What is the difference between polyethylene pipes and polypropylene pipes?

Despite the general properties and external similarity, popular polypropylene and polyethylene pipes have distinctive features. The first of them, of course, is the formula: polyethylene - (C2H4)n, polypropylene - (C3H6)n.
To understand exactly what advantages each applicant can be "proud of", it is better to compare the lists of their advantages and disadvantages relative to the main competitor in the struggle for the title of "optimal choice".
The difference between polyethylene
The main advantage of cross-linked PE is its elasticity. Polyethylene is flexible, and polypropylene loses in this nomination, since it cannot be bent due to the complexity of the operation. It is not recommended to practice this approach due to the decrease in the strength of such a section. Other differences of PE:

- Frost resistance. The characteristics of polyethylene will not be affected in any way by temperatures down to -50 °. Polypropylene, on the contrary, is capable of collapsing at -15 (-20) °.
- Cross-linked polyethylene is better able to withstand sudden changes in thermal and physical stress. Its density is also higher: 940-960 kg / m3 versus 920-930 kg / m3 for PP.
- Versatility. For this reason, polyethylene is used not only for the manufacture of pipes, but also in the production of films, packaging, and insulation products.
- Chemical resistance to solvents, reagents. This is where XLPE has a slight advantage. It is protected by a layer of anti-diffusion coating, and special stabilizers are added to protect the PCB.

There is one more serious difference between polyethylene pipes and polypropylene pipes. The disadvantage of PE is its insecurity. When heated (burning, melting), the material releases a small amount of toxic substances. Polypropylene is absolutely harmless. PE-X is extremely reliable due to its high density, it does not allow liquids or gases to pass through. PP "breathes", that is, it does not have oxygen impermeability.
The inability to apply the welding method using soldering equipment used for welding polypropylene can be considered a disadvantage of installing polyethylene pipes. In this case, either fittings or special couplings and a welding machine are used.
Properties of polypropylene

PP also has a slight advantage - easy care of products due to the fact that polypropylene is very easy and quick to clean. This material is not much, but lighter than the competitor: the difference is 0.04 g / m3. Other features:
- Melting temperature. For PP it is 160-170 °, for ordinary polyethylene - 140 °, but for sewn -200 °.
- High coefficient of thermal expansion. Because of this property, PP pipes often sag after installation. When the temperature rises by only 1 °, an elongation of 0.15-0.20 mm / m occurs. Cross-linked PE, on the contrary, is devoid of this significant drawback. Its indicator is only 0.024 mm / m.
- The hardness of the material. To compare polymers, the method of a Swedish engineer is often used - the so-called Brinell scale. It consists in pressing a steel ball into the surface with a certain force. For polypropylene, this indicator ranges from 6-6.5 kgf / mm², for polypropylene - 1.4-2.5 kgf / mm².

In tensile strength, both competitors (PP and PE-X) have minimal differences: the indicator of the former is 350-800%, the latter is 200-800%. However, polypropylene, as already noted, has a drawback. It can withstand sudden changes in load worse, but its resistance to cracking is higher.
For some owners, it is not only the quality of the product that is important, but also its price. The main difference between polypropylene and plain PE is the more expensive PP production
The reason is in technology, in the high cost of raw materials.If we compare PP and PE-X, then the difference is often not so significant.
The first option - we use metal-plastic for a warm floor
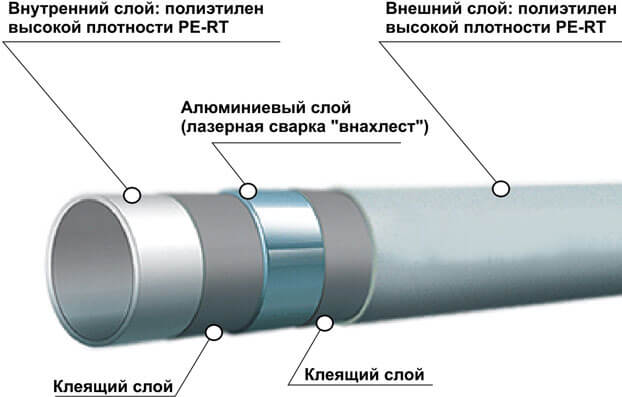
A metal-plastic pipe is a high-tech product, marking (MP), which is a composite. Five layers form the basis of the structure, fulfilling their specific functions. The inner and outer layers are polyethylene, tightly connected to the inner layer made of foil. Between the foil and the polyethylene layers, there are two adhesive layers that provide the entire structure with the necessary stability.
At first glance, the channel is a complex typesetting structure - a composite. However, it is precisely this design that was created specifically for warm floors. Due to the presence of a metal layer inside the channel, the maximum possible transfer of thermal energy occurs. Reinforced-plastic pipes for underfloor heating allow you to create uniform heating of the floor surface, using a fairly wide step when laying the water contours.
The inner layer has smooth walls, which makes such pipes resistant to the formation of calcium deposits. Corrosion is not terrible for such material. The combination of aluminum foil and polyethylene provides the entire circuit with the necessary strength, not inferior in strength to copper pipelines. This consumable has both obvious advantages and disadvantages. However, for a number of reasons, it is MP pipes that are often chosen for the installation of warm water floors.
The warm floor, in which metal-plastic pipes are used, has the following advantages:
- a metal-plastic pipeline has a low coefficient of expansion, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the concrete screed;
- water circuits resistant to corrosion and inert in terms of reaction to exposure to chemicals;
- water heating loops keep the working pressure of the coolant well;
- heating circuits made of this material have high noise insulation;
- the pipeline keeps its shape in the process of pouring the surface with concrete.
The last advantage that influences the choice of this particular type of consumable is durability. Pipes laid in a concrete screed can function normally for 30-40 years.
Metal-plastic can withstand working pressure up to 10 atmospheres and retains its main technological characteristics at a coolant temperature of 95C. From the point of view of practicality and manufacturability, metal-plastic pipes behave perfectly during the installation of heating circuits. The channel is easily bent, which makes it possible to lay the contour in any way, snake or spiral, schemes in which a large number of bends are provided.
The disadvantages of metal-plastic are rather the nuances of the technological use of pipelines made from this material. These include the following:
- with poor manufacturing quality, delamination of the aluminum and polyethylene layer may occur (the difference in the parameters of the linear expansion coefficients);
- the use of metal fittings for joints can lead to the formation of scale on the inner surface of the joints;
- pinching the fitting during the installation of the pipeline can lead to the formation of cracks in the polyethylene;
Reinforced plastic and underfloor heating in your home is a good combination, a reasonable, worthy and justified choice. In this case, you can get a reliable and efficient heating system, while saving quite significant amounts on consumables. Therefore, you can safely start calculating the flow of pipes required for the installation of heating circuits.
Material features

The pipeline for underfloor heating is made from various raw materials: copper, metal-plastic, but the most modern type is a tube made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Cross-linked polyethylene is a type of ethylene obtained by chemical and physical action on it.During production, a three-dimensional mesh network is formed from ethylene molecules. This model is called PEX.
Strength
The strength of this product is given by the transverse, formed in the production process, in addition to longitudinal joints. The expansion rate of the PEX tube ranges from 250 to 800%.
In addition, unlike polypropylene, the material has increased durability and does not deteriorate even with significant temperature changes.
Temperature resistance
When using XLPE hoses, a maximum temperature of 140 degrees is recommended. But the melting processes begin when heated from +190 degrees.
Minus temperatures that this pipeline can withstand, and at which the strength and elasticity of the product is maintained -50 degrees Celsius.
Therefore, it is recommended to use it in a low-temperature heating system, where the heating is not significant, and there are frequent temperature drops. But, polyethylene should be used where the pipeline is constantly hot.
Physical properties
Despite the high density of PEX tubes, the material is soft and elastic and has the following properties:
- liquid and gases do not pass through it;
- it bends easily, allowing for the tightest turns.
Chemical properties
Improved production process - stitching, made polyethylene more resistant to organic and inorganic influences, and also solvents do not have a destructive effect on it.
In addition, the material is riser to the negative effects of the environment: sunlight and oxygen. This quality is due to the presence of a protective anti-diffusion coating on most PEX models.
Other characteristics
Polyethylene contours have a diameter of 10 to 200 mm. For water-heated floors, the recommended size is 16 mm.
Main technical characteristics:
- wall thickness - 2 mm;
- meter weight - 110 g;
- meter volume - 0.113 l;
- density - 940 sq. m3;
- degree of thermal conductivity - 0.39 W / mK.
Polyethylene and polypropylene: general properties
Until recently, there were only two materials from which pipes were made, which were necessary for arranging various systems at home. They were "heavyweights" - steel and cast iron.
Polymers appeared only in the middle of the 20th century, but quickly entered our life, and then became completely irreplaceable. Few would agree to do without bags, handbags, multi-colored basins or greenhouse film. Plastic teapots, disposable tableware and, of course, modern double-glazed windows make life much easier.

Polypropylene (PP, PP) and polyethylene (PE, PE) are "close relatives" materials. Both are related to polymers, which are in great demand in the industry. They are used for pipe production, plastics, various containers, packaging materials, etc. Both candidates have very similar properties.
However, not all consumers believe in the reliability of polymer products: many new products on Russian soil take root with difficulty. What do they prefer to buy in Europe? If we turn to statistics, then in these countries the situation is as follows: 80% is the share that is almost equally divided by polymer and copper pipes. We are talking about the construction of a new house, or about the overhaul of an already "old" building.
Advantages
Both polymers have several advantages in common. It:
- long service life;
- smooth inner surface;
- sufficient strength, but elasticity;
- ease of processing in the manufacture of products;
- resistance to organic / inorganic sediment;
- low thermal conductivity when compared with metals;
- ease of self-assembly due to its light weight.

One of the main advantages of polymers is their practicality, which makes pipes versatile. Both materials are chemically resistant, they successfully resist "unfriendly" impurities in water, hardness salts (alkalis), acids.The roughness coefficient for PP and PE products is equal, it is 0, 0007 mm. Another attractive quality of polyethylene and polypropylene is the lack of electrical conductivity. Polymer pipes are absolutely safe for residents.
disadvantages
And the disadvantages of PP and PE are the same: both materials cannot withstand high temperatures, in such conditions their strength decreases. Polymers burn, their long exposure to ultraviolet light leads to aging of materials: they become brittle. Hard types of pipes cannot be bent because they break under strong pressure.

The disadvantages rightfully include a high coefficient of thermal (linear, especially for PP) expansion: this indicator is an order of magnitude higher than that of steel. However, it is compensated to some extent by the elasticity of the materials. These polymers (and PVC) are classified as thermoplastic materials.
It is necessary to briefly dwell on the method of producing polymer pipes. With strong heating, they turn into a viscous, plastic state, and when cooled, they solidify again, practically without losing their properties. Such products are produced using extrusion technology. The heated auger acts as a tool in this case. A simple example of a cold extruder is a conventional meat grinder.
2 HENCO

The lowest price
Country: Belgium (produced in Costa Rica)
Rating (2018): 4.9
HENCO INDUSTRIES is one of the most renowned manufacturers of fittings, manifolds and sanitary pipes in the world. Due to the low prices, the brand's products are in great demand in our country. For the Russian market, HENCO produces a huge number of products, including a large assortment of metal-plastic pipes. They use a conventional five-layer system that can withstand temperatures up to 110 degrees. HENCO metal-plastic pipes have a unique feature - the presence of high-strength extrusion polyethylene inserts in the inner layer, which significantly increase the reliability of the product.
In reviews of HENCO metal-plastic pipes, users note the low cost and high strength of the products. They are completely silent and electrically safe, which means they are best suited for home heating or plumbing systems.
At the same time, some customers noticed the low maximum operating temperature and the lack of flexibility of the pipes.
Metal-plastic pipes for heating
As the name implies, these elements combine the most optimal characteristics of plastic and metal. Such a pipe is multilayer, its outer and inner layer consists of polyethylene, and the middle one is made of foil tightly glued to aluminum.
When arranging pipes for such communications as heating, metal-plastic or polypropylene occupy a leading position, but the first material is worth noting for its following advantages:
- the installation of metal-plastic is quick and without any problems;
- the material is resistant to high temperatures;
- metal-plastic can withstand any pressure;
- such pipes are not prone to corrosion on them;
- the inner walls of the heating elements made of metal-plastic do not collect any salts and harmful precipitation.
A feature of a metal-plastic pipe is that it practically does not allow oxygen to pass through, which has a positive effect on its service life. Due to the smoothness of the coating used inside, it does not form limescale or rust, therefore it will not be necessary to clean the pipe for a very long period of time. In addition to protection, metal-plastic also plays the role of an insulator that prevents the appearance of condensation on the outer layer of the polyethylene pipe. Some experts sometimes call this a five-layer design, which is due to the presence of two layers of adhesive.
It is also convenient to work with metal-plastic because it bends well, so there is no need to precisely adjust the linear dimensions. The material holds its shape well, so you will not need to use any clamps. Due to the versatility of such a design, it can be placed both inside and outside the premises without any fear, the main thing here is to provide access to the places where the pipe parts are fastened. The heating system can be installed not only completely from metal-plastic, but also vary this material with others. Another indisputable advantage of such products is that no complicated tools are required to connect their functional ones, and there is no need to perform difficult welding work.
Candidate # 1 - metal-plastic pipes
Internal structure and characteristics
If you look at a cross-section of a metal-plastic pipe, you can see a five-layer composition, consisting of:
- made of cross-linked polyethylene (PEX and PE RT);
- glue;
- aluminum foil;
- another layer of glue;
- another layer of cross-linked polyethylene (PEX and PE RT).
Metal-polymer pipes (MPT) are durable and reliable in operation, therefore, their service life is calculated in tens of years. The products are resistant to wall clogging and silting, as well as to corrosion and salt deposition on them. The material used for the manufacture of pipes has absolute oxygen resistance, resistance to aggressive media, and anti-toxicity.
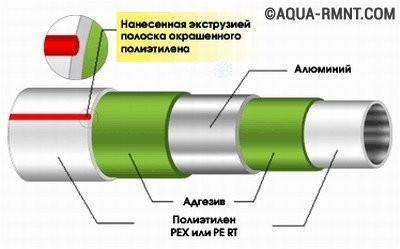
Schematic representation of the device of a metal-plastic pipe. A layer of cross-linked polyethylene is applied from the inside and outside of the product, and a layer of aluminum is applied inside.
The throughput of metal-plastic pipes is 1.3 times higher than that of steel products, and the thermal conductivity is 175 times lower. When calculating linear dimensions, perfect accuracy is not required. Low weight and high plasticity of MPT facilitates pipeline installation.
When performing work, a minimum of tools are used. Possible hidden wiring of communications, including pouring them into a concrete screed. The advantages of using these products can also be attributed to their high maintainability, the absence of the need to involve complex and heavy equipment when performing repair work, good noise absorption capacity, aesthetics of the pipeline layout and antistatic properties.

Reinforced-plastic pipes and fittings required for their strong connection. Press fittings are installed using a special crimping tool
Features of installation technology
Reinforced-plastic pipes are supplied in coils. When unpacking the material, do not use a sharp cutting tool, as it is likely to be damaged. A metal-polymer pipe of the required length is unwound from the coil and this section is straightened manually. Then the exact amount of the pipe is measured with a tape measure. Mark the mark with a felt-tip pen, along which the measured piece is cut, using a pipe cutter or other tool with functions suitable for this operation.
The cross-section of the pipe must be strictly circular. To meet this requirement, it is necessary to chamfer a chamfer from the inner layer of the pipe with a calibrator. Some craftsmen use a regular knife instead of a calibrator.
Metal-polymer pipes can be connected with crimp fittings or press fittings.
Working with compression fittings
The rubber o-rings in the compression fitting must be located in the grooves provided for them. The presence of bumps and other irregularities is not allowed. The fitting must have a Teflon insulating washer. Before you put the fitting on the pipe, put a union nut on it, and then a "cracker". After that, twist the pipe a little and put a fitting on it. Then it is necessary to move the "cracker" and the union nut to the body of the fitting, screwing the latter tightly by hand.Take two open-end wrenches and use them to tighten the nut by the required number of revolutions.
Working with press fittings
Taking a press fitting, check the presence of O-rings in it, as well as a dielectric gasket. Then the product is put on the pipe so that its wall appears in a special window located near the base of the sleeve. Next, the connectors are crimped using hand pliers. In this case, the tool is inserted onto the press fitting in such a way that the collar of the sleeve is in the corresponding recess of the press attachment. Having fixed the position of the tool, the clip is closed until the lock clicks into place. Next, the liner is crimped. If pinches are formed, then the crimping must be repeated, slightly shifting the crimp axis.

Expensive professional equipment for making connections of metal-plastic pipes with press fittings. The tool can be rented from the store by paying a deposit
Please note that it is recommended to use press fittings for autonomous heating systems installed in country houses. In crimp fittings, due to the frequent temperature difference when the boiler is turned on / off, the sealing rubber bands weaken, as a result of which the connection begins to leak
In practice, it has been found that a leak appears after six months of operation of the heating system.
Read more about the installation of metal-plastic products in the article - How to work with metal-plastic pipes: an overview of connection methods.
Specifications
For a long time, polymer materials have been trying to get rid of their main drawback - increased thermoplasticity. Crosslinked polyethylene is an example of the victory of chemical technology over previous shortcomings. The material has a modified mesh structure that forms additional bonds in the horizontal and vertical planes. In the process of cross-linking, the material acquires a high density, does not deform when exposed to heat. It belongs to thermoplastics, products are manufactured in accordance with GOST 52134-2003 and TU.
The main technical characteristics of the material include the following parameters:
- weight - about 5.75-6.25 g per 1 mm of product thickness;
- tensile strength - 22-27 MPa;
- nominal pressure of the medium - up to 10 bar;
- density - 0.94 g / m3;
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.35-0.41 W / m ° С;
- operating temperature - from −100 to +100 degrees;
- toxicity class of products evaporated during combustion - T3;
- flammability index - G4.
Standard sizes range from 10, 12, 16, 20, 25 mm to a maximum of 250 mm. Such pipes are suitable for both water supply and sewer networks. The wall thickness is 1.3-27.9 mm.

The marking of the material in the international classification looks like this: PE-X. In Russian, the designation PE-S is most often used. It is produced in straight-type lengths, as well as rolled into coils or on spools. The service life of cross-linked polyethylene and products made from it reaches 50 years.
The production of pipes and casings from this material is carried out by processing in an extruder. Polyethylene passes through the forming hole, is fed into the calibrator, passing through cooling using water streams. After the final shaping, the workpieces are cut according to the specified size. PE-X pipes can be manufactured using several methods.
- PE-Xa. Peroxide stitched material. It has a uniform structure containing a significant proportion of crosslinked particles. Such a polymer is safe for human health and the environment, and has high strength.
- PE-Xb. Pipes with this marking use the silane crosslinking method. This is a tougher version of the material, but just as durable as the peroxide counterpart. When it comes to pipes, it is worth checking the hygiene certificate of the product - not all types of PE-Xb are recommended for use in domestic networks. Most often, the sheath of cable products is made from it.
- PE-Xc.A material made from radiation cross-linked polyethylene. With this method of production, the products are quite tough, but the least durable.

XLPE pipes
XLPE pipes - REX pipes. REX stands for Crosslinked Polyethylene. This flexible, durable material is becoming an increasingly popular material. To give the polyethylene strength and resistance to temperature influences, it is subjected to high pressure processing. This leads to the formation of additional molecular bonds. This processing method is called * crosslinked *, which is why polyethylene is called cross-linked polyethylene.
Due to the three-dimensional molecular bond in the structure of polyethylene, there are a number of advantages over traditional metal pipes. Three-dimensional molecular bond increases the resistance of pipes to thermal deformation, abrasion, scratches, shrinkage, cracks due to internal stress.
When choosing REX pipes, attention should be paid to the degree of crosslinking. The standard requires a certain degree of crosslinking, at least 65%, ranging from 65% to 80%
The stitching method affects the durability and performance as well as the cost of the pipes.
There are three ways to obtain crosslinked polyethylene, which affect the degree of crosslinking.
- Pyroxide (REX - a) - pyroxides are introduced into polyethylene. The degree of crosslinking is up to 85%.
- Silane (REX - b) - organosilanides are added to polyethylene. The degree of crosslinking is not less than 65%.
- Radiation (REX - c) - the degree of crosslinking is 60%.
If the degree of crosslinking is 0%, then the pipes become too brittle and prone to cracking. Too little stitching can have equally serious consequences.
Pros of REX pipes
REX pipes have a number of advantages:
- low noise level of pipes due to its flexibility and ability to absorb pressure surges;
- ease;
- ease of installation;
- have * shape memory *, can easily restore their original shape;
- corrosion resistance;
- strength, operation is designed for a period of at least 50 years;
- resistance to freezing in cold weather;
- flexibility;
- minimum probability of * explosions * after defrosting the system;
- withstand high temperature and pressure drops.
XLPE pipes are affordable. REX pipes are installed using specialized fittings. This can significantly reduce hydraulic losses in the pipeline. The lifespan of the underfloor heating system is extended as fewer fittings are used on fractures, which reduces the risk of leaks and costly repairs in the future.
Cons of XLPE pipes
The disadvantages include the following:
negative effects of direct sunlight;
REX pipes, unlike metal-plastic ones, do not have an aluminum layer, therefore it is more difficult to work with them, since more movements are required to fix the pipe and keep its shape;
the anti-diffusion protection is on the outside of the pipe as long as the pipe is handled carefully so as not to have problems with installation. If the installation rules are not followed, the anti-diffusion protection can be damaged.
This is also one of the reasons why, regardless of the type of pipe used, the installation must be carried out by experienced certified technicians.
When comparing metal-plastic pipes and pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene (REX), it can be seen that these types of pipes have many of the same characteristics, such as anti-oxygen barrier, corrosion resistance, flexibility, strength, durability, ease of installation. But there are also some differences.
Metal-plastic pipes heat up faster, have greater thermal conductivity, and are easier to install. But the cost of XLPE pipes is lower than metal-plastic pipes.But REX pipes have a greater heat transfer, so the underfloor heating system becomes more economical, which allows pipes to be laid with a large gap during installation. This contributes to less power consumption for heating the area of the room.
The installation of REX pipes must be done with more care so as not to damage the pipes and not damage the diffusion protection.
In any case, these two types of pipes are high quality and reliable, meet modern technical requirements, and are ideal for underfloor heating.
Features of XLPE heating pipes
The difference between plain and XLPE for heating is the formation of strong internal bonds during production. Cross-sectional molecular connections provide the product with mechanical strength and resistance to high temperatures. At the same time, the advantages of simple polyethylene and its disadvantages remain. These features of cross-linked polyethylene must be taken into account when developing a heating system.
Advantages of XLPE
These pipes have all the advantages of polymer products - they are not subject to corrosion, have a low specific gravity, smooth inner walls do not allow the formation of deposits from calcium carbonate, magnesium, salts. With proper installation and operation, XLPE heating will last a long time. The main thing is to observe the temperature regime and control the system pressure.
Advantages:
- The operating temperature of the coolant is up to + 90 ° С. In some models, short-term temperature exposure up to + 100 ° C is allowed.
- Minimum value of thermal expansion. During the design of heat supply, it is not necessary to provide compensation rings, as for polypropylene pipes.
- Choice of connection methods - electrofusion, press or crimp fittings. The method depends on installation conditions and budget.
- Low weight. Transportation and installation is simplified.
The shape memory effect is pronounced. After mechanical or thermal impact, the product tends to return to its original shape.
The main disadvantages of the material
But despite the advantages, XLPE pipes have disadvantages that must be taken into account in heating. The main one is the destruction of the material when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Therefore, in the distribution of heat supply, it is necessary to exclude a direct effect on the line of sunlight. If brass fittings are used for the connection, the finishing material should not destroy this metal.
Additional disadvantages:
- Oxygen diffusion. It penetrates through the walls of cross-linked polyethylene, enters the coolant. The enrichment of water with oxygen leads to the destruction of the metal elements of the system - the heat exchanger, fittings. Therefore, for heat supply, you need to choose models with an oxygen barrier made of ethylene vinyl alcohol.
- The limitation of the method of laying. For heating, two conditions must be met - protection from sunlight and reduction of sagging after starting hot water. Therefore, polyethylene pipes for heating are often installed on a sub-floor.
- All the disadvantages of concealed installation. For the repair and maintenance of the heating supply, the decorative coating will have to be dismantled.
Due to the low coefficient of thermal conductivity, heat is not transferred to the room from the pipes. But this can be considered an advantage, since heat losses in the pipeline are reduced when hot water flows.
