3 Testing information for carbon wire and its packaging
According to Gosstandart 9389-75, finished products undergo the following types of quality checks:
- according to the requirements of GOST 1763 - to the depth of decarburization;
- according to standard 1545 - for twisting (a sample is taken with a length of 100 wire diameters);
- according to GOST 10447 - for winding;
- according to standard 10446 - tensile strength and resistance indicator for a certain period of time.
With the naked eye, inspect products for the presence of surface defects and fractures on them. If necessary, Gosstandart 9389-75 allows the use of magnifying devices with a magnification of 5 times.
Checking the spring wire
Waviness is determined with a micrometer on PP segments with a length of 195–205 mm. In this case, 10 measurements are taken. Samples must be fixed in a special unit (for example, in a tensile testing machine), which makes it possible to apply the required load on the test material.
If 3 or more measurements show a deviation of the product from the section specified in the standard 9389-75, the material is referred to the wavy group. It should not be delivered to consumers. It should be noted that such results are observed extremely rarely; the PCB manufacturing technology itself excludes a high probability of waviness formation.
Tests are carried out on samples that must be taken according to Gosstandart 9389-75 from each coil or from each of the two ends of the coil. In some cases, it is allowed to use non-destructive and statistical analysis techniques when checking.
Testing spring wire GOST 9389–75
Spring wire with a cross section of up to 0.6 mm is tied with twine, other sections - with a soft wire material. The surface of the coils is covered with K-17, NG-203 (type A or B) grease (preservative) to ensure anti-corrosion protection of the PP.
For packing finished products, two-layer, oiled or waxed paper, fabrics made of chemical fibers, glued or canvas-stitched packing cloth, polymer film are used. Storage of wire products should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of standard 15150 (section 3).
2 A little about surfacing technologies
There is a lot to talk about the methods of surfacing, since their variety is truly great. Let's just list the types with brief characteristics in order to have a general idea.
Arc, using electrodes. The most common way due to its versatility. It melts the base metal and mixes it with the electrode. The chemical composition is heterogeneous, the internal properties are unpredictable, and therefore only "cosmetic" surface restoration is possible.
Plasma. There are two types - arc and jet. The first is distinguished by its high productivity, since it melts metals using the high temperature created by an electric discharge. The second is the absence of a high-temperature regime, which leads to a small deformation of the treated surface.
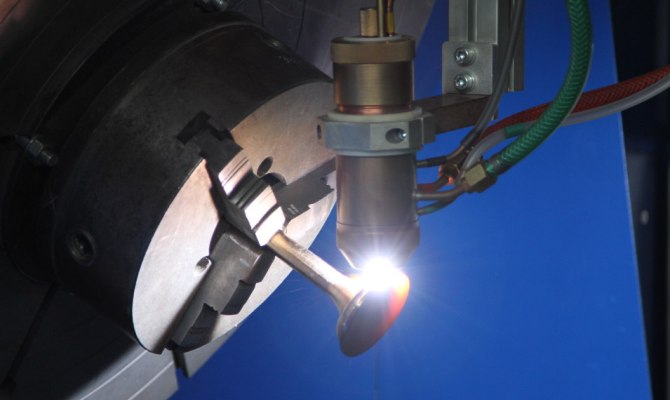 Plasma technology
Plasma technology
Gas. The peculiarity of this surfacing technology is the use of either flux-cored wire or with a solid section. The flame temperature can be varied to provide different coating thicknesses. A lot of energy is spent on heating the surface to be treated, which can lead to deformation.
Laser. Quite an effective method of surfacing, allowing you to make a thin and rather strong layer on the surface to be treated. Nevertheless, it is quite expensive: special expensive equipment and trained specialists are required.
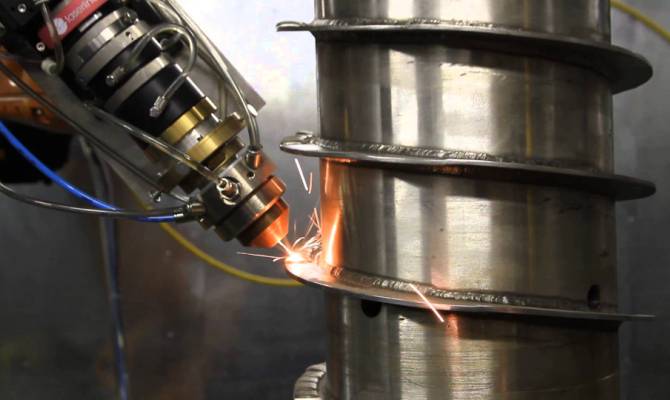 Laser cladding
Laser cladding
Electron beam.It is done in a special vacuum chamber using an electron beam, the intensity of which can be changed. Due to the absence of air, oxidation and burnout is absolutely excluded. It is also a very expensive and costly method, which also has a low efficiency.
Submerged arc surfacing. Due to the use of various types of wire and tape. Probably the most preferable way to strike a balance between smooth surface, metal mixing and energy management. Let's consider it in more detail.
1 General information about steel wire
The joint venture is actively used in various spheres of the modern national economy. It is indispensable for any construction work, it is used by all modern industrial production, whether it is a machine-tool plant or a heavy engineering plant.
The joint venture is manufactured on drawing mills from wire rod by gradually reducing its initial section to the required parameters. The technological process of obtaining wire does not require serious costs, therefore the cost of its production is low. Due to this, the finished product has an affordable price.
Steel wire fabrication
Since steel wire is used for different purposes, modern industry produces several types of it. The most popular wire variations are listed below:
- low-carbon (manufactured in accordance with GOST 3282-74);
- spring carbon (GOST 9389–75);
- tinned cable for the production of cables and wires (GOST 3920-70);
- ropeway for the manufacture of ropes and cables (GOST 7372–79).
The most widely used joint venture is general purpose. It is a long piece of metal with a low carbon content, due to which it obtains excellent strength and a high level of ductility.
General purpose steel wire
If an additional zinc layer is applied to the surface of a general purpose joint venture, it acquires high anti-corrosion properties. Galvanized wire can be operated in conditions of constant humidity, retaining its initial mechanical and other characteristics for a long time.
We add that steel wire according to Gosstandart 3282–74, which has passed the annealing operation, becomes soft. This property allows it to be used for reinforcing work, in the production of various parts, for tying reinforcement and packaging of various products. General-purpose wire is the most common, so we will tell you about it in as much detail as possible.
Welding wire VT1-00
Titanium wire VT1-00 is produced from titanium of high chemical purity. Titanium VT1-00 is a technical titanium characterized by high corrosion resistance and high strength. Wire VT1-00, according to GOST 19807-91, contains in its chemical composition from 99.58 to 99.99% pure titanium and only a small amount of impurities - iron, silicon, carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen. Wire VT1-00 retains useful characteristics in a wide temperature range - from -253 to + 150 ° C, perfectly weldable, has a high technological plasticity, low strength. Technical titanium is characterized by low creep, sufficient toughness and elongation. Due to the high plasticity, titanium foil of very small thickness is obtained from VT1-00 titanium.
The use of a welding titanium wire in a shielding gas environment allows obtaining a welding joint of the highest quality, in addition, the characteristics of the metal make it possible to connect welded parts with a thickness of 1 - 1.5 cm in just 1 pass. VT1-00 wire is the hardest titanium welding wire. does not contain aluminum and is characterized by high chemical purity.
Welding titanium wire should be selected based on the chemical composition of the metal to be welded, for example, wire with high purity is also used for welding pure titanium.
Classification
By size and shape
Depending on the size and shape of the section, all finished products are conventionally divided into several groups. The first one includes the thinnest, the thickness of which is not more than 0.1 mm. Products with a cross-sectional parameter exceeding 8 mm are referred to the 9th group. All products, in accordance with the standards, are made in a round, square, as well as a multifaceted or shaped profile.


By type of finishing
Finishing the wire to a large extent provides the necessary mechanical and physicochemical parameters. That is why, to give maximum strength, the wire is additionally hardened, fired and stabilized. The material that has not gone through these manipulations has a narrowly limited scope of use.

By surface type
Steel wire can be polished, etched, as well as polished or drawn as a result of preliminary turning and roughing. Wire release is allowed without any preliminary finishing. The coating can be metallic (copper-plated, brass-plated, galvanized or aluminized) or non-metallic (polymer or phosphated, in a PVC sheath).
Uncoated products are usually processed at high temperatures. Products processed in a thermal oven are produced in black or light shades, while its thickness can vary from 0.16 to 10 mm.


By chemical composition
Steel wire is made from:
- a low-carbon alloy with a carbon fraction of less than 0.25%, it is needed for reinforcing concrete products;
- made of carbon alloy with a carbon fraction of more than 0.25, it is used for the manufacture of springs, as well as wires and ropes.
Steel can be alloyed or high alloyed. Production from alloys with special physical and chemical parameters (heat-resistant, corrosion-resistant and precision) is allowed.


By area of application
Depending on the field of application, the following groups of steel wire are distinguished.
- Stainless - made from a special alloy with increased heat resistance parameters. This material is not susceptible to rust and oxidation, it is mainly used in the production of hardware products.
- Welding - produced with a cross-sectional size from 0.5 to 8 mm, mainly used for the installation of electric arc welding.
- Reinforcing wire - as the name suggests, such wire is widely used to strengthen reinforced concrete structures of all types. They can be without tension or under increased pressure. Due to the sections present in the steel material, maximum adhesion to the porous concrete base is ensured during the reinforcement process.
- Spring - is used when the springs are released, which are performed by the cold winding method, without subjecting them to further heat treatment.
- Rope - is relevant for the manufacture of sea, river and other ropes. Optimal for braiding cables, has found wide application in the field of their production.
- Knitting - made of low-carbon steel, it is characterized by increased ductility and, at the same time, strength. It is universally in demand in agriculture and construction.


2 How is the wire marked?
Any welding wire - steel, aluminum, brass, flux-cored, and activated - is marked taking into account certain rules in accordance with GOST. This is of great importance, because only alloyed welding wire is represented by about 80 brands. How is the decoding of the designation of a particular wire material carried out?
Take, for example, the Sv-06X19H9T grade used for electric welding. The letters "Sv" at the beginning of the marking indicate that we have a wire in front of us, which is used specifically for performing welding activities. And the numbers and letters behind them describe its composition:
- 06 is the carbon content in hundredths of a percent (0.06%);
- X is chromium, of which 06X19H9T contains 19% (the figure following the letter);
- N - nickel in the amount of 9%;
- T is titanium.
After the letter "T", as we can see, there are no numbers. This means that titanium in the 06X19H9T grade contains no more than one percent. Any alloy welding wire or titanium welding wire can be deciphered in a similar way - just look closely at its certificate. Here you just need to remember which chemical element this or that letter in the marking corresponds to.
Brass products for welding are “encrypted” even easier. First, the diameter of the welding wire is indicated (for example, 3 mm), and then the grade of the alloy from which it is made (L63, LS-59-1). Thus, having seen the 3.0 L63 marking, the welder immediately realizes that in front of him is a brass wire with a cross section of 3 mm. According to GOST 7871, aluminum wire may have the following marking: Sv1201, SvA99, SvAK5, SvA85T.

Steel
The wire is distinguished by its purpose: for welding or surfacing.
In total, about 80 brands of wire are produced.
The letters "Sv" mean that the wire is welding. The brand of steel from which the wire is made is indicated with a hyphen. The first number corresponds to the carbon content in hundredths of a percent. Letters indicate the presence of alloying elements in percent, which are indicated by the number following the letter designation.

Six grades are used for welding low-carbon steels: Sv-08, Sv-08A, Sv-08AA, Sv-08GA, Sv-10GA, Sv-10G2,
For low and medium alloy steels - 30 grades, for example: Sv-08GS, Sv-08G2S, Sv-18KhGS, etc.
For welding high-alloy steels, 41 grades of wire Sv-08X14GNT, Sv-12X13, etc. are used.
If there is no number after the letter, then the amount of this element does not exceed 1%. The letter "A" at the end of the marking indicates a reduced content of sulfur and phosphorus, and the letter "AA" - about even less of them.
Low-carbon and alloyed wires are produced non-copper-plated and copper-plated (symbol - O). Copper plating protects the wire from oxidation and improves the current supply.
At the end of the marking, there may be the letter "E". "E" means that the wire is used to make electrodes. The letters "Ш", "ВД" or "VI" indicate that the steel for the wire was made, respectively, by electroslag, vacuum-arc remelting or in vacuum-induction furnaces.
An example of a symbol for a welding wire with a diameter of 3 mm, grade Sv-08A, with a copper-coated surface made of steel obtained by electroslag remelting:

|
Welding conditions |
Recommended wire |
|
Low carbon and low alloy steels in carbon dioxide and active gas mixtures |
Sv-08G2S |
|
Low carbon and low alloy steels in argon and helium |
Sv-08GS |
|
Outdoor carbon dioxide welding |
Sv-20GSYUT |
|
Construction metal structures from 16G2AF steel in carbon dioxide |
Sv-10HGSN2MYu |
|
Metal structures made of steel 10ХСНД in carbon dioxide |
Sv-08G2SDU |
|
High-strength low-alloy steels (type 14ХГНМ) in carbon dioxide |
Sv-10KhN2G2SMA |
|
Steel 08Х22Н6Т and 08Х18Г8Н2Т in carbon dioxide |
Sv-08X20N9S2BTYu |
Welding wire for medium carbon and heat resistant steels
|
steel grade |
Welding wire grade |
|
|
in nitrogen, helium |
in carbon dioxide |
|
|
20HGSA |
Sv-15XMA, Sv-18HGSA |
Sv-08G2S |
|
30HGSA |
Sv-15XMA, Sv-18HGSA |
Sv-10GSM, Sv-10GSMT, CB-08X2CMA, Sv-15XMA, Sv-18HGSA, Sv-08KhZG2SM |
|
12XM |
Cw-08XM |
Sv-10HG2SMA |
|
15XM |
Sv-08XM |
Sv-08HNSMA, Sv-08HG2SM, Sv-08HGSMA |
|
12Х1МФ |
Sv-08KhMFA |
Sv-08HGSMFA |
|
15Х1МФ |
Sv-08XM |
Sv-08X1M1GSF |
|
15X5M, 15X5, 15X5VF |
Sv-10X5M, Sv-08G2S |
Sv-08G2S |
Steel welding wire is produced in the following diameters (mm): 0.3; 0.5; 0.8; 1.0; 1.2; 1.4; 1.6; 2.0; 2.5; 3.0; 4.0; 5.0; 6.0; 8.0; 10.0 and 12.0, The wire is supplied in coils with a diameter of 150-750 mm, weighing from 1.5 to 40 kg, as well as wound on spools and cassettes.
The surface of the wire must be clean and smooth, without cracks, delamination, captivity, sunsets, shells, nicks, scale, rust, oil and other contaminants.
If necessary, the wire is cleaned with a sandblaster or etching in a 5% hydrochloric acid solution. You can clean the wire by passing it through special mechanical devices, as well as with sanding paper to a metallic sheen. Before cleaning, it is recommended to anneal a coil of wire at a temperature of 150-200 ° C for 1.5-2 hours.
A certificate is required indicating the manufacturer, wire symbol, heat and batch number, surface condition and its chemical composition. If the certificate is lost, the wire can be used only after determining its chemical composition.
Inert gas arc welding wire
|
steel grade |
Wire grade |
|
Chromium |
|
|
08X13 |
Sv-12X13, Sv-08X14GNT |
|
08X17T |
Sv-07X25N13, Sv-06X25N12TYu, Sv-08X25N12TYu, Sv-10X17T |
|
15X25T |
Sv-06X25N12TYu, Sv-08X25N13BTYu, Sv-10X17T |
|
0X13 1X13 |
Sv-10X13, Sv-06X14 |
|
2X13 |
Sv-08H14GT |
|
Highly alloyed |
|
|
12X18H10T, 12X18H12T, 08X19H10T |
Sv-06Х19Н9Т |
|
03X18H11 |
Sv-01H19N9 |
|
08Х22Н6Т |
Sv-07H25N13 |
|
08Х18Н12Б |
Sv-07H19N10B |
|
10Х17Н13М2Т, 08Х17Н15М3Т, 08X21Н6М2Т |
Sv-06Х19Н10М3Т |
|
08Х20Н14С2 |
Sv-04H19N9S2 |
|
10X23H18 |
Sv-10X20N15, Sv-07X25N13 |
|
06X23H28MDT |
Sv-01H23N28M3D3T |
|
03X16H15M3 |
Sv-04H19N11MZ |
|
08Х18Г8Н2Т |
Sv-08X20N9S2BTYu |
Chemical composition for welding steel
The steel filler material guarantees good mechanical properties of the weld. The main grades of wire filler used for welding carbon steels are shown in the table below:
| Filler wire marking | ||
| Protection: nitrogen and helium | Protection: CO2 | |
| 20HGSA | Sv-15KhMA, Sv-18KhGSa | Sv-08G2S |
| 30HGSA | Sv-15KhMA, Sv-18KhGSa | Sv-10GSM, Sv-10GSMT, Sv-08CH2SMA |
| 12XM | Sv-08XM | Sv-10HG2SMA |
| 15XM | Sv-08XM | Sv-08KHNSMA, Sv-08KHG2SM |
| 12Х1МФ | Sv-08KhMFA | Sv-08HGSMFA |
| 15Х1МФ | Sv-08XM | Sv-08H1M1GSF |
| 15X5M, 15X5, 15X5VF | Sv-10X5M, Sv-08G2S | Sv-08G2S |
According to the state standard, filler wires for welding stainless steel and ordinary steel are divided into:
- carbon, intended for joining products from low and medium carbon steels;
- alloyed, for welding low-alloy and heat-resistant metals;
- high-alloyed, used when working with chrome-nickel, stainless or other alloyed steels.
Filler materials for stainless steel are chrome or nickel-containing steels.
The main advantages of specialized welding consumables for joining stainless steel products are:
- high quality of the weld;
- homogeneity and absence of pores in the compound;
- corrosion resistance;
- minimum metal spatter ratio;
- stable burning of an electric arc during operation.
When trying to calculate the consumption of the additive per seam, it should be borne in mind that the additive for stainless steel has an increased resource.
Consumables used when working with high-alloy or stainless steels are divided into two types:
- powder;
- solid.

Argon welding method.
Powder additives allow welding without the use of shielding gases. In the simplest case, the powder additive is a hollow tube with a flux inside.
During operation, the flux and filler elements form a gas cloud, which contributes to high-quality weld welding. Such wires can be used in conditions of limited space, since the welding machine without a gas cylinder can reach even the most inaccessible places.
Solid wires are common fillers designed for welding in shielding gases such as Argon or carbon dioxide.
It is worth noting that the filler elements used for welding stainless steel are divided into classes:
- normal accuracy;
- increased accuracy with P.
The most commonly used types of filler materials for welding stainless steel products are:
- Sv06X20N11M3.
- Sv01Х18Н10.
- Sv01Х19Н9.
When decrypting, it should be remembered that:
- A stands for nitrogen;
- B - niobium;
- B is tungsten;
- D - copper;
- M is molybdenum;
- C is silicon;
- T is titanium;
- X is chromium;
- H - nickel;
- Yu - aluminum;
- F - vanadium;
- C - zirconium.
Drawing stages
The wire production technology is divided into five stages.
Stage 1
Etching procedure in order to remove the surface layer of the material - scale, which interferes with drawing:
 Metal pickling in a continuous pickling unit
Metal pickling in a continuous pickling unit
- Surface preparation: degreasing, sanding, polishing, cutting out defective areas.
- The scale contains complex compounds of other elements; therefore, the feedstock is subjected to chemical or mechanical treatment.
- The choice of etching method depends on the nature of the metal.Descaling is carried out with phosphoric, hydrochloric, nitric, hydrofluoric or sulfuric acid heated to 50 ° C.
- The surface to be treated is cleaned of etching products. This is the washing of workpieces using a special solvent or water.
- After the procedure, the metal should acquire a matte shade.
- Drying the wire for an hour at a temperature of 75-100 ° C. For this, special machines with drying chambers are used.
Stage 2
 Thermal processes include
Thermal processes include
Heat treatment is carried out in order to make the workpiece semi-soft, with a fine-grained structure, free from internal stresses. The metal is heated to a certain temperature, kept under such conditions for some time, and cooled.
Annealing changes the properties of the material and makes the wire drawing process easier. The heating rate depends on the thermal conductivity of the metal. The cooling rate is determined by the hardness to be achieved after annealing. Steel wires cool more slowly than carbon compounds.
Stage 3
Using a special hammer or forging rolls, the ends of the workpiece are flattened and leveled. The procedure allows the metal to be fixed on the drum of the machine and passed through the die.
 Wire drawing die
Wire drawing die
Stage 4
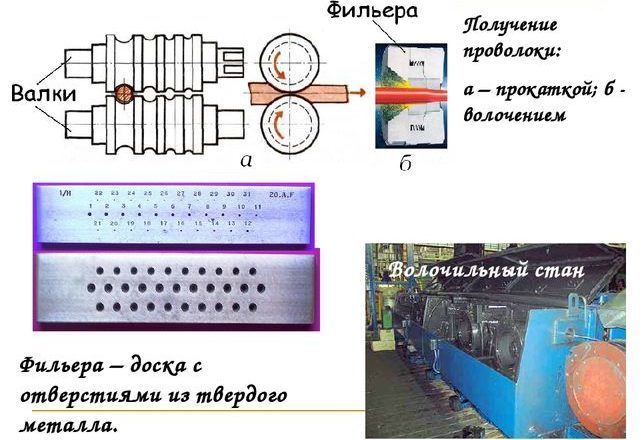
Wire drawing: the pickled processed raw material is drawn on the machine at maximum speed through a smoothly tapering channel. According to the number of simultaneously pulled rods, the process is:
- Single strand.
- Multi-line.
By type of end product:
- Long products in the form of coils or spools.
- Calibrated bars.
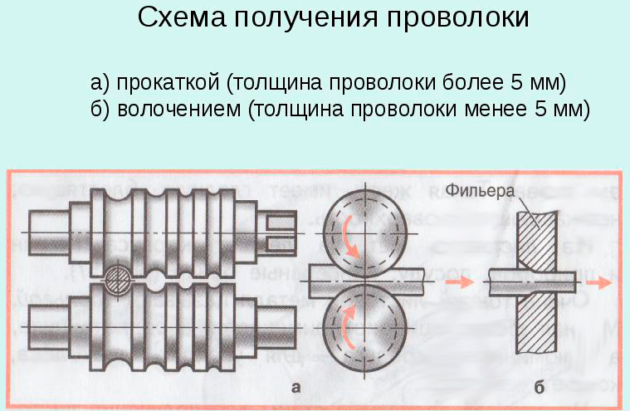
By the number of transitions, wire drawing has two varieties:
- Single - in which the pulling is carried out through one drag. The process is suitable for thick, poorly deformed wires.
- Multiple, when the material is compressed in succession on several dies.
The drawing machine forms the profile and dimensions of the finished product.
Stage 5
The final stage involves performing annealing. This is done in order to eliminate the harmful stress after drawing. The product becomes soft, tear resistant, pliable to bends, elongation and twisting. After heat treatment, additional finishing operations are carried out, including:
- Wire zinc plating.
- Conservation grease.
- Cutting into pieces.
- Marking.
 Finished wire type after all processing processes
Finished wire type after all processing processes
Legend in the marking of the welding wire
The marking of the welding wire has a certain order, which is responsible for the data that is transmitted by the letters and numbers contained in the brand name. This shortens its length, making everything more compact, and helps to better reveal the necessary nuances of the content.
The first number that stands in front of all the letter designations and often somehow stands out from the main mass, at least by the fact that it stands apart, is the diameter.
Behind the number there is a letter designation that reveals the purpose of the wire. There are two options here. The first of them is "Np", which means surfacing wire, the second is "Sv" - welding. If there are more numbers next to these letters, then they indicate the carbon content of the material. For example, if Sv2, then the carbon content in hundredths will be 0.2%, and if Sv06, then the carbon content is 0.06%.

Example for marking a welding wire
After indicating the type of material and the carbon content in it, there may still be separate letters that give an indication of the purity of the composition for harmful impurities. Phosphorus and sulfur often become such impurities. In the marking, these are the letters "A" and "AA" If we consider the example of CB08, then in the absence of letters, 0.04% of the content of impurities of phosphorus and sulfur is allowed, in the CB08AA brand - up to 0.02%, and in the CB08A brand - up to 0, 03%.
The following is a list of alloying elements in the composition. The following designations exist:
- M is molybdenum;
- C - silicon;
- H - nickel;
- X is chromium;
- C - zirconium;
- D - copper;
- F - vanadium;
- T is titanium;
- G - manganese;
- Yu - aluminum.
Not all letters contain numbers. There is a peculiarity here. If there is no number, then the content of this element in the wire is only 1 percent. If there is any number after the letter, then it shows the percentage of the content. For example, 2 - 2%, and 25 - 25%.
After specifying the chemical composition, one of the methods of wire melting is indicated, which can be very important under critical conditions of use. There are such basic designation methods:
- VI - smelting in vacuum induction furnaces;
- VD - smelting in vacuum arc furnaces;
- Ш - smelting using electroslag remelting.
If the same wire can be used for the production of electrodes, then the letter "E" is put in the designation. If it has only one application and is used exclusively for gas welding, then no additional designation is given.
Often, wire with a copper-plated surface is produced. In this case, the letter "O" is added at the end - copper-plated.
At the very end of the brand, the GOST is put according to which it is manufactured. To shorten, many manufacturers miss this point, but all this must be present in the complete labeling.
Types and properties of aluminum wire
Aluminum wire has a number of significant advantages:
• good strength,
• plasticity,
• little weight,
• high electrical and thermal conductivity,
• resistance to moisture,
• durability,
• good wear resistance.
Compared to wire made of silver, copper or gold, aluminum wire has a lower thermal conductivity. But its cost is also much cheaper.
Like all aluminum products, aluminum wire has a high corrosion resistance, including in wet rooms. This is the reason for its frequent use in the construction of facilities that will come into contact with water.
Aluminum wire has many valuable qualities. The main ones are: ease of processing and plasticity, good electrical and thermal conductivity. The magnetic properties of the wire are weak.
Aluminum wire, made of technical or primary aluminum, meets sanitary standards and is absolutely safe. These qualities allow the product to be used even in the food industry.
One of the main advantages of aluminum wire is its price. It is available not only to businesses, but also to any individual.
According to the production method, aluminum wire can be drawn and extruded.
It can also be divided into areas of application:
• for cold disembarkation;
• for wires of power lines;
• for electrical engineering;
• for welding works.
Aluminum wire also differs according to the condition of the material:
• hot pressed (without heat treatment);
• annealed (soft);
• hard-worked (H);
• hardened (naturally (T) or artificially (T1) aged).
Aluminum wire made of thermally hardened alloys is hardened by cold deformation (autofrettage). These wires include AMg5, AD1, AMg3. Plasticity appears after annealing. There is a wire made of heat-strengthened alloys (D16P, D1P, D18, etc.). Its strength is increased by natural or artificial aging, as well as by hardening. Artificial aging is suitable for almost all alloy grades. A wire rope made of alloys D18, D1P, D16P is suitable for processing at + 40 ° C. The wire made of B65 alloy is aged at temperatures from + 75 ° С to + 90 ° С.
Supplied aluminum wire in spools, coils or bundles.
Production
The release of steel wire is carried out by drawing wire rod on specialized equipment with further firing in a special furnace or without it.
The broaching and drawing process is not particularly difficult from a technical point of view. Compressed wire rod is used as a working raw material, all manipulations are performed on drawing machines. Compared to metal rolling, this operation has many advantages:
- automated operation of machine tools provides increased productivity;
- Drawing allows to obtain products of ideally regular shape with a clean and leveled surface - due to this, the degree of subsequent processing is greatly reduced, and the wire itself acquires improved mechanical properties.


In general, the production of twisted steel wire involves several steps.
- At this stage, etching is performed, the main task is to remove the surface layer of metal and scale, which can interfere with drawing. Surface preparation is performed by degreasing, grinding, polishing and mechanical cutting of rejected areas. Since complex chemical compounds can be present in the scale, the wire rod is treated with acid solutions heated to 50 degrees. After that, the workpiece is washed and dried when heated to 75-100 degrees in special drying chambers.
- At this stage, heat treatment takes place, the purpose of which is to make the metal workpiece softer, relieved of internal stresses. For this, the material is heated, kept for some time and cooled. As a result, the properties of steels change significantly and the wire drawing and firing process is facilitated.
- Further, with the help of a hammer, the steel billets are flattened and leveled. In this way, you can fix the metal on the drum of the drawing machine in order to pass it through the die.
- At this stage, drawing is performed directly. For this, the processed and flat raw materials are drawn on the machine at the highest possible speed through a tapering channel. Depending on the amount of wire drawn, this process can be single or multi-strand.
- At the final stage, firing is performed - the main task of these manipulations is to minimize the stress after drawing the metal. The steel becomes elastic, tensile-resistant and stiff, at the same time pliable to elongation and twisting, such parameters as resistivity and weight of 1 meter are improved.

There are two types of heat treatment.
- Light firing - performed in a furnace filled with inert gas. Due to this, the metal does not undergo oxidation, and scale does not form on it. Finished products acquire a light shade and a very impressive cost.
- Black firing - in this case, the simplest atmosphere is used, scale forms on the surface of the finished products, therefore it acquires a dark color. The cost of such wire is much lower than that of light wire.


Given that the steel alloy belongs to the category of metals that corrodes quickly, galvanizing is often included in the production cycle. The best and highest quality wire is produced using the hot-dip galvanizing technique, since in this case the maximum adhesion of the zinc directly to the wire is ensured.
The finished products at the exit are not afraid of rust and at the same time have an increased level of protection against such unfavorable external factors as the action of ultraviolet rays, wind and temperature fluctuations. In addition, galvanized steel wire is much more ductile than non-galvanized, and thus more durable. After that, the products are cut into pieces and marked.

In accordance with GOST 3282–74, steel wire is produced from steel in accordance with the current standard No1050. The finished wire with a cross-sectional area of 0.5 to 6 mm, which has not undergone heat treatment, at the exit must withstand at least 4 bends without violating the overall integrity and destruction of the metal structure.On the surface of a product not coated with zinc, technological standards allow the presence of small dents and scratches - while their depth should not be more than 1/4 of the size of the deviation of finished products in diameter. But the presence of all kinds of cracks, scales and films of any size is strictly not allowed.
Galvanized wire may have a slight whitish coating on the surface, as well as glitter - but only if they do not impair the overall quality of the coating. It is strictly forbidden to sell and use in the production process steel wire with unmetallic areas and black spots.


