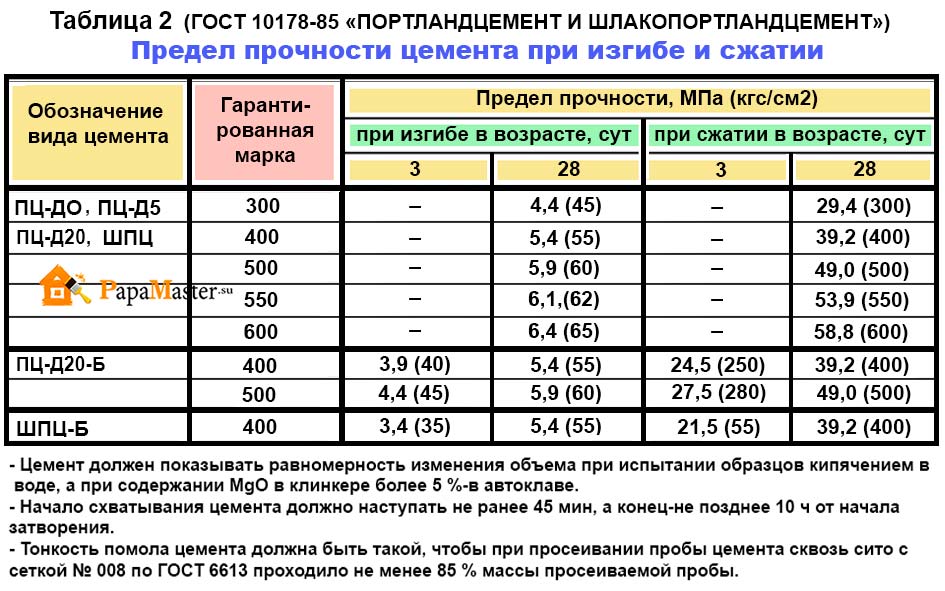
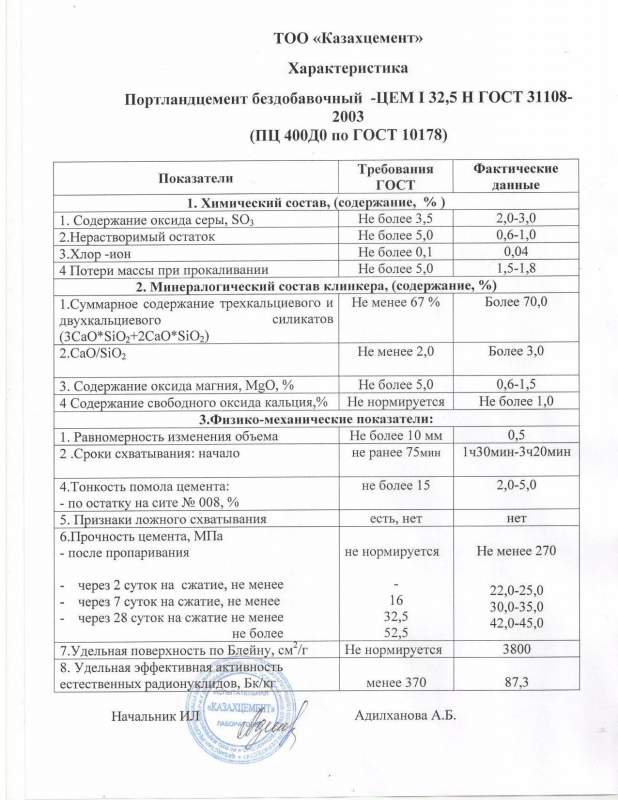
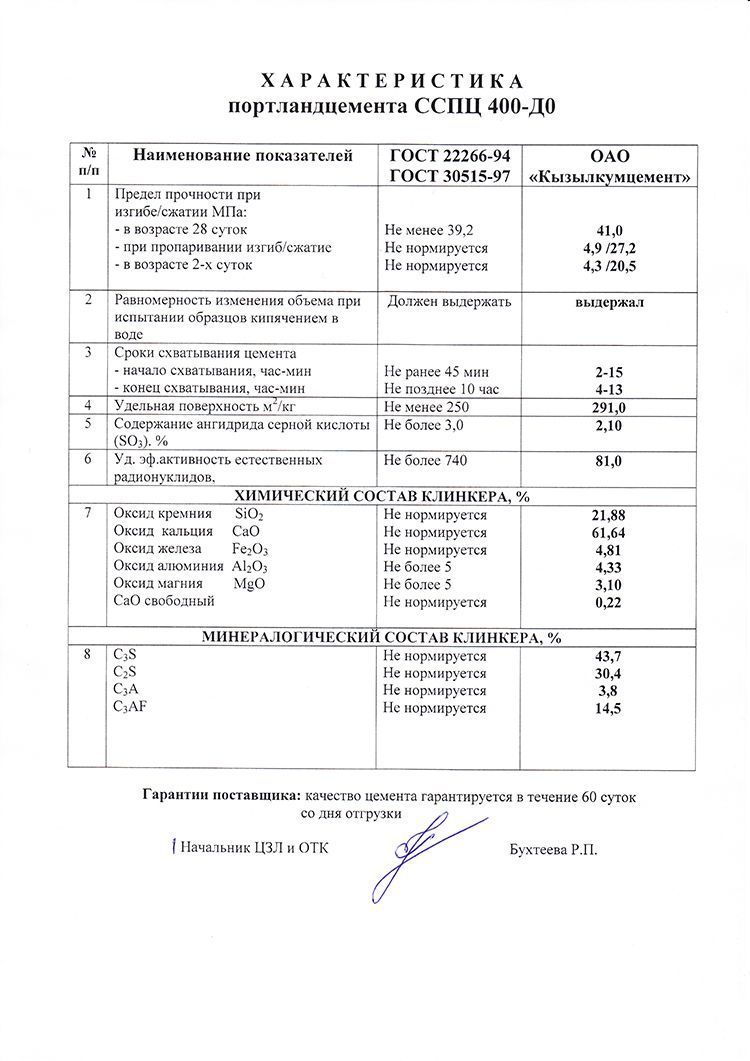
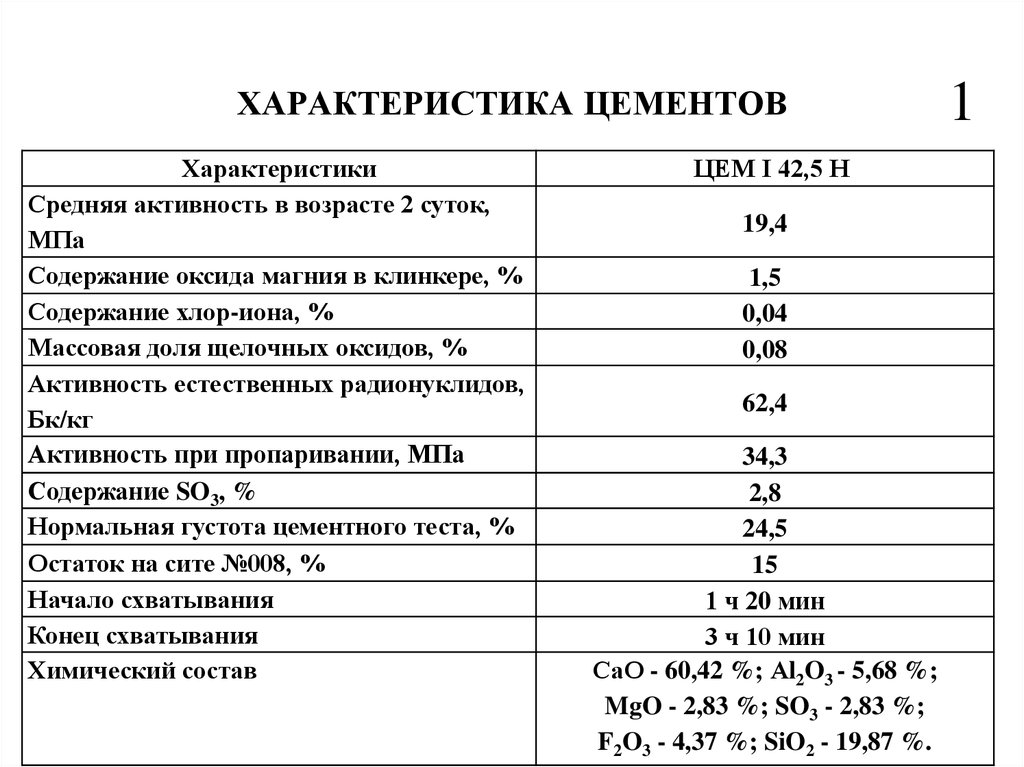
Cement grades according to GOST 31108
The new standard was developed in 2003 to harmonize the current labeling with the one adopted in the EU countries. At the moment, the latest version from 2016 is operational. As usual, the previous standard has not been reversed - both work in parallel.
Labeling can also be mixed
Name and material composition
In a new way, cement grades are determined by their material composition. The marking contains three Cyrillic letters - ЦЕМ and Latin numbers behind them. The composition is encoded in Latin numbers and encrypted:
- The abbreviation CEM I stands for Portland cement. There can be no additives in it. It consists only of ground burnt clinker and technological additives in an amount of not more than 5% by weight.
- CEM II - Portland cement with mineral additives. Mass fraction of additives - from 6% to 35%. By the number of additives, it is divided into two groups:
- group A with a content of 6% to 20%;
-
group B says that the additives are from 21% to 35%.
- If you see CEM III, this is Portland slag cement. This grade contains from 36% to 65% slag ground into dust. By the number of additives, there are three subtypes:
- A - from 6% to 20%;
- B - from 21% to 35%;
- C - from 36% to 65%.
- Pozzolanic cement is designated CEM IV. It is a volcanic additive. It is usually produced in those places where this mineral is mined.
- Marking of composite cement CEM V. This grade of cement can contain several types of additives: slag, ash and limestone.
Cements from CEM II to CEM V can have subtypes depending on the additives. They are denoted by the Latin letters A, B and C. After the group designation, they put a slash, followed by a letter indicating the type of additive, then a letter through a dash that encodes the additive itself. For example, TSEM N / A-I. If there are several additives, their designation is indicated through a dash, and the entire group is taken in brackets: for example: CEM IV / A (P-Z-Mk).
Additives in the composition
Additives and designation of concrete grades with them are in the table. As you can see, CEM I is made only from crushed clinker with a small amount (no more than 5%) of technological substances. The second group of Portland cement has the most modifications and varieties.
Portland cement grades depending on the additives in the composition
Slag Portland cement and lower grades of cement also have additives, but the variations are much less. All additives and additives in the labeling are shown in capital letters:
- W - granulated slags;
- Mk - microsilica;
- P - pozzolana;
- G - glezh;
- З - ash;
- C - burnt shale;
- And - limestone.
Cement grades depending on the composition of the additives
Pure Portland cement - CEM I, always comes without additional components, since, by definition, it cannot have them. Consider a few examples of marking other brands of cement. If we see CEM II / V-Sh. This means that we have Portland cement of the second type, that is, with additives. This is indicated by the letters after the slash. The letter "B" says that the amount of additives is more than 21%, and the letter "W" - slag is used. The inscription CEM III / C denotes Portland slag cement with the addition of burnt shale. In general, the way of decoding the marking is probably clear.
Compressive strength class
In the new standard, the composition should indicate the compressive strength that this brand of cement is able to give. According to GOST, there are only three values:
- 22.5 H;
- 32.5 H;
- 42.5 H;
- 52.5 N.
Designation and rate of curing according to the standard for cement of different grades
Strength is checked on days 2, 7 and 28. Almost all cements are checked 7 days after mixing, and CEM III (slag Portland cement) is checked after 2 days. According to the speed of hardening, the grade of cement can be:
- normally hardened - denoted by the letter H after the compressive strength class;
- slow-hardening - M;
- fast-hardening - B.
The graph of the strength development of cement according to the new standard in MPa
All this information is displayed in the label. For example: CEM III / V-SH 32.5M. Designates slag Portland cement with B-type additives - granular slag, compressive strength 32.5 M, slow-hardening.
Marking of cement products for different delivery methods
It's one thing when the grout is made on site. When the raw material is delivered, its brand is known, it is clear what the ratio is, for what types of work it is used. Another thing is when the products need to be delivered to the customer. How should products be labeled?
When shipped, cement 300 400 can be distinguished by the marking applied to the packaging or by the accompanying documents, where they make the appropriate mark. Shipment can be carried out from the manufacturer in two ways:
By car:
- in bulk;
- packaged.
By rail in special wagons - hoprah:
- in bulk;
- in the package: wagons with access to the inside.
Delivery by car
The packaging in which the products are packed must be marked with the product M-300 or M-400 indicating the purity of the product, its use and the date of manufacture. If raw materials are moved in mixers, the product brand is indicated in the accompanying documents. Also weight and consignee.
Delivery by rail
When transporting by hopram (in bulk), a note is made on the weight and marking of the goods in the railway consignment notes: "Cement of the M-300 brand." In covered wagons, when transporting packaged goods, a corresponding mark is put on the railway waybills about the number of seats and the total weight, indicating the brand of the product.
With the development of the construction industry, ready mixes of different composition are used. New types of binders are emerging. The old, the weak are gradually leaving the construction market. Production of M-110 and M-200 was discontinued. Grade 400 is gradually squeezing out the 300th grade.
Both brands are used to prepare solutions. They are involved in construction work. We have already said how to distinguish 300 from 400 cement on a construction site, as well as during transportation. I would like to add that they have practically no differences. They are akin to twin brothers. Only one of them is a little older. The 400 has a larger area of use. M-300 has interior decoration and exterior decoration of buildings. Even when laying bricks, in the presence of two types, more than 400 racks are chosen. Their main difference from each other is the compression ratio. Naturally, the 440 is above the 300. Find out also why cement grade m700 is better than other materials by clicking on this link.
Manufacturers
Cement production facilities are located in almost every region of Russia. The proximity to the manufacturer will significantly reduce the cost of transporting large quantities of cement. In addition, at regional factories, various substances are added to cement that improve the physical and mechanical properties of structures, taking into account the peculiarities of the weather and water conditions of the area.
Here are some examples of businesses located in different regions:
- Association "Yakutcement" - Republic of Sakha.
- Podolsk Cement Plant - Podolsk, Moscow Region.
- Teploozersk Cement Plant - Jewish Autonomous Region.
- Novotroitsk Cement Plant - Orenburg Region, Novotroitsk.
- Verkhnebakansky cement plant - Krasnodar Territory, Novorossiysk.
There are dozens of similar enterprises. There are also large manufacturers on the market, known throughout Russia and even in Europe. For example:
Types of cement grade 400
A binder with a strength grade M400 can be produced on the basis of different components, depending on this, the material is divided into several main groups:
- Portland cement (PC) is the most common type produced on the basis of calcium silicates (alite). These are metamorphic rocks. It is characterized by medium-term hardening and high technical characteristics.
- Alumina cement (HC or VHC) is produced on the basis of oxides of aluminum, calcium, iron and silicon in accordance with GOST 969-91.The material is characterized by accelerated setting and hardening. Suitable for urgent construction, including in winter.
- Magnesia cement (MGC) is a grinding product of clinker with a high magnesium content. The hardened stone is characterized by high wear resistance and density.
- Pozzolanic cements (PPTs) are made from volcanic rocks, carefully ground to a pulverized state. Suitable for production are silica and aluminous minerals, some types of slags and fly ash, which have a high viscosity.
- Slag Portland cement (SPTs) is a binder made of clinker and blast-furnace or electrothermophosphoric slags with the latter amount not exceeding 20%. Such a binder is cheaper than the classic one, it is used when it is necessary to equip structures in aggressive environments and saline waters.
Types and characteristics
Despite the fact that GOST for construction cements, issued instead of GOST 31108-2003, suggests a new designation for brands of construction mixtures, many are still guided by the old numbers and letters. Therefore, manufacturers, in an effort to facilitate consumer choice, indicate the following labeling on the packaging:
- М400 Д0 - does not contain any additives and consists only of clinker. This mass is characterized by high frost resistance, medium speed of solidification and deformation during shrinkage. As a rule, this is a mixture for general construction purposes.
- М400 Д5 - contains up to 5% additives that improve the water-repellent properties of the product and increase corrosion resistance. Recommended for the construction of load-bearing structures and floors.
- M400 D20 - it contains up to 20% of active additives, allowing it to be used both for residential and industrial premises. Such cement is used both in Russia and in Europe. It has very good frost resistance and is excellent for underwater structures as it is water resistant.
Oddly enough, but the increase in additives in cement leads to a decrease in its cost. The most expensive is the M400 D0 brand, and the more budgetary option is the M400 D20.
There are also specific types of cement that give the product the required properties. For example, a sulfate-resistant composition that allows the use of cement products in aggressive environments and mineral waters. Products with such cement have a very high resistance to aqueous media. Such mixtures can be distinguished by the CC marking in the brand name.
Another example is expanding cement, which is indispensable for repairing cracks in walls and for gluing pipes in mines and tunnels. It fills cracks and joints and contains additives that, when dry, increase the volume of the mixture. Thus, the tightness of the product is restored.


Its other feature is its low deformability and fire resistance. Typically, this type of mixture is used for quick installation of foundations, as well as for the repair of underwater structures. For quick-drying cements, use the additional letter "B" in the marking.
Of course, the specificity of the additive always leads to an increase in the price of the cement. However, do not forget that such additives are used in small quantities and their use is economically justified.


The characteristics of the cement are influenced by the conditions and shelf life after production. For example, the bulk density of fresh cement depends on the degree of grinding, but on average is 1000-1200 kg / m3. If the cement is stored in conditions that do not meet the manufacturer's recommendations, then it cakes to a density of 1700 kg / m3, and at high humidity it can weigh up to 3000 kg per cubic meter. This can lead to premature hardening or loss of strength properties of the concrete. Instead of a mass for active chemical interaction, an inert mineral crumb will be obtained.

Cement is sold weighing up to 50 kg in strong paper bags. The package clearly indicates the brand of the mixture, recommendations for use, as well as the batch number and production date. It is the freshness of the cement that guarantees the quality of future products.Therefore, you should choose packaging with a release date as late as possible.
Looking at the date of production, it should be borne in mind that every 3 months cement loses about 15% of its original properties. If, however, old cement is still used during construction, it is necessary to provide for its increased consumption to obtain concrete of a given strength.
Bulk technical cement is also sold. It is more convenient to purchase it for large volumes of work. Its cost is 15-20% lower than packaged. This is due to the lack of packaging and the large volumes of purchases. However, with bulk mix, it is more difficult to track the date of manufacture, and, consequently, the quality of the starting material.


Features when working with white cement
White cement is an excellent material for the implementation of original design ideas, finishing work, pouring structures, etc. When working with white cement M600, you need to remember some important rules that will allow you to achieve maximum results.
Points to remember when working with white cement:
- All tools and mechanisms must be clean, with stainless steel working parts.
- To get a light solution, you need to add white fillers (or at least light ones) to the mixture - it can be transparent sand, white crushed stone. It is not recommended to exceed the proportions of normal sand due to the risk of discoloration.
- If white cement M600 is used to create a structure with a reinforced frame, rods and all iron parts must be covered with an anti-corrosion compound.
- this type is possible only with clean water, preferably non-rigid.
By mixing white cement with pigment and marble, granite crushed stone, you can achieve a complete resemblance of the solidified stone to natural material. Often such solutions are used to create decorative tiles, bricks, and plaster mixes.
Cement M600 is a high-quality and fairly expensive building material, the properties of which are not relevant in all areas. But in some cases, the technical characteristics of the binder help to achieve the assigned tasks quickly and reliably.
You can buy cement in Moscow and the regions in any construction supermarket, but before choosing this material, you need to carefully calculate the loads and requirements, as well as the optimality of high costs.
Production
CPB is a binder based on crushed clinker with a standardized composition. There is a standard GOST 10178-85, according to which the content of magnesium oxide and the proportions of other ingredients are selected.
Organic minerals are used as feedstock, such as:
- Aliit.
- Alumina.
- Magnesite.
- Gypsum.
With the help of firing technology, clinker is created from this raw material. The base substance is combined with mineral additives that affect the final properties of the working mixture and stone.
Additives can also be added to the composition that increase plasticity, resistance to frost and aggressive environments. Their total concentration should not exceed 5% by weight.
For industrial purposes, plasticized cement subspecies are created, which are characterized by increased fluidity and guarantee improved compaction when arranging concrete structures. The mixture contains clinker and gypsum, as well as an active additive. It can be a concentrate of sulfite and alcohol, containing 0.2% of the total weight of cement m400.
The material differs from other varieties in improved resistance to frost, corrosion and stress.

Specifications
Cement grade M500 demonstrates high performance characteristics. The mixture is especially popular due to its strength, reliability and durability, as well as its versatility.
The main properties of Portland cement M500:
- The beginning of setting - 45 minutes after mixing
- Complete hardening and strength gain - within 28 days
- Frost resistance - about 70 freeze / thaw cycles
- Bending load - up to 6.3 MPa (63 atmospheres)
- Fineness of grinding - 92%
- Hygroscopic expansion - maximum 10 millimeters
- Compressive strength - 59.9 MPa (591 atmospheres)
- The shelf life of the dry mix - in its original packaging, not broken, is about 1 year (despite the fact that M500 is usually indicated on the packages for 12 months, after 3-6 months it gradually loses its properties)
- Radioactivity - up to 370 BQ / kg (class 1)
- Density - up to 3200 kg / m3
Density
Density is an informative indicator that is responsible for the quality of the binder. It is the density that affects the reliability and strength of the solidified stone. The higher the bulk density is demonstrated by Portland cement (PC) 500, the lower the porosity of the monolith will be and the worse it will absorb water, collapse during frost, and various loads.
The bulk density of M500 cement can vary between 1100-1600 kg / m3. In the calculations, an indicator of 1300 kg / m3 is usually used. The true density of the material is 3200 kg / m3.
Additives
Various additives are introduced into Portland 500 cement, designed to improve one or another of its properties, to perform other tasks.
The main types of cement additives:
- To regulate properties - they affect strength, setting time, plasticity, water absorption.
- Substantial - affect the passage of the processes of hydration and hardening. These can be active mineral additives or fillers.
- Technological - they affect the grinding process, which can in a certain way affect the characteristics of the material, but it is not at all necessary.
The amount of additives can be different, which is indicated by the marking. D0 is cement without additives, D5 or D20, for example, it is cement, which contains 5% and 20% of different substances, respectively. All additives are designed to improve the characteristics of the binder, in one way or another.
Consumption rates
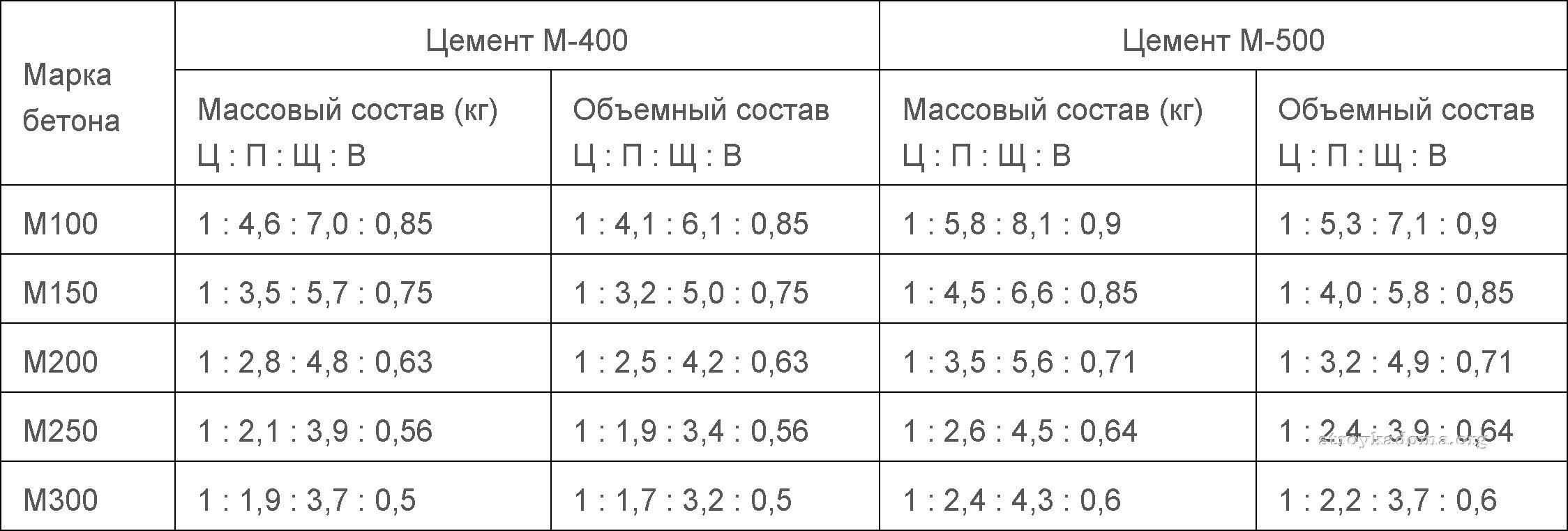
Portland cement M500 is supplied in bags of 25 kg, 50 kg (more in demand). And the question of how much binder is needed to prepare the solution is relevant for all masters. Consumption rates depend on what kind of concrete needs to be prepared and for what. Masonry and plaster mixes are made from cement and sand in a ratio of 1: 3, 1: 2.
As a rule, for pouring and creating strong structures, the following components are used: clean sand (without clay, silt, garbage, fine gravel), crushed stone with frost resistance F-65 and at least M1000 strength, Portland cement M500.
M500 for different solutions:
- M200 concrete - 250 kilograms
- M250 - 300 kilograms
- M300 - 350 kilograms
- М350 - 400 kilograms
- М400 - 450 kilograms
At home, it is almost impossible to prepare concrete with a strength of M300 and higher grade, since it requires thorough mixing, which is extremely difficult to achieve without the use of technological equipment.
Packing and packaging
Cement is produced and supplied in any volume. Standard packing of M500 is in bags of 25, 50 kg (you can find M500 40 kg, but less often). After production, the cement is distributed in sealed towers, where a powerful ventilation system is equipped with a low level of air humidity. The astringent can be stored here for up to 14 days.
Then Portland cement is packed in paper bags. The gross weight of the bag is no more than 51 kilograms. Bags must be made of several layers of polyethylene to prevent moisture from penetrating into the powder. The packaging indicates the date of packing and marking with the main designations that give information about the material.
Under production conditions, the M500 should be stored only in its original container and no more than a few months. If you plan to store for a long time, the bags are stacked on special pallets, turned over every 2 months.
Storage conditions - normal humidity level, air temperature up to +50 degrees. Contacting with air, cement absorbs moisture from it, which reduces its properties. Also, the binder loses its parameters every few months, so the highest quality mortar can be obtained from fresh cement.
Specifications
Cement grade M500 demonstrates high performance characteristics. The mixture is especially popular due to its strength, reliability and durability, as well as its versatility.
The main properties of Portland cement M500:
- The beginning of setting - 45 minutes after mixing
- Complete hardening and strength gain - within 28 days
- Frost resistance - about 70 freeze / thaw cycles
- Bending load - up to 6.3 MPa (63 atmospheres)
- Fineness of grinding - 92%
- Hygroscopic expansion - maximum 10 millimeters
- Compressive strength - 59.9 MPa (591 atmospheres)
- The shelf life of the dry mix is in its original packaging, not broken, about 1 year (despite the fact that M500 is usually indicated on the packages for 12 months, after 3-6 months it gradually loses its properties)
- Radioactivity - up to 370 BQ / kg (class 1)
- Density - up to 3200 kg / m3

Density
Density is an informative indicator that is responsible for the quality of the binder. It is the density that affects the reliability and strength of the solidified stone. The higher the bulk density is demonstrated by Portland cement (PC) 500, the lower the porosity of the monolith will be and the worse it will absorb water, collapse during frost, and various loads.
M500 can vary between 1100-1600 kg / m3. In the calculations, an indicator of 1300 kg / m3 is usually used. The true density of the material is 3200 kg / m3.

Additives
Various additives are introduced into Portland 500 cement, designed to improve one or another of its properties, to perform other tasks.
The main types of cement additives:
- To regulate properties - they affect strength, setting time, plasticity, water absorption.
- Substantial - affect the passage of the processes of hydration and hardening. These can be active mineral additives or fillers.
- Technological - they affect the grinding process, which can in a certain way affect the characteristics of the material, but it is not at all necessary.
The amount of additives can be different, which is indicated by the marking. D0 is cement without additives, D5 or D20, for example, it is cement, which contains 5% and 20% of different substances, respectively. All additives are designed to improve the characteristics of the binder, in one way or another.

Consumption rates
Portland cement M500 is supplied in bags of 25 kg, 50 kg (more in demand). And the question of how much binder is needed to prepare the solution is relevant for all masters. Consumption rates depend on what kind of concrete needs to be prepared and for what. Masonry and plaster mixes are made from cement and sand in a ratio of 1: 3, 1: 2.
As a rule, for pouring and creating strong structures, the following components are used: clean sand (without clay, silt, garbage, fine gravel), crushed stone with frost resistance F-65 and at least M1000 strength, Portland cement M500.
M500 for different solutions:
- M200 concrete - 250 kilograms
- M250 - 300 kilograms
- M300 - 350 kilograms
- М350 - 400 kilograms
- М400 - 450 kilograms
At home, it is almost impossible to prepare concrete with a strength of M300 and higher grade, since it requires thorough mixing, which is extremely difficult to achieve without the use of technological equipment.

Packing and packaging
Cement is produced and supplied in any volume. Standard packing of M500 is in bags of 25, 50 kg (you can find M500 40 kg, but less often). After production, the cement is distributed in sealed towers, where a powerful ventilation system is equipped with a low level of air humidity. The astringent can be stored here for up to 14 days.
Then Portland cement is packed in paper bags. The gross weight of the bag is no more than 51 kilograms. Bags must be made of several layers of polyethylene to prevent moisture from penetrating into the powder. The packaging indicates the date of packing and marking with the main designations that give information about the material.
Under production conditions, the M500 should be stored only in its original container and no more than a few months. If you plan to store for a long time, the bags are stacked on special pallets, turned over every 2 months.
Storage conditions - normal humidity level, air temperature up to +50 degrees. Contacting with air, cement absorbs moisture from it, which reduces its properties.Also, the binder loses its parameters every few months, so the highest quality mortar can be obtained from fresh cement.