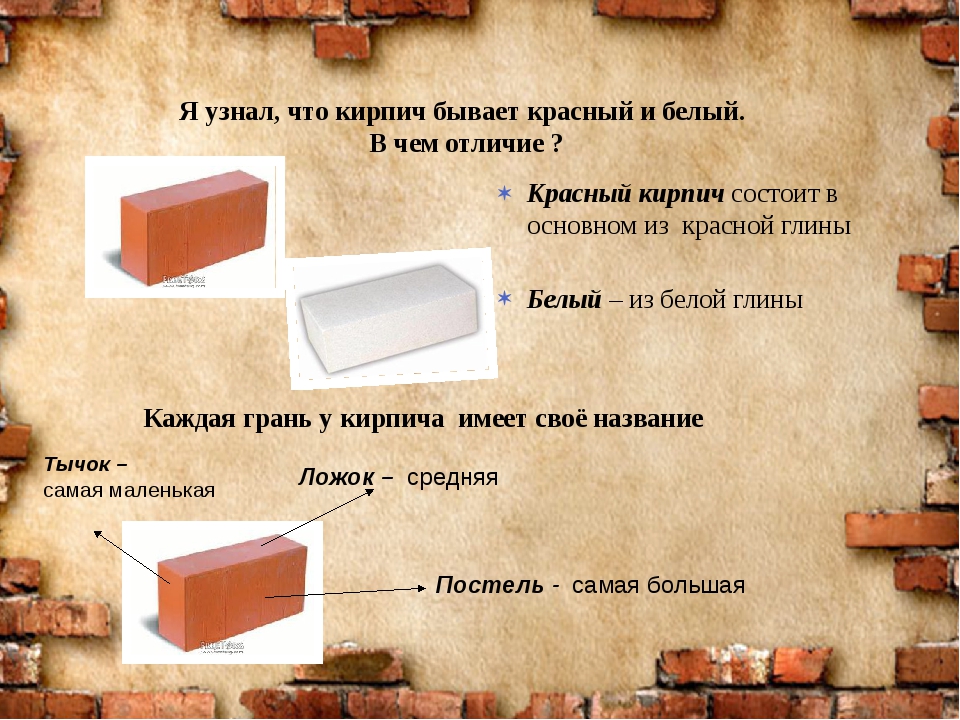
Types of bricks, manufacturing methods and applications
Bricks are classified into four main types: silicate, facing, refractory and ceramic. To understand their purpose and properties, it is necessary to consider each type separately:
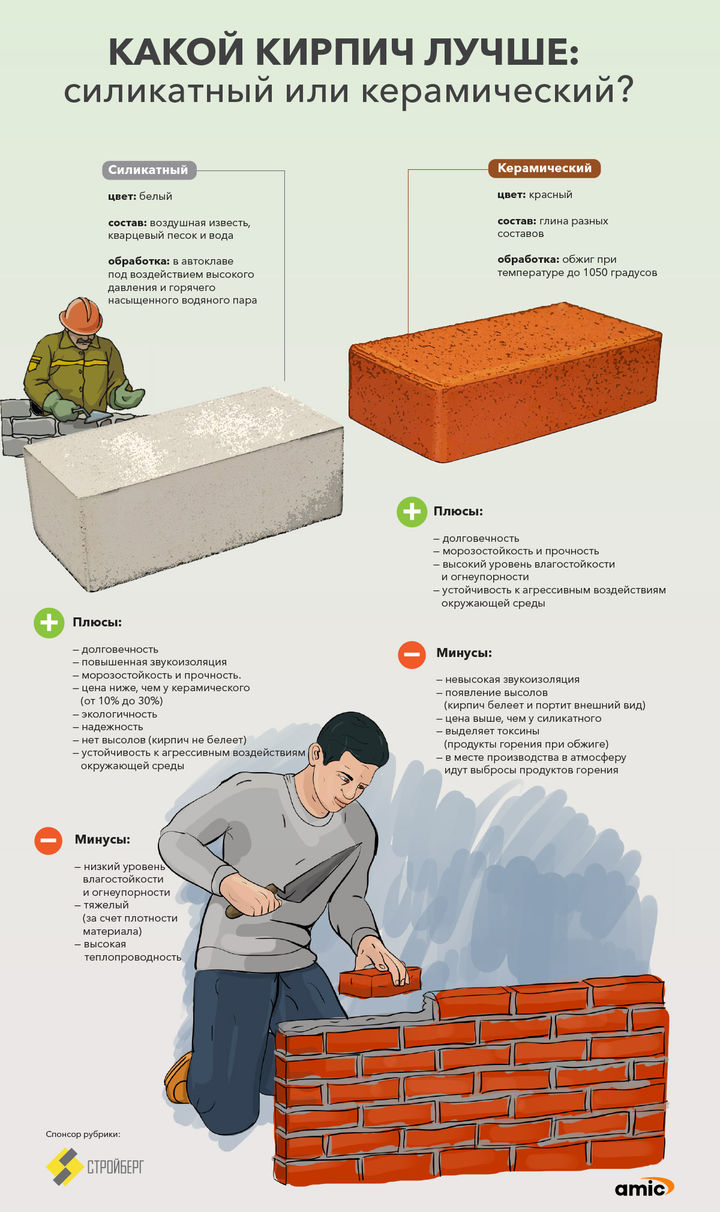
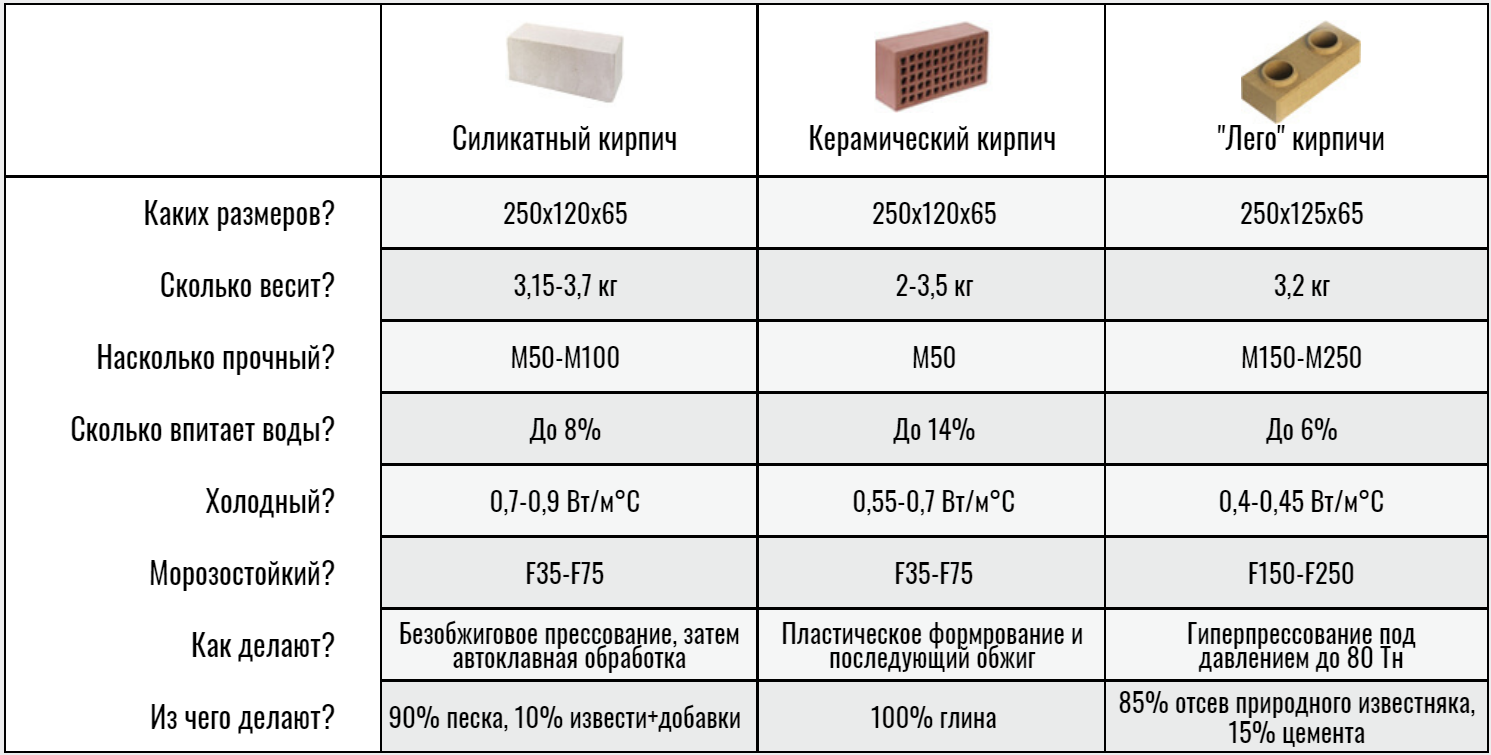
• Ceramic - classic red brick. It is made from baked clay. The building material has high strength, is versatile, therefore it is widely used in construction. The ceramic brick building is durable and reliable. Today, there are products of almost any color. By its structure, a brick can be solid or hollow - its cost and strength depend on this criterion. • Silicate - white brick. It is made from sand and lime. The production technology is autoclave synthesis. In order for the building material to acquire additional performance properties or another shade, coloring pigments and functional additives are added. Silicate brick, in contrast to its ceramic counterpart, has a higher sound insulation, but low moisture resistance, so it is not used in the construction of facilities with overestimated requirements for durability and strength. • Refractory bricks. Produced from refractory baked clay - chamotte. In order to increase the strength, graphite or coke is added to the composition. This building material, in turn, is divided into four types - alumina, quartz, carbon and lime-magnesian. Refractory bricks are commonly used for the construction of chimneys, stoves and fireplaces. • Facing brick is a reliable and durable building material. It has a long service life and a presentable appearance. Brick perfectly protects the walls of the building from all weather conditions and precipitation. Brick is made from cement, a pigment component and limestone using pressing technology. The scope of application is the restoration of the facades of old buildings and the decoration of new ones, the laying of walkways and sidewalks, the construction of fences, walls and architectural elements. The original appearance of the brick is preserved for many years, it does not fade and does not accumulate dirt.
Application
You can find several types of silicate bricks, depending on the purpose:
- Ordinary silicate brick is used for laying out ordinary and bearing walls, and front surfaces can be used for laying facade surfaces. At the same time, they produce bricks with a smooth or textured surface, as well as bricks with a decorative coating. Such a brick is used for facing window openings and solving various design ideas.
- Silicate brick has a number of disadvantages, which determine the scope of its application. The main disadvantage is the ability to absorb moisture. Therefore, it is not suitable for construction and cladding work in rooms with high humidity, such as swimming pools, saunas, bathrooms, etc.
- Its use is limited in conditions of elevated temperatures, large temperature differences, in conditions of the action of aggressive media, as well as aggressive substances in groundwater. In this regard, it is impossible to lay out the basements of buildings, foundations with silicate bricks, to erect stoves and fireplaces.
- When using silicate bricks, the question of the use of bonding solutions arises. In this case, it is better to consult with the manufacturer of silicate bricks regarding the use of the composition of the mortar mixture, which will allow for better construction work. It is possible that it will not be possible to do with a simple cement-sand mortar.
- In the case of using silicate bricks as the main building material, and using ceramic bricks as facing, you should take into account the fact that they have different coefficients of thermal expansion. This means that it is impossible to connect the elements of the masonry of these bricks with each other, since cracks may subsequently appear. The best option in this case is to provide a gap of 1-2 cm between the two masonry.
Attention: If you are making housing from this material, then you immediately need to think about the heat capacity of the room. This material will be required much more compared to clay brick.
Or you will have to do mandatory insulation. Therefore, the construction price rises significantly.
Transportation rules
Silicate brick does not need special storage and transportation conditions. The main thing is that it has as little contact as possible with conditions with high humidity, due to its hygroscopicity.
It can be stored or loaded either manually or using special equipment.
- As a rule, modern enterprises, both public and private, strive to automate all processes of sand-lime brick production, including the processes of storage and packaging, and transportation.
- Finished products are stacked on special wooden pallets, which allow them to be used for moving and loading, forklifts, and the brick itself is packed in plastic wrap, which ensures the tightness of the brick, both during storage and during transportation.
Attention: When storing it on the site, you should choose an elevation. Otherwise, after the rain, it gains a lot of moisture.
It is also necessary to cover the top with non-soaking materials.
You now know what sand-lime brick is made of and now you have a good idea about it. The instruction will help you understand the entire scope of work that will need to be done for production. So take a look at the photo, study the whole process and you can already think from production.
Chamotte brands
It determines the technical characteristics and composition of fireclay bricks:
- SHA, SHB, SHAK are universal blocks. You can make a stove, a fireplace from them. They are very durable and can withstand temperatures up to 1600 ° C. The value for money is perfect.
- ШУС, ШВ - these blocks are characterized by high heat capacity. They are used in industry for lining (protection) of walls of mines and gas ducts.
- PB. Products are used for laying barbecue ovens.
- PV. Blocks of this brand are used for the construction of internal walls of fireplaces.
- ShK. The brand is irreplaceable in the manufacture of facilities for the production of coke.
- SHL. This is a lightweight chamotte, which is suitable for furnaces with a low heating temperature (up to 1300 ° C).
- SHTSU. These blocks are used for laying rotary kiln structures.
Each brand has its own size, weight, composition. Before buying, you need to carefully study the markings, after which you can start choosing a block.
Preparation of concrete bricks
In this section, we will acquaint you with the process of making concrete blocks at home.
- Work begins with the preparation of the workspace, it is necessary to find a flat area on which the vibrating table, concrete mixer and materials for bricks will fit.
- Also set aside some storage space where the workpieces will be stored.
Note! As we already said, it is better to dry concrete bricks for a little longer than a week, so that they acquire increased strength. The conditions for this, were also indicated earlier, now, a small amendment - the blanks can be taken out of the mold no earlier than 6 hours later (with the addition of a plasticizer).
- According to the section on how to prepare the mortar, mix all the ingredients in a concrete mixer and wait until a homogeneous mixture is obtained.
- Fill out the form with the solution.
- Turn on the vibrating table and put the mold on it.
- Wait until the solution has settled a little and add the insufficient amount.
- Wait no more than 1 minute and turn off the machine.
- Remove the mold and set it aside to dry.
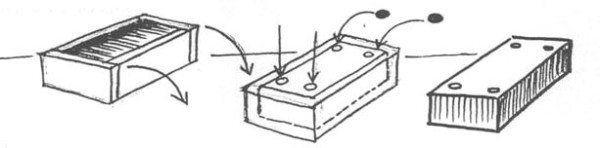
Removable holes on the bottom of the mold will help you painlessly reach the workpiece
This must be done with each form, depending on how many of them you have. If the vibrating table allows, then several forms can be placed on it at once.
Wait a few hours, remove the blank from the mold and repeat the above steps. This is exactly how, without unnecessary tweaks, you can make a concrete block or mud brick in your suburban area.
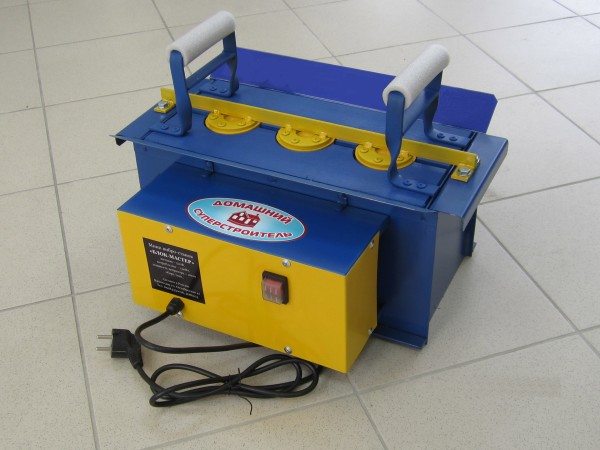

There is another option, how to make a brick of concrete with your own hands - purchase the machine indicated in the photo with a form and a built-in vibrator
Concrete finishing material
However, brick is not all that can be done on your own, using all the same tools, for example, facing concrete tiles under a brick is considered an actual material. The ingredients for cooking are the same, but the forms will either have to be bought or made by yourself.
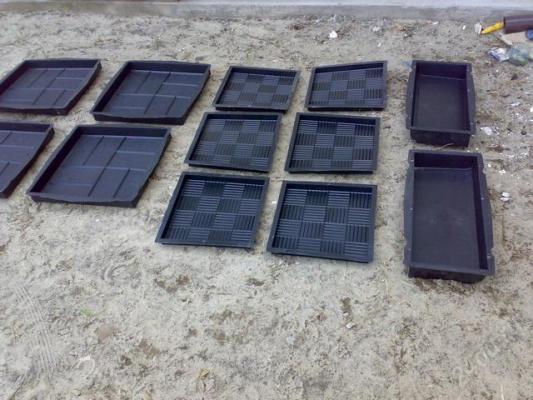

There are a lot of forms sold, so it is not a fact that you will opt for a "brick"
The second option is quite painstaking and laborious, since you will need to weld a square or rectangular shape with many transverse sides, imitating brickwork... and also take into account the thickness of the seam and the uneven edges of the clay blocks.
It is worth remembering that building bricks are called construction bricks because they are intended for the construction of structures of any area and height. Whereas a brick made of concrete is still more acceptable for low-rise buildings, outbuildings or fences. Although the use of high quality raw materials makes it possible to challenge the advantages of fired material.
In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic (also find out the weight and dimensions of fireclay bricks).
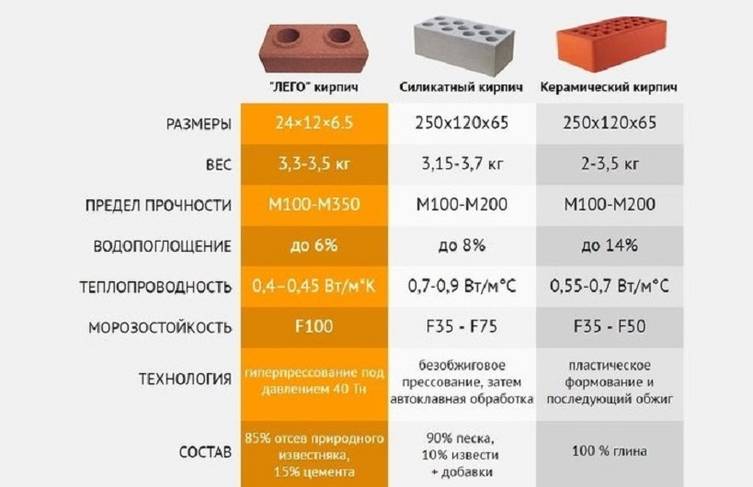
Basic properties of bricks
When choosing a brick, you should pay attention to its technical characteristics, on which the quality of the future structure depends. Knowing what the brick is made of, you can determine its properties: • Porosity
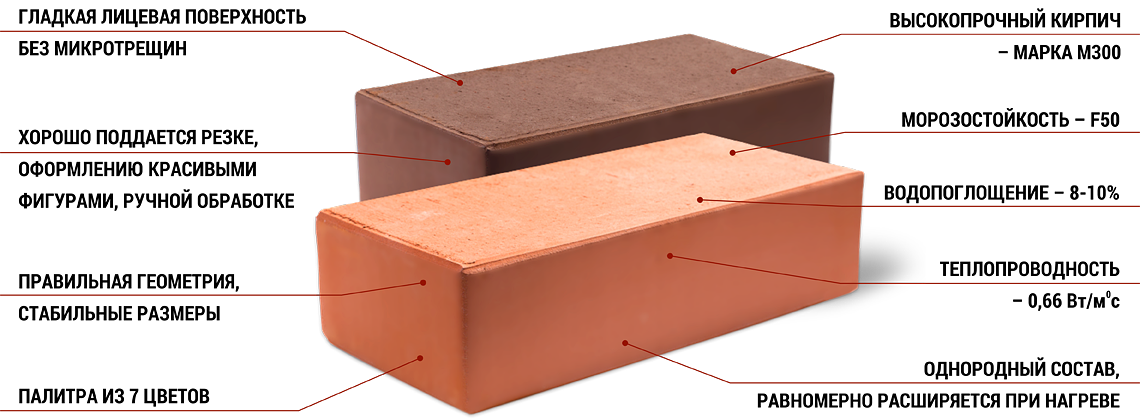
The degree of filling the volume of a brick with pores determines its structure. The porosity factor affects the performance characteristics of the material, such as thermal conductivity, frost resistance, etc. • Density. The parameter is determined by the ratio of the volume and mass of the brick. The indicator to some extent reflects the thermal conductivity and porosity of the material. • Durability. This criterion is numbered. The strength of the brick testifies to its resistance to certain conditions and loads without damage or deformation. The permissible load is indicated on the basis of 1 sq. see immediately after the letter "M". For example, M100 or M300. The higher the number, the higher the strength. • Thermal conductivity. Indicates the ability of a brick to transfer heat to other surfaces or the atmosphere when there is a difference in temperature. • Frost resistance. The parameter is extremely important for the regions of those countries where the climate is changeable. It is taken into account in the manufacture of bricks and is indicated by the manufacturer. Frost resistance refers to the amount of freeze and thaw (complete cycles) that will maintain the strength of the material. Frost resistance is marked with the letter "F", after which a number is written indicating the number of cycles. For example, F25 or F100. For the construction of residential buildings, brick with a minimum marking of F35 is usually used.
• Porosity. The degree of filling the volume of a brick with pores determines its structure. The porosity factor affects the performance characteristics of the material, such as thermal conductivity, frost resistance, etc. • Density. The parameter is determined by the ratio of the volume and mass of the brick. The indicator to some extent reflects the thermal conductivity and porosity of the material.• Durability. This criterion is numbered. The strength of the brick testifies to its resistance to certain conditions and loads without damage or deformation. The permissible load is indicated on the basis of 1 sq. see immediately after the letter "M". For example, M100 or M300. The higher the number, the higher the strength. • Thermal conductivity. Indicates the ability of a brick to transfer heat to other surfaces or the atmosphere when there is a difference in temperature. • Frost resistance. The parameter is extremely important for the regions of those countries where the climate is changeable. It is taken into account in the manufacture of bricks and is indicated by the manufacturer. Frost resistance refers to the amount of freeze and thaw (complete cycles) that will maintain the strength of the material. Frost resistance is marked with the letter "F", after which a number is written indicating the number of cycles. For example, F25 or F100. For the construction of residential buildings, brick with a minimum marking of F35 is usually used.

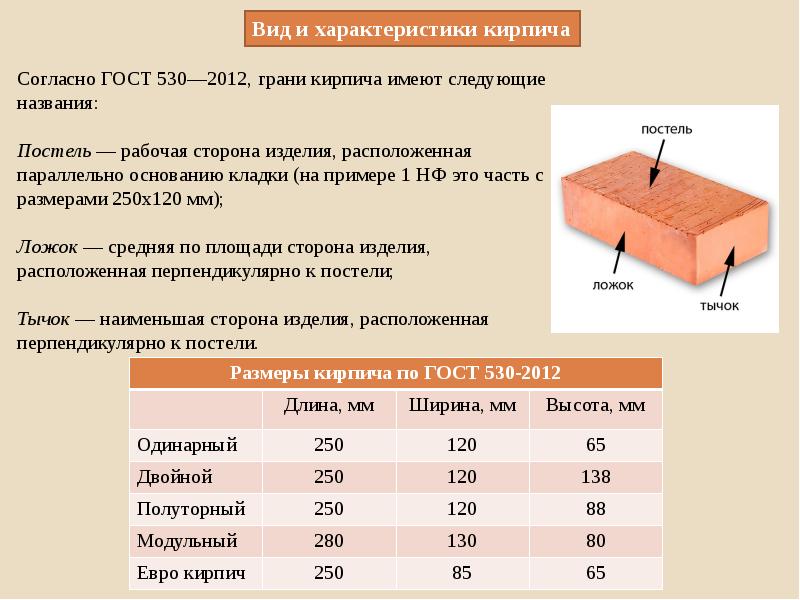
In addition to what the brick is made of, you should pay attention to its size and shape. In the construction market, consumers have access to a wide range of materials that will allow them to implement any design solutions at the highest level.
What non-fired bricks are made of
Today, various materials are widely used in economic activities - bricks and blocks obtained by the following non-fired technologies:
- autoclave hardening of lime-sand mixture;
- hyper-pressing of a mixture of crushed limestone rocks with water and cement.
Regardless of the type of raw material, they are united by the absence of high-temperature processing of brick blanks.
Silicate brick
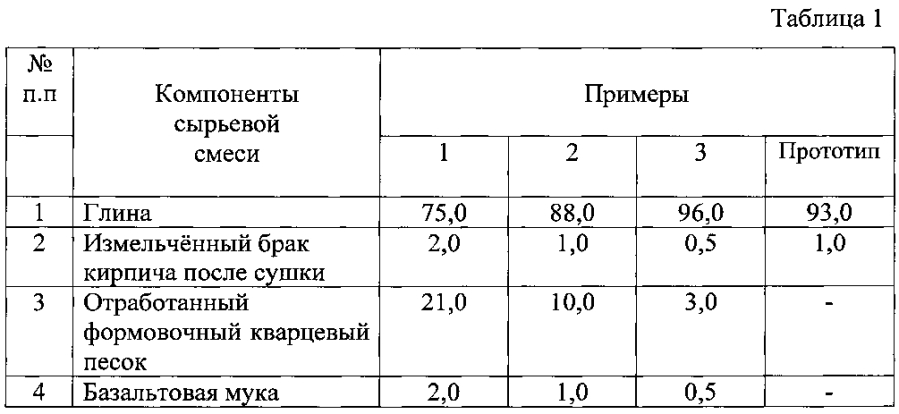
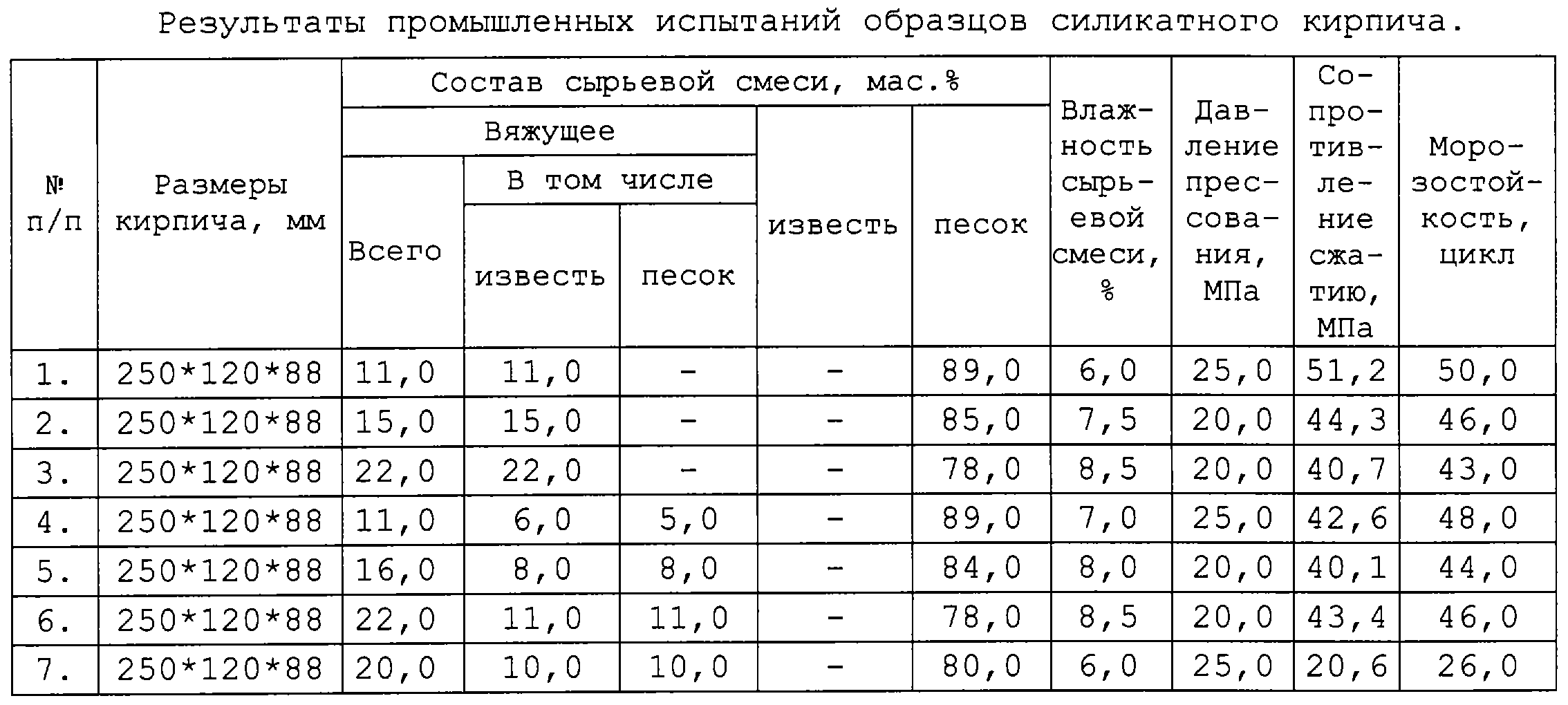
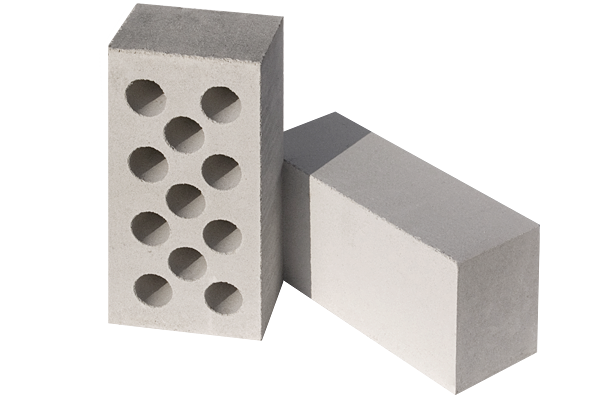 A common example of a material obtained by autoclaving a lime-sand mixture is white silicate brick. The primary composition of silicate bricks consists of approximately 9 parts of quartz sand and 1 part of lime. Wetting the mixture with water initiates the quenching reaction of the lime component, as a result of which a plastic mass is formed, from which brick blanks are formed, which are subjected to autoclaving - steam treatment at a temperature of 170-200 ° C and a pressure of 8-12 atm. Sometimes dyes and substances are introduced into the mixture that contribute to the resistance of the brick to the weather.
A common example of a material obtained by autoclaving a lime-sand mixture is white silicate brick. The primary composition of silicate bricks consists of approximately 9 parts of quartz sand and 1 part of lime. Wetting the mixture with water initiates the quenching reaction of the lime component, as a result of which a plastic mass is formed, from which brick blanks are formed, which are subjected to autoclaving - steam treatment at a temperature of 170-200 ° C and a pressure of 8-12 atm. Sometimes dyes and substances are introduced into the mixture that contribute to the resistance of the brick to the weather.
Mix components
Sand is a natural or artificial (industrial waste) loose mass of homogeneous small, from 0.1 to 5 mm, grains from various minerals. The quality of the sand included in the brick determines the quality of the finished product and the features of the production technology. The geometric shape and texture of the surface of the grains of sand are important for the ease of giving the crude mixture the desired shape and the intensity of interaction with lime when heated in an autoclave. Sharp-angled mountain sands, in contrast to smooth river sands, adhere better to lime. Quarry sand must be pre-cleaned from foreign inclusions.
The next component is lime, obtained by crushing to a size of 40-100 mm and subsequent firing at a temperature of 1100-1200 ° C of rocks containing at least 90% of calcium carbonate - chalk, limestone, limestone tuff and marble. Under the influence of temperature, limestone decomposes into carbon dioxide and lime. At all stages of the manufacture of silicate bricks, water from artesian wells is used.
Also in brick production are used lime-slag and lime-ash mixtures with full or partial replacement of sand with silica-containing industrial waste - ash from thermal power plants and slag. Made from waste and ordinary sand-lime bricks are identical in their qualities.
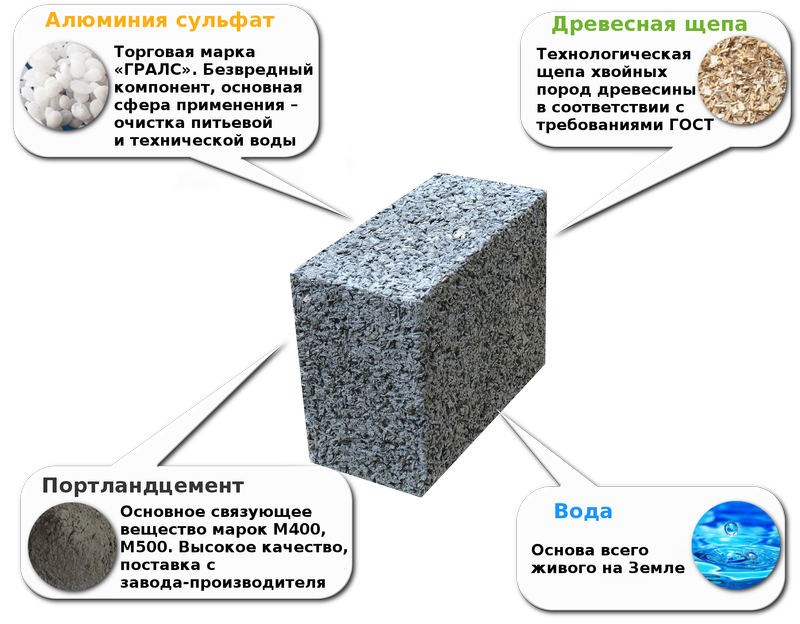
Hyper-pressed bricks
The raw material of non-fired bricks is a mixture consisting of Portland cement or lime as a binder, various mineral fillers (sand, crushed shell rock), water and inorganic dyes. In non-fired technologies, water, hydrating the components of hydraulic binders, is necessary to artificially create a stone-like structure, due to which the disadvantage of such bricks is their low heat resistance.When critical values are reached, as a rule, above 300 ° C, the reaction of release of chemically bound water is triggered, due to which the brick quickly loses its strength.
Technology features
At the stages of preparing raw materials and forming blanks, non-fired technology resembles the manufacture of blocks from concrete, however, the source material of such a brick includes a filler compacted by pressing - crushed shell rock, waste stone processing, etc. Since water is consumed only for the hydration of cement, much less water is required. The final shape is given by hyper-pressing - strong, up to several tons per 1 sq. cm, by compressing the mixture in a special form, after which the products are stored or sent for steaming in order to accelerate the process of acquiring the required strength.
The simplicity of the technology, due to the absence of expensive high-temperature stages, made it possible to make it ubiquitous, often at the expense of the quality of the finished product.
These are the main materials and technologies used for the manufacture of various bricks, blocks and facing materials used in residential and industrial construction.
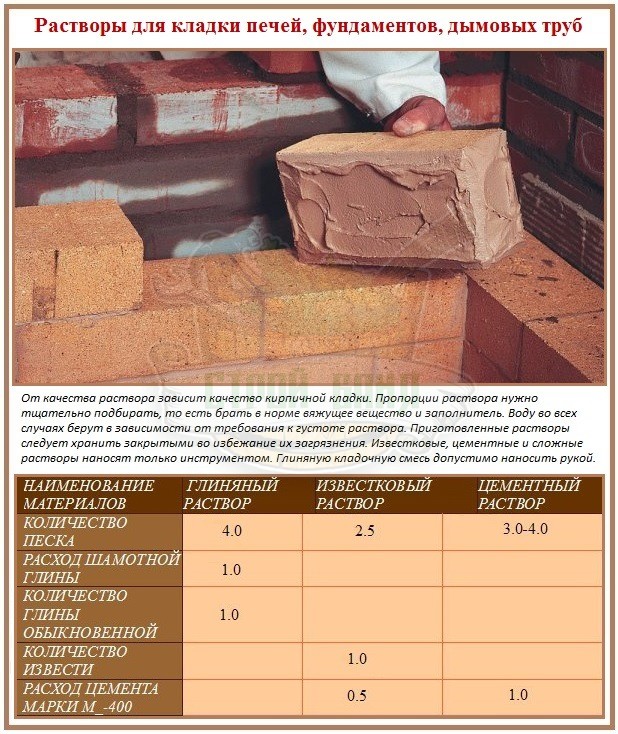
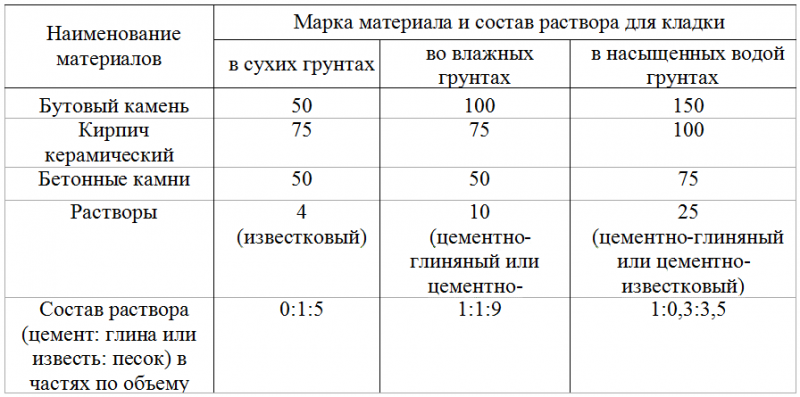
What mortar is needed for bricklaying
Correctly formulated masonry mortars must comply with the following standards:
- Competent choice of recipe for mortar for masonry, proportions of sand and cement and volumes of raw materials.
- The use of quality components.
- Thorough preparation of materials.
- Compliance with production technology.
- Optimum plasticity of the mixture. This parameter contributes to the effective filling of recesses in masonry layers.
- Curing time. Large volumes of mortar that harden quickly are unusable. To eliminate this phenomenon, you need to add lime to the composition.
- Increased strength. When the mixture hardens, the strength characteristics of the cement layers will be increased, and the brick wall will become resistant to deformations and other negative factors.
To ensure the effective formation of solid CPL, it is necessary to correctly select the proportions of the solution. In the process of the reaction of the components with water, the strength indicators increase, and the binder component combines the building materials into an integral structure.
Regardless of the formulation used, the masonry mortar and the proportions of sand and cement must include the following ingredients:
- Knitting part. In most cases, masonry cement is used, which begins to harden when interacting with the liquid, combining with the rest of the mortar.
- Filler substance. Designed to improve the performance and increase the volume of the mixture.
- Liquid. The water is used to react with the astringent part of the additive and aids in normal hydration.
The role of a substance with astringent properties can be played by the following types of raw materials:
- Portland cement.
- Lime.
- Lime-cement mixture.
When figuring out which cement is best for laying bricks, it is necessary to take into account the type of tasks for which it will be used and the characteristics of the brand.
Cement mortar for brickwork must also contain additional components, including:
- Additives for increasing frost resistance. Their task is to prevent crystallization of the liquid under the influence of frost and to normalize hydration.
- Plasticizing additives. They contribute to the workability of the working composition and facilitate its operation.
- Hardeners. They improve the process of polymerization of binder additives and reduce the period of a set of strength indicators.
- Dyes. With the help of colored pigments, you can change the range of materials and improve the aesthetic properties of the wall.
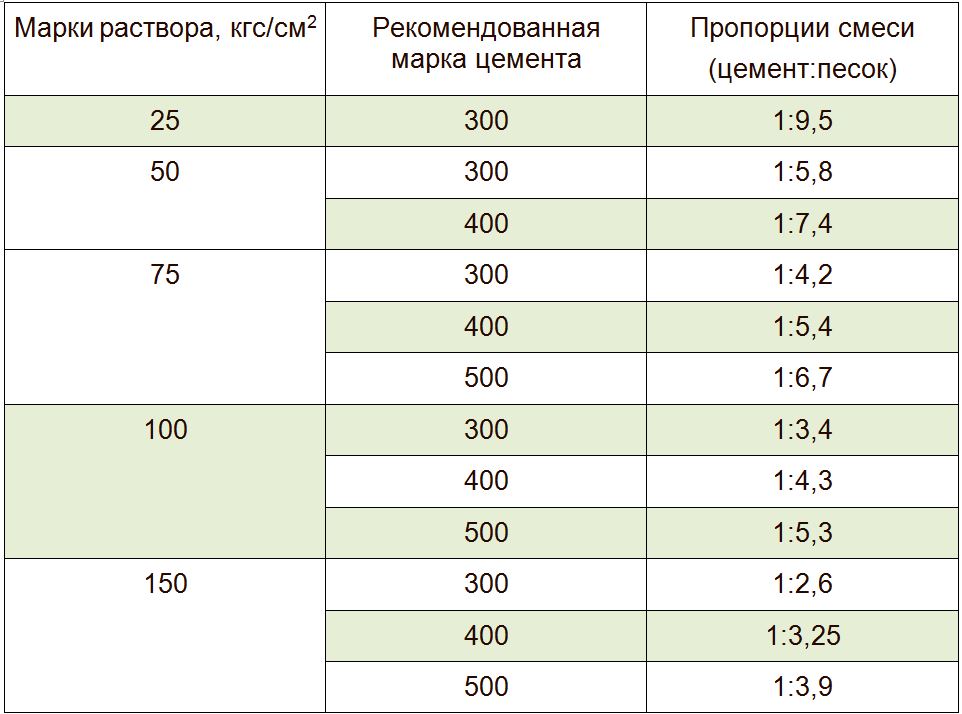
The final grade of the composition is determined by the proportions of sand and cement for brickwork. As the content of sand increases, the grade decreases, and as the proportion of cement increases, it increases.For mixing mortars, different brands of cement-sand mixture are used for brickwork, but the most common is M75. In this case, the proportions of cement and sand for brickwork are selected in a ratio of 1: 5: 0.8.
The masonry mortar can differ in a different ratio of ingredients. They are selected taking into account the purpose and scope of application.
Lime
For the construction of brick fences and wall structures, it is customary to use mortars for brickwork with high plasticity. Therefore, lime combined with sand is added to their composition. Dry additives are thoroughly mixed, and then filled with liquid. Then the ingredients are mixed again until a creamy consistency is formed without lumps and solid impurities.
The optimal proportions are chosen at the rate of 1 part of lime to 2-5 parts of sand.
Cement
Interested in how to prepare a mortar for laying bricks, the proportions of sand and cement must be chosen taking into account some requirements. Depending on the brand of the second component, the ratio of the ingredients is determined: for example, 1 part of cement can have 3-6 parts of sand.
Cement-lime
The composition of a masonry mortar based on a cement-lime mixture is created from the following ingredients:
- Slaked lime, diluted in water until thick. The lime mass is carefully filtered.
- Dry cement for masonry and sand.
Each part is thoroughly mixed. The presence of lime in the composition of cement increases the plasticity of the mixture and allows it to be used with any kind of bricks.
Simple mix
A simple mixture is created on the basis of a binding agent and sand. Clay can be used as the first, but this option is in demand only for narrow-profile tasks.
Complex mix
Complex kneading is a formulation of various additives and an astringent base. These include cement-lime-clay and other solutions. The presence of clay in the composition contributes to easy and neat styling.