AC or DC
AC and DC welding has its own special characteristics.
The main advantages of constant voltage: savings in welding consumables due to low spatter; comfort and ease of work; high-quality seam; high welding performance; lack of untested areas. The disadvantage is the high cost of equipment capable of delivering direct current. More details here.
The main advantages of alternating current are: lightness and affordable price of equipment that works during breaks; ease of welding; quality connection guarantee. The main disadvantages: less stability of the arc; a large amount of splashing contributes to a significant consumption of materials. Details here.

Corrosion-resistant steels can be welded in a variety of ways. However, most often, two joining methods are used to weld stainless steel:
- Manual welding with coated electrodes.
- Gas-shielded tungsten electrode welding.
Depending on the welding method, a different type of voltage is used, and accordingly electrodes suitable for alternating or direct current are used.
Stainless steel direct current electrodes
Getting started, the master must decide which electrodes can be used to cook the stainless steel. Coated consumables ensure optimum joint quality without any problems. Manual welding is carried out, as a rule, with a constant voltage of reverse polarity. Therefore, the following brands of stainless electrodes are used: TsL-11 is one of the most popular brands among welders; used on steels with a high chromium and nickel content. The weld deposited using these consumables has several advantages: strength; plastic; accuracy; sufficiently high level of impact strength; no splashing.
TsL-11 is one of the most popular brands among welders; used on steels with a high chromium and nickel content. The weld deposited using these consumables has several advantages: strength; plastic; accuracy; sufficiently high level of impact strength; no splashing.
OZL-8 electrodes are designed for welding structures that will be operated at high temperatures - up to 1000 ° C. At the same time, the advantages of this brand are in many respects similar to the TsL-11.
NZh-13 are successfully used for welding food steel parts. Consumables of this brand perfectly weld alloys containing chromium, nickel and molybdenum. The main distinguishing feature of such electrodes is the formation of a thin layer of slag crust, which separates spontaneously.

NII-48G electrodes.
Below is a list of a few more popular stainless steel electrodes:
ZIO-8 are intended for heat-resistant corrosion-resistant steels.
NII-48G electrodes are used to work with critical structures.
OZL-17U are suitable for stainless steel working in environments where sulfuric or phosphoric acids are present.
In the corresponding section, the rest of the brands of electrodes for welding stainless steel are presented.
AC electrodes for stainless steel
Not all performers have constant voltage equipment. Because of what the question arises: is it possible to cook a stainless steel with alternating current?
There are such electrodes, for example, these are brands OZL-14, LEZ-8, TsT-50, EA-400, OZL-14A, N-48, ANV-36 and others.
Welding with tungsten electrodes (pictured) in gases can also be carried out with alternating current of direct polarity. This connection method is used in the following cases:
- welding of thin-walled products;
- increased requirements for the weld.
This information will help the performer of any level to determine which electrodes for welding stainless steel with alternating current should be used in solving specific problems.
As a conclusion, it should be noted that electrodes for AC stainless steel are less in demand. This fact is due to the lesser popularity of alternating voltage as compared to direct voltage.
The constant has a wide range of advantages and is used by professionals much more often.
Necessary welding equipment and gas mixtures
The most common methods for welding alloys of aluminum, copper, cast iron and stainless steel are argon-arc (TIG) and semi-automatic (MIG) methods. Both methods allow the use of an inert gas protective environment, which increases the strength of the seam. The difference is that the TIG welding scheme involves manual wire feeding into the arc and the work is carried out with a refractory tungsten electrode. With the MIG method, a welding wire for semi-automatic machines is mechanically fed into the melt zone, which serves as an electrode.

It should be noted that semi-automatic devices are more expensive, but they provide a higher level of comfort and quality of work. The built-in electrical circuit allows you to start the regulator of the wire feed speed of the welding semiautomatic device, which makes it possible to work at different rates. For welding with this method, you need to select a set of equipment that may not be included in the supply of the inverter and is partially purchased separately. It includes the following components:
- an inverter MIG / MAG machine with a gas hose connection unit, a Euro connector and a welding-type wire feed circuit;
- torch with tips for different wire diameters, nozzle for gas supply and control button;
- European hose for feeding the gas mixture and passing the wire;
- gas cylinders for the mixture, equipped with pressure gauges and a reducer;
- a hose for supplying gas from the cylinders to the inverter, as well as the gases themselves and the coil with the corresponding wire.
The welding machine, as a rule, has a built-in circuit for delaying the mechanism of movement of the wire electrode relative to the supply of shielding gas to the seam zone, which prevents oxidation of the workpieces.
As for the composition of the gas, argon is usually used in pure form or in a mixture with helium, carbon dioxide or active compounds. In order to reduce costs, an expensive inert gas is mixed in a ratio of 75% -80% argon with 20% -25% carbon dioxide. It is also possible to combine helium with argon in different proportions and it is allowed to cook some materials using only carbon dioxide, but the quality of the weld deteriorates.
In difficult cases, when selecting a gas mixture, it is necessary to consult a specialist and study reference materials, because the composition of a metal or alloy may require an ambiguous solution.

Welding of stainless parts with a semiautomatic device
Welding stainless metals requires a special approach to the cleanliness of the edges to be joined and their preparation for work. When working with thick metal, it is necessary to remove the edges at an angle of 45 ° to 60 °, and clean the joints with an angle grinder. In addition, with the help of solvents, it is necessary to degrease the welding place, and the parts must be fixed with a gap of 1.5 mm to ensure the most complete penetration through the entire thickness of the metal. Then it is necessary to adjust the supply of inert gas or gas mixture, taking into account the thickness of the workpieces.
Presettings for a semiautomatic device are made based on the following proportions, namely:
- with a metal thickness of less than 1 mm, a wire of 0.6-0.8 mm is used with a feed rate of 150 m / h and a gas flow rate of 6-7 l / min;
- metal with a thickness of 1.5 mm is welded with a wire 0.8-1 mm in diameter at a speed of 150 to 200 m / h and a shielding gas supply of 6-8 l / min;
- stainless steel 2 mm is connected with products with a diameter of 1-1.2 mm, speed 200-250 m / h, gas flow rate from 7 to 9 l / min;
- for stainless steel 3 mm, use a wire of 1.2-1.4 mm, at a speed of 250-300 m / h and with a gas supply from 9 to 11 l / min;
- for parts over 4 mm thick, a wire of 1.4-1.6 mm is required when moving above 300 m / h, and gas is supplied at a flow rate of more than 11 l / min.
The arc voltage depends on its length and is set from 19 V to 30 V with an experimental selection, as well as the stickout of the electrode. On a number of high-end MIG / MAG inverters, there is an inductance adjustment mode, which determines the penetration depth and the width of the weld.
The presets are advisory in nature and are selected individually depending on the composition of the metal, wire type, gas mixture and welding speed.
After the selection of the wire for welding with a semiautomatic device applied to the material of the workpieces, it is necessary to place the drum on the shaft and insert the wire into the feeder. Then adjust the travel speed, which is usually related to the strength of the welding current, the higher the speed, the higher the applied value. The last stage of preparation for work is to adjust the parameters of the gas mixture, adjust the voltage and inductance.
It is important to follow the instructions for use of the semi-automatic inverter and follow the safety rules for welding.
Application nuances
Today, many welding methods have been developed based on different principles. But to say that one way is better to say is difficult. Each of them has pros and cons. But sometimes it turns out that it makes sense to use only one, specific type of welding. One of these types is welding with powder or flux-cored wire.

Filler wire application process
In fact, this wire is a tube with flux and metal powder inside it.
There are such requirements for the material of this class, for example, its use should not create problems during ignition and arc tracking. The wire should melt evenly without creating a lot of sparks around the weld pool. The resulting slag is evenly distributed over the entire surface of the seam and as it cools, it should be easily separated.
The seam must meet all the requirements of regulatory documents and there must be no defects on it - undercuts, lack of penetration, pores and cracks. These properties determine the possibility of using flux-cored wire for work. Meanwhile, to establish some properties of the welding wire, it is necessary to perform experimental welding. To do this, you need to take a roller and weld it onto a metal plate. Welding should be carried out evenly, in the lowest position of the working tool. Average modes are accepted as welding modes for the welded metal. After carrying out such experiments, it will become clear when and under what conditions it makes sense to use such a wire.

Welding scheme when using filler wire
Electrodes for welding stainless steel 12X18H10T
12Х18Н10Т is austenitic grade stainless steel. This type of stainless steel is the most common, used in many industries: food, chemical and pharmaceutical. Quite often, welded apparatus and vessels, pipes for pipelines are produced from this type of steel.

TsL-9 electrodes in a package.
The following is information with which you can determine with which electrodes to cook stainless steel 12x18n10t.
The most popular brand is TsL-9. Welding can be carried out in all spatial positions.
OK 61.30 electrodes have several advantages: good weld formation; easy ignition; self-separation of slag.
Welding consumables NZh-13 are used in cases where high requirements for resistance to ICC are imposed on the deposited metal.
OZL-14 - consumables used when strict requirements are not imposed on the weld metal against the IWC.
Varieties of wire for stainless steel 12x18n10t
To weld stainless steel parts, it is necessary to use argon arc welding and an additive made of the same material. It can have different properties, which may be suitable for other cases. Long products are produced from 12 × 18N10T steel. The filler material of this grade must meet the requirements of GOST 18143-72.
Welding filler wire has found its application in the machine-building and food industries, at construction sites, etc. It has not only high corrosion resistance, but also resistance to the effects of chemically aggressive environments. It contains a sufficient amount of chromium, which protects it from rust.
For welding, products made using cold drawing technology are used. It has a fairly low price and at the same time, such processing retains all its properties. This wire ensures the quality of the seam when processing any material.
Stainless wire 12X18H10T
So, water supply systems are often assembled from pipeline fittings made from this steel grade. When assembling and repairing, the use of a welding additive of 12X18H10T grade is considered optimal.
This steel grade is available in several versions. Hot or cold rolling technologies are used for its production. They make it possible to obtain a product with a diameter of 0.2 to 6 mm. When using wire of this brand, it must be borne in mind that it can change some of its parameters based on the diameter.
Welding stainless steel parts is a complex technological process and if you violate its rules, the result can be a large number of substandard products. To avoid this, it is necessary to make the right choice of wire material. Wire made of steel 12X18H10T is a specific product and may not be suitable for most types of alloy steel. The main rule for choosing a material for welding is the identity of the chemical composition. The wire made from this wire is good because the industry produces a wide range and, as a rule, there are no problems with the choice. By the way, when welding, preheating and smooth cooling may be required. Heating is performed using a gas burner.
Filler wire and its features
Wire is a metal product that has a small cross-section. Moreover, it is so small that it is incomparable in size with its length. For the production of wire, various types of metals are used - both ferrous, non-ferrous and stainless.

Flux cored wire
A separate class of products is welding. It is used for automatic and semi-automatic welding. It is used to make electrodes, rods and other products used in manual and automatic welding of parts.
In fact, it replaces the electrodes used in welding. Through it, electricity is supplied to the welding zone, which is necessary to ignite and maintain the arc. In addition, the wire takes part in the formation of welds and provides their physical and mechanical parameters.
For the production of wire used for welding, various types of metal are used. In this case, the scope of use of the finished wire may change. For example, aluminum can be used in the production of welding wire. It can be used to work with alloys based on magnesium, aluminum and a number of others. If the wire is made of stainless steel, then it is used when welding parts made of steel resistant to corrosion.
In the construction of ships, flux-cored wire is most often used. In addition, there is copper-plated wire. Its use entails obtaining quality seams.Not so long ago, wire was used without any coating at all.

Copper-plated filler wire
When choosing a wire for welding, you must always remember that there are several types of similar products on the market. They differ from each other not only in chemical composition, but also in structure, in the amount of alloying components.
The wire must be selected based on the marks applied to its surface or packaging. The markings tell the consumer about the physical and technical parameters of the wire and the scope of its application.
For example, in GOST 2246-70, this is a document that standardizes technical specifications for steel welding wire. So, it says that for the production of this welding material it is permissible to use low-carbon steel (Sv-08AA, Sv-08GA) alloyed (Sv-08KhN2GMYu, Sv-08KhN2G2SMYU) and high-alloyed alloys (Sv-10Kh16N25AM6, Sv-09Kh16N25M6AF).
In addition, the welding wire is divided into the one that is used to perform welding and the one from which the electrodes are produced. It can be manufactured with or without copper plating. All subtleties regarding the diameter, grade of steel alloy, the presence of coating should be discussed when placing an order.
Advantages
Filler wires can be classified as self-shielded and gas-shielded. The protection of the wire can be provided by various types of gases. The use of welding wire makes it possible to obtain:
- Due to the high heat flux, the electrode forms a narrow area of thermal action on the metal.
- The necessary effect on the metal of the formed weld by changing the gas composition and wire grade.
- High labor productivity during welding.

Self Shielded Flux Cored Wire
The use of welding wire provides great opportunities for mechanization of work.
One of the obvious advantages is that due to the use of wire for electric arc welding, there is a decrease in the main and auxiliary time for performing work, as a result, overhead costs are reduced and the cost of finished products is reduced.

Filler wire with polished surface
There are two types of filler wire - polished and copper-plated. And the state of the wire surface has a significant effect on the quality of the arc, the resulting seam, the number of molten metal droplets and, of course, on the reliability of the welding equipment.
Chemical composition of welding wire for stainless steel 12X18H10T
The properties of a product are determined by its composition. This brand includes the following chemical elements:
| Chemical element | Content in the composition,% |
| Carbon | 0,11 |
| Silicon | 0,8 |
| Manganese | 2 |
| Nickel | 10 |
| Chromium | 18 |
| Titanium | 1 |
| Iron | The foundation |
Nomenclature
Welding wire for stainless steel 12X18H10T has a fairly wide range and is available in the following diameters:
- 6;
- 5;
- 4;
- 3;
- 2,5;
- 2;
- 1,6;
- 1,5;
- 1,4;
- 1,2;
- 1;
- 0,8;
- 0,7;
- 0,6;
- 0,5;
- 0,45;
- 0,4;
- 0,3;
- 0,25;
- 0,2.
Brand specifications
Wire for welding stainless steel 12X18H10T can change its properties, depending on the diameter. These are minor deviations that should still be taken into account when selecting material for work. The characteristics table looks like this:
|
Wire grade |
Filler material diameter, mm | Hot rolled | Cold rolled | ||
|
Temporary tensile strength, N / mm2 |
Elongation,% with a sample length of 0.1 m. |
||||
| 1 class | 2nd grade | ||||
|
12Х18Н10Т |
0,2-1 |
590-880 | 25 | 20 | 1130-1470 |
|
1,1-3 |
540-830 |
||||
| 3,1-7,5 |
1080-1420 |
Features of choice
Welding stainless steel products is a very difficult process, which can lead to a lot of scrap. To avoid this, it is required to select the composition of the material very precisely. Welding wire for welding steel 12X18H10T is a specific product that is not suitable for all types of alloy steel. After all, the main rule of selection is the identity of the composition. The most convenient option here would be to weld stainless steel pipes of the same grade.It is worth noting that when selecting a filler material in production, where all components can still be changed, everything is done for convenience, since you can change the composition of the base metal so that it is convenient to connect it with this wire, and there are practically no problems with the selection of other welding materials. ... In the private sector, the situation looks somewhat different, since there materials are used mainly for repairs and an accurate choice is required. Having studied the composition of the base metal and filler wire, you can accurately determine the choice.
The wire brand is convenient because it has a wide range of products. There are no problems with the selection of the required thickness. Even in those moments where a large spread and error are not allowed, when it comes to small sizes, here the diameter step is 0.1-0.2 mm. All this makes it possible to obtain a high-quality welding joint without problems with burning through the base metal. Naturally, not everyone has the opportunity to have the entire row, therefore, when choosing, it is worthwhile to be guided so that the thickness of the base metal coincides with the size of the wire diameter.
Decoding
Wire marking contains information about those elements that determine the basic properties of the material and their content turns out to be decisive. In this case, the situation is as follows:
- 12 - the carbon content is 0.12%;
- X18 - the chromium content is 18%;
- Н10 - the nickel content is 10%;
- T - the titanium content is about 1%.
Welding features
In order for the connection to be of the highest quality, and during the process itself a minimum number of problems arose, you should adhere to the exact connection modes:
|
Wire thickness, mm |
Type of |
Current strength, A |
| Manual welding | ||
| 1 2 3 | Flanged metal |
35-60 65-120 100-140 |
| 1 2 3 | Metal butt position |
40-70 75-120 120-160 |
| Automatic welding | ||
| 1 2,5 4 | Butt position |
60-120 110-200 130-250 |
| 1 2 4 | Butt position with additive |
80-140 140-240 200-280 |
Welding of steel grade 12X18H10T
Electrodes
12x18n10t electrodes are often rods made of high-alloyed metal with a basic coating, which also contains alloying components. The composition of such electrodes is in many ways similar to the composition of stainless steel itself. Therefore, the seams are of sufficient quality and durable. But this is not the main advantage.
The correct choice of electrodes can not only be supplemented, but also slightly changed the chemical composition of the deposited metal. Do not forget that when melting, the electrode mixes with the base metal in the weld pool, so it is possible to change the composition of the weld.
Therefore, electrodes for welding stainless steel must be selected with special care. Indeed, with their help, you can significantly change the operational characteristics of the weld
Fluxes
A few words about fluxes. They are also used in stainless steel welding. The most commonly used fluoride fluxes. They should be used in combination with high alloy filler wires. In our opinion, the most optimal flux for welding steels of the 12x18n10t type is ANF-5. It not only protects the weld pool from oxidation well, but also alloy the weld metal. Since titanium is also present in its composition.
ANF-5 flux prevents the formation of pores in the weld, which is often found due to the large amount of hydrogen. Also oxide-based fluxes can be used instead of fluoride fluxes.
Modes
Now that you have selected the electrodes and flux, it's time to think about the welding mode.
The main thing to pay attention to is the amount of heat input. Heat input is the speed at which current is transferred from the welding arc to the metal.
In the case of stainless steel welding, the heat input should be low.
It is also recommended to form thin seams with a small cross-section. This can be achieved by using a small diameter filler wire, up to 3 mm. Please note that stainless steel has a reduced electrical conductivity.So that this feature does not become a headache for you, reduce the stick out of the electrode by one and a half to two times compared to the stick out for welding carbon steel.
Technologies
Let's move on to the most interesting thing - technologies. When welding stainless steel, you can apply the technology of semi-automatic welding in a shielded atmosphere, resistance welding technology, welding with a non-consumable electrode and welding with stick electrodes. V as shielding gas most often they use argon, a mixture of argon with carbon dioxide, and sometimes helium. Let's take a closer look at two welding technologies: argon arc and non-consumable electrode welding.
Argon arc welding using consumable and non-consumable electrodes is used most often in professional production. To do this, we recommend setting reverse polarity and boiling with direct current. As a protection, as it is not difficult to guess, argon gas is used. You can use either pure argon or a mixture of it with carbon dioxide or oxygen. The use of mixtures will stabilize the arc burning, simplify the formation of the weld and reduce the likelihood of pore formation.

If you decide to use non-consumable electrode technology, then set the polarity to direct and weld with direct current. Use tungsten electrodes. The use of alternating current is possible, but not always advisable. If the metal contains a large amount of aluminum (which is rare), then you can use "change".
Let's also add a few words about stick welding. This method is considered unprofessional and is only used at home or in small businesses where the quality of work is not critical. This method is good if you are a garage welder and do not want to spend money on additional equipment. You just need to have a simple inverter and pick up the electrodes. But if you are applying for a decent quality of seams, then we recommend that you still opt for welding in a shielded gas environment. And for such work, you need a semiautomatic device, a gas cylinder and a welding wire or electrodes. This is the minimum set for more or less high-quality welding in a workshop or even a garage.
Features of the brand
Before we proceed to a detailed description of welding, familiarize yourself with some of the features of stainless steel grade 12x18n10t.

The main thing you need to know is that stainless steel is extremely prone to intergranular corrosion. Even though the overall resistance to corrosion is quite high. But there is one good news. Intercrystalline corrosion occurs only when the metal is calcined in a furnace. A temperature of 500 degrees is enough for the structure of stainless steel to change and increase the likelihood of corrosion.
Manufacturers are well aware of this, and therefore add alloying elements to stainless steel. In the case of our brand 12x18n10t, this is titanium. This is evidenced by the letter "T" at the end of the marking. Before welding, find out the exact marking of the steel and make sure it contains alloying elements. In addition to titanium, niobium is used, in the marking it is denoted by the letter "B".
Usage Tips
To get a good connection, many welders use semi-automatic machines when working with stainless wire. This equipment protects the seams from extraneous influences, automatically feeds the filler wire to the welding place, forcibly cools, and can be used in hard-to-reach places.
Before doing the work, it is worth doing the preparatory stage, that is, to perform a number of activities.
- Eliminate contamination from the treated surface.
- Degrease the weld on the workpieces.
- Remove excess moisture from surfaces by heating them to 100 degrees.

In order to obtain a small transitional seam thickness between the parts to be welded, you can use several welding methods:
- short arc method;
- inkjet transfer;
- universal impulse method.

To achieve a high-quality result of working with a stainless additive, the welder will need to fulfill the following requirements:
- position the burner at a negative angle;
- drive the head at a distance of 1.2 cm from the metal surface;
- melting the wire should be done in small portions; large drops should not be used here.

Welding stainless wire is an important attribute, without which it is difficult to imagine the welding process. Consumers can purchase this product in a skein, reel or coil. This universal type of raw material has high technological properties and therefore is used in many industries and construction.
For tips on choosing a wire for welding, see the following video.
Decoding of marking
Stainless welding wire is designated in the same way as alloyed. The only difference can be called the presence of chrome and nickel in large quantities in stainless steel. Solid stainless wire is marked in accordance with GOST 2246-70.
The designation may contain the following letters:
- A - the wire contains a standard amount of phosphorus and sulfur;
- AA - the above substances are contained in a reduced amount;
- Ш - the product was produced by electroslag remelting;
- E - the wire is used to prepare the electrodes;
- О - there is a copper coating on the surface of the product, therefore the wire is used in the case of making critical connections with a stable arc.
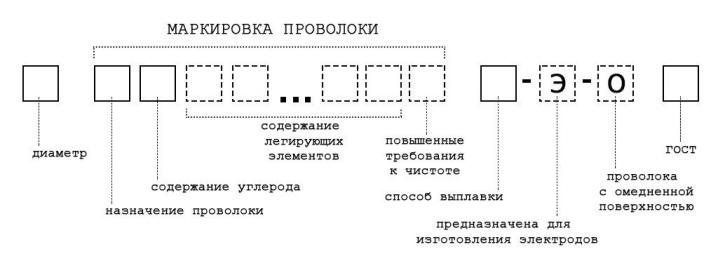
According to GOST standards, the marking of steel wire may contain the following designations:
- X - cold rolled product;
- T - thermally processed;
- P - increased production accuracy;
- TS is a light-colored metal, in which there are no oxides.


Depending on the diameter, 100 m of stainless steel wire for welding has the following weights:
- 0.5 mm - 0.31 kg;
- 1 mm - 0.62 kg;
- 1.5 mm - 1.4 kg;
- 2 mm - 2, 48 kg.

Types of welding wire for semiautomatic devices
Under normal conditions, just over a dozen types of welding wire are used, out of more than seventy types produced. This is due to the industrial specificity of using most types of welding machines, and the high cost of some of them. The most popular types are products with a diameter of 0.6 mm to 2 mm, weighing from 1 kg to 5 kg. Products are divided into solid wire and tubular wire with filler fillers, which have various purposes. In terms of chemical composition, it can be aluminum, copper-plated, doped with titanium and alloying.
Particularly carefully selected wire for welding stainless steel semiautomatic because it should be as close as possible in composition to the material to be welded. The current parameters are also important, since overheating when welding stainless steel leads to a loss of the physical properties of this material.
When joining different grades of stainless steel, the following types of stainless welding wire should be selected:
- for chromium-nickel steels 12X18H9T and 08X18H10T, use grades SV-06X19H9T, SV-01X18H10 or an analogue of OK Autrod 347 Si in argon;
- steel types 03X17H14M2 and 08X18H10T are welded using grades SV-01X18H10, SV-06X19H9T and OK Autrod 308LSi in inert gas;
- stainless steel of chromium-nickel-molybdenum composition is welded with wire SV-06Kh20N11M3TB, SV-08Kh19N10M3B and OK Autrod 318 in argon atmosphere.
These wire types match stainless steel grades and provide high tensile strength, elongation, toughness and flow properties, making the joint strong and elastic after cooling and slag removal. When working with high-frequency inverter or direct current, the metal in the welding bath does not overheat, which means that the corrosion resistance at the junction of the parts is not disturbed.
The parameters and composition of the wire are regulated by GOST 18143-72, which determines the criteria for assessing quality and the method of production.
Also, for joining stainless materials and dissimilar steels, flux-cored wire with rutile filler is used. It is used for welding difficult-to-weld, carbon-manganese and stainless steels in a gas mixture of 80% argon and 20% carbon dioxide. Powder products make it possible to work in any position, and are doped with molybdenum, which gives the seam high physical and chemical properties.
For steel grades E 2209, OK Tubrod 14.27 is used, for stainless steel 317 and 317L, OK Tubrod 14.25 is used, and for grade 309, OK Tubrod 14.22 is suitable. For welding other metals, you can use self-shielding powder products with flux (for example, SV-000009283), which does not require an inert gas environment.

What electrodes to cook 1 mm stainless steel.
 Welding thin metal is a difficult process not only for beginners, but also for experienced welders. This process has several complications:
Welding thin metal is a difficult process not only for beginners, but also for experienced welders. This process has several complications:
- strong heating of the product can lead to burnout and the formation of a hole;
- a high heating temperature can also lead to a change in the geometry of thin sheets;
- the short arc, with the help of which the connection is made, goes out with a slight separation.
These problems can significantly complicate welding work.
Therefore, in order to avoid such difficulties, it is very important to know which electrodes are needed for welding thin stainless steel.
OK 63.34 are intended for welding thin metal. Also, the brand is perfect for thick-walled products. The electrodes are characterized by improved slag separation.
OK 63.20 (in the picture) are especially in demand for connecting pipes and thin metal. The welding process takes place during short-term ignition and extinguishing of the arc.
