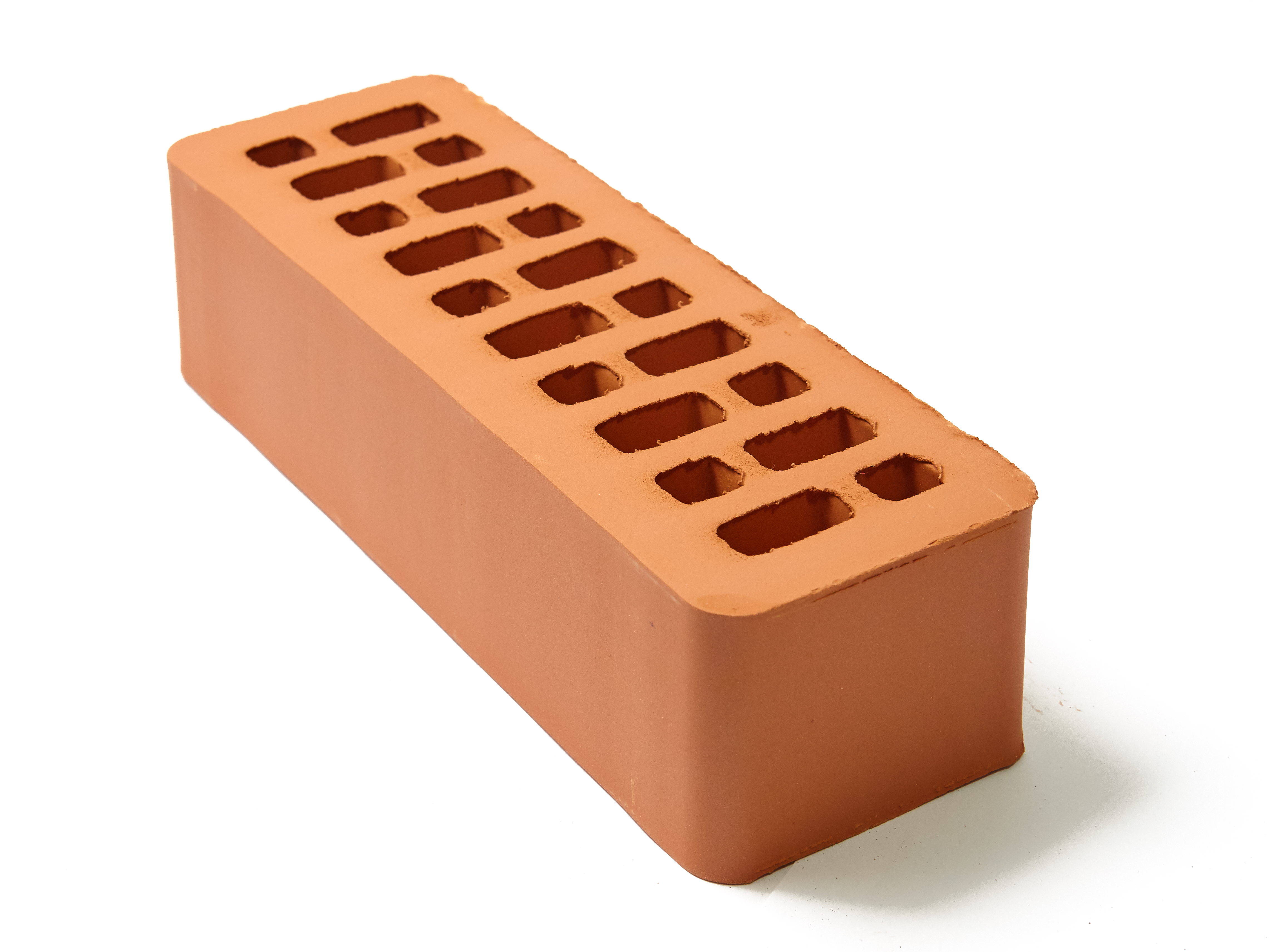
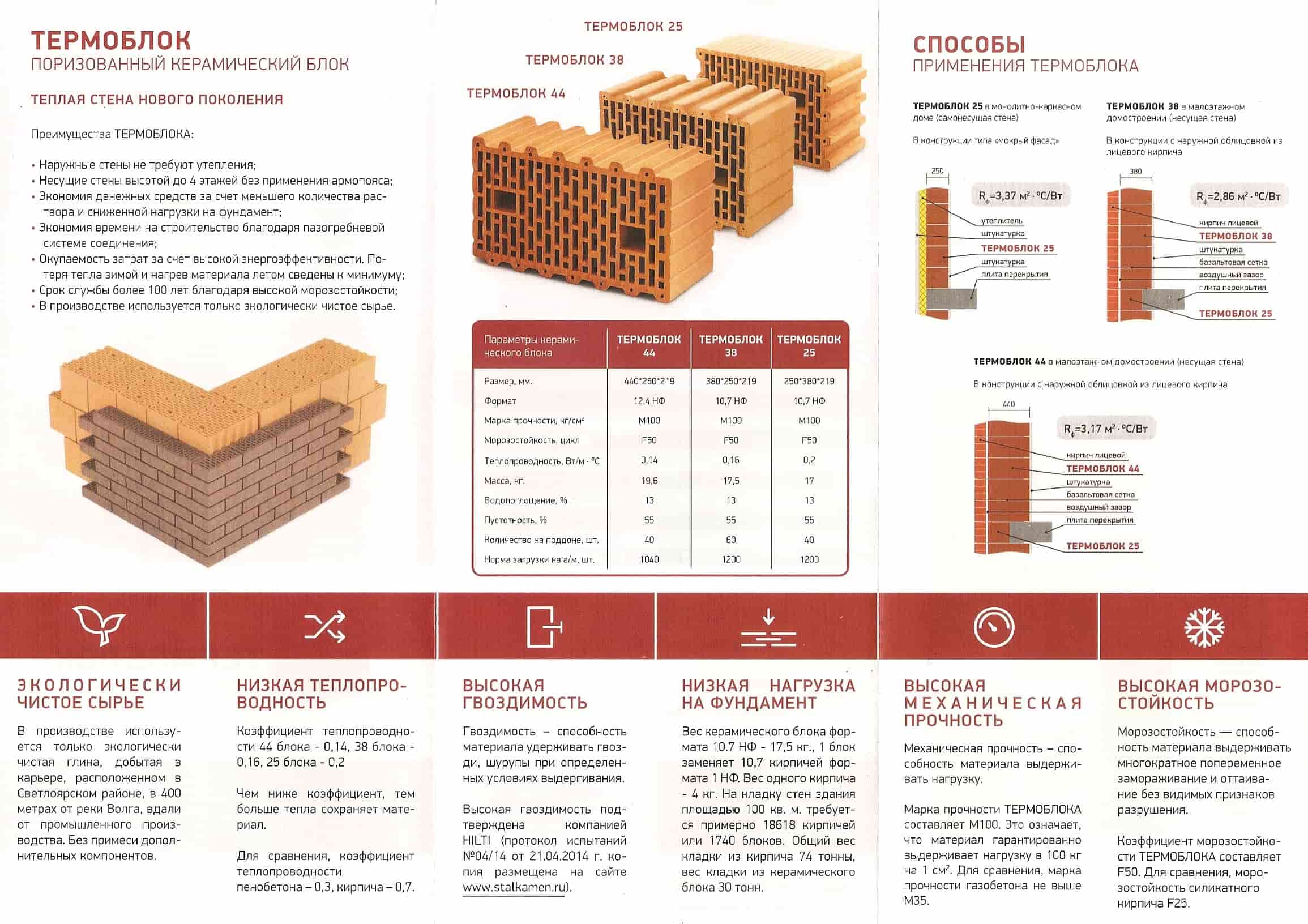
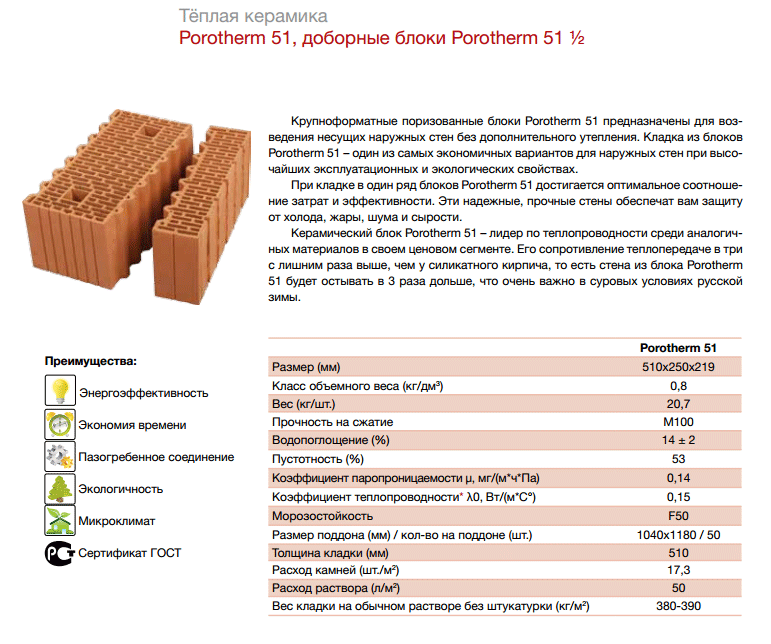
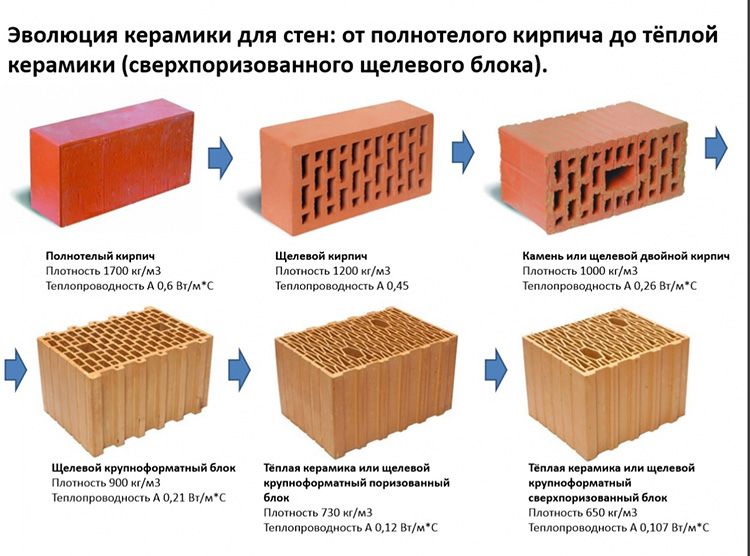
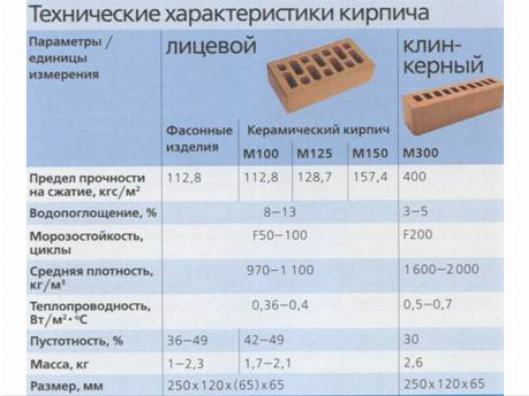
Hollow brick: types, advantages and disadvantages of slotted bricks
Hollow brick is currently a fairly popular building material. It is also called slotted, perforated and effective. It has earned similar names due to the presence of cavities in its design. This constructive solution does not carry an aesthetic burden, but is a way to save some money.
Due to temperature changes at different times of the year, builders have to make the walls thicker in order to protect residents from the cold in winter, and from the heat in summer. It goes without saying that thicker wall structures require more bricks, which leads to a significant increase in construction costs. Hollow bricks require fewer raw materials to make than conventional bricks, so they are much cheaper. In this article, we will talk about the properties of hollow bricks.
How to identify a load-bearing wall?
A load-bearing wall is one that takes on the load of the overhead beams, slabs and other elements. The easiest way to define a load-bearing wall is through a house plan. Everything is clearly marked there, including the elements of the post-and-beam system. If there is no plan, then you will have to go a slightly different path.
To find out which wall is the bearing, you need:
- Consider the location. This includes internal, "looking" at the adjacent rooms; facing the staircase; external and self-supporting walls.
- Consider the thickness and material used. The bearing wall can be brick, the thickness of which is more than 38cm. Or a reinforced concrete panel, at least 14-20cm. Provided that the house is monolithic, the walls are more than 20-30cm load-bearing.
- Consider the support of floor slabs and beams. Floor slabs should rest on the walls with their short side.

Additionally, I will add that there are still self-supporting and non-bearing walls. Self-supporting ones are not a support for anything, but they are affected by loads from higher floors. Non-bearing, as you can understand from the name, are subject only to their own load (usually external walls). You can also add partitions here, which also carry only their own weight.
Bottom line: the choice of bricks for supporting structures is a troublesome business that requires knowledge and attention. At the same time, all the effort spent and your time will pay off with more than good quality and decently saved finances.
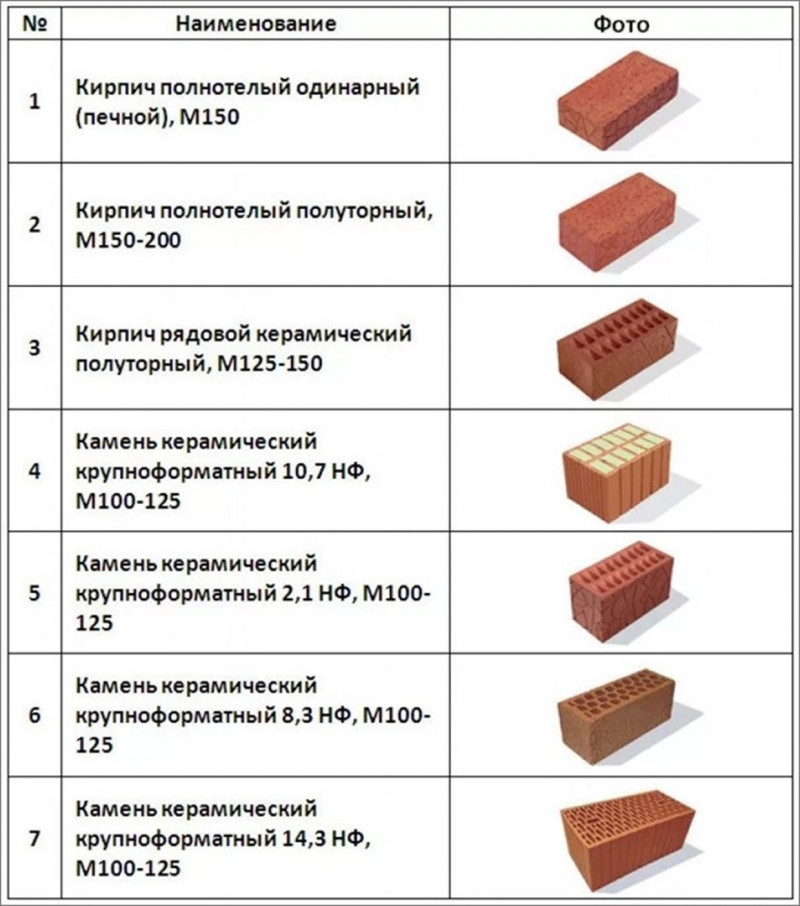
Appointment of an ordinary single brick
Ordinary brick, which is the basis of installation masonry work, is called ordinary brick.
Types of ceramic bricks.
In doing so, it is important to observe the relevant material characteristics. So, in the case of the construction of structures with an increased load, a product of strength grades M250 and M300 is used, frost-resistant at a level of at least 50-75 cycles, demonstrating a porosity of no more than 8%
It should be noted that solid brick is worse than the hollow version, it retains heat in the room. To eliminate this problem, builders are forced to produce additional thermal insulation of the walls.
For highly effective insulation of premises, a solid block is also replaced with a hollow one. However, this can be done only in those cases when it comes to the construction of low-rise buildings that do not experience constant heavy loads. The supporting frame and partitions (not supporting) in multi-storey buildings are also filled with hollow ordinary bricks.
The economic benefit from the use of this or that material is of great importance in modern construction. This quality is quite characteristic of the hollow version, since less clay is consumed for the production of an artificial building block with voids making up more than 13% of its volume.This circumstance ultimately reduces the cost of construction work.
When choosing a hollow brick according to the structure of voids, it should be borne in mind that a block with horizontal voids is less durable than an analogue with vertically located voids.
Choosing bricks for load-bearing walls
There are two main types of modern bricks: ceramic and silicate. Ceramic (red) consists of clay, and silicate (white) - of sand and lime. The rest are subspecies of these two.
Advantages of silicate: strength, frost resistance, insulation, creating a comfortable microclimate, fire resistance, heat accumulation. Disadvantages: fragility, poor thermal insulation.

Advantages of ceramic: moisture resistance, frost resistance, heat retention. Disadvantages: fragility when exposed to water during the off-season. The most important advantage of this building material is strength. There are solid and hollow bricks in terms of filling.
There are also three strength classes:
For construction, you can use corpulent and hollow. But at the same time, it must be remembered that solid red brick (ceramic) is used in the construction of multi-storey buildings, basements, basements, vaults of the foundation, pivot arches, chimneys and more. Hollow ceramic is better for filling voids and openings in a monolithic building.
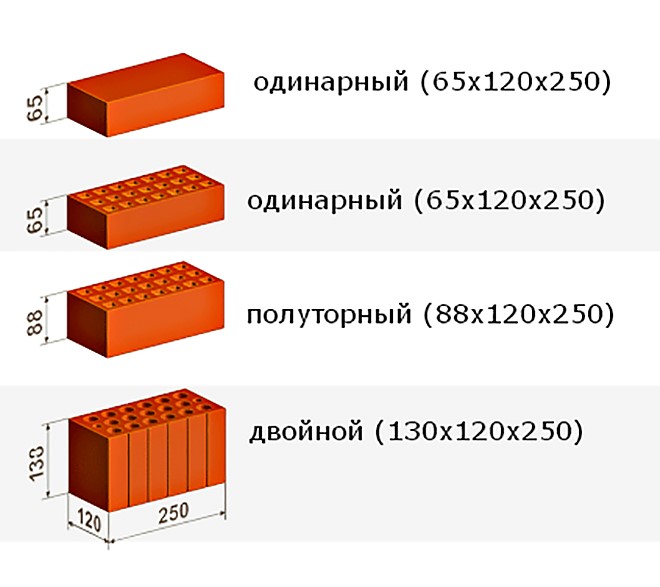
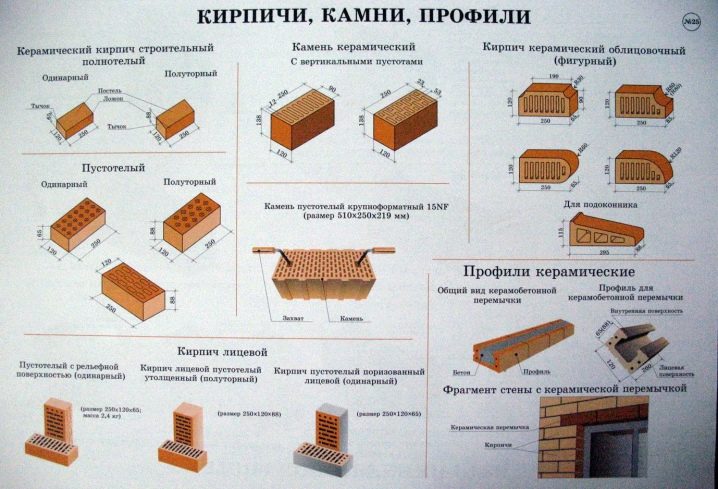
Types of bricks and their sizes
When starting the search for a suitable material for cladding or wall construction, you should pay special attention to the standards for the edges of the product. This will help you to correctly calculate the masonry step and choose the amount you need. ... There are the following 3 standard brick sizes:
There are the following 3 standard brick sizes:
| Name | Size, mm |
|---|---|
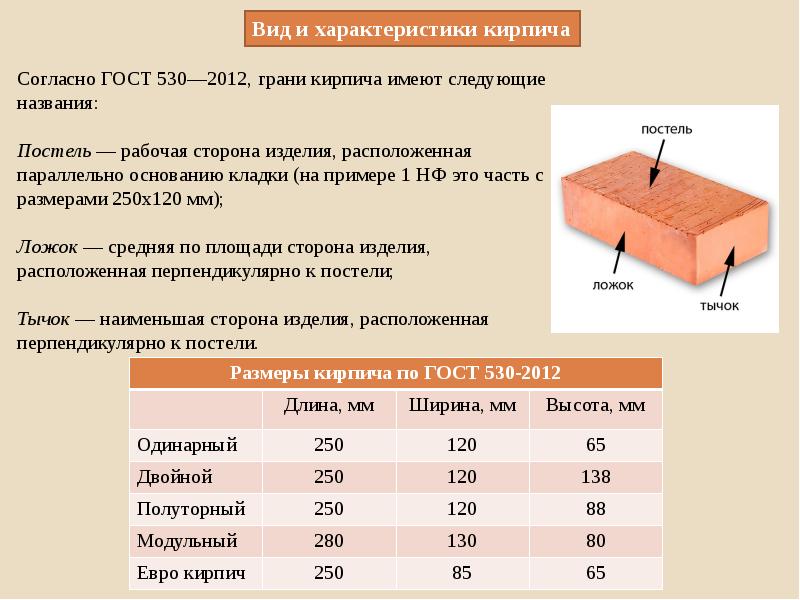
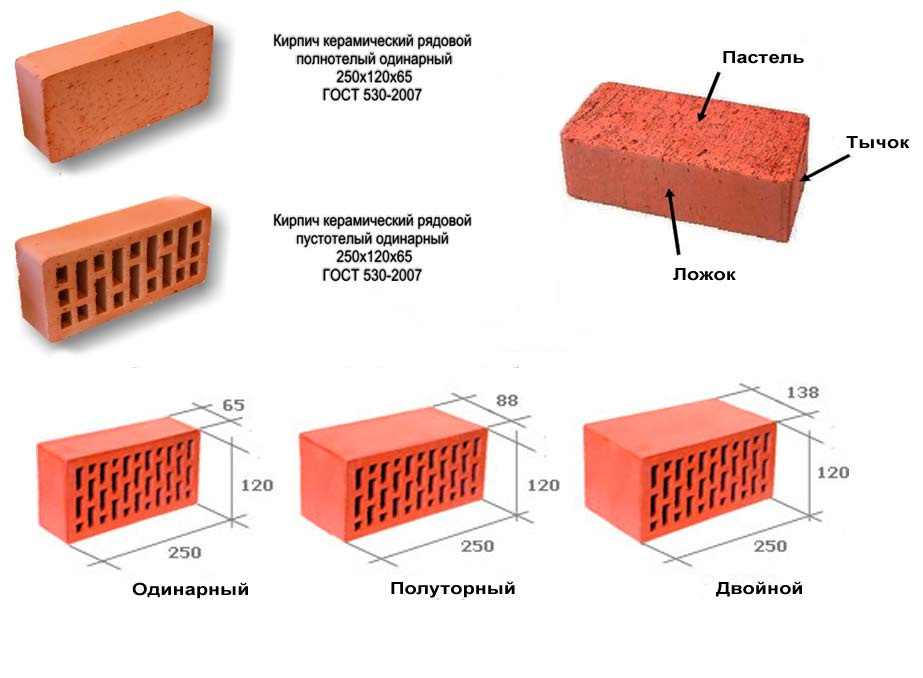
| Single | 250x120x65 mm. |
| One and a half | 250x120x88 mm. |
| Double | 250x120x138 mm. |
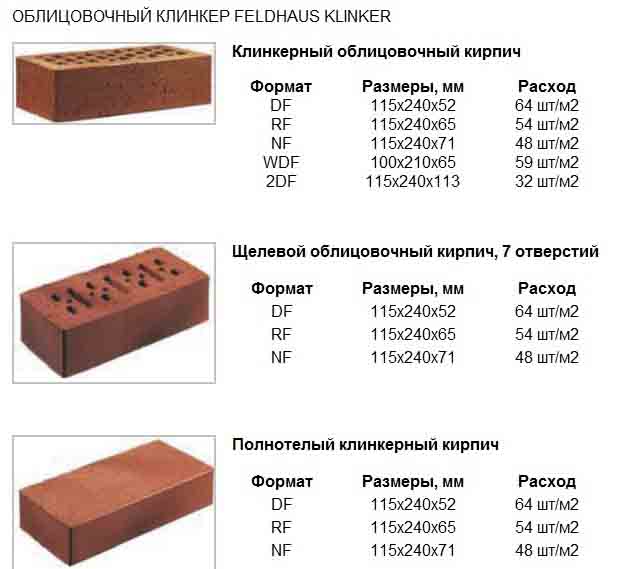
European standards have the following standard sizes:
DF-240x115x52 mm;
2 DF-240x115x113 mm;
NF-240x115x71 mm;
RF-240x115x61mm;
WDF-210x100x65 mm;
WF-210x100x50.
Regardless of the size, each brick has the following 3 faces:
1. The bed is the working part of the product on which it is laid.
2. The spoon part of the stone is the facet of the product.
3. A jab is the smallest edge of the product.
At the end of the topic, I would like to add some tips for choosing brick products.
The first thing to do when choosing a brick is to find out its brand, strength, resistance to external influences. Explore already built structures or buildings from it. Find out how long the building has been in operation, if there are any delamination, cracks on the walls, corners.
The second, and probably the most important rule, inspect the production or warehouse before buying for a battle, defects in size, leftovers, not sold lots. The appearance of the product and the neatness of production can tell a lot about quality.
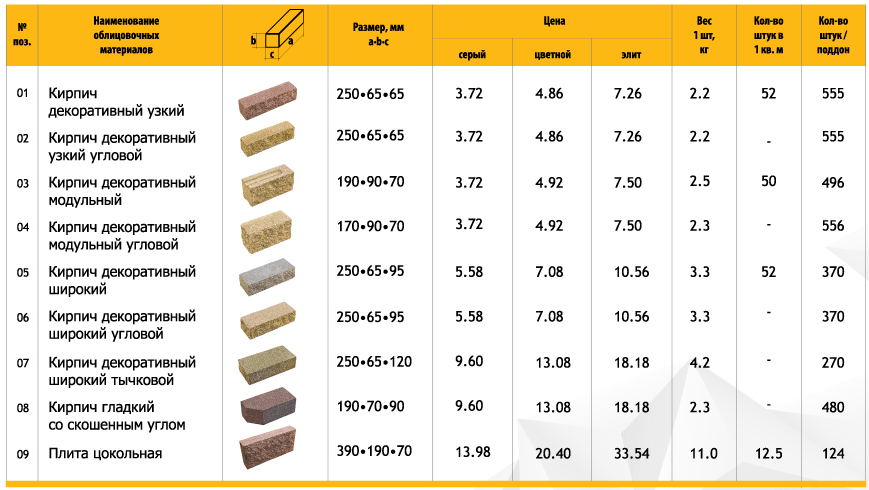
Colored and figured bricks
This is a special type of facing brick, which is given a special shape, surface relief or a special color to enhance the decorative effect. The relief can be simply repetitive, or it can be processed under "marble", "wood", "antique" (textured with worn or deliberately uneven edges). Shaped bricks are called shaped bricks in another way, which speaks for itself. Distinctive features of figured bricks are rounded corners and edges, beveled or curved edges. It is from such elements that arches, round columns are erected without any special difficulties, and the decor of facades is performed.
Among the enterprises of our region in the field of colored and figured bricks, the palm is again shared by NPO Keramika and Pobeda Knauf. The latter, last year, launched the production of engobered bricks (brick of volumetric coloring, resistant to various kinds of influences) of an expanded color range.
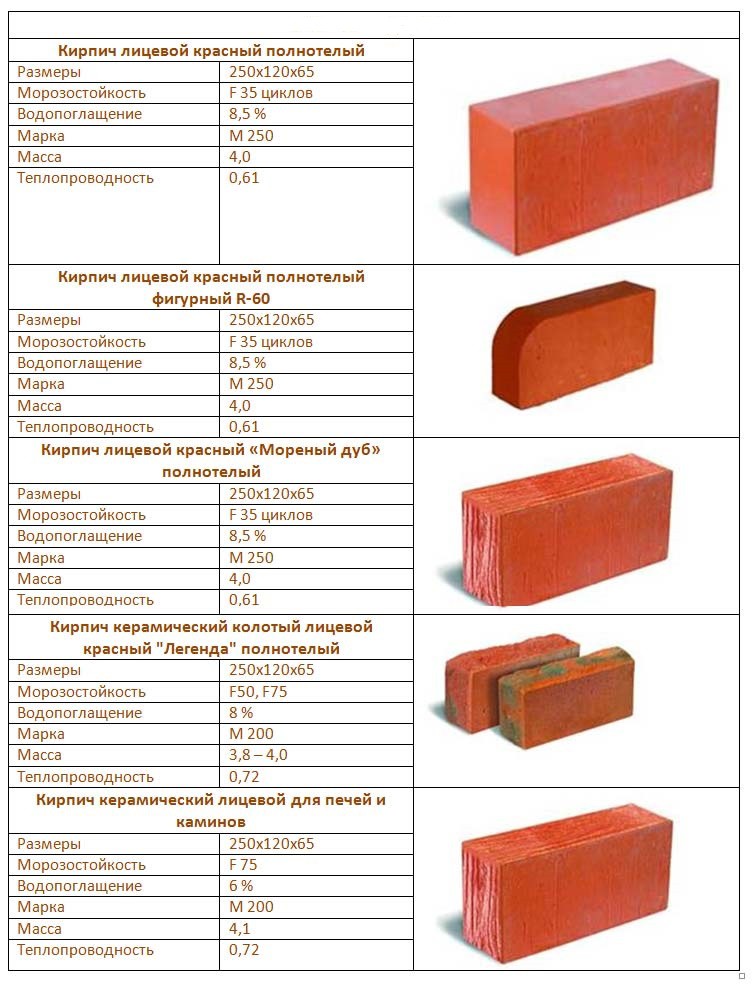
Ceramic facing bricks, hollow, colored and brown
Cream front brick, dyed in bulk (Pobeda plant) |
|
Size (mm): 250х120х65 Weight (kg): 2.4–2.5 Density (kg / m³): 1200–1300 Brand: М150 Frost resistance: F50 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° С) |
| Cream is the original color and warmth of soft cream colors. Cream brick is intended for cladding external and internal walls. |
Facing white brick with textured surface (Pobeda plant) |
|
Size (mm): 250х120х65 Weight (kg): 2.4–2.5 Density (kg / m³): 1200–1300 Brand: М150 Frost resistance: F35, F50 Water absorption: (%) 6–7 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° С) |
| Designed for facing the outer walls of buildings and structures of any number of storeys. The production technology allows achieving color uniformity. |
Facing straw bricks with textured surface (Keramika plant) |
|
Size (mm): 250x120x65 Weight (kg): 2.2-2.5 Density (kg / m³): 1130-1280 Brand: M125, M150 (M175 on request) Frost resistance: F35, F50 Water absorption (%): 6-8 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° C) |
| Designed for facing the outer walls of buildings and structures of any number of storeys. The production technology allows achieving color uniformity. |
Colored front bricks with textured surface (Ceramics plant) |
|
Size (mm): 250x120x65 Weight (kg): 2.2-2.5 Density (kg / m³): 1130-1280 Brand: M125, M150 (M175 on request) Frost resistance: F35, F50 Water absorption (%): 6-8 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° C) |
| Designed for facing the outer walls of buildings and structures of any number of storeys. The production technology allows achieving color uniformity. Color pink, gray, light green, green, yellow, light blue, blue |
Facing brick with a relief surface "Reed", red ("Keramika" plant) |
|
Size (mm): 250x120x65 Weight (kg): 2.2-2.5 Density (kg / m³): 1130-1280 Brand: M125, M150 (M175 on request) Frost resistance: F35, F50 Water absorption (%): 6-8 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° C) |
| Used for facade and interior work. The front surface of the brick resembles reed stalks in texture and allows you to enrich the ceramic masonry with decorative strokes, to give it a picturesque expressiveness. |
Facing brick with a relief surface "Oak bark", red ("Keramika" plant) |
|
Size (mm): 250x120x65 Weight (kg): 2.2-2.5 Density (kg / m³): 1130-1280 Brand: M125, M150 (M175 on request) Frost resistance: F35, F50 Water absorption (%): 6-8 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° C) |
| Used for exterior and interior work. The texture of the brick surface resembles the bark of a tree, which determines the expressiveness and attractiveness of this material. |
Hollow face brick figured red, brown |
|
Size (mm): 250х120х65 Weight (kg): 2–2.2 Density (kg / m³): 1130–1280 Brand: М125, М150 Frost resistance: F35, F50 Water absorption (%): 6–8 Thermal conductivity (W / m ° С) |
| Figured brick is an original material for home decoration, allowing you to make any building individual. The use of shaped bricks avoids labor-intensive cutting operations for conventional facing bricks and provides architects with the broadest opportunities for creating individual architectural elements of facades: rounding and framing window and door openings, erecting arches and columns |
Masonry features
In order for the construction of this brick to be durable and of high quality, you must adhere to the following rules:
- do not use bricks with defects;
- initially determine the type of masonry;
- fill the voids between the bricks with mortar;
- use plumb lines and cords to determine the vertical and horizontal masonry;
- ensure the solidity of the structure with the help of reinforcing materials;
- to allow the mortar to set during laying, so that the base does not shift;
- make seams at least one centimeter thick to avoid cracking.


In the video below, you will learn about the mistakes of novice bricklayers in brickwork.
Classification of bricks depending on the purpose of use
In construction, several types of bricks are distinguished, depending on the field of application.
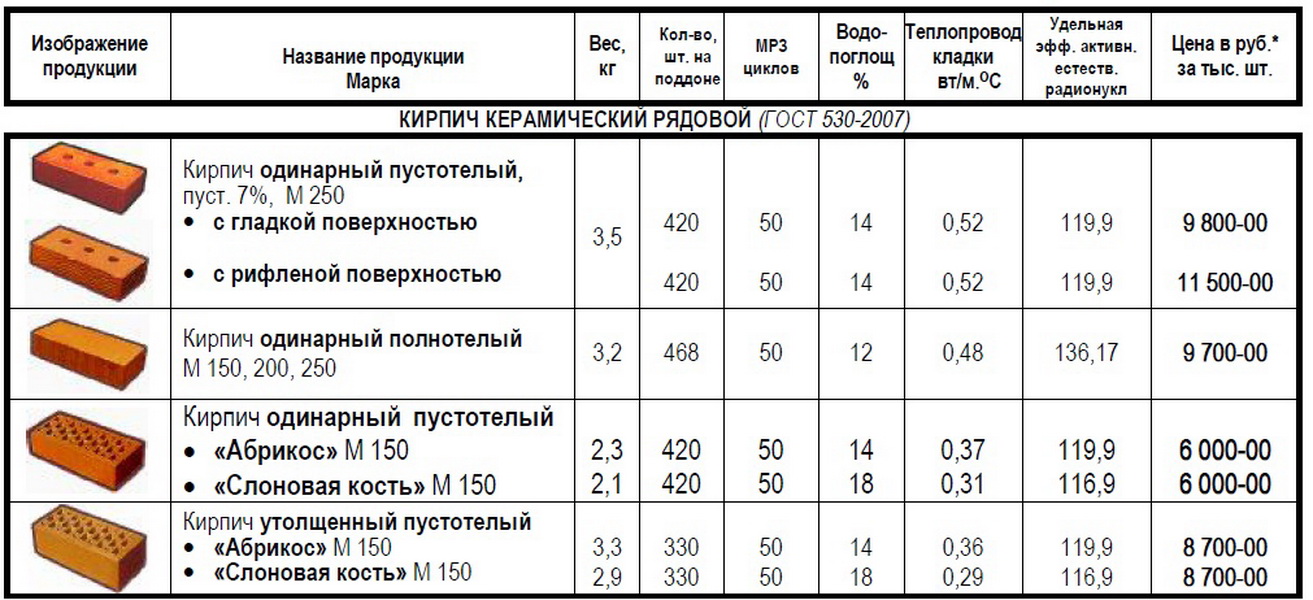
Construction or private
Building or ordinary bricks (GOST 530-2007 dated 01.03.2008) are used in the arrangement of both the inner walls of buildings and the outer ones.It is possible to use such types of bricks for building a house, but only with subsequent insulation or protective finishing of the facade. This type of brick is far from ideal and may contain small chips, which, however, do not affect its strength.
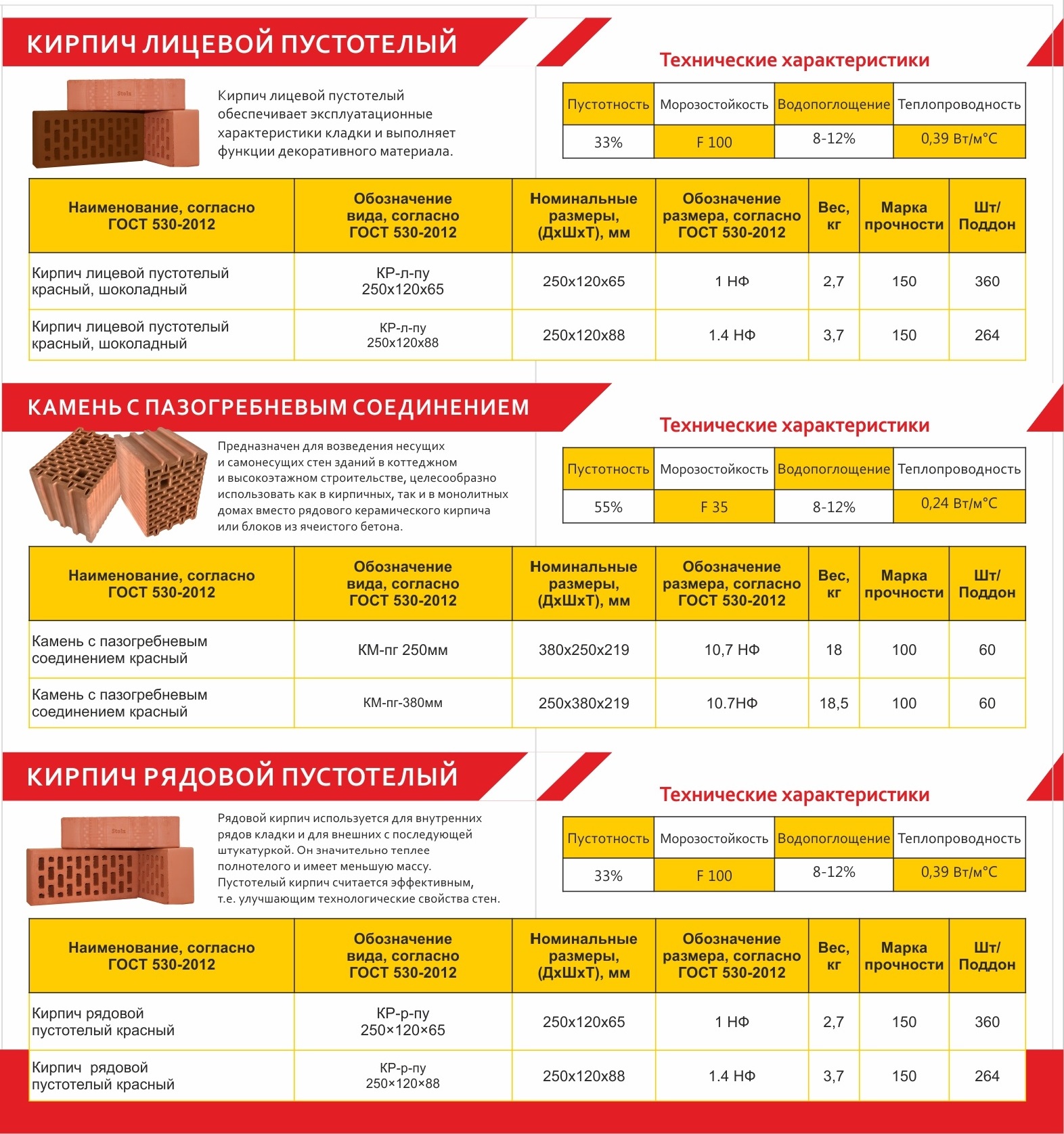
Facing brick
Facing brick (other names: front, front) is the smoothest and most ideal material that does not have defects. The maximum permissible deviations according to GOST are no more than 4 mm. in length, 3 mm. in width and 2 mm. in height. Ceramic, silicate or hyper-pressed bricks can be used as facing.
Among the facing bricks, two types are distinguished - these are textured and shaped bricks.
1. Textured bricks with smooth or uneven edges (Torn stone) are produced for cladding facades of buildings and arranging fences. The edges of such a product can be either rolled, smooth or without processing.
2. Shaped version with different profile configurations, designed for laying complex shapes around windows, window sills, arches, pillars, fences, arbors. For example, shaped types of building bricks with round edges for corners are perfect for arranging complex building facades, namely corners.
The range of colors of facing types of bricks is large and ranges from a light yellow shade to almost black.
Furnace, fireclay brick
Furnace, fireclay bricks, this is a refractory product in accordance with GOST 390–96, has a regular geometric shape, a granular base and can be straw in color, with reddish or brown blotches. They serve for the insulation and construction of objects exposed to constant high temperatures (stoves, fireplaces). Forming a heat-resistant shell, with the function of protecting the furnace from direct fire or hot coal.
The main qualities that such products must possess: heat resistance, high cyclicity, low thermal conductivity. Chamotte must withstand a fairly long heating and many cycles up to a temperature of 1000 ° C without loss of quality and strength. The refractory version is made not necessarily of the correct shape, there are other formats of such products (SHA-25 and SHA-47) - wedge-shaped.
Clinker brick
Ceramic clinker bricks are made from refractory clay layers, which are sintered to form a homogeneous mass. The choice of clay mass as a raw material for production is carefully considered. The composition of the clay should be clean and plastic, it should not contain chalk and alkali metal salts, unnecessary minerals. In the heat treatment process, the clinker acquires the highest strength and good density. Low hygroscopicity and unpretentiousness to negative temperatures. Shale clay has a suitable composition for this, it is elastic and refractory.
This brick comes in many colors and textures. Therefore, clinker bricks are used for cladding walls, plinths, paving garden paths.
Hollow brick classification
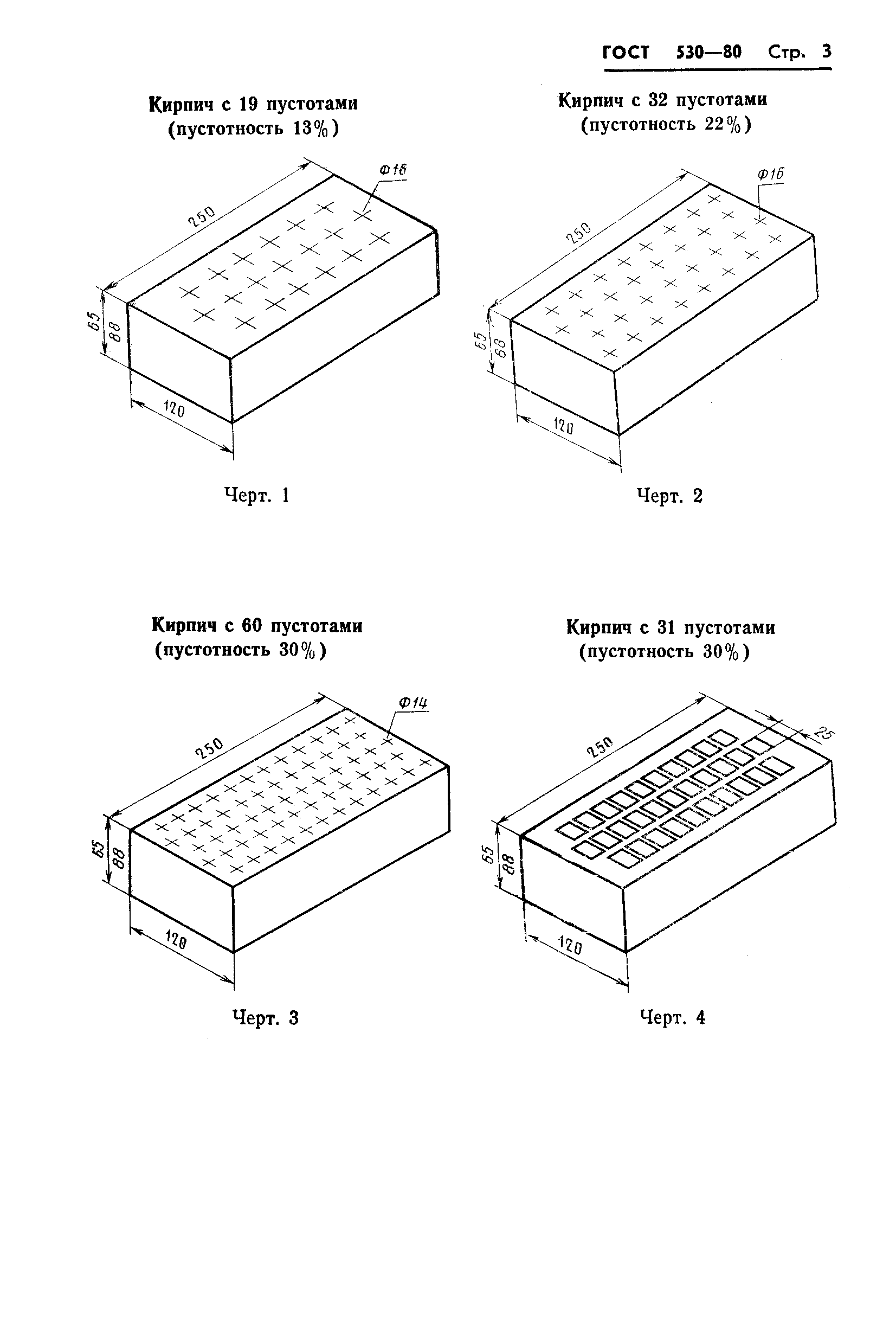
In the modern world, the following types of hollow bricks are distinguished by the shape of the holes in them:
- with oval holes;
- with round;
- with square;
- with rectangular.
Also, the material is divided into types by purpose:
- if there is a relief pattern on the building material, then it can be used for the construction of decorative fences;
- building material with beveled corners or rounded edges is used for the construction of vaulted structures and the arrangement of arched passages.
Hollow bricks are manufactured using various firing technologies:
- in ring furnaces;
- in tunnel ovens.
This building material is made from various raw materials:
- clay;
- cement.
Characteristics of hollow bricks, according to which the material is also divided into groups:
- the thermal conductivity coefficient of hollow bricks, a low indicator is achieved due to the presence of cavities in the building material;
- firing temperature;
- the degree of porosity.
Hollow brick is divided into groups according to the method and material of manufacture:
Porized. This building material is used for facing work. The porous structure significantly reduces the weight of the hollow brick. Among the advantages are high levels of thermal insulation and sound absorption.

Double porous brick
Heat efficient. This material allows you to significantly save money on construction. Its thermal insulation performance allows laying not in two, but in one row. The relatively low weight of the building material greatly facilitates the wall structures, which in turn exert less stress on the base of the building. Maintains the required temperature in the home both in winter and in summer.

Heat-efficient hollow brick
Cement-sandy. As the name implies, cement, sand and various binders are used to make this material. Since no clay is needed for its production, the material comes out almost twice as cheap. The peculiarities of its manufacture do not affect the rate of thermal insulation, the sound insulation of hollow cement bricks is the same as that of clay bricks.

Cement sand hollow brick
Foamed diatomite. This building material is used for the construction of buildings that in the future will be constantly exposed to high temperatures, for example, blast furnaces or smelting furnaces. Such a brick can be used in ordinary construction, but this is just an extra waste.

Foam diatomite hollow brick
Ceramic. This type of material has an attractive appearance and high thermal insulation performance. It can be used for external and internal work.

Ceramic hollow brick
Masonry features
Ceramic bricks are laid out orderly, which ensures its ligation. It is recommended to make reinforcement every 5-6 rows of bricks to strengthen the walls. When laying, the cords are pulled, which ensure the flatness of the base and facilitate work. Masonry starts from the corners with strict observance of horizontal position.
Let's dwell on some tips from bricklayers:
- in order to avoid differences in the color of building stones, you need to purchase them to fulfill the entire construction order from one batch;
- it is recommended to moisten hollow bricks with water before laying in order to achieve greater strength of the base;
- when laying, care must be taken that the mortar does not dry out quickly in the wall, and other external factors do not affect it until it grasps;
- it is better to lay the masonry at a temperature not lower than +10 degrees;
- when laying walls in winter, plasticizers must be added to the solution so that it does not freeze and cracks do not appear on the base;
- it is recommended to order the volume of bricks for carrying out work by 10% more than is required according to the calculations;
- Before buying, you need to check the quality certificates for the products.

You will learn about the production and laying of ceramic bricks from the video.
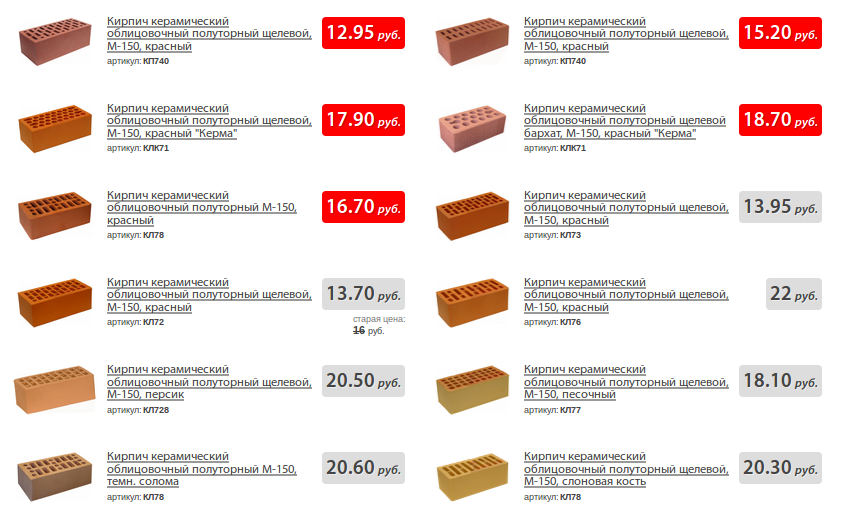
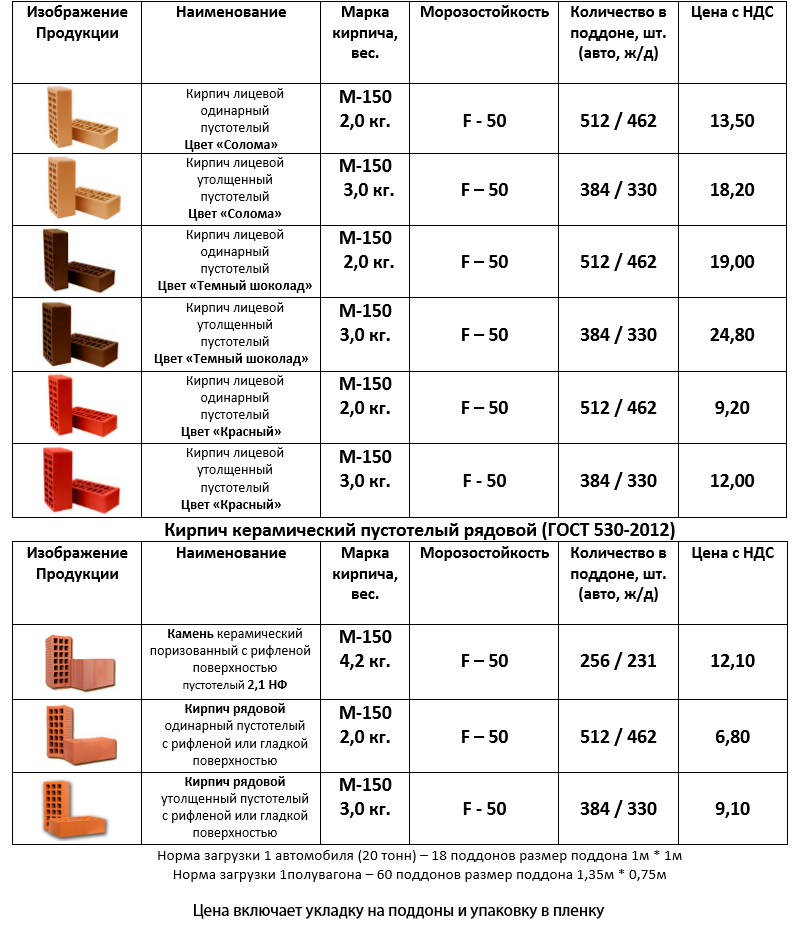
How much does it cost to buy a facing brick: price per piece
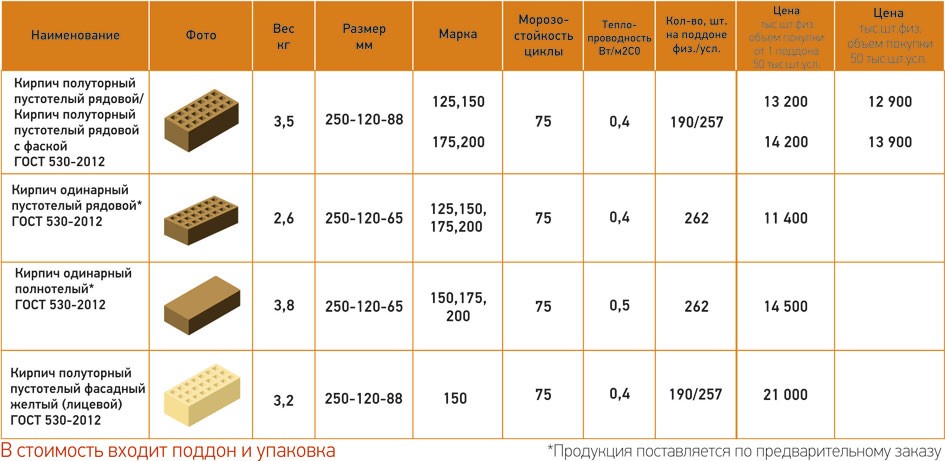
In order to understand how much bricks cost, you need to familiarize yourself with the norms that are established by GOST. It is there that it is spelled out what sizes of bricks are standard, and what should be the weight of one brick of one kind or another.
Facing brick reliably protects the foundation and walls of the building from the negative effects of atmospheric phenomena
First of all, it should be noted that both domestic and European standards are equally recognized in the modern market, therefore, when choosing a suitable material, you need to pay attention to this. Due to such double standards, all material is additionally divided into 2 more categories:
- NF - normal size - 240x115x71 mm;
- DF - thinner - 240x115x52 mm.
The second option is more consistent with the architectural classics, but when choosing and buying material, it is imperative to ensure that all elements are of the same standard.Otherwise, in the process of facing, you will have to face a lot of difficulties.
Considering the existing types of material, the cost of facing bricks was briefly considered. But it will still be useful to once again compare how much a facing brick of one type or another costs in order to come to a conclusion about the advisability of one or another choice.
Clinker cladding brick with ombre effect
So, a scene of one hollow ceramic brick at standard sizes will be from 12 to 20 rubles. But the price of a one-and-a-half facing brick, the size of which is 250x120x88 mm, will be slightly higher - from 20 to 28 rubles.
Clinker bricks are more expensive than ceramic bricks. For example, with the parameters of the product 250x85x65 mm, at least 29 rubles will have to be paid for one piece, and this is taking into account the fact that its surface will be smooth. Bricks with an applied textured pattern are even more expensive - from 34 rubles.
Approximately the same brick price per piece for hyper-pressed material. The lower limit of the cost is 23 rubles, and for textured elements - 25-30 rubles per unit.
Types of facing brick masonry
Almost as available as ceramic colored silicate bricks. Its cost, provided a smooth surface is 15 rubles per unit, and if the texture is textured, the price increases markedly - 24-26 rubles.
The cost of a brick is highly dependent on its size, strength, and frost resistance. But there are other factors, for example, a product from a foreign manufacturer will cost much more than a domestic one. So it is worth considering in advance whether you are ready to overpay for the name of the company or prefer the simpler and cheaper option.
Interesting! You can find goods at such low prices only among offers from domestic manufacturers. The prices of foreign companies are usually much higher, and the cost of some elite bricks can reach 100-130 rubles per piece.
An example of a successful combination of using facing bricks and natural stone for finishing the facade of a building
Why is the brick hollow
Since ancient times, people have used fired clay blocks as building materials. The first pyramids were built of bricks, just like the oldest temples in the world.
However, with the development of building technologies and an increase in the consumption of materials for the construction of residential and commercial objects, people have a need to change the foundations of architecture. The builders had to solve 3 main tasks:
Hollow brick production line.
- reduce the cost of the material;
- improve its thermal insulation qualities;
- improve soundproofing.
All this was achieved with the advent of hollow bricks on the market of building materials. With standard dimensions, it was much lighter. And this has become its main advantage over the "old models" of materials.
And along the way, the builders managed to solve another problem: when laying the porous building material, the consumption of binders, cement and other mixtures significantly decreased. The strength of the walls remained the same as when the work was done according to tradition.
The new type was named ordinary brick, since it is used for laying walls (rows), both outside and inside the object.
Specifications
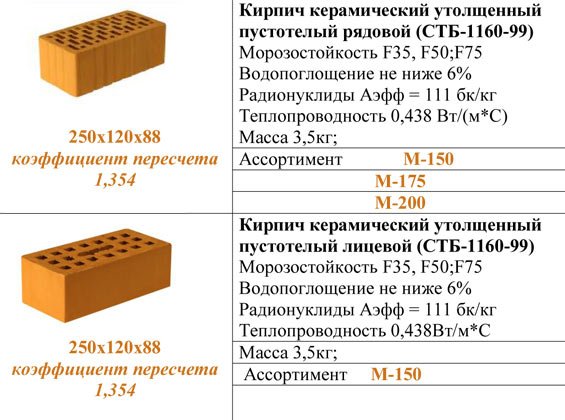
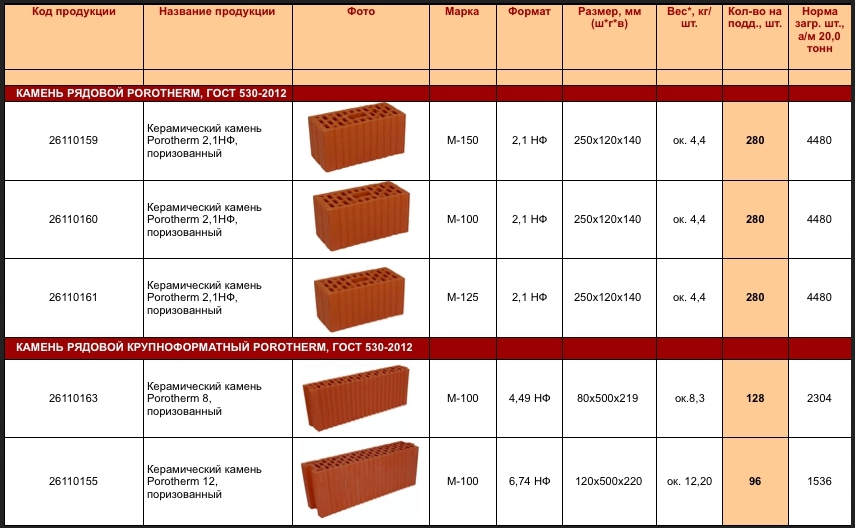
The standard defines strength grades, frost resistance and density class. Strength grades represent the load that a material can bear. It is easy to decipher this value. The number that follows the letter "M" is the number of kilograms per square centimeter that the material can withstand without destruction. Example: M150 means that ceramic bricks of this batch will withstand a load of 150 kg / cm².
| Strength grades | Ceramic bricks | M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300 |
| Ceramic stone | M300, M400, M500, M600, M800, M1000 | |
| Clinker bricks | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300; | |
| Brick and stone with horizontal voids | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100 | |
| Frost resistance | F25, F35, F50, F75, F100, F200, F300. |
Strength and frost resistance grades for ceramic stone and bricks are indicated.
Frost resistance is indicated by the letter F and a number. The figure shows the number of freeze / thaw cycles that do not change characteristics and appearance. For example F50 - 50 frost and defrost cycles. For internal partitions in heated buildings, frost resistance can be taken low - a positive temperature will still be maintained.
Thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal resistance
The density class corresponds to the average density of the material, but the energy efficiency of the material also depends on the density. The lower the density, the better the thermal insulation properties. But it will not be possible to significantly reduce the density for external walls. They must carry a certain level of stress. Therefore, in recent years, a brick house has been made with insulation.
The ratio of the average density of the product and the density class
How to work with the last two tables? The density class is indicated in the marking. By this characteristic, you can find out the mass of a ceramic brick cube. It is listed in the first table. The second table helps to compare the density of the material and the coefficient of thermal conductivity of masonry from it. For example, the density class of ceramic bricks is specified as 1.0. This means that the cube should weigh 810-1000 kg, and the masonry on a minimum layer of glue after drying will have a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.20-0.24 W / (m * ° C).
Groups of ceramic bricks and blocks according to the thermal characteristics of masonry (with a minimum amount of mortar)
It is worth saying that according to modern standards, none of the types of bricks gives the necessary thermal resistance. Unless the thickness of the wall will be more than a meter.
Masonry made of ceramic bricks of one and a half or two bricks does not meet modern requirements for thermal conductivity of external walls
In this case, a hollow brick or a building ceramic block wins, since they have the best thermal conductivity characteristics. The wall will be a couple of tens of centimeters already - not 147 cm, for example, but only 105. So, in any case, it is worth considering additional insulation of the outer walls.
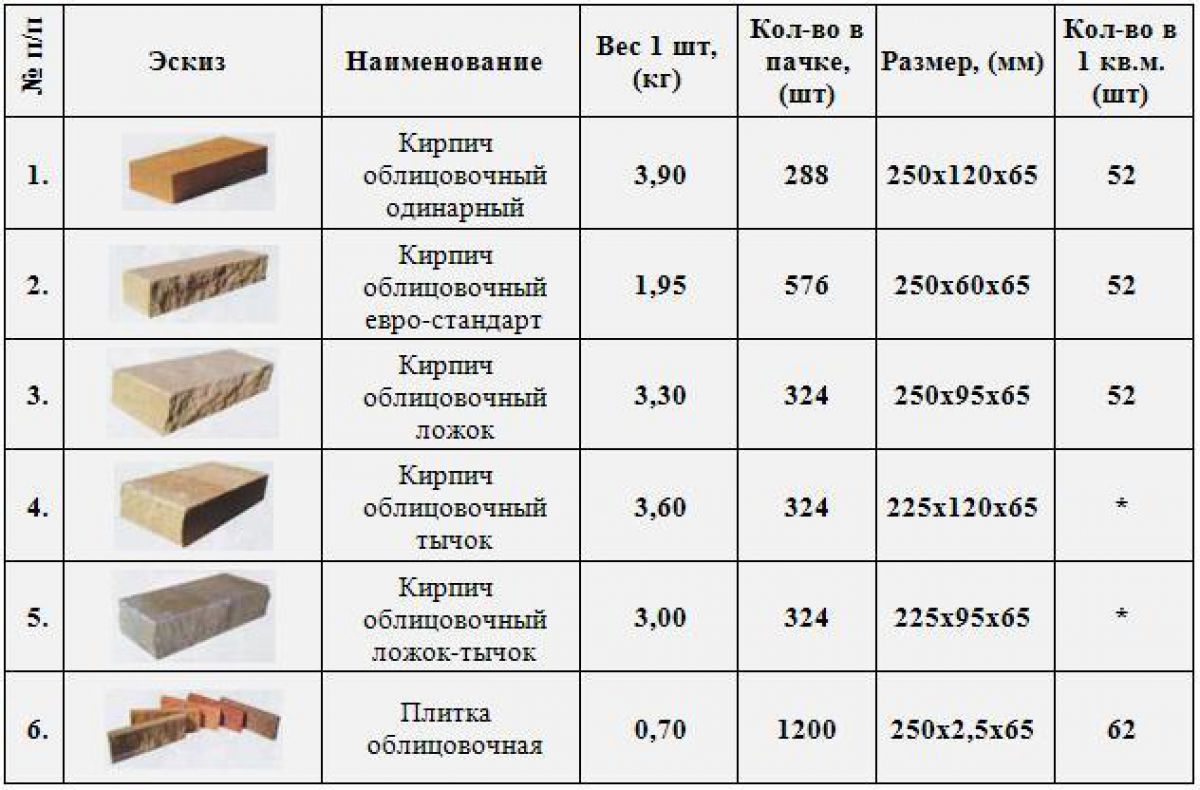
Ceramic brick weight
The weight of ceramic bricks depends on the density and the presence / number of voids. The exact figure is recognized in the accompanying documents, and then, the spread within one batch is up to 10%.
The characteristics indicate the weight of different types of bricks: masonry, finishing, with and without voids
Using the old terminology, the approximate weight of ceramic bricks will be as follows:
- Single (type 1 NF, size 250 * 120 * 65 mm):
- corpulent (private, masonry, construction) 3.3-3.6 kg / piece;
- worker (private, masonry) hollow - 2.3-2.5 kg / piece;
- facing (front, finishing) hollow - 1.32-1.6 kg / pc.
- One and a half has a mass (type 1.4 NF, dimensions 250 * 120 * 88 mm):
- full-bodied private - 4.0-4.3 kg / piece;
- hollow private - 3.0-3.3 kg / piece;
- facial hollow - 2.7-3.2 kg / pc.
- Double weighs (1.8 NF 288 * 138 * 88 mm.):
- ordinary corpulent - 6.6-7.2 kg / piece;
- ordinary hollow - 4.6-5.0 kg / pc.
Comparison of the characteristics of ceramic bricks - hollow, different density, solid
We will give an approximate weight, since the density and number of voids for each plant can differ significantly. The number of voids is not regulated, so the finishing materials can be lightweight.
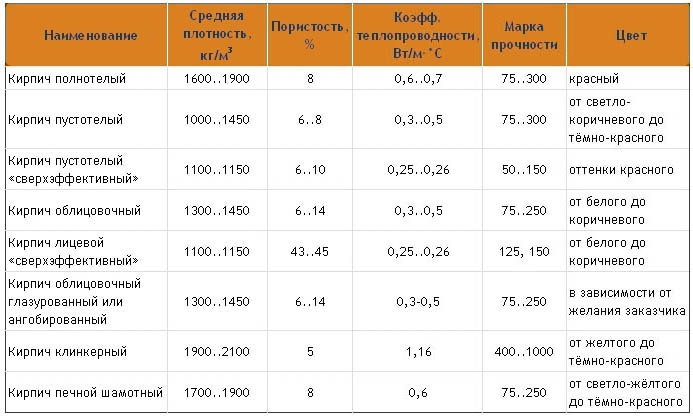
Density of ceramic bricks
Physical and chemical properties and technical parameters of the product largely depend on the internal structure. One of the indicators that clearly characterize the named qualities of ceramic bricks is density. It directly depends on the fractional composition of raw materials, the variety and porosity of building bricks.
Data on the density and some other indicators of ceramic bricks are given in the table:
| A kind of brick | Average density | Porosity | Strength grade | Frost resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg / m3 | % | |||
| Private corpulent | 1600 — 1900 | 8 | 75 -300 | 15 — 50 |
| Private hollow | 1000 — 1450 | 6 — 8 | 75 — 300 | 15 — 50 |
| Facial | 1300 — 1450 | 6 — 14 | 75 — 250 | 25 — 75 |
| Facial engobed | 1300 — 1450 | 6 — 14 | 75 — 250 | 25 — 75 |
| Clinker | 1900 — 2100 | 5 | 400 — 1000 | 50 -100 |
| Chamotny | 1700 — 1900 | 8 | 75 — 250 | 15 — 50 |
The density of ceramic bricks determines its class, which is indicated by a numerical code ranging from 0.8 to 2.4. The figure given indicates the weight of one cubic meter of building material, expressed in tons. In total, there are six classes of products, the introduction of this indicator greatly simplifies accounting and office work in the construction industry.
Knowledge of such an indicator as density is necessary for carrying out design and design work and determining the ultimate loads on the foundations and load-bearing elements of the building. The homogeneous structure of the brick provides it, on the one hand, with high mechanical strength, and on the other hand, with low thermal insulation properties. In the case of using monolithic bricks for the construction of a building, additional measures should be taken to insulate the walls.