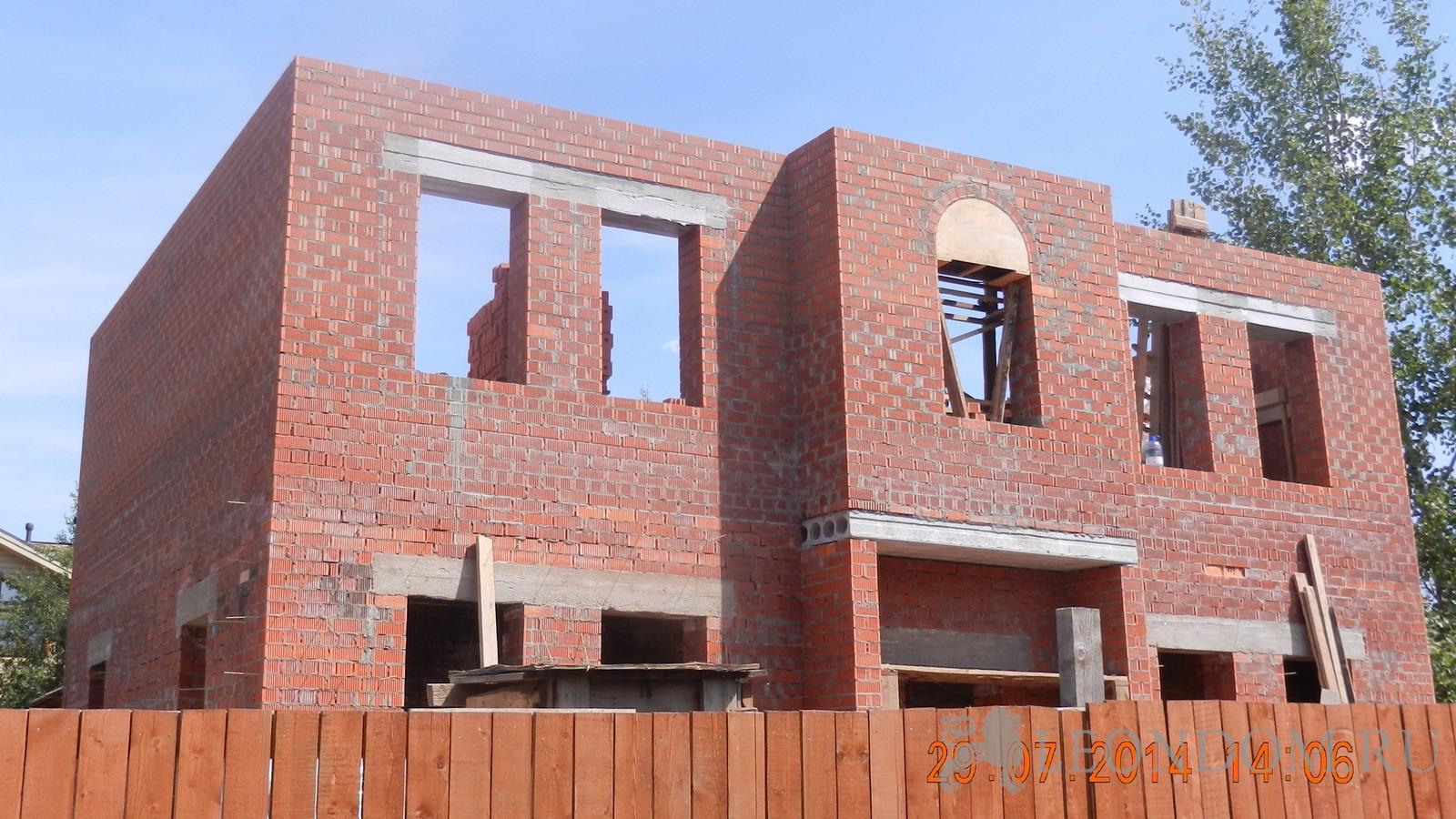
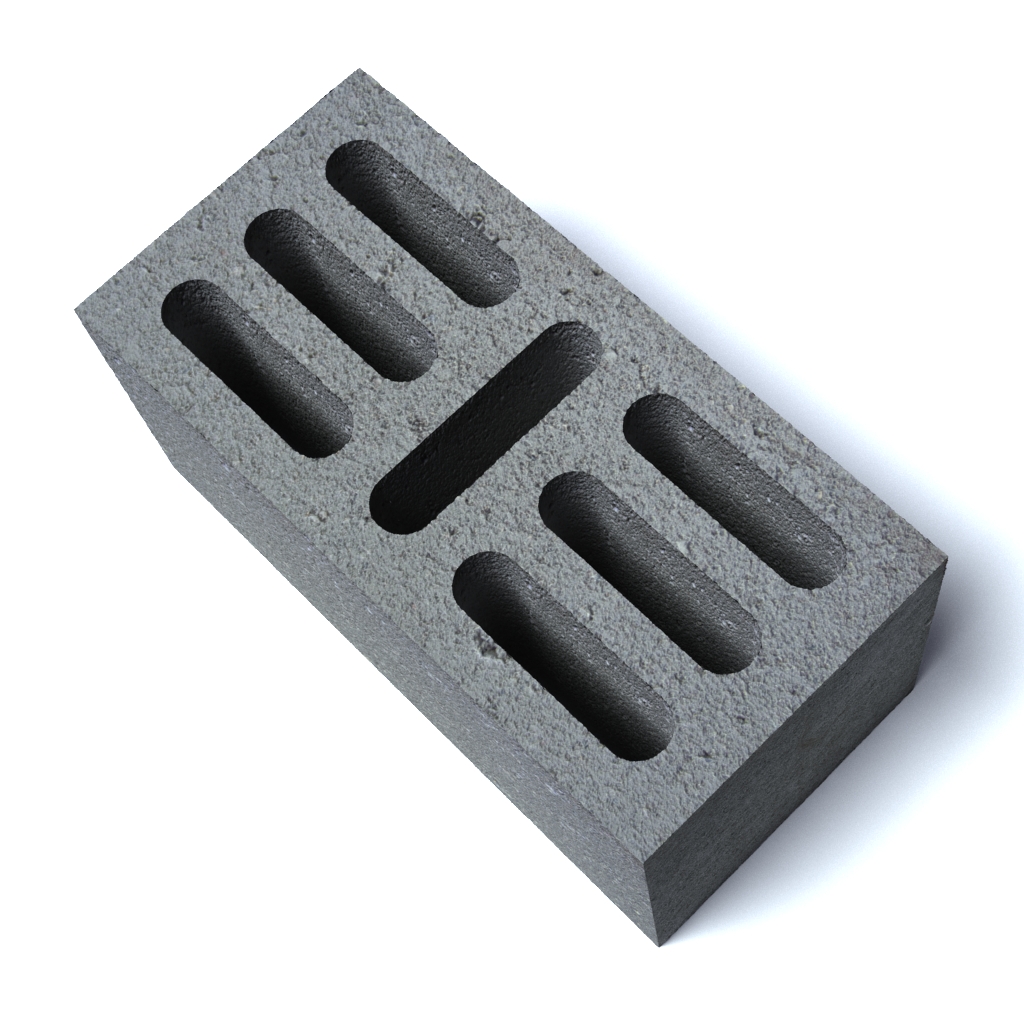
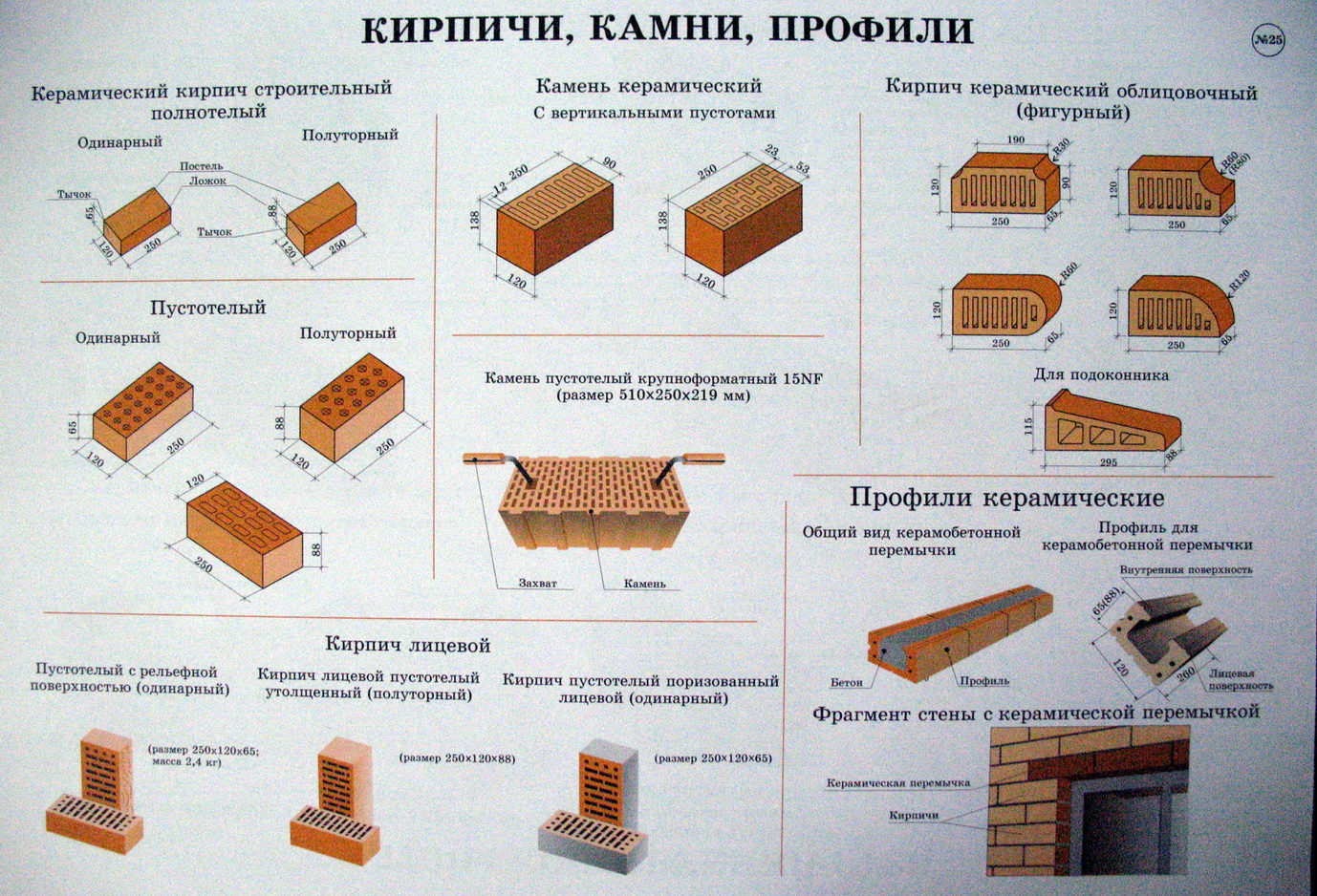
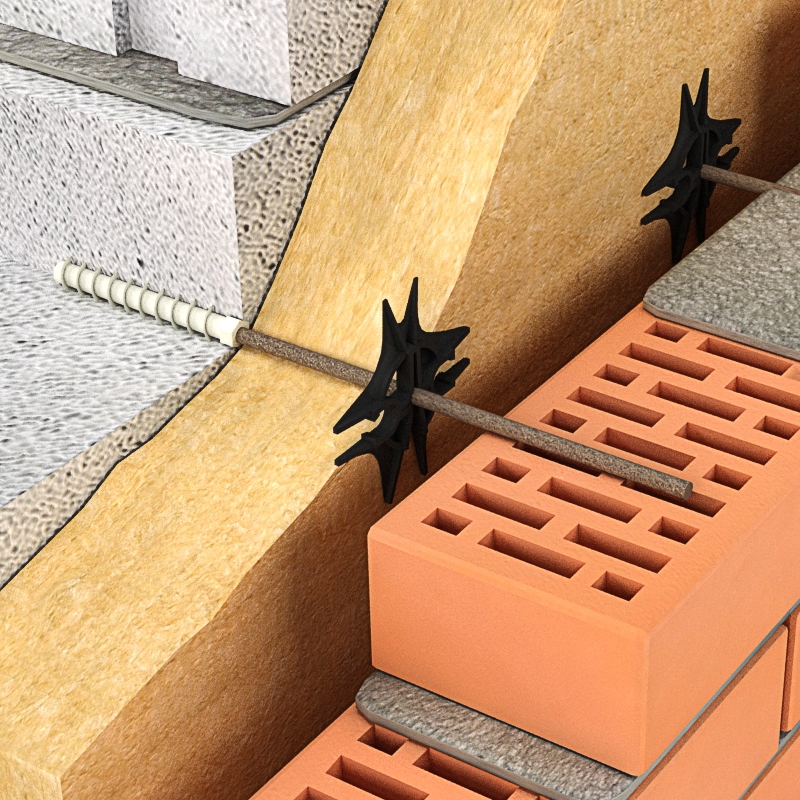
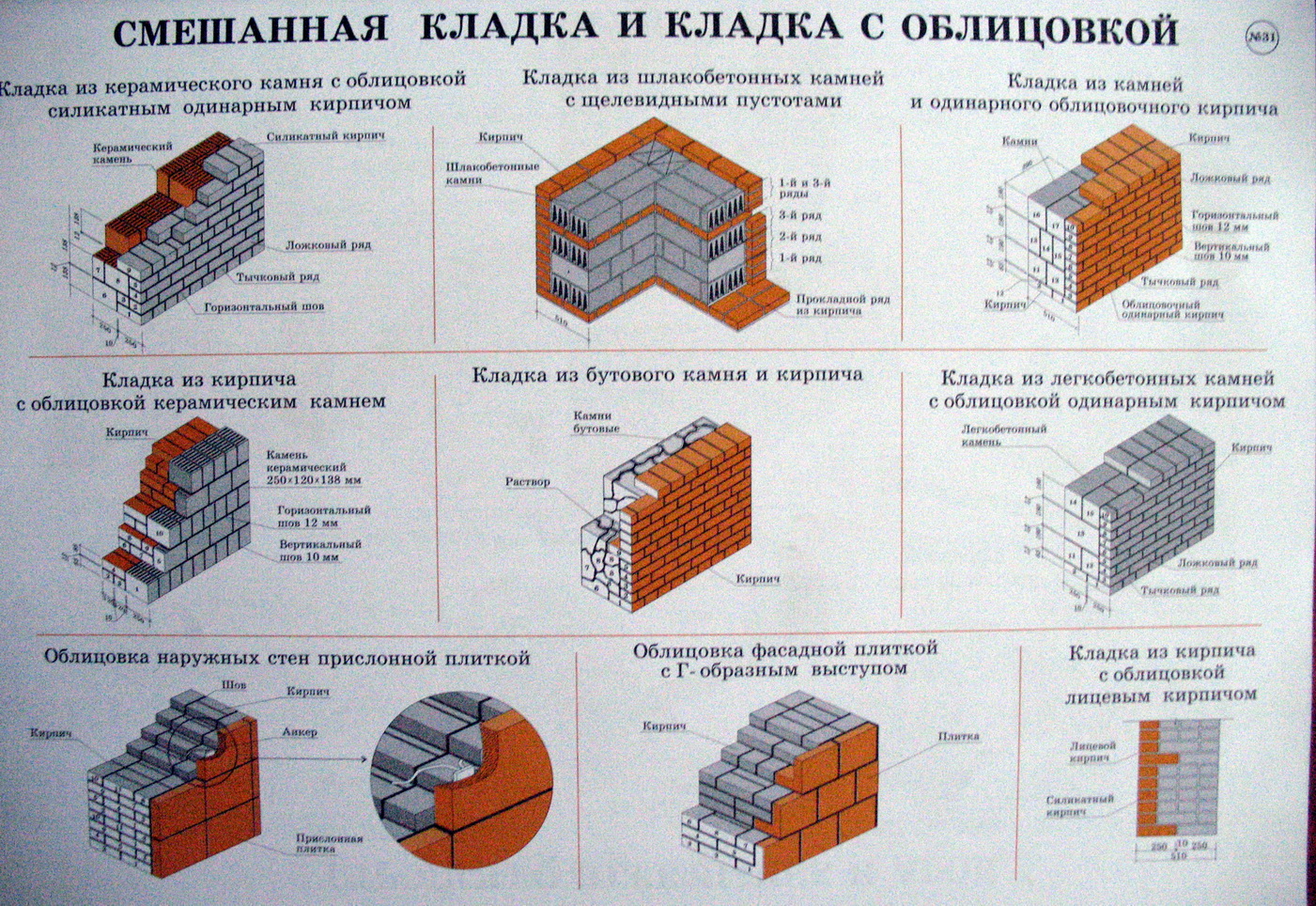
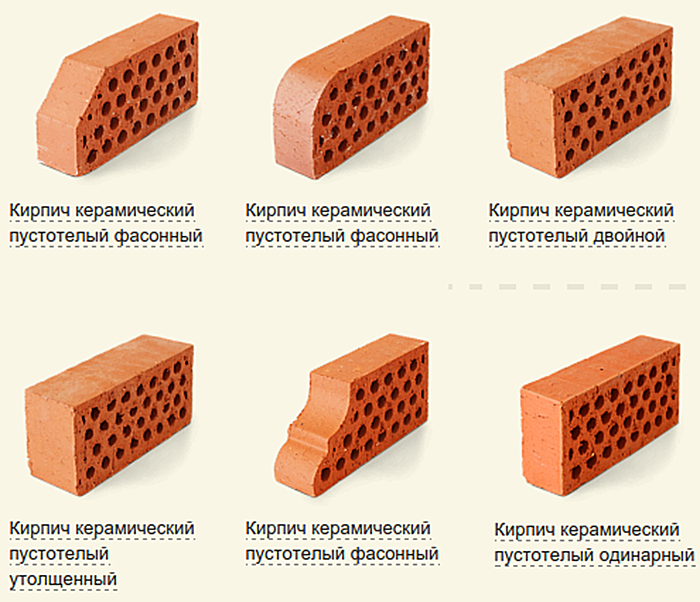
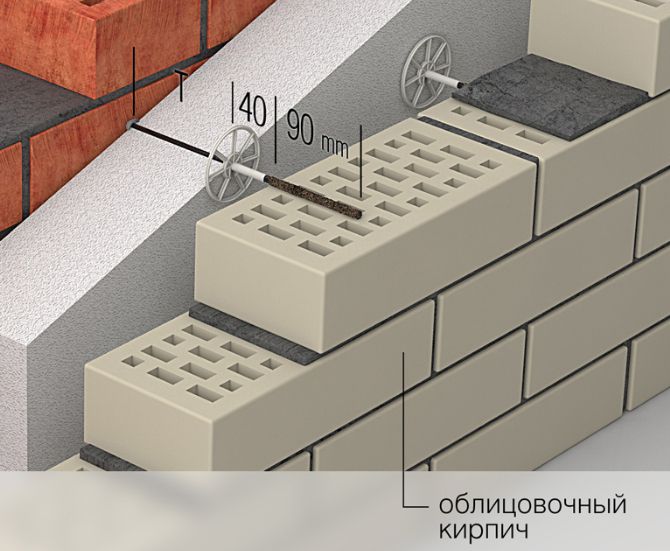
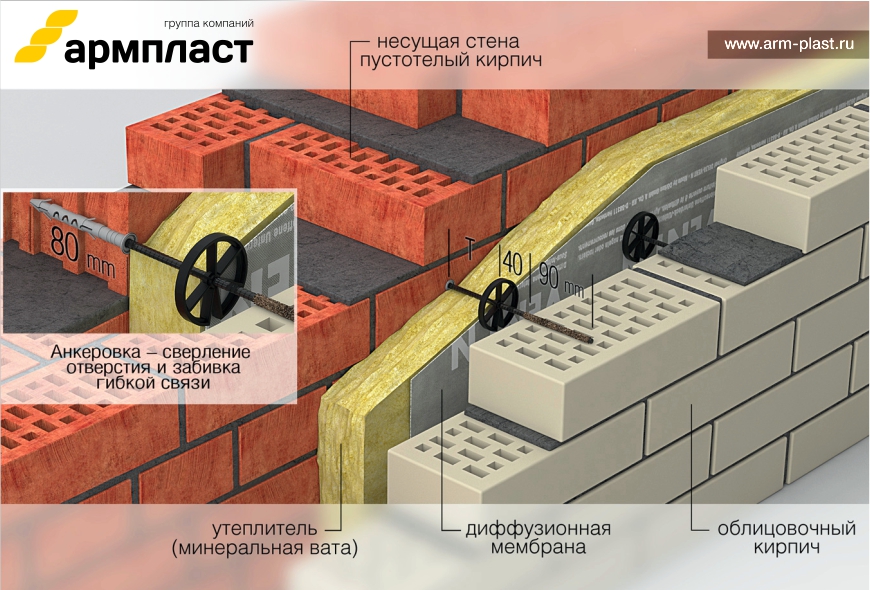
Masonry features
In order for the construction of this brick to be durable and of high quality, you must adhere to the following rules:
- do not use bricks with defects;
- initially determine the type of masonry;
- fill the voids between the bricks with mortar;
- use plumb lines and cords to determine the vertical and horizontal masonry;
- ensure the solidity of the structure with the help of reinforcing materials;
- to allow the mortar to set during laying, so that the base does not shift;
- make seams at least one centimeter thick to avoid cracking.


In the video below, you will learn about the mistakes of novice bricklayers in brickwork.
Masonry calculation
Do-it-yourself masonry is insurance against hack-work and a big saving of your money. Before starting work, it will be useful to review the theory and read SNiP (Building Norms and Rules). If your building meets the established requirements, then this will help to officially take it into operation.
The stability calculation is carried out on the basis of the classification specified in the documentation. Remember that stability depends on thickness and height. The thicker the better. To avoid undesirable phenomena, carefully read clauses 6.16 - 6.20 of SNiP II-22-81. The tables provide data and calculation methods that will help you do everything right.

When deciding on masonry, pay attention to some things:
- Wall load (this affects the number of storeys in the building).
- Climate (it is necessary to ensure not only strength, but also proper thermal insulation).
- Aesthetic factor (for example, a single brick masonry will look much more sophisticated than one and a half and double).
Brick is a reliable material with excellent load-bearing capacity. The wall, which has been folded "in one brick", will withstand almost any load. You need to thicken it if you want to increase the thermal and insulating properties. The reason may be the climate of the region or the presence of factories, airports, etc. near your home.
There are such masonry structures:
- In half a brick - 120 mm;
- One - 250 mm;
- One and a half - 380 mm;
- Two - 510 mm;
- In two and a half - 640 mm.

For load-bearing walls, the minimum thickness is one and a half bricks (380mm). One-brick walls can only be used for the last floors, single-storey buildings and internal partitions.
Front brick and ordinary what is the difference
According to their purpose, clay bricks are divided into two types:
- Private;
- Facial.
Ordinary brick
Ordinary brick is used in the construction of a load-bearing wall, foundation or partition. Further, these objects, as a rule, are plastered or faced with other materials.
Ordinary brick can be both solid and hollow (slotted)
They do not pay attention to the appearance of an ordinary brick, since it does not matter how it looks. Eventually, it will be hidden behind a decorative façade.

The main indicators of an ordinary brick are its technical characteristics. And the main technical indicator is brand strength.
This is an indicator of how much weight, pressing on one square centimeter, a given product can withstand.
For example, a product under the brand name one hundred and fifty will withstand the pressure of one hundred and fifty kilograms per one centimeter squared.
Depending on this strength indicator, ordinary bricks are used either in walls, partitions, or when laying a foundation.
What is the difference between solid and slotted bricks
The difference between a solid ordinary brick and a hollow brick lies in the following factors:
- The weight. Due to the voids, slotted brick is much lighter than a solid product.
- Strength.Again, voids "take" the strength of the product. Slotted brick is unable to withstand heavy loads, and has a lower grade strength.
- Thermal conductivity. Air has a lower thermal conductivity than bricks. Accordingly, hollow bricks have a lower thermal conductivity than solid bricks.
These are the main differences between solid and slotted bricks.

Face brick
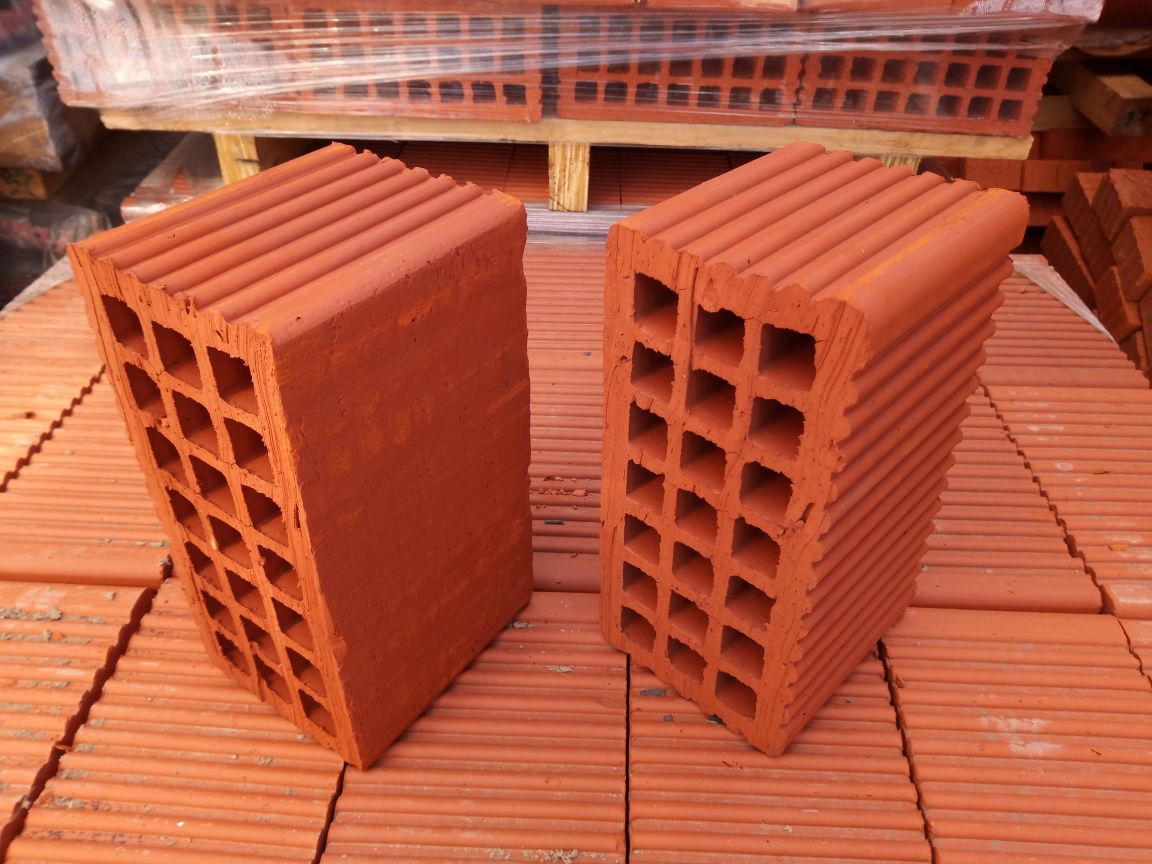
From the name itself, it becomes clear that the facing brick is the face of the building. More precisely, a facing material intended for finishing construction projects.
Therefore, the main indicators of this building product are:
Colour. Currently, you can find finishing bricks of any color. However, the most common are three, basic colors: red, brown, yellow.
Texture
The texture of decorative bricks is also important. Someone prefers a smooth surface, but someone likes a relief
It all depends on personal preference.
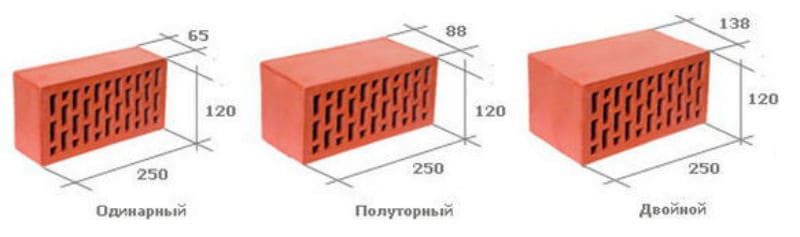
The size. The size, of course, is not so important, but, nevertheless, the pattern, the pattern on the facade of the building depends on it. There are several formats of facing bricks: single, one and a half, double size
So, when choosing a facing material, pay attention to the dimensions of the product.
Material. There are two main types of facing bricks, namely ceramic and clinker bricks.
Their differences are in technical characteristics. In Russia, ceramic bricks are produced for finishing the facades of buildings. Clinker bricks are of foreign production, they are distinguished by great strength and durability. Clinker bricks are often used for paving paths and sidewalks. Since it, in terms of strength, is in no way inferior to paving slabs.
When choosing a facing brick, it is not worth saving. And although a brick of good quality is more expensive, it will also last much longer.
And if you take into account the cost of facing work, then you get big savings due to the repair of the facade.
And the beautiful appearance of the house will tell a lot about its owner. It's like the owner's business card.
What is the difference between an ordinary brick and a front one, conclusions
As you can see from the review, the main differences between ordinary and facing bricks are in their application. One is used for the construction of objects, the other is used for decoration. And if for an ordinary brick, the main thing is strength, then for a front brick, a beautiful appearance is more important.
Also, for facing bricks, the indicator of resistance to atmospheric phenomena is important. Such as precipitation, frost, extreme heat and so on.
Now you know how an ordinary brick differs from a front one, and what you should pay attention to when choosing a brick. Video review of ordinary and facing bricks
How to choose a brick, what should you pay attention to first.
Video review of ordinary and facing bricks
How to choose a brick, what should you pay attention to first.
Types of bricks and their differences:
Ceramic brick;
Clinker bricks for stoves and fireplaces;
Brick brand: types and characteristics;
Facing brick;
Solid brick: definition, types, production;
Silicate brick, advantages and disadvantages, application.
Masonry mortar
If the external laying of the wall is carried out "for joining", then the quality, composition and correct application of the solution depends on how aesthetically pleasing the brick wall will look. The thickness of the seams must be the same everywhere, and they must be filled completely, voids are not allowed. The solution must be prepared just before starting work and applied within two hours. For plasticity, clay, lime or marble pulp are added to it.
For horizontal joints, a thickness of 10 to 15 mm is used, for vertical joints - from 8 to 10 mm.
When building a brick building, you need to know that any deviation from the project can subsequently lead to unpredictable consequences. The stability and strength of brick load-bearing walls can be easily reduced if:
- reduce their thickness;
- increase their height;
- increase the area or number of openings;
- reduce the width of the walls between the openings;
- arrange additional niches or channels in the walls;
- use heavier slabs.
A brick wall, the thickness of which is less than the design one, must be additionally reinforced.
All changes in the project must be made by specialists, you cannot do this on your own.
Brick buildings have obvious advantages that put them a step above houses made of any other materials. Made according to original designs, they have their own style and charm. It is also a good option for investing funds and transferring real estate to descendants by inheritance.
10 mystical places in the world, where it is forbidden to step a person's foot There are certain directions where access is restricted or simply prohibited for people. Be it a beautiful cave or a mysterious island inhabited by huge ones.
Fashion for Naked: the best images of the stars. We select a Naked cosmetic bag for your make-up It's nice when fashion pushes us not only to experiment, but also to accept ourselves and our beauty. Fashionable positive attitude to your own body.
Toxicosis: causes, consequences, treatment The assumption that nausea worries a woman only in the morning is incorrect. It can last all day, but is most pronounced in the morning. It comes from.
Unforgivable mistakes in films that you probably never noticed There are probably very few people who would not like to watch films. However, even in the best cinema there are mistakes that the viewer can notice.
Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few thought about why it might be needed. It is interesting that originally it was a place for the Chr.
What does the shape of your nose say about your personality? Many experts believe that looking at the nose can tell a lot about a person's personality.
Therefore, when you first meet, pay attention to the nose of the unfamiliar
The choice of bricks for load-bearing walls
There are two main types of modern bricks: ceramic and silicate. Ceramic (red) consists of clay, and silicate (white) - of sand and lime. The rest are subspecies of these two.
Advantages of silicate: strength, frost resistance, insulation, creating a comfortable microclimate, fire resistance, heat accumulation. Disadvantages: fragility, poor thermal insulation.

Advantages of ceramic: moisture resistance, frost resistance, heat retention. Disadvantages: fragility when exposed to water during the off-season. The most important advantage of this building material is strength. There are solid and hollow bricks in terms of filling.
There are also three strength classes:
- weak;
- medium;
- durable.
For construction, you can use corpulent and hollow. But at the same time, it must be remembered that solid red brick (ceramic) is used in the construction of multi-storey buildings, basements, basements, vaults of the foundation, pivot arches, chimneys and more. Hollow ceramic is better for filling voids and openings in a monolithic building.
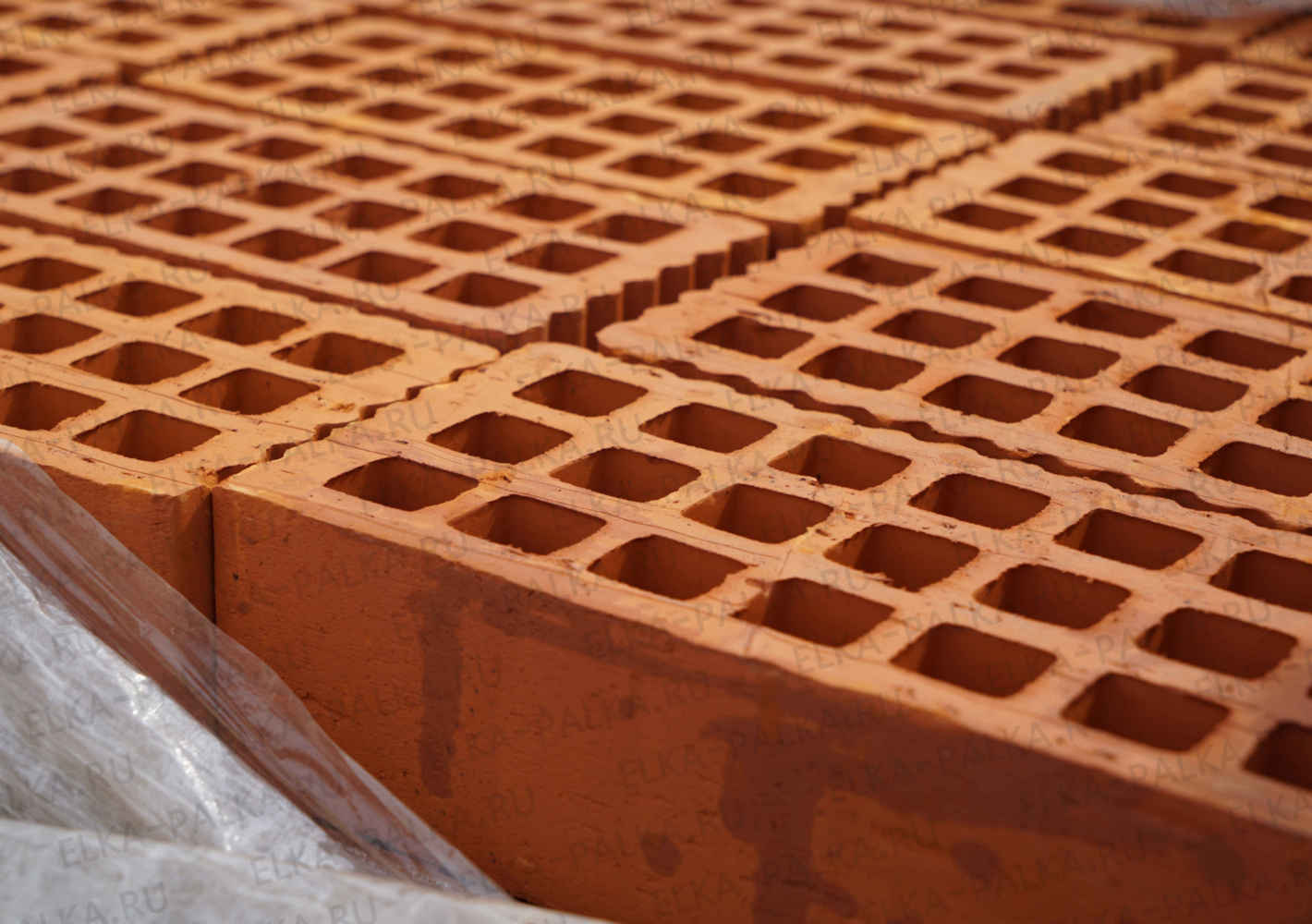
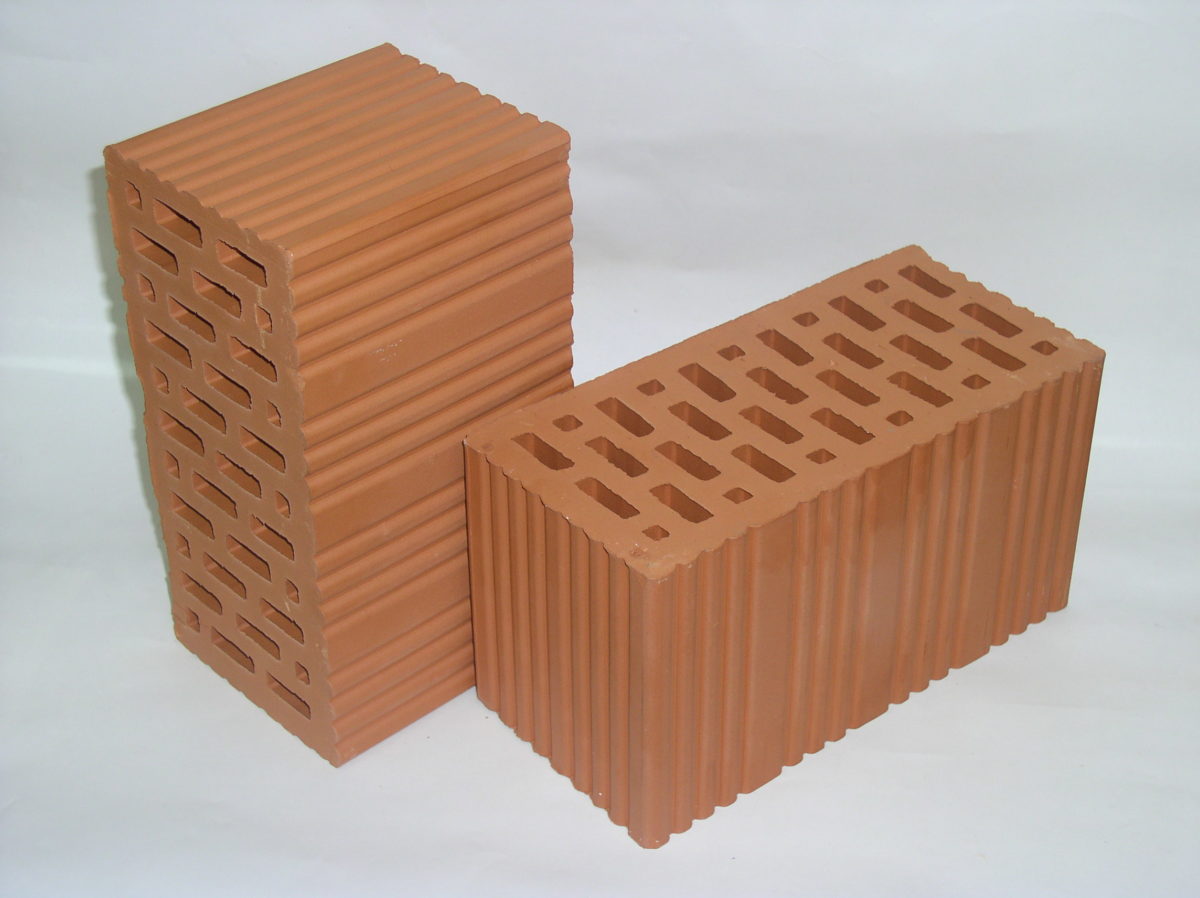
Hollow brick specifications
The volume of voids has a significant effect on the properties of the product. Their number varies from 13% to 55%. The larger this value, the higher the thermal insulation properties of the brick, but less weight and lower strength indicators.
This pattern can be seen in the following table:
| Index | Unit rev. | With the volume of voids, in% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 40 | ||
| Brick grade | M175, M200, M250 | M125, M150, M175 | |
| Thermal conductivity | W / m * C | 0.24 | 0.20 |
| Density | kg / m3 | 1700 | from 1120 to 1190 |
| Frost resistance | F | 35.5 | 35.5 |
| Moisture absorption | % | 6 | 6 |
| The weight | Kg | 3,4 | 2,3 |
Slotted brick is used for the construction of load-bearing walls and partitions in buildings for various purposes, but the material is most widely used in private housing construction.
If we consider the pros and cons of hollow bricks, then they have practically one drawback.It is impossible to build foundations and basements of buildings from slotted blocks, since moisture will accumulate in cracks, holes and pores during operation, and this will certainly destroy the structure of the brick and lead to its destruction.
This category of building materials has much more positive qualities. Here are the main ones:
The low weight of the slotted brick makes any structure lightweight and avoids the construction of a strong foundation for the building.
High thermal insulation performance is the first thing a developer pays attention to. Provided that the masonry work is performed correctly, a favorable microclimate will always be maintained in a hollow brick house.
Sufficient strength and good resistance to external factors - a guarantee of a long service life
Slit brick structures can operate for 50 years or more, without changing their properties.
Excellent noise and sound insulation qualities.
Reducing the cost of construction by saving raw materials and construction materials.
High resistance to the appearance of service cracks.
A beautiful appearance is also not in the last place, especially when the masonry is done by professionals with the correct jointing.
Hollow and solid product
Depending on the needs, this brick can be produced solid, which is made in the form of a solid bar without through holes. This material has good sound insulation and can keep the building warm. It is resistant to water and other aggressive environments. The weight of one brick is 3 kilograms. They use it for the following purposes:
- arrangement of furnaces;
- laying of foundations;
- the construction of load-bearing walls;
- manufacture of partitions.


Hollow brick has holes. They can be square or round. The presence of such cells improves the thermal insulation properties and reduces the weight of the product. But at the same time, the strength of the brick deteriorates. The weight of such a product is 2-2.5 kg.
It is used for such work:
- erection of buildings with a height of no more than 3 floors;
- constructions of various decorative structures;
- erection of structures that will not be affected by a high load.


Advantages and disadvantages
Block bricks have positive and negative properties. In addition to environmental friendliness, they have good ventilation and sound insulation properties. Construction products have a low coefficient of thermal conductivity combined with reliability. The increased dimensions of block products, low weight lead to an economical masonry. In addition to advantages, blocks of different composition have a number of disadvantages. Foam blocks give great shrinkage. The gas silicate block is fragile, and the walls freeze under the influence of severe frosts, therefore insulation and cladding are necessary.
Hollow brick advantages
Low thermal conductivity
It is the main factor that the consumer pays attention to when buying. Correctly selected building material will maintain the required temperature in the room
Double slot bricks adequately cope with this task, because the walls made of it do not need additional insulation.
Long service life. This indicator is due to such properties as product strength and resistance to external factors. Without losing its properties, a double slot brick can serve for at least 50 years.
Noise isolation. In addition to its low thermal conductivity properties, a hollow brick block will provide good sound insulation to the room. The internal free space is filled with air, creating a shield and preventing the propagation of sound.
Saving consumables. High thermal insulation properties allow to reduce the consumption of the main building material. And if a one-and-a-half or double slot brick is used, the amount of masonry mortar is significantly reduced.
If you still have questions, we recommend watching the following video:
Take part in the survey:
Loading …
- Bricklaying and dimensions of a tandoor made of bricks;
- Calculating the number of bricks
- Porous ceramic block
- Concrete brick
Varieties of bricks and their characteristics
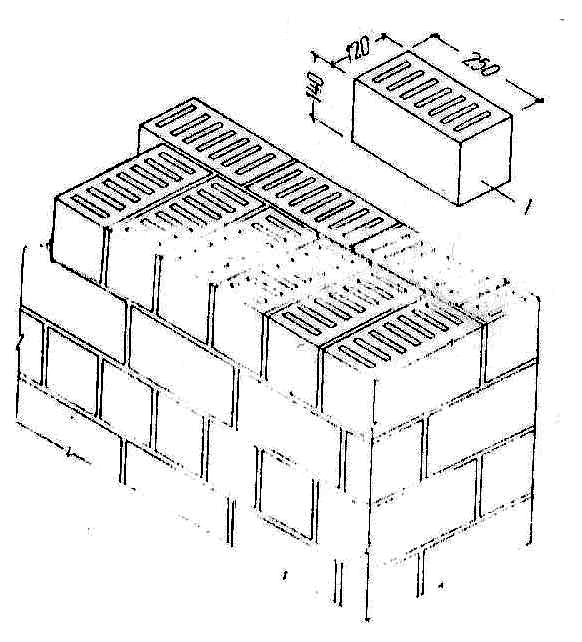
Slotted bricks are presented in a wide range, so you can easily purchase the most suitable material for the construction of a particular building. Products are classified according to a number of features:
- size;
- the shape and number of slots;
- appointment;
- properties.
Shapes and number of slots /
Slotted products are different in size: single, one-and-a-half and double bricks are on sale. For the construction of large objects, slotted double bricks are most often used, because it significantly speeds up the workflow and reduces the consumption of cement slurry. In addition, this material can be laid in 1 row, and at the same time the strength and thermal insulation characteristics of the structure will be quite high.
The number of cracks in a brick can vary between 15-55% of its total volume
It is important to take into account that the more voids in the product, the lower its strength, but at the same time, the thermal insulation qualities will be much better. The holes are round, square, rectangular and oval in shape. As for the purpose, the slotted brick is divided into the following types:
As for the purpose, the slotted brick is divided into the following types:
- Porous - designed for facing work. Such material is lightweight due to its porous structure, but at the same time it is able to provide the building with good heat and sound insulation.
- Cement-sand is the cheapest brick, the characteristics of which are in no way inferior to other materials. For its manufacture, cement, sand and synthetic additives are used.
- Heat-efficient - a material with low thermal conductivity and low weight. It allows you to create lightweight structures with high performance. The heat-efficient single slotted brick, when laid in 1 row, will keep the building warm in winter and provide a pleasant coolness in summer.
- Foamed diatomite - designed for the construction of objects that are exposed to high temperatures, such as blast furnaces or smelters. Such products are able to withstand up to 900 ° C. In ordinary construction, diatomite foam brick is not used due to its high cost.
- Ceramic is a material with an aesthetic appearance and high thermal insulation properties. It is used for interior and exterior wall decoration.
List of sources
- .
- .
- .
Features of calculating wall thickness
- The thickness of the walls according to the heat engineering calculation does not always coincide with the calculation of the value according to the strength characteristics. Naturally, the more severe the climate, the thicker the wall should be in terms of thermal performance.
- But according to the conditions of strength, for example, it is enough to lay out the outer walls in one brick or one and a half. This is where the "nonsense" is obtained - the thickness of the masonry, determined by the heat engineering calculation, often turns out to be excessive due to the strength requirements.
- Therefore, in terms of material costs, and under the condition of 100% use of its strength, lay a solid masonry of walls made of solid bricks only in the lower floors of high-rise buildings.
- In low-rise buildings, as well as in the upper floors of high-rise buildings, hollow or lightweight bricks should be used for external masonry, lightweight masonry can be used.
- This does not apply to external walls in buildings where there is a high percentage of humidity (eg laundries, baths). They are usually erected with a protective layer of vapor barrier material from the inside and of solid clay material.
Now I will tell you about the calculation of the thickness of the outer walls.
It is determined by the formula:
B = 130 * n -10, where
B - wall thickness in millimeters
130 - the size of half of the brick, taking into account the seam (vertical = 10mm)
n - an integer of a half brick (= 120mm)
The size of the solid masonry obtained by calculation is rounded up to an integer number of half-bricks.
Based on this, the following values (in mm) of brick walls are obtained:
-
120
(brick floor, but this is considered a partition); -
250
(into one); -
380
(one and a half); -
510
(at two); -
640
(two and a half); -
770
(at three o'clok).
In order to save material resources (brick, mortar, reinforcement, etc.), the number of machine - clock mechanisms, the calculation of the wall thickness is tied to the bearing capacity of the building. And the heat engineering component is obtained by insulating the facades of buildings.
How can you insulate the outer walls of a brick building? In the article, insulating a house with expanded polystyrene outside, I indicated the reasons why brick walls should not be insulated with this material. Check out the article.
The point is that brick is a porous and permeable material. And the absorbency of expanded polystyrene is zero, which prevents moisture migration outward. That is why it is advisable to insulate a brick wall with heat-insulating plaster or mineral wool slabs, the nature of which is vapor-permeable. Expanded polystyrene is suitable for insulating a base made of concrete or reinforced concrete. "The nature of the insulation must match the nature of the load-bearing wall."
There are a lot of heat-insulating plasters
- the difference lies in the components. But the principle of application is the same. It is carried out in layers and the total thickness can be up to 150 mm (with a large value, reinforcement is required). In most cases, this value is 50 - 80 mm. It depends on the climatic zone, the thickness of the walls of the base, and other factors. I will not dwell in detail, since this is a topic for another article. We return to our bricks.
The average wall thickness for an ordinary clay brick, depending on the area and climatic conditions of the area at the average winter ambient temperature, looks like this in millimeters:
- - 5 degrees - thickness = 250;
- - 10 degrees = 380;
- - 20 degrees = 510;
- - 30 degrees = 640.
I would like to summarize the above.
The thickness of the outer brick walls is calculated based on the strength characteristics, and the heat engineering side of the issue is solved by the method of wall insulation. As a rule, the design firm calculates the external walls without the use of insulation. If the house is uncomfortably cold and there is a need for insulation, then carefully consider the selection of insulation.
Where is it used
Hollow bricks are used in the construction of not very heavy structures.
The presence of cavities affects the strength of the material. Therefore, experienced builders do not use hollow bricks for the construction of the basement of the house, as well as walls that carry a high load. Because of this, it is recommended to use standard solid material for the first floor of multi-storey buildings.
Ordinary brick with cavities inside is in demand for the construction of residential buildings in regions where there are sharp changes in temperature. Due to its low thermal conductivity properties, this material does not need additional thermal insulation.
Ceramic blocks with voids are very popular in suburban residential construction. They are cheaper than conventional solid material, have less weight, which means that all the work can be done with fewer people and in a shorter time.
In addition, hollow brick looks much more attractive than other building materials, such as cinder block or shell rock blocks. And it does not need external finishing, which significantly reduces the cost of construction. In some cases, this material is used as a facing. In addition to everything, it has good thermal insulation and sound absorption properties.
Facing brick is also in demand when erecting various gazebos, pavilions, ovens in open areas for cooking various dishes in summer cottages and garden plots.Decorative fences made of such blocks also look very beautiful.
By the way, using a single brick or a double brick, builders make a steep mortar so that it does not flow into the cavity.
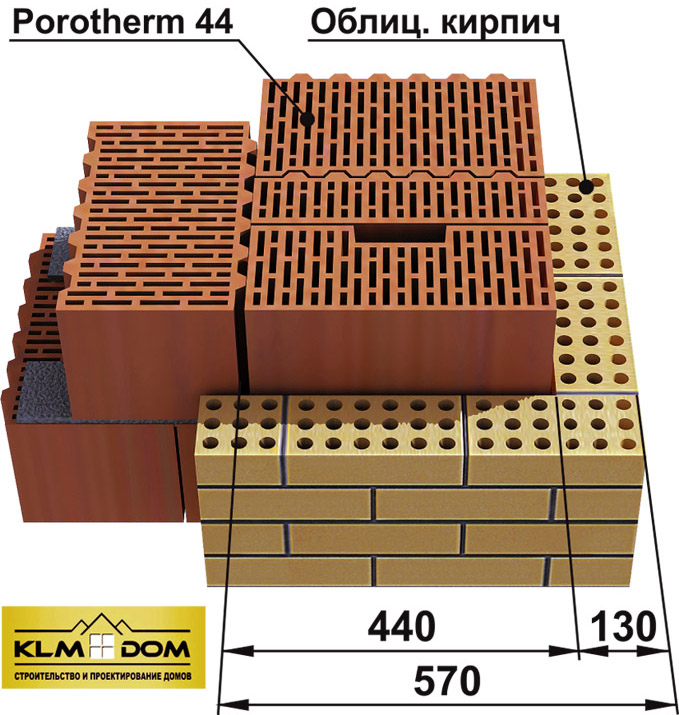
Brick load-bearing wall thickness
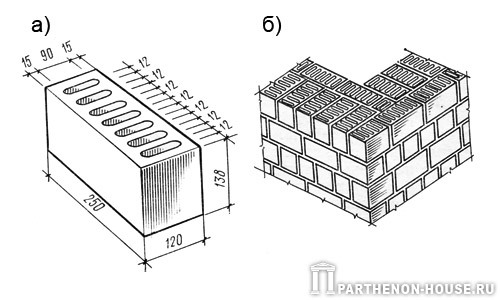
A building material such as brick has been used for construction for several hundred years. The material has standard dimensions 250x12x65, regardless of the type. Determining what should be the thickness of a brick wall, it is from these classic parameters that they proceed.
Load-bearing walls are a rigid frame of the structure that cannot be torn down and replanned, as the reliability and strength of the building is compromised. Bearing walls can withstand colossal loads - these are the roof, floors, dead weight and partitions. The most suitable and time-tested material for the construction of load-bearing walls is precisely brick. The thickness of the load-bearing wall must be at least one brick, or in other words - 25 cm. Such a wall has distinctive thermal insulation characteristics and strength.
A properly constructed bearing wall made of bricks has a service life of more than one hundred years. For low-rise buildings, solid brick with insulation or perforated is used.
Brick wall thickness parameters
Both external and internal walls are laid out of bricks. Inside the structure, the wall thickness should be at least 12 cm, that is, in the brick floor. The cross-section of pillars and piers is at least 25x38 cm. Partitions inside the building can be 6.5 cm thick. This method of masonry is called “on the edge”. The thickness of the brick wall, made by this method, must be reinforced with a metal frame every 2 rows. Reinforcement will allow the walls to acquire additional strength and withstand more substantial loads.
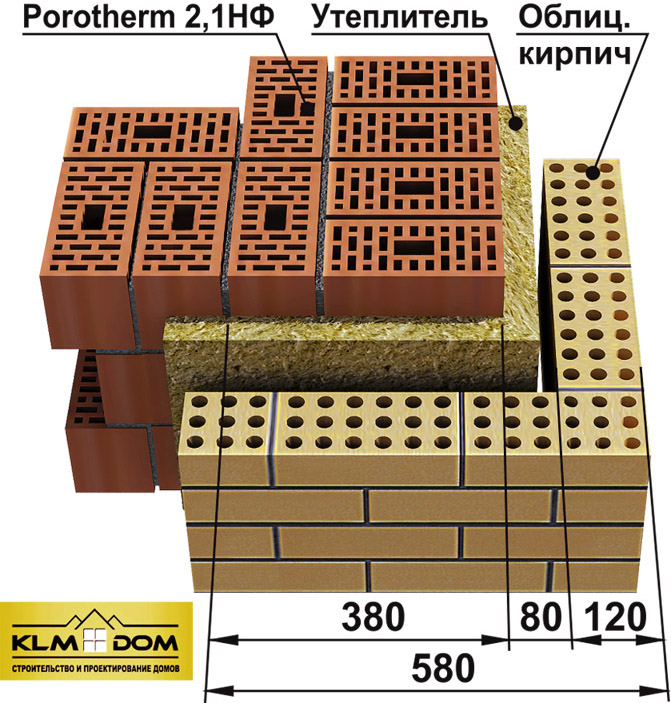
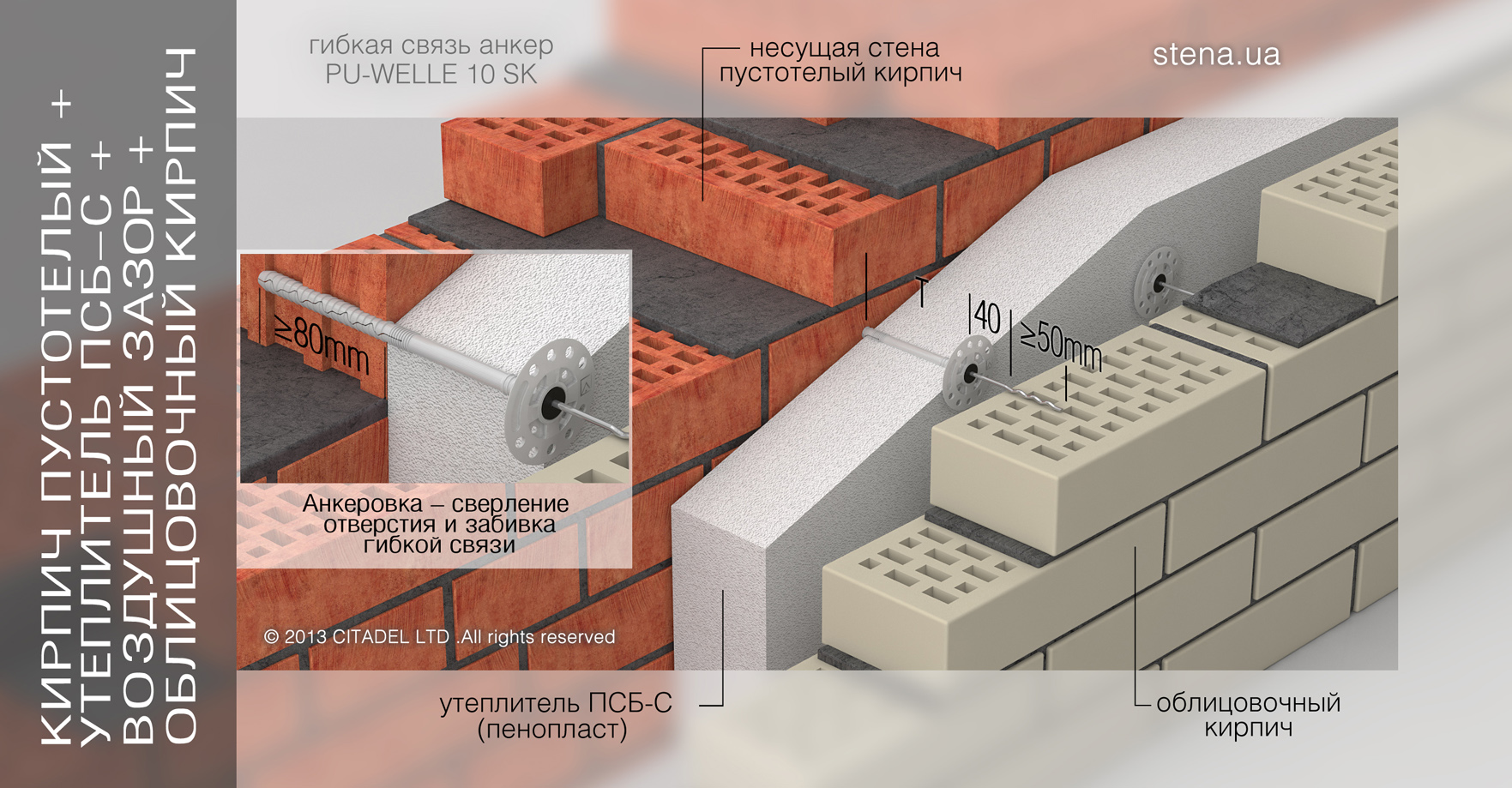
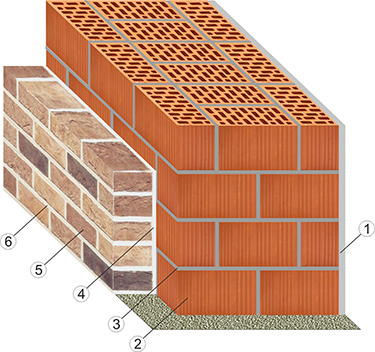
The method of combined masonry, when the walls are made up of several layers, is very popular. This solution allows you to achieve greater reliability, strength and thermal resistance. Such a wall includes:
- Brickwork consisting of porous or slotted material;
- Insulation - mineral wool or foam;
- Cladding - panels, plaster, facing bricks.
The thickness of the outer combined wall is determined by the climatic conditions of the region and the type of insulation used. In fact, the wall can have a standard thickness, and thanks to the correctly selected insulation, all the standards for the thermal protection of the building are achieved.
Wall masonry in one brick
The most common wall laying in one brick makes it possible to obtain a wall thickness of 250 mm. The bricks in this masonry do not fit next to each other, since the wall will not have the required strength. Depending on the expected loads, the thickness of the brick wall can be 1.5, 2 and 2.5 bricks.
The most important rule in this type of masonry is high-quality masonry and the correct dressing of the vertical seams that connect the materials. The brick from the top row must necessarily overlap the bottom vertical seam. Such a dressing significantly increases the strength of the structure and distributes the loads evenly on the wall.
Types of dressings:
- Vertical seam;
- Cross seam that does not allow materials to be shifted along the length;
- Longitudinal seam that prevents horizontal movement of bricks.
Laying a wall in one brick should be carried out according to a strictly selected scheme - it is single-row or multi-row. In a single-row system, the first row of bricks is laid with the spoon side, the second with the butt side. The transverse joints move half the brick.
The multi-row system assumes alternation through a row, and through several spoon rows. If thick bricks are used, then the spoon rows are no more than five. This method provides maximum structural strength.
The next row is stacked in the opposite order, thereby forming a mirror image of the first row.Such masonry has special strength, since the vertical seams do not coincide anywhere and are overlapped by the upper bricks.
If it is planned to create a masonry of two bricks, then, accordingly, the thickness of the wall will be 51 cm. Such construction is necessary only in regions with severe frosts or in construction where insulation is not supposed to be used.
Since the brick has its own standard dimensions (6.5 x 12 x 25), then the thickness of the brick wall will have several standard dimensions, given the thickness of the joint between adjacent bricks.
There are other sizes, but they mainly differ in height, and the height of the brick does not affect the thickness of the wall.
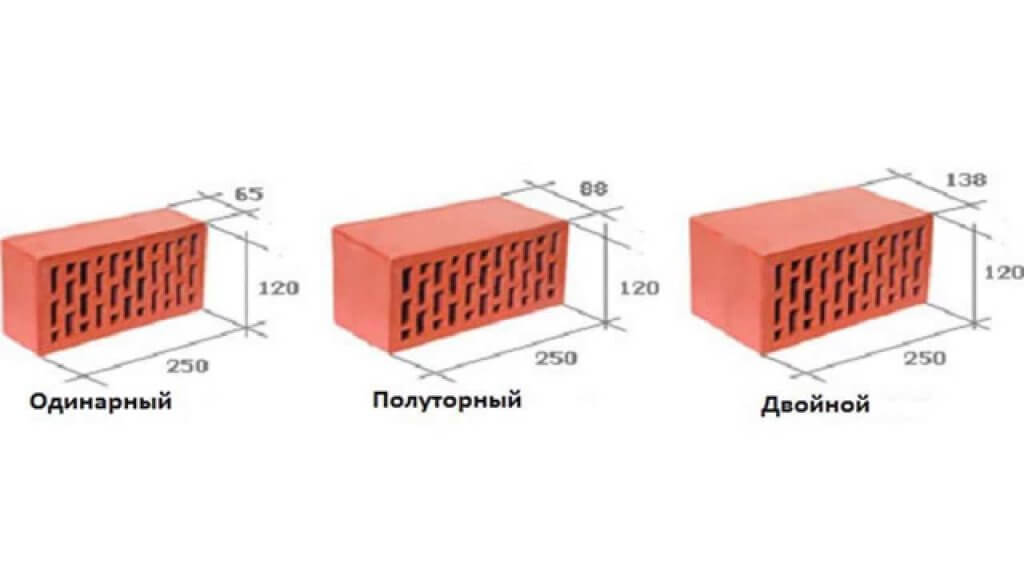
Standard brick wall dimensions
Number of bricks, pcs
Wall thickness, cm
0,5
12
1
25
1,5
38
2
51
2,5
64
In addition to a thickness of 65 mm, there is a brick thickness of 88 mm - one-and-a-half brick and 138 mm - double. Those. dimensions 8.8x12x25
and 13.8x12x25
... In general, the thickness (height) of the brick does not affect the thickness of the brickwork in any way.
The main criterion when choosing the thickness of a brick wall is the purpose and location of the wall itself.
Ordinary brick laying
Rules:
A stone with color defects (the surface is not red, but mottled) is not used.
Initially, the type of masonry is determined.
In the transverse and longitudinal direction, the distances and voids are filled with a solution.
If the wall is then plastered, the seams are filled only by 10-15 mm with a total thickness of 8-10 mm.
Arrangements and a cord are used for horizontality, a plumb line for verticality.
It is important to ensure the solidity of the masonry.
Under the load of the overlying rows of masonry, the brick on the mixture should not move. It is impossible that the thickness of the seam decreases or its cracking is observed.
The laying of ordinary building material is done by hand, but differs from the type of brick used and the need for plastering after. There are 2 techniques: with full and incomplete filling of the seams. If full filling is applied, the mortar is squeezed out onto the face and then trimmed with a trowel. The mix for masonry includes cement with sand (1: 4). After laying, the dressing of the seams is performed using a double-row or multi-row technique. For pillars, a four-row system is used.
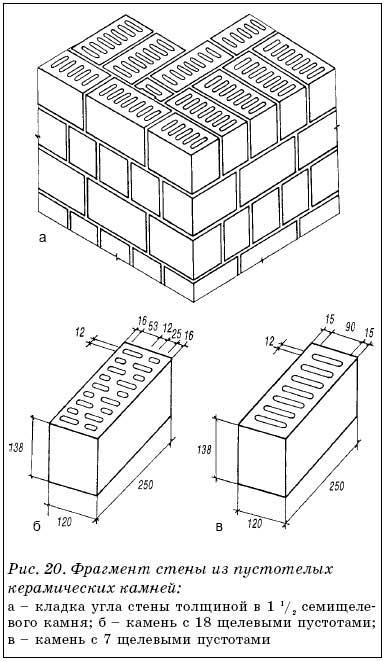
Solid and hollow bricks
A single private is:
- hollow - one block weighs from 2.3 to 2.7 kg;
- full-bodied - up to 3.6 kg, respectively.
There are almost no voids in the full-bodied. Their overall volume is only 13%. Compared to hollow, it is much stronger. Therefore, it is used in the construction of internal walls, external, internal and supporting structures, pillars, columns, foundations. Due to its fortress, this product is very popular, allowing you to build reliable buildings. The appearance of such samples is also highly valued.
The volume of voids in a hollow sample ranges from 13 to 40%. They are different:
- closed;
- cross-cutting;
- oblong;
- round, etc.
They put lightweight partitions and walls, fill the frames of multi-storey buildings.
If the correct sample of brick is chosen for construction, then it will serve for a long time, and the constructed objects will be reliable and strong. Each of these types has its own characteristics and is intended for established types of work. Expert advice will help you choose the best option.
External load-bearing brick walls
The strength and stability of the entire building is provided by the outer walls. They are called load-bearing because they distribute the entire load acting on the building. They bear the weight of ceilings, higher walls, roofs, operational loads (furniture, things, people) and snow.
The starting point for any masonry is the corners of the building. A lighthouse is made on each of them (an angle is taken out of bricks, aligned vertically and the axes of the building). Corner masonry rises 6-8 rows. It is recommended to reinforce the corners of the outer walls with a metal mesh made of wire with a diameter of 6 mm.Then, between the beacons at the level of the upper brick, a string is pulled along the edge of the wall, which marks the outer axis of the structure. Brickwork is carried out from one lighthouse to another, the thickness of the walls consists of the outer, inner and middle parts, which are filled with insulation or filled with another material. A brick on the wall is laid with a bandage, after three or five spoon rows, one butt is needed. There are many brick laying patterns. Depending on the chosen scheme, the order of arrangement of spoon and butt rows may differ. The same applies to the seams, they should not be located on top of each other. With the help of halves and quarters, the brick can be easily shifted to the side relative to the bottom row. After laying several rows with a level, the verticality of the wall is checked in order to avoid various curvatures of the plane, which can spoil the aesthetic appearance of the building.
The thickness of the brick bearing wall is selected based on the climatic zone, environmental characteristics and own capabilities. But for any calculations, it should not be less than 380 mm (masonry "one and a half bricks"). In the northern regions, the thickness is usually increased to 510 mm, or even up to 640 mm.
To reduce the load of the walls on the foundation and to lighten the structure, the outer walls are laid from hollow bricks. It is unprofitable to make continuous masonry, it is expensive and reduces the thermal protection of the building.
Weight of 1 solid red brick.
The standard option is a red brick with dimensions of 250x120x65 mm and a weight of 4.3 kg. The mass of a large-format wall block can reach 24 kg, depending on the size of the brick - height, length and width.
The product can be divided into types:
- By material, bricks are divided into two types: ceramic (red) and silicate.
- According to the purpose, the brick is divided into working, facing (front), clinker, refractory (fireclay).
- The sizes are: single, one and a half and double.
- In shape: corpulent or hollow (slotted).
Calculation table of the weight of 1 brick of all types.
In the table below, you can find out the weight of building bricks both by piece and by m3, according to GOST standards.
| Ceramic brick GOST 530-2007 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| The size | Weight of 1 brick, kg. | Brick weight on a pallet, kg (Pieces per pallet) * | Brick cube weight, kg. (Number of pieces in a cube) |
| Worker corpulent | |||
| single | 3,3 — 3,6 | 660-1440 (200-400) | 1693-1847 (513) |
| one and a half | 4 — 4,3 | 800-860 (200) | 1515-1630 (379) |
| double | 6,6 — 7,2 | 1320-1440 (200) | 1597-1742 (242) |
| Worker hollow | |||
| single | 2,3 — 2,5 | 810-1110 (352-444) | 1180-1283 (513) |
| one and a half | 3 — 3,3 | 865-1148 (288-348) | 1137-1250 (379) |
| double | 4,6 — 5 | 810-1120 (176-224) | 970-1210 (242) |
| Facing (front) hollow | |||
| single | 1,32 — 1,6 | 634-662 (480) | 675-820 (513) |
| one and a half | 2,7 — 3,2 | 950-1125 (352) | 1023-1630 (379) |
| Silicate brick GOST 379-95 | |||
| The size | Weight of one brick, kg. | Brick weight on a pallet, kg (Pieces per pallet) * | Brick cube weight, kg. (Number of pieces in a cube) |
| Worker corpulent | |||
| single | 3,7 | 740-1410 (200-380) | 1900 (513) |
| one and a half | 4,2 — 5 | 840-1400 (200-280) | 1592-1895 (379) |
| Worker hollow | |||
| single | 3,2 | 810-1110 (200-380) | 1640 (513) |
| one and a half | 3,7 | 865-1148 (200-280) | 1400 (379) |
| double | 5,4 | 810-1120 (200) | 1305 (242) |
| Facing (front) hollow | |||
| one and a half | 3,7 — 4,2 | 740-1175 (200-280) | 1400-1590 (379) |
| double | 5 — 5,8 | 1000-1160 (200) | 1210-1405 (242) |
| Refractory (fireclay) solid brick GOST 390-96 | |||
| The size | Weight of 1 brick, kg. | Brick weight on a pallet, kg (Pieces per pallet) * | Brick cube weight, kg. (Number of pieces in a cube) |
| single | 3,5 — 4 | 1350-1600 (385-400) | 1745-2050 (513) |
In the above table, you can find out the weight of m3 of brick, as well as the piece weight. All data are taken from GOST.
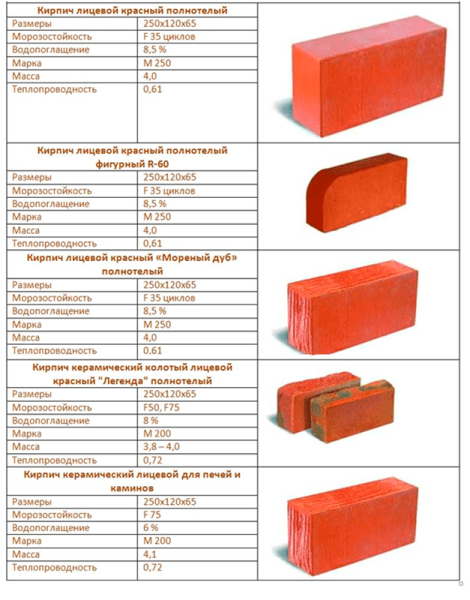
Brick weight table.