Non-compacted density of material - technological and commercial value
Mass in construction practice is the ratio of mass to volume that a material occupies in a compacted or non-compacted state. This number is especially significant from the economic and technological point of view.
To make a concrete mixture or mortar in order to create a sand cushion, it is necessary to use a material with known characteristics.
Determining the density of sand is important in terms of the ratio of its mass to the actual volume occupied. From an economic point of view, density affects money, what the customer is willing to spend - he must purchase a suitable material for use, of sufficient volume.
Density
To do this, it is advisable to establish the number of particles in a volumetric unit without seals and take into account moisture indicators, which significantly affect the weight.
Determination of the density of a material in an uncompacted state in accordance with GOST should be carried out according to a standard procedure.
How to calculate?
Many builders and gardeners are faced with the need to calculate or determine the amount of material they need to fill the available space. The calculation process is as follows:
- estimate the required volume using geometric formulas and plans or measurements;
- the approximate density of the sand is 1600 kg / m3;
- multiply volume by density (in the same units) to get weight.
If you compare, you can see that there is fine and coarse sand. This can be seen in the size of its grains. This is why the density is different when calculated. For this reason, as well as due to potential losses, it is necessary to buy 5-6% more material than expected.


For calculations, you must use the following formula:
- M = O x n
- m - represents the melted mass, which is measured in kilograms;
- О - volume expressed in cubic meters;
- n is the density that sand possesses even before it is compacted.
If we consider a cubic meter, then the indicator is identical to material density. In the event that the goods are sold by the manager and delivered unconsolidated, then the indicator is reported in advance. If we talk about the average value, then the accumulation of moisture should be from 6 to 7%. When the sand contains more moisture, the percentage rises to 15-20%. The described difference must be added to the resulting weight of sand.
River sand will have a specific gravity of 1.5 tons, sea sand - 1.6. When it is mined in a quarry, the indicator is equal to that of the river. The sand made from the slag mass is also different. Its weight can be from 0.7 to 1.2 tons per m3. If it was made on the basis of expanded clay, then the indicator varies from 0.04 to 1 ton.


For information on how to choose the right construction sand, see the next video.
Factors and properties of construction sand
Density reference values are derived under laboratory conditions. The characteristic is necessary for carrying out assessment work on the quality of the completed order and compliance with the requirements.
To determine the quality of the material, regulatory documents are used in which reference values are prescribed. Most of the prescriptions can be found in GOST 8736-93, GOST 7394-85 and 25100-95 and SNiP 2.05.02-85. Additionally, it can be specified in the project documentation.
In most cases, the compaction ratio is 0.95-0.98 of the standard value.
| Type of work | Compaction factor |
| Re-filling of pits | 0,95 |
| Sinus filling | 0,98 |
| Reverse filling of trenches | 0,98 |
| Repair of trenches near roads with engineering structures | 0,98 – 1 |
"Skeleton" is a solid structure that has some parameters of looseness and moisture. Bulk density is usually calculated based on the interdependence of the mass of solid particles in the sand, and that which the mixture would acquire if water occupied the entire space of the soil.
The best way to determine the density of quarry, river, building sand is to conduct laboratory studies on the basis of several samples taken from the sand. During the survey, the soil is gradually compacted and moisture is added, this continues until the normalized moisture level is reached.
After reaching the maximum density, the coefficient is determined.
Varieties
There are many varieties of sand and each has its own application.
River
Outwardly, it is a free-flowing material, not ore. You can find the material at the bottom of the river, it is from there that it is mined. What distinguishes it from others is that it is the purest of all other types of sand. Its plus is that it does not contain clay, dust, salt, pebbles, and so on.
River
This type of sand is mined in two ways - by excavators, draglines and hydro-mechanized method.
It is used in everyday life and construction. If we talk about construction, then it is used for the production of reinforced concrete structures, in the production of paving slabs, slabs and so on. Characteristics: density - 1.5 kg / m3, humidity - 4%, specific gravity - 2.65 g / cm3;
Quartz
It is a special bulk material, which consists of small granules with a diameter of 0.05-3 mm. Quartz sand is formed as a result of the destruction of rocks that contain quartz. In its composition, it can have various kinds of impurities (clay materials, iron oxide, slags, and so on).
Quartz
It is the impurities that give the sand a certain shade, if we talk about pure quartz sand, then it is milky white.
Due to its good characteristics, such sand can be painted in any color, which helps to create decorative plaster. Characteristics: moisture less than 10%, clay content 1%;
Career
In essence, it is ore, free-flowing and granular type. It contains particles ranging in size from 0.7-5 mm. Quarry sand itself contains many additives: clay, all sorts of small stones, dust, and so on.
Career
Characteristic features of sand: size 0.7-5 mm, impurity content 10%;
Nautical
It is a non-metallic bulk material. It is easy to find it on the seabed. Its advantage is that there are almost no impurities in its composition, but there is salt during cleaning.
Nautical
But unfortunately, this type of sand is quite rare, since it is not always possible and convenient to extract it;
Artificial
Since the above types of sand are natural (except for quartz), artificial sand can also be noted, which can be created by grinding marble, limestone, granite. In fact, it has a homogeneous composition, without impurities, and this allows the correct calculation of its consumption.
Artificial
Before choosing the right sand, you need to know all of its characteristics, and correctly calculate the amount of sand using the rules and formulas.
The main characteristics of sand include:
- sizes, size index;
- radioactivity;
- a direct indicator of the bulk volume;
- the amount of impurities in the sand;
- filtration coefficient.
Factors affecting density
It is far from always necessary to focus on a certain indicator of the bulk density of sand, since it can change over time depending on several fairly important factors.
These include materials scientists and builders:
the degree of compaction. There are small gaps of air between any particles of sand. The more pressure on the material, the less these layers. Accordingly, this also affects the density level.This is due to the fact that the mass of sand consists precisely of grains of sand, and not of air;
the bulk density of average sand according to its compaction is most often in values from 1400 to 1700 kilograms per cubic meter;
method of extraction and origin of the material. Most often, the sand that is washed out of the water has a higher bulk density than that which is quarried;
separately, we can also say about an artificially created type of material, which, due to the fact that the process of its manufacture occurs by means of mechanisms, also has higher quality characteristics;
emptiness. The more different gaps between sand particles, the lower its bulk density will be. In most cases, after transporting the material, the number of voids decreases, since the sand is compacted a little;
size of fractions. The bulk density of medium-sized sand is most often higher than that of a material with large particles, and lower than a material consisting of small grains of sand;
This is due to the fact that the smaller the fractions, the more tightly they adhere to each other, which accordingly affects the decrease in the volume of air layers. In general, the average density of sand is about 1450-1550 kilograms per cubic meter;
it is quite simple to determine the size of grain fractions - for this you should use several sieves with holes of different diameters;
mineral composition of the material. Quite often, many do not pay attention to this factor, although in fact sand can be based on completely different substances. These include quartz, mica, feldspar, etc .;
all these components, although in a crushed form, are very similar, but differ slightly from each other, including in weight. The material itself can be monomineral and polymineral.
In the second case, it is most often based on two different components;
humidity
This factor can change the bulk density of the material by about 20 percent, so it is very important to pay attention to it when buying sand. The higher the humidity, the higher the level of a given physical quantity.
All of the above factors related to sand, one way or another, to varying degrees, affect its bulk density.
Therefore, you need to pay attention to them. Due to the fact that some of them can change all the time, the compaction indicators should be checked immediately before handling the material.
Varieties of natural sand
Natural and artificial sand is increasingly found on store shelves today.
River
The one that is mined from the river bottom. It stands out for its cleanliness indicators. May have a yellowish or grayish tint.
River
Particle dimensions reach 0.3 to 0.5 mm. It is used at the stage of mixing mixtures for construction, as well as mortars, during the installation of drains. It is considered the most used and popular type.
Career (dusty)
Dusty is extracted in the classical way. Its shade is brownish or yellowish. The material contains dusty impurities and small stones.
Career
In a purified and classical form, quarry sand is used for a thick lime mortar and a complex of construction work related to the exterior and interior decoration of buildings; on its basis, a cement screed is created.
Extracted from the seabed and characterized by improved quality.
Nautical
Artificial
Artificial is made from mountain material.
As a result, it is possible to obtain a homogeneous material, in the composition of which there are no chemical elements that have passed into the composition of the alloy during their production, but the particles have an acute-angled shape.
Artificial
It is used to create a cement-sand mixture with increased density. The most common types are:
based on quartz.It is mined by crushing and sieving a snow-white mineral. Quartz sand is used for a complex of construction work related to external and internal decoration;
Quartz
based on expanded clay. It is mined by crushing expanded clay clastic rock in the form of small stones and inorganic materials. It is also possible to burn small residual clay impurities. It is used at the stage of mixing concrete, for filling the foundation pit in order to level the surface;
Expanded clay
based on slags. The crushing of this material into small particles is carried out by their instant cooling with H2O. This material is characterized by a variety of grain sizes: from 0.6 to 10 mm. Used when mixing mortar for construction.
Slag
According to the content of minerals, several groups are distinguished, which include one or more minerals.
How to determine how much a cube of sand weighs: material characteristics
Many country house owners are trying to calculate how much sand is in one cube. This indicator is especially relevant for suburban construction, affecting such serious arrays of work as the construction of a building or the arrangement of the courtyard and the local area. How much does 1 cube of sand cost with delivery is one of the burning questions of any person who undertakes independent construction or is concerned about the purchase of material for hired workers.
Depending on how many kilograms of sand are in a cube, the basic proportions of the concrete mixture will be calculated. This point is very important, since an incorrect calculation will lead to a violation of technology and serious consequences.

Sand is used for a wide range of construction works
Why is it so important to determine how many cubes of sand are in 1 ton
An indicator reflecting how many kilograms in 1 cube of sand, with erroneous calculations, can cause many difficulties:
- violation of the formulation of a mixture of concrete;
- incorrect consistency of the finished solution;
- loss of adhesive properties;
- poor concrete quality;
- disturbances in the solidification process;
- decrease in the strength of concrete;
- premature destruction of a structure made of cement mortar.
For this reason, it is very important to determine not only how much sand is in 1 cube, but also how much material is contained in this volume.

When calculating the required number of cubes of sand, take into account its specific gravity
The indicator reflecting 1 cube how many kg of sand is contained in a specified volume is called specific gravity or specific gravity. This measure, applicable to bulk materials, is in the range of 1500-2800 kg / m2. Accordingly, you can now estimate how many kg are in a cube of sand.
The specific gravity of a material can be influenced by various factors, including:
- composition of minerals;
- grain composition;
- size of fractions;
- humidity level;
- the percentage of compaction;
- impurities.

Tamping paving slabs using wet sand
Sand density
Today, many are concerned about the cost of a cube of sand, but few know that the final price is influenced by the characteristics of the material, one of which is density. Sand, like crushed stone, belongs to the category of bulk materials. Its density depends on the air spaces that form between the solid particles.
The density of sand is:
- technological;
- real;
- bulk - represents the ratio of the specific gravity of sand to the volume occupied by this material. In this case, the volume includes not only solid particles of sand, but also all the pores, as well as voids in the composition of the embankment (taken as a basis for determining how many cubes of sand are in a bag or bucket);
- true or conditional - the value is considered as the limit of the ratio of the specific gravity of the material to the volume it occupies, minus all pores and voids present in the embankment.
The density of sand varies in the range of 1.3-1.8 t / m ?, and is equal to 1.3 t / m? for river sand, and 1.4 t / m? - for a career.

Density of construction sand is from 1.3 to 1.8 tons per 1 cubic meter
Sand fraction size
How many cubes of material are in a bag of sand can be determined taking into account its grain composition. To do this, it is enough to sift the grains of sand using special sieves. As a result, you will be able to determine the level of content in the material of gravel particles with certain dimensional data. Usually, the size module of the material is used in calculations.
Table 1. Sand size modulus:
| Material type | Size of material fractions, mm |
| Small | 1,5-2 |
| Average | 2-2,5 |
| Large | more than 2.5 |
If you have fractions in front of you that exceed 2.5 mm, most likely you are dealing with quarry or river sand, how much a cube of material weighs in this case will depend on water demand.
According to the particle size, the material is divided into 2 classes:
- I - more than 1.5 mm;
- II - with any dimensional data.
The class of material and the size of its fractions determines how much 1 cube of sand costs for construction work.

There are three sizes of sand grains - fine, medium and coarse
Properties
One of the important advantages of river sand is its natural purity and flowability.
Due to the size of the grains of sand, such sand is divided into:
small;

Small
average;

Average
large.
The size of small particles is 0.6-1.5 mm, 2.0-2.8 mm for medium and up to 5 mm for large. Most grains of sand are of medium size (fractions are predominantly 1.68 mm). This type is ideal for the production of concrete, for the arrangement of road surfaces, airfields.
This is an excellent compound that is also used for the production of building mixtures.
Usually they are used in decoration, laying bricks or stones, design solutions and so on. They are also used for the production of bricks.
Coarse sand is an irreplaceable assistant in design work and on personal plots. This is facilitated not only by its composition, but also by its neutral color.
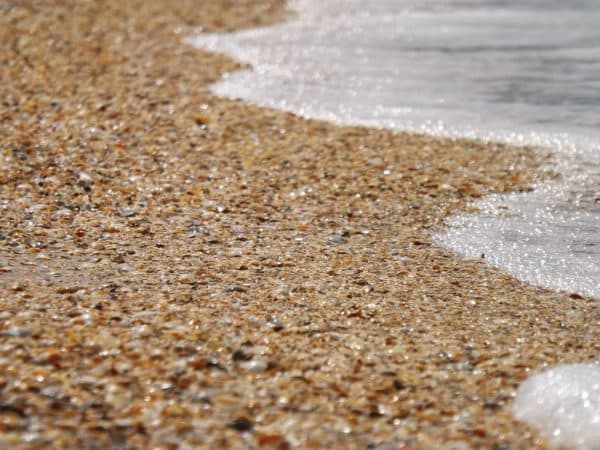

Coarse-grained
Nature also did not skimp on its shades and endowed with variety. In appearance, such microscopic particles are predominantly gray, golden or yellow. They are attractive enough.
The truth is that its grains are round, not pointed, does not always justify itself well. It is this structure of this material that prevents it from firmly adhering to cement. In this he loses to his mountain variety.
What is quarry sand?
This is one of the most common types of sand used in various fields - construction, road works, landscaping and other areas.
Quarry sand, in contrast to quartz sand, can be mined in different ways (washing, screening, open method), which also affects its final properties.
By fractions, the material is divided into:
fine-grained - grains of sand up to 2 mm in size;

Fine-grained
medium-grained - particle diameter up to 3 mm;

Medium-grained
coarse - grain size from 5 mm or more.

Coarse-grained
It is worth noting that quarry sand includes third-party components, the content of which can reach up to 7%. This can be both a disadvantage and an advantage. It all depends on the location of the mining site, the depth of the sand and the number of third-party inclusions.
In this case, the building material does not shrink, and the finished mixture is mobile and elastic.
Technical characteristics of cars
|
Index |
Meaning |
||||||||
|
MMZ -585 |
MAZ-503, |
KrAZ 256B |
KamAZ 5511 |
Kamaz from the side |
MAZ 5516 |
MD 290, Magirus |
Tatra 815, 815S1 |
VolvoFH420 |
|
|
Carrying capacity, |
4,5 |
7 |
11* |
10 |
7 |
16,1 |
14,5 |
15,3 |
27 |
|
Capacity, m3 |
3 |
3,8 |
6 |
7,2 |
7,9 |
11 |
14 |
9 |
17 |
|
Body dimensions, |
|||||||||
|
length |
2595 |
3280 |
4585 |
4525 |
5000 |
4450 |
5400 |
4300 |
6500 |
|
width |
2210 |
2284 |
2430 |
2310 |
2320 |
2300 |
2650 |
2290 |
2500 |
|
height |
650 |
676 |
650 |
816 |
635 |
1080 |
1200 |
970 |
1700 |
|
Also a dump truck, |
|||||||||
|
length |
5475 |
5970 |
8190 |
7140 |
7570 |
7530 |
8400 |
7190 |
9900 |
|
width |
2415 |
2600 |
2650 |
2500 |
2320 |
2500 |
2800 |
2500 |
2500 |
|
height |
2510 |
2700 |
2780 |
2700 |
2900 |
3160 |
3530 |
2900 |
3200 |
|
Weight, kg |
4570 |
6750 |
1140 |
9000 |
8480 |
12400 |
15500 |
11300 |
16000 |
*) 12 - for work in a career
2.1. Concepts and definitions
2.1.1. Required volume of natural sand
additions in concentrated reserves or quarries (), when it is used according to the transport scheme
directly for the construction of structural elements of the subgrade
(embankment or additional underlying layers of pavement), should be determined
according to the formula
where V2 - the geometric volume of the soil arranged
structural element (subgrade, additional sub-base layer) in
compacted condition;
- coefficient of relative compaction
(the ratio of the required density (skeleton) of dry soil in the structural
element to the density (skeleton) of dry soil in the source of production).
The required volume of sand, calculated in
vehicles (dump trucks, railway gondola cars and
etc.), when it is in a loosened state, should be calculated by
formula
where V2 - the volume of soil arranged by the constructive
an element of the subgrade in a compacted state (at the required density);
K1 - coefficient of relative compaction (the ratio of the required density of dry (skeleton) sand in
structural element to the bulk density of dry soil, determined at
natural humidity in a standard 10-liter container in accordance with GOST 8736-93.
2.1.2. The required amount of sand can be
calculate by volume or by mass. In the first case, the measurement is carried out either
by regular geodetic survey of the generated source of material,
either directly in vehicles (railway cars,
cars, barges, etc.).
When calculated by weight, the shipped material in
wagons or cars are weighed on railway or truck scales.
In accordance with GOST 11830-66
the weight is indicated on the bill of lading.
The amount of sand delivered by barges or
ships are determined by the draft of the latter.
2.1.3. The amount of sand is recalculated from
units of mass per unit of volume and vice versa according to the value of the bulk density of sand,
determined at the moisture content of the material during shipment, in accordance with GOST
8735-88. Bulk density and moisture content of building sand are indicated in
passports for each shipped batch.
2.1.4. To bring the volume of sand,
delivered in a wagon or car, to the volume in a compacted state, i.e. v
structural element, the resulting initial volume is multiplied by the factor
relative compaction. The latter depends on grain composition and moisture content.
material, method of loading and distance of transportation.
2.1.5. When developing design solutions
the coefficient of relative compaction should be assigned depending on
the required density of the material in the structural element or its corresponding
horizon (SNiP 2.05.02-85,
tab. 22) roughly:
□
when calculating volumes,
supplied from industrial quarries in vehicles, according to SNiP
4.02-91; 4.05-91;
□
when using sands
natural density in the source of production - according to SNiP 2.05.02-85.
2.1.6. In cases where POS and PPR
provide for dumping of subgrade elements, additional
underlying layers in winter (directly or through intermediate
accumulated volumes - stacks) sand volumes calculated in transport
means, it is necessary to increase by the appropriate coefficients given
in this Methodology.
2.1.7. Additional volumes of soil,
associated with losses during transportation, depending on the method and distance
carriage in accordance with SNiP 3.02.01-87 follows
take equal
□ 0.5% - at a distance of transportation up to 1 km;
□ 1% - at longer range.
It is allowed to accept a larger percentage of losses
with sufficient justification and a joint decision of the customer and the contractor,
the consumer and the owner of the quarry.
2.1.8. To determine the coefficient
relative compaction requires the following input data:
□ compaction factor and density
soil of a structural element;
□ standard maximum density and
optimal moisture content of the material;
□ bulk density.
2.1.9. In the adj. a more complete
list of terms and definitions.
Density types
There are three parameters, the value of which is measured empirically and can be either unchanged or depending on the degree of compaction, humidity and other factors:
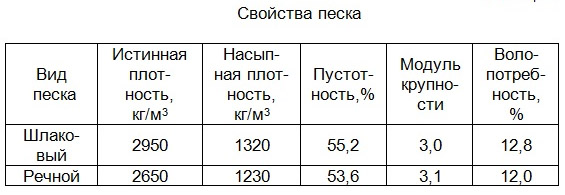
- True density is a constant value that characterizes the mass of the extremely compressed material per unit of occupied volume. It is measured in kg / m3 and is determined exclusively under laboratory conditions. For sand, it is at least 2500 kg / m3, since it is a product of grinding hard and high-strength rocks. According to GOST 8736-93, the true value is rechecked once a year (experiment with water displacement).
- Bulk density is the main parameter of free-flowing mixtures and building materials, showing their specific gravity in a suspended and dry state. It is determined by filling a flask with a known capacity with sand, poured from a height of 10 cm, without compaction. The average value is 1.5 g / cm3 (1500 kg / m3), the minimum is observed in dry fine-grained river varieties, the maximum is in building sand and compositions based on heavy rocks. The bulk density takes into account the volume of the gaps between the individual particles, but not the internal voidness.
- Average density is a characteristic that takes into account the influence of pore volume and the degree of moisture saturation. This value reflects the real mass of the material in the occupied volume in its natural state, as a result, it is higher than the bulk one, but less than the true one. The minimum is observed when the moisture content of sand is within 5-7%, a high value of the indicator under such conditions (≥1550 kg / m3) indicates good strength and frost resistance of the grains. To obtain a more accurate result, the average density is found several times.
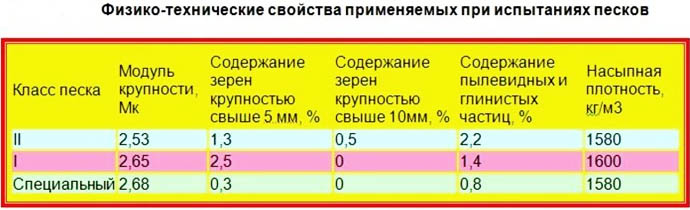
From external factors, the value of the indicator is influenced primarily by the moisture content of the sand. The coefficient does not change linearly: with an increase in the degree of water saturation up to 10%, the density of the material decreases due to sticking and clumping of grains, then air is displaced by water and the specific gravity begins to increase. In practice, free-flowing mixtures never dry out to the end, the density of building sand in its natural state will differ from the laboratory bulk, most often - in a larger direction.
Bulk density values for different types of sand
| Type of sand | Production method, description | Density of dry sand (bulk) | |
| g / cm3 | kg / m3 | ||
| River sand | Harvested from the bottom of the river, dry | 1,5-1,52 | 1500-1520 |
| The same with a grain size of 1.6-1.8 | 1,5 | 1500 | |
| The same, compacted | Washed, no clay fractions | 1,59 | 1590 |
| River alluvial | Extracted from the bottom of the river by alluvial method | 1,65 | 1650 |
| Quarry sand | From quarries, alluvial | 1,5 | 1500 |
| The same, fine-grained | Seeded dry | 1,7-1,8 | 1700-1800 |
| Building | Complies with GOST 8736-93, obtained during the development of sand and sand and gravel deposits, the density of sand is considered optimal for the preparation of concrete, including heavy | 1,68 | 1680 |
| Loose | 1,44 | 1440 | |
| Quartz | Obtained by crushing and sieving milky white quartz | 1,4-1,9 | 1400-1900, average 1650 |
| Nautical | From the bottom of the sea | 1,62 | 1,62 |
| Ravine | Open pit mined, contains a large proportion of unwanted impurities | 1,4 | 1400 |
| Gravelly | With an admixture of fine gravel particles | 1,7-1,9 | 1700-1900 |
| Perlite | Based on swollen volcanic rocks | 0,075-0,4 | 75-400 |
| Slag | Products of crushing and dry screening of metallurgical waste | 0,7-1,2 | 700-1200 |

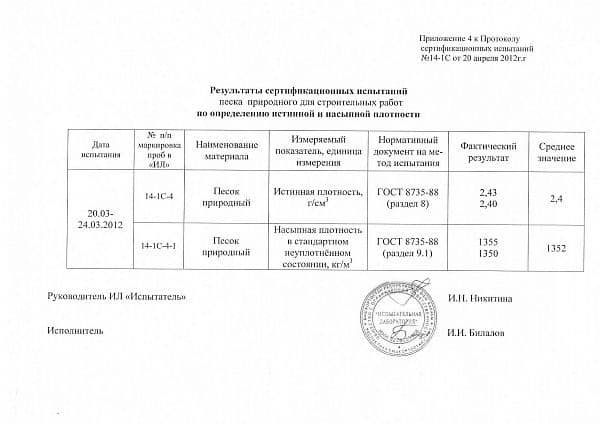
The general technical conditions of building sands are regulated by GOST 8736-93, molding (used for the manufacture of cast products) - 2138-91. The main classification is related to the location and method of extraction. The most popular varieties include:
1. River sand is a product of crushing hard rocks in estuaries and riverbeds. Granules of these grades have a round shape, the size of fractions varies from 0.3 to 0.5 mm. Scope of application includes the preparation of mortars for screed, finishing works, sandblasting, concrete, drainage systems.The characteristic features of river sand include rapid settling during the kneading process; mixtures based on it require periodic mixing.
2. Quartz, characterized by high quality grains and uniformity of composition. This type refers primarily to molding, it is used for the manufacture of glass melts, earthenware and porcelain solutions. Quartz sand with medium grain size is used in filtering installations.
3. Mined in quarries: by washing or dry screening. The first type of quarry sand has practically no dust and clay particles in its composition, the second is simply cleared of stones. Sown dry varieties are recommended for mixing masonry, plaster and asphalt concrete mixtures. Washed quarry sand is prized for its high purity and uniformity.
