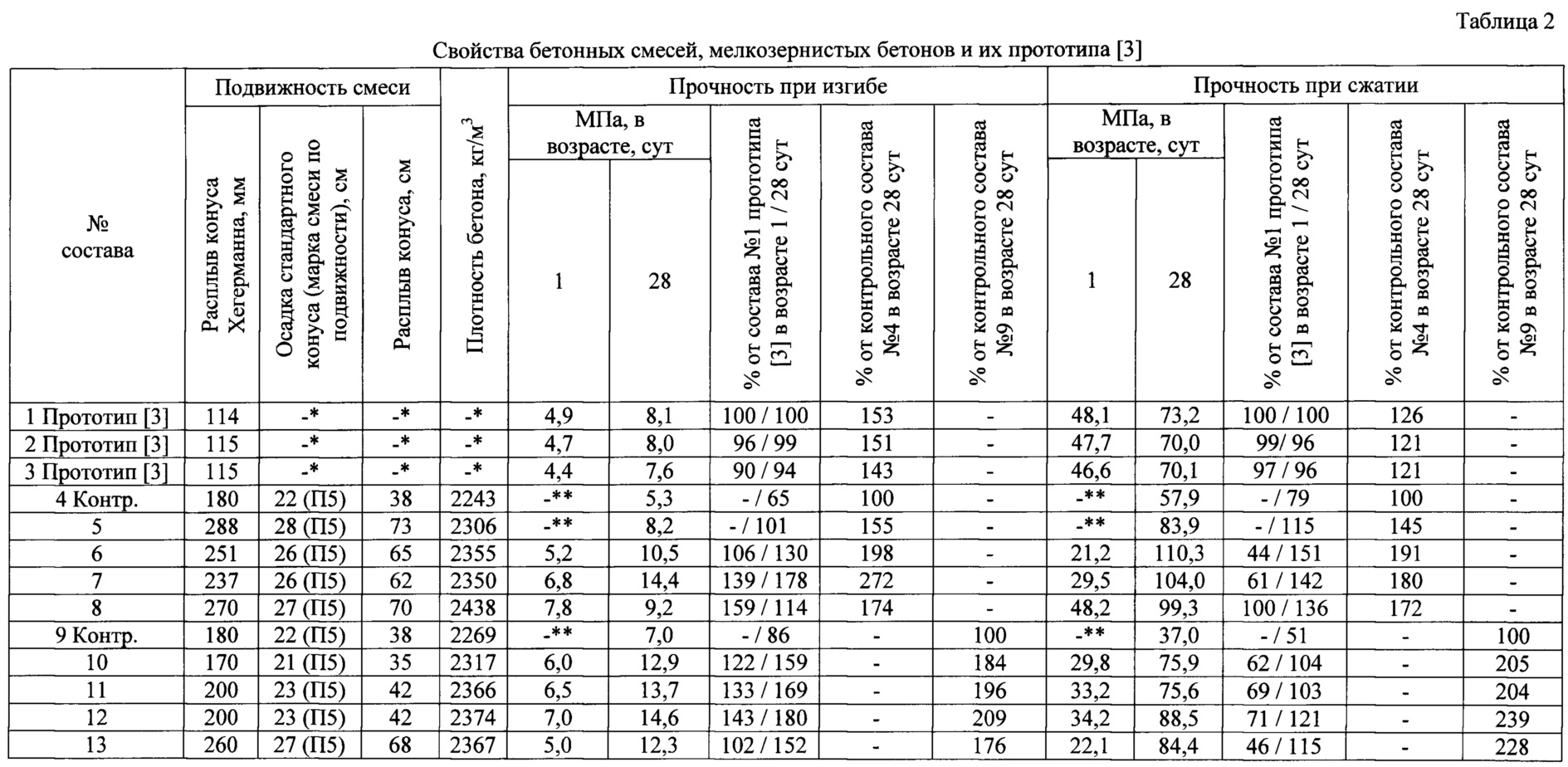
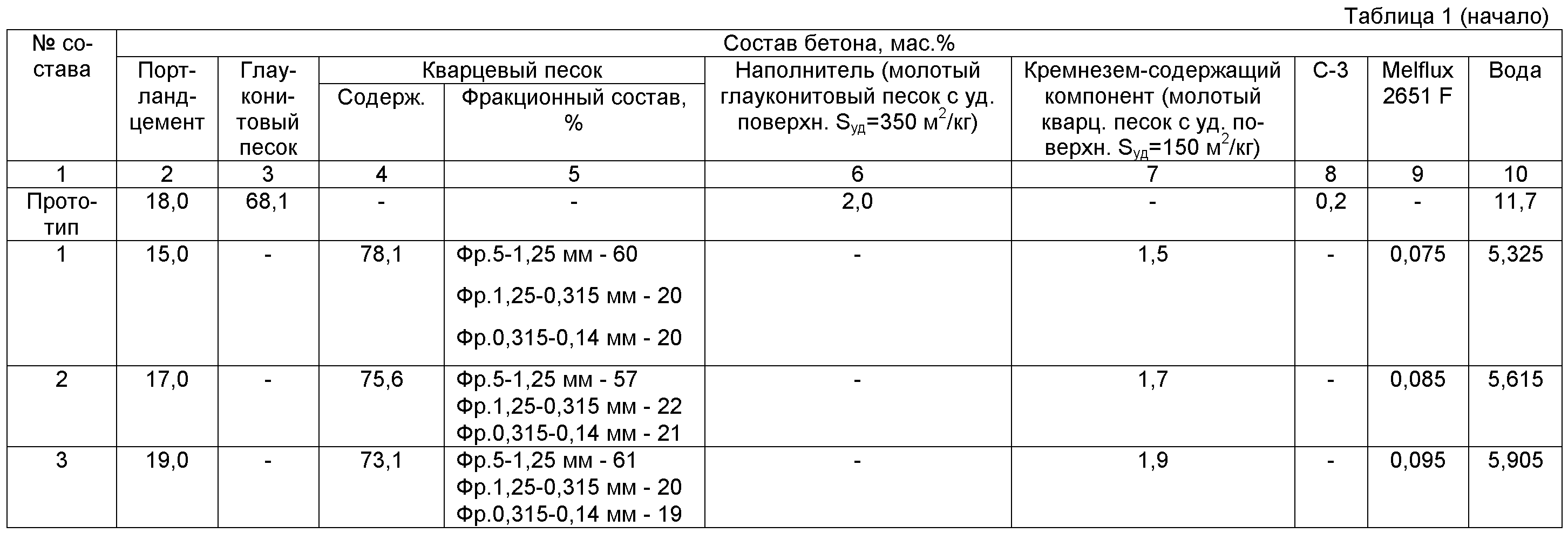
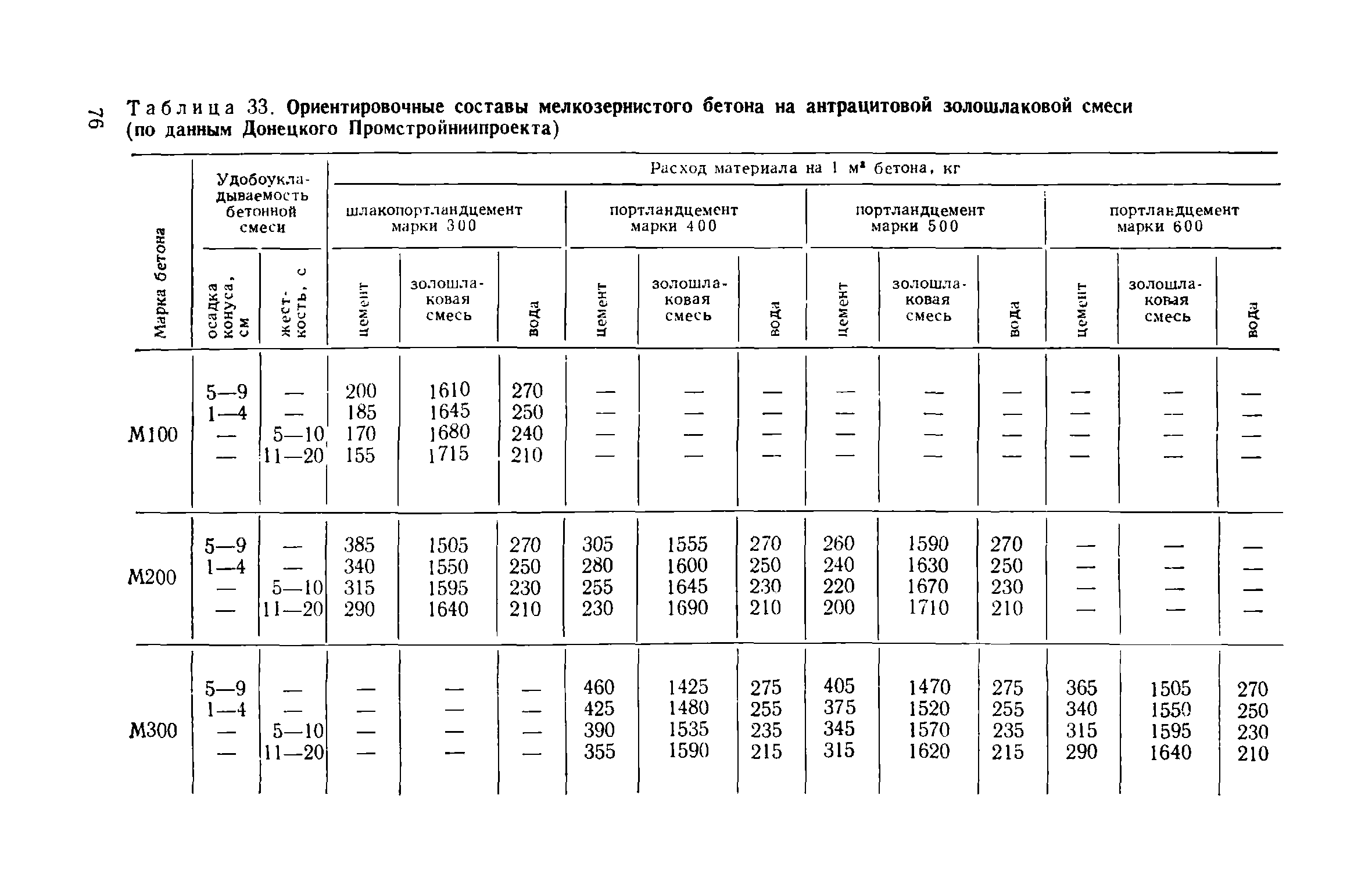
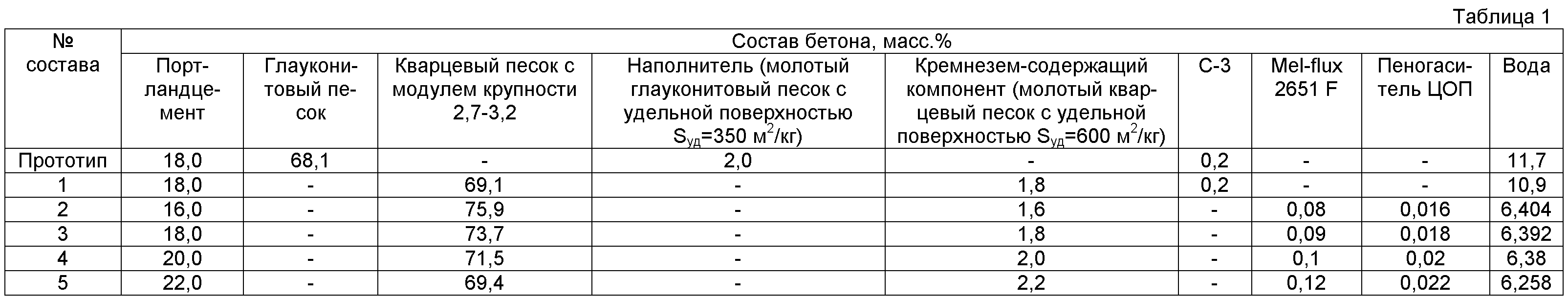
Methods for forming art-concrete
Archibeton is formed in several ways, depending on the method of work, the tools used, the principles of influence and the scope of operation.
The main methods of forming an archstone:
1. Stuffing (ramming) - the solution is poured, and then rammed with a stick or a rod (manual work). In this way, the most complex, tough decorations are created.
2. Pressing - mostly thin-walled, frost-resistant and durable, parts are created using molds and hydraulic presses.
3. Vibrocompression - pressure during vibrations. The work is carried out using a mold and a vibrating press. Thus, paving slabs, paving stones are made. The objects are durable, easy and quick to manufacture, and the process is relatively inexpensive.
4. Casting - the solution is poured into molds on vibrating platforms, it is possible to use deep vibrators. The products are inexpensive, but not very high quality.
5. Embossing - the work is performed using matrices used to obtain the desired texture of the base. Often the technology is used when finishing sites, paths on the territory, when decorating the vertical surfaces of structures and buildings.
Scope of application
The use of MB is due to the absence of open deposits of rocks with the presence of coarse fractions in the area of production of cement-sand mixtures.
Delivery of crushed stone or gravel to remote areas significantly increases the cost of concrete, which affects the cost of the final product. This reason is the most common when deciding on the production of concrete using fine fractions.
In addition to purely economic reasons, there are many products and structures that cannot be produced using traditional concretes with large fractions. These include:
- asphalt concrete pavement;
- large and small diameter concrete pipes;
- structural elements for the construction of hydraulic structures;
- pipes with special properties for the removal of aggressive waters;
- any thin-walled reinforced structures (for example, spherical products are cast from MB, which have high strength and, at the same time, low weight);
- floor slabs for equipping sheds in agricultural buildings where large spans need to be covered;
- bunker structures, large tanks for the storage of bulk and liquid substances and materials;
- products with dense reinforcement;
- arched structures capable of covering large spaces (for example, when equipping exhibition pavilions).
Manufacturing technology of architectural concrete
It is quite realistic to make an architectural composition, having determined in advance in accordance with the required characteristics and properties. First, all components must be sieved through a sieve to avoid lumps. Then mix the filler (quartz sand, crushed stone, other materials) and cement, add pigment and special mixtures that enhance the desired properties.
You should get a homogeneous dry mass. They make a depression in it and fill it with water. The proportions of materials depend on the purpose of the art stone production and the cement grade, but the volumes for the most common M-500 grade are indicated above. Further, various material processing techniques can be used.
Methods for decorating architectural concrete:
Spraying
This option suitable for processing vertical surfaces. An acid dye and a special spray bottle are used to carry out the work. The paint is sequentially, in layers, applied to the concrete solution, achieving the desired shade.

Stencil painting
This is how large flat surfaces are treated.Stencils can be bought ready-made in specialized stores or made yourself from any suitable sheet material. So often they perform various patterns, brickwork.
Stamping
A common method for machining vertical and horizontal surfaces using dies made of silicone or rubber. The dies are coated with moisture-resistant additives, pigments, and then pressed into concrete, achieving the desired effect. After solidification, the surface of the matrix is removed, and protective impregnations are applied to the finished concrete.
It is necessary to prepare architectural concrete, the production technology of which is quite simple, only if all proportions and components are accurately calculated. In this case, further processing and design will allow you to achieve an ideal result.
Application area
Most often, fine-grained concrete is used in places of residence where there is a shortage or absence of aggregates with a coarse fraction (gravel, crushed stone, etc.). This avoids the high financial cost of shipping traditional, large-sized ingredients. A roadbed, pipes, various water treatment systems and other hydraulic structures are made from such raw materials.
These include domes, vaults and shells. At the same time, despite the small wall thickness, such structures will have a high bearing capacity, will be lightweight and relatively inexpensive.
In addition, fine-grained mortar is used for buildings with large spans that are used to store bulk materials or various liquids (concrete tanks, bunker-type structures, silos, etc.). It can also be used for the construction of arched structures, which have recently been in great demand for the construction of exhibition complexes.
The composition and types of fine-grained concrete
The main difference between fine-grained concrete and other types of artificial stone is, of course, its composition. No coarse aggregate is used in the manufacturing process. Thanks to this technique, the final product acquires a homogeneous structure with a specific surface area of the solid mass and high porosity.
Main components:
- Portland cement or fine grain cement. The latter is used in cases where the production of any reinforced products and structures is required.
- Fine-grained filler. Various materials can act as it. For example, crushed lime or ordinary ash. But, most often, coarse sand is used. When fine sand is used, it is enriched with crushed gravel.
In addition to the key components, depending on the planned area of concrete use, a unique component is added to it, which gives the artificial stone special properties. It is the introduction of such materials that makes it possible to classify fine-grained concrete into various types.
Reinforced
In addition to using the main constituents of small fractions, during the production process, the finished solution is additionally reinforced with a masonry mesh. This tandem gives the end product strength that works well in both compression and bending. This type of fine-grained concrete is actively used in the construction of load-bearing structures of low thickness.
Silicate
To increase the resistance of products to the effects of a humid environment and high temperatures, calcium silicate is introduced into its composition. Ordinary fine-grained concrete can easily withstand temperatures up to 300 C, and the similar ability of structures on liquid glass increases almost 4 times.
High strength
To increase the strength characteristics of fine-grained concrete, additional plasticizing additives of narrowly targeted action are introduced into the composition. To increase the effect they create, instead of the usual aggregate, glauconite sand is used.
Modified
Special additives are added to the modified concrete. Only now they are selected from a number of modifying chemical compositions capable of improving all the performance characteristics of the material to the maximum level. Using them in various proportions allows you to “play” with the structure of an artificial stone, each time achieving the desired properties and characteristics.
Working mixtures
The composition and proportions for the preparation of the mixture may vary somewhat both in terms of the binder and the filler and the use of special additives.
The composition of the mixture
Portland cement of the M400 or M500 brands can be used as a binder. Depending on the operating conditions, corrosion-resistant pozzolanic and sulfate-resistant cements can be used.
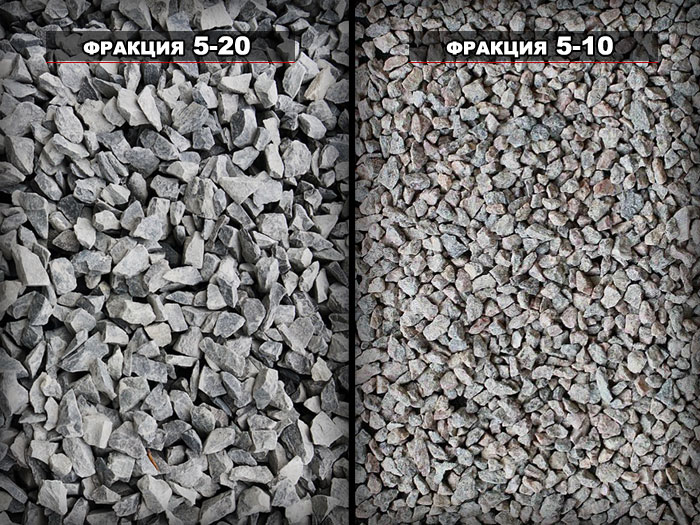
A fine-grained, homogeneous structure occurs when a fine filler is used. In this capacity, coarse, well-washed river sand with a grain size of 0.3 to 5 mm is used.

When selecting the size of the sand, you should adhere to the "golden" mean. The use of particles larger than 5 mm leads to a decrease in cement consumption and, at the same time, decreases the strength of the final product. Fine (dusty) sand increases the density of fine-grained concrete, but at the same time leads to a sharp increase in the consumption of the binder.
The optimal particle size distribution of the filler is obtained if a three-stage preparation method is used. In this case, sand fractions of different sizes are mixed in a certain ratio.
Preparation of dry components
To obtain a working solution of proper quality, a number of conditions must be met:
- the expiration date of the cement should not go beyond the limits established by the manufacturer;
- in the mass of the binder, the presence of hardened and caked lumps is not allowed;
- the filler should be free of clay impurities, debris, traces of organic matter.
Clean and washed sand is sieved. To obtain different fractions, a three-stage preparation method is used on sieves with different mesh sizes:
- 5-1.25 mm;
- 1.25-0.3 mm;
- 0.3-0.15 mm.

Then the resulting fractions are mixed with each other in a certain ratio:
- the first (largest fraction) - 50-60%;
- the remaining 50–40% falls on the other two fractions, which are taken in equal proportions.
Mixing
Next, you should mix the binder and filler. Depending on the operating conditions and the required strength characteristics, the composition of fine-grained concrete may vary somewhat. The ratio of cement to sand can range from 1: 1.5 for high-strength "greasy" mortars, up to 1: 3.5 for "lean" compounds.
The amount of water and, if necessary, the plasticizer to be added is determined in each case separately. The determining parameter will be the rheological characteristics of the working solution. The appropriate density, fluidity of the mixture and the strength of the concrete monolith when solidified must be ensured.
Scope of application of fine-grained concrete
- Filling of densely reinforced structures. In particular, structures, the dimensions of the reinforced belt of which, according to the terms of the project, do not allow "shedding" heavy concrete prepared on the basis of gravel or granite crushed stone;
- Repair work in the area of cracks and joints;
- Waterproofing works;
- Road pavement construction;
- Production of paving slabs and road curbs.
Fine-grained concrete is widely used in the regions of the Russian Federation, where there are no large-scale deposits of gravel or granite stone - the main fillers of heavy concrete.
In this case, the rise in the cost of the final product due to the increase in the amount of cement, several times covers the transportation costs for the delivery of gravel or crushed granite from other, often very remote regions of the Russian Federation.
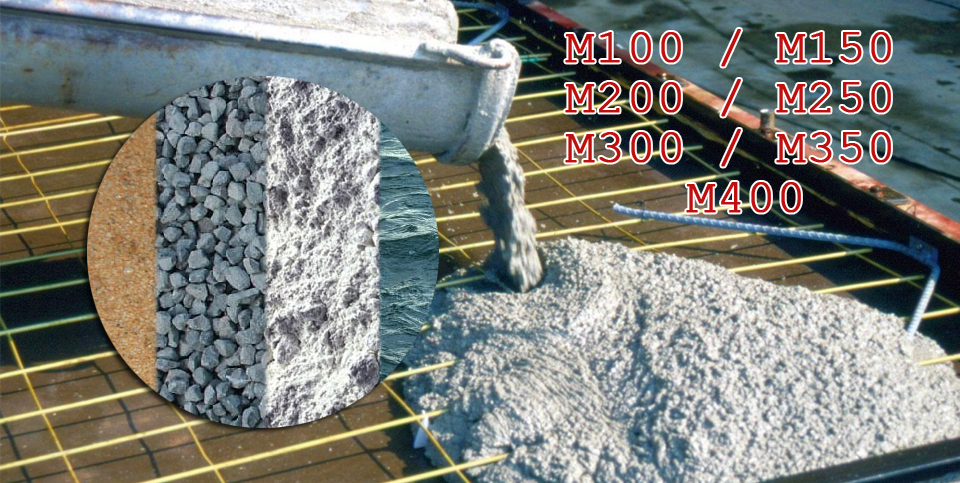
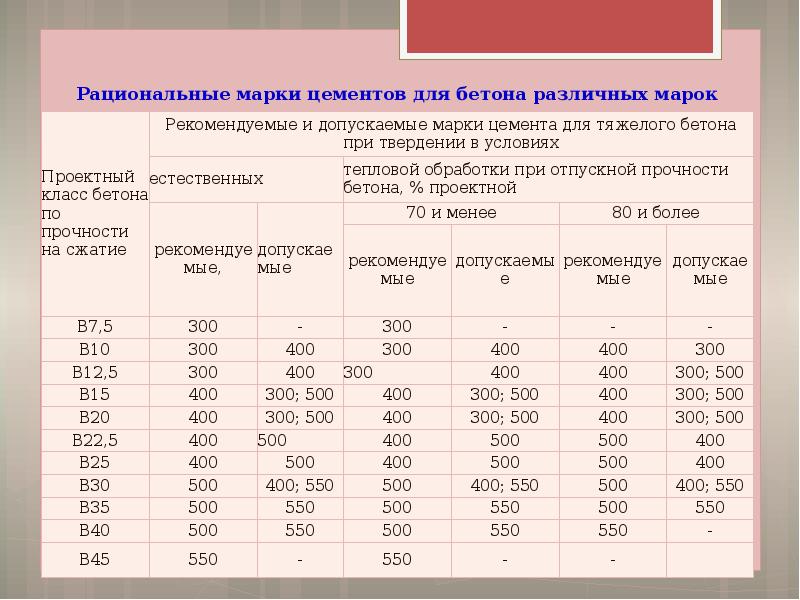
Grades and classes of fine-grained concrete
Like any other concretes, the "family" of fine-grained concretes is classified by grades and strength classes. In accordance with them, the immediate area of use is selected. All these data are presented in the table below.
| Project brand | Class | Application area |
|---|---|---|
| M50 | AT 3 | This type of low grade concrete is used for various rough construction works and for the production of garden curbs. |
| M100 | B7.5 | This brand is characterized by low performance characteristics. It is commonly used as a base for pouring roads, tiles, curbs and foundations. |
| M150 | AT 10 | Although the strength of this brand is low, its frost resistance is higher than that of the previous type - F30. Most often, concrete of this brand is used as the base of various foundations. |
| B12, B12.5 | Frost resistance grade - F50. The scope of application expands slightly to use in landscape design | |
| M200 | B15 | Such concrete is very popular when pouring monolithic foundations, some types of building structures, as well as when creating screeds. |
| M250 | IN 20 | They have grades for water absorption W6 and respectively W8, W9, W11 for frost resistance F150. Most often they are used when pouring foundations, casting slabs and stairs, as well as when creating garden and park paths. |
| M300 | B22.5 | |
| B25 | ||
| M350 | B27.5 | |
| M400 | B30 | Concrete of such grades has not only excellent strength and density, but also a high water permeability grade. Therefore, it is mainly used in the construction of bridges, stairs, swimming pools, basements and many load-bearing structures. |
| M450 | B35 | |
| M500 | B40 | |
| M600 | B45 | |
| M700 | B50 | |
| M750 | B55 | |
| M800 | B60 | Such concretes are distinguished not only by their high strength characteristics, but also by their resistance to aggressive influences. Therefore, they are often used in the construction of special-purpose facilities. |
| M900 | B65 - B70 | Concrete of this type is distinguished by increased strength indicators. Therefore, they are popular in those areas where it is required to erect extra strong structures. |
| M1100 | B75 - B80 | Such grades belong to special-purpose concretes, as they are highly resistant to moisture and aggressive influences. Most often used in the construction of military and hydraulic facilities, mines and bridges |
The success of using fine-grained concrete is not only high-quality raw materials and the correct selection of the composition, but also the competent use of building material, in accordance with the recommended areas of use.
Composition
The classic constituents of sandy concrete are sand and cement in a 3: 1 ratio. For construction, such a concrete mixture is available, since it is not required to additionally purchase crushed stone or gravel, which are introduced to save cement.
For example: to test a brand for compressive strength, take a sample: 0.50 kg of cement and 1.50 kg of sand (fraction - 2.5-2.8), stir and add 200 g of water, mix until complete homogeneity is formed. This mix is used to fill a demountable form, ram and incubate for 28 days at a temperature of 20 ° C. Samples are tested for compression (at least 3 samples). If the destruction of the sample occurs at a pressure, say 300 kg / cm2, then the cement is assigned the M 300 grade.
You need to know that in order to save cement, it is better to use different fractions of sand.
To improve some properties of concrete, chemical and mineral additives are introduced during preparation.
Cooking process
Regardless of whether you need a fine-grained solution within Moscow or in the region, you can order such a mixture at any plant. You can also cook it yourself - there are certain nuances in the process, but difficulties should not arise.
What to pay special attention to:
- The cement must be as fresh as possible in order to maintain all characteristics.
- There should be no hardened lumps in the solution.
- All fillers are thoroughly cleaned from dirt, clay, impurities.
Distribution of sand into fractions
First, all dry ingredients are prepared, paying particular attention to the sand. The sand should be clean, sifted through three sieves and mixed in this way: coarser in a volume of 50-60% of the total volume, the rest is taken off medium and fine fractions in equal volumes
What sieves are used:
- Coarse fraction - 5-1.25 millimeters.
- The middle fraction is 1.25-0.3 millimeters.
- Fine fraction - 0.3-0.15 millimeters.

Binder compound
Next, sand and cement are mixed. Usually they take Portland cement of grades M400 / M500, corrosion-resistant sulfate-resistant and are suitable. The proportions of the components can be different depending on the purpose of the concrete, operating conditions, other requirements and expected characteristics. To obtain durable concrete, cement and sand are taken in a ratio of 1: 1.5, a weaker one is obtained in a ratio of 1: 1.35.
The standard recipe (1: 3) is not suitable, since the sand is fine and there will simply not be enough cement to envelop each particle. Thus, the mixture is not strong enough and does not meet the requirements.
Measuring water
The volume of water and additives can also vary. If plasticizers are introduced into the composition, then they are added to the measured water. There should be enough water in the composition to ensure the fluidity, density, strength of the solution when solidified into a monolith. The determining parameter in this case is the rheological properties of the working solution.

Connecting components
All components are thoroughly mixed in a concrete mixer container. Here the preparation and compaction of the solution is carried out
It is very important to pay attention to the characteristics of the mixture, to follow the proportions and in case of an increase in the volume of cement, add more water
But it is not worthwhile to deviate greatly from the technology, since such experiments can cause an increase in density and a decrease in strength. If there is not enough cement in the solution, this will affect the comfort of the masonry and may violate the integrity of the structure.
Pneumatic spraying
This technology is becoming more and more popular every day due to its efficiency, quality of the result, speed and simplicity. Fine-grained concrete in terms of parameters is perfectly suited for the specified specific method of installation.
Pneumatic spraying involves applying a mortar using a special gun and mortar (cement, sand, fiberglass). All components are fed into the vessel of the apparatus at the same time, they are already mixed inside and sent to the pipe, where, under the influence of compressed air, a mixture of fiber with a solution comes out. A previously prepared form is filled with such a substance, then the material is rolled with a roller.
A feature of the procedure is that the mixture is constantly exposed to compressed air, even during transportation. This technology makes it possible to improve the quality of concrete by displacing water and the resulting monolith differs from sand-cement in its properties for the better.
Concrete types
Heavy concrete, the composition of which is based on the highest, can be used for different purposes.
Depending on the area of application, there is the following material classification:
- High strength. In the process of mixing, the best cement mixture, clean sand and coarse crushed stone are introduced. The production is carried out using vibrating equipment, which gives the concrete an increased density of heavy concrete. In order to increase the strength, additional components are introduced into the composition - plasticizers.
- Reinforced concrete. It is used for the construction of reinforced concrete blocks, floors and other reinforced concrete structures.
- Quick-setting. It contains a mixture and additional elements, including hydrogen chloride. The presence of additives helps to reduce the hardening time without losing the quality of the final product.
- For hydraulic structures. It is a special type of concrete that is used for the construction of structures in a humid environment.The material is not afraid of exposure to water, and it retains its original appearance even after several years of intensive use.
- Road. It is used for covering highways and is resistant to heavy technical loads.
- Cast. It is created on the basis of a fast-setting cement with plasticizers and a high liquid content in the composition.
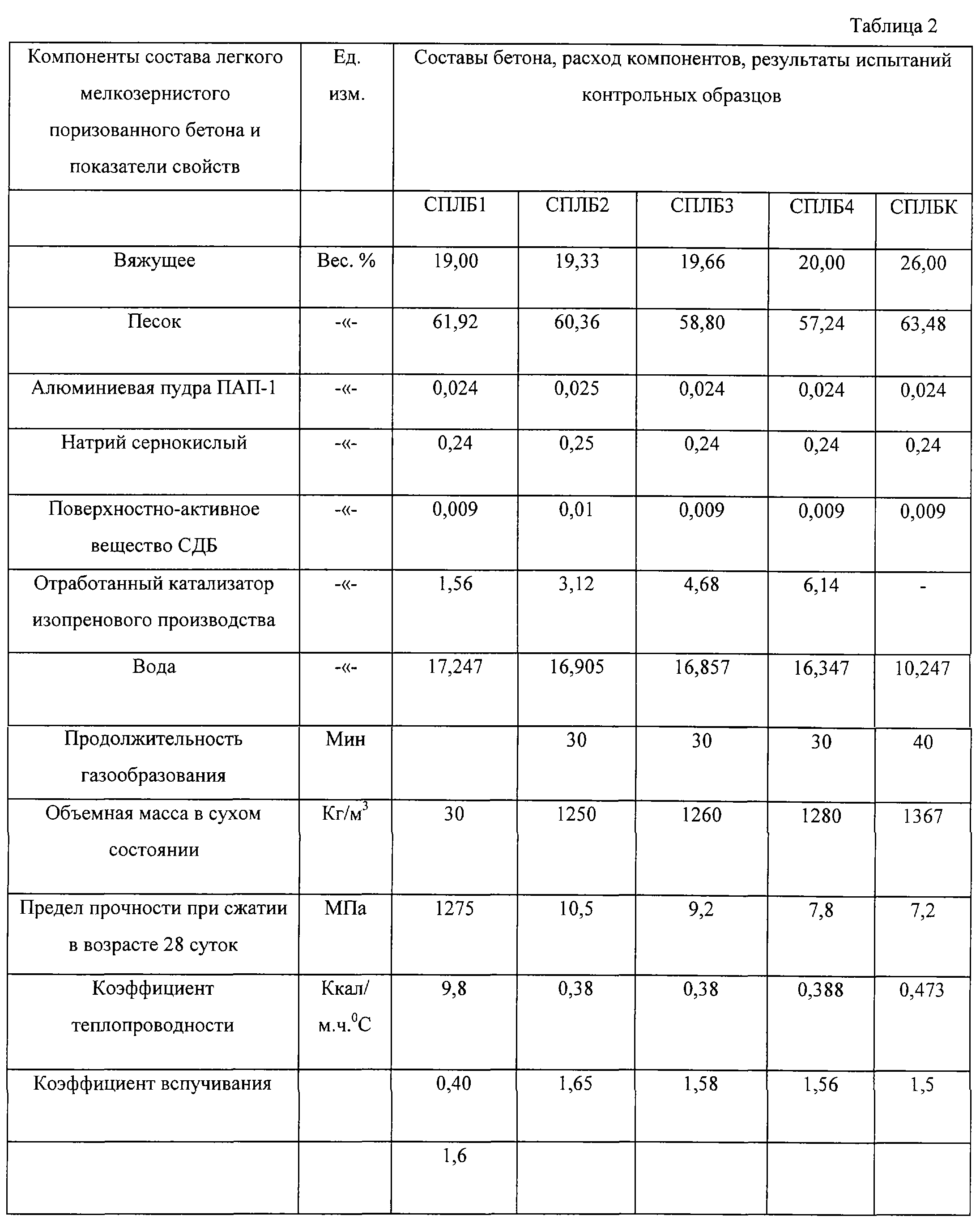
- Fine-grained. It is created on the basis of cement stones without the presence of large and heavy components. It is in demand when erecting buildings with walls of small thickness.
- Acid resistant. It is resistant to aggressive substances and acids, therefore it is used for the construction of chemical-type premises.
- Heat resistant. It is not afraid of prolonged stay in a high-temperature environment. On the base, industrial furnaces are equipped, operating with temperatures up to 12000 ° C.
- Polymer varieties. During the production process, raw materials are impregnated with special resins and polymer additives. This provides an increased degree of strength and reliability.
- Decorative. It is produced with the use of dyes and special fillers such as natural colored marble stone. The material is in demand when building alleys and parks, decorating garden paths and borders, decorating facades, etc.
There are also special ones that differ in their composition and class.
Application area
In most cases, fine-grained concrete is used to create reinforced structures and products. Due to the frequency of the rods of the located reinforcement, the classic solution cannot penetrate into all places, and the fine-grained solution is poured into all hard-to-reach areas.
The main advantage of fine-grained concrete is its mobility, therefore, the mixture is often used in the repair of joints, cracks, and when sealing various deformations. Before waterproofing work, the screed is often prepared by pouring a fine-grained solution. They do not do without a fine-grained solution in road construction, it is relevant for production.

Where fine-grained concrete is commonly used:
Creation of concrete products by the method of ebb (arches, curbs, paving stones, etc.).
Production of thin-walled structures with dense or complex reinforcement.
Preparation of mortars for sealing various types of cracks and seams in monolithic concrete.
Construction of structures and buildings on sand pits, crushed stone.
Laying of road surfaces - high indicators of frost resistance, strength, water resistance of fine-grained concrete are relevant here.
A variety of reinforced cement structures.
Production of small / large diameter, including pipes for the removal of aggressive waters.
Creation of elements for the installation of hydraulic structures.
Casting for the installation of awnings in agricultural buildings (where it is important to cover large spans).
Arched structures for covering impressive spaces (in the equipment of exhibition pavilions, for example).
Bunker structures, outflow of large containers for the storage of liquid / bulk materials, substances.

Basic properties
The main properties of concrete include:
- Strength.
- Water resistance.
- Porosity.
- Frost resistance.
- Thermal conductivity.
- Refractoriness.

Strength
The key indicator of the high quality of concrete is its strength. Heavy varieties must cope with intense loads, therefore high requirements are imposed on the strength properties.
They must be observed both at the stage of mixing the mixture and when solving all construction problems. Since concrete is considered a material with a heterogeneous structure, fluctuations in strength are considered normal.
Water resistance
Concrete is considered to be a waterproof material that does not lose its initial characteristics when it is kept in a humid environment for a long time. Water resistance indicators depend on the ratio of components in the composition and are shown under the letter W. The value range varies from W2 to W20.
Porosity
Even the strongest grades of concrete have small cells, which determine such a property as porosity. The intensity of the porosity is determined by the type and volume of the filler, as well as the ratio of water to cement. The degree of vibration processing and a host of other factors are also taken into account. The base value ranges from 6 to 15%.
Frost resistance
The degree of frost resistance indicates the resistance of the material to the destructive effects of negative temperatures or loads during thawing of moisture after a long winter. Frost resistance means the amount freeze and thaw cycles... The more such cycles, the higher the indicator. Commercially available grades range from 50 to 300 cycles.
Thermal conductivity
The weak point of concrete is its thermal conductivity. Despite the improved strength characteristics and long service life, the material is subject to severe freezing and cannot retain heat inside itself. As the density increases, the thermal conductivity increases.
Refractoriness
Refractoriness is considered the most important property of a material, which determines its resistance to fire. When exposed to temperatures up to 200 ° C, the strength characteristics are reduced by 30%. When the temperature rises to 500 ° C, deformation of the structure occurs.
Types of architectural concrete
According to the composition of the mixture, properties and method of molding, archstone is:
- Geometric - for creating conventional monolithic structures in formwork, in operation it is similar to construction from simple concrete.
- Decorative - for finishing finished structures using various tools and technologies.
- Sculptural - for creating volumetric decorative compositions. It is distinguished by increased plasticity, resistance to external influences, long-term hardening (so that something can be modified in the process). The process of producing sculptures is simple: a frame is created, covered with a mesh, concrete is applied to it, after a light grasping with tools and hands, a shape is created.

According to its intended purpose, the material is white decorative (for finishing facades, various internal surfaces) and white lightweight (for creating products and elements with low weight). Among modern materials for decoration, there are colored and polished and photoconcrete, translucent and textured with formaliners. Complex materials are created only in industrial production on special equipment.
Main characteristics
High-strength fine-grained concretes have many advantages, due to which the service life of the resulting products increases.

A solution of concrete in liquid form has the following characteristics:
- Delamination is minimal.
- The amount of oxygen in the mixture is not more than 1%.
- The density of the structure ranges from 1-1.4.
- Rheological characteristics are maintained for up to 4 hours.
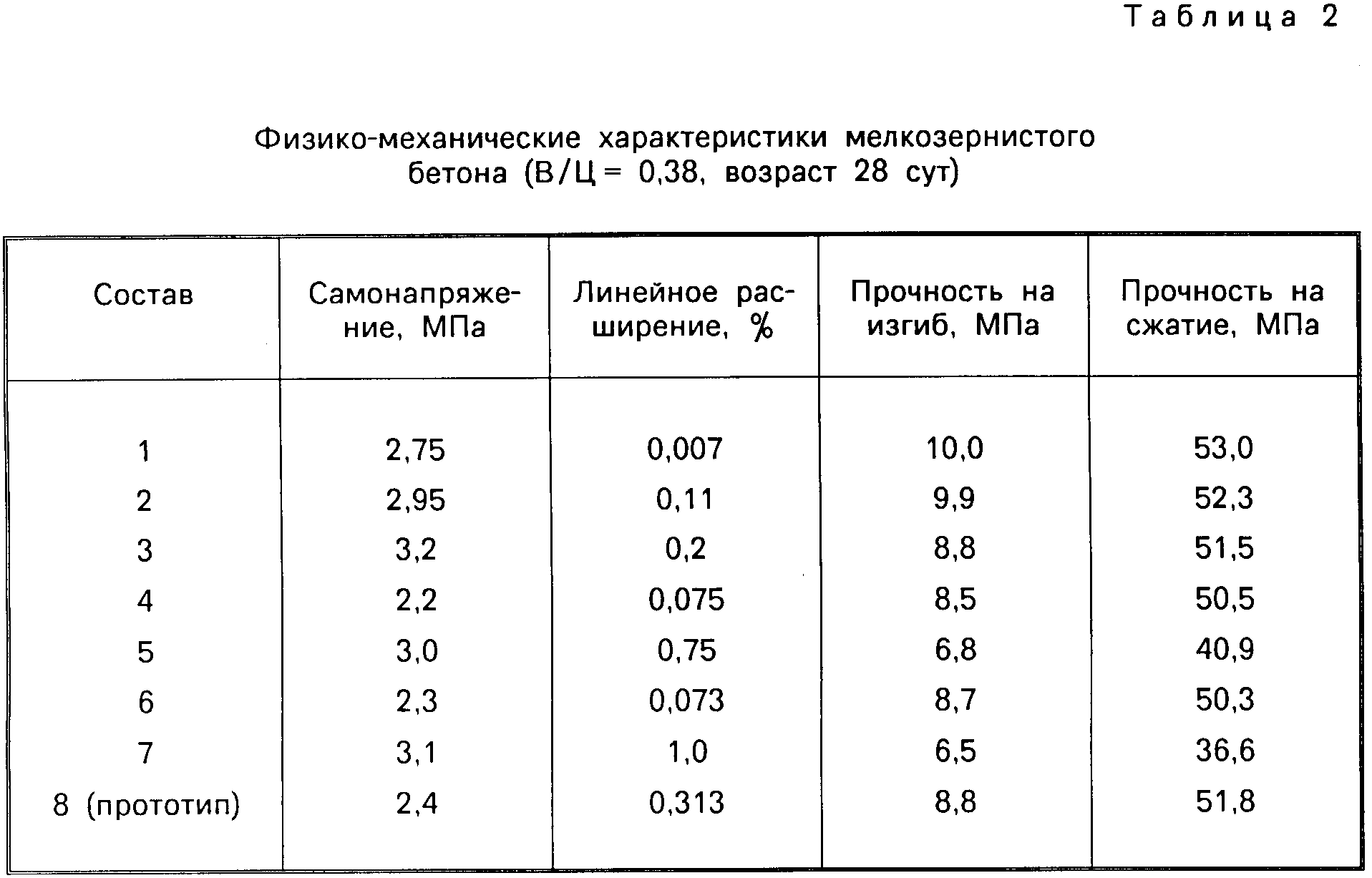
A distinctive feature of high strength concrete is that it retains its working properties for a long time.
This is important, since the material can be transported within two hours to the place where all the work is carried out. But the indicator of the density of the mixture also affects
It must be homogeneous, otherwise the likelihood of its delamination increases in the future.

Cured monoliths of high strength concrete have the following properties:
- Curvature is minimal.
- High wear resistance.
- Press strength - from 50 to 100 MPa.
But it must be remembered that there is a likelihood of microscopic cracks in high-density concrete when squeezed and simultaneously in contact with water.
Preparation of fine-grained concrete
Composition
Due to the fact that the composition of fine-grained concrete does not contain coarse aggregate, an important point in its manufacture is the optimization of the granulometric composition of fine aggregates of various fractions
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of the aggregate, on which the final quality of the composition depends.

Portland cement
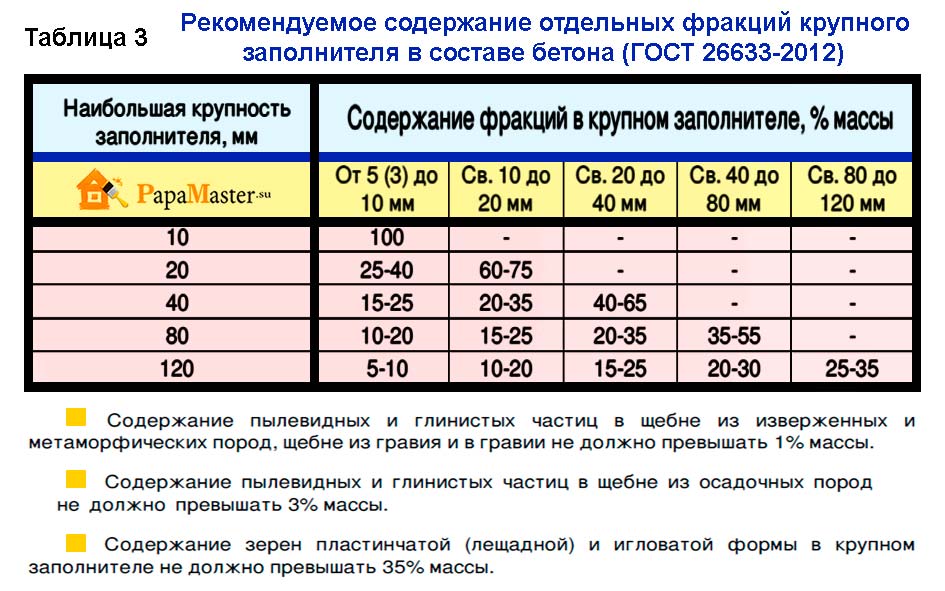
GOST for heavy and fine-grained concrete allows the use as a filler homogeneous clean sand with fineness module no more than 2.5, together with fine crushed stone of fractions - 2.5 - 5.0 mm. The quality of the material can be significantly improved by adding plasticizers. This allows you to reduce the water demand of the solution, the W / C decreases, etc.
As for the binder, heavy and fine-grained concretes in accordance with GOST 26633-91 are based on:
- Portland cement;
- Portland slag cement;
- Sulfate-resistant and pozzolanic cements, as well as other types of cements, depending on the field of application and types of structures being built.

Filler for fine concrete
Features of the preparation of the mixture
With W / C values equal to 0.4 or more, the best strength of the material is achieved with a certain ratio of sand and cement. With an increase in the cement content, the amount of water in the mixture also increases, which leads to a decrease in strength and an increase in porosity.
If the content of cement in the solution is below the optimal rate, then the structure of the material becomes more difficult, which also leads to a decrease in density and its strength.
Therefore, when making a solution, it is extremely important to observe the proportions that are regulated by GOST for heavy and fine-grained concrete.
Note! In some cases, when preparing a cement-sand mixture and using vibrating plants to compact the composition, the mixture draws in air, as a result of which the mass is filled with small bubbles. This phenomenon reduces the strength of the material, as its porosity increases.
Especially the tendency to draw in air appears with an increase in the hardness of the solution.
When dosing the ingredients, it should be borne in mind that when the cement content in the solution is more than 1: 3, there may not be enough cement paste to envelop the sand grains and fill all the voids formed. As a result, the porosity of the mass increases, which significantly reduces the strength of the material.
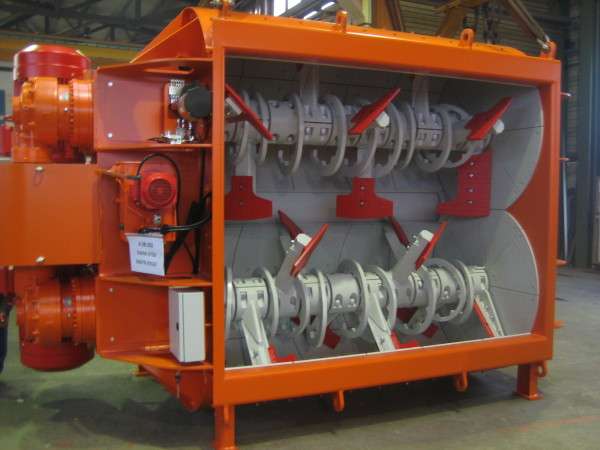

In the photo - a machine for vibrocompression of concrete
As a result of this circumstance, it is rather difficult to obtain durable sandy concrete with a low cement consumption (within 200-300 kilograms per cubic meter). The situation can be somewhat improved by using coarse clean sands or enriching fine sand with fine gravel or coarse bran from crushing the rock.
It should also be said that due to the increased need for water, for the preparation of mixtures similar in mobility and strength to ordinary concrete, the consumption of cement increases by 20 - 30 percent.
To improve the quality of the cement-sand mixture, as a rule, it is compacted in the following ways:
- Pressing;
- Roller seal;
- Vibrocompression;
- By ramming.
Advice! It is advisable to carry out material tests on small samples. To assess the strength, you can use halves of beams measuring 4x4x16 cm. The fluidity of the solution is checked by pouring on the table.

Concrete preparation
Concrete preparation procedure
The instructions for preparing fine-grained concrete are as follows:
First of all, you should prepare fractional sand.
For this, quartz or other sand is preliminarily scattered into three fractions:
- 5-1.25 mm;
- 1,25-0,315;
- 0.315-0.14 mm.
Then the fractional sand is mixed in the following ratio:
- 5-1.25 mm - 57-63%;
- 1.25-0.315 mm - 17-23%;
- 0.315-0.14 mm - 17-23%.
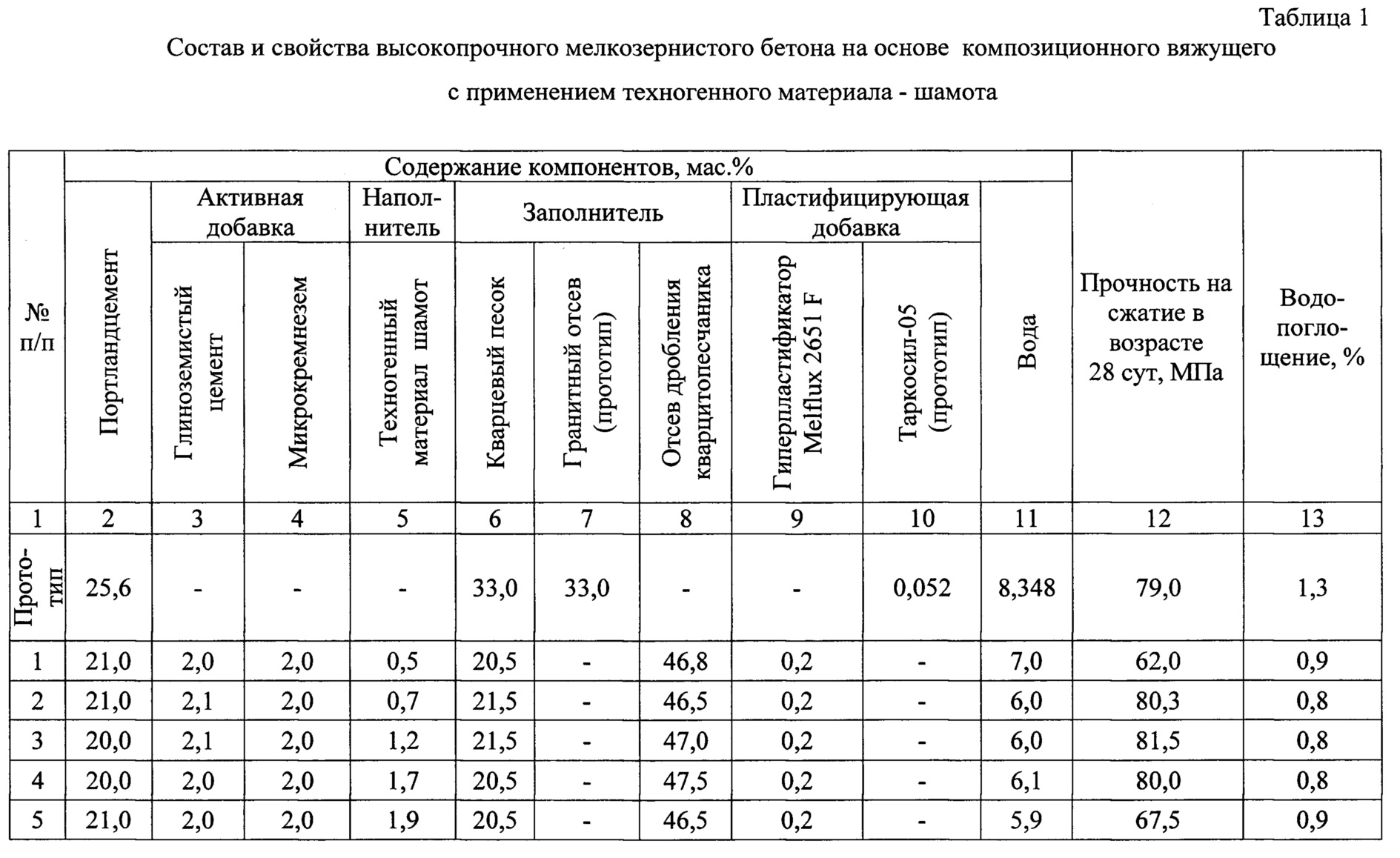
Next, it is necessary to dose Portland cement, fractional sand and a silica-containing component, which is quartz ground sand with a specific surface area equal to 120-170 m2 / kg.
The water is then dosed.

Plasticizer
The next step is the dosage of the plasticizer. For example, you can use Melflux 2651 F.The product must be added to the prepared water.
Further, all of the above components must be added to the concrete mixer, where they are mixed before preparing the concrete mixture. In this case, vibratory installations can be used to compact the composition.
Advice! Certain studies of fine-grained concrete have shown that it is useful to add sodium nitrite to the composition in an amount of two percent by weight of the cement. This additive will prevent corrosion of the thin reinforcing mesh.
This completes the preparation of concrete with your own hands.