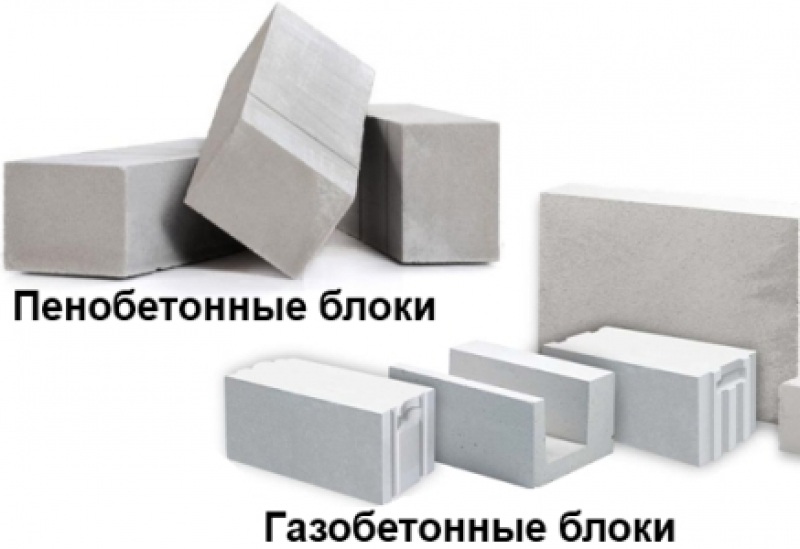
Features of the production of foam concrete blocks
The most important differences between foam concrete and aerated concrete are to be found in their production technology.
So, foam concrete blocks are obtained by adding special foaming additives of organic or synthetic origin to an ordinary cement mortar. The foam is formed on the basis of water, and the water itself evaporates naturally during the drying process. Foaming additives foam the concrete, thereby filling it with air bubbles. Such bubbles are distributed throughout the entire volume of concrete, and after hardening, they make it much easier, adding heat-insulating and sound-insulating properties.
Such a process can be carried out directly at the construction site, since especially specific and high-tech equipment is unnecessary. Due to the shapes used in the manufacture of the foam block, finished products may differ in size, sometimes by 10-20 mm.
Production technology and composition
To understand the difference between aerated concrete and foam concrete, you need to understand the technologies by which these building materials are made. During the production process, an internal porous structure is formed at the calculated density and strength - characteristics that determine the main advantages. In this case, components that are harmless to health are used, which significantly expands the scope of application of such concretes.
Foam concrete production
Foam concrete is produced using a simplified technology that is available even at home. The production components are: cement, water, sand, slag and other fillers. The main substance that provides the porosity of the material structure is sulphite liquor. For foam concrete you will need: Portland cement 36%, sand 47%, 16% water. Foaming additives and fibers to increase strength do not exceed 1%. Production stages:
- All ingredients are thoroughly mixed in dry form, after which a small volume of water is added to them.
- A foaming component is added - sulphite lye. Stirring continues until a homogeneous structure is achieved. In the course of chemical reactions, gas is released, as a result of which the material receives a porous structure.
- The prepared mortar is placed into the prepared formwork in the shape of the required blocks or structures. Foam concrete sets in 10 hours, the minimum time is 5 hours. After being removed from the formwork, the blocks are placed outdoors or in a dry room for final drying.
- The required strength, allowing the use of this material, is achieved in 14-21 days.
Aerated concrete production
Aerated concrete is manufactured in industrial plants with special equipment. The main components are cement, quartz sand and lime, water. The foaming component is aluminum paste. The composition is similar to that used for the preparation of foam concrete. A pure substance is environmentally hazardous, but during the production process it is completely neutralized. Stages of aerated concrete production:
- The components are poured into the concrete mixer in proportions and filled with water, kneaded to a homogeneous consistency, according to a previously developed technological map. The added aluminum paste, sometimes powder, reacts with the solution, saturates it with gas, creating a cellular structure and at the same time neutralizing.
- The resulting solution is poured into previously prepared forms. It should be borne in mind that as a result of the reaction of aluminum compounds, its volume will increase during setting.
- The solidified monolith is removed from the molds and cut into blocks, slabs, lintels, and other elements of the required dimensions.
- To increase the strength and waterproofing characteristics, the resulting products are processed in autoclaves under steam at 12 bar or high temperature in electric furnaces.
The resulting aerated concrete and materials from it have increased strength, correct geometry.
Advantages and disadvantages of the gas block
Aerated concrete is a more modern block material. In the manufacture of gas blocks, autoclave hardening technology is used. Thanks to the special processing in autoclaves, the material becomes stronger and harder. These blocks are characterized by durability and lack of shrinkage. Such blocks can be produced only in high-tech factories and plants. Portland cement, quartz sand, lime are used as components in the manufacture of blocks. Hence the other name of the blocks - gas silicate. To impart porosity, aluminum powder is added, which enters into a chemical reaction with lime. As a result, hydrogen gas is formed and pores appear in the material (a cellular structure is obtained).
Portland cement, quartz sand, lime are used as components in the manufacture of blocks. Hence the other name of the blocks - gas silicate. To impart porosity, aluminum powder is added, which enters into a chemical reaction with lime. As a result, hydrogen gas is formed and pores appear in the material (a cellular structure is obtained).
Gas silicate elements differ:
- good heat conservation and at the same time the ability to pass air (vapor permeability);
- resistance to precipitation and temperature extremes;
- hypoallergenic;
- durability due to low drying shrinkage;
- resistance to decay, mildew and mildew.
Such material is easy to process, and it does not crumble.
This makes it possible to build absolutely any structures from aerated concrete, including multi-storey ones, in the shortest possible time. When calculating the amount of materials, it should be borne in mind that gas blocks are not only standard sizes (200x300x600 mm), but also various other shapes.
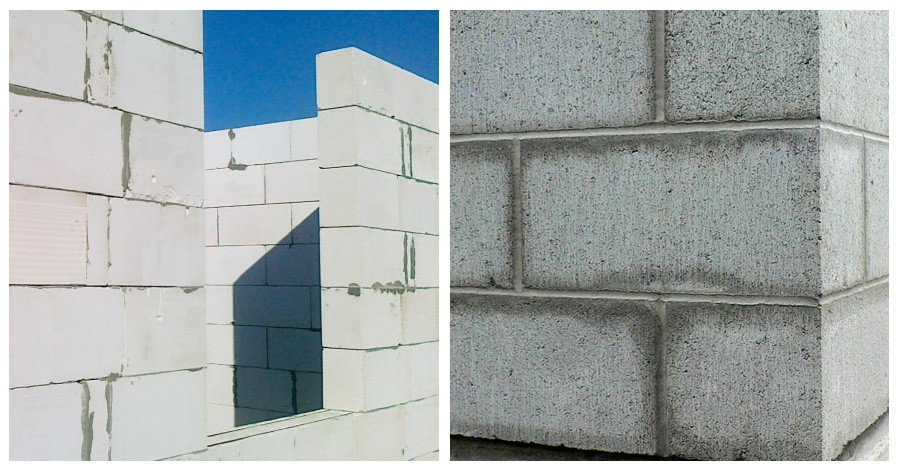
Compared to foam concrete, gas silicate factory blocks have ideal geometric shapes. This speeds up the masonry process, reduces the consumption of glue. Thin seams from 1 to 3 mm can significantly reduce the heat loss of the building.
The disadvantages of aerated concrete include its quite high cost and need for delivery from a large plant, which may be located far from the construction site.
It also loses to foam concrete in terms of moisture permeability. This fact must be taken into account when designing a house. For example, plan a high basement of a building (60 cm for the Moscow region) in order to avoid moisture accumulation in the first row of blocks. Plan a facade made of facing materials (panels, bricks, siding, etc.) or plaster to protect against slanting rain.
Foam block or gas block: which is more profitable for construction
There is no doubt that a cellular concrete building will be much more economical than a brick building. But the debate continues about which of its varieties is better suited for individual construction. Not everything is clear here and opinions are divided. The fact is that, other things being equal, foam concrete will be cheaper. This is due to the low production cost. However, the overall construction costs may be more significant.
A geometrically correct gas block can be placed on special glue. The thickness of a strong seam is only 2-3 mm, so the consumption of an expensive compound will be minimal. Whereas the foamed module most often has significant irregularities, as a result of which it can only be laid on a cement mortar. To obtain reliable seams of the latter, a lot will be required, which will increase the expense item.
disadvantages
As with any building material, foam blocks also have disadvantages.
- Fastener problem. For such a material, it is useless to use nails, they will simply fall out. All fasteners will have to be done on self-tapping screws.
- Cracks due to improper installation of the foundation. If the foundation is improperly mounted, during shrinkage, it can cause cracks both at the places where the blocks are glued to each other, and on the blocks themselves.
- High hygroscopicity. Aerated concrete absorbs moisture due to its foamy structure.He can absorb it up to a third of its volume, while not letting it go out. If the material is saturated with moisture, then its thermal insulation properties will deteriorate. For this reason, aerated concrete blocks require external finishing, for which you can use any materials (from bricks to tiles).


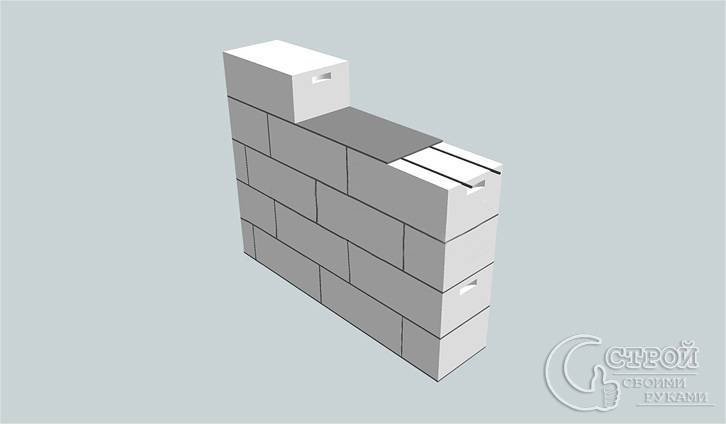
Tips for using foam blocks
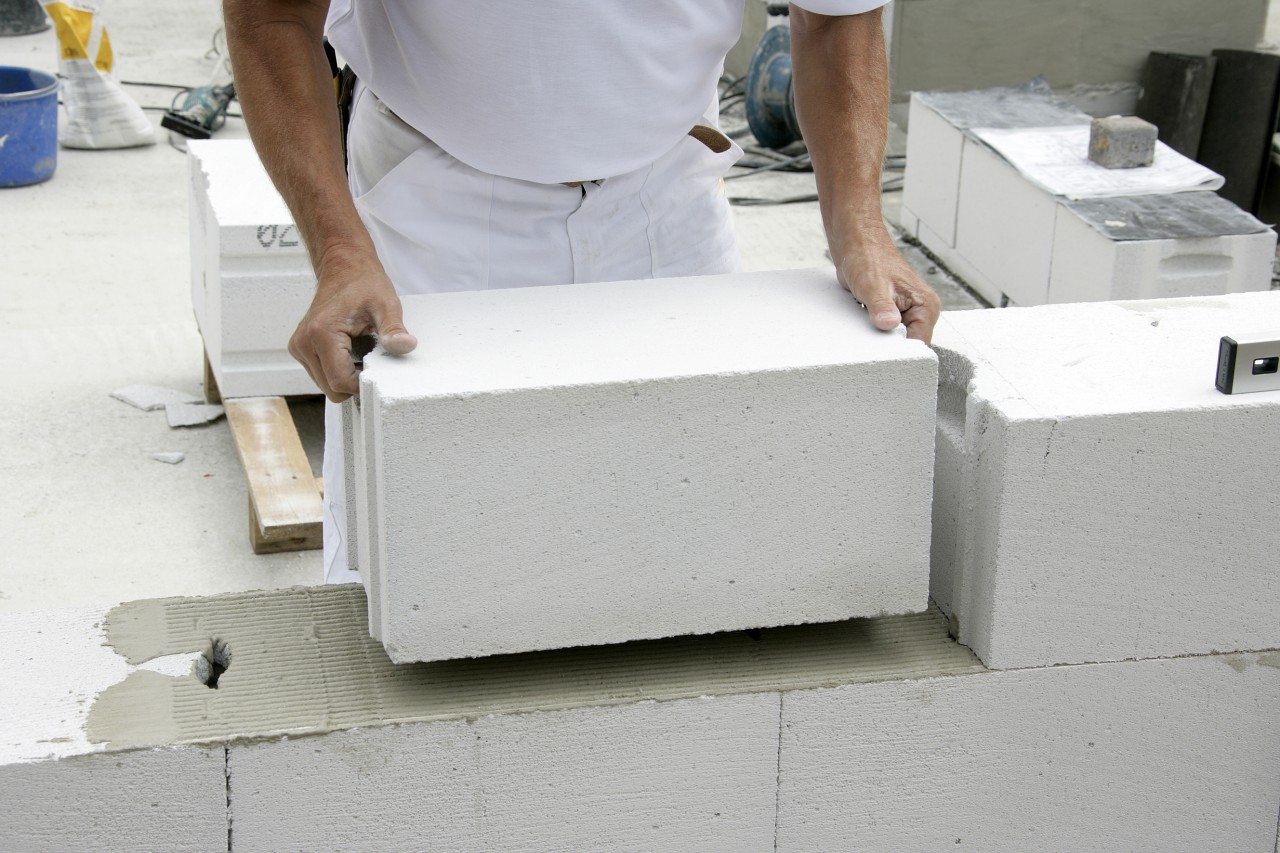
This infographic shows the features and nuances of performing masonry from foam blocks.
Tip 1
Since foam concrete blocks are easily damaged on the edges, try to unload them carefully. It is better to put them not on a standard solution (although this is also possible for them), but on a special glue with a cement base
Its layer (only 2 or 3 millimeters) will turn out to be much thinner than a layer of ordinary cement mortar, and cold bridges will not appear. But the thick seams between the blocks will inevitably release some of the heat outside.
Tip 2. Walls lined with foam concrete, without fail, need cladding. Do not trust manufacturers who claim otherwise - they shamelessly lie. Rain, snow, winds and hurricanes will gradually erode foam concrete if left unprotected. The facing material may well be plaster (both ordinary and mineral), as well as the material used for ventilated facades. As for the plaster, it will be necessary to lay a mesh under it, fixing it on the foam concrete wall.
Advice 3. When facing foam blocks with bricks, be sure to leave an air gap - after all, these materials have different air permeability. With their tight fit, water vapor will not be able to break through the brick cladding. They will bounce off it, go back through the foam concrete and return to the house. You shouldn't let this happen.
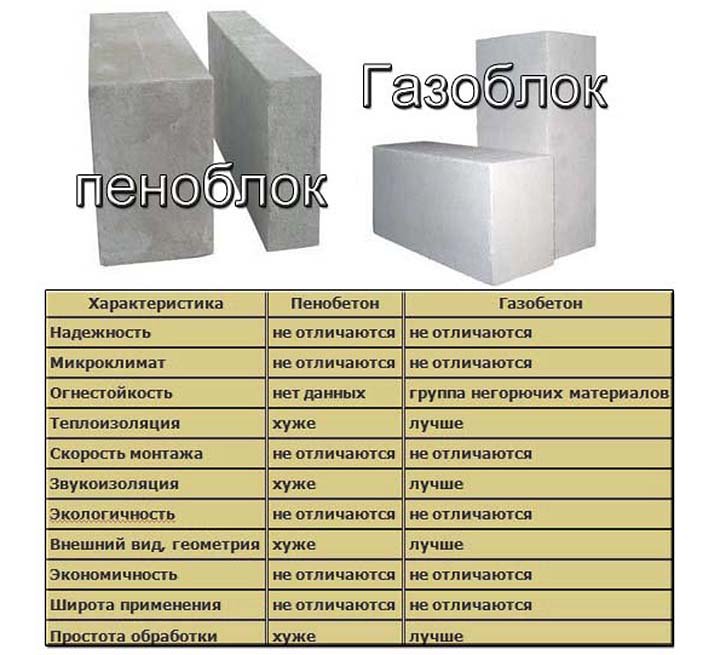
Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each of the materials
Each of the blocks has its own characteristics. Their analysis will make it possible to make the right choice of the material used in wall construction for the construction of the required facility.
Which is stronger
Since the blocks have a porous structure, the question arises which is stronger. This indicator directly depends on the density of the material.
For foam concrete it is 700 kg / m³, and for aerated concrete - 450 kg / m³. Foam concrete is a more durable product, but with proper installation, the strength of buildings made of aerated concrete and foam concrete is approximately the same.
Which is easier
Due to the porous structure, the products are lightweight, which allows them to be used in the construction of any facilities. The foam block has less weight due to the foam structure. Small pores are not filled with moisture. And its counterpart changes weight depending on the humidity of the environment around.
Which is warmer
An important factor when building a house is warm walls. Frost resistance of materials is almost the same when properly installed using special glue and mixtures. But according to technical indicators, the foam block is a more frost-resistant material. Here it is worth considering production indicators: brand, block thickness.
The foam block is a warm material, it retains heat. However, the thermal resistance of the gas block is much higher.
Water absorption
The gas silicate block quickly absorbs water. This is due to its structure. Foam concrete is moisture resistant, but both materials require additional insulation. Correct surface treatment prevents the threat of deterioration due to water and mold.

.
Convenience in construction
The materials are convenient in the process of construction work. Their indicators are approximately equal. Both materials are used in the construction of walls for both low and multi-storey structures. What are their advantages:
- high strength foundation is not required, since the materials are lightweight;
- a high thermal insulation index allows you to save on heating;
- a flat surface allows you not to carry out complex finishing work.
The cellular structure of the foam block does not allow it to be used for the construction of buildings above 2 floors, with the exception of using it as a heater for brick structures.
The gas block is stronger and has a wider scope. It is used for masonry partitions, load-bearing walls, fences, floors.
What is more natural
The composition of gas and foam concrete includes environmentally friendly materials. Despite the fact that aluminum paste is included in the raw material for the manufacture of gas silicate, it is safe. A solution of aluminum is extremely harmful in a concentrated state, however, during the production of concrete, it volatilizes during the reaction.
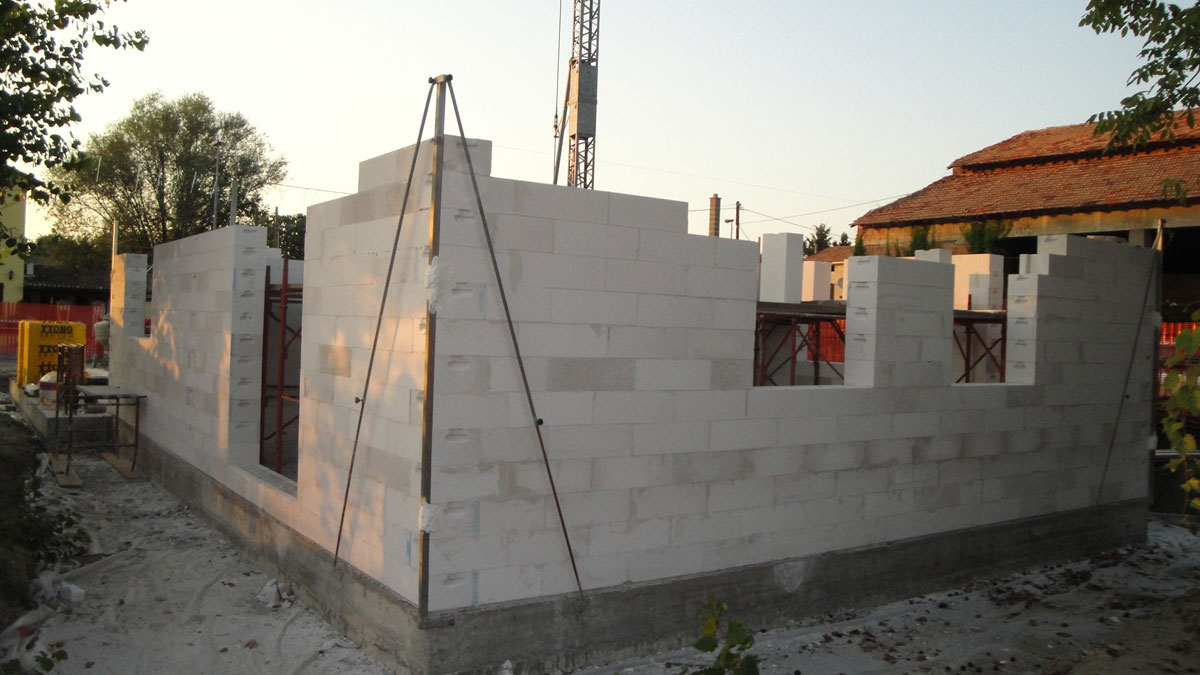
 Foam concrete construction.
Foam concrete construction.
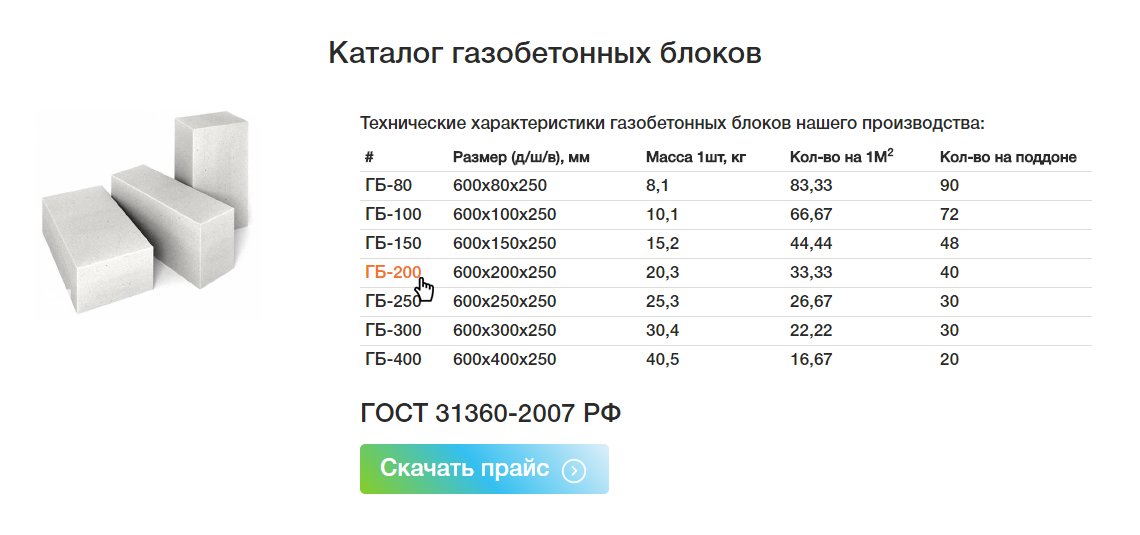
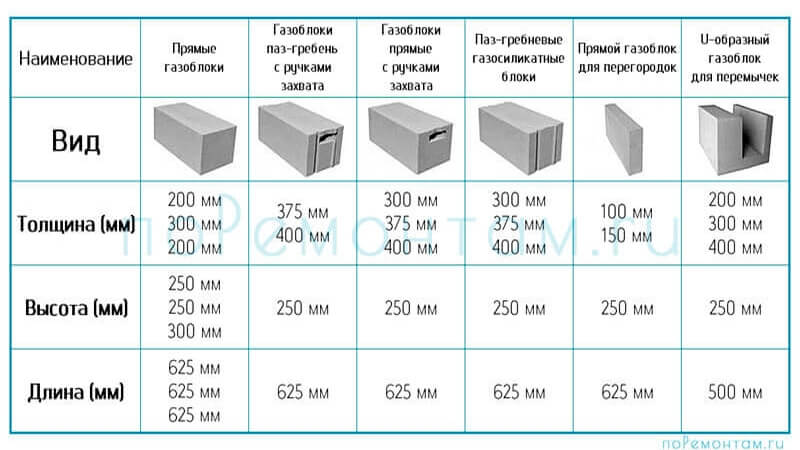
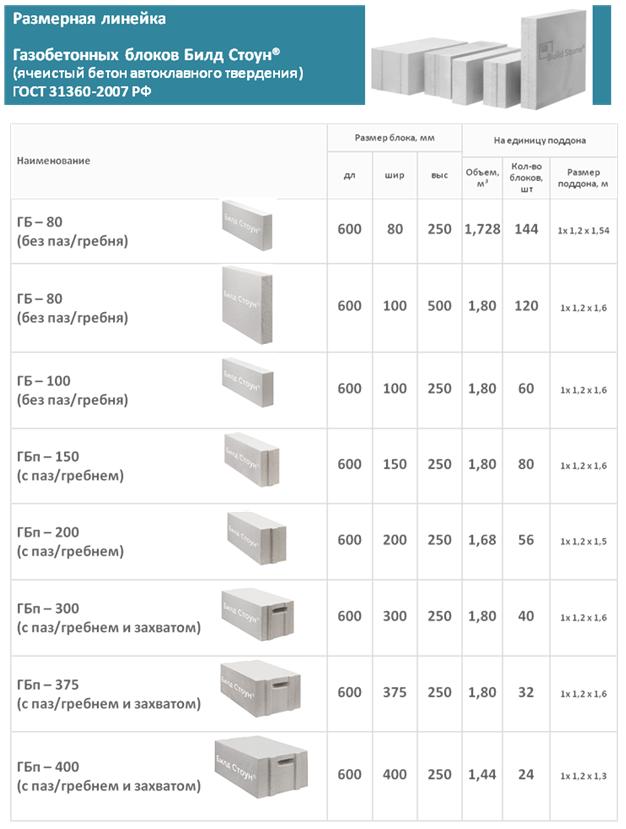
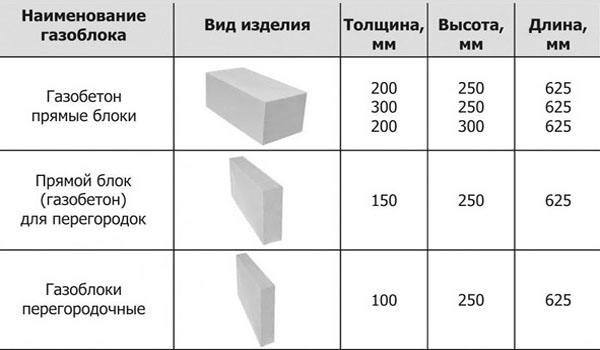
What sizes
Manufacturers present a whole line of concrete materials. The most popular block has indicators of 625x25 mm, the thickness varies depending on the purpose: 10 mm, 15 mm, 20 mm - for partitions and insulation, 25-60 mm - for the construction of walls.
Durability
Manufacturers claim that foam and aerated concrete have a 50-year warranty, but it only lasts if all installation and operating conditions are met.
What is the price of materials
Due to the complex production technology, a gas silicate block is much more expensive than a foam block. However, when calculating the construction estimate, it is worth considering other manipulations. So, for example, in order to achieve the required thermal insulation effect, you will need a larger amount of foam block. In addition, an uneven surface requires a larger volume of binder solution.
For building a house with your own hands from lightweight concrete, both a foam block and a gas silicate block are suitable. The main condition is to select high-quality material.
How much do foam blocks and gas blocks cost?
The cost of building materials is an important argument in favor of one type or another. Especially when it comes to similar specifications. But you need to understand what to compare. There will be a strong price bias when comparing products of different quality. Handicraft foam blocks using outdated technology will be significantly cheaper than gas blocks from a plant with advanced equipment. But this approach will not be beneficial, since the savings mean the loss of quality.

We will analyze the price of certified products from large manufacturers with a good reputation. The price of blocks depends on the grade of strength and size.
In Moscow and the Moscow region, the cost of one wall foam block of the D600 brand and the size of 600x300x200 from different manufacturers ranges from 100-115 to 160 rubles. At the same time, 1 m3 costs 2900-3750 rubles.

The price of heat-insulating and structural aerated concrete wall blocks of the D500 brand and the size of 600x300x200 in Moscow and the region starts from 110-112 rubles. per piece, and the upper limit is at around 167-175 rubles. per piece 1 m3 contains 27.8 blocks, respectively, the average price of 1 m3 of gas blocks is 3058-3700 rubles.
The price of blocks in remote regions (Siberia, the Far East), like other building materials, will, on average, be 1.5 times higher than in the Central region. In addition, during construction, thicker walls must be laid to increase thermal insulation.
The budget also needs to include the costs of paying for masonry services. On average, 1 m2 of a wall made of cellular blocks costs 1500-1700 rubles. The price list of contractors indicates the cost per cubic meter, which varies from 2,400 to 4,000 rubles.
Gas block and foam block: what is the difference
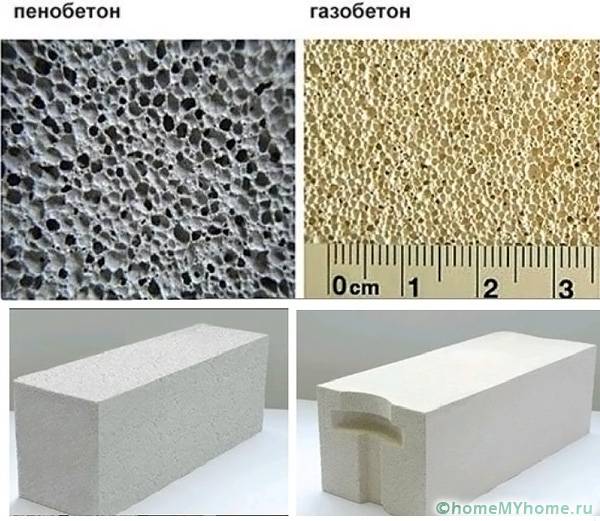
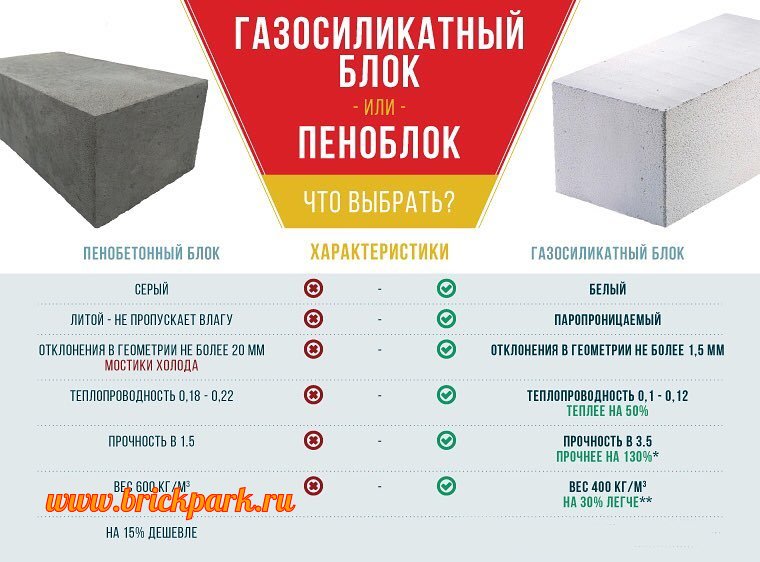
It may seem that these types of aerated concrete have a set of almost identical properties. However, there is a difference between them and it is significant. Let's compare the most significant characteristics.
Module geometry
The better it is, the easier it is to style. So, flat structures can be mounted using special glue. The seam thickness is only 2-3 mm, which allows you to completely get rid of cold bridges. At the same time, the speed of work with geometrically correct elements is much higher. Finishing costs are also reduced as no alignment is required.Foam blocks are noticeably different in this indicator. The error of their sides is 3 mm and more, for gas blocks it is no more than 1 mm.
Insulating properties
Both varieties are filled with air bubbles, but their number is not the same. Aerated concrete is more porous, therefore, it retains heat better and drowns out noise. However, the differences are small. In both cases, structural and insulating models are available. The latter are intended for insulating buildings made of "colder" materials, for example, cinder blocks.
How the gas block differs from the foam block in composition
Aerated concrete block includes the following ingredients:
- Portland cement marked M400, the concentration of which reaches 50% of the total volume of the mixture;
- sand fraction based on quartz, which is an aggregate and is introduced in the amount of 30–40%;
- lime in the amount of 10–25%, participating in the chemical reaction of gas formation;
- aluminum powder, which promotes vaporization and is introduced in an amount of not more than a tenth of a percent;
- calcium chloride and calcium silicate introduced into the working mixture as special additives.
The amount of ingredients introduced into the foam concrete products is determined depending on the required specific weight of the blocks. The simplified technology makes it possible to obtain products with a density of 0.35–1.25 t / m³.
 Cement brand M500
Cement brand M500
The mixture contains the following components:
- cement grade M500. Added as a binder;
- medium coarse sand. Replacement of sand with expanded clay is possible;
- foaming additives. Their number determines the porosity of the product.
The amount of sand is three times the volume of cement for expanded composites with increased bulk density.
Foam concrete blocks: types, brands and basic parameters
There are 4 types of non-autoclaved foam concrete.
1. Materials of grades from D150 to D400 are called heat-insulating materials. Their density varies from 150 to 400 kilograms per cubic meter. Grades below D400 are not standardized by strength class. And for the D400, this parameter ranges from B0.5 to B0.75. This corresponds to a tensile strength of 9 kilograms per cm3. Frost resistance of the listed brands of foam concrete is not subject to standardization.
2. Materials of grades from D500 to D900 are called structural and thermal insulation. They have a density of 500 to 900 kilograms per cubic meter. The strength of the D500 brand is 13 kilograms per square centimeter. Its class is not standardized, as well as frost resistance. Strength classes for other grades:
- D600 - from B1 to B2 (strength 16 kilograms per square centimeter);
- D700 - from B1.5 to B2.5 (strength 24 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D800 - from B2 to B3.5 (strength 27 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D900 - from B2.5 to B5 (strength 35 kilograms per square centimeter).
Frost resistance coefficient F in ascending order of the brand: 15-35, 15-50, 15-75, 15-75.
3. Materials of grades from D1000 to D1200 (structural) have a density of 1000 to 1200 kilograms per cubic meter. According to the strength class, the parameters are as follows:
- D1000 - from B5 to B7.5 (strength 50 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D1100 - from B7.5 to B10 (strength 64 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D1200 - from B10 to B12.5 (strength 90 kilograms per square centimeter).
The frost resistance coefficient F is the same for any of the brands: its value is 15-50.
4. Materials of grades from D1300 to D1600 are called structurally porous. Their density varies from 1300 to 1600 kilograms per cubic meter. They are produced in small batches, therefore the characteristics of foam blocks of these brands are not designated in GOST.
The specific strength indicator depends on the temperature and humidity at which the foam concrete was produced, as well as its filler and the brand of cement used. Dividing the number of the brand of foam concrete by 20, you can get an approximate indicator of strength (albeit slightly underestimated). Take D1600 aerated concrete, for example.We get (with a decent margin) a tensile strength of 90 kilograms per cm2. However, the stock in this case will only benefit.
Consider the thermal conductivity of various brands of dry aerated concrete filled with sand. The unit of measurement is watt per meter per degree Celsius. And also, under the same conditions, we will compare the vapor permeability coefficients of these brands of foam concrete. The unit of measurement is kilogram per meter-hour-Pascal.
| Foam concrete block brands | Thermal conductivity, (W * m * C) | Vapor permeability coefficient, (Kg * m hour * Pa) |
|---|---|---|
| D300 | 0,08 | 0,26 |
| D400 | 0,1 | 0,23 |
| D500 | 0,12 | 0,2 |
| D600 | 0,14 | 0,17 |
| D700 | 0,18 | 0,15 |
| D800 | 0,21 | 0,14 |
| D900 | 0,24 | 0,12 |
| D1000 | 0,29 | 0,11 |
| D1100 | 0,34 | 0,1 |
| D1200 | 0,38 | 0,1 |
As for the dimensions, the D600 and D800 brands have dimensions of 20 by 30 by 60 centimeters. The D600 is also available in 10 x 30 x 60 centimeters.
Application of materials
Foam concrete and aerated concrete are building materials that are gaining popularity because they have sufficient strength and low thermal conductivity. The porous structure reduces the density and mass of the blocks made from them. Air-filled cells account for the thermal insulation. Despite the similarity of characteristics, the scope of application of these formulations varies.
Strength, low specific density of foam concrete increases the service life of this material. Therefore, it is used for residential buildings - houses, cottages, backyards, baths. The only limitation in the use of foam concrete is that buildings erected from it should not be higher than three floors. It is used when the device:
- load-bearing walls of buildings and structures;
- interior walls for planning premises;
- fences, fencing of territories;
- floors with steel bar reinforcement.
The uniformity of the structure of aerated concrete explains one of its main features - the increased resistance to cracking and shrinkage of structures created from it. This allows it to be used for the construction of residential buildings, industrial, public and commercial facilities. It is used for:
- interior partitions;
- filling spans in frame buildings;
- load-bearing structures and walls;
- multi-storey structures and buildings.

On the cons of aerated concrete blocks
1. Due to its low compressive strength and low bending strength, aerated concrete is a brittle material. The strength of aerated concrete walls directly depends on the correct structure of the foundation. A foundation should be erected that gives minimal shrinkage. Otherwise, the gas blocks will begin to crack within a couple of years after construction. A strip monolithic foundation and reinforcement of masonry blocks with a mesh every 2-3 rows are recommended.
2. High water absorption of aerated concrete is an obstacle to quality finishing work. It is not uncommon for a layer of plaster applied to an aerated concrete wall to not adhere to its surface. To reduce the water absorption of aerated concrete walls, they are treated deep penetrating primers.
3. Gas blocks are a weak basis for fasteners. It is quite problematic to fix massive objects in aerated concrete walls. Plastic butterfly dowels do not always come to the rescue, unlike self-tapping screws, which twist well and hold perfectly in the walls. But there is a danger of oxidation, after which they can rust and become unusable. There are some fasteners that hold pretty well though.
Video: Fasteners for gas silicate blocks
4. The declared frost resistance of aerated concrete is a publicity stunt. The optimal density of the used constructional and thermal insulation materials is considered to be the density of the D500 grade. Its frost resistance indicators do not exceed 25 cycles. Although it takes 50 cycles for facade finishing. Aerated concrete sellers clearly overestimate the frost resistance parameters that are inherent in products with a higher density.
5. Aerated concrete has rather high indicators of free lime, which contributes to the activation of corrosion processes of metal inclusions: reinforcement, pipeline, frame, lintels.
6. The low cost of aerated concrete blocks, declared by manufacturers, taking into account the guaranteed durability of the material, turns out to be somewhat exaggerated.
7. The durability of aerated concrete raises doubts due to the fact that the massive development of gas silicate blocks began relatively recently, and the forecasts of their fundamental nature have not been confirmed by anything.
The main disadvantages of aerated concrete blocks are listed. In addition to them, there are a number of disadvantages, which are more likely associated with violations of the technology of laying aerated concrete blocks and with the desire to sell more expensive material to developers. A detailed examination of such shortcomings often proves their groundlessness.
To build a house with your own hands, you can use completely different materials: brick, wood, aerated concrete, etc. All of them have their pros and cons and can be successfully applied in certain conditions.
Laying of foam concrete and aerated concrete
Comparison of differences within the construction process (assembly, installation, processing)
Foundation requirements
Identical, since both types of cellular concrete are lightweight. However, an unprotected aerated concrete block, after getting wet, becomes heavier by almost half, which creates additional pressure on the foundation. Foam concrete does not possess such a feature.
Cutting, sawing, drilling of blocks and additional elements
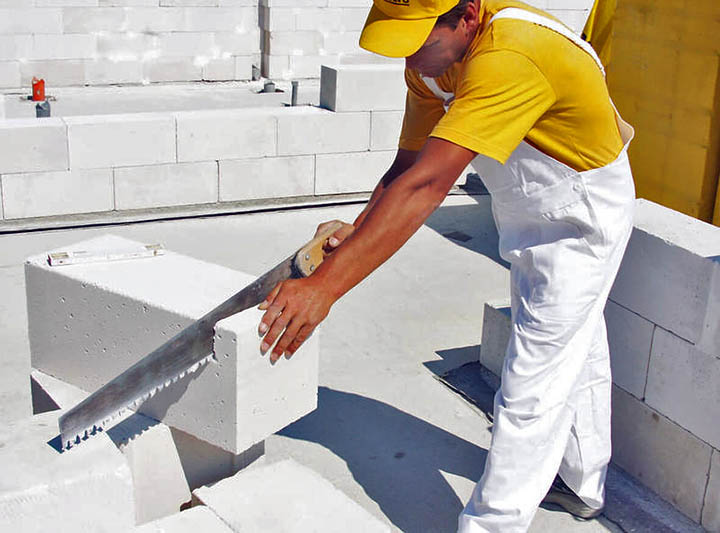
Identical, due to their structure and composition, you can give the aerated concrete blocks the desired shape using a conventional hand saw. Drilling, punching a hole or groove (groove) is also easy.
Construction speed (laying, installation)
The low weight of both materials being compared makes the construction process quick and easy, in comparison, for example, with block bricks.
Requirements for mortar, glue for laying
For aerated concrete, you need to use a special adhesive mixture, this allows you to reduce consumption and provide a thin seam.
Foam concrete can be laid on glue or sand-cement mixture.
Protection (conservation)
If there is a need to suspend or stop construction work, for example, for the winter, the materials need to be preserved. At the same time, walls from a foam block will stand for a certain period without problems, but from a gas block you need to wrap it in a film so that it does not pull moisture. Moreover, aerated concrete needs protection at any time of the year. Of course, in summer this is not so critical, a wall of aerated concrete will dry out in a week or two (is it worth interrupting work for so long?), Then in winter - this wetting followed by freezing-thawing can lead to destruction;
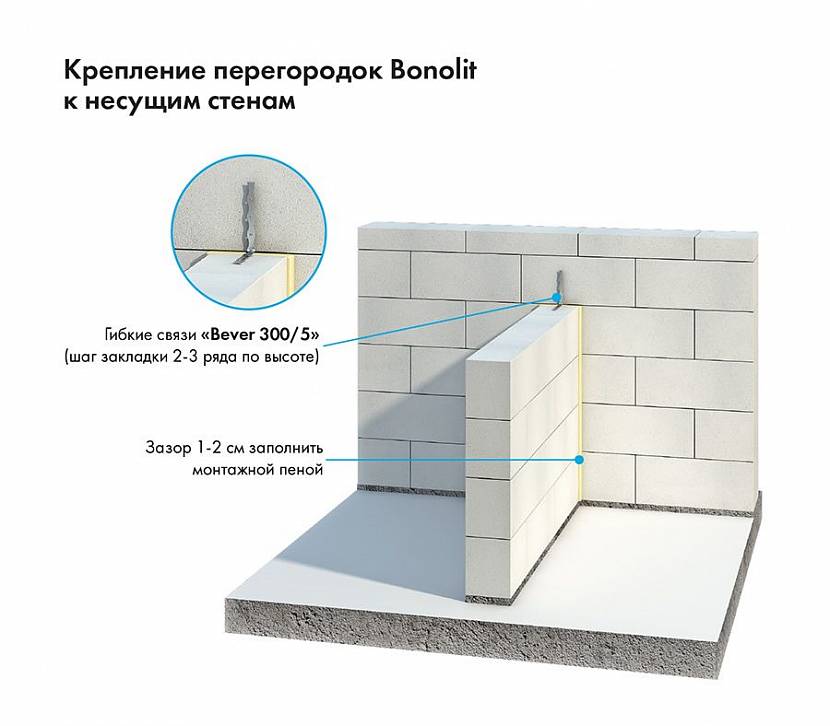
The ability to hold fasteners
For both materials, you need to use special fasteners (hardware, screws, chemical anchors). They are specially designed to be anchored in porous block walls.