Dimensions and weight
There are a large number of clamp models on the market, while the range of possible diameters for all designs is different.
- Worm gear. The smallest clamping diameter is 8 mm, the largest is 160 mm.
- Screw - 18-76 mm.
- Spring-loaded - 13-80 mm.
- Spiral - 38-500 mm.
At the same time, worm clamps have the largest adjustment range. This means that one and the same clamp can be used to secure a pipe both 110 mm and 200 mm in diameter. After installation, the excess part of the clamp is simply cut off. This is actively used by installers.
The sizes of all types of clamps change stepwise and are prescribed in GOST. It also indicates the width of the tape, weight and maximum load.
Standard sizes of worm gear clamps are shown in the table.
The diameter of the plumbing (pipe) clamps is usually indicated in inches (1 inch - 25.4 mm). This is convenient because the size of the pipes is also counted in inches.
For metal models with a hairpin, the number of standard sizes is slightly different.
It should be borne in mind that with an increase in diameter, the width and wall thickness always increase, especially in repair models
This is important when there is a lack of working space or a short pipe length.
The width of the fastening clamps is usually 20-25 mm.
The internal thread of the union nuts usually ranges from M6 to M10. It makes no sense to put large nuts, since the size of the clamp increases greatly.
Nuances of operation
It is recommended to lubricate the screw connections with machine oil or silicone oil before installation. This will not only make the screws easier to tighten, but will also prevent further corrosion. Just keep in mind that industrial oil corrodes some types of rubber.
When mounting, always balance the applied force and the dimensions of the fastener. In addition, the spring clip may jump off and fly to the side when compressed. Be careful.
Make sure that no dirt or dust gets on the work surface. Not only will it scratch the pipe, but it can also lead to premature corrosion.
Tighten screw connections periodically, especially if the pipe is vibrated. If the tool is difficult to operate, buy a wing clamp instead of the screw. No tool is required to tighten it.
Do not allow the screws to become dirty with dust. This not only extends the service life, but also allows the clamp to be reused after removal. The clamp is in good condition without signs of corrosion and is designed for a minimum of 50 assembly-disassembly cycles.
And always follow safety precautions. And also do not skimp on fasteners, because most often the pipe breaks down precisely at the joints.
An overview of useful tools for working with clamps from China in the video below.
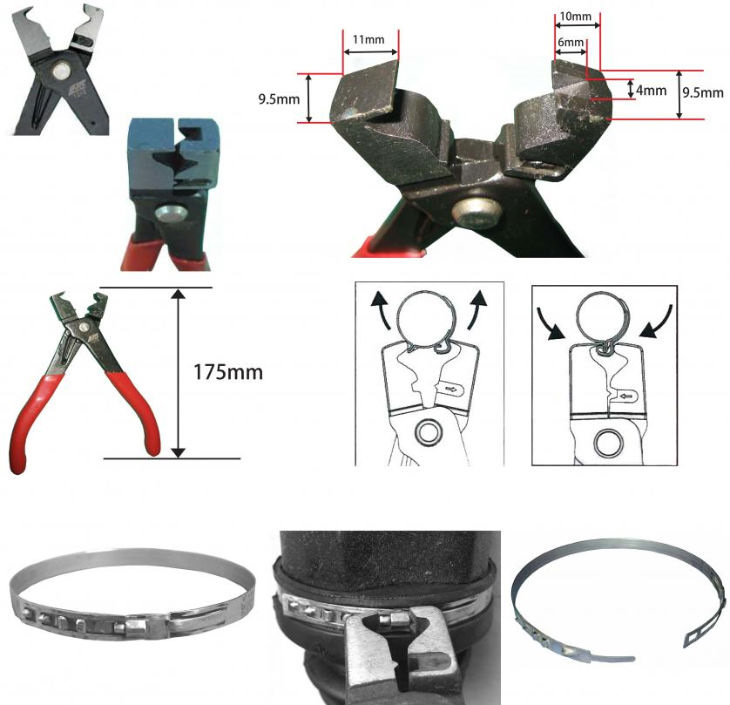
How to tighten the U-shaped CV joint boot clamp
Now the covers are made of harder
material than ordinary rubber. They can be difficult to tighten with
ordinary tape clamps. Therefore, many car enthusiasts prefer
upgraded devices. There are different options for them, among the inexpensive ones -
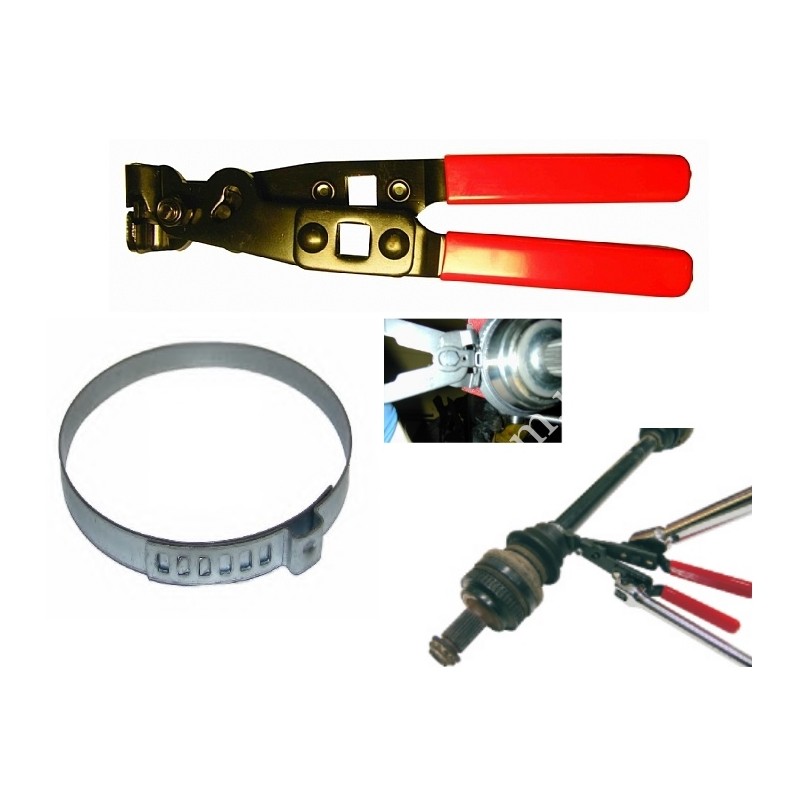
fasteners with U-shaped ears. They are tightened with ticks, most often Licota brands
ATC-2190.

These ticks are a little expensive - up to 20 euros, but
there are also cheaper options. Better to use pliers with a square cutout
1/2. The handles on them can be extended with cranks. Principle of operation
the device is simple: it compresses the U-shaped tubercle on the clamp, and the fasteners
tightens well. Tools with extended handles are especially effective. By them
even covers made of dense material shrink well.
Choose fixtures according to
the manufacturer's recommendations. Make sure that the installation of the clamps is
carried out correctly - then you won't have to worry about replacing them for a long time.
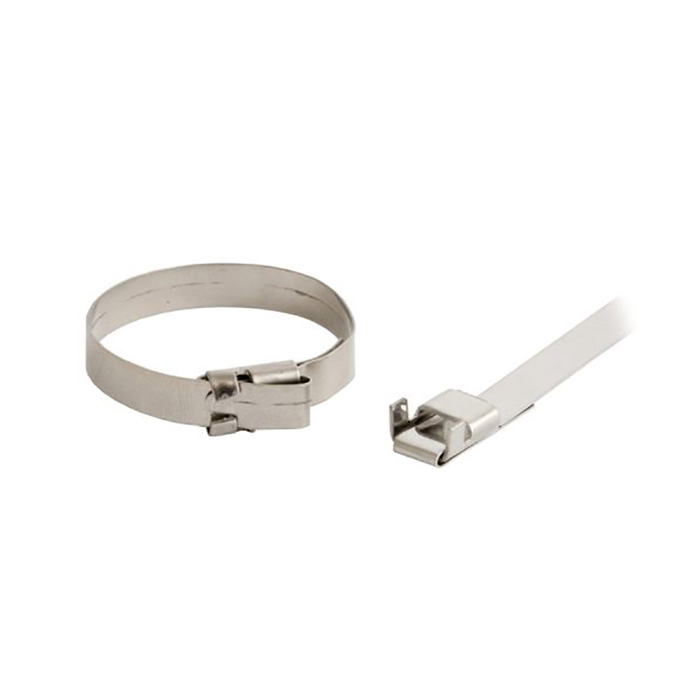
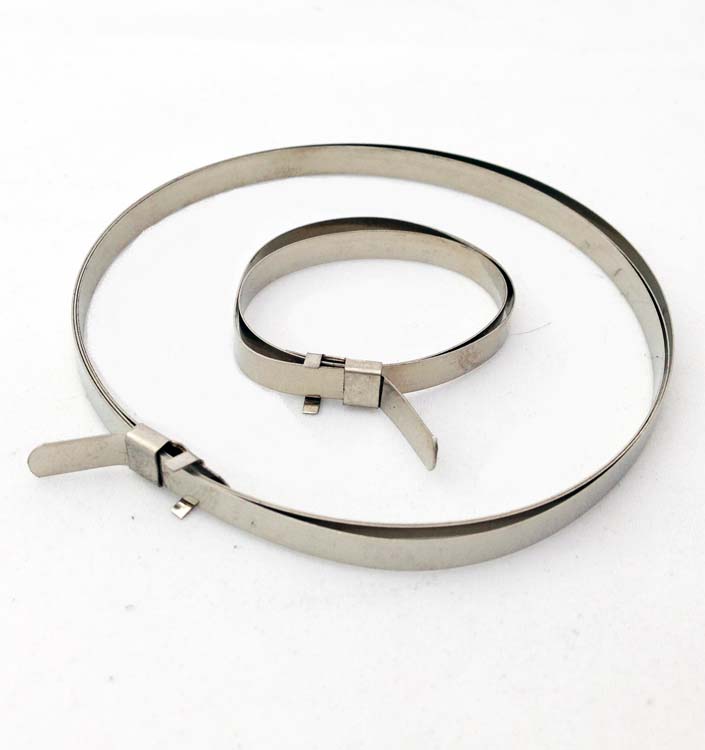
Steel AISI 316
 It would seem that 304 steel is quite enough for the full-fledged performance of all types of work. But what if the installation is carried out in a chloride environment, at facilities with phosphoric acid? Or where seawater, pitting and crevice corrosion are constantly present.
It would seem that 304 steel is quite enough for the full-fledged performance of all types of work. But what if the installation is carried out in a chloride environment, at facilities with phosphoric acid? Or where seawater, pitting and crevice corrosion are constantly present.
In these conditions, it is already necessary to choose steel No. 316. This is an improved version of 304 steel with higher nickel and molybdenum content. For its anti-corrosion properties, it is also called ship steel.
316 steel and polymer coating make it possible to use SKS and SKS-P screeds at facilities with special requirements for the reliability and durability of structures.
They are ideal for areas with maritime climates, on ships, floating platforms, offshore structures, as well as in underground communications and tunnels. They must be used at such critical facilities as nuclear power plants, thermal power plants, subways.
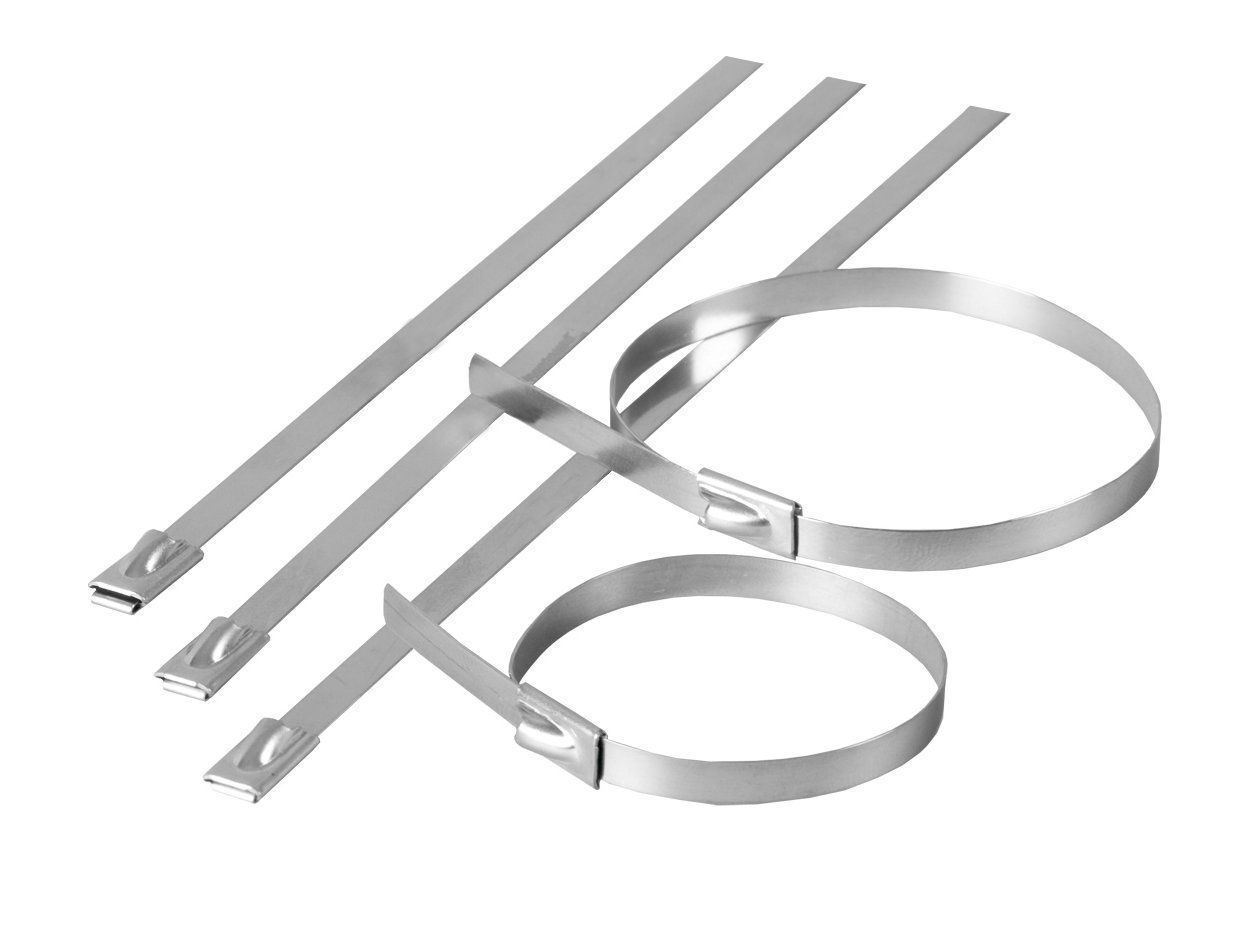
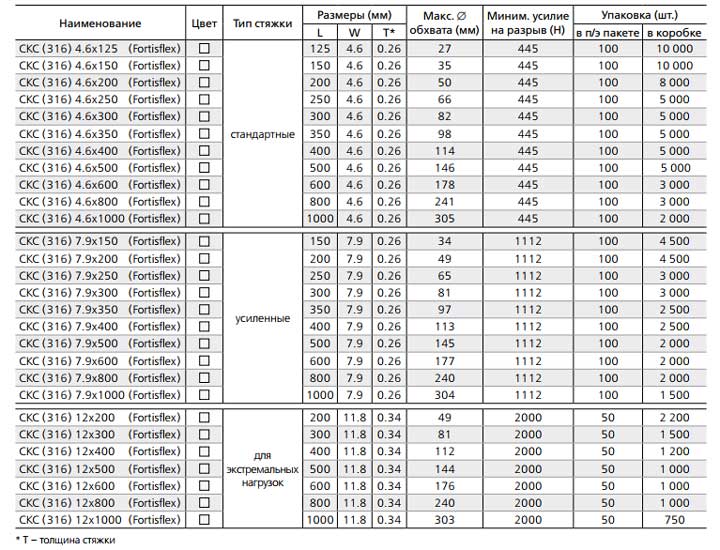
These screeds SKS (316) and SKS-P (316) are presented in three sizes:
standard, 4,6mm wide
reinforced - 7.9mm
for work with extreme loads - 12mm
The length of the ties is in a wide range - from 125mm to 1 meter. Tables of technical characteristics for screeds made of 316 SCS Fortisflex steel:


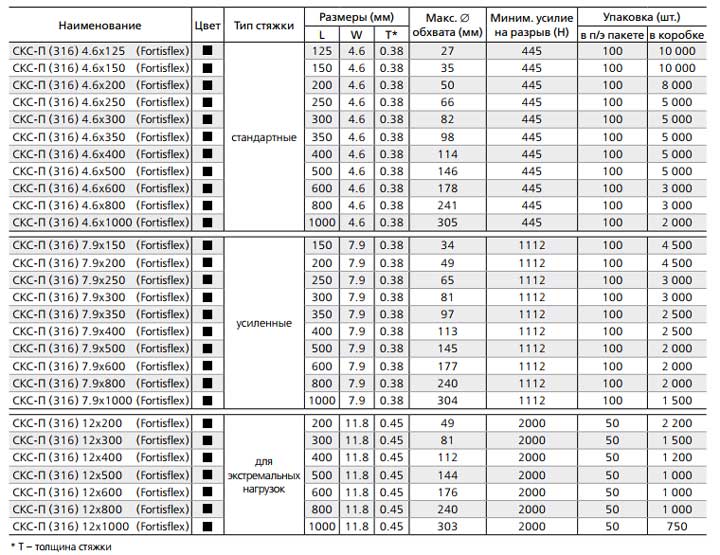
SCV couplers (316)
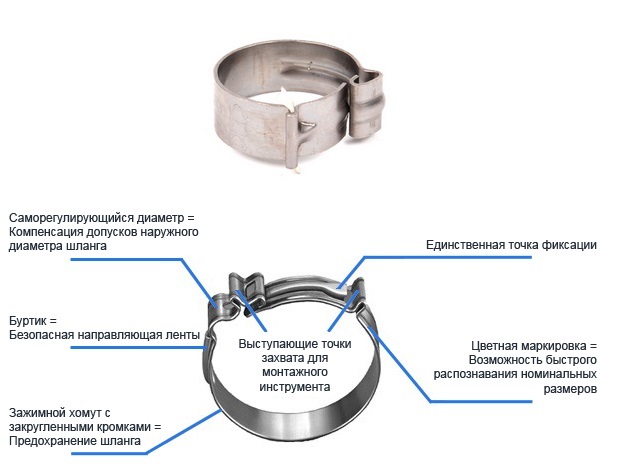
 Due to the wave damper on these ties, the intensity of mechanical vibrations is reduced. Simply put, SCRs are vibration-proof and will not degrade under continuous shaking and vibration conditions.
Due to the wave damper on these ties, the intensity of mechanical vibrations is reduced. Simply put, SCRs are vibration-proof and will not degrade under continuous shaking and vibration conditions.

It is the ideal solution for attaching cables, hoses or pipes to vibrators, test benches, etc. This tie is like a spring, which guarantees a constant tension of the fastener during the entire service life. In addition, SCR (316) compensates for thermal expansion during constant heating-cooling cycles.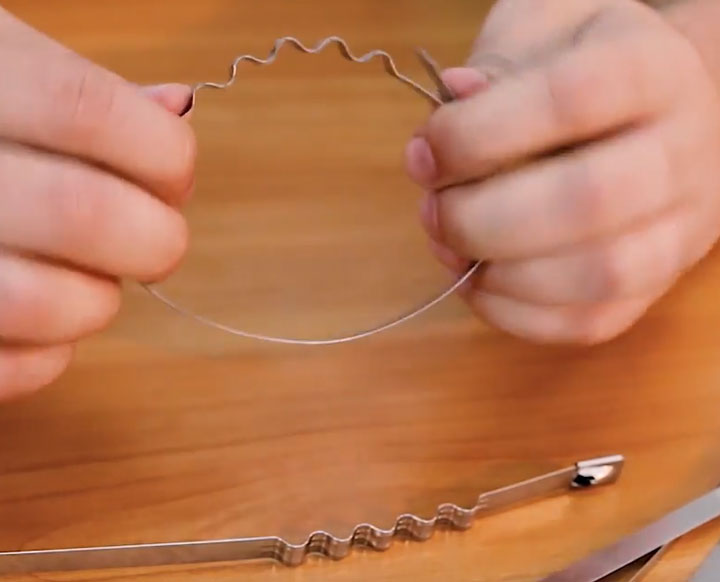
Its operating temperature is from minus 80 to + 538 degrees Celsius.
The SKV (316) also has an automatic self-locking ball-type lock that prevents the belt from going backwards.
Technical parameters and characteristics of SKV 316 fortisflex steel couplers:
SKL coupler (316)
 SKL is a ladder-type steel cable tie. It has a rigid clutch and multilock lock.
SKL is a ladder-type steel cable tie. It has a rigid clutch and multilock lock.
 The holes in the screed blade mesh with the metal teeth of the lock. At the same time, reverse movement is excluded and high strength of the fastening structures is ensured.
The holes in the screed blade mesh with the metal teeth of the lock. At the same time, reverse movement is excluded and high strength of the fastening structures is ensured.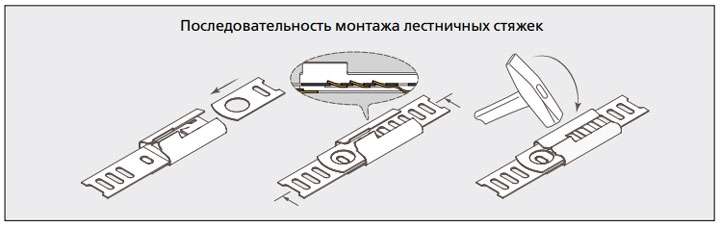
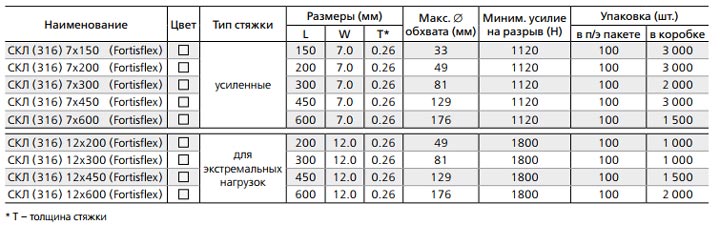
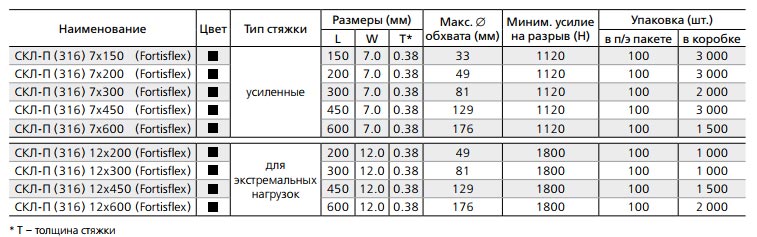
SKL 316 has two main sizes:
reinforced version 7mm wide
screeds for extreme loads 12mm wide
Their length starts from 150mm and ends with a maximum size of 6 meters. SKL is also produced with an additional polymer coating. Their marking is SKL-P (316).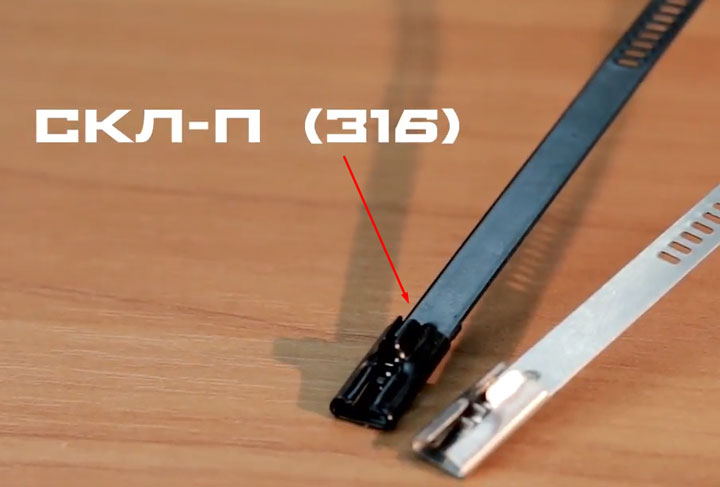
The round hole at the end of the tie is needed to tighten the tie with a special lashing hook.
Technical data and characteristics of SKL and SKL-P 316 (dimensions, wrap diameter, tightening force):

Coupler SKB-P (316)
 SKP-B stands for cable tie. During installation, the tie strap is bent into the yoke lock mechanism. The result is a reliable clamp.
SKP-B stands for cable tie. During installation, the tie strap is bent into the yoke lock mechanism. The result is a reliable clamp.
Lug-shaped side clamps provide additional fixation of the tape in the lock.
Such a tie is reusable and can easily be used several times on various fasteners. The polymer coating protects the product from galvanic corrosion between heterogeneous materials.

Specifications and size table SKB-P:
Benefits from the OPM company
In the OPM company catalog, fasteners are widely presented not only for industry, construction or everyday life. Also here you will find ties, clamps for connecting a wide variety of types and types of pipes - plumbing, water, gas, heating, etc.
If necessary, you can be consulted on all issues related to the use of one or another type of fastener in this section, be it a tie or a clamp.For each specific task, the necessary and most suitable fasteners will be selected for each individual case. All products are only from leading world and domestic manufacturers, which guarantees its high quality. We have ties, clamps, clamps and much more. More details can be found here:
Goods
1 - 44 of 44
Home | Prev | 1 Track. | End
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
Goods
1 - 44 of 44
Home | Prev | 1 Track. | End
|
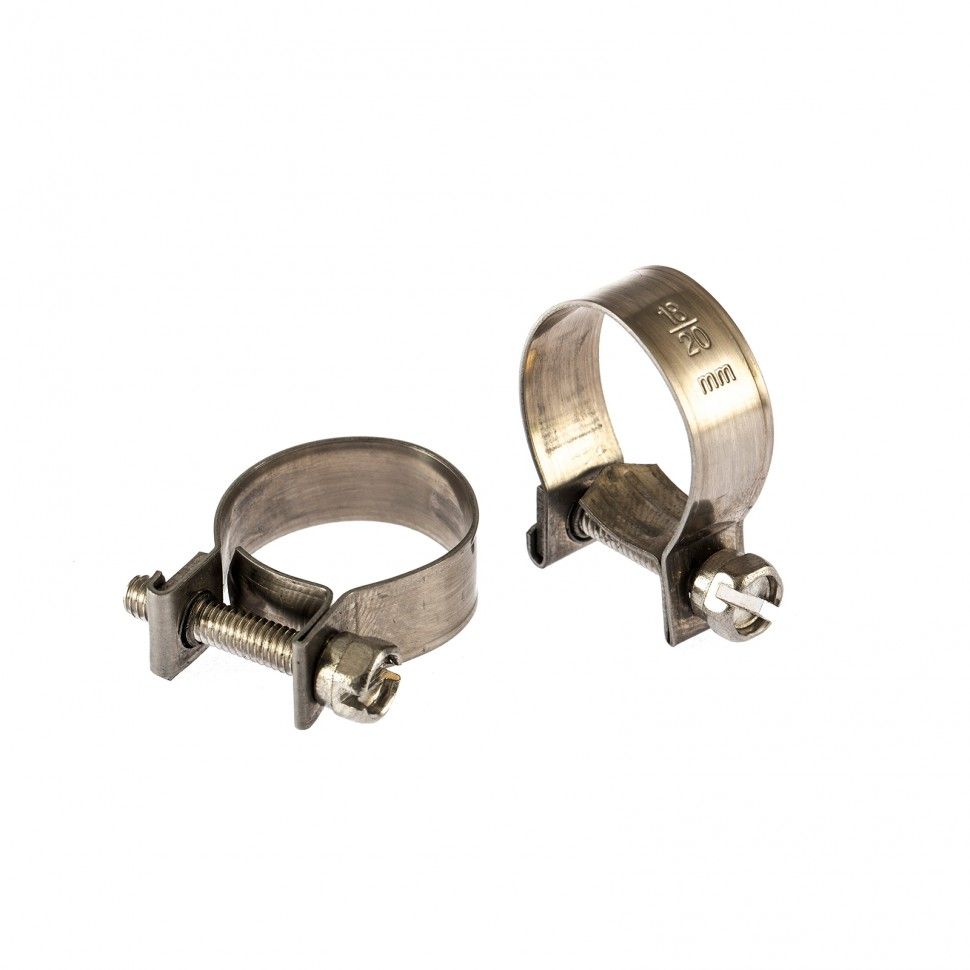
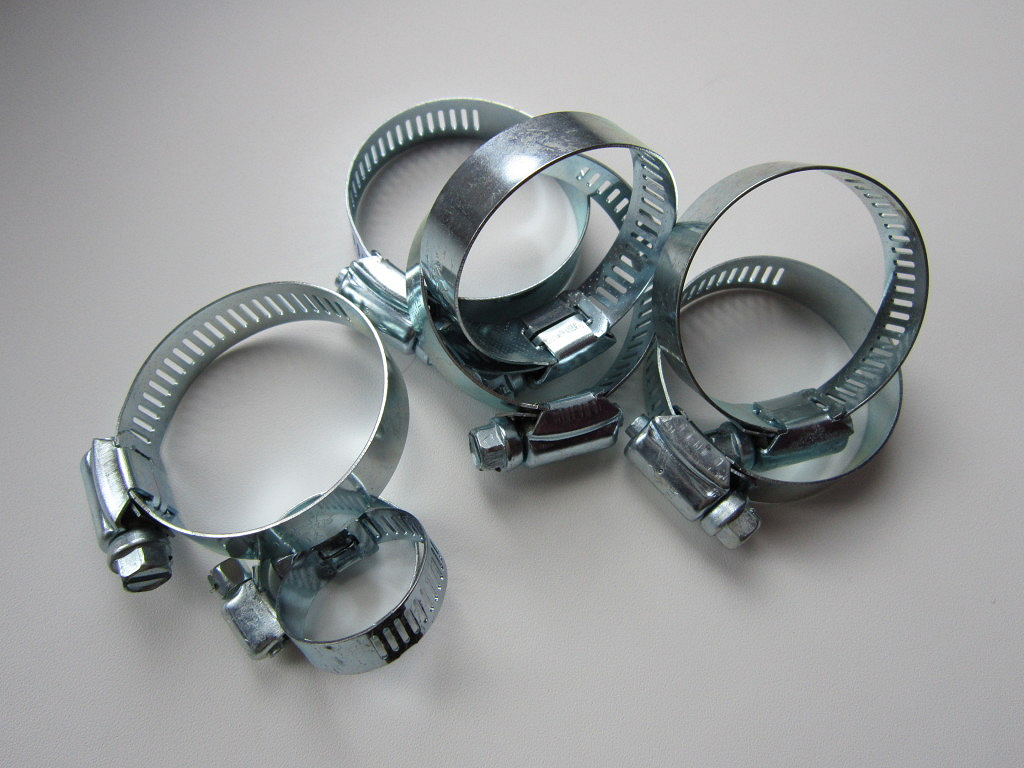
What are the metal clamps for high pressure hoses
Crimp metal reinforced clamps are equally important for main pipelines and flexible hose lines. For such systems, either worm-type clamps or power ones are provided.
Hose clamps have a large clamping ratio
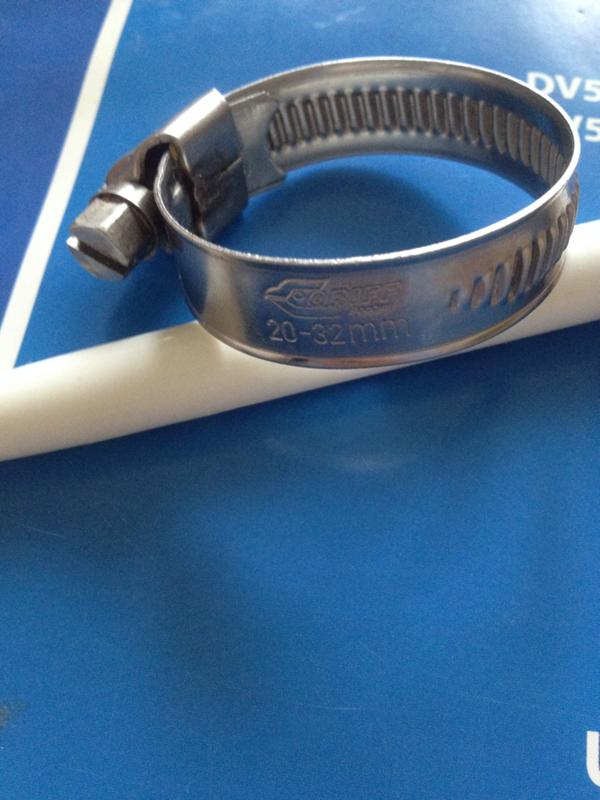
Worm Gear Hose Clamps
The worm-type fastening is a ring with a bolt and serifs, which are applied to the inner edge of the clamp. This helps the fixture to hold the connection more tightly.
You can fix the fasteners with a Phillips screwdriver
Power Clamps for High Pressure Hoses
Devices for fastening the power type in connections do an excellent job with their tasks, while there are several subspecies of them:
- strip and wire galvanized have a bolted connection as a clamp;
- reinforced hose clamps - have clamps on both sides;
- universal cast, equipped with two bolts.
Such clamps are equipped with fastening bolts and have massive spacers.
All these types of clamps are made exclusively from stainless steel. All of them are equally easy to use and relatively cheap, so some stock of such fasteners on the farm will not hurt.
We recommend watching a video review of clamps, which tells about the purpose for which this or that type is used, which of them is better to buy.
Dear users, if you still have questions on the topic of the publication, be sure to ask them. Our team will be happy to answer them as soon as possible. If you have experience using this or that crimp - share it with us.
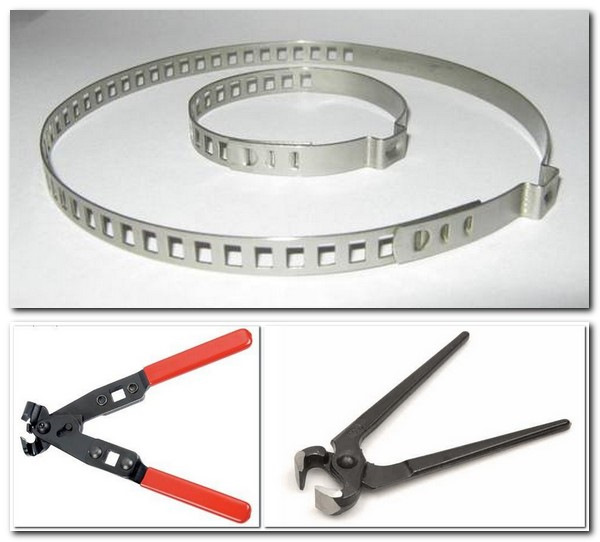
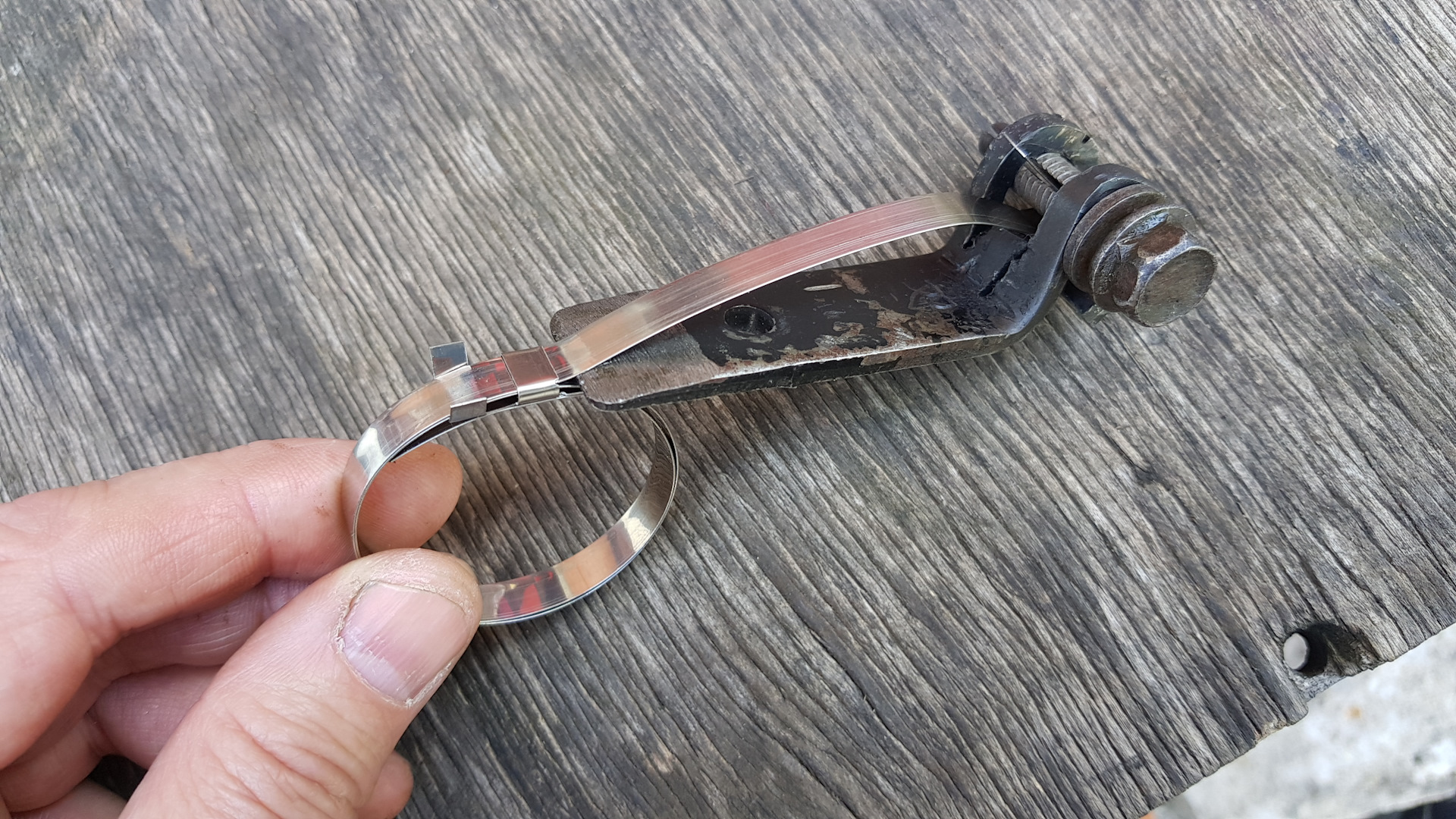
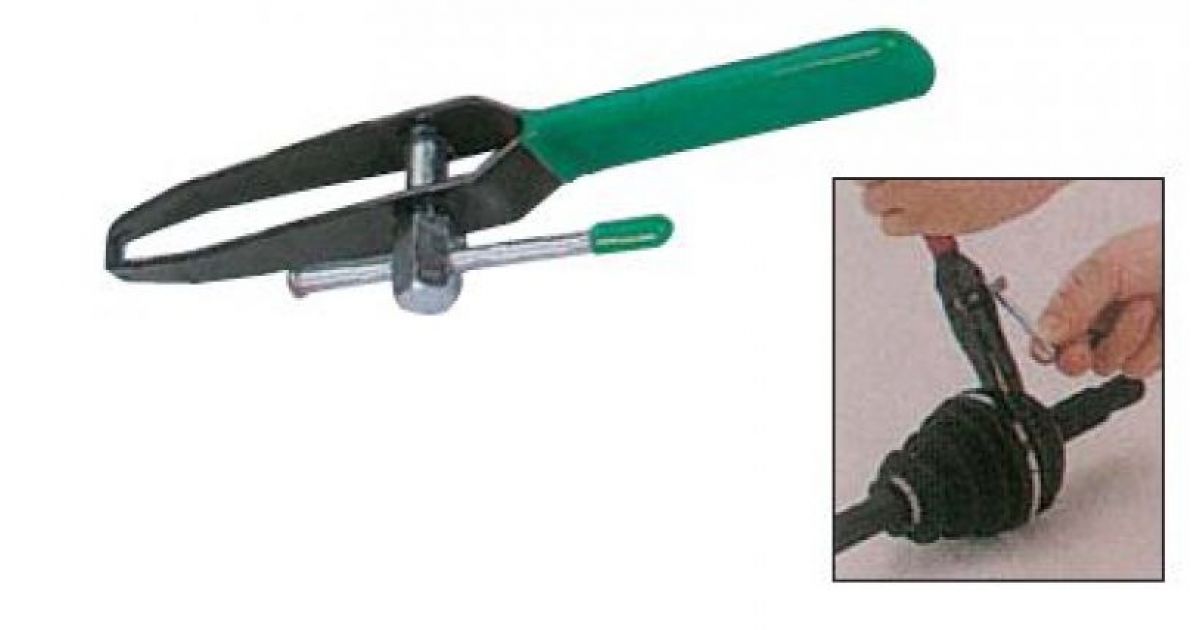
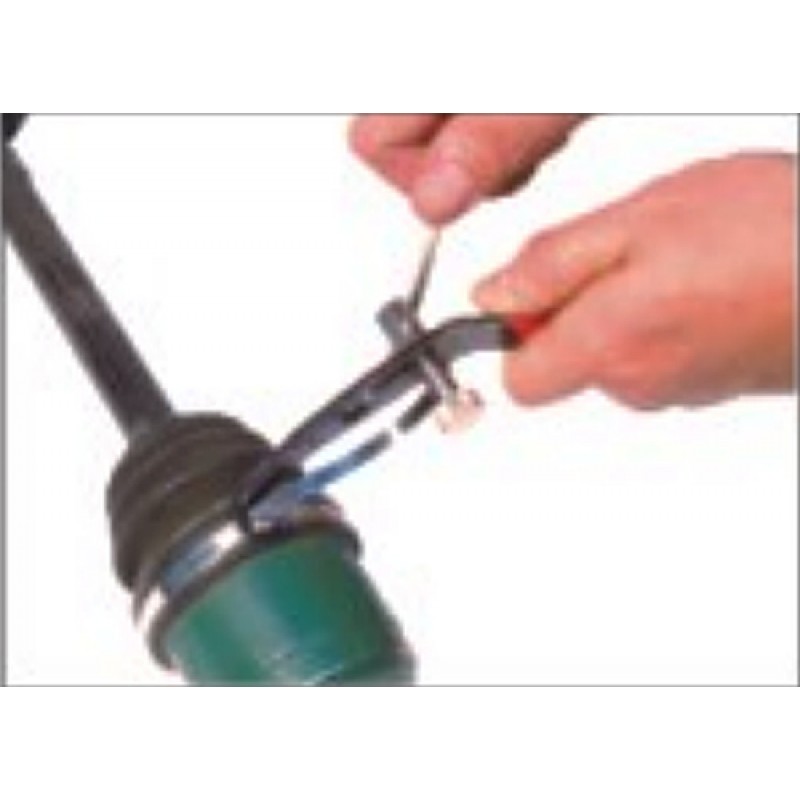
How to tighten the band clamp on the CV joint - manual method
Installing such a device is easy, and
its fixation is reliable enough.When choosing a device, look at the quality
steel from which it is made. To fasten it, you will have to use
device for tightening tape clamps. To tighten the device, you can
apply pliers.

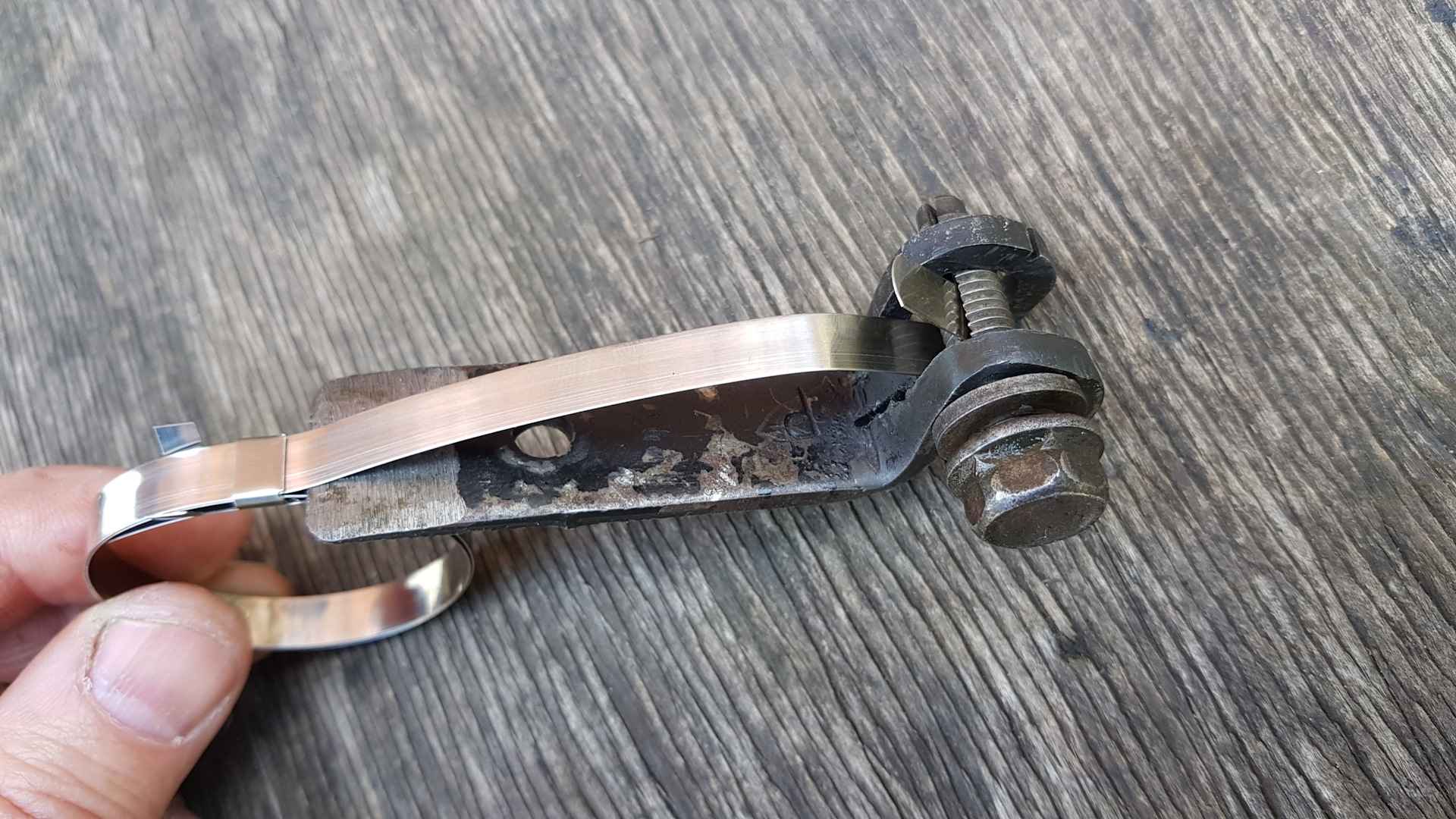
We act like this:
- We put the clamp on the boot,
grab its tip with pliers. - Then we pull the tip towards ourselves,
making an effort. During the procedure, we make sure that tightening
happened without distortions. - We wind the tip up a little and
bend the antennae. - Fasten the end of the tape. By
at the end of the installation, we check the uniformity of the fit.
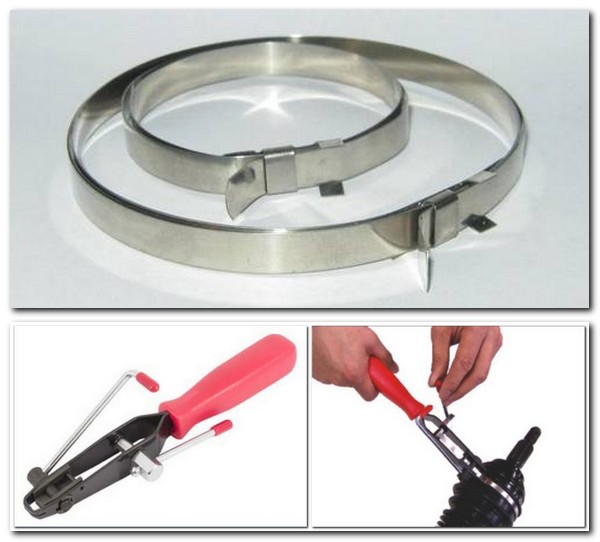
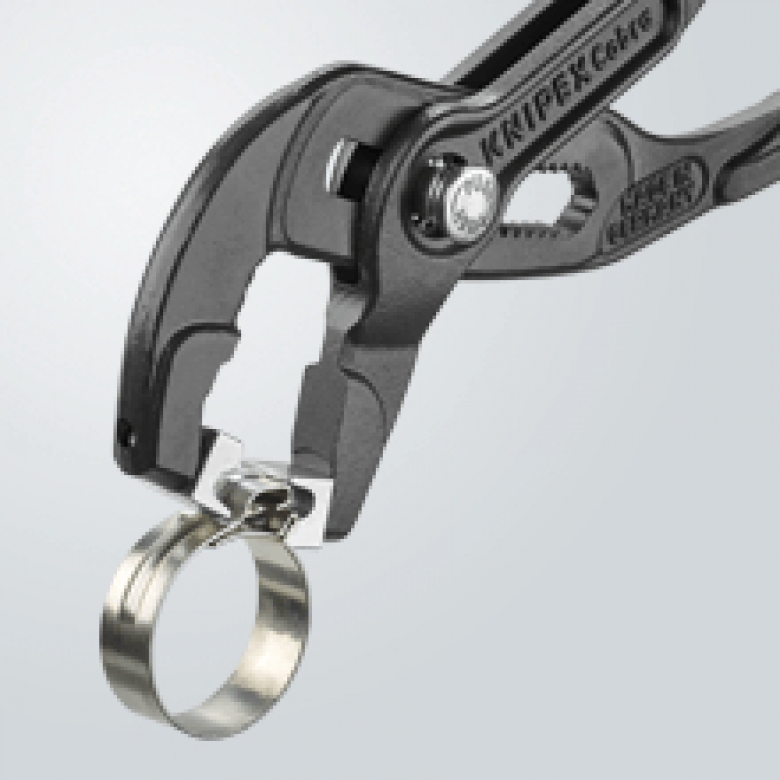
But how to properly carry out the procedure using
tightening machines:
- Place the tape on top of the boot.
We insert its tip into the holder (there is a cut for this). - Press the holder to the lock
collar. - We wind the tape on the tool
rotational movements. When the tension is normal, bend the tape. - We control the installation.
Consider the pulling force. Grease should not come out after tightening
out. If you overtighten, the boot will burst.
The procedure for replacing the boot of the outer CV joint
The procedure for replacing the boot of the outer CV joint, which has a unified design, is identical for most cars with front-wheel drive. Work is carried out on a flyover or inspection pit.
Required tools
The minimum set of tools required to complete the repair:
- mechanical or hydraulic jack;
- wheel stops and auxiliary stands for supporting the body;
- a metal brush for cleaning the surface from adhered dirt;
- hammer and chisel;
- cleaning rags;
- a set of wrenches and heads;
- torque wrench;
- flat blade screwdriver and pliers;
- a spatula for applying grease into the cavity of the cover.

Progress
Sequence of actions when replacing the external boot:
- Put the car on the pit, apply the hand brake and place stops under the rear wheels.
- Loosen the nuts or bolts securing the wheel to the hub, and then raise the body on a jack.
- Install safety stops under the threshold (if they are absent, it is allowed to use a spare wheel with a board).
- Dismantle the wheel, and then remove the retainers of the central nut (a cotter pin or the bevel of the nut bent into the grooves is used to hold it).
- Unscrew the nut, to complete the procedure, you will need the help of a second person who presses the brake pedal.
- Dismantle the brake pads and the caliper, which folds to the side (removing the hose is not required). The caliper is bolted to the steering knuckle, the size and position of the heads vary by vehicle model.
- Pull off the brake disc. If the part is stuck to the hub, then you must use a hammer. The blows are delivered through a wooden spacer that prevents damage to the surface of the disc.
- Remove the bolts connecting the hub and strut housing. Before disassembling, clean off the dirt layer with a brush and wipe the surface with a rag.
- Pull the hub towards you, moving the shaft splines out of the hole.
- Dismantle the old cover using a knife or screwdriver. Old clamps are removed at the same time; it is not recommended to reuse the fasteners.
- Carefully remove old grease with traces of water or dirt from the joint surface. The grease is removed with a wooden spatula and a clean rag or rags.
- Remove the outer hinge together with the body. To complete the task, you will need the help of a partner who does not allow you to disconnect the shaft hinge near the gearbox housing. The hinge is removed from the axle using a chisel and hammer (the design uses an internal retaining ring, which compresses on impact).
- Wipe the shaft and CV joint from grease residues, it is allowed to disassemble the unit and wash the parts with gasoline.
- Assemble the assembly and apply a layer of lubricant to the parts, the substance is tightly packed into all cavities and grooves.
- Put a new boot on the shaft, a portion of grease is added to the cavity of the boot.
- Connect the hinge and the axle shaft, having previously aligned the landing teeth.
- Put on the clamps on the regular places, and then install the removed parts. When tightening the threads, the tightening recommended by the manufacturer is required.

Option without removal
The procedure for removing and installing the boot without disconnecting the shaft and the hinge involves the use of a special tool that stretches the rubber boot. The method is used in cases where it is impossible to separate parts without destroying metal elements (due to corrosion or design features).
Possible problems
A common problem is the adhesion of the joint to the shaft. If the hub is fastened with a bolt, then to separate the parts, it is necessary to screw the bolt into the hole until it stops. After the part rests against the end of the axle, you should still make 2-3 turns with a wrench, which will allow you to remove the hinge. If the fastening is carried out with a nut, then you will need to completely remove the axle shaft, and then clamp the drive in a vice. Tight fixation of the part will allow you to knock down the hinge with a chisel, but if the contact cannot be disconnected, you will have to cut the inner ring of the CV joint with a grinder.
Self-production
If it is impossible to purchase a factory clamp, making fasteners with your own hands will not be difficult. The crimping element can be made from a 1 mm thick galvanized sheet. To do this, you need to cut a strip, the width of which can be 4-8 cm. To determine the length, measure the pipe diameter and multiply by 3.14. The resulting numerical value will be the length of the strip. To this value, you need to add another 3-4 cm, necessary to form the fastening ears, and then cut out the workpiece.
On the sides of the strip, two holes should be drilled at a distance of 5-7 mm from the edge. If it is planned to manufacture a wide clamp, the number of holes should be increased. So, for products up to 6 cm wide, two fasteners are enough, while for a model 8 cm wide, 3 bolts are required. After checking for the coincidence of the holes made, insert the gasket into the clamp and tighten the bolt.

A simple device, low cost and easy installation significantly expand the scope of use of clamps, distinguish them favorably from other fasteners and allow you to install them yourself.


For a stainless steel pipe clamp, see the next video.
How to make a wire clamp - step by step diagram
Step 1: measure the required wire length
First of all, let's bite off the wire as much as the diameter of our connection requires. We do not need measuring instruments, it is enough to wrap the edge of the wire around the branch pipe and estimate the ends for twisting by eye, usually 50-60 millimeters are enough. Then we fold the wire in half and bite off the excess with pliers. We bring the ends together, so that they are on the same level.
Step 2: Correct Clamp Design
Now that you have a double-bent wire in your hands, you need to make the correct "eyelet" at the place of the fold, and the diameter of the "eyelet" must coincide with the screwdriver, which must freely enter it. To maintain this size, it is enough to unbend the ends, insert a screwdriver between them and bring them together again. Of course, a Phillips screwdriver is best suited for such purposes, it is flat along its entire length and does not have expansion, unlike a flat one. Next, you need to bend the resulting "eyelet" to the side, relative to the length of the wire, it will serve as a lock.
Step 3: detailed installation of a homemade clamp
You just made a clamp from DIY wire, nothing, if it looks unprepossessing, the main thing is that it performs its functions efficiently.It remains to install it in its place of honor and twist it tightly. To do this, go around it around the pipe, always in the form in which it is, namely doubly, and cross the ends together. Then we insert a screwdriver into the “eyelet”, catch the second end and turn it clockwise several times until a tight connection appears. Remember not to be too zealous during clamping, you should feel when to stop so that the wire does not burst. If there are too long ends on the newly installed clamp, we recommend that you bite them off with pliers.
It is possible that the first time you will not be able to install a self-made wire clamp, you may not be able to twist, or you will drag it, but do not despair, repeat the procedure for making the fastener again. We are sure that after several attempts you will get a high-quality and tight connection, and this simple technology will always help you out in difficult times. Patience and a little effort! But still, keep several clamps of different diameters on the farm for the future, they will definitely come in handy!
Design features and purpose
The clamps are made in the form of rounded plates that clasp the pipes and hold them with bolts. For a tighter fixation of the pipeline and to reduce the mechanical load on the fasteners, the structure provides for sealing gaskets made of profiled rubber or food-grade rubber. It evenly wraps around the pipeline and protects it from damage when tightening the staples. On some models, the tightening nuts also have gaskets and sealing elements to ensure a tighter fit between the elements.
The scope of use of clamps is very extensive. Elements are used to securely fix water and heating pipes to the walls, which provides the structure with complete immobility and is often a prerequisite for arranging communications. Clamps are widely used as sealing brackets for weak joints and leaks. The staples firmly press the gaskets against the damaged area and eliminate the leakage. Products can be applied to vertical and horizontal pipelines and installed at any temperature and humidity. Due to the presence of a rubber seal, models are often used to ground the water supply system.
Often, with the help of clamps, they block the hole from the inset, the need for which has disappeared at the moment. The part perfectly copes with corrosion damage, cracks of small and medium size, and is indispensable for pipe fractures. In these cases, a special type of clamps is used, fixed to walls or ceilings and supporting the damaged area. Fasteners can be installed on reinforced concrete, plastic, cast iron, steel, copper and aluminum pipelines and can replace the welding process. The only limitation on the use of clamps is their installation at cross joints and curved sections of the pipeline. In such curved structures, the use of clamps is ineffective.
The main difference between clamps and fittings and other shaped parts of the pipeline is the moment of their installation. And if other elements are mounted into the system in the process of its formation, then the clamps are installed on the already finished structure and complete the stage of its installation. One of the important performance properties of clamps is their ability to allow longitudinal movement of pipes resulting from linear expansion. However, lateral displacement is not possible in this case. Thanks to this quality, the pipeline can react to temperature changes in the network, while remaining immovable and rigid structure.
Despite the relative simplicity of the device, strict GOST requirements are imposed on all types of clamps. This is due to the functional significance of the models and their significant impact on the overall strength of backbone systems. Each type of fastener has its own standards. So, marking 24137 80 regulates a number of requirements for metal products in the form of a horseshoe, a ring and two half rings. The document specifies in detail the standard sizes, steel grade, maximum permissible loads and the value of the maximum tightening. The set of each product necessarily includes a fastening in the form of a self-tapping stud, a plastic dowel or a connecting nut. Polymer models comply with the requirements of GOST 17679 80, which also specifies the design characteristics and features of the use of plastic products.


Do-it-yourself clamp-tie
Immediately, I note that the use of homemade cable ties is more suitable for emergency cases. When choosing fasteners for electrical wiring, preference should be given to professional (purchased) fasteners. This will save you time and hassle, and will contribute to the longevity of the wiring harness.
But there are times when you have not calculated the number of cable ties required for the installation of electrical wiring, or you urgently need to fix one wire on the surface and the ties are over, but there is no store nearby or it does not work. What to do then? You can get out of the situation by making screed clamps with your own hands.
Cable tie clamp
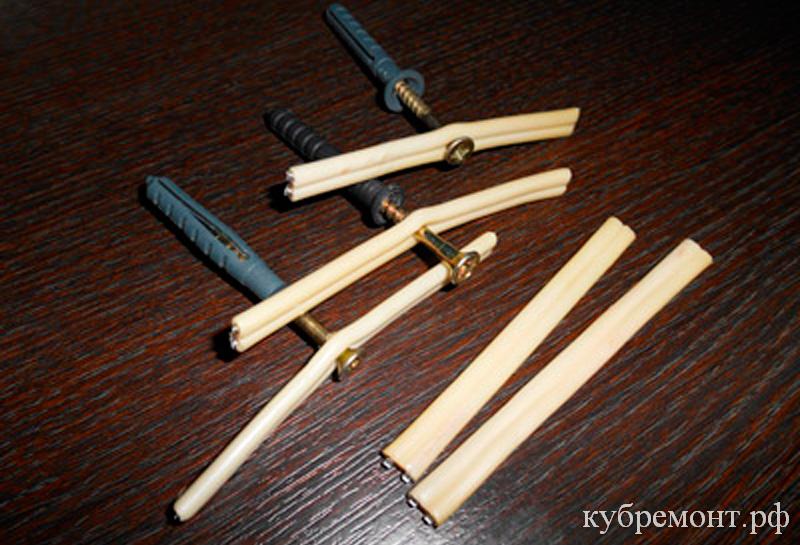

To make a cable tie-clamp, you will need ordinary dowel nails, preferably with a flat head and cable cuttings remaining after installation. If the cable is flat two-core, then we drill a hole, punch a piece of cable in the middle between the cores, so that from both sides remained the same in length the segments with which we will tighten the mounted electrical wiring.
If you use one core of the cable, then the cut prepared taking into account the required length must be bent in half, and wrap it in several coils around the dowel or screw. Then you need to hammer in the dowel or tighten the screw and fix the wiring with the free ends of the trim.
Clamp-coupler made of metal
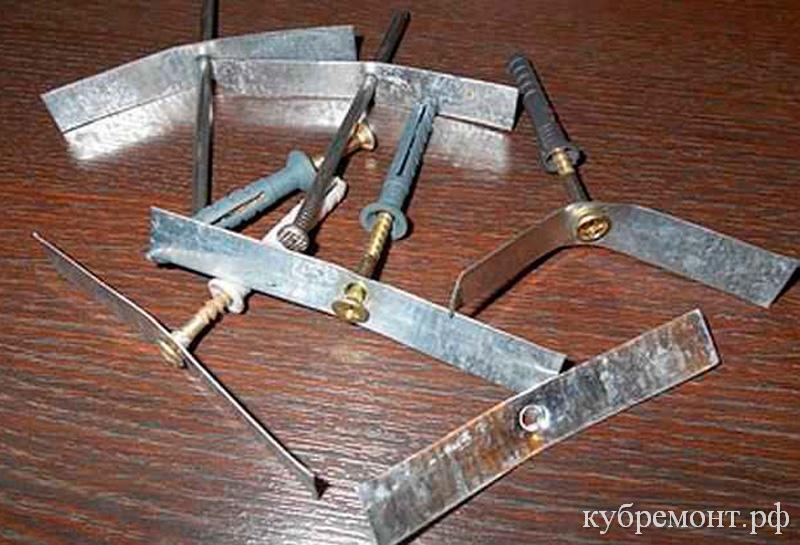

Metal strips can also be used for homemade screed clamps. Despite the fact that this method of fastening electrical wiring is quite ancient, such strips of thin galvanized steel can still be found in electrical shops. Recently, however, preference has been given to more modern materials.
In the absence of a purchased metal strip, you can cut thin metal strips yourself. For greater reliability and durability, it is better to use galvanized steel for this, but in extreme cases, you can use the old old-fashioned method - cut strips of metal from a tin can.
A strip of metal cut off to the required length is punched with a dowel or screw and fixed to the surface. The wiring is fixed by bending the edges of the homemade metal clamp into the lock.