Varieties
High density polyethylene sheets are produced in different categories depending on the production technique used. In the raw material, the presence of all kinds of impurities is allowed, which can be both precipitation of accompanying substances and the main participants in the reaction being carried out.


Suspension
Such polyethylene may include chemical stabilizers. During the polymerization of ethylene, they contribute to the formation of a suspension substrate from the granulate. Usually this includes alcohols, oxides of light metals, slightly aggressive acids, as well as certain types of clay.


Solution
In most cases, contains residues of catalysts that are involved in the polymerization under the influence of high temperature.

Gas phase
The structure of such polyethylene is composed of fragments of ether components, as well as gases. And of all the listed varieties, it has the weakest structure, since it is relatively heterogeneous and contains less wear-resistant areas.

Distinctive features of LDPE film
Like any other polyethylene product, LDPE film is resistant to external influences and provides excellent protection against liquid and water vapor. At the same time, high-pressure polyethylene gives it special properties:
- Low density for transparency;
- Increased resistance to cuts and physical damage;
- High flexibility, elasticity and extensibility;
- Possibility of easy recycling and subsequent reuse.
In Japan, the recycling of LDPE films is put on stream, only 5% is not recycled and utilized. In Russia, this figure is negligible. Enterprises that are engaged in the processing of polymer materials can be counted on one hand. So, annually in Moscow, only 3% of the used polyethylene film is sent for recycling. The rest ends up in landfills. Recycled film is slightly less transparent, but cheaper, which allows us to predict significant benefits from its production and sale.
What can be found in the rules of GOST
The standard itself can always be found in the databases of legal portals or downloaded on the same page. To make it easier to navigate in all the rules describing HDPE polyethylene in it, you should immediately refer to the content of this document.
Document structure
- The relevance of the prescribed rules (dates of adoption and amendments),
- Links to additional necessary legislative acts,
- Decoding of markings with an explanation of the meaning of each position from the 8-digit code,
- Full description of HDPE existing grades with standards for all technical indicators for each grade - in terms of chemical composition and physical and mechanical properties,
- List of permitted additives with their individual properties, separately for gas-phase and suspension types,
- Safety requirements both for the polyethylene composition itself and for the rules for working with the finished product,
- Rules for the acceptance of finished lots of HDPE with a description of the tests carried out and the determination of the grade,
- The issues of proper packaging, safe transportation and non-destructive storage of products,
- Warranties that a polyethylene manufacturer can provide for their goods.
Useful Apps
At the end of the document, as many as 5 annexes are waiting for you, which describe not only the physical and mechanical properties of polyethylene, but also give recommendations for its manufacture and further use:
- The first appendix gives markings for the first and second grade of each base grade.
- The second will help you choose the right (and allowed) recipe for additives in the manufacture of products for various purposes:
- for those in contact with food,
- intended for children
- for the manufacture of packaging,
- pipelines and fittings,
- medical devices and even prosthetic products.
- The next page (Appendix No. 3) provides instructions for the use of polyethylene of each of the described brands - both a complete description of the field of application and processing methods.
- The fourth sheet will be necessary for those who need to dye low-pressure polyethylene in any color: here is given a table of the correspondence of color and substance that will dye HDPE products into it.
- The last appendix describes all the physical and mechanical characteristics of grades, from melting points to a list of dielectric properties.
IMPORTANT! GOST is not only instructions for action for manufacturers, but also useful information for consumers. Knowing the standards, you will be able to select products that fully meet your needs and safety rules
Applications
The presence of extraneous components, including catalysts, determines the widespread use of HDPE for industrial purposes, where strength and strength are considered more important criteria than toxicity and environmental friendliness. Only a small part of the finished product is used to meet household needs.
The scope of use of the material directly depends on the method of processing polyethylene. In accordance with GOST, the following areas are distinguished - extrusion, injection molding, as well as blow molding and rotational molding.


Extrusion
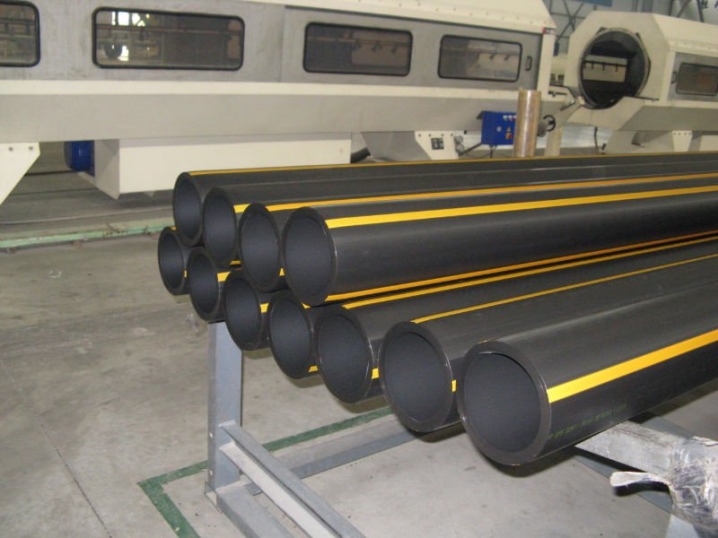
This method involves the production of polyethylene from polymer raw materials by forcing the finished material through the forming cone - the hole of the extruder. The method makes it possible to produce packing bags, conveyor belts and air-bubble belts for packing goods, as well as electrical wires and nets of various types (household, agricultural and construction). There is a wide demand for material for the production of sewage pressure pipes, drainage and gas pipes of different diameters. HDPE retains its characteristics when exposed to temperatures from -60 to +100 degrees.
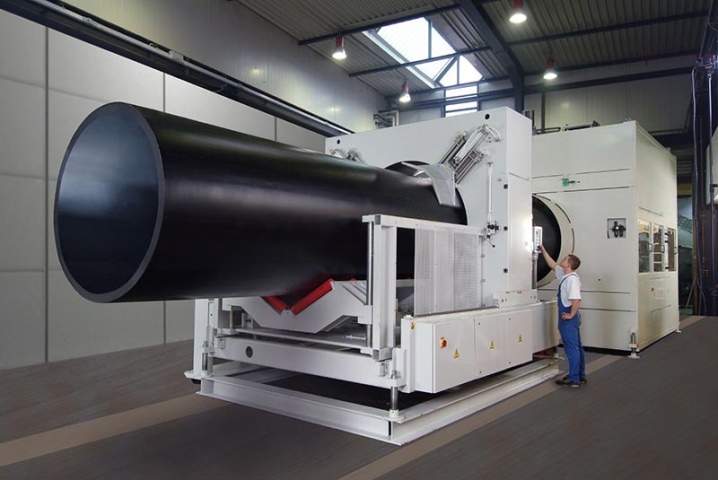

Injection molding
This method of processing polymer raw materials involves the injection of a melt under high pressure into a mold with its subsequent cooling. In this way, fittings, kitchen attributes, as well as furniture fittings, plastic covers, tare boxes and some types of plumbing are produced.
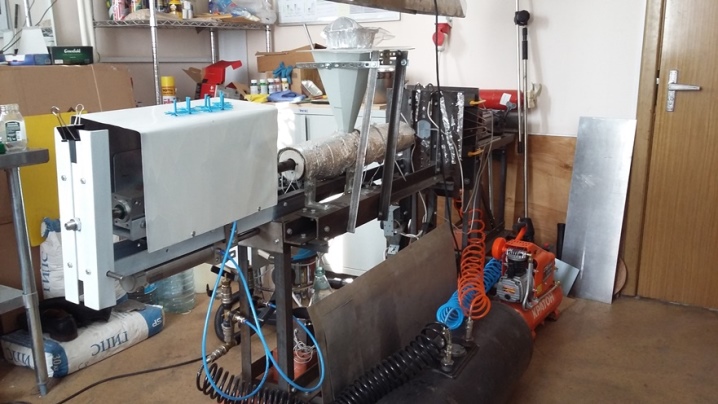

Blowing out
During processing, heated plastic is injected under pressure into a special cavity shaped like the product to be manufactured. The technology allows you to get tanks, tubs, cisterns, barrels and all kinds of cosmetic bottles.
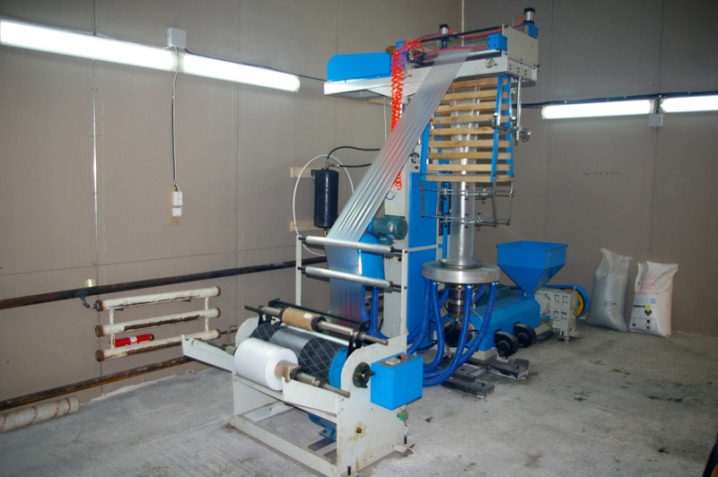

Rotational molding
This method of manufacturing polymer products in our country appeared relatively recently. It allows you to make a variety of products according to customer drawings. Rotoforming is used to create children's playgrounds, mobile dry closets, garbage containers, traffic cones and many other products. This direction of using HDPE is considered one of the most promising.


From high-strength polyethylene, you can get the thinnest film, the thickness of which is comparable to tissue paper and does not exceed 7 microns. It can be a good alternative to heat-resistant paper, for example, parchment - unlike the latter, HDPE has good water resistance, exceptional aroma and vapor barrier characteristics.
It is noteworthy that objects made of PVP that have served their time do not decompose under the influence of external natural factors. That is why the issue of their recycling is especially relevant - such a solution can be not only economically profitable and safe for the environment. The processing of polyethylene in recent years has become one of the most promising areas of the industry.Recyclable materials are widely in demand in the manufacture of plastic containers, dishes and other products that do not require high quality products.

What is the difference between LDPE polyethylene and HDPE, you can find out from the video below.
Specifications
Polyethylene sheets are produced in strict accordance with regulatory documents that specify how this material is manufactured, transported and stored. At the moment, the most used types are sheets made from high-density polyethylene (LDPE) and low-pressure (HDPE). Separate standards have been developed for these types, GOST 16338-85 for HDPE and 16337-77 for LDPE.
Low density polyethylene sheets have the following characteristics:
- very high density - more than 0.941 g / cm³;
- excellent frost resistance;
- moisture resistance;
- well tolerates contact with oily and greasy liquids;
- environmentally friendly.


High pressure polyethylene sheets have such basic properties as:
- flexibility and plasticity;
- density 0.900–0.939 g / cm³;
- melting temperature - + 103– + 110 degrees Celsius;
- withstands low temperatures of about minus 120 ° С.
The standards indicate all the parameters for both groups, having studied them, you can familiarize yourself with everything in detail. Both materials do not emit harmful substances and are absolutely harmless to the human body in direct contact with them
And also, when using it, no precautions are needed. You can also find less common - high molecular weight polyethylene
This type of material has increased resistance to mechanical stress, rigidity, reliability and wear resistance. It is able to resist impacts even at minus 200 ° С, begins to melt at + 150 ° С, its density is 0.95 g / cm³.

Polyethylene grades
Basic grades of polyethylene are of 2 types, depending on the type of device that produces them (autoclave or tubular reactor) and 3 grades (higher, first and second). If LDPE is produced in granular form, then all its particles must be of the same shape and size. The size limits for LDPE particles are normally from 0.2 to 0.5 cm. Also, in each batch, slight deviations from the norm are allowed (i.e., the presence of particles larger than the baseline indicator), but it should be noted that their percentage should not exceed the limits established by GOST.

In total, GOST establishes 8 basic grades of LDPE for autoclaves and 21 grades for tubular radiators. The digital code embedded in the name of each brand allows you to easily determine which product is in question (for LDPE the first digit is always 1, it indicates the presence of high pressure in the system), on which equipment the LDPE is produced (the second and third digits in the brand name, numbers from 01 to 49 are assigned to LDPE made on an autoclave, numbers from 50 to 99 are assigned to LDPE from tubular reactors), how the polymer compound was averaged (0-cold mixing, 1- when melted), what is the density of the substance (there are 6 classes in total), and also an indicator of LDPE fluidity (number separated by a dash).
At the moment, domestic producers of polyethylene are located in Angarsk, Tomsk and Kazan. In the CIS countries, LDPE is produced in Belarus (Novopolotsk). The most famous foreign manufacturers of LDPE: TVK, Vordian, Polimeri Europa, NOVA Chemicals, Basell, etc.
Along with the classical forms of LDPE, in recent years, the production of a similar modification - linear polyethylene (LLDPE or LLDPE) - has begun to gain momentum. Its structure is the same linear as that of low pressure polyethylene, but it has a larger number of branches.

LHPPE is a much more promising substance than classical LDPE, since it has several times higher strength, while the thickness of the resulting films is much lower. In addition, unlike other polyethylenes, LLDPE can be used for packaging hot food, due to a larger range of operating temperatures.It also doesn't crack and has a shiny surface.
Now the price is almost one and a half times lower than the price of LPEVD, but the hour is not far off when LPEVD will catch up with its "closest relatives" in class.
Every year, LLPE is becoming cheaper and cheaper, which means that in the near future it can squeeze out LDPE and HDPE from the leading positions in the polymer market.

Peculiarities
Granulation is the final stage of any technological stage in the manufacture of ethylene polymers. The overwhelming majority of all polyethylene is produced in the form of granules, that is, solid particles of certain dimensions.
The granulation technique helps to solve three problems at once:
- finishing of polymers - removal of residues of additives and chemical solvents, improvement of the mechanical characteristics of the material, degassing, as well as homogenization;
- giving the product the performance characteristics necessary for a more rational use of polyethylene in the creation of plastic products;
- creation of materials with all kinds of additives capable of changing the parameters of chemical stability, density, optical, and dielectric properties of polyethylene.
Polyethylene in the form of granules has significant advantages in comparison with flake and powder.
- Reduction of volume by half (density of bulk polyethylene in powder and granular forms - 0.20-0.25 g / cubic cm and 0.5-0.6 g / cubic cm, respectively). This allows you to significantly reduce the costs of warehousing, movement and packaging of the product.
- High flowability - the use of granules does not create any problems during packaging and transportation. Plastic granules do not stick to the walls of equipment, do not collect in the nodes of transport mechanisms, do not electrify and do not form "dead zones" that cause instability of production processes and shutdown of technological equipment.
- Minimizing the loss of a presentation - polyethylene granules are poured out of containers and loading mechanisms in full.
- Low susceptibility to photoaging and destruction. Reducing dust generation during production to zero and, as a result, improving working conditions.
After drying and all tests for compliance with product quality requirements, granular polyethylene is packed in 25 kg bags and marked. In accordance with GOSTs, granules from a batch must have the same geometry and size in all directions within the range of 2–5 mm, be equally colored. Each batch may contain granules of 5–8 mm and 1–2 mm in volume not exceeding 0.25% and 0.5%, respectively. Elements with pronounced defects (foreign inclusions and a rough surface due to polymer degradation) are rejected.
The main methods of connection and installation of LDPE pipes
Currently, there are several technologies for joining LDPE pipes and fittings:
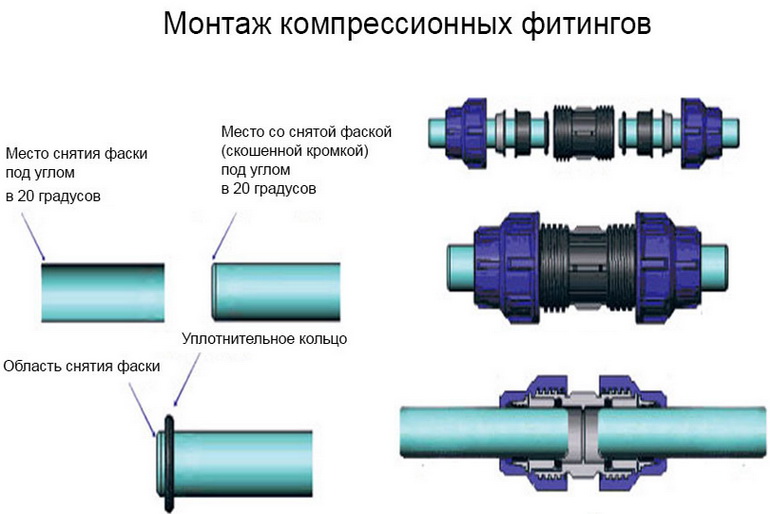
Docking with compression fittings.
The pipeline is connected by means of special clamping and sealing rings. This method is easy to implement and does not require special equipment, but it is not recommended for pressure systems and pipelines laid in hard-to-reach places. It is mainly used for pipes with a diameter of up to 65 mm.
The compression assembly diagram is shown below in the photo:
Direct welding.
The technology involves the use of a special welding machine (soldering iron) with nozzles, with the help of which the extreme part of the elements to be joined is melted. The result is a strong, sealed and durable joint.
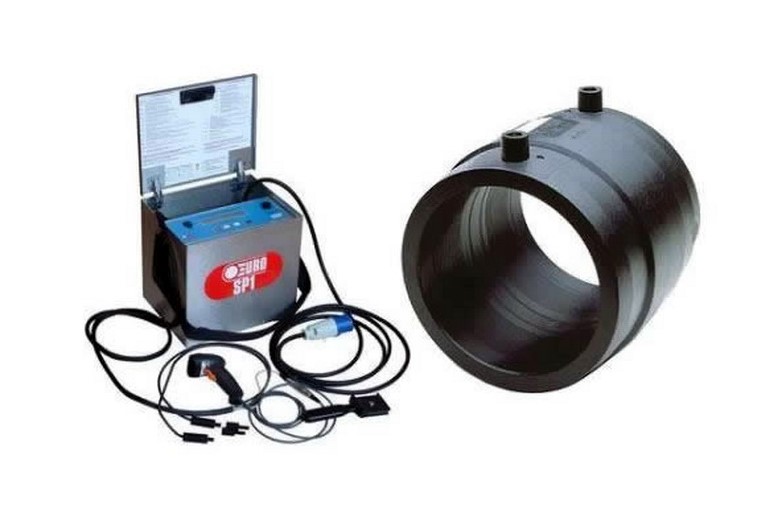
Connection by means of electrofusion fittings.
Fitting parts are equipped with a special spiral, which, heated by a special welding unit, fuses the fitting and the pipe into a single whole. Such a connection is recognized as the most durable.

Classification of linear low density polyethylene
There are several classifications of linear polyethylene:
- LDL are copolymers of ethylene with higher alpha-olefins - hexene, butene, octene. It would be appropriate to clarify here that copolymers are one of the types of polymers, the chain of molecules of which consists of 2 or more different structural units. So, in accordance with the above, there are three groups of linear polyethylene - hexene, butene and octene. They vary in strength. Octene LDL is the most durable, hexene is the least durable and butene LLDP is the least strong of the three. In terms of cost, they are also different. The most expensive is, accordingly, the most durable - octene LDL, hexene costs slightly less and butene polyethylene is the least expensive.
- Classification according to the processing method. There are three types of LDL: injection, stretch films and a linear polyethylene tank.
LDL injection molding. Injection molded linear polyethylene is characterized by high elongation at break and excellent tensile strength. Its high melting point of 118 ° C made it suitable for filling hot food. Injection-molded LPVD has good melt elasticity.
LDL film. In almost all areas of film production, linear polyethylene is used - in its pure form, as well as in mixtures with high-density polyethylene. The use of LDL makes it possible to reduce the film thickness by approximately 20-40% in comparison with traditional polyethylene, which naturally leads to savings in raw materials.
LDL rotary. Rotational molding is a fairly new polymer processing method that has developed rapidly over the past decade.
This method produces a wide range of products (tanks, road blocks, containers for liquids and products, plastic pallets, overall design, and so on).
Currently, LDL is used in many areas of human activity and, due to its excellent characteristics, promises to replace the usual LDPE in the next 10-20 years.
