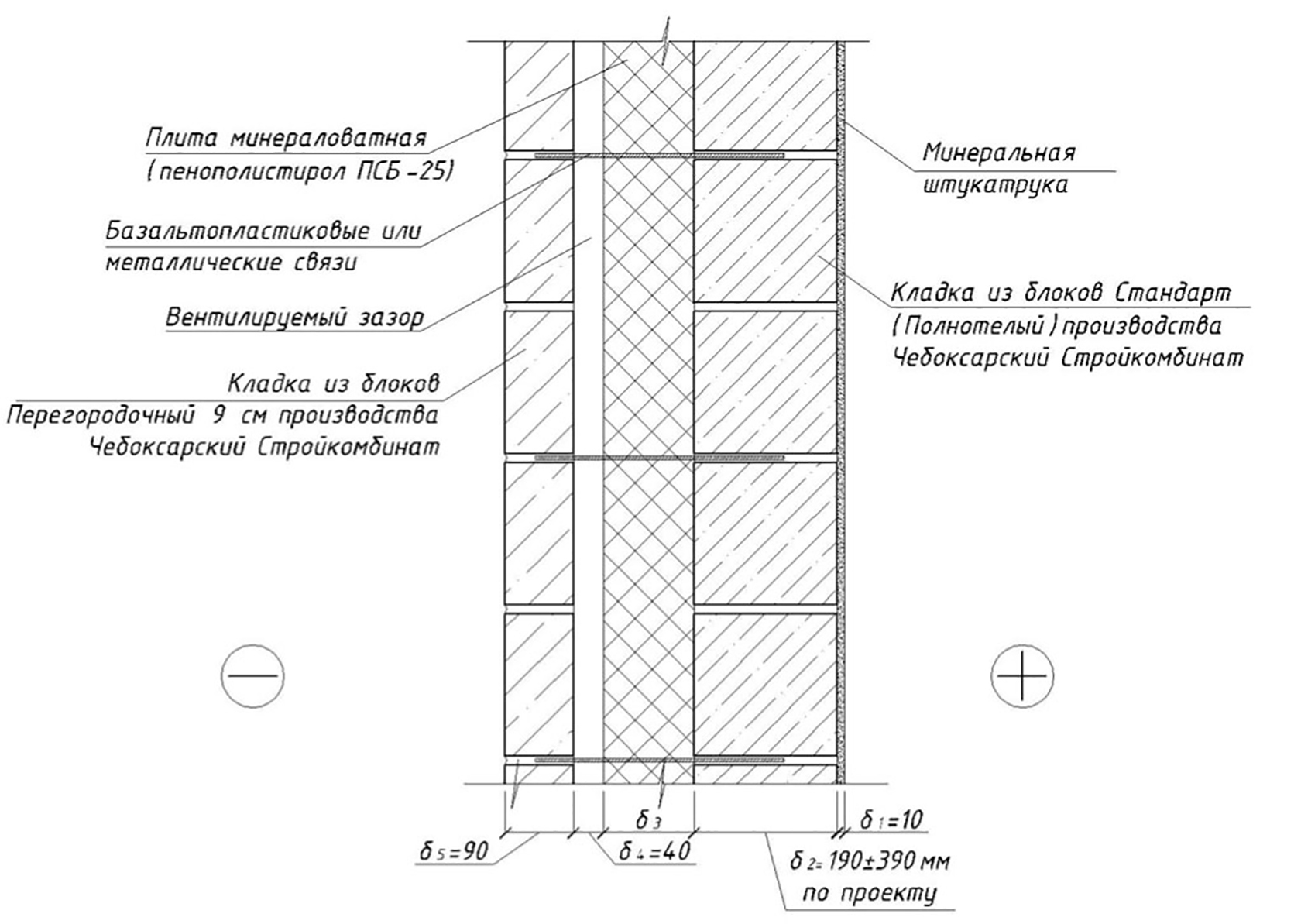
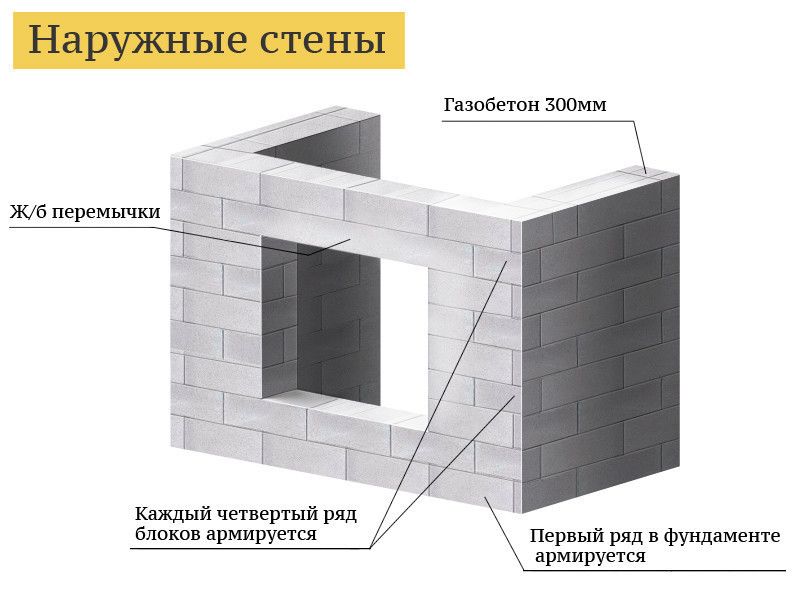
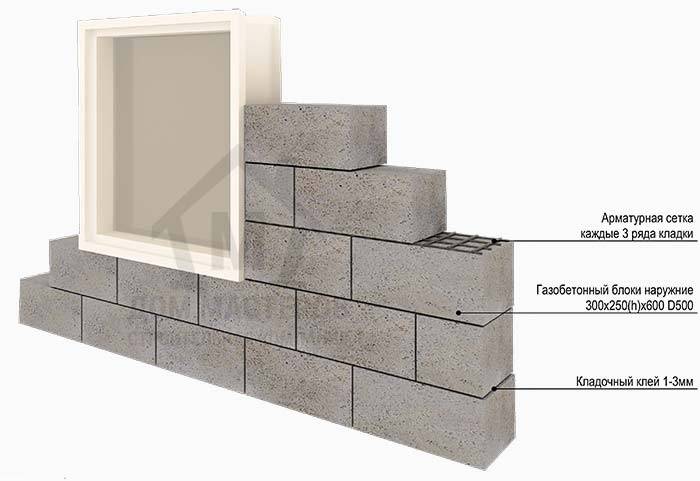
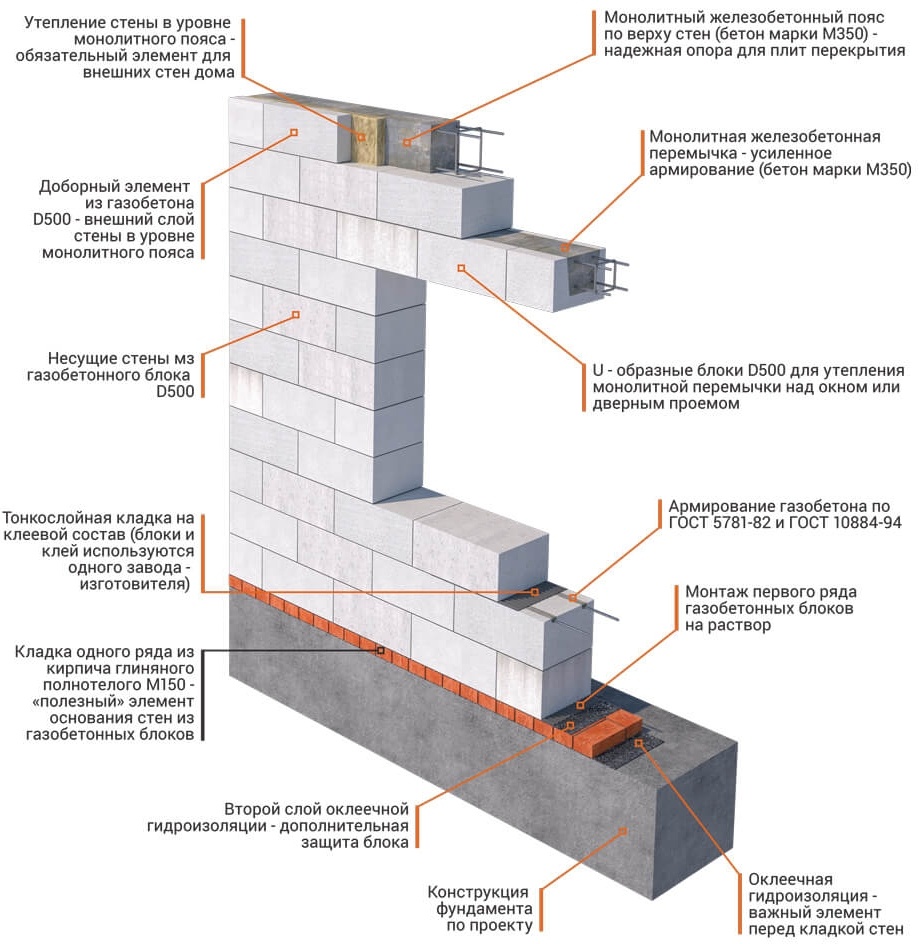
Reinforcement of aerated concrete masonry walls
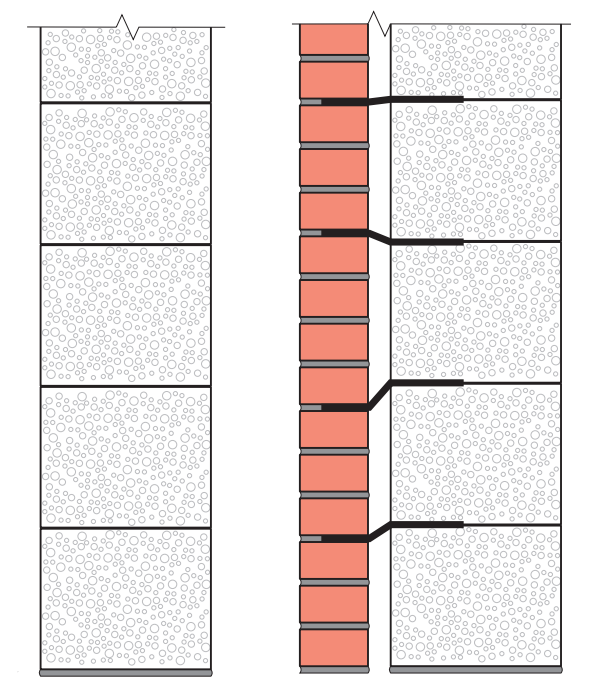
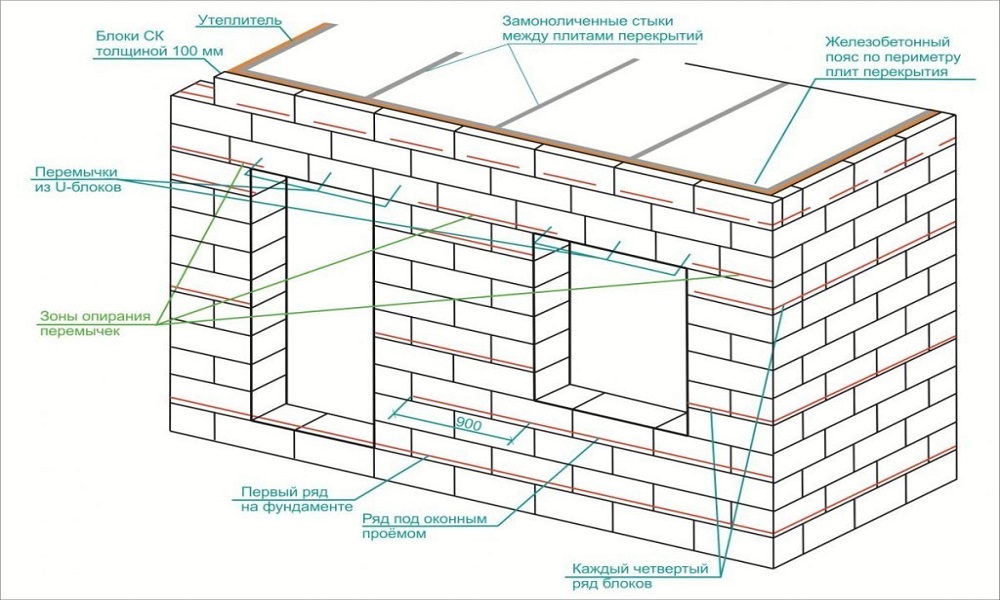
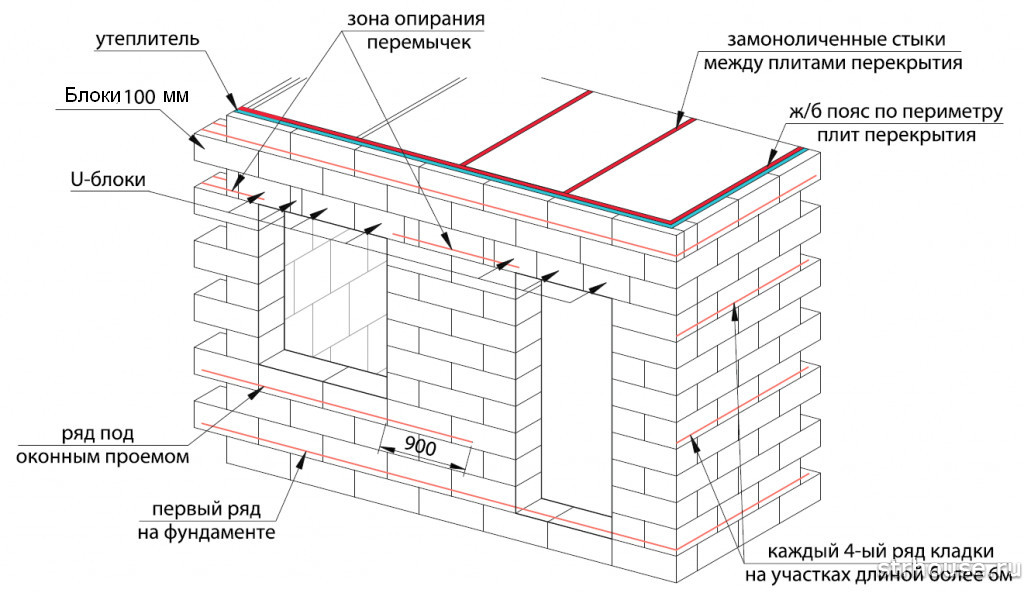
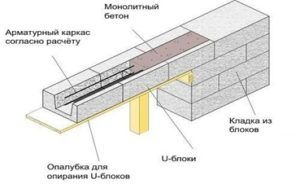 Diagram of the device of a band of U elements
Diagram of the device of a band of U elements
What is the reason for the device of reinforced belts in aerated concrete walls? First of all, the reinforcement of the masonry with metal reinforcement increases the bearing capacity of the walls. Consequently, it can be concluded that the reinforcement of the outer walls of the building allows the fences to be made thinner. This brings significant cost savings on the construction of the entire home.
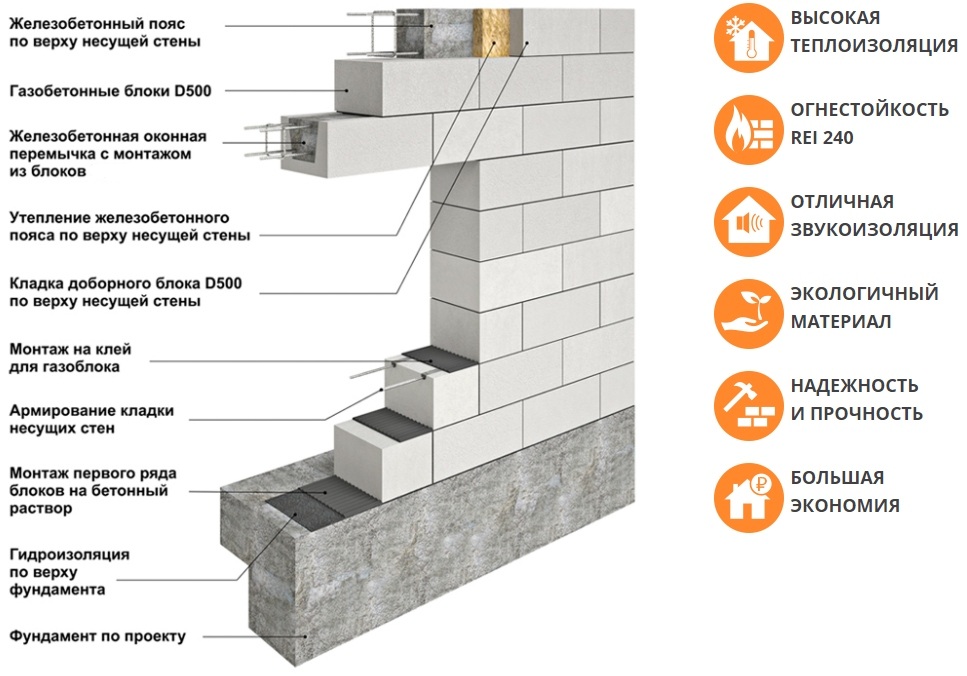
According to the established practice, a reinforced belt (band) is arranged in the upper row of the floor masonry. The bandage is of two types.
This is a belt of trough-shaped blocks (U elements) and laying reinforcement in the grooves of aerated concrete masonry:
- The last row of the floor is laid out of U elements. A frame made of reinforcement is laid in the cavity. Then the cavity is poured with liquid concrete.
- The second type of reinforcement is that grooves are cut in the blocks of the last row of the floor. Usually, two parallel grooves are cut along the perimeter of the building, which are filled with adhesive. Reinforcement with a diameter of 8 to 10 mm is pressed into the grooves. Then the surface of the grooves is finally leveled with glue.
 Reinforcement insertion into grooves
Reinforcement insertion into grooves
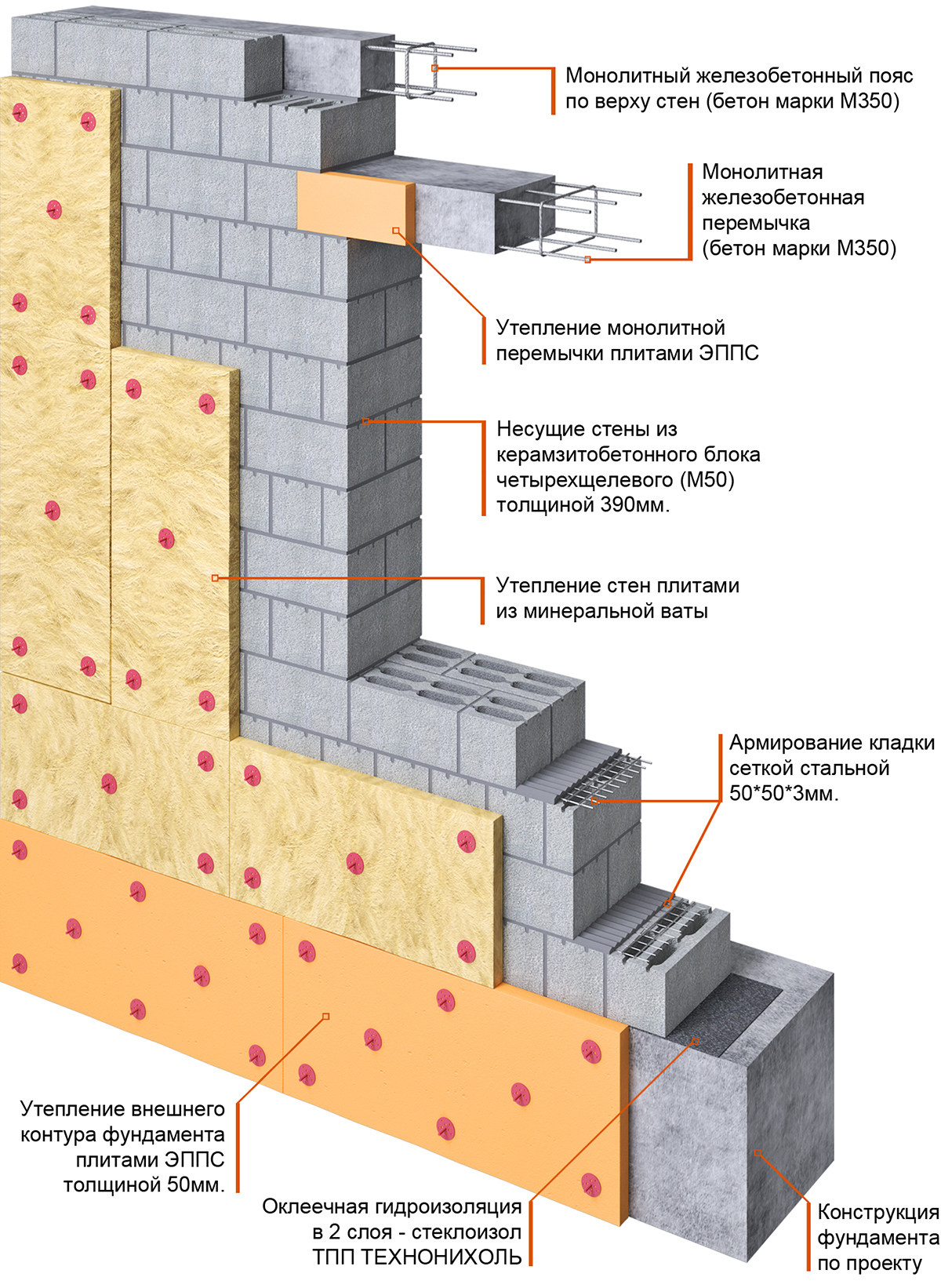
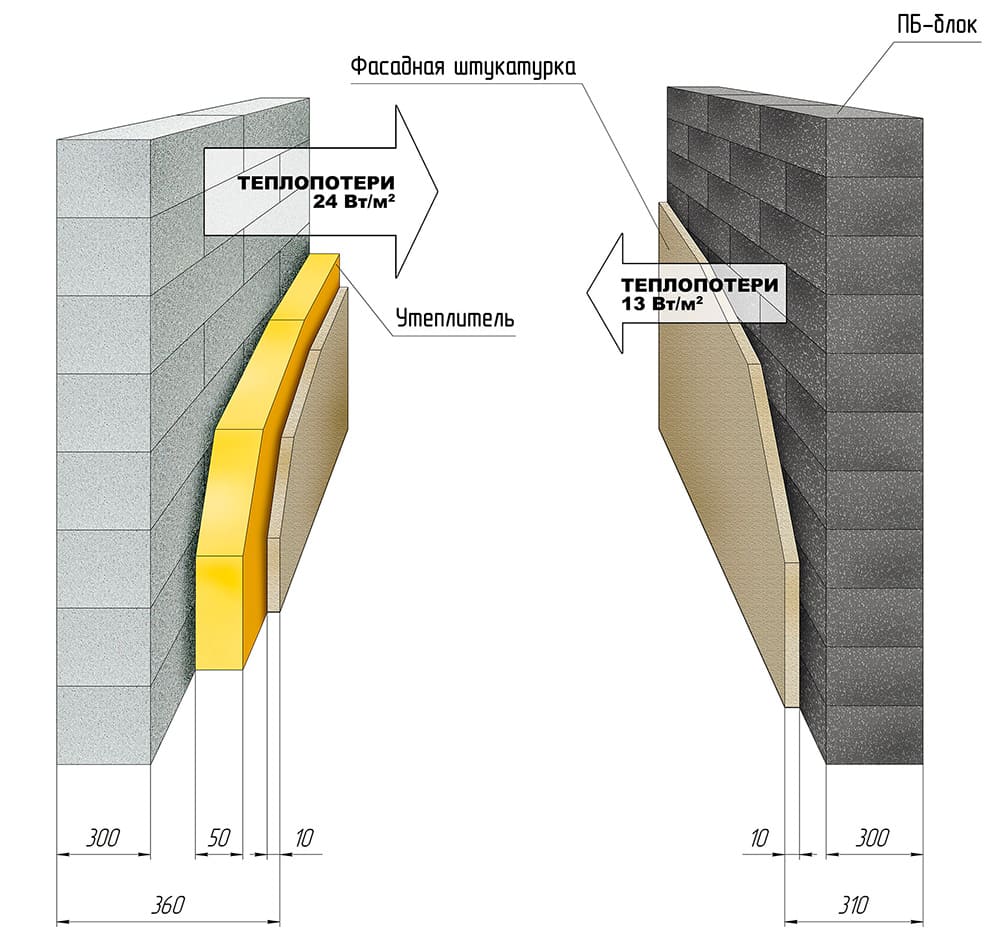
Due to the reinforcement of the external fences with reinforced belts, the thickness of the masonry instead of 400 mm can be made 300 mm wide.
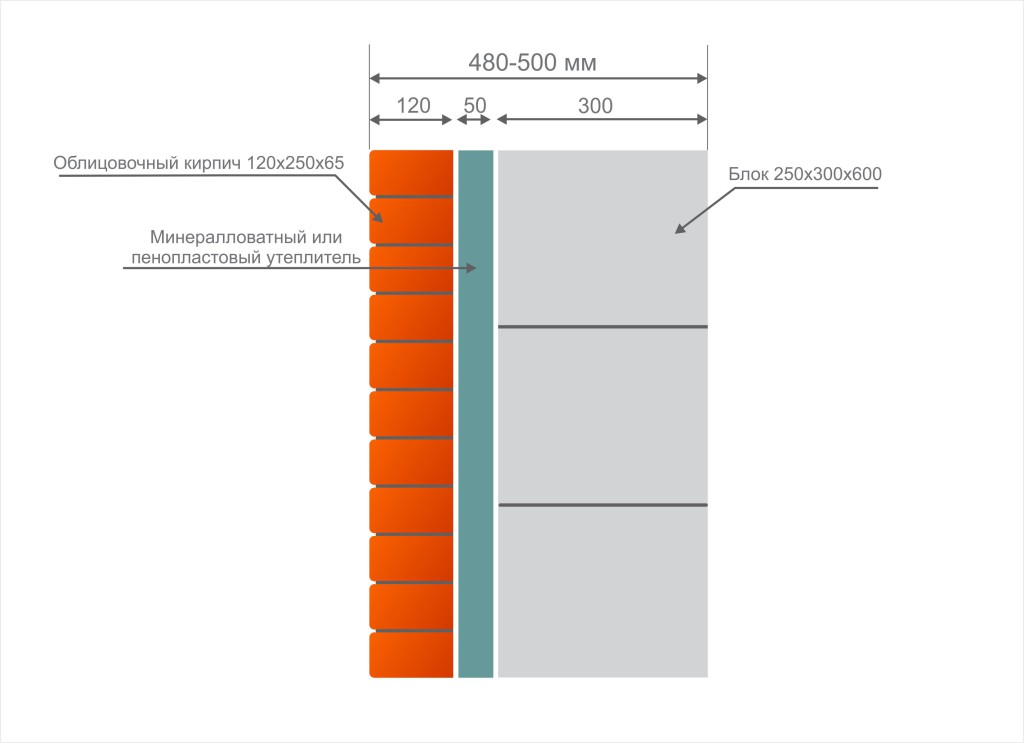
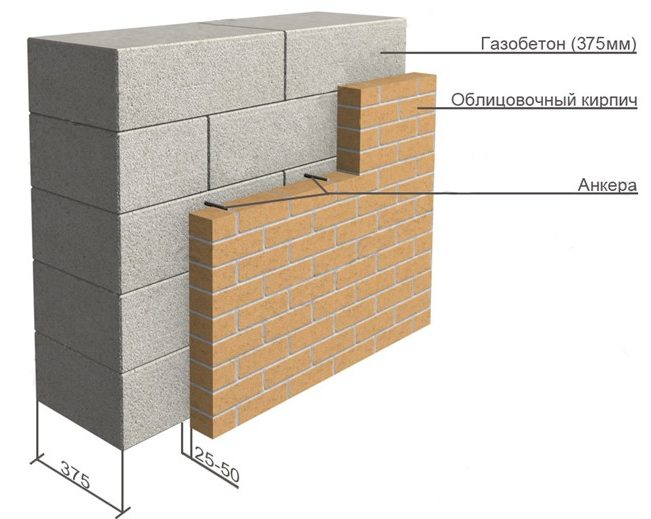
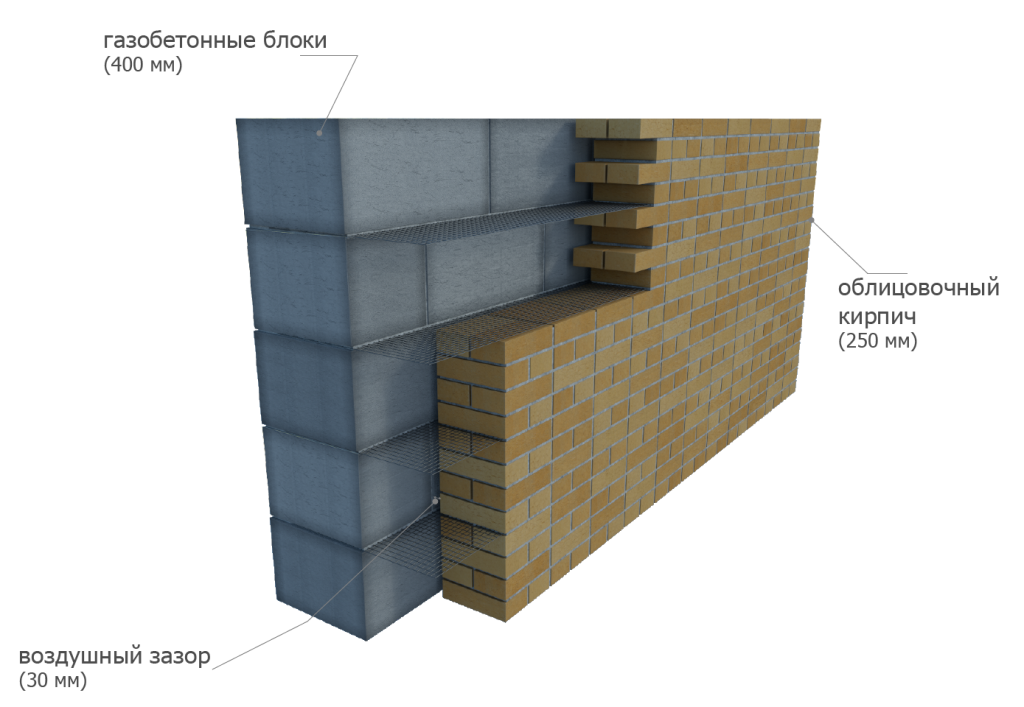
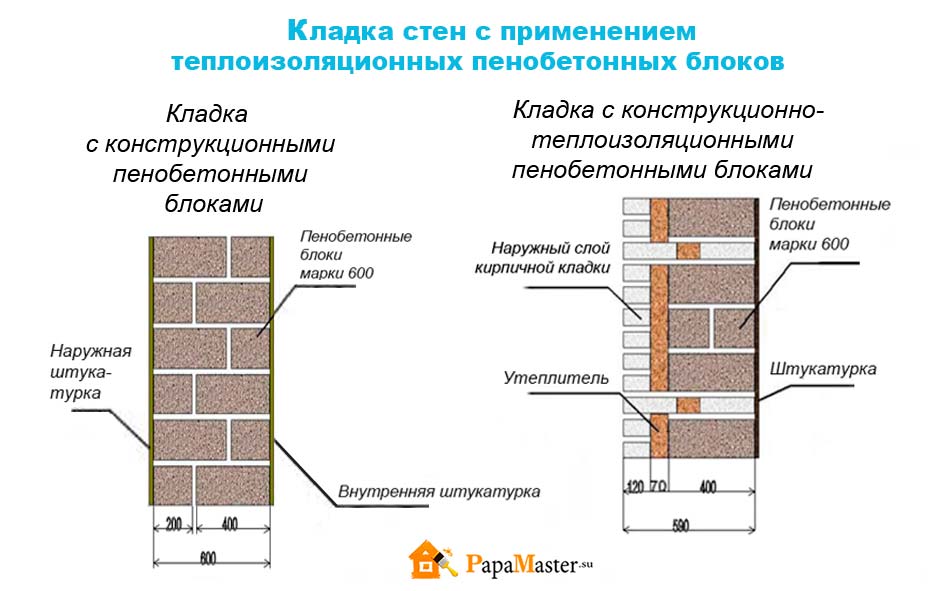
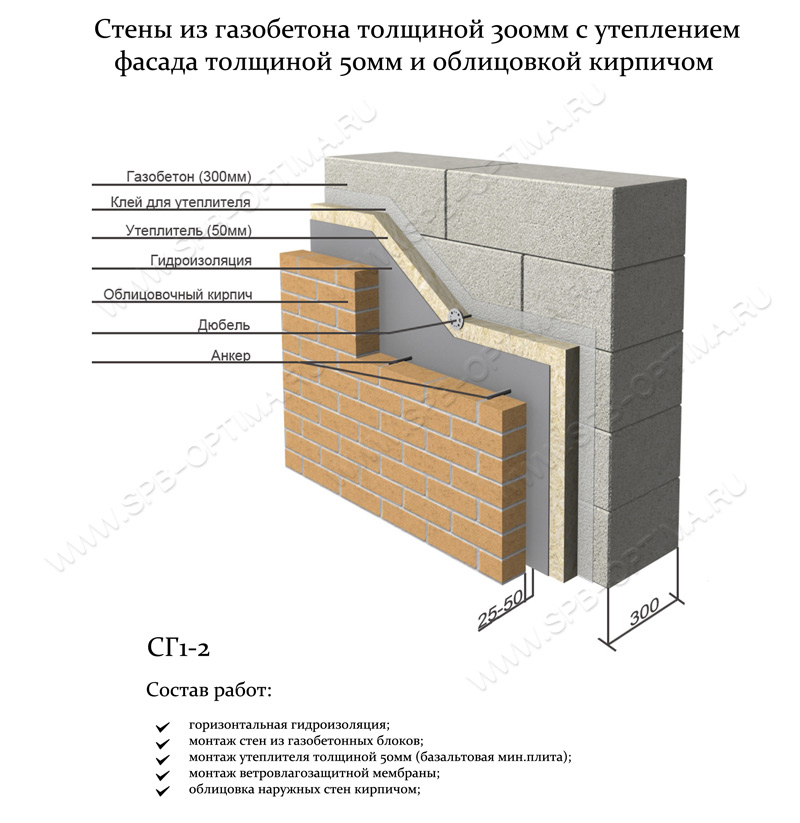
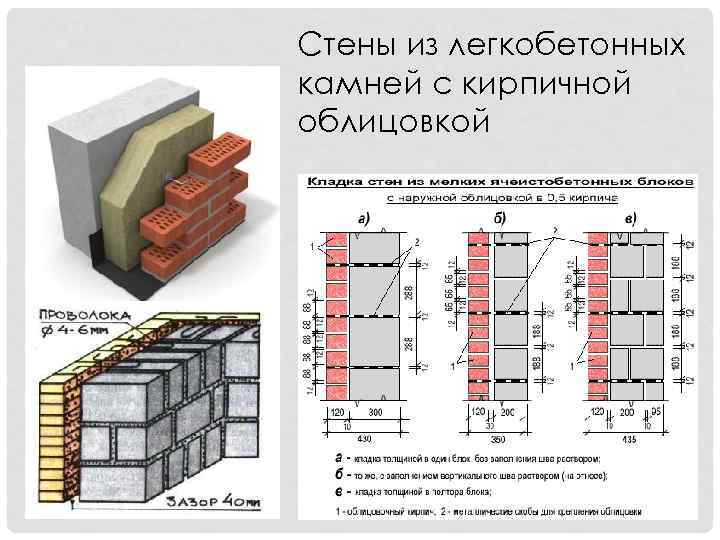
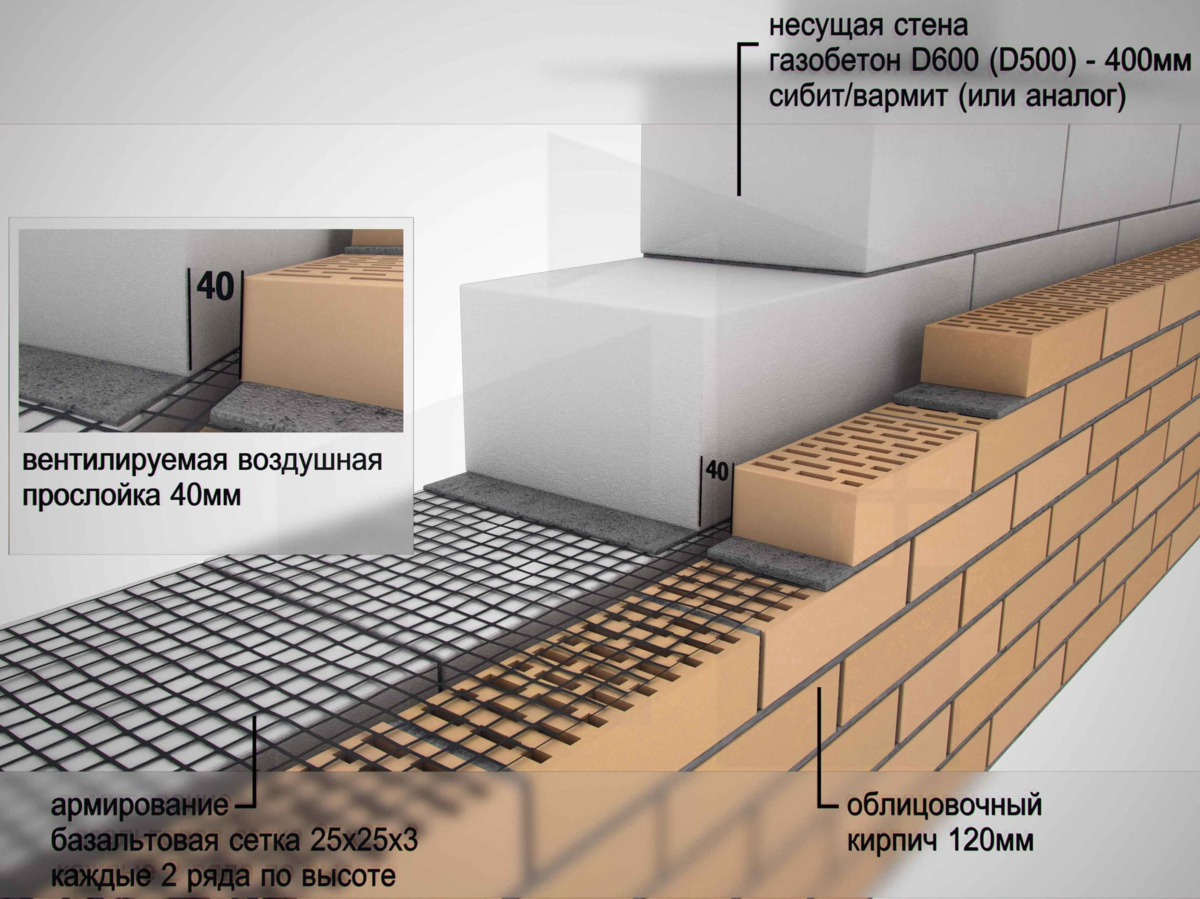
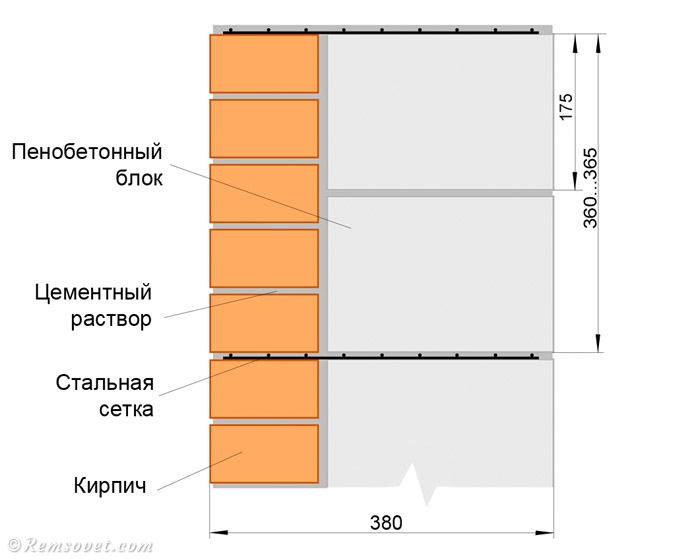
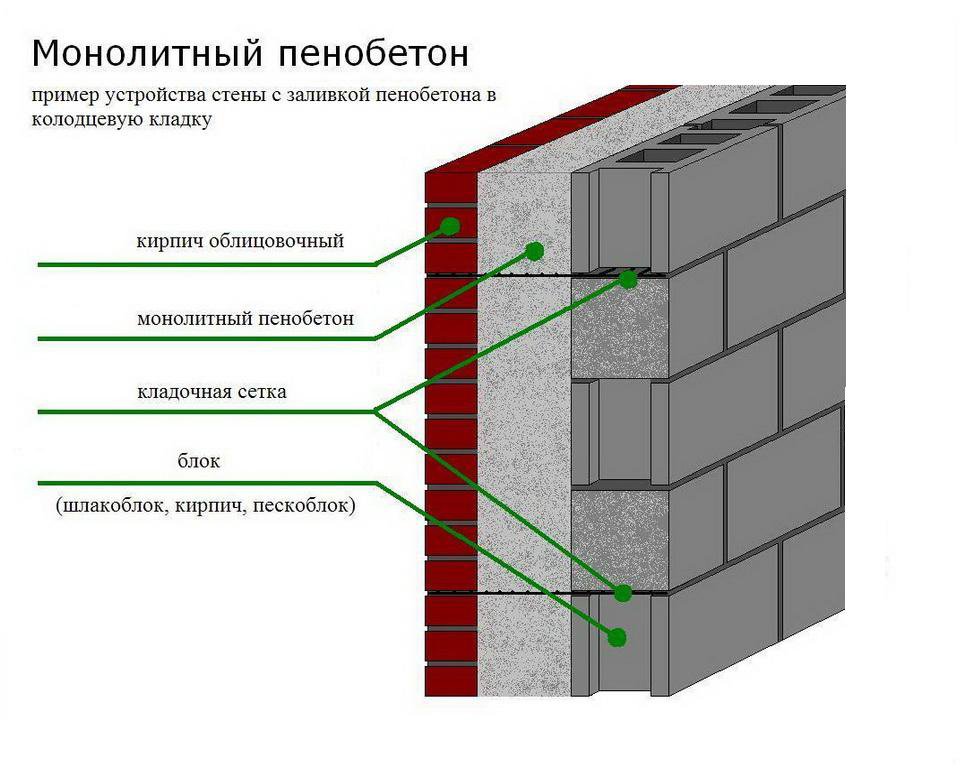
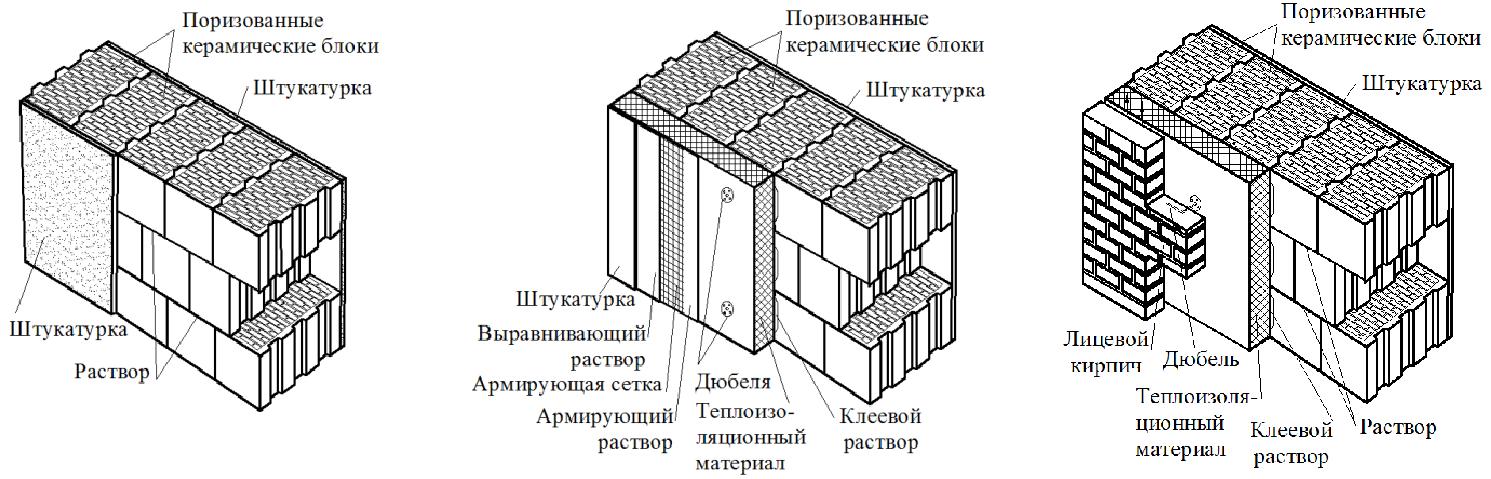
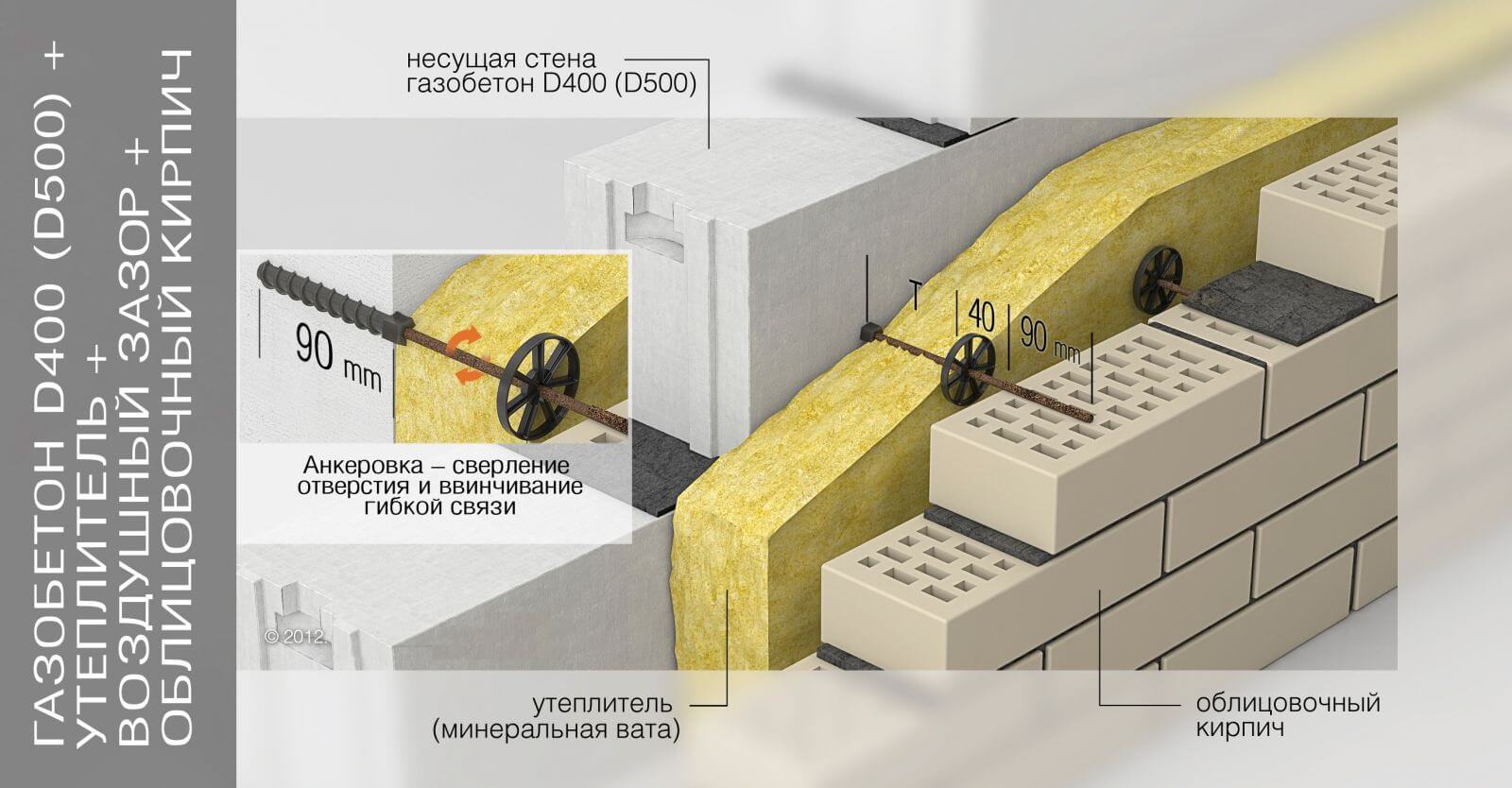
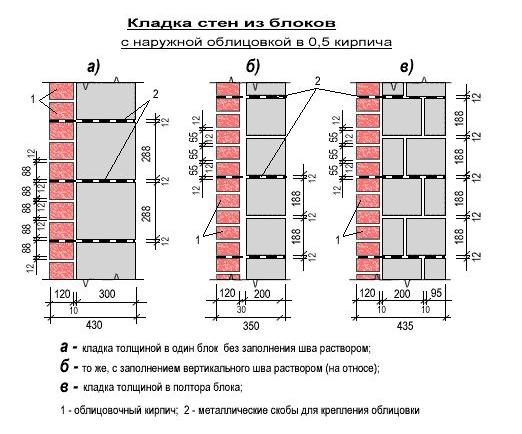
Facing of aerated concrete walls
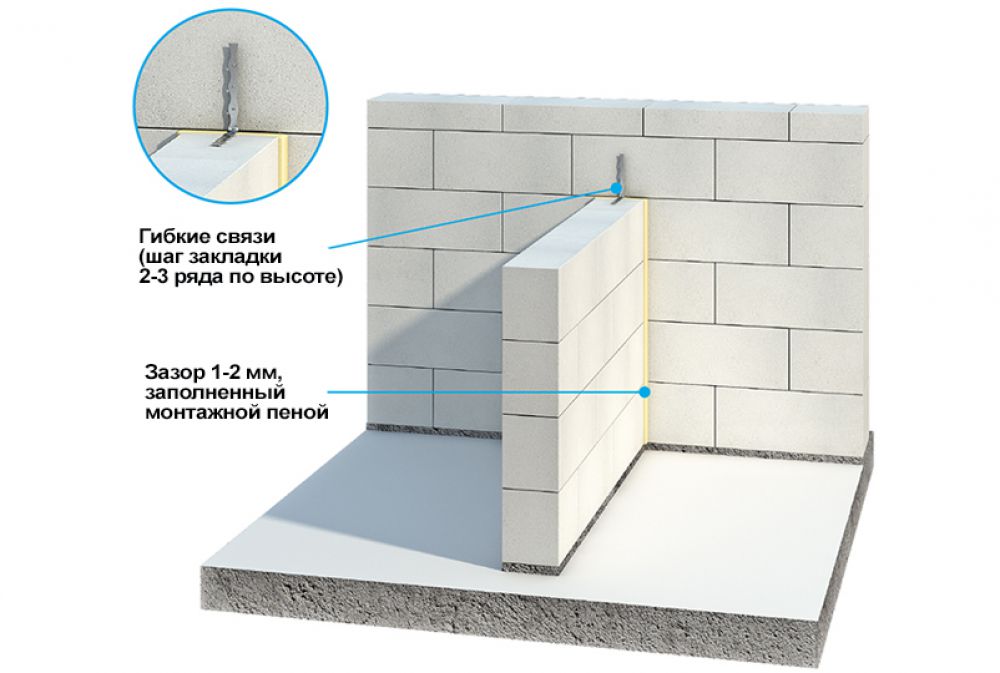
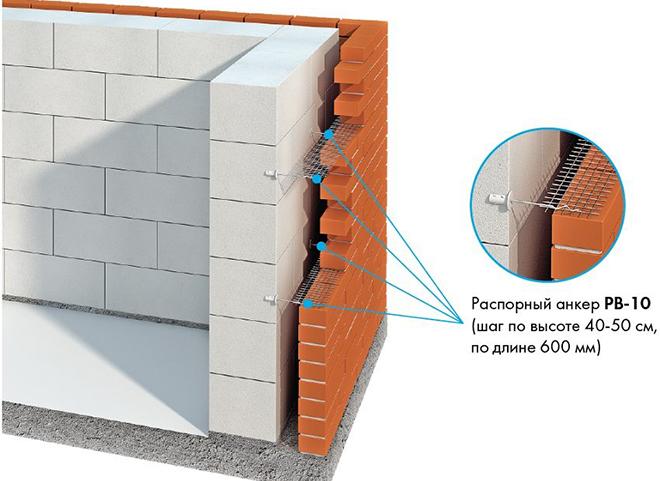
Fences made of gas silicate products are often faced with decorative bricks. This is done in order to form the aesthetic appearance of the facade of the building. At the same time, the cladding is performed at a distance from the base of the aerated concrete walls. The gap between the walls is filled with a reinforcing cage with insulation laying.
Facing of aerated concrete walls with decorative bricks
Reinforcement outlets are laid in horizontal interblock seams on one side. On the other hand, the reinforcement is laid in the brickwork. As a result, the entire structure of the external fence is a single structure.
Due to this, a high thermal insulation of the external fences of the house is achieved. For masonry walls, high-density aerated concrete is used, which makes it possible to increase the number of storeys of the building and arrange floors from reinforced concrete slabs.
More details on the video:
In any case, the thickness of the walls of the aerated concrete blocks should be calculated in such a way that the house is strong and warm.
Internal partitions made of aerated concrete
The thickness of the aerated concrete partition must be selected in accordance with several factors, including the calculation of the bearing capacity and height.
When choosing blocks for the construction of non-load-bearing partitions, it is imperative to pay attention to the height indicators:
- the height of the structure being erected does not exceed three meters - building material 10 cm thick;
- the height of the internal partition varies from three to five meters - the building material is 20 cm thick.
If you need to get the most accurate data without performing independent calculations, you can use standard tabular information, taking into account the interface with the top floor and the length of the structure being erected. It is also necessary to attach particular importance to the following recommendations for the choice of building material:
- determination of operational loads on internal partitions allows you to choose the optimal material;
- it is best to erect non-bearing interior walls from products of the D500 or D600 brand, having a length of 625 mm and a width of 75-200 mm, which creates a strength of 150 kg;
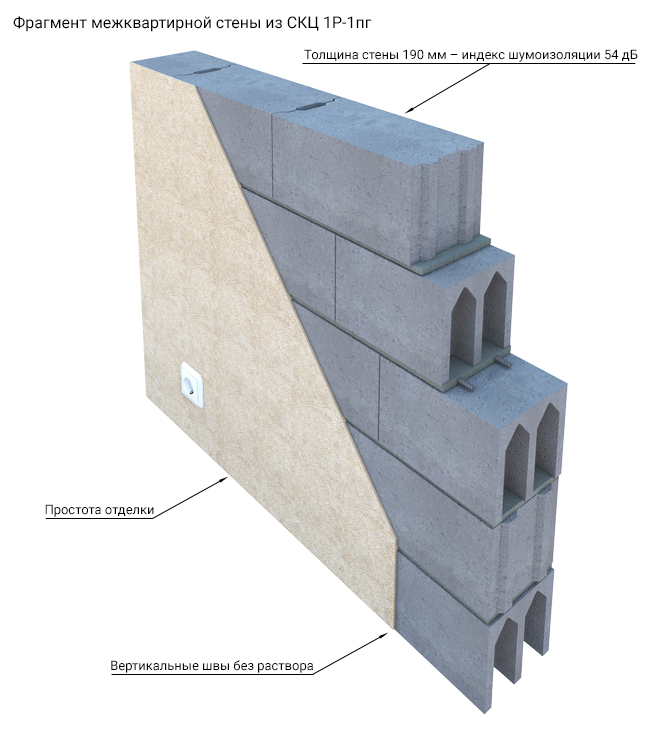
- installation of non-supporting structures allows the use of products with a density of D350 or D400, which helps to obtain standard noise insulation up to 52 dB;
- the parameters of sound insulation directly depend not only on the thickness of the building blocks, but also on the indicators of the density of the material, therefore, the higher the density, the better the sound insulation properties of aerated concrete.

With the length of the partition structure of eight meters or more, as well as the height exceeding four meters, in order to increase the strength characteristics, it is necessary to strengthen the frame with the help of load-bearing reinforced concrete structures. The required strength of the partition is also achieved due to the adhesive layer that holds the block elements together.
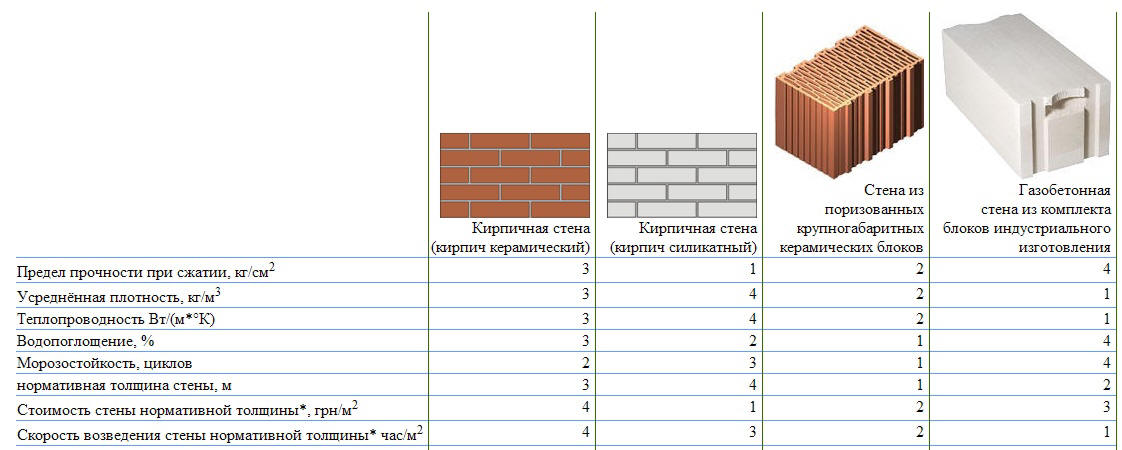
Affordable cost, manufacturability and excellent quality characteristics have made aerated concrete blocks popular and in demand in the market of modern building materials. Correctly calculated wall thickness made of aerated concrete allows to provide the erected structures with a high level of strength, as well as maximum resistance to almost any static load or shock factors.
How to prepare the glue?
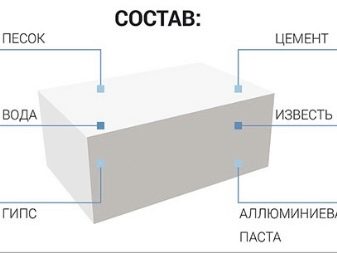
Aerated concrete masonry is made on a glue joint, which is created from a dry mortar with special characteristics, and consists of sand, cement and various kinds of water-retaining, plasticizing and hydrophobic additives. The minimum seam thickness should be 2-5 millimeters, but laying on such a mass is possible with a seam thickness of 8-10 millimeters. Aerated concrete can also be placed on a sand-cement mortar with an average horizontal joint thickness of 12 millimeters and vertical - 10 millimeters.


Creation of adhesive mortar for the construction of wall aerated concrete partitions should be started right before work is carried out.
Moreover, the preparation work should be done clearly according to the instructions:
First, pour a certain amount of water, indicated on the package with the mixture, into a bucket made of plastic.
Now carefully pour in a dry solution in the required proportion, stirring constantly. It must be left for 10-15 minutes, and mixed again.
In the process of masonry, it is necessary to stir the mixture several times so that its consistency remains at the desired level.
To carry out laying in a cold period of time, it is better to use an adhesive solution that contains antifreeze additives.


Foundations. Why do walls crack in spring?
The light weight of a gas block house can help save on the width of the foundations, but that's all! The deepening of the foundation, its reinforcement must be carried out in accordance with all the rules.
The most common problem associated with foundations is the appearance of cracks in the walls after the first winter. You can often come across the misconception that cracks appear due to the low weight of the blocks, as a result of which the house "floats", as it were. Even more erroneous is the recommendation to be sure to pour a foundation slab under such houses. In conditions of frost heaving, the heaving forces will be the greater, the larger the contact area of the soil with the underground part of the building. With a significant rise in the level of groundwater, the Archimedean force will be proportional to the volume of the part of the building immersed in the ground. In both cases, a slab foundation will do nothing.
The main nuance of building a foundation for building a house from an aerated block is its insulation. A properly reinforced, sufficiently deep foundation is not a guarantee of the absence of cracks in the walls after the very first winter. Especially with a basement.
Let's consider a real case with a specific example.
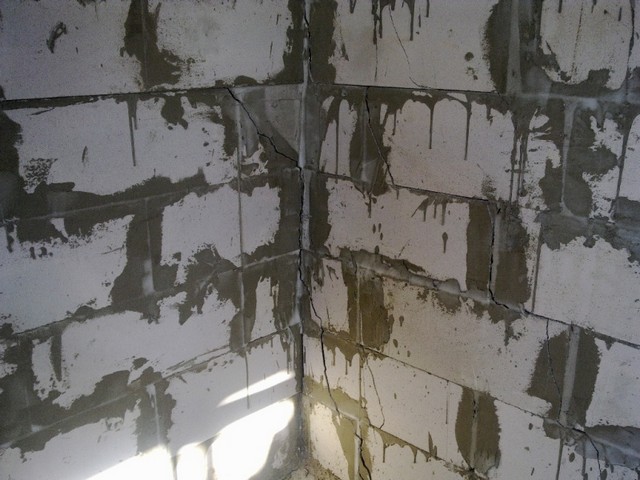

The cracks in the corner of the building are not high from the floor.
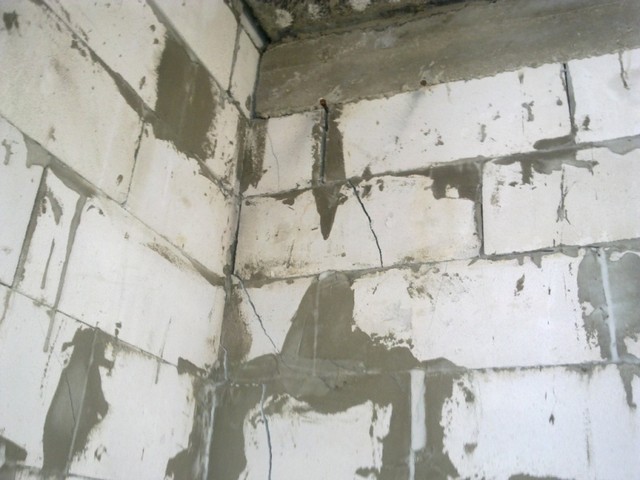

Cracks in the corner of the building at the level of the first floor ceiling.
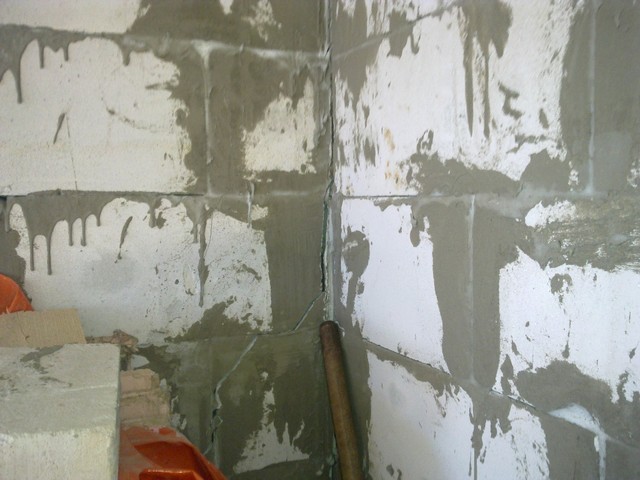

The crack in the corner of the building is the middle of the floor.
The walls were built from high quality aerated concrete blocks. The foundation is tape, reinforced. There is a basement. Before the onset of cold weather, the house was covered with a roof, windows and doors were installed.
Factors influencing the appearance of cracks
The reasons for the appearance of cracks were:
- The construction was carried out on frosty soils. Despite the sufficient depth of the foundations (below the freezing depth), due to the lack of heating through the basement space, the house froze through. The outer contour, obviously, froze through at a different speed than the inner space. As a result, the uneven heaving created dangerous internal stresses in the walls.
- Reinforcement was not provided in the gas-block masonry.
- A monolithic belt for overlapping with reinforced concrete slabs does not encircle the building around the perimeter. Monolithic reinforced concrete is poured only in the places where the slabs are supported, which is why it does not perform the function of a belt.
As you can see from the above list of factors, it is highly undesirable to leave a newly built house for the winter without insulation or heating. The boundary depth of soil freezing is due to the presence of molten magma in the center of the globe. The upper (freezing) layer of the soil is a kind of jacket, deeper than which the cold cannot penetrate due to the presence of heat in the center of the planet. Sampling of soil under the basement opens the way for freezing to an even greater depth.
The method for solving this problem is obvious - if the building is not put into operation before the onset of cold weather, the foundation (especially its basement) must be carefully insulated
This is critical for heaving soils. Insulation can be done by backfilling with expanded clay gravel or blast-furnace slag, spreading mineral wool mats or straw, etc.
It is highly undesirable to backfill the pit sinuses (trenches) with ordinary soil. Preference should be given not only to non-heaving materials, but also to warmer ones.
Perlite sand is ideal. In the absence of an opportunity to purchase it, you can limit yourself to the usual. In this case, the negative heaving effect on the underground part of the basement walls will be completely excluded.
The appearance of cracks not in winter, at the height of frosts, but in spring, is associated with a fairly high stability of the soil in a frozen state. During thawing, the soil is reconsolidated, forming shrinkage. The result of these processes is shown in the above photos.
Sound insulation of aerated concrete
Although sellers of gas silicate blocks talk about high performance in sound insulation, they greatly exaggerate. Even a standard block 200 mm thick conducts sounds and noises well, and even thinner partition blocks, even more so.
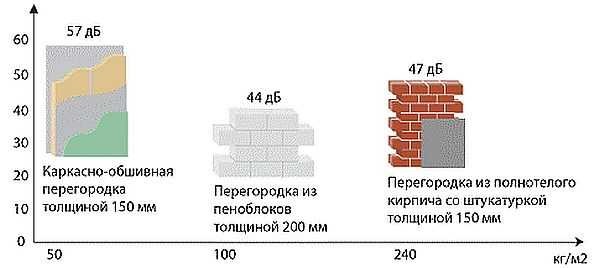
Comparative characteristics of sound insulation of partitions made of different materials
According to the standards, the sound impedance of the partitions should not be lower than 43 dB, and it is better if it is higher than 50 dB. This will provide you with silence.

Sound insulation standards for different rooms
To have an idea of how "noisy" the gas silicate blocks are, we present a table with the standard sound resistance values of blocks of different densities and different thicknesses.
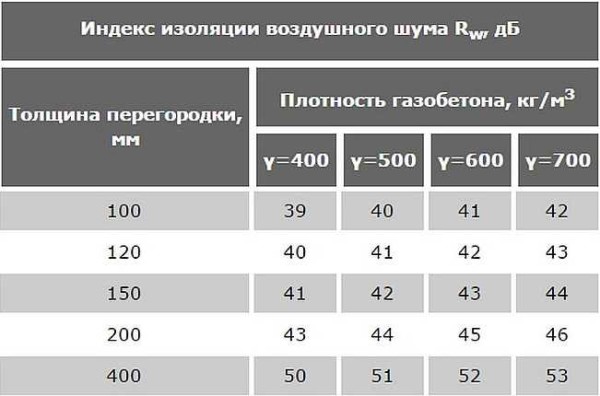
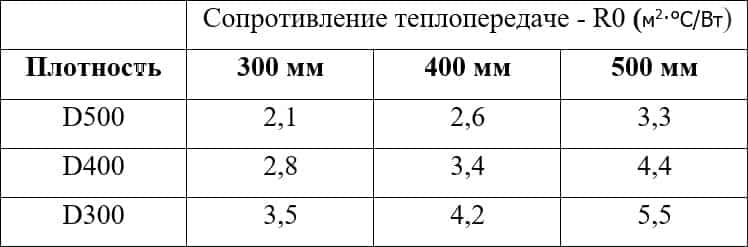
Sound absorption coefficient of aerated concrete blocks
As you can see, the block, 100 mm thick, falls short of the lowest requirement. Therefore, when finishing aerated concrete, you can increase the thickness of the finishing layer in order to "hold out" to the standard. If, however, normal sound insulation is required, the walls are additionally sheathed with mineral wool. This material is not soundproofing, but it reduces noise by about 50%. As a result, the sounds are almost inaudible. Specialized soundproof materials have the best indicators, but when choosing them, you need to look at the vapor permeability characteristics so as not to lock moisture inside the gas silicate.
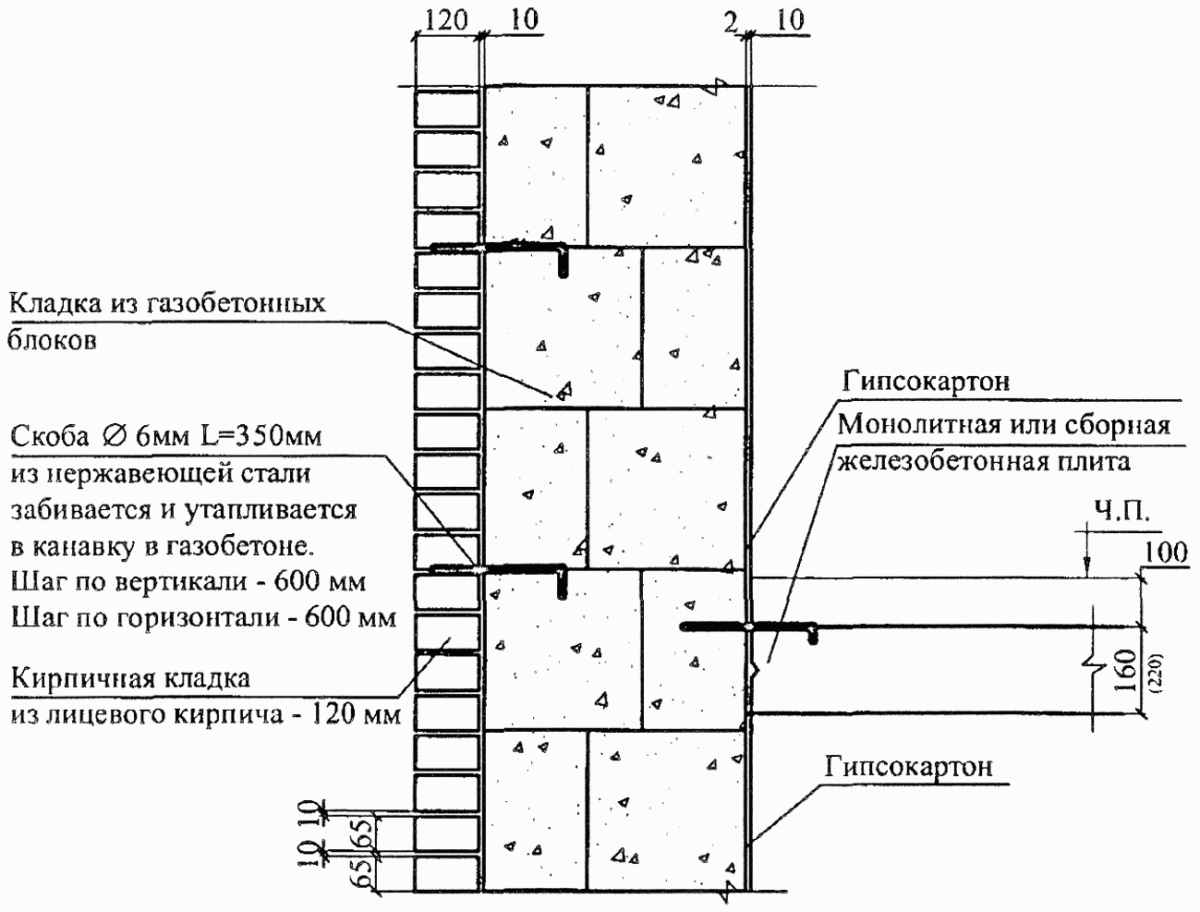
If you need absolutely "quiet" walls, experts advise to install two thin partitions with a distance of 60–90 mm, which should be filled with sound-absorbing material.