Security measures
From a hygienic point of view, white spirit is unsafe. This imposes certain restrictions on its use. Previously, the specified solvent was used in copiers as a carrier fluid, making it harmful to work with this technique. At one time, solvent gasoline almost completely replaced turpentine used earlier in the paint and varnish industry, which acted as the main solvent. The liquid that replaced turpentine belongs to the 4th class in terms of hazard level, which includes non-hazardous, low-toxic substances.
The high volatility of solvent vapors, harmful to health, explains the corresponding requirements for the quality of exhaust ventilation systems in rooms where it is supposed to be used. Manufacturing facilities where such substances are used should be equipped with an effective local ventilation system. If white spirit is used in a domestic environment, then when working with it, you should ensure that the room is well ventilated or work outdoors. However, this solvent has a low level of toxicity and is one of the most preferred for work in confined spaces.
Long-term exposure to volatile white spirit vapors on the respiratory tract can be toxic.
You can determine the poisoning of the body by the following symptoms:
- dizziness and headache;
- drowsiness;
- irritation of the eyes and mucous membranes;
- itching of the skin, skin rash in people prone to allergies, eczema, dermatitis.
The solvent should be stored in the temperature range from -40 to +40 degrees Celsius in a place protected from direct sunlight in a tightly closed container. Handling containers containing white spirit should be carried out away from sources of ignition, heat and flame. In case of fire of white spirit, sand, foam or carbon dioxide should be used for extinguishing, water is not used in this case.
In the next video you will find a mini-presentation of the white spirit Lakkabensiini 1050 from Tikkurila.
Precautionary measures
Before you start working with a solvent, you need to get adequate preparation and protect yourself from harmful vapors. Remember that the individual components that make up the composition can negatively affect your well-being and health. Hydrocarbons, ketones, as well as other compounds and components cause the development of skin diseases, headaches, allergic reactions and discharges of varying severity. Volatile elements, which cause harmful fumes, affect the mucous membrane of the eyes as well as the respiratory tract. Sometimes, when using these formulations, nausea is noted.
Considering all of the above, it is worth taking care of reducing the negative effect. Special work clothing and accessories are needed not only to protect the hands, but also the face, eyes and nose. You will definitely need special goggles, a respirator mask and gloves. Since the composition is flammable, refrain from smoking and using open flames during work.
This is interesting: How to repair a stretch ceiling?
Tips and tricks for use
Degreasing agents should be used with extreme caution, avoiding contact of the liquid with the skin. All work is carried out in a given sequence:
- the metal is predominantly cleaned mechanically before processing. This must be done to eliminate various defects and rust. You can use regular sandpaper, as well as a grinder;
- areas that do not need to be processed are covered with special canvases;
- it is best to apply a degreaser to the treated fragment with a piece of cloth;
- the solvent is kept on the surface for a certain period of time, after which the excess is removed, and the metal section is primed and then painted.
It is imperative to use a degreaser before painting. You should not make the mistake of many who decided to save time by skipping this important stage of metal processing. Rust on the surface that appears over time will cause the owner to re-incur significant time and financial costs.
Solvent R-5 - complex chemistry in construction
Solvents are special formulations designed to react with a binder and at the same time reduce the viscosity of the paint. This is their main difference from thinners used to lower the viscosity of paints and varnishes.
In this article, we focus on technical fluids of complex composition, the representative will choose the solvent R-5
What is this solvent?
In the modern paint and varnish industry, a huge variety of organic and inorganic substances are used as solvents. To improve the quality of the resulting products, manufacturers usually use mixtures. They are called numbered.
Organic composition P-5 is used for diluting various paints to obtain a working viscosity, as well as for thorough cleaning of painting tools and equipment.
The popularity of this mixture is due to its excellent performance characteristics. The large number of components that make up this mixture determines its broad specialization and, in addition, the ability to dissolve a variety of organic substances.
Characteristics and application of R-5
This solvent in its appearance is a completely colorless or slightly yellowish transparent liquid without the presence of visible suspended inclusions. This mixture has a rather pungent specific odor.
Solvent R-5, the composition of which includes 30% butyl acetate and acetone, as well as 40% toluene, is one of the most active and aggressive. Therefore, its use in works requires special care and accuracy. In some cases, it may be more appropriate to use weak formulations.
This combined mixture is purchased for diluting paintwork products (paints and varnishes), based on the resin PSH-LS and PSH LP. In addition, it interacts well with other substances based on rubber, polyacrylic and epoxy, organosilicon resins and other film-forming components.
This combination is added to paints and varnishes in small portions with constant stirring until the final product is given the required viscosity. The shelf life of the finished composition does not exceed 1 year from the date of manufacture. Solvent R-5, GOST 7827-74, is produced in appropriate proportions in large mixers at factories, but for laboratory needs it is easy to prepare it yourself.
This solvent mixture is widely used, but not universally applicable. In some cases, it is more expedient to use the R-5a solvent. It is derived from the previous one, and its only difference is that the mass fraction of one of the components, namely butyl acetate, should not exceed 30%.
Precautions for work
These solvent mixtures contain aromatic hydrocarbons, amines, halogen derivatives and ketones, which can cause various skin diseases as well as serious poisoning. The vapors are irritating to the respiratory tract and eyes.
With prolonged contact, solvents can have a negative effect on the bone marrow and blood. When working with these mixtures, it is necessary to put on special clothing, and also use gloves, a respirator and goggles.
In addition, these mixtures are fire and explosive.Do not work with them near open flames, while smoking, etc. The room where the work takes place must have good ventilation, because dangerous air pollution happens very quickly. Among other things, these mixtures are very corrosive to some plastics.
Degreasing pipes and hoses
8.1. Need
degreasing of assembled pipelines with a pressure of over 4.0 MPa (40 kgf / cm2)
determined by the technical documentation, a degreasing decision is recommended
take after inspection of the open ends of the pipeline, according to OST 26-04-2574.
8.2. Pipelines
liquid oxygen are checked for the presence of fatty contamination at least once
once a year, in the case when oxygen is transported through it containing
fatty contamination is higher than the requirements of GOST 6331.
Control check
areas with the lowest speed are exposed to the presence of fatty contamination
flow, and with a uniform flow - inlet sections. Control is carried out
according to section 5 of the standard.
In case of exceeding
standards OST 26-04-1362, the entire pipeline is subject to degreasing.
8.3. When degreasing
by immersion in baths, pipes are placed in special baths filled with
aqueous cleaning solutions or solvents, and cured in accordance with
instructions
standard.
8.4. For degreasing
using the circulation method, pipelines are connected to a special system,
equipped with a pump through which aqueous cleaning solutions are pumped or
solvents (see standard).
8.5. Degreasing
the inner surface of the pipes by the filling method is performed as follows:
technological plugs are installed on the ends of the pipes. Through the appropriate
the fitting in the plug is poured with a solvent, after which the fitting is closed, and the pipes
or the hoses are laid horizontally. In a horizontal position, the pipes must
stay for 10-20 minutes, during this time they should be turned 3-4 times to
wash the entire inner surface with solvent. Pipes filled
solvent, can also be moved in special rockers or swivel
mechanisms.
8.6. Plots
the installed pipeline is degreased by circulating the solvent or
aqueous detergent solution.
8.7. Indicative
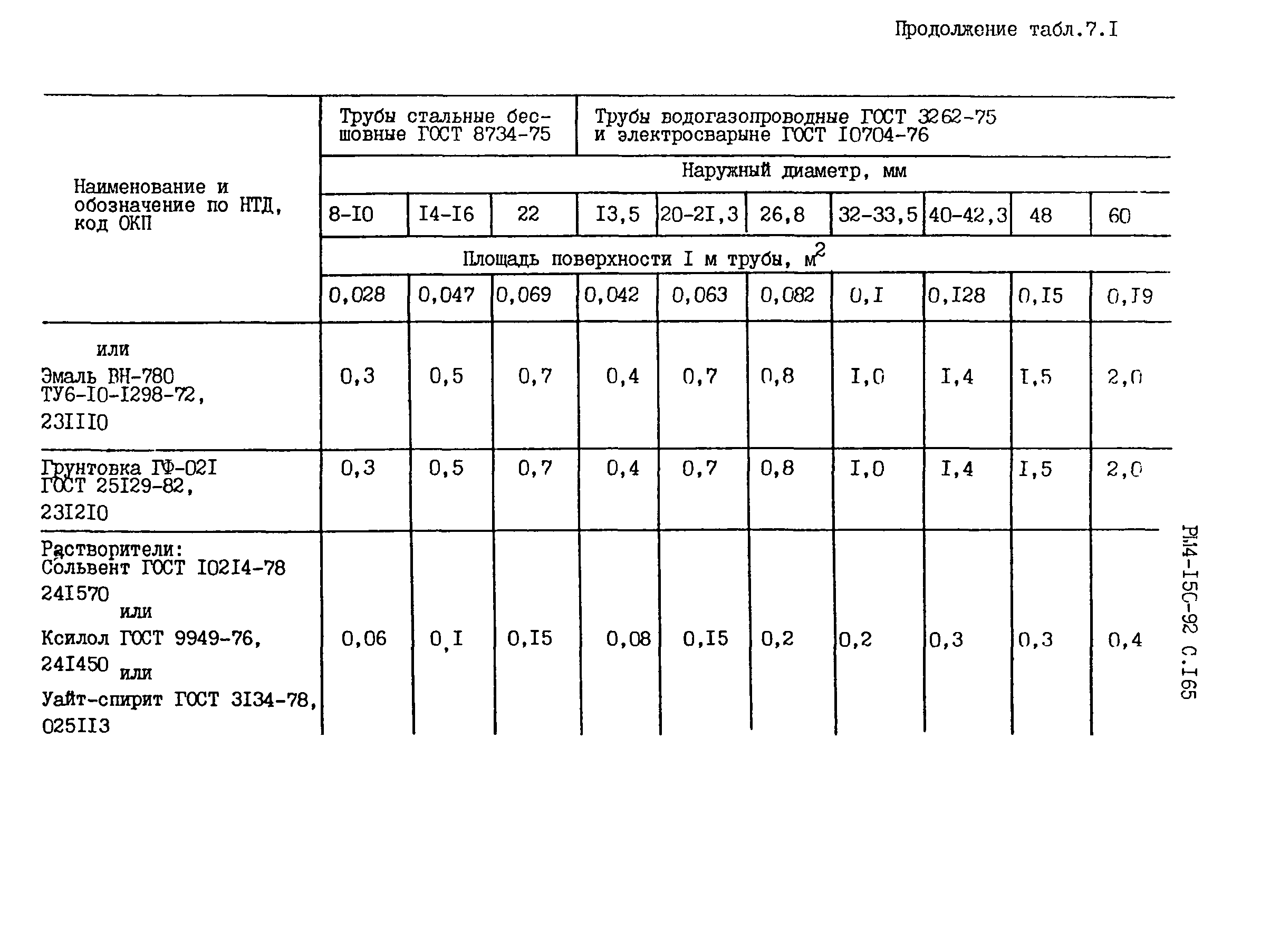
solvent consumption required for one-time degreasing of the internal
surface of one running meter of pipe, calculated by the formula:
(2)
where Q - consumption
solvent, dm3 / m;
D
- inner diameter of the pipe, see.
Solvent consumption
for a single pipe degreasing is given in table. 2.
table 2
Solvent consumption for single
degreasing pipes
|
Interior |
3 |
b |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
32 |
|
required amount of solvent, dm3 / m |
0,02 |
0,04 |
0,06 |
0,09 |
0,12 |
0,20 |
0,25 |
Continuation of table. 2
|
Interior |
40 |
50 |
70 |
80 |
100 |
125 |
200 |
|
required amount of solvent, dm3 / m |
0,25 |
0,30 |
0,40 |
0,50 |
0,80 |
1,00 |
1,60 |
Continuation of table. 2
|
Interior |
300 |
500 |
750 |
1000 |
|
required amount of solvent, dm3 / m |
2,40 |
4,00 |
6,00 |
8,00 |
8.8. Small areas
pipelines can be degreased by wiping or blasting
water cleaning solution using special tools.
8.9. Outdoor
the surfaces of the ends for a length of 0.5 m during installation are wiped with napkins,
soaked in a solvent or aqueous detergent solution, and dried on
open air.
8.10. All details,
intended for connecting hoses to the container must be degreased
by wiping, if contamination was possible during storage.
8.11. Tank hoses
medical oxygen are defatted together with the vessel.
8.12. Low fat
sections of pipelines to be stored or transported must be
must be plugged and sealed.
8.13. Plots
pipelines subjected to chemical passivation prior to assembly or
other types of chemical surface treatment may not be degreased if
the requirements of the standard are met.
8.14. Sections
pipelines and hoses, degreased during manufacture, received for installation from
caps and having the corresponding marks in the passport are not degreased.
8.15. Degreasing is not
complete pipelines are subjected to pressure up to 4.0 MPa (40 kgf / cm2),
if sections of pipelines before assembly or pipelines assembled were subjected to
cleaning from scale, slag, etc. by pickling, sandblasting and shot blasting
processing.
8.16. Trunk
oxygen pipelines and inter-workshop pipelines, pressure up to 1.6 MPa (16
kgf / cm2), assembled are not degreased, if before connection
individual pipes, visual inspection confirmed the absence of grease stains
contamination on the surface of pipelines, for which an act must be drawn up.
Solvent R-5 and R-5A.
Solvents R-5 and R-5A are widely used in the paint and varnish industry. They are intended for diluting enamels and primers based on polyvinyl chloride and perchlorovinyl resins, copolymers based on vinyl chloride, chlorinated rubbers, epoxy resins, organosilicon and polyacrylic paintwork materials (see Table 1):
Main brands of paintwork materials
For dilution of paints and varnishes based on resins PSH LS, PSH LN, rubbers, epoxy, polyacrylic, organosilicon resins and other film-forming substances.
Varnishes: KhV-139, AS-16, AS-82, AS-516, AS-552, AK-113.
Enamels: KhV-124, KhV-125, KhV-160, KhV-16, KhV-782, KhV-536, KhS-1107, AS-131, AS-560, AS-599, AK-192, EP-56, EP-140, EP-255, EP-275, EP-525, EP-567, KCh-767, KO-96, KO-811, KO-814, KO-818, KO-822, KO-841.
Primers: AK-069, AK-070, EP-0104
Putties: EP-0020, EP-0026, EP-0028.
For dilution of paints and varnishes (based on resins PSKh LS, PSKh LN, rubbers, epoxy, polyacrylic organosilicon resins and other film-forming substances), the technology of which excludes the possibility of using the R-5 solvent.
As follows from Table 1, the fields of application of both solvents are almost identical. GOST 7827-74 defines the difference in the use of the R-5A solvent with the vague phrase "For diluting paints and varnishes ... the technology of which excludes the possibility of using the R-5 solvent".
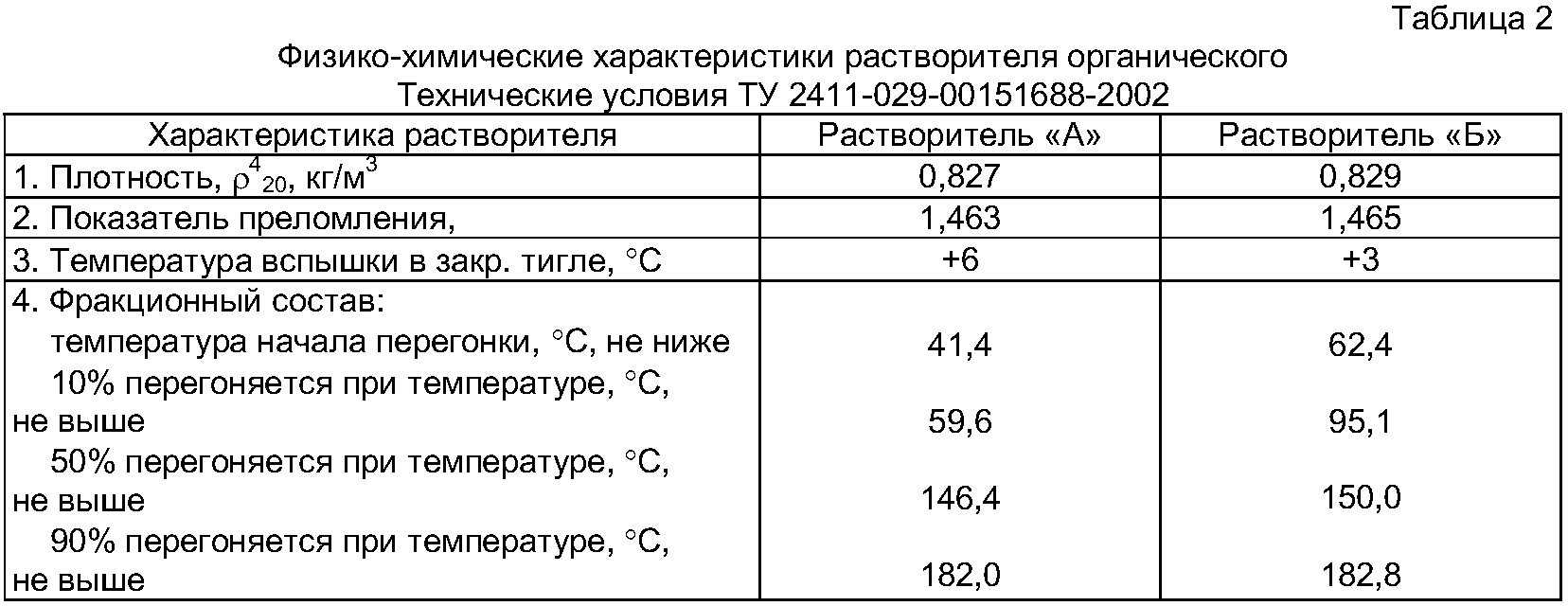
Quality indicators of R-5 and R-5A solvents:
The norm for the brand according to GOST 7827-74
1. Color and appearance
Colorless or slightly yellowish homogeneous transparent liquid without visible suspended particles
2. Mass fraction of water according to Fischer,%, no more
3. Volatility with ethyl ether
4. Acid number, mg KOH / g, no more
5. Coagulation number,% not less
6. Diluting action
There should be no coagulation and delamination of paintwork materials.
After drying, there should be no film behavior on the surface, as well as whitish or dull spots.
7. Flash point in a closed crucible, ° С,
Obviously, in terms of their technical characteristics, both solvents are similar. So what, then, is the difference that "excludes the possibility of using the R-5 solvent"?
Of course, it's all about the composition of the solvents. Although both R-5 and R-5A are made by mixing both the same solvents, their ratio is different.
The composition of the solvents will determine their volatility. As shown in Table 3, the P-5A solvent contains three times as much butyl acetate. The more butyl acetate in the mixed solvent, the lower its volatility. Those. R-5A is a slower solvent than R-5. For many paints and varnishes, the volatility of the solvent used to dilute to the working viscosity is one of the defining criteria.
Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide more specific instructions for the use of solvents R-5 and R-5A, because everything depends on the composition of paints and varnishes, and this information is a trade secret of manufacturers. It remains only to rely on the practical experience and recommendations of manufacturers of paints and varnishes.
Other articles
Classification by chemical composition and designation of paintwork materials
Purpose, types and composition of paints and varnishes
23 October 2020
Why do you need a primer. Application advantages.
What is the difference between solvents 646 and 647?
Solvents are presented in stores with a rather diverse assortment, but numbers 646 and 647 are the most popular. At first glance, the compositions seem to be identical: they are produced by domestic enterprises, packaged in similar containers, and are used in some areas. However, there are minor but very important differences between the products.
A distinctive feature is the chemical composition of the solvents. The components that make up 646 we have given above, so we will talk about 647. It is also a multicomponent mixture, which includes the following substances:
As you probably noticed, acetone is absent in the list of active ingredients. Due to this feature, solvent 647 is less active, therefore it can be used on surfaces requiring gentle care. The difference in chemical composition was reflected in the field of application. In particular, 647 is intended to increase the viscosity of nitrocellulose formulations.
Degreasing of air separation units
2.1. Degreasing of the assembled separation units is performed only with solvents of group 1 (see Table 1) of the standard.
The use of solvents of group 2 for these purposes is not allowed.
2.2. The amount of solvent required for degreasing depends on the size of the separation unit and the degree of contamination with oil. The approximate amount of solvent required for a single flush of some blocks is given in table. 1.
Table 1
Approximate solvent consumption for a single flush of air separation units
|
The amount of air processed by the separation unit, m3 / h |
The amount of solvent required for a single flush, dm3 |
|
180 |
70 |
|
1000 |
260 |
|
2400 |
700 |
|
up to 7000 |
1100 |
|
up to 15000 |
2500 |
2.3. To avoid corrosion, before degreasing with solvents, all separator units must be thoroughly dried.
2.4. Before degreasing the air separation units, the equipment should be checked for leaks and all detected gaps should be eliminated.
2.5. Degreasing of communications and internal cavities of heat exchangers is carried out by circulating the solvent in the washed cavities for 1-1.5 hours.
2.6. Degreasing of devices (condensers, bottom column cube, regenerators, etc.) is carried out by filling up to 3/4 of the volume with a solvent, followed by bubbling with air or nitrogen for 1-1.5 hours or by condensation of vapor solvents.
2.7. Degreasing of adsorbers is carried out after removing the adsorbent from them by wiping the adsorber body and basket. Do not degrease the assembled acetylene adsorbers.
2.8. Degreasing of the filtering elements of expander filters is carried out with aqueous washing solutions, for example, in washing machines, or by circulating the solvent through the filtering element in a special device. It is not allowed to degrease the filter cloth by hand washing in a solvent.
Solvent R 4
Composition and properties
P 4 is an organic solvent containing aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones and ethers. It consists of 62% toluene, 26% acetone, 12% butyl acetate. A mixture of these components effectively dissolves and liquefies various paints, varnishes, resins and other organic substances.
There is a variety of it - the R-4a solvent, the peculiarity of which is the absence of butyl acetate in the composition.
This tool is manufactured in accordance with GOST 7827-74. R-4 GOST is produced with the following technical characteristics:
- looks like a clear liquid without color or yellowish, without suspension (P-4 and P-4a look the same);
- water content - 0.7%;
- volatility - from 5 to 15;
- acid number, mg KOH / g - no more than 0.07;
- coagulation number - not less than 24%.
Application
This tool is used to dilute and dissolve varnishes, putties, enamels, primers, paints marked with XB, XC, HSL, EP, Vinicolor, Vinicor, Evikor, Evinal, HS-500 primer-enamel.
Also, R-4 is used for washing dishes, hands and arms after working with paints and varnishes.
This solvent is suitable for dissolving and thinning enamels, varnishes, primers and putties with markings XC, XB, PVC, MS, EP-0020, except for XB-124 gray and protective enamel. The R-4a modification of this solvent can also dissolve the gray and protective enamel XB-124.
It is volatile, and its use is based on this: after adding a solvent to the paint and applying it to the surface, it quickly hardens and forms a film.
Important! Do not allow water to get into solvents R-4 and R-4a. This will lead to whitening of the paint film, since water easily mixes with acetone, which is part of the product.
Security
Solvent R 4 is toxic, fire and explosive, therefore, when working with it, safety precautions must be observed.
- It is necessary to store the composition in fireproof ventilated rooms, away from sunlight, in sealed containers;
- it is also necessary to work with the solvent in rooms with good ventilation;
- avoid contact with eyes;
- work in protective gloves, avoid contact with skin, in case of contact with skin, wash off with plenty of warm water and soap.
Due to the fire hazard of the solvent in the room where it is stored and works with it, sparks, open fire, and smoking must be excluded. In case of fire, P-4 is extinguished with foam, carbon dioxide, sprayed water. It should be remembered that vapors of the solvent and its components (butyl acetate, acetone, toluene) are heavier than air, can accumulate near the floor and are explosive.
The toxicity of the drug is manifested by narcotic effects (dizziness, headache, disorientation, blurred consciousness with prolonged inhalation), irritation of the eyes and other mucous membranes, and coughing. With prolonged inhalation of vapors, poisoning is possible, similar in symptoms to food, toxic damage to the nervous system.
Therefore, when working with a solvent, you should use protective equipment (goggles, gloves, respirator), work only in a well-ventilated area. If the product comes into contact with the skin, it must be washed off, if in the eyes, rinse them and seek medical attention.
Solvent brands R-4 and R-4a are also fire and explosive, forms explosive compounds with acids and oxidants (acetic, nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide), reacts with chloroform and bromoform, reaction products are fire and explosive. In relation to some types of plastics, they are aggressive.
It is interesting: The foundation for a foam block bath - we get to know the essence
R646 consumption
The solvent is added to the paint and varnish base in small portions with constant stirring until the desired viscosity is reached.
P646 is highly active, so handling this product requires care, otherwise the surface to be treated may be damaged.
Material consumption when degreasing per 1 sq.... m is:
- for facade work, the required volume will be 0.147 liters;
- for surfaces made of metal or wood indoors - 0.12 l;
- for a layer of concrete - 0.138 l;
- for all types of surfaces in conditions of high humidity - 0.169 l.

Solvent brand 646 is rightfully considered one of the most effective solvent compositions, therefore it is widely used in the repair of technological equipment.
- Together with varnishes XB-784. They are often used in production workshops to cover decarbonizing water tanks and liquid chemical cleaning, condensate tanks, water desalination tanks and purification pipelines. It is possible to use varnishes and enamels for this purpose only with solvent 646. Its standard consumption will be 0.086 l / m2.
- Together with NTs-11 enamel. which is suitable for processing metal surfaces operating in changeable weather conditions with a high degree of exposure to moisture, including sea water, as well as oil products. P646 is used to dissolve this paint at the rate of 0.528 kg per sq. m.cover. For non-metallic coatings operating under similar conditions, NTs 1200 enamel is used, it is diluted based on the standard of 0.147 l / m2.
- For internal repair work, it is worth giving preference to NTs-25 enamel. The proportion of its dilution is 0.120 liters per square meter of surface.


To protect porous layers of concrete and brick from the adverse effects of alkalis and acids, a putty is used. At the same time, it can only show its consumer properties more efficiently when diluted with a high-quality solvent - this will require 1.2 liters of P646 per square meter. If the putty is used to protect the insides of lighting tanks, containers for acid-base compounds and the insides of sodium cation filters, the solvent consumption will be lower - 0.138 l / m2.
EP-5116 enamel, used for treating the coating of pipelines and oil reservoirs, is diluted with a solvent at a ratio of 0.169 liters per square meter.


Degreasing of fittings and devices
9.1. Degreasing
produced after manufacture, before installation and after repair, i.e. v
cases where it was possible contamination of the reinforcement.
9.2. Armature
degreased in disassembled form with aqueous detergent solutions. Allowed
pre-wipe with a cloth soaked in white spirit or kerosene
In that
case, special attention should be paid to fire safety measures
9.3. When
for technical reasons, it is allowed to degrease the fittings without disassembling. For
determining the possibility of degreasing purchased fittings without disassembly is recommended
degrease it, dry it, and then disassemble and check for residual
the content of fatty contaminants. If the residual content is
comply with the norms, according to. standard, hereinafter reinforcement
can be degreased without disassembling.
Special attention
should be addressed to the gland and its packing. 9.4
When degreasing
fittings without disassembly, the compatibility of all materials should be taken into account, from
which fittings are made, especially seals, with used detergents
by means
9.4. When degreasing
fittings without disassembly, the compatibility of all materials should be taken into account, from
which fittings are made, especially seals, with used detergents
means.
9.5. The armature is not
must be degreased before installation, if degreasing was carried out on
manufacturer (which must be confirmed by the accompanying documents
or with the appropriate branding) and the packaging is not damaged.
9.6. Gaskets from
rubber, paronite, fiber, PTFE packing rings, details from
fiberglass, polycarbonate and textolite are degreased by wiping with water
detergent solutions and rinsed with water.
9.7. Asbestos,
used for stuffing box packing of fittings, degrease by calcining at
temperature of 300 ° C for 2-3 minutes.
9.8. Degreasing
devices for measuring flow and pressure are produced in accordance with OST 26-04-2158.
Solvent requirements
Incoming control
|
Indicator name |
Norm |
Control method |
|
1. Appearance |
Colorless, transparent liquid |
Determined visually |
|
2. Content of mechanical impurities and water |
Should be transparent and not contain suspended or settled to the bottom |
Pour the solvent into a glass cylinder with a diameter of 40-50 mm |
|
3. Reaction of the environment |
The water layer should not turn pink |
The solvent in the amount of 15 cm3 is stirred in |
|
4. Oil content |
Section 2 of the standard, table. 2 |
According to OST 2 6-04-2574 |