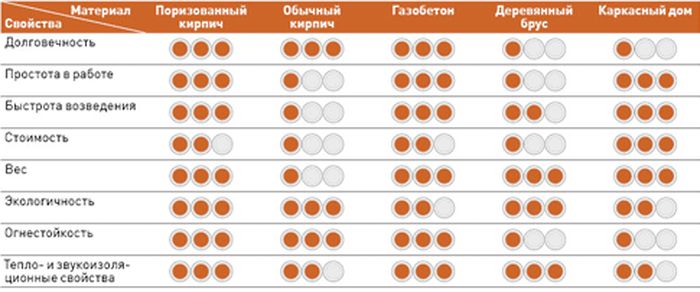
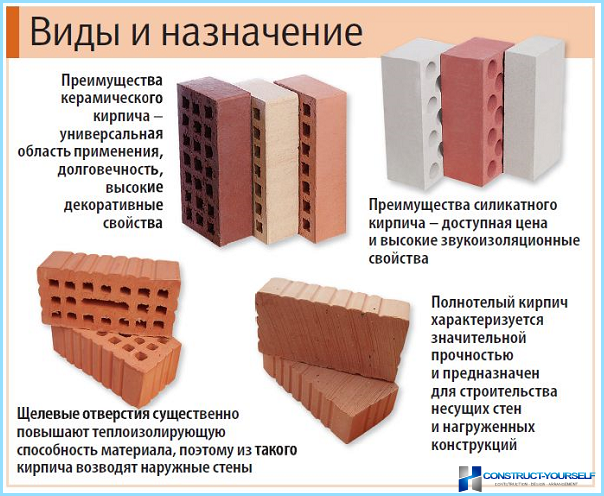
The main properties of ceramic bricks
Ceramic bricks are rated for a number of characteristics:
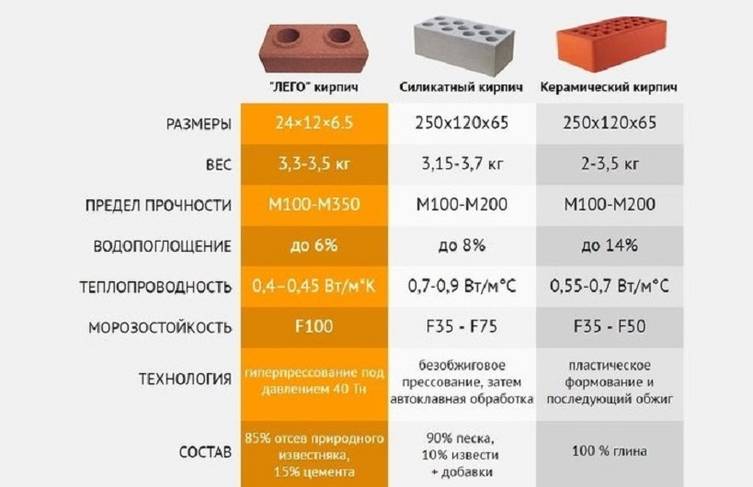
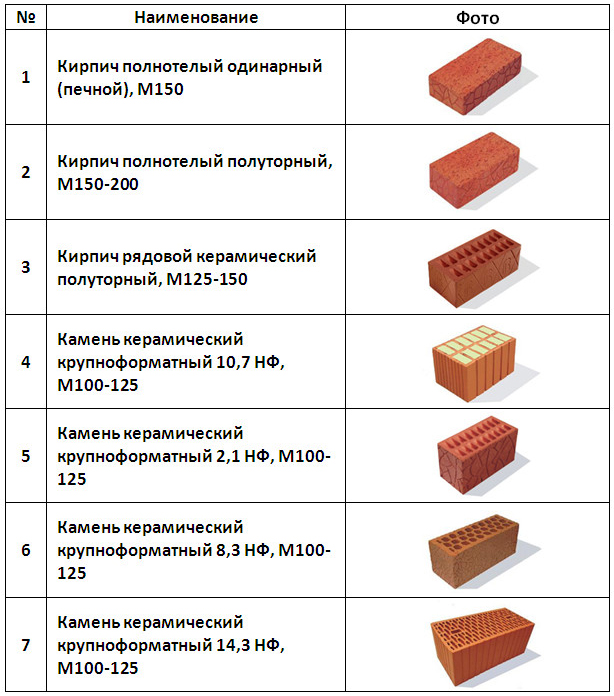
- the strength grade shows what load in kg 1 cm2 of brick can withstand. If this indicator is 100 kg / cm2, then this is the M100 brand, if 150 kg / cm2 - M150, etc. Bricks of the M75-M100 brands are used for the construction of partitions and walls in low-rise buildings. For the foundations of country houses, it is better to use brick M150, and brick M200-M300 is suitable for the construction of the foundation of apartment buildings;
- thermal conductivity depends on the number of pores and cracks in the brick. Solid brick has low thermal insulation properties, it is only suitable for the construction of load-bearing walls. Hollow ordinary brick can be used for the construction of low-rise houses, it allows you to make the thickness of the walls much smaller;
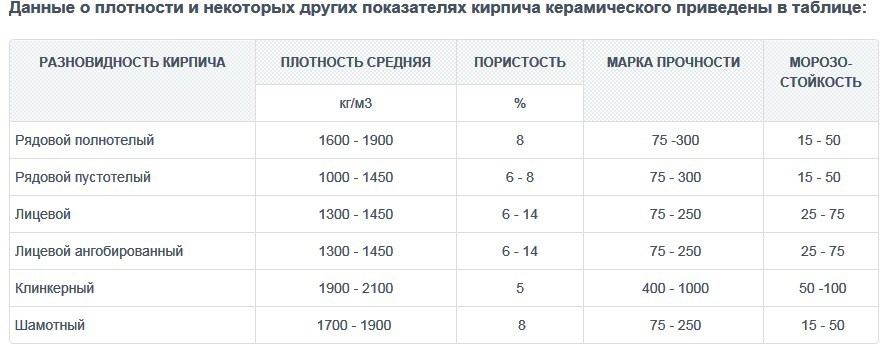
- the moisture absorption of ceramic bricks is low, which, in particular, is due to its widespread use in construction. Solid brick has a moisture absorption of 6-14%. However, when the room temperature drops to the level of street moisture can penetrate into the pores of the material and crystallize, which will gradually reduce the strength of the structure;
- the vapor permeability of ceramic bricks is about 0.14-0.17 Mg / (m * h * Pa), which is enough to create a normal microclimate in the room and remove excess moisture from it;
- frost resistance is expressed in freeze / thaw cycles. For the construction of load-bearing walls, it is better to take a brick with frost resistance F50, and if the construction will be carried out in a difficult climate, then - F75-F If facing brick will be used for wall decoration, then it must also have high frost resistance. Engobbed and clinker bricks show themselves best in this regard;
- fire resistance of ceramic bricks is the highest among other building materials. It resists direct fire for more than 5 hours. For comparison, the analogous figure for reinforced concrete is 2 hours, and for metal structures - generally 30 minutes. Ordinary ceramic bricks withstand a maximum temperature of 1400C, and clinker bricks are able to survive a temperature effect of 1600C;
- soundproofing. Brick dampens noise well. A brick wall in two bricks (530 mm thick) is able to detain 60 dB of noise, in one brick - 50 dB.
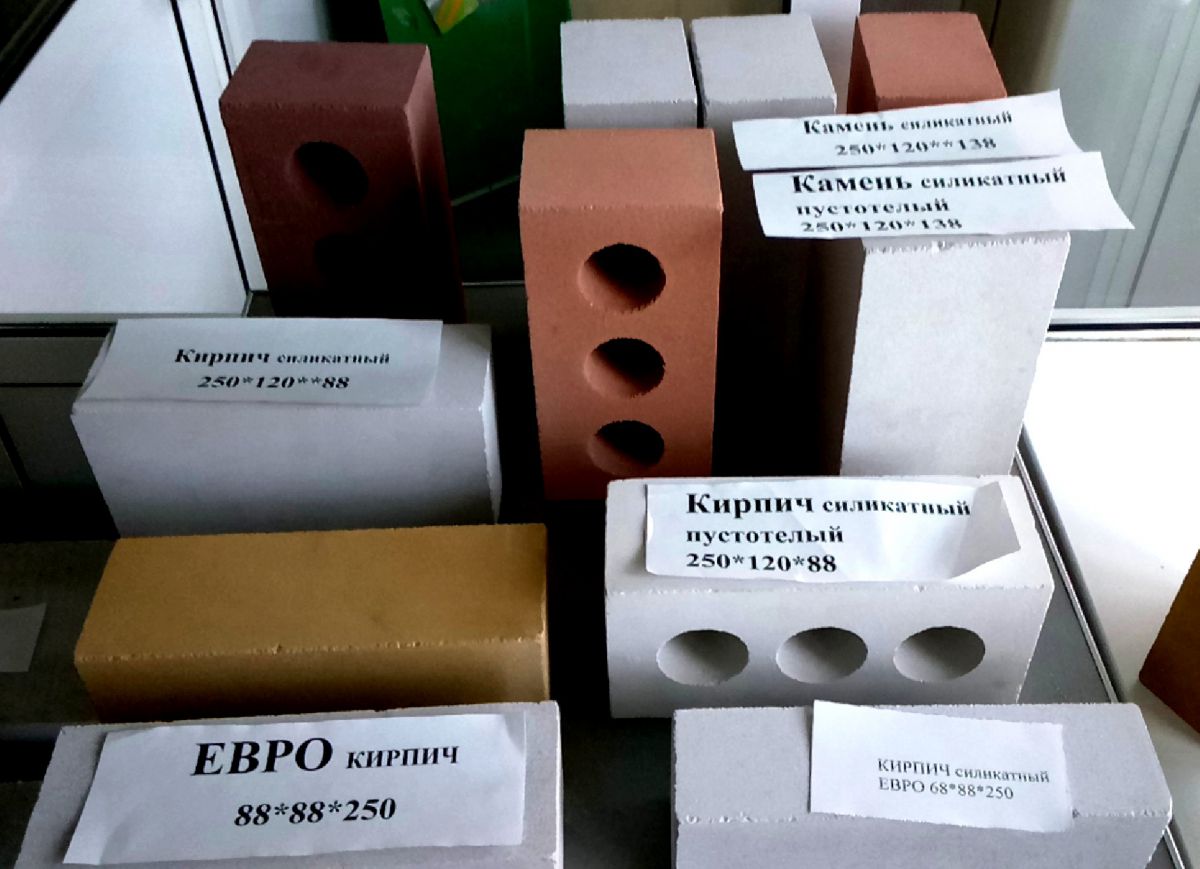
Types and sizes of silicate bricks according to the state standard
The dimensions and properties of sand-lime bricks and stones are described in two standards. GOST 379-95 and GOST 379-2015. The latter provides additional information on silicate blocks, colorants and lightweight fillers that have come into use in recent years. According to the standard, there are the following sizes of sand-lime bricks:
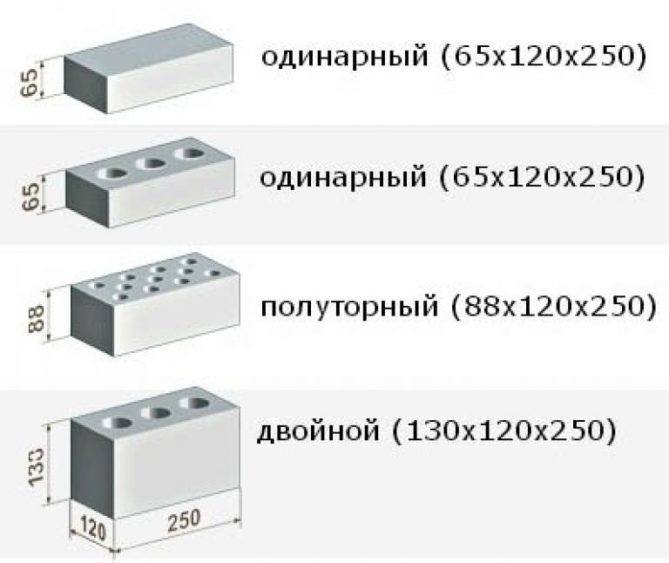
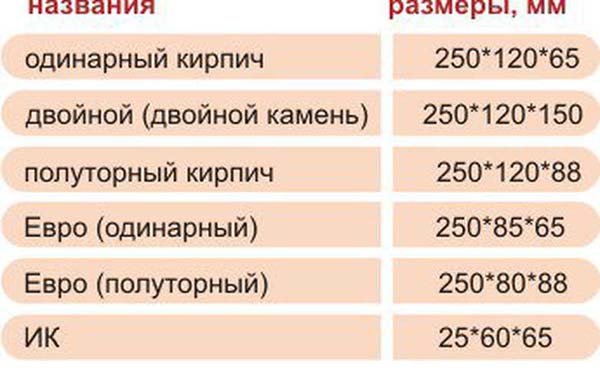
- Single. Has dimensions 250 * 120 * 65 mm. In the marking is indicated by the letter "O".
- Thickened or one and a half. Differs in greater thickness, has dimensions of 250 * 120 * 88 mm. It is marked with the letter "U".
- Sand lime brick EURO. Has dimensions 250 * 85 * 65 mm or 250 * 60 * 60 mm. This is a finishing material, ordinary ones are not produced in this format. In the marking, they usually write EURO SL and further parameters.
- Silicate stone. It is twice as thick as single. That is, it has dimensions of 250 * 120 * 138 mm. Double silicate brick is often called, but this is not a GOST name.
- Silicate block (in the SB marking) and enlarged silicate block (designated by the SBU). A product with a poke width of more than 130 mm. The sizes of silicate blocks are given in the tables. They are used for the construction of partitions, there are no finishing blocks. Their end parts (butts) can have formed tongue-and-groove edges.This makes it possible to increase the thermal insulation characteristics of the masonry, since a direct freezing seam is excluded.
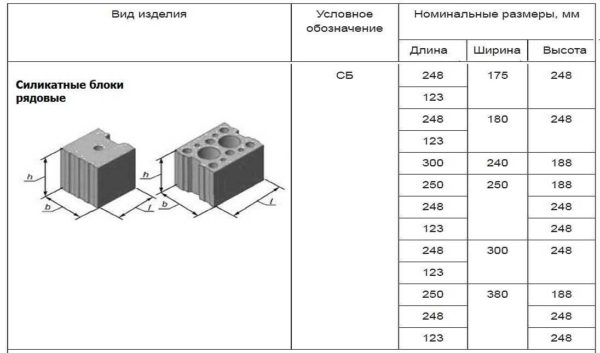
Silicate block and standard dimensions
That is, according to the standard, the width and length of the silicate brick are the same. The width is 120 mm and the length is 250 mm. Only the thickness changes. Moreover, a deviation from the nominal dimensions is allowed only within ± 2 mm.
Varieties: finishing and masonry
Silicate bricks and stones can be facing and ordinary. Private - ordinary, for laying walls and partitions. In the marking it is indicated by the letter "P". Facing silicate brick (marked with the letter "L") has one or more smooth or decorative sides. It can also be called finishing or decorative. There are these types of facial stone:
- Smooth surface:
- White.
- Dyed in mass (volume dyed). The pigment is added to the mass prior to molding. On chips it has the same color as on the surface. The marking contains the letters "About".
-
Coated with paint, glaze or polymers.
- Textured or decorative with a raised side. It is indicated in the marking with the letter "D". It can have only a front decorative surface, or front and butt.
- Chipped. With a "torn" surface on the spoon, which is formed when the stone is cracked. It is designated by the letter "K".
- Rusty. With a surface "like a natural stone". The marking is designated "Ru".
One or two faces of any type of facing brick can be coated with a hydrophobic compound. This impregnation reduces water absorption, extends the service life and improves the appearance of the material. The letter "G" is added to the marking. Another finishing sand-lime brick can be with rounded edges or beveled.
Corpulent and hollow
There are two types of sand-lime bricks: with voids and without them. Solid brick in the marking is designated as "Po", hollow - "Pu". The number, size and location of the voids is determined by the manufacturer. Voids can pass through or not. There are two requirements for them:
- located should be perpendicular to the brick bed;
- the thickness of the outer walls must be at least 10 mm.

The shape, size, location of voids are not standardized. The outer wall must be at least 10 mm. These are all requirements
Neither the shape nor the location of voids on the surface are standardized. Therefore, the weight of the hollow brick may differ in each plant. Moreover, the marking and all other indicators will be the same.
Specifications
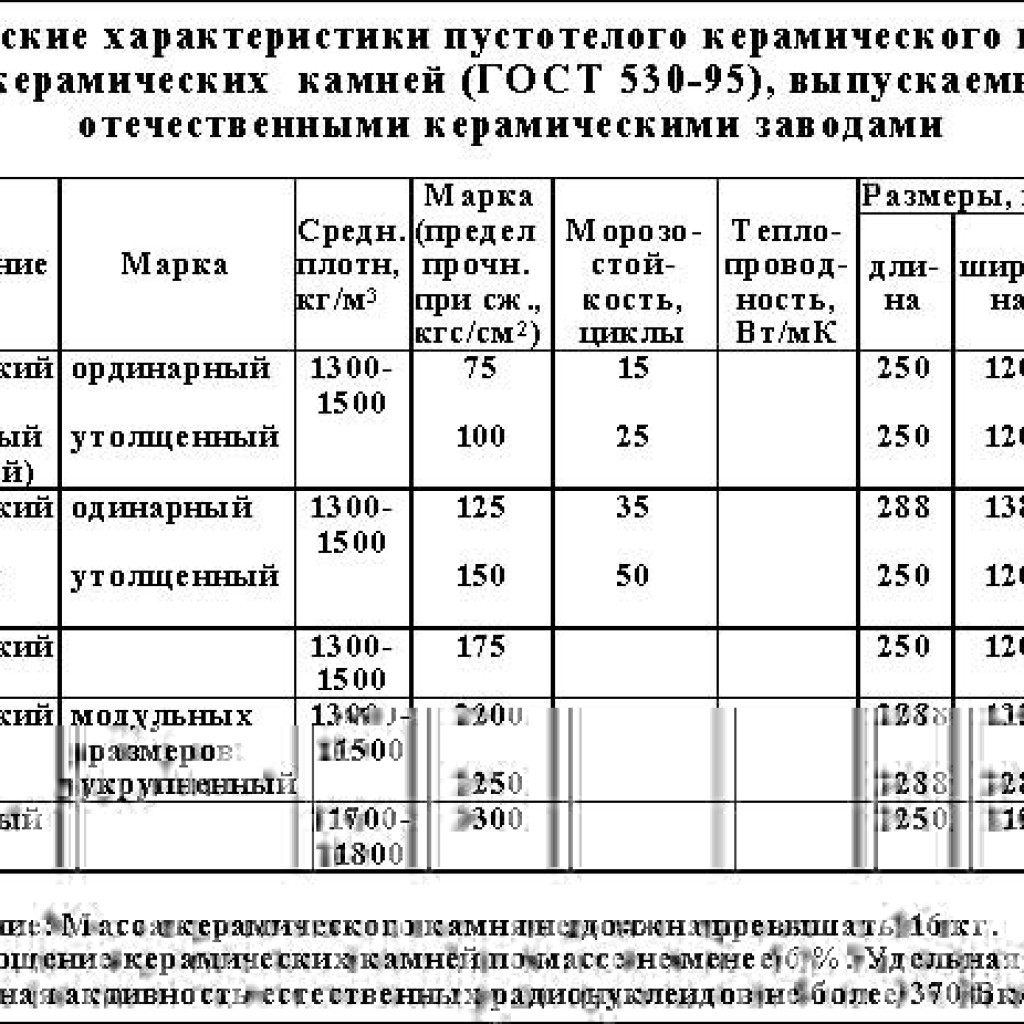
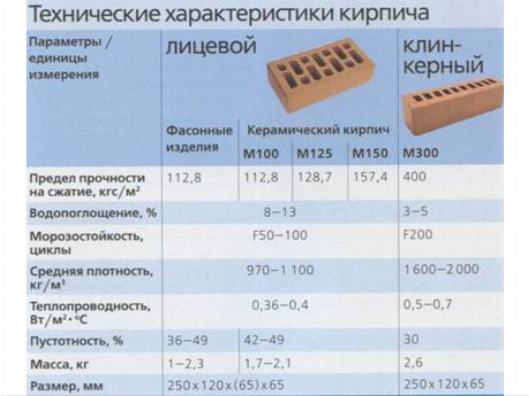
The standard defines strength grades, frost resistance and density class. Strength grades represent the load that a material can bear. It is easy to decipher this value. The number that follows the letter "M" is the number of kilograms per square centimeter that the material can withstand without destruction. Example: M150 means that ceramic bricks of this batch will withstand a load of 150 kg / cm².
| Strength grades | Ceramic bricks | M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300 |
| Ceramic stone | M300, M400, M500, M600, M800, M1000 | |
| Clinker bricks | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300; | |
| Brick and stone with horizontal voids | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100 | |
| Frost resistance | F25, F35, F50, F75, F100, F200, F300. |
Strength and frost resistance grades for ceramic stone and bricks are indicated.
Frost resistance is indicated by the letter F and a number. The figure shows the number of freeze / thaw cycles that do not change characteristics and appearance. For example F50 - 50 frost and defrost cycles. For internal partitions in heated buildings, frost resistance can be taken low - a positive temperature will still be maintained.
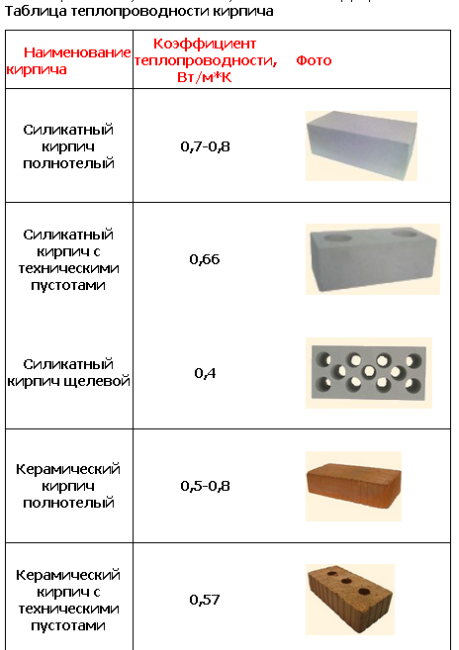
Thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal resistance
The density class corresponds to the average density of the material, but the energy efficiency of the material also depends on the density. The lower the density, the better the thermal insulation properties.But it will not be possible to significantly reduce the density for external walls. They must carry a certain level of stress. Therefore, in recent years, a brick house has been made with insulation.
The ratio of the average density of the product and the density class
How to work with the last two tables? The density class is indicated in the marking. By this characteristic, you can find out the mass of a ceramic brick cube. It is listed in the first table. The second table helps to compare the density of the material and the coefficient of thermal conductivity of masonry from it. For example, the density class of ceramic bricks is specified as 1.0. This means that the cube should weigh 810-1000 kg, and the masonry on a minimum layer of glue after drying will have a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.20-0.24 W / (m * ° C).
Groups of ceramic bricks and blocks according to the thermal characteristics of masonry (with a minimum amount of mortar)
It is worth saying that according to modern standards, none of the types of bricks gives the necessary thermal resistance. Unless the thickness of the wall will be more than a meter.
Masonry made of ceramic bricks of one and a half or two bricks does not meet modern requirements for thermal conductivity of external walls
In this case, a hollow brick or a building ceramic block wins, since they have the best thermal conductivity characteristics. The wall will be a couple of tens of centimeters already - not 147 cm, for example, but only 105. So, in any case, it is worth considering additional insulation of the outer walls.
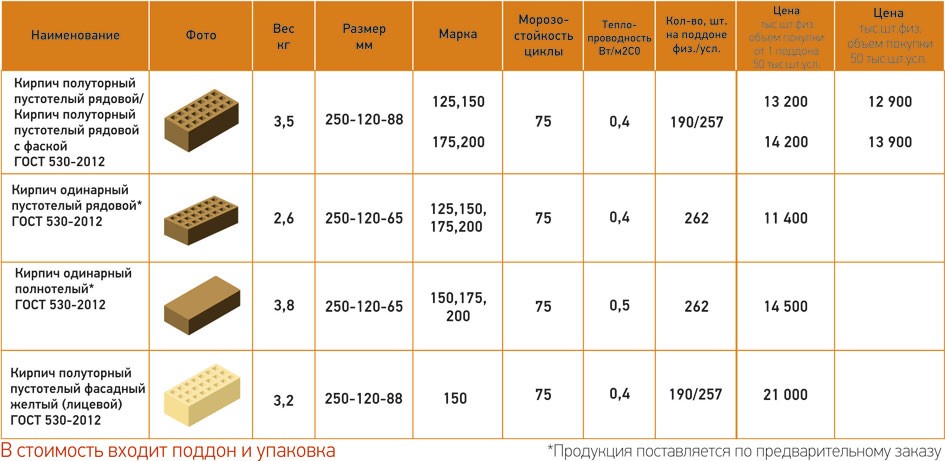
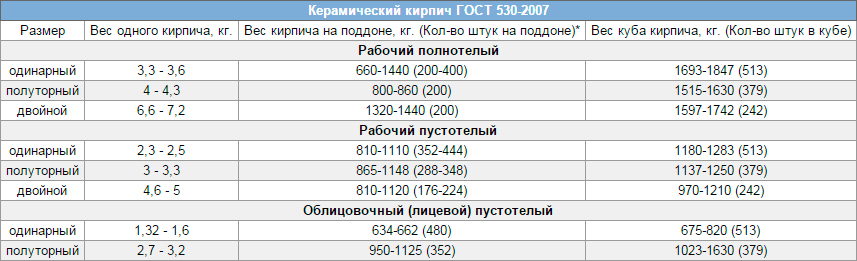
Ceramic brick weight
The weight of ceramic bricks depends on the density and the presence / number of voids. The exact figure is recognized in the accompanying documents, and then, the spread within one batch is up to 10%.
The characteristics indicate the weight of different types of bricks: masonry, finishing, with and without voids
Using the old terminology, the approximate weight of ceramic bricks will be as follows:
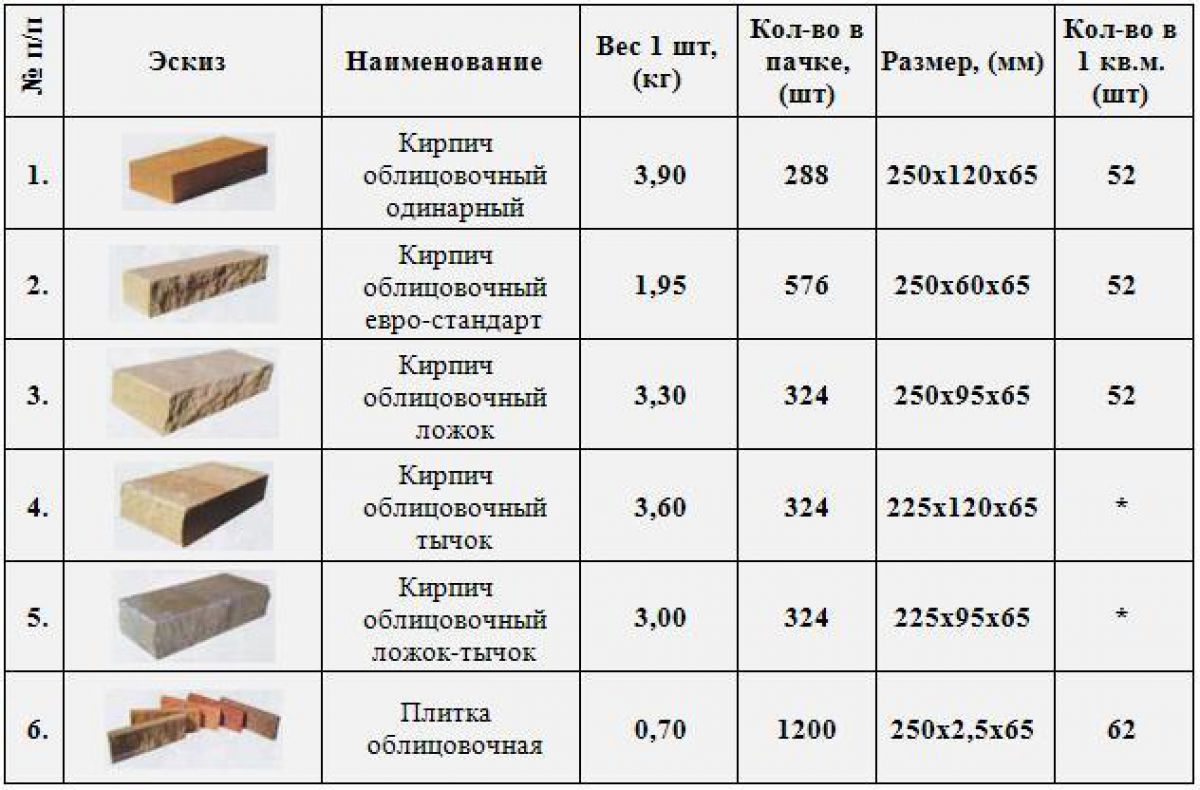
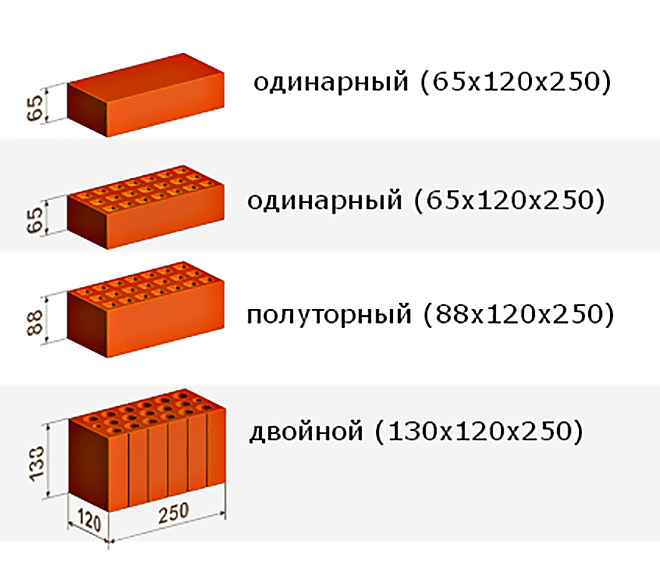
- Single (type 1 NF, size 250 * 120 * 65 mm):
- corpulent (private, masonry, construction) 3.3-3.6 kg / piece;
- worker (private, masonry) hollow - 2.3-2.5 kg / piece;
- facing (front, finishing) hollow - 1.32-1.6 kg / pc.
- One and a half has a mass (type 1.4 NF, dimensions 250 * 120 * 88 mm):
- full-bodied private - 4.0-4.3 kg / piece;
- hollow private - 3.0-3.3 kg / piece;
- facial hollow - 2.7-3.2 kg / pc.
- Double weighs (1.8 NF 288 * 138 * 88 mm.):
- ordinary corpulent - 6.6-7.2 kg / piece;
- ordinary hollow - 4.6-5.0 kg / pc.
Comparison of the characteristics of ceramic bricks - hollow, different density, solid
We will give an approximate weight, since the density and number of voids for each plant can differ significantly. The number of voids is not regulated, so the finishing materials can be lightweight.
Pros and cons of ceramic bricks
The advantages of ceramics include naturalness, harmlessness. If we compare ceramics and silicate, then clay products win a little in terms of thermal conductivity. If you look at the indicators, then the difference is very small. But a ceramic house is much warmer than a silicate one. The point is in the higher heat capacity. Clay can store more heat and is therefore warmer at home.
Ceramics are inferior to silicate in sound insulation properties, as well as in geometry and stability of characteristics. This is its main disadvantage. Moreover, at a high price, often efflorescence, with which it is very, very difficult to fight. Another drawback is that even the front surface is rarely even.
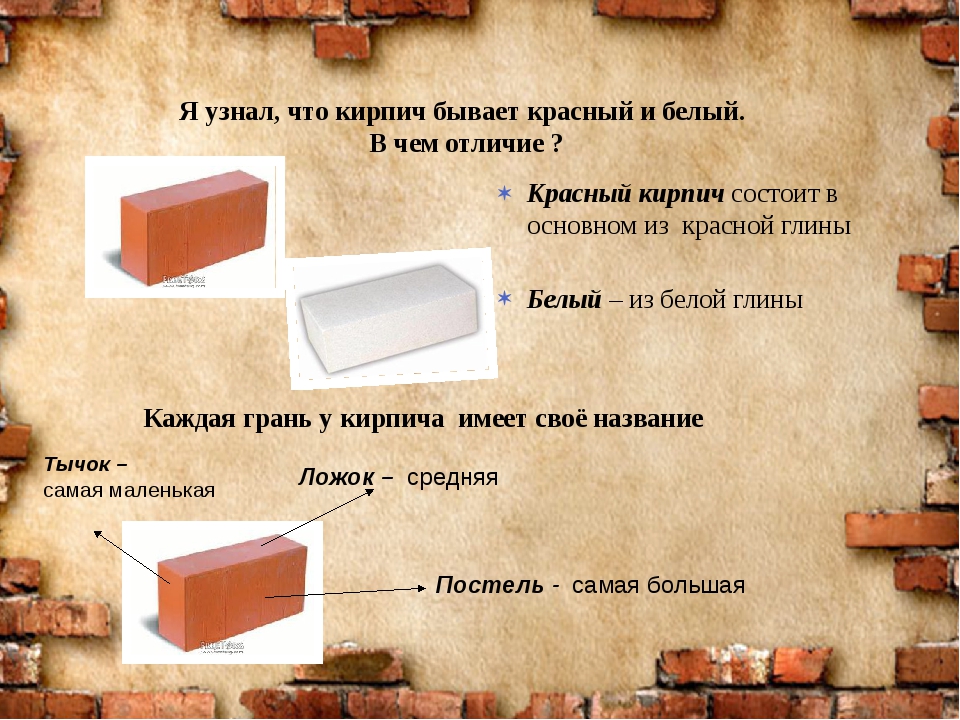
Ceramic brick is a traditional material for building houses, which is more than one hundred years old.
All these shortcomings are understandable. Ceramic bricks are obtained by firing pre-shaped parallelepipeds from clay mortar. Clay is a natural material that has various properties. The different properties of different types of clay are the main reason that the size of ceramic bricks does not differ in stability. Moreover, a significant spread can be within the same batch. And from party to party, in general, there may be significant differences.The different characteristics of the feedstock also cause a wide variation in the characteristics of the finished product. Such as strength and density.
Service life - reality is not happy
In many respects, ceramics should be better than the same silicate, but the reality turns out to be different. Recently, too often there is a red ceramic brick crumbling, dilapidated after several years of operation under normal conditions. The reasons are the complexity of the technology. For a good result, careful processing and preparation of the clay is required in order to exclude lime inclusions, which are the reasons for "shooting". And this is additional time in an already not short production cycle. And extra energy. And expensive equipment, which is not bought by everyone.
Not the best picture
The second point: holding the temperature regime of firing. Burnt ceramic bricks behave normally in masonry. It only looks worse, as it is darker than the "norm". It's not so scary. But the unburned one collapses, crumbles. And this is why he is dangerous. Ceramics are fired in the furnace for a long time, and so it takes a little to reduce the time in order to increase productivity. Hence the underburning. Or fuel economy, which is far from cheap. So compliance with the technology for the production of ceramic bricks is a high price for products. And expensive bricks are bought very reluctantly. So the collapsed red brick most likely had a low price. And everyone knows that cheap is very rare. Nevertheless, the budget for a construction site is usually not a rubber one and you have to save money.
In terms of thermal conductivity and some other parameters, ceramic bricks should be better
No matter how complex the production technology is, European supplies have a geometry close to ideal, and the dimensions are standard, and the quality is stable. Their price is far from budget, but quality problems are rare. So if the funds allow, they try to buy imported bricks. Domestic clay, even expensive, still cannot boast of stability of quality. That is why, although ceramics should be better in many respects, more and more often the choice is made in favor of silicate. Because for quite reasonable money you can buy good quality building material. He is chosen even though he is much colder. All the same, in order to achieve the required level of energy efficiency, it is necessary to insulate the ceramics too.
Dimensions (edit)
Before calculating how many bricks per cubic meter, you should decide on the dimensions of the bricks used.
Whether it will be a single, one and a half or double brick.
Each of them has its own, standard dimensions, differing only in the height of the product. At the same time, the length and width remain unchanged.
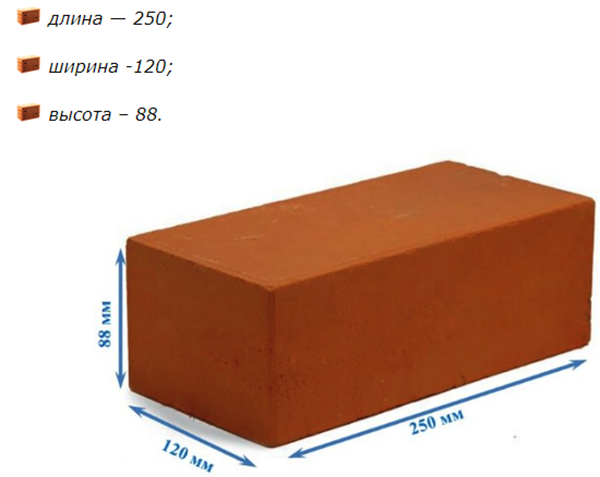
A single brick has the following dimensions:
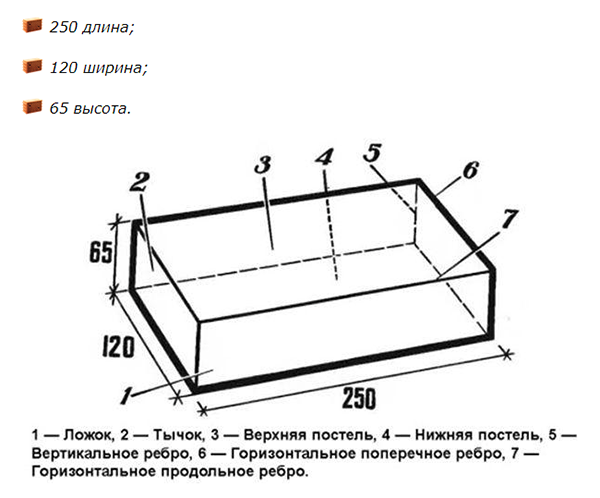
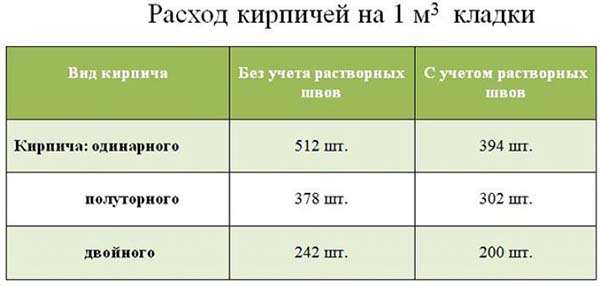
Based on these dimensions, as mentioned above, the number of bricks in one cube is 512-513 pieces.
And in order to calculate the number of bricks in a cube of masonry, you should add the size of the joints that the mortar occupies.
For example, if we take the size of the seam - 1 centimeter, then the number of building bricks in a cube of masonry will be about 394-395 pieces.
One and a half brick, differs in that it has a height of 88 millimeters. One-and-a-half bricks in a masonry cube are about 378-379 pieces.
And when calculating how many bricks are in a cube of brickwork, taking into account a seam of 1 centimeter, the number of bricks will be 302 pieces.
The double brick has a height of 138 millimeters. Most often it is hollow inside. Without taking into account the mortar, the number of double bricks in 1 cube is 242 pieces.
And the number of double bricks in a cube of masonry will be about two hundred pieces, with seams equal to one centimeter.
How to calculate how many bricks are in a cubic meter
In addition to standard sizes, there are custom bricks. In this regard, I would like to know by what principle how many pieces of bricks are calculated in a cube.
To determine how many bricks in 1 cubic meter of clean brick, excluding seams, you must:
- Calculate the volume of one brick, in meters;
- Divide the Unit by the obtained value;
- Round the resulting number to an integer value.
Let's calculate with a specific example.
As you know from school, to determine the volume, you need to multiply the length, height and width of the product.
Let's calculate the volume of a single, standard brick 250x120x65. Just so as not to get confused in the calculations, let's immediately convert millimeters to meters. So that everything is in the same units.
There are one thousand millimeters in one meter, which means that you need to divide the length, width and height indicators by one thousand.
The volume of one cube is equal to one. As you remember, the volume is calculated by multiplying the width, height and length, that is, 1 * 1 * 1 = 1 cubic meter.
Now we divide the unit by the volume of one brick and get - 1: 0.00195 = 512.82
The resulting value is rounded to the nearest whole number. This will be 512 full bricks, or slightly less than 513 bricks.
How many bricks are in one cube of masonry
Calculating how many pieces of single brick in a cube of masonry, you need to add the approximate height of the mortar to the height.

Let's take, as in the example above, the height of the seam for one centimeter, that is, 10 millimeters. Add to the brick height and get - 75 millimeters or 0.075 meters.
The same applies to the length of the brick. As you can imagine, there is also a mortar between the bricks in the masonry. 250 millimeters plus ten equals 260 millimeters or 0.26 meters.
In a similar way, you can calculate as many conventional bricks in a masonry cube.

Conditional brick means:
- How many silicate bricks are in one cube;
- How many basement bricks are in a cube;
- How many red bricks are in the cube, and so on.
The number of cubes in one thousand pieces of bricks
Sometimes it is required to calculate how many cubic meters are in a certain number of bricks. This is not difficult to do.
For this you need:
- Calculate the volume of one brick;
- Multiply the resulting value by the amount.
For example, we have one thousand standard, single bricks. As in the examples above, we will convert all values to meters and multiply the height, width and length.
That is, almost 2 cubic meters. Which, however, has already been seen from the example above. Where we got the result a little more than 512 bricks per cubic meter. Accordingly, in two cubic meters there will be one thousand and fifteen whole bricks.
When calculating bricks in masonry, do not forget to take into account the volume of the mortar. Which is added to the height and length of the brick.
And in the case when the masonry is not in one brick, for example, during the construction of columns, then the volume should be added to the width of the brick.
How to calculate the number of bricks in a cubic meter
Useful articles:
Brick fence reliability and protection;
How to make a new opening in a brick wall;
DIY brick fireplace;
Brick stove for a bath: reality or luxury;
Brick wall;
Brick cottage: briefly about everything;
Show off your hand-built brick barbecue to your friends;
Let's make a dream brazier out of bricks;
What you need to know about brick for the construction of a stove or fireplace.
Strengths and weaknesses of both materials
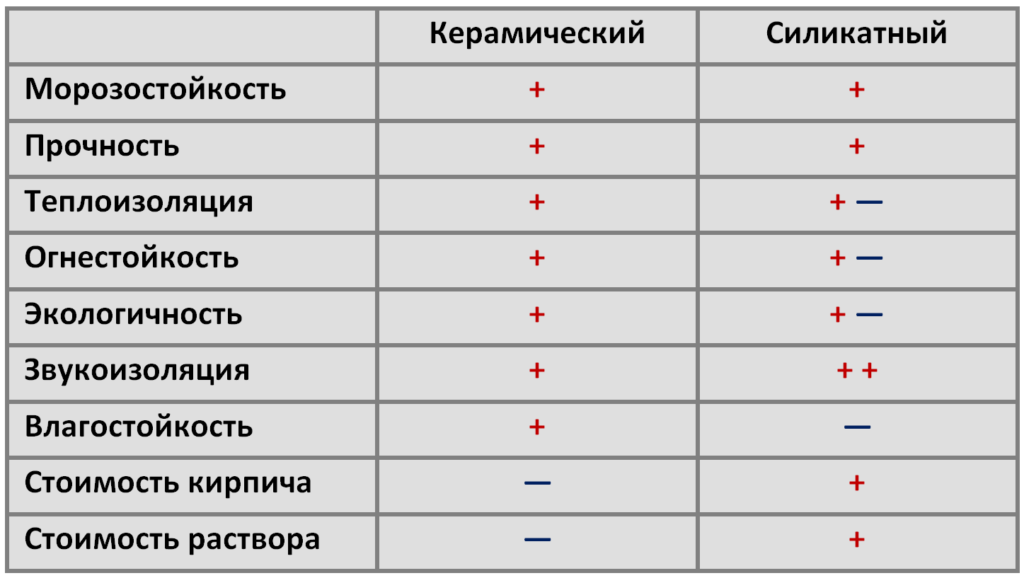
Since we have already examined the indicators, let's analyze what advantages and disadvantages both materials have and find out: which is better - silicate or ceramic bricks? Which of the products are most vulnerable?
Pros and cons of silicate products
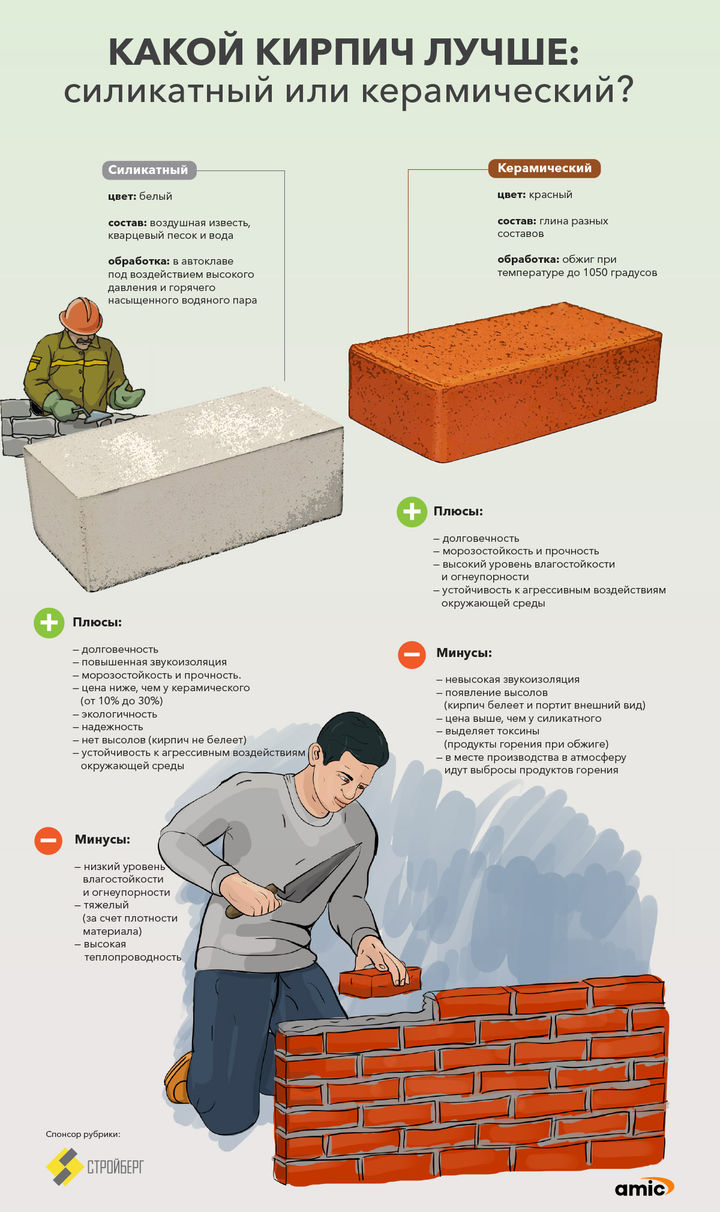
Silicate brick has a number of positive characteristics. The pluses include:
A sufficiently high index of frost resistance indicates the practicality and high performance of the material;
Indicators of density and strength allow to erect not only small, but also multi-storey buildings using these products;
The wide scope of application of the material indicates its partial versatility;
The composition determines environmental friendliness and, accordingly, safety for the environment;
Fire resistance is a definite plus, products can also withstand elevated temperatures, which is also important;
The ratio of density and coefficient of thermal conductivity is quite acceptable;
Low price;
The ability to do the masonry with your own hands. In this case, you will need instructions and a minimum set of materials and tools;
The sound insulation indicator will be able to make the stay in the room comfortable, protecting those in it from extraneous noise;
A variety of manufacturers, types and shades of products allow each developer to choose the right option for themselves;
It is also worth noting the high aesthetic qualities and good geometry of the brick. The main disadvantages are as follows:
The main disadvantages are as follows:
- Hygroscopicity of bricks. Products absorb moisture quite intensively, therefore, they need additional protection from its effects, since the consequences can be very unpleasant;
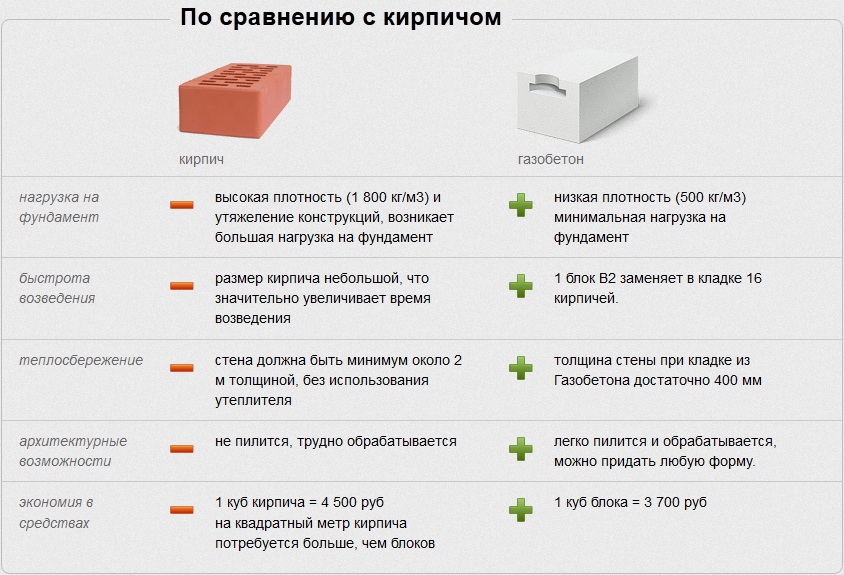
- Large weight of products. If we compare silicate bricks, for example, with masonry made of foam or aerated blocks, then the load on the foundation, when constructing a building using silicate bricks, will be much higher;
- Reduced construction speed due to the small size of the products;
- Lack of decorative elements in the product range;
- It is not recommended to use silicate bricks in the construction of objects that are characterized by constant high humidity. For example: a bathhouse or a sauna, as well as the foundations of buildings.
Advantages and disadvantages of ceramic products
Ceramic brick has the following positive characteristics:
- First of all, it is worth noting the durability of products and high performance characteristics. In many ways, these qualities have determined the particular popularity of the material, which only grows over the years due to the constant improvement of technology and equipment for production.
- A variety of choices. The market provides an opportunity to purchase products of different types and drivers. This applies to shape, size, structure and color.
- As in the case of silicate bricks, if we compare the thermal conductivity coefficient with the density index, then this fact is undoubtedly a plus.
- High rate of sound insulating properties.
- According to the manufacturers, the material is environmentally friendly, so we will attribute this quality to the pluses. However, it should be noted that environmental friendliness largely depends on the deposit of raw materials, that is, clay.
- Frost resistance of bricks is at the proper level. As already mentioned, the products are able to withstand up to 200 freeze-thaw cycles, but this applies to especially dense and high-quality bricks.
- Wide architectural possibilities. This is primarily due to the variety of products. They can be used to build amazing and incredible building structures. Sights of many countries of the world are built using this material.
Like any other material, ceramic brick is not without its drawbacks. Consider them as well:
Let's pay attention to the high selling price of products. Building a ceramic brick house is not cheap.
Again, the material is hygroscopic
It is characterized by moisture absorption, which, if construction technologies are not followed, will lead to a loss of quality indicators for products and the entire building.
For bricks, the appearance of efflorescence is characteristic, which can significantly worsen the external characteristics of the structure.
Low-quality products crumble and crumble.
And in general: defective and low-quality goods are not uncommon in the ceramic brick market.
The products have no more significant drawbacks.
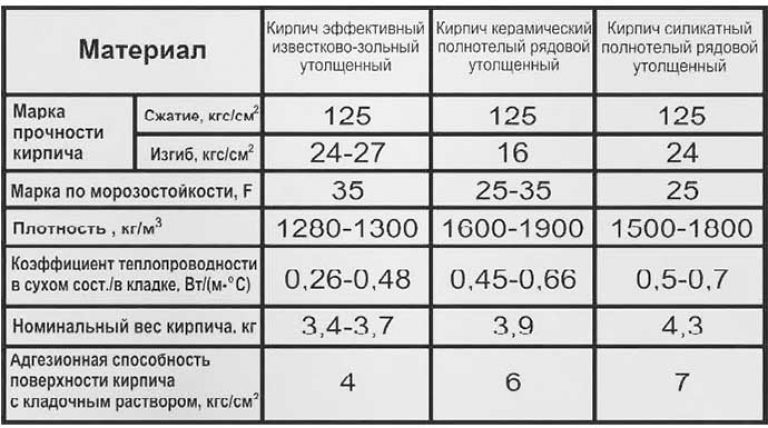
Brick technical parameters
To find out which brick is better and how silicate differs from ceramic brick, you should study the main characteristics of the materials.
Preparation method
The composition of the two types of bricks and the methods of their manufacture are fundamentally different:
- Ceramic bricks are made of clay that is molded, dried and fired in kilns.
- The composition of silicate bricks includes 90% quartz sand, 10% quicklime, water, and some additives. The mass is formed and subjected to pressure and steam in an autoclave.
Strength
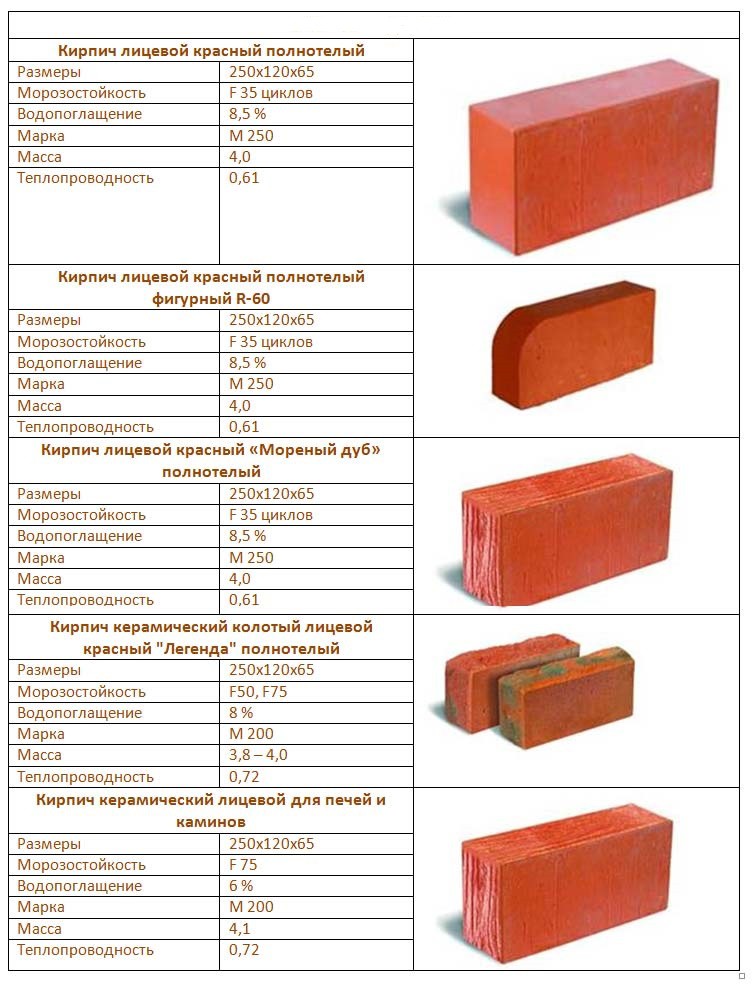
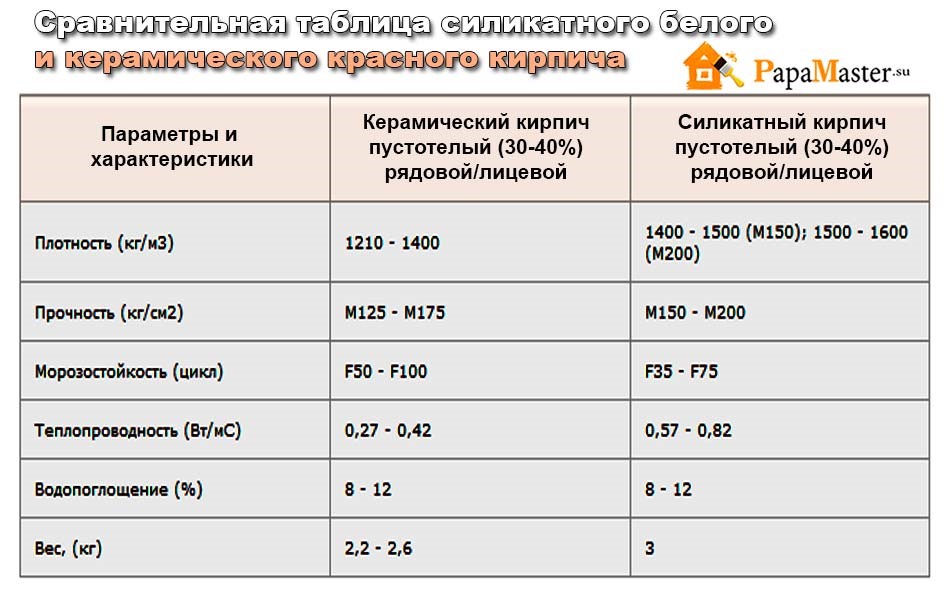
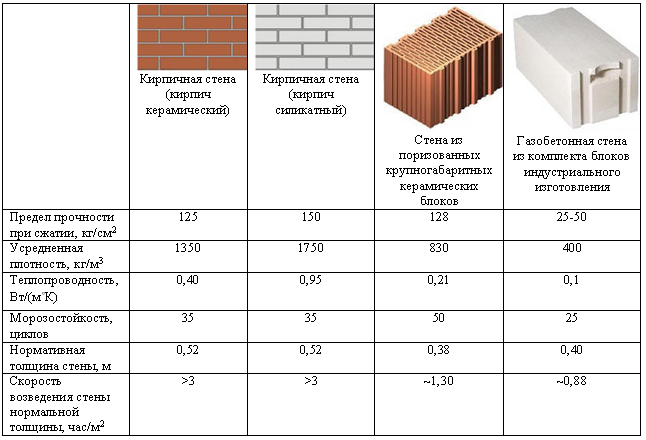
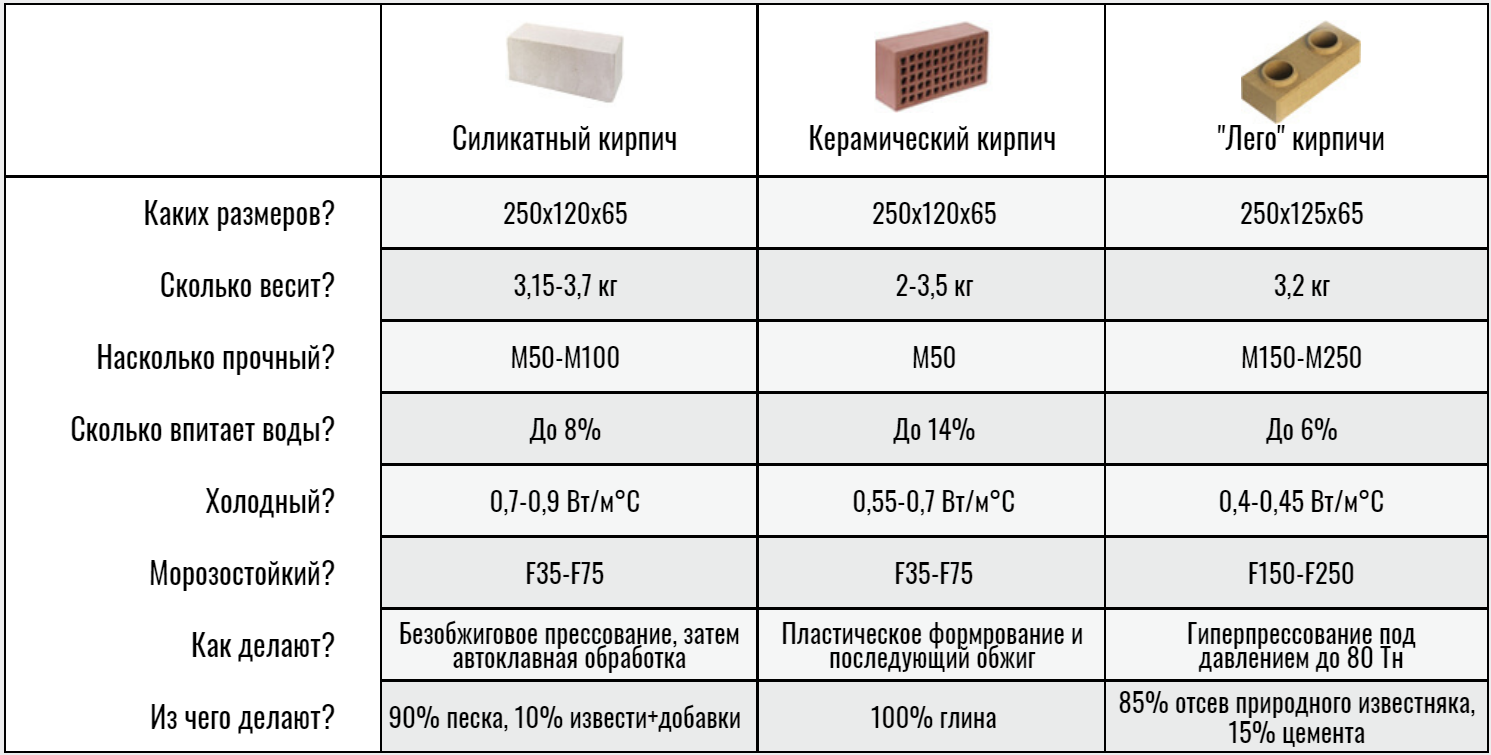
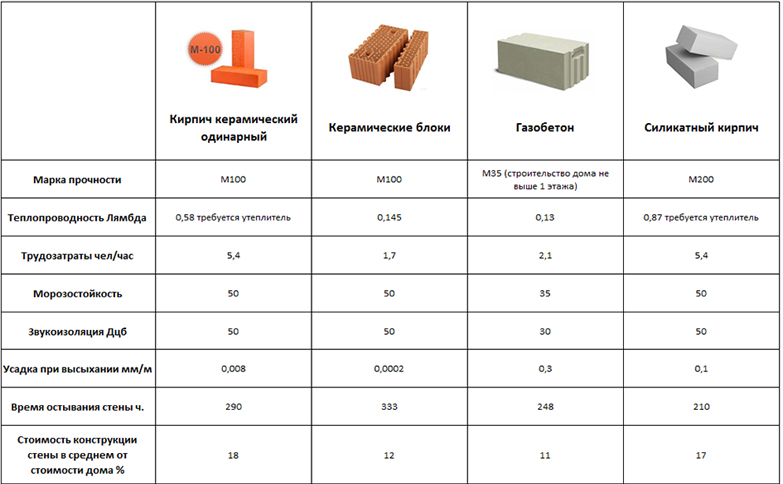
The difference between ceramic bricks and silicate bricks lies in their strength, which characterizes the ability of the block to withstand a certain weight per 1 square centimeter. For silicate, the strength is 150-200 kg / cm2, and for clay - 50-200 kg / cm2. The superiority of the lime-sand block is clearly observed here. It is from this material that it is recommended to erect buildings above 1 floor.
Density and weight
Solid silicate has a density of 1600–2000 kg / m3 and a higher weight. Red brick has a density of 1400–2000 kg / m3. A hollow lime-sand block has a voidness of 15–30%, and its density is 1400 to 1600. A hollow ceramic block has a voidness of 40–55% with a density of 1200–1400. As you can see, silicate is superior to clay in these indicators.
By weight, solid bricks are about the same, but the weight of hollow silicate is slightly higher than the weight of a clay analogue.
Fire resistance
Choosing blocks for the construction of structures in contact with an open flame (fireplaces, stoves, barbecues), many ask the question: which is better, ceramic or silicate bricks? The answer is clear. It is recommended to use the ceramic version, which successfully withstands high temperatures for 6 hours. But its silicate analogue is destroyed already at a temperature of 600 degrees, and an open fire can withstand only 3 hours.
There is a kind of ceramic brick - fireclay block. It is made of fireclay clay, therefore it has an increased degree of fire resistance. It is used for laying fireboxes in stoves and fireplaces.
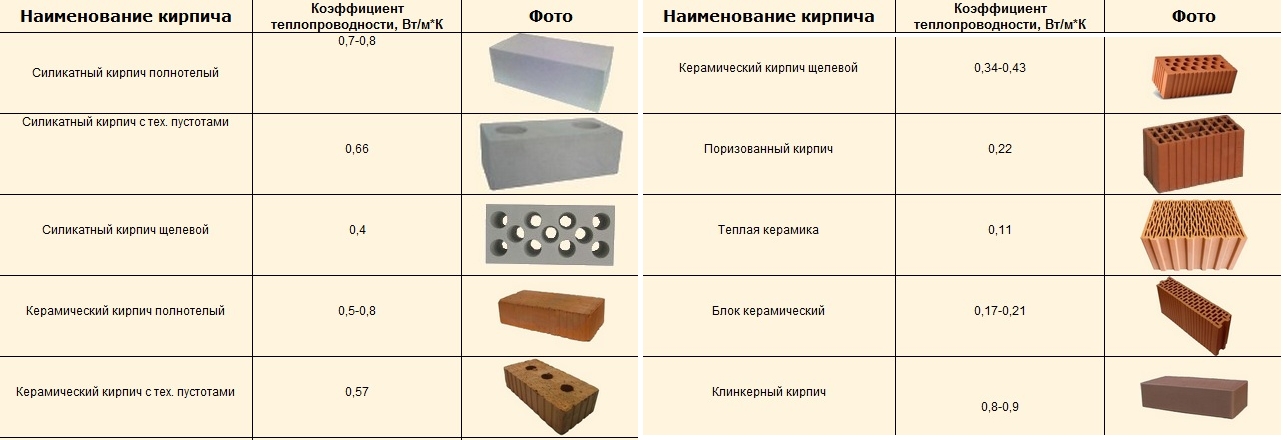
Thermal conductivity
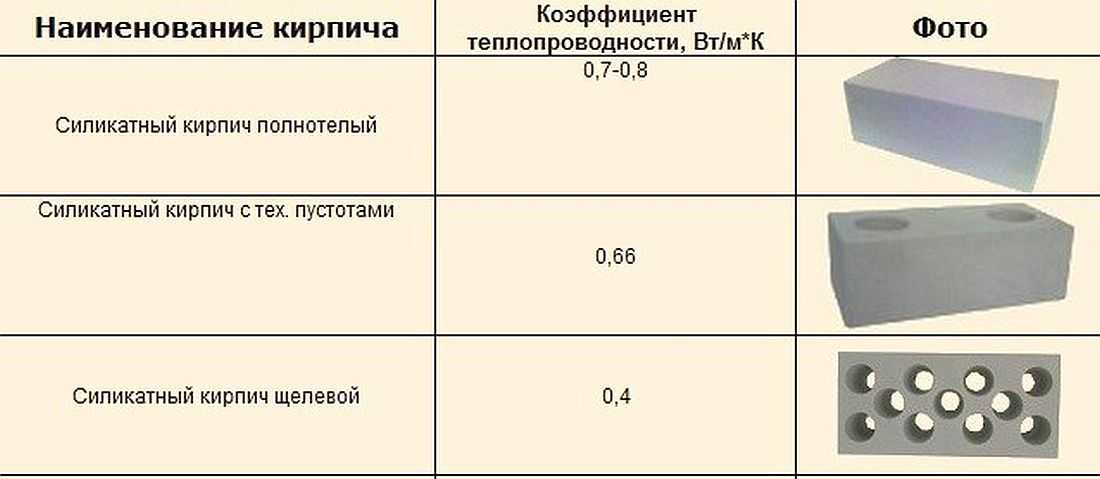
The warmth in your home depends on which brick to use, silicate or ceramic. A silicate brick has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.4–0.7 W / M * K. If the material is not new, the coefficient can go up to 0.95. Ceramic brick has a lower thermal conductivity, at the level of 0.34-0.57 W / M * K. Consequently, the walls from it will give off less heat, and the house will be more comfortable.
Frost resistance
This indicator determines the number of freezing and thawing cycles during which the material does not lose its properties. It is designated by the letter F. For silicate, it is 15–35, and improved grades have an indicator of 50. For ceramics, F50 is the norm, and some types are characterized by high values. So, the clinker has F100.
Soundproofing
Silicate is superior to ceramic in terms of noise absorption. This indicator is 50–51 dB for him, while for ceramics it is 45–46 dB. The construction of interior partitions from white blocks leads to a tangible increase in the level of noise protection.
Water absorption
The silicate material has a water absorption rate of 12%. Quartz sand, which is part of it, has a crystalline structure. It absorbs moisture quickly, but also quickly releases it to the air. But the layered structure of ceramics makes it difficult for water to penetrate between the layers. However, once there, the fired clay dries for a long time. This is especially dangerous during frosts, because of which the block can be torn apart. For ceramics, this figure is 6-14%. The durability of the silicate is also related to this.
Price category
Cost is also an important parameter when choosing a material. Silicate is almost twice as low in price as red brick, if we focus on volume.
Material features
The type and amount of additives are strictly regulated depending on the characteristics that are required from the blocks at the outlet. The brick acquires its final properties after firing in special furnaces.
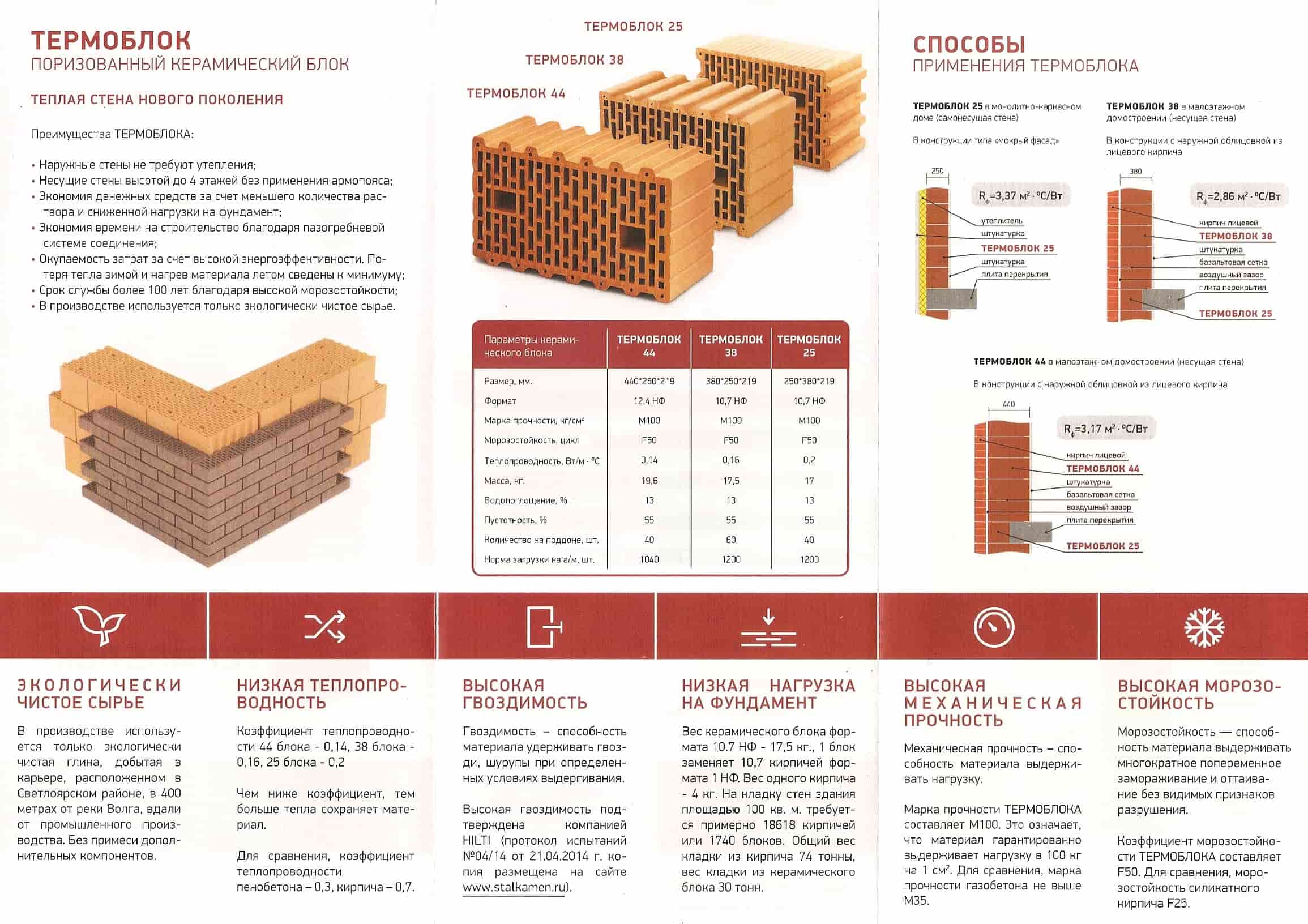
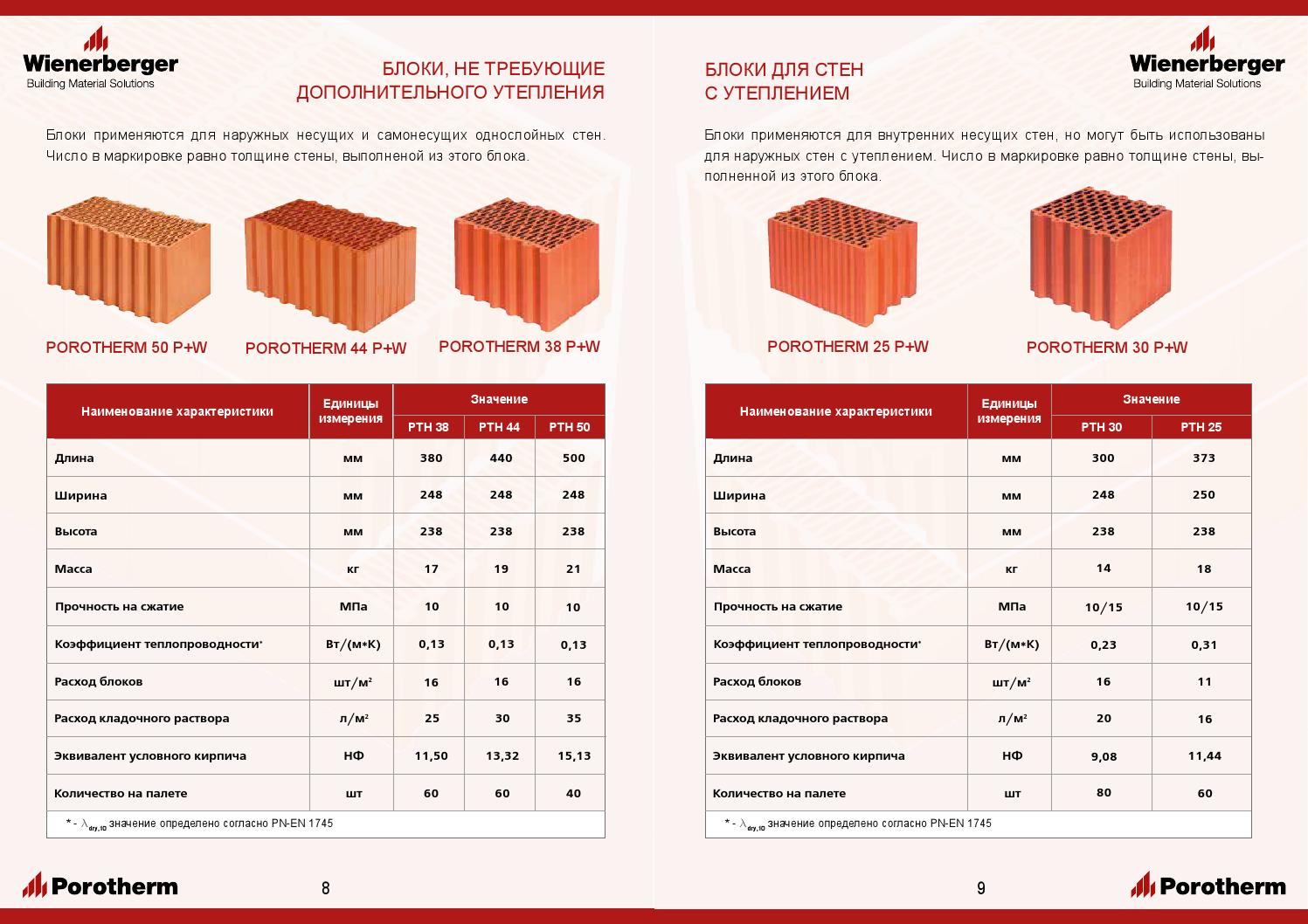
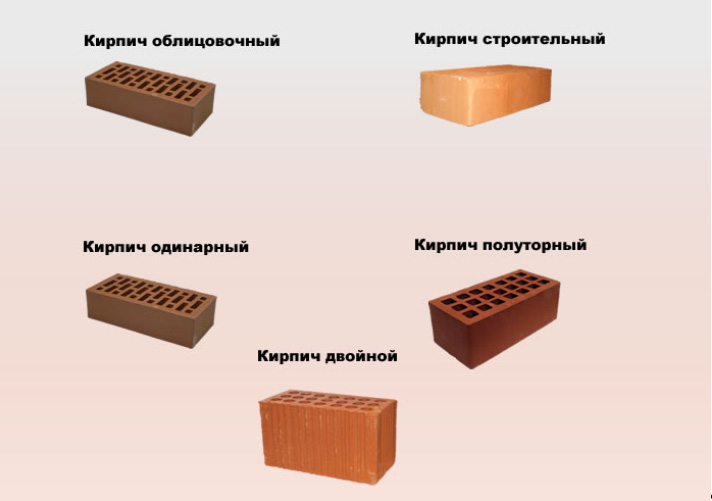
Varieties of ceramic bricks:
Dimensions of ceramic bricks.
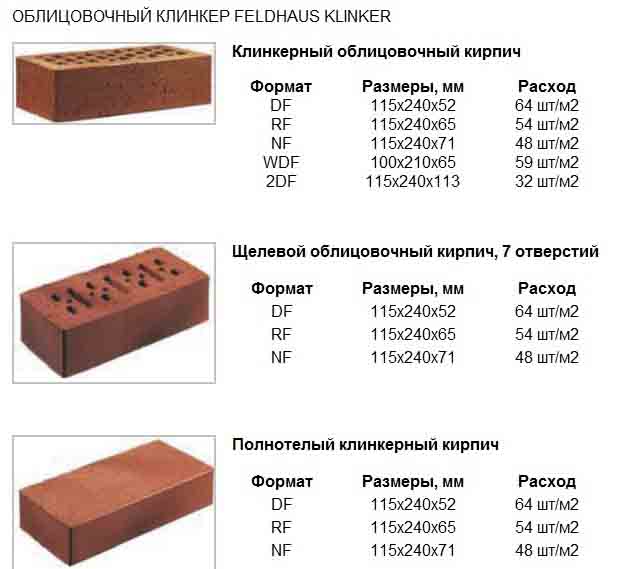
- To size.Standard ceramic material has the same length and width - 250x120 mm. The name and marking of the brick depends on the height of the product. Produced: single brick (height 65 mm), one and a half or thickened (height 88 mm), double (height 140 mm). Another type of material is euro bricks (250x85x65 mm) and ceramic blocks of fourteen types.
- According to the standard classification, bricks are distinguished: class I (used for the construction of load-bearing walls), class II (used for ordinary buildings, interior partitions, enclosing structures), class III (used for facing buildings).
- By the type of surface: smooth and grooved.
- By structure (presence of voids): solid (without holes) and hollow (with holes in the form of circles or squares).
There is also a special refractory ceramic brick that is used in the construction of fireplaces, stoves and chimneys.
A variety of types and a wide area of application of ceramic material are an undoubted advantage when building a house, since there is a brick for building a foundation, and for erecting walls, and for final cladding.
Ceramic brick marking
In the marking of ceramic bricks, complete information about its type is indicated. The size of the brick is indicated in millimeters in the format: length * width * height. The main characteristics given above must be indicated. To decipher the information, you must remember the conventions of each type of material:
- K - brick
- Cl - clinker.
- P - private (construction).
- L - front (finishing, decorative).
- Г - horizontal voids.
- Po - corpulent.
- Pu is empty.
- Ш - polished.
- PG - tongue-and-groove.
All key characteristics are indicated on the label, including size and type
After specifying the dimensions, the strength class, average density class and frost resistance are indicated through the oblique. Here are some examples of marking and its decoding:
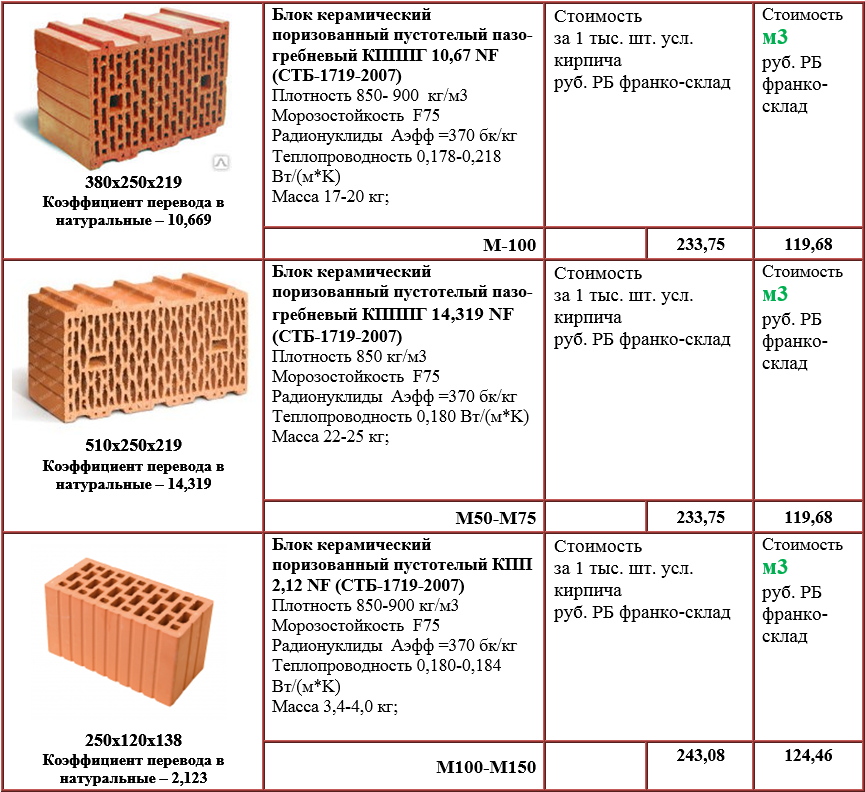
- KR-r-on 250 * 120 * 65 / 1NF / 200 / 2.0 / 50. You need to read it this way: ceramic brick (KR), ordinary (p), corpulent (by). Dimensions 250 * 120 * 65 mm, 1NF - format and dimensions. Then there are: strength class M 200, average density class 2.0, which corresponds to 1410-2000 kg / m³, frost resistance F50 (50 cycles).
- KRG-l 250 * 120 * 88 / 1.4NF / 50 / 1.2 / 75. It sounds like this: ceramic brick (KR), with horizontal voids (G), front (l). The size of the ceramic brick is 250 * 120 * 88 mm, the standard size is 1.4 NF. Strength class M50, average density class 1.2, which corresponds to a weight of 1010-1200 kg / m³. Frost resistance 75 cycles (F75).
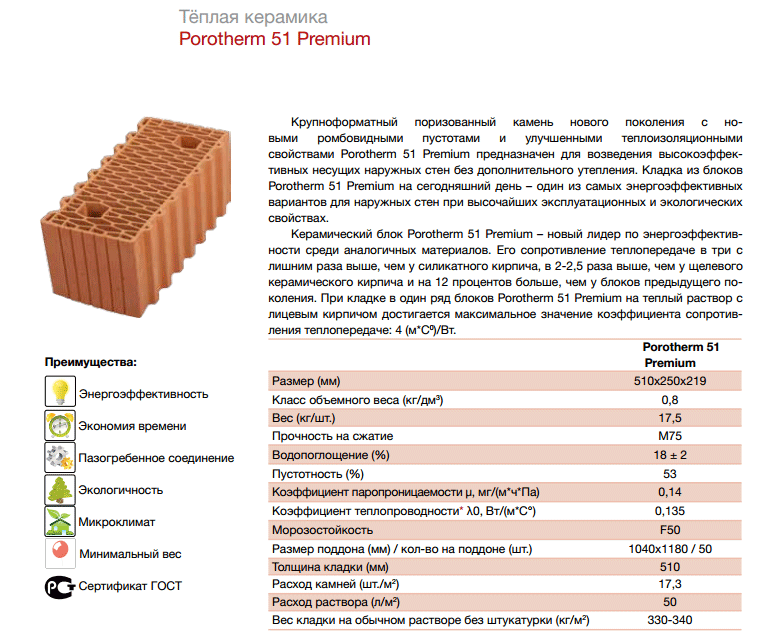
- KM-pg 510 / 10.7NF / 150 / 0.8 / 75. This designation is deciphered as follows: a ceramic stone (KM) with a tongue-and-groove connection (PG), the size of the working part is 510 mm, standard size is 10.7 NF. Strength grade M150, density class 0.8 (energy efficient), frost resistance F 75.
The package (pallet) may have a logo or other information at the discretion of the manufacturer
The new labeling method is close to EU standards. The standard does not prohibit factories from specifying additional characteristics in the accompanying documents. You can also add additional information to the package, which makes it easier to identify the manufacturer.