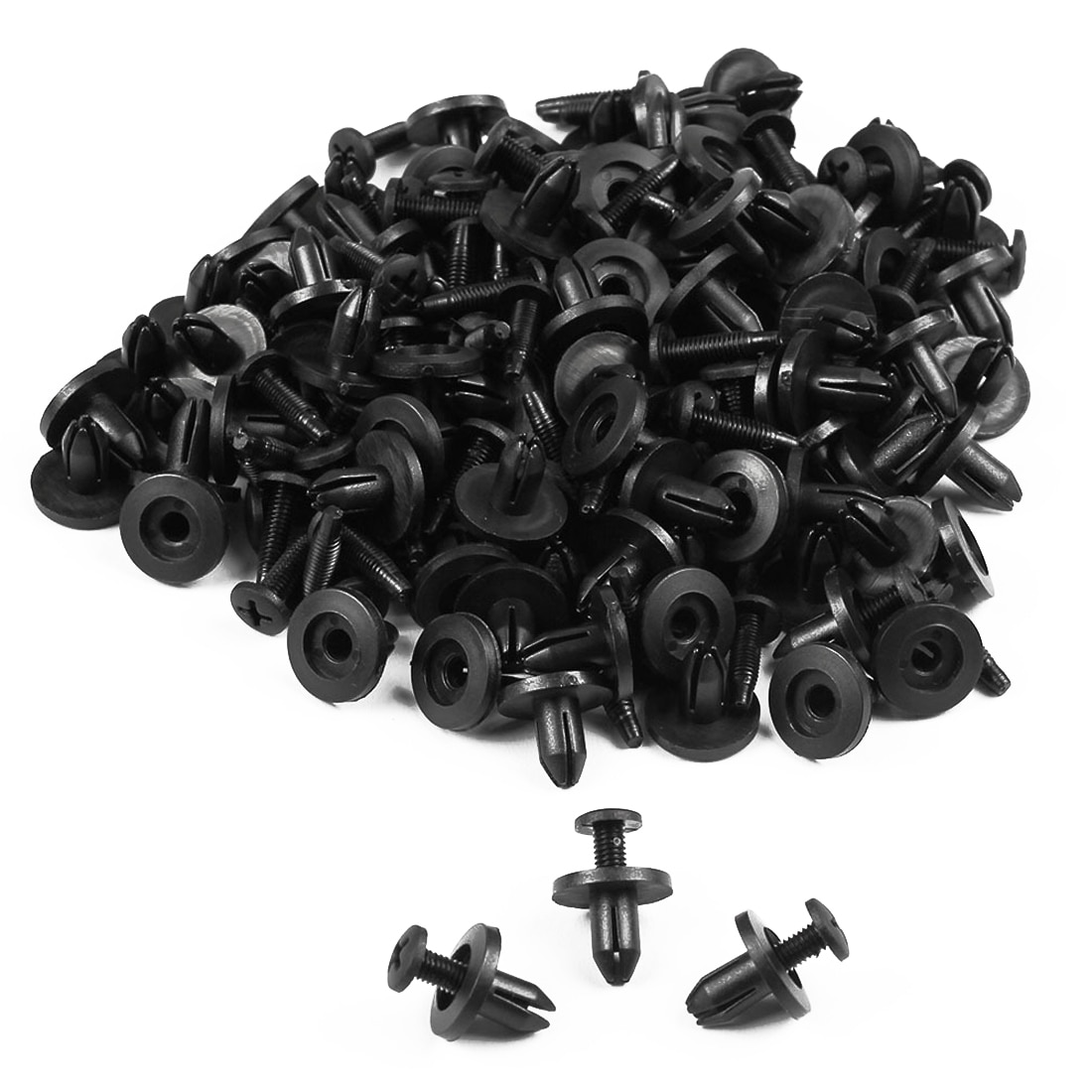
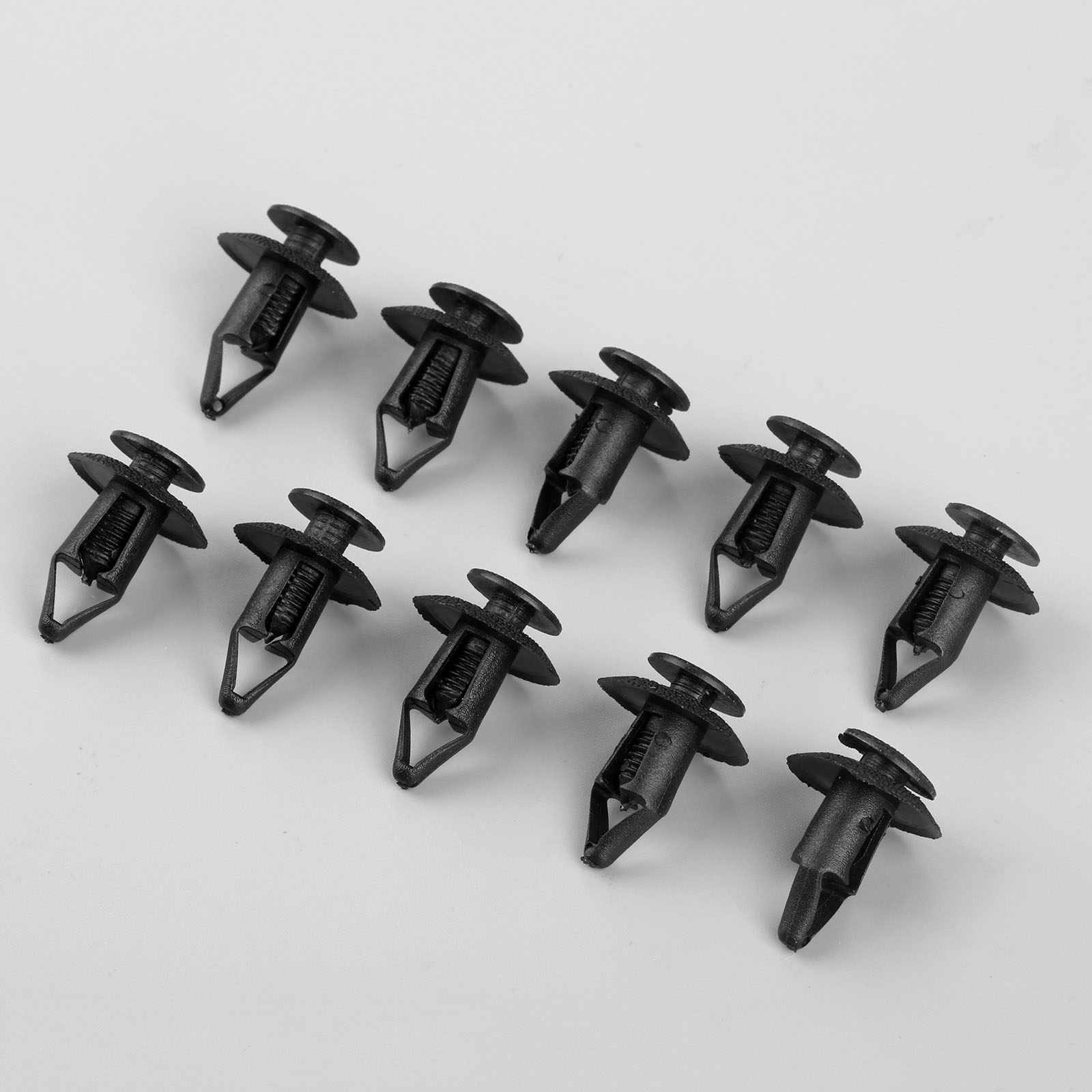
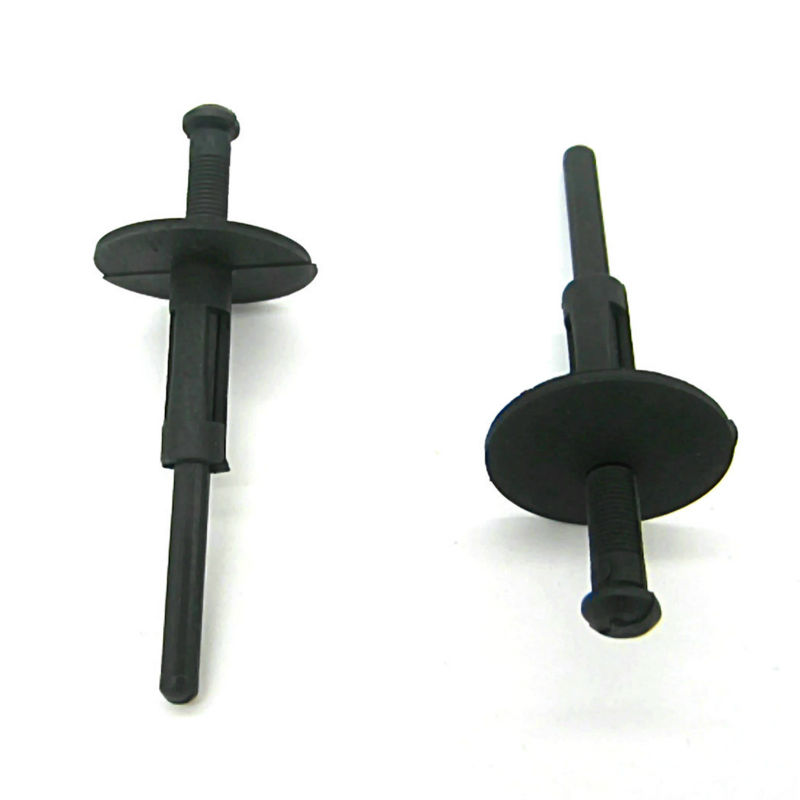
What is riveting
The mechanical connection of parts using a series of rivets is called a riveting, and the connection itself is a riveted seam. It is used where it is inconvenient to weld parts or where non-weldable materials are connected. Not only metals are riveted, thus they connect parts in clothes, accessories, etc. But there it is more of a finish than a loaded connection. So further we will talk about riveting in construction or home improvement. In principle, instead of riveting, you can use a screw connection, but bolts and nuts are more expensive, and their installation takes more time.

This is what a riveted joint looks like
If we talk about installing fences made of profiled sheet, rivets are more reliable, since they can only be removed by reaming the fasteners. When installing screws or self-tapping screws, they can be unscrewed and carried away both metal and hardware. In some cases, riveting is more convenient when installing a roof from corrugated board or metal. On the roof, the installation of screw connections is problematic and time-consuming. And with rivets, and with a good tool, you can do it in an hour or even less.

The most common use in the personal household
How are parts connected with rivets? The rivet is inserted into the prepared through hole. It has a head that rests against the material and the rod. During the riveting process, the end of the rod is flattened, changing its shape under the influence of force. Therefore, plastic metals are used for these hardware.
How to install?
Self-made plastic rivets can be obtained from ampoules or ballpoint pens. But you can also use many other types of sticks or plastic tubes. The plastic should be riveted using a soldering iron with a power of 25 to 400 watts. Together with it, a power regulating device is used.
For your information: the regulating block is also sometimes made by hand. In this case, the main component is a thyristor of suitable power. Without adjusting the power of the soldering iron, it will not be possible to choose the most effective temperature for melting the plasma mass, as a result of which the rivet can be burned and not melted.

The procedure consists of three stages:
-
a rivet is inserted into a prepared channel;
-
put a heated sting, press;
-
continue to work after solidification of the plastic.
The sting itself is first filed. In the middle, a recess is made with a drill. This is exactly what allows you to give the necessary shape. Round caps are easiest to form. They simply lean against the ball removed from the bearing and hit it lightly with a hammer (it is absolutely impossible to press it in).


How to install plastic rivets, see below.
Description
The conversation about plastic (plastic rivets) should start with the fact that they are all made of polyamide.

There are no special technical differences from typical blind rivets. Plastic constructions:
-
do not pass electric current, stray currents and static discharges;
-
absolutely resistant to corrosion processes;
-
are distinguished by an increased level of moisture resistance;
-
ideal for working with cardboard, plastic and fiberglass joining products.

Even with the continuous improvement of bolted and welded connections, rivets remain a highly sought after fastener. They are more attractive when exposed to shock or vibration. Technically, a plastic rivet is a short bar with a flat-convex head. In this case, the leg has an oblong shape. All rivets are permanently installed.


Types of riveted seams
If we talk about the method of joining sheets, then riveted seams are overlapped (one sheet is superimposed on another) and end-to-end. Docking seams can be with one or two overlays. More reliable with linings, used in critical and loaded places.
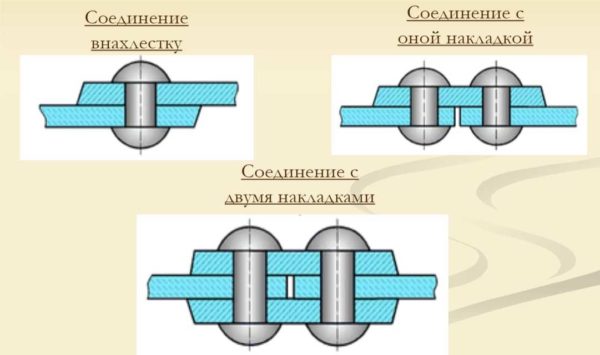
Types of riveted seams: overlap and butt with overlays
By location of rivets:
- single row;
- double row;
- multi-row.
They can be located opposite each other or in a checkerboard pattern. Seams can be strong, tight (sealed) or strong-tight. Dense ones are performed using elastic gaskets laid between the parts to be joined. Strong-tight are mainly used in boilers. Now they are more often replaced by welding.
Sizing rivets
The rivets are selected based on the thickness of the metals to be joined. In this case, the following are important: the parameters of the insert head, the diameter of the rod. The diameter of the bar determines the diameter of the drill, which is used to prepare a hole in the parts to be joined. You can roughly determine the diameter of the rivet by doubling the thickness of the parts to be joined. The length of the rod is at least 2 diameters of the rivet, and the protruding part must be at least 1.25-1.5 of the diameter.
| Rivet diameter | 2.0 mm | 2.3 mm | 2.6 mm | 3.0 mm | 3.5mm | 4.0 mm | 5.0 mm | 6.0 mm | 7,0 mm | 8.0 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hole diameter for precision assembly | 2.1 mm | 2.4 mm | 2.7 mm | 3.1 mm | 3.6 mm | 4.1 mm | 5.2 mm | 6.2 mm | 7.2 mm | 8.2 mm |
| Hole diameter for rough assembly | 2.3 mm | 2.6 mm | 3.1 mm | 3.5mm | 4.0 mm | 4.5 mm | 5.7 mm | 6,7 mm | 7.7 mm | 8,7 mm |
In general, the diameter of the rivet shank can be from 1mm to 36mm, and its length can be from 2mm to 180mm. Moreover, a larger diameter is not equivalent to a greater bond strength. Here both the material from which it is made and its type (hollow or solid) play a role. How do you choose? According to the characteristics of rivets. After all, you choose them for the connection of certain materials of a certain thickness. You know about the load that will be applied to the connection.
Therefore, when selecting, pay attention to what the manufacturer recommends

How to choose a rivet according to the thickness of the material to be fastened? According to the manufacturer's instructions, but in general, the diameter of the rod should be at least twice the thickness of the materials
It must be indicated:
Recommended connection diameter. You just have to pick up the drill and make a smooth hole without burrs.
Minimum and maximum thickness of the bundle to be joined
It is important that your connection is in the specified range.
Shear force. This is the load applied perpendicularly to the joint that the rivet can withstand without breaking.
Breaking force
At what load along the rivet will it collapse?
It is the tensile and shear forces that determine the strength of the future seam. The higher these values are, the more loads it will withstand.
What material should the rivet be of
Rivets are usually taken from the same material as the parts to be joined - this avoids electrochemical corrosion
Pay attention to the strength characteristics. But, as a rule, when connecting aluminum parts, the strength of aluminum hardware is sufficient
In general, rivets are made from the following metals:
- steel:
- ordinary - grades St2, St3, St10;
- corrosion-resistant Х18Н9Т;
-
galvanized;
- alloyed (stainless) - 9G2, 304, 316.
- copper MT and M3;
- aluminum alloys (more often AD1, D18);
- aluminum-magnesium (AlMg2.5; AlMg5; AlMg3),
- brass (L63).
When connecting copper parts, the installation of brass and copper is permissible. Aluminum is bonded with aluminum alloys. Steel sheets - corresponding grades of steel rivets. There are also mixed hardware - from two different metals (chemically non-conflicting). Most often, there are aluminum-steel.
For the installation of facade elements, slopes, ebbs, metal tiles and profiled sheets, blind rivets made of galvanized painted steel are usually used. Coloring - in tone with the details.
Where are they used?
Automotive plastic rivets are in demand primarily where it is impractical or extremely difficult to use similar metal products. An important condition is also the absence of increased requirements for the strength of the fasteners. You need to focus on the materials that are available. It is worth considering that rivets are used not only for cars. They are used for holes in many other areas.

Fixation of sheet finishing materials on vertical surfaces is also provided. It is also worth mentioning the following industries and devices:
-
car building;
-
aircraft construction;
-
food industry;
-
radiators;
-
various household appliances (for example, fans, air conditioners);
-
separate parts of medical and food equipment.



























