Advantages and disadvantages
The manufacturer positions Borrex cellular polycarbonate as a premium brand. Therefore, in comparison with Sotalight, Berolux and Siberian Greenhouses, SPK Borrex:
- More durable. Calculated for 1 m², Borrex 4 mm polycarbonate weighs 0.8 kg, while Berolux with the same thickness - 0.7 kg, and "Siberian Greenhouses" - 0.6 kg.
- More durable... The manufacturer's warranty for Borrex transparent cellular polycarbonate is 15 years versus 10 years and even less for other brands.
- More varied... The choice of structure is extremely important for high strength requirements. Borex has a greater number of variants of the internal structure, even without taking into account the reinforced modification "Titan".
Compared to other brands of the same plant, Borex cellular polycarbonate has only one drawback: the price. It costs 15-60% more, depending on the brand and thickness.
The denser the better the UV protection
The weight of 1 m² of cellular polycarbonate or, more precisely, its density, with the same structure, depends on only one thing: the thickness of the backing sheets. And then everything is simple: the thicker these sheets, the thicker the layer that protects the material from UV rays can be applied to it; the thicker the protective layer, the longer the polycarbonate sheet will last.
Otherwise, the benefits are standard:
- translucency - transmits up to 88% of the rays of the visible spectrum;
- impact resistance - cellular polycarbonate Borrex 6 mm and more absorbs from 27 N * m, and 4 mm - 21.3 N * m;
- flexibility - bending radius up to 700 mm;
- ease - 1 m² of sheet with a thickness of 4 mm weighs only 0.8 kg, and 6 mm - 1.3 kg;
- wide operating temperature range - from -50 to +120 ° С;
- keeps warm - the thermal conductivity of the material reaches 1.5 W / (m² • ° С);
- sound insulating material - reduces the noise level by 16-23 dB;
- fire safety - Borrex polycarbonate sheet is hardly flammable (group B1), does not spread flame (group RP1), practically does not smoke (group D2), almost does not burn (group G2);
- resistance to a range of chemicals: acids, solutions of salts, fats;
- easy assembly and processing - you can cut the material with an ordinary circular saw;
- low price - cellular plastic is cheaper than most other building materials.
Some of these properties are typical for polycarbonate in general, for example, fire safety. But most of the benefits are due to the hollow structure.
There are also disadvantages of cellular polycarbonate sheets:
- Droplet formation during combustion. Polycarbonate itself is self-extinguishing and does not spread flame, but when melted, it flows down. These hot drops can easily set fire to the insulation or wood frame underneath.
- Possibility of cavity contamination. If the joints between the sheets are poorly sealed, then dirt, dust, water will get into the cavities, and microorganisms will multiply. This will irreversibly reduce the light transmission and aesthetics of the material.
- Slight rigidity. Polycarbonate plastic flexes even under very small point loads.
- The complexity of waterproofing. Cellular polycarbonate changes its size depending on temperature: it expands at high temperatures, decreases at low temperatures. Fasteners should allow the material to "play", but at the same time maintain the tightness of the coating. This is difficult to do, and any flaws in the installation lead to roof leakage.
- Strong electrification. The material is electrified from literally everything: friction during transportation, wiping with a rag before installation. Because of this, dust adheres well to it, therefore, it is necessary to wash the roof and facades with polycarbonate glazing often enough to maintain transparency.
- Short service life... Cellular polycarbonate lasts 10–20 years, depending on the brand, and then the sheets need to be changed. This is not bad when compared to other clear plastics, but practically nothing compared to glass.
- Not resistant to alkalis, aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones.
How to work with the material?
At home, a sheet of monolithic or molded polycarbonate can be subjected to different types of processing. Most often, bending, cutting, connection of individual layers to each other by gluing are carried out. This polymer does not create any particular difficulties in processing, it is well suited for cutting with hand or power tools.
Home cutting
Cast or extruded polycarbonate without meshes cannot be simply sawed without prior preparation. Best of all, it lends itself to cutting with a grinder with a disc for metal No. 125 installed on it. In this case, the cut is obtained without burrs and chips. And you can also perform laser cutting of sheets, use a jigsaw with a fine file. The sharper the cutting element, the better the procedure will be.
In the course of cutting, it is worth adhering to certain recommendations.
- The sheet is cut only in a horizontal position, placing it on a clean, flat surface. Any protrusions or other obstructions will lead to cracks or deformation.
- The cutting line must be applied in advance. The most convenient way to do this is with a marker.
- Panels less than 2 mm thick are cut in a stack, connected with clamps. This will avoid cracking the material.
- Cutting must be done from the side with UV protection. The protective film is not removed until the completion of the work.
Elements that are large in size are easiest to cut by placing them on a flat floor surface. A board is laid on top, on which the master can freely move.
How to bend a sheet at home?
Monolithic polycarbonate lends itself quite well to bending, but taking into account its characteristic radius. You can give the sheet the desired shape using a locksmith's workbench and a vice. Transparent or colored material is placed on a workbench, clamped, and then manually adjusted to the desired bending level
It is important not to use excessive force to maintain the integrity of the slab.
Bonding technology
The need to glue polycarbonate most often arises when joining sheets in greenhouses or other structures. The connection of the elements is carried out using special chemical compositions that do not affect the main characteristics of the material. In light, unloaded products - greenhouses, sheds - you can use several options for adhesives.
- One-component adhesives. They are also suitable for mounting polycarbonate sheets on rubber, metal, glass or polymer surfaces. There are many products in this category, you can choose Vitralit 5634, Cosmofen, Silicone mastic. One-component adhesives are characterized by fast curing, they are not afraid of moisture and high temperatures.
- EVA. Adhesives based on ethylene vinyl acetate are suitable for connecting polymeric materials to each other in different planes. It is a good choice for creating multi-layer products.
- Hot curing adhesives. Provides maximum bond strength. The best formulations have a polyamide base.
In structures operated under loads, two-component adhesives should be used - Acrifix, Altuglas. Formulations on a polyurethane base, which form a transparent elastic seam, are suitable. Silicone adhesives are often used to seal joints. Polycarbonate can be attached to flat surfaces with a special double-sided tape on an acrylic foam base. It is recommended to apply adhesives of thermoplastic, silicone, polyurethane types, as well as fast curing with a mounting gun.
What is cellular polycarbonate
In cross-section, the sheet resembles a honeycomb of a rectangular or triangular shape, hence the name of the material itself.The raw material for it is granular polycarbonate, which is formed as a result of condensation of carbonic acid polyesters and dihydroxyl compounds. The polymer belongs to the group of thermosetting plastics and has a number of unique properties.
Industrial production of cellular polycarbonate is carried out using the technology of extrusion from granular raw materials. The production is carried out in accordance with the technical specifications TU-2256-001-54141872-2006. This document is also used as a guide for the certification of material in our country.
The main parameters and linear dimensions of the panels must strictly comply with the requirements of the standards.
The structure of cellular polycarbonate in cross-section can be of two types:
Its sheets are produced with the following structure:
2H - Two-layer with rectangular cells.
3X - three-layer structure with a combination of rectangular cells with additional inclined partitions.
3H - three-layer sheets with a rectangular honeycomb structure, produced with a thickness of 6, 8, 10 mm.
5W - five-layer sheets with a rectangular honeycomb structure, as a rule, have a thickness of 16 - 20 mm.
5X - five-layer sheets consisting of both straight and inclined ribs, produced with a thickness of 25 mm.
The linear dimensions of the sheets of cellular polycarbonate are given in the table:
| Specifications | Unit measurements | Options | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheet thickness | mm | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 25 |
| Number of layers (walls) | 2H | 2H | 2H | 2H | 3X | 3H | 6H | 5X | |
| Honeycomb structure | |||||||||
| Distance between stiffeners | mm | 6 | 6 | 10,5 | 10,5 | 25 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| Sheet width | m | 2,1 | 1,2 | ||||||
| Minimum bending radius | m | 0,7 | 0,9 | 1,2 | 1,5 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 3,0 | Not recommended |
| Specific weight of the sheet | kg / m2 | 0,8 | 1,3 | 1,5 | 1,7 | 2,5 | 2,8 | 3,1 | 3,4 |
| Panel length | mm | 6000 and 12000 (deviation from the nominal size of 1.5 mm for transparent sheets and 3 mm for colored sheets is allowed) |
It is allowed to issue panels with other parameters besides those specified in the technical conditions as agreed with the customer. The thickness of the stiffeners is determined by the manufacturer, the maximum permissible deviation for this value is not set.
Advantages of monolithic polycarbonate
Traditionally, it is believed that monolithic polycarbonate is more often used in construction due to the fact that it degrades more slowly and is more resistant to external influences. But these are far from its only advantages.
You need monolithic polycarbonate if the following qualities are the most important in the design requirements:
- Strength. Unlike cellular polycarbonate, monolithic is much stronger and better copes with shock loads. That is why it is recommended to be used as walls for temporary structures or for canopies over entrances. The use of a sheet without cavities provides more reliable protection against objects falling from a height.
- Resistance to constant loads. For example, if we are talking about a greenhouse, snow will regularly accumulate on it in snowy regions. The same can be said about buildings in places where strong winds often rage. In such conditions, monolithic polycarbonate will last much longer than a cellular one.
- Transparency. Another indisputable advantage of sheets without internal bridges is high transparency. High-quality non-profiled plates may well “compete” with glass in transparency. The absence of stiffening ribs inside the sheet allows you to see through it very clearly, especially if tinting is not used.
- Saving the parameter of light transmission in the presence of tinting. If you add a colored layer to cellular polycarbonate, it drastically loses the percentage of light transmission and cannot be used for a greenhouse. But a weak tinting for a monolithic sheet provides enough light for the plants. Thus, it can be used when covering greenhouses or greenhouses. It is recommended, however, to avoid dark shades.
- Aesthetic appearance.The absence of stiffening ribs inside the sheet makes the monolithic polycarbonate almost completely transparent, which gives a special appearance. Both materials look modern, but it is the monolithic sheets that add elegance to the building and add elegance to the forms.
Main characteristics
| Colors: | Thickness, mm: | Sheet size, mm: | Wed prices, rubles: |
|---|---|---|---|
| transparent, yellow, orange, burgundy, red, brown, bronze, blue, green, turquoise, silver, milky | 4 | 2100/12000 | 4 650 |
| 6 | 2100/12000 | 8 100 | |
| 8 | 2100/12000 | 9 600 | |
| 10 | 2100/12000 | 10 700 | |
| 16 | 2100/12000 | 18 600 | |
| 20 | 2100/12000 | 22 100 | |
| 25 | 2100/12000 | 26 700 |
High impact resistance - Karboglass polymer plates are distinguished by high strength and are significantly superior in resistance to both silicate and acrylic glass. Moreover, they are characterized by an affordable cost. Judging by consumer reviews, this is the best material for the construction of greenhouses, greenhouses, greenhouses and the like.
- Safety - its superiority is expressed not only in incombustibility, but also in low injury hazard, since cellular polycarbonate Carboglass is distinguished by good impact strength. In case of severe damage, the sheet does not crumble into fragments, but deforms and breaks, forming fragments with non-sharp edges, which significantly reduces the threat to health.
- UV protection - Polycarbonate partially absorbs UV light, protecting plants from burns. However, the polymer itself is not sufficiently resistant to UV rays. To ensure the products have a long service life, Karboglass polycarbonate is covered with three layers of a protective coating.
- Light transmission is the most important parameter for a translucent material. For Karboglass products, this figure is one of the highest - up to 86%.
- Working range - the panels perfectly tolerate both the action of heat and the most severe cold. Operating temperature range: from -40 to +120 C.
- Thermal insulation - the material provides first-class heat and sound insulation of the room, thereby reducing the need for heating. According to consumer reviews, savings can be up to 30%.
- Chemical resistance - the positive characteristics of the polymer include resistance to the action of most aggressive chemicals. Therefore, honeycomb panels are willingly used in the construction of industrial facilities.
Flexibility - flat and sloping greenhouse roofs are characterized by one drawback - snow and moisture are retained on their surface, which significantly reduces the level of illumination and necessitates periodic cleaning. Rounded designs do not have this disadvantage. Cellular polycarbonate Karboglass allows you to easily implement such projects. The cellular structure makes it possible to bend the sheet without losing its properties. The photo shows a greenhouse with a rounded roof.
Forms of product release
The dimensions of the Carboglass honeycomb panels correspond to the standards: the length of the product is 6 or 12 m, the width is 2.1 m. The thickness of the sheet and its structure are different. The manufacturer produces panels of the largest sizes.
4 and 6 mm - lightweight material recommended for the construction of spring-summer greenhouses. Two-layer sheet with rectangular or triangular honeycomb.
- and 10 mm - can be used in the construction of winter greenhouses and greenhouses, as it is very durable and is able to withstand high snow and wind loads. The honeycombs in the panels are only rectangular, but the product itself can be made of two or four sheets.
- 16 mm - can have a two-layer or four-layer structure. The number of layers increases the degree of thermal insulation.
- 20 and 25 mm - consist of four sheets. 25 mm are also available in a five-chamber form. Such material can be safely classified as acoustic.
The color range of Karboglass polycarbonate is very wide: transparent panels - actually for greenhouses, translucent - crushed ice, and sheets in different color shades - blue, turquoise, red, green, as well as yellow, burgundy, silver and brown.There is also a trendy bronze color.
When choosing the appropriate color, you should pay attention to the fact that the coefficient of thermal expansion and the level of translucency to a large extent depend on the color. So, for example, the transparent version reacts least of all to the effect of temperature, while bronze panels are characterized by a coefficient of thermal expansion of 2.5 mm / m, which must be taken into account during installation
The photo shows the colored Karboglass panels.
Installation of cellular polycarbonate
how to cut polycarbonate
Cutting polycarbonate sheets is very easy. If the thickness is from 4 to 10 mm, the cellular polycarbonate is cut with a knife.
True, in order for the cutting to be straight, it is better to use a saw with an emphasis and high speed, which has a blade with undivided fine teeth and hard reinforced alloys.
After the cutting is completed, it is necessary to remove the chips from the internal cavities.
How to drill
To drill cellular polycarbonate, the thickness of which ranges from 4 to 40 mm, metal sharp drills are used. In this case, it is necessary to drill between the stiffeners. In this case, you need to remove the hole from the edge of the panel by about 4 cm.
drilling polycarbonate
Sealing joints
Particular attention should be paid to the correct closing of the ends of the panels. If a vertical or inclined arrangement is assumed, then the ends located on top must be closed with a continuous self-adhesive aluminum tape, the lower ones with a perforated tape, which will prevent the penetration of contaminants and ensure the drainage of condensate
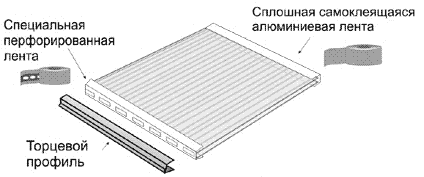
end sealing
If the installation of cellular polycarbonate is carried out under the arch, then all ends must be covered with a perforated film.
The profile for cellular polycarbonate has such a design that ensures reliable fixation of the ends, so no additional fastening is required.
In order to ensure the drainage of condensate, you need to drill holes in the profile with a thin drill.
Golden rules for editing
- In no case should the ends be left open, as this will reduce the translucency and service life.
- Do not use regular tape to seal the ends.
- The lower ends must not be closed tightly.
If you have chosen cellular polycarbonate, installation should be carried out, only taking into account the fact that the ribs located inside are located along a length that can reach 12 meters. In this case, the panel in the structure must be oriented so that the condensate that will form in it can drain and be discharged without hindrance.
For outdoor installation, it is better to use cellular polycarbonate, which has a protective UV stabilizing layer, which is applied to the sheet from the outside.

remove the protective layer
You can not bend a sheet of cellular polycarbonate - deformations may form on the material and its service life will be significantly reduced.
Fastening sheets
Fastening of cellular polycarbonate is carried out using self-tapping screws or special thermal washers.
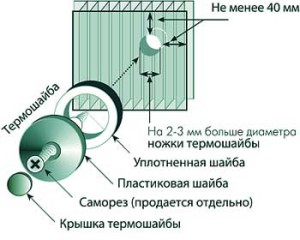
fastening with thermal washers
The thermal washer includes a plastic washer with a foot that matches the panel thickness, a snap-on cover and a sealing washer.
Thanks to thermal washers, a tight and reliable fastening is ensured, and the so-called "cold bridges", which are formed when using self-tapping screws, are also eliminated. In addition, the thermal washer prevents the panels from crushing.
Do not forget that you cannot rigidly fix the panels, however, as well as fix the panels with nails, rivets and unsuitable washers. It is also not necessary to overtighten the screws. Incorrect fasteners can increase the weight of the polycarbonate, which will negatively affect its service life.
Installation of profiles
types of profiles
One-piece panels are mounted by inserting a groove into profiles that correspond to the thickness of the polycarbonate.The profile is fastened with self-tapping screws to the longitudinal supports.
Installation with split profiles
Several holes need to be drilled every 30 cm.
Next, you need to attach to the frame and lay the panels on it, while leaving a gap of 3.5-5 mm
Here it is very important not to forget to "walk" along the profile with a sealant and do everything very carefully, because if you use transparent cellular polycarbonate, then all flaws will be visible through it and the aesthetic appearance will suffer. However, if you think that using colored cellular polycarbonate, you will be able to do the job "anyhow", then you are greatly mistaken: aesthetics, of course, will not suffer, but reliability and durability are definitely.
At the end, you need to snap the profile using a wooden mallet.
Technical characteristics of polycarbonate
Strength - both impact and flexural strength is far superior to conventional glass and its acrylic counterpart. Its use in the construction of large objects - exhibition halls, industrial workshops, voluminous outdoor sheds, is based on this very quality. Polycarbonate takes the first place in strength of translucent materials. Density - ranges from 0.68 to 3 kg / sq. m depending on the thickness of the sheet and its structure. Obviously, even very bulky panels will be lightweight, which greatly facilitates the installation process. Small objects, like a greenhouse in a garden or an attached veranda, can be easily done by hand. Light transmission - has a range from 75 to 86%, which is quite comparable with the parameters of silicate glass. In this case, the polymer partially absorbs ultraviolet radiation
Adequate dissipation factor provides protection from direct sunlight, which is very important for greenhouses. Thermal insulation properties - 0.36-0.57 m2С / W, which significantly exceeds the performance of silicate glass
A greenhouse covered with polycarbonate will save its owner up to 30% on heating. Flexibility is a quality highly appreciated by designers, thanks to which the material is so widely used in advertising projects. It is possible to construct curved elements of almost any kind from panels without the use of special equipment. The temperature range of use is from -40 to +120 C. Polycarbonate is the most frost-resistant polymer plastic. Fire safety is a characteristic that allows the material to gain superiority over acrylic glass. Unlike the latter, polycarbonate is non-flammable and does not support combustion.
Cellular polycarbonate
Main characteristics
At the production stage, polycarbonate molecules enter a special device - an extruder. From there, under increased pressure, they are extruded into a special shape to create sheet panels. Then the material is cut into layers and covered with a protective film. The technology of manufacturing cellular polycarbonate directly affects the performance properties of the material. In the course of processing, it becomes more durable, resistant to mechanical stress, and has exceptional bearing capacity. Cellular polycarbonate in accordance with GOST R 56712-2015 has the following technical and operational characteristics.
Strength
Resistance to impacts and other mechanical damage of cellular polycarbonate is many times higher than that of glass. These properties make it possible to use the material for the installation of anti-vandal structures, it is almost impossible to damage them.
Resistant to moisture and chemicals
The plates used in finishing are often exposed to external unfavorable factors that worsen their structure. Cellular polycarbonate is resistant to the vast majority of chemical compounds. He is not afraid:
- high concentration mineral acids;
- salts with a neutral or acidic reaction;
- most of the oxidizing and reducing agents;
- alcoholic compounds, with the exception of methanol.
At the same time, there are materials with which it is better not to combine cellular polycarbonate:
- concrete and cement;
- harsh cleaning agents;
- sealants based on alkaline compounds, ammonia or acetic acid;
- insecticides;
- methyl alcohol;
- aromatic as well as halogen type solvents.
Light transmission
Cellular polycarbonate transmits 80 to 88% of the visible color spectrum. This is less than that of silicate glass. Nevertheless, this level is quite enough to use the material for the construction of greenhouses and greenhouses.
Thermal insulation
Cellular polycarbonate is characterized by exceptional thermal insulation properties. Optimum thermal conductivity is achieved due to the presence of air particles in the structure, as well as due to the high degree of thermal resistance of the plastic itself.
Life time
Manufacturers of cellular carbonate claim that this material retains its technical and operational properties for 10 years if all the requirements for installation and maintenance of the material have been met. The outer surface of the sheet is treated with a special coating, which guarantees high protection against UV radiation. Without such a coating, the transparency of the plastic can decrease by 10-15% during the first 6 years. Damage to the coating can shorten the life of the boards and lead to their premature failure. In places where there is a high risk of deformation, it is better to use panels with a thickness of more than 16 mm. Besides, cellular polycarbonate has other characteristics.
- Fire resistance. The safety of the material is ensured by its exceptional resistance to high temperatures. Polycarbonate plastic is classified in category B1, in accordance with the European classification, it is a self-extinguishing and hardly flammable material. Near an open flame in polycarbonate, the structure of the material is destroyed, melting begins, and through holes appear. The material loses its area and thus moves away from the source of fire. The presence of these holes causes the removal of toxic combustion products and excess heat from the room.
- Light weight. Cellular polycarbonate is 5-6 times lighter than silicate glass. The mass of one sheet is no 0.7-2.8 kg, thanks to which it is possible to build lightweight structures from it without the construction of a massive frame.
- Flexibility. The high plasticity of the material distinguishes it favorably from glass. This allows you to create complex arched structures from the panels.
- Load bearing capacity. Certain varieties of this type of material are characterized by a high bearing capacity, sufficient to withstand the weight of a human body. That is why, in areas with increased snow load, cellular polycarbonate is often used for installing roofing.
- Soundproofing characteristics. The cellular structure results in reduced acoustic permeability.
