Production and properties of technical bricks
In many ways, the technical indicators of product quality depend on production methods, so it is worth paying attention to this point as well. Each manufacturer uses its own method of producing ceramic bricks
There are two popular production methods:
- plastic. When using this method, a plastic method of forming a brick is used. In the production, clay is used, the moisture content of which should be no more than 30%. The bricks are formed on special equipment, and then they are sent under the belt press;
- when the pressing process is complete, the product is sent to a special furnace for subsequent firing. This is how ceramic bricks are made;
Kiln firing
semi-dry method. Here, a press is used to shape the future brick. Clay is used as a raw material, its moisture content should not be higher than 10%.
Classification - hollow and corpulent
When choosing a ceramic brick, you should decide which type you need. The buyer can choose from a number of possible options:
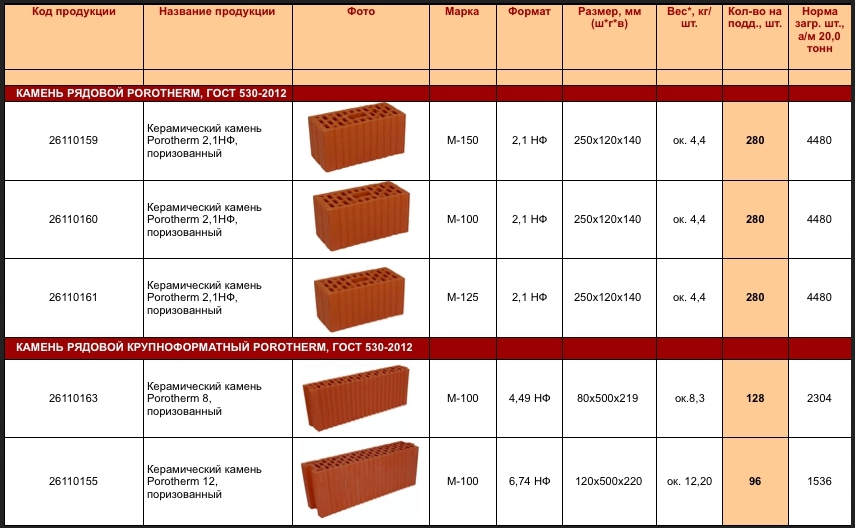
solid brick GOST 530 2012. Here is its size;
Corpulent
hollow brick GOST 530 2012.
Hollow
The weight characteristic is of great importance during construction. Therefore, more and more construction companies are using a variant of hollow ceramic bricks for building, with the same characteristics as that of a solid one.
Required documents for ceramic bricks
When choosing a building material, the buyer must make sure that the bricks comply with generally accepted technical standards. For this, there are special documents in which all the necessary information is spelled out in detail:
- certificate of technical conditions or TU;
- Gost certificate.
If the manufacturer has all the documents that the buyer can familiarize himself with, you can be sure of the quality of the building material being purchased.
What should be included in the content of the document? Any manufacturer draws up a technical certificate based on the following points:
- technological process of brick production. It should indicate what is included in the mixture, as well as the scheme for making the material;
- product safety, that no radioactive substances were used in its manufacture and the brick is safe and environmentally friendly;
- environmental friendliness of the material guarantees environmental protection and will not harm it;
- production quality control of products and instilled reception. It describes how only manufactured bricks are tested in order to assess their quality;
- technical data on how the material should be transported and stored;
- in what areas it can be applied;
- manufacturer's warranty.
Taking into account the general rules for drawing up that, the manufacturer has the right to independently draw up this document and, at his discretion, indicate the characteristics of the brick. Therefore, there is no guarantee that the manufactured ceramic bricks meet the standards. To be on the safe side, the buyer is obliged to make sure that the manufacturer has a gost certificate.
Therefore, there is no guarantee that the manufactured ceramic bricks meet the standards. To be on the safe side, the buyer must make sure that the manufacturer has a gost certificate.
Carefully studying the GOST certificate, make sure that it is issued specifically for the products you need. The first three digits indicate the name of the product, the rest indicate the year in which the document was issued.
Certificate
GOST 530 for ceramic stone and brick meets the requirements that were adopted in 2012. And it looks like this.
- document number and its validity period;
- the name of the body that certified the products;
- a complete listing of the products that have been studied with a full description and technical specification;
- what exactly does the ceramic brick meet according to GOST;
- full name of the manufacturer of the product;
- to whom this document is issued;
- description of the documents on the basis of which the certificate was issued, research protocols;
- stamp and signature of the person in charge.
Pros and cons of ceramic bricks
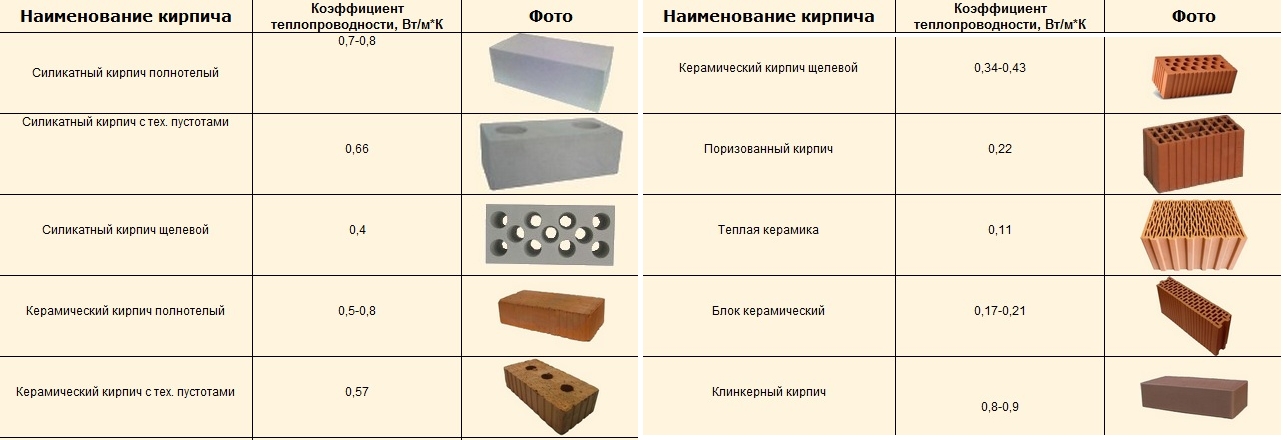
The advantages of ceramics include naturalness, harmlessness. If we compare ceramics and silicate, then clay products win a little in terms of thermal conductivity. If you look at the indicators, then the difference is very small. But a ceramic house is much warmer than a silicate one. The point is in the higher heat capacity. Clay can store more heat and is therefore warmer at home.
Ceramics are inferior to silicate in sound insulation properties, as well as in geometry and stability of characteristics. This is its main disadvantage. Moreover, at a high price, often efflorescence, with which it is very, very difficult to fight. Another drawback is that even the front surface is rarely even.
Ceramic brick is a traditional material for building houses, which is more than one hundred years old.
All these shortcomings are understandable. Ceramic bricks are obtained by firing pre-shaped parallelepipeds from clay mortar. Clay is a natural material that has various properties. The different properties of different types of clay are the main reason that the size of ceramic bricks does not differ in stability. Moreover, a significant spread can be within the same batch. And from party to party, in general, there may be significant differences. The different characteristics of the feedstock also cause a wide variation in the characteristics of the finished product. Such as strength and density.
Service life - reality is not happy
In many respects, ceramics should be better than the same silicate, but the reality turns out to be different. Recently, too often there is a red ceramic brick crumbling, dilapidated after several years of operation under normal conditions. The reasons are the complexity of the technology. For a good result, careful processing and preparation of the clay is required in order to exclude lime inclusions, which are the reasons for "shooting". And this is additional time in an already not short production cycle. And extra energy. And expensive equipment, which is not bought by everyone.
Not the best picture
The second point: holding the temperature regime of firing. Burnt ceramic bricks behave normally in masonry. It only looks worse, as it is darker than the "norm". It's not so scary. But the unburned one collapses, crumbles. And this is why he is dangerous. Ceramics are fired in the furnace for a long time, and so it takes a little to reduce the time in order to increase productivity. Hence the underburning. Or fuel economy, which is far from cheap. So compliance with the technology for the production of ceramic bricks is a high price for products. And expensive bricks are bought very reluctantly. So the collapsed red brick most likely had a low price. And everyone knows that cheap is very rare. Nevertheless, the budget for a construction site is usually not a rubber one and you have to save money.
In terms of thermal conductivity and some other parameters, ceramic bricks should be better
No matter how complex the production technology is, European supplies have a geometry close to ideal, and the dimensions are standard, and the quality is stable. Their price is far from budget, but quality problems are rare. So if the funds allow, they try to buy imported bricks. Domestic clay, even expensive, still cannot boast of stability of quality. That is why, although ceramics should be better in many respects, more and more often the choice is made in favor of silicate. Because for quite reasonable money you can buy good quality building material.He is chosen even though he is much colder. All the same, in order to achieve the required level of energy efficiency, it is necessary to insulate the ceramics too.
Scope of application
It is worth abandoning the purchase of handicraft bricks, since the low cost can cause a short-term operation of buildings and entail the need to purchase an additional batch of bricks.
As you can see, GOST for bricks is useful not only for manufacturers, but also for buyers. If you own the above information, then you can protect yourself from buying low-quality products and at the same time purchase the optimal type of brick that is suitable for certain purposes.
In some cases, according to GOST, a deviation of geometric parameters is allowed, but they should not exceed the norm, which is 1-2 mm.
Such indicators are compared with the dry weight of the brick and recorded in the documents.
If it is necessary to erect multi-storey buildings, it is worth paying attention to the strength of the brick. To do this, it is placed under a press and exerted a certain load, up to its destruction.
The more weight the brick can withstand, the longer it will last and stay in the masonry.
It is also important when designing objects where bricks will be used in the form of a building material, initially to be determined with frost resistance, density and other parameters of products, which will help them to stand in the wall longer and not collapse. All these points are prescribed in the documentation for the product, and the requirements must be strictly met by the manufacturers.
For information on how to choose a ceramic brick, see the next video.
Let’s block ads! (Why?)
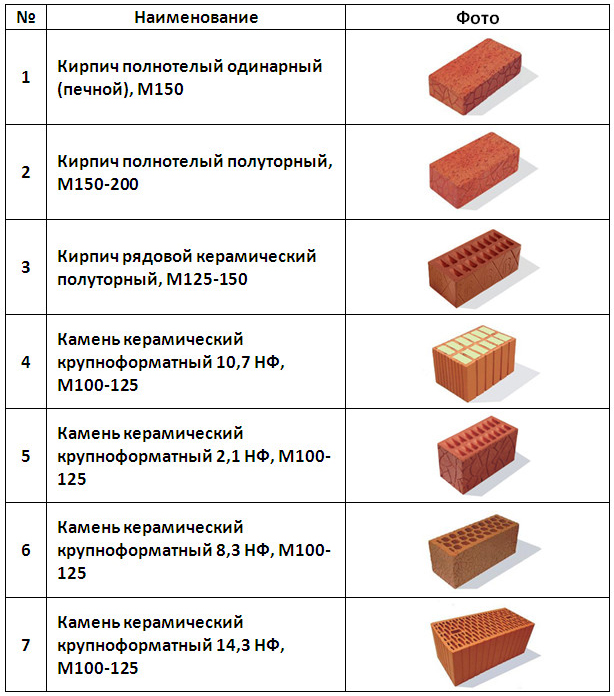
Brick types
All ceramic bricks, both facing and for construction purposes, are made according to the standard.
Such material differs in composition:
- high strength characteristics, which allows it to withstand heavy loads and makes it possible to build foundations from it;
- resistance to negative external factors;
- the ability to withstand high temperatures.

Currently, there are the following types of bricks.
- Private single. An ordinary brick, which has no voids, is inexpensive and is not decorated in any way. It is the most common.
- Corpulent. May have one or more voids.
- Hollow. It has many voids of various configurations and sizes.
- Facade. It is produced in any shape and geometry.
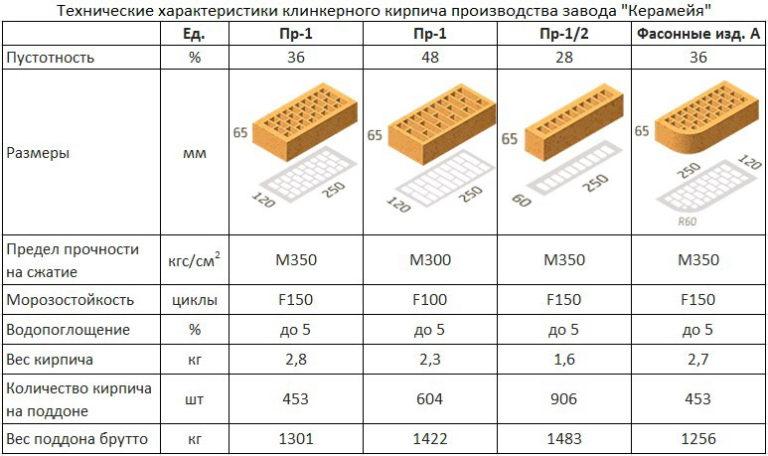
- Clinker. A durable material that is used in landscaping and as a decorative material. The parameters correspond to the standard ones, but, if necessary, they can be produced in various other forms.
- Facial. Refers to decorative materials and has characteristics similar to conventional bricks. It has strength and at the same time has a decorative base.
- Ceramic block. Has a void inside, is large. Designed for masonry walls.

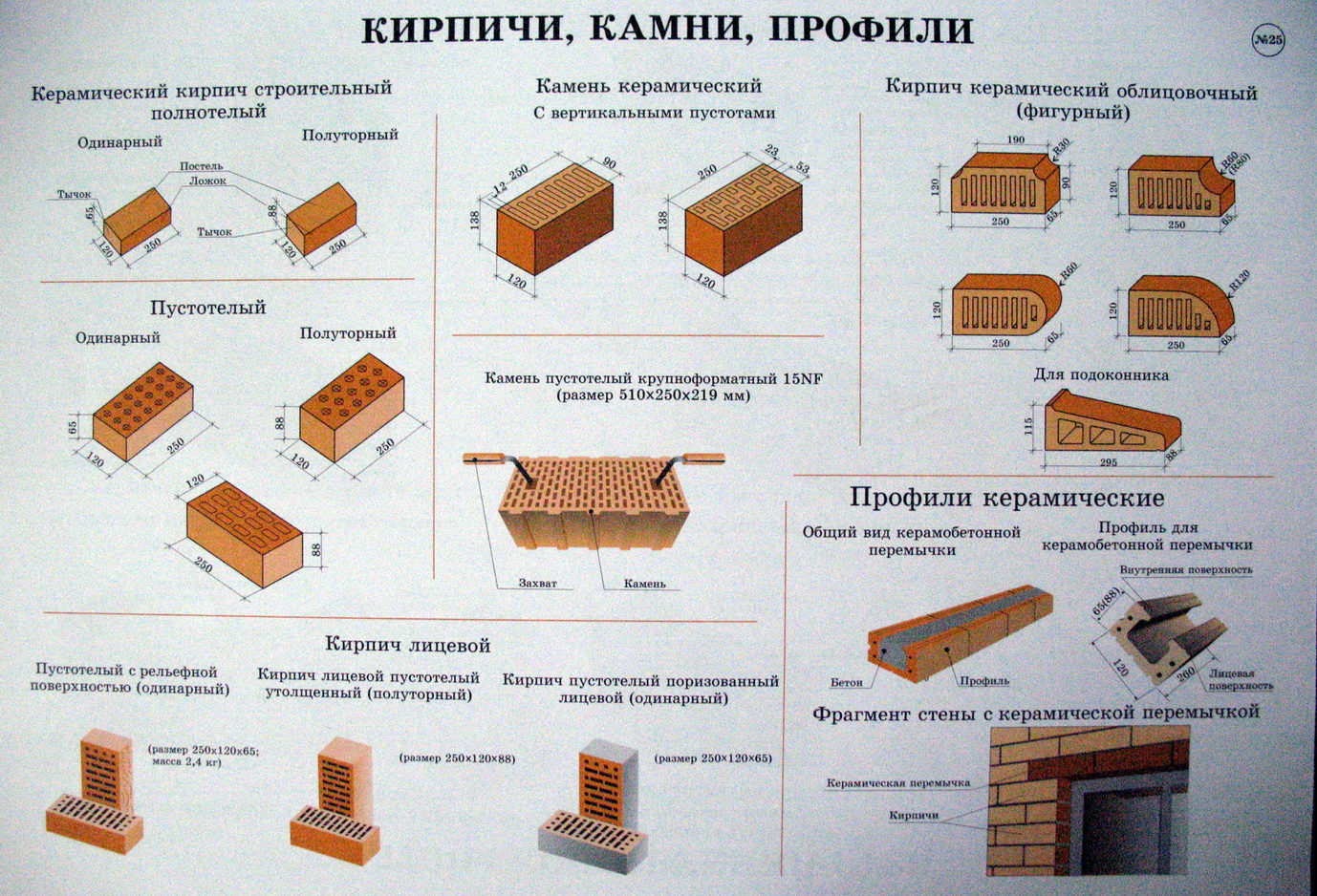
Standard type brick size - Table.
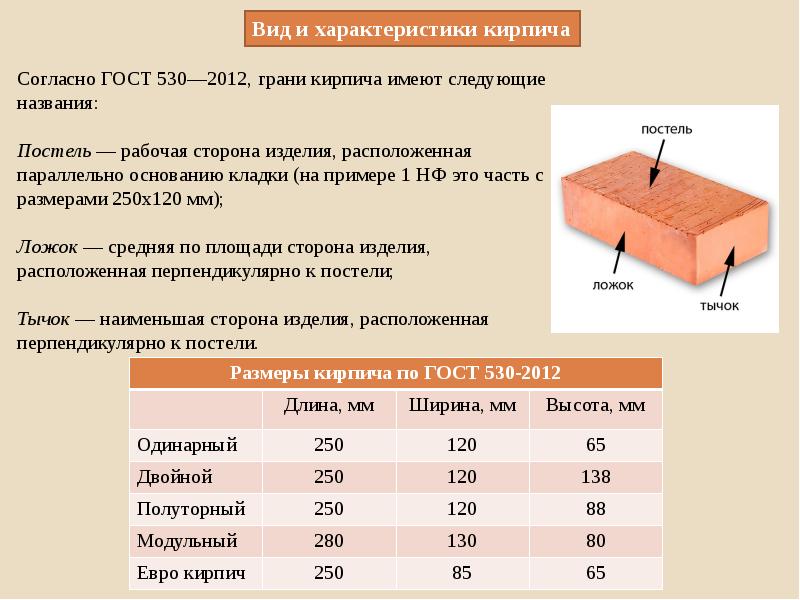
Brick is a stone of the correct form of artificial origin, which is very widely used in construction.
He has three surfaces:
- the bed is the largest;
- spoons - medium;
- butt is the smallest surface.
Dimensions and marking of bricks from domestic manufacturers.
In the table below, you can find out the size of the required brick block, as well as its marking, which is used in our market.
| Name | Dimension marking | Dimensions, mm. | Name marking |
| Single | 1-NF | 250x120x65 | O |
| "Euro" | 0.7-NF | 250x85x65 | E |
| Modular single | 1,3-NF | 288x138x65 | M |
| One and a half | 1,4-NF | 250x120x88 | Have |
| Thickened brick with horizontal voids | 1,4-NF | 250x120x88 | UG |
| Double brick (stone) | 2,1-NF | 250x120x140 | TO |
| 3,7-NF | 288x288x88 | ||
| 2.9-NF | 288x138x140 | ||
| 1,8-NF | 288x138x88 | ||
| 4,5-NF | 250x250x140 | ||
| 3,2-NF | 250x180x140 | ||
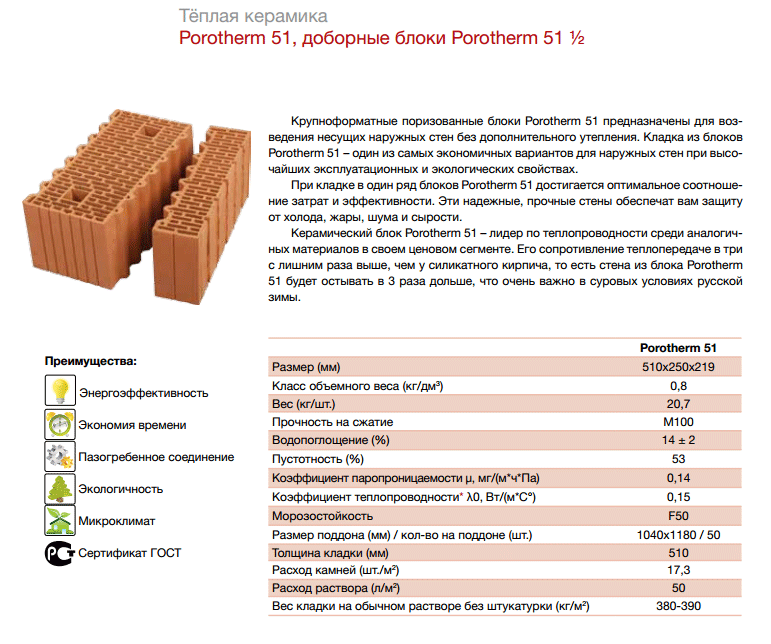
| Large-format stone (porous ceramic block) | 14,3-NF | 510x250x219 | QC |
| 11,2-NF | 398x250x219 | ||
| 10,7-NF | 380x250x219 | ||
| 9,3-NF | 380x255x188 | ||
| 6,8-NF | 380x250x140 | ||
| 4.9-NF | 380x180x140 | ||
| 6.0-NF | 250x250x188 | ||
| Stone with horizontal voids | 1,8-NF | 250x200x70 | KG |
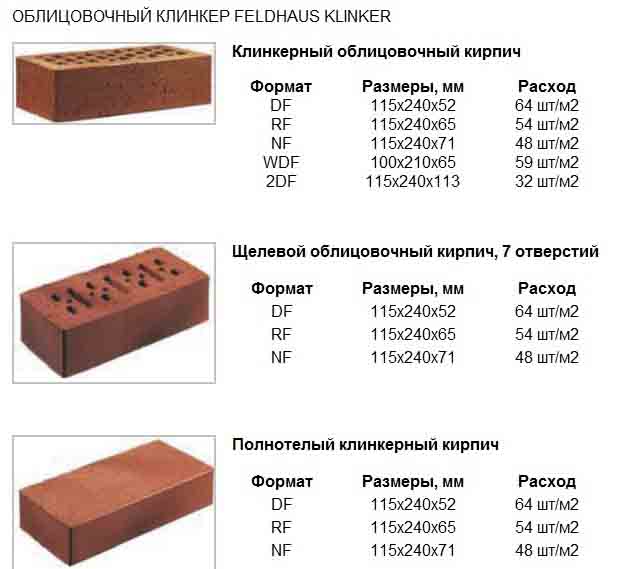
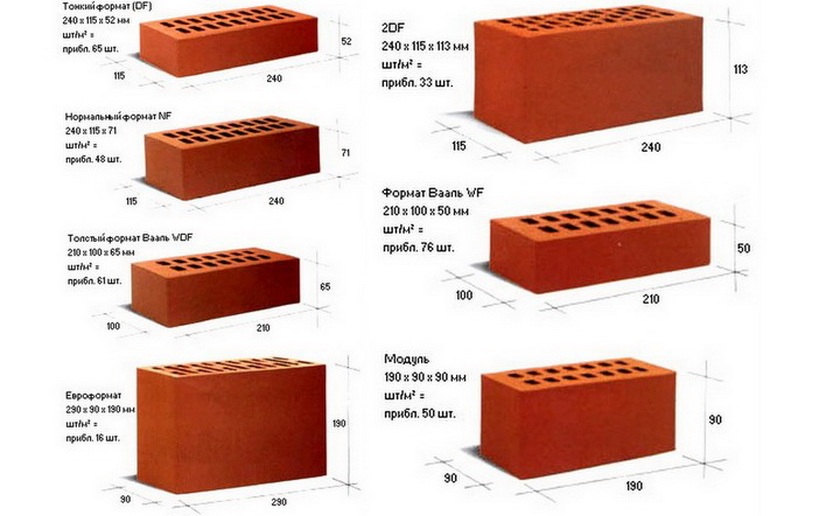
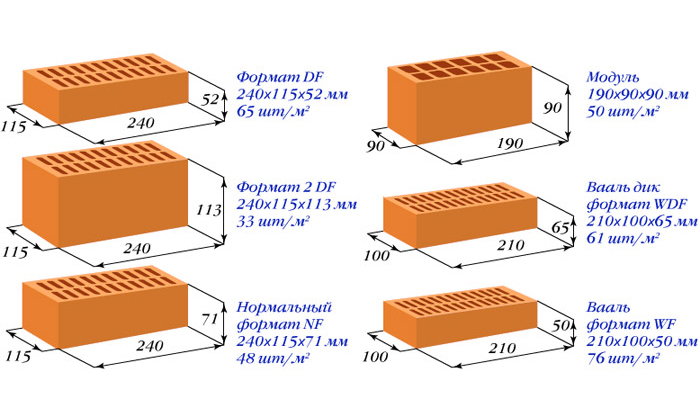
Size marking of European bricks.
Foreign manufacturers have completely different standards and sizes differ from domestic ones. Therefore, for complete convenience, the following table of brick sizes is presented:
| Marking | Dimensions, mm |
| DF | 240x115x52 |
| 2DF | 240x115x113 |
| NF | 240x115x71 |
| RF | 240x115x61 |
| WDF | 210x100x65 |
| Wf | 210x100x50 |
Knowing the size is good, but you also need to know the species, and there are many of them.
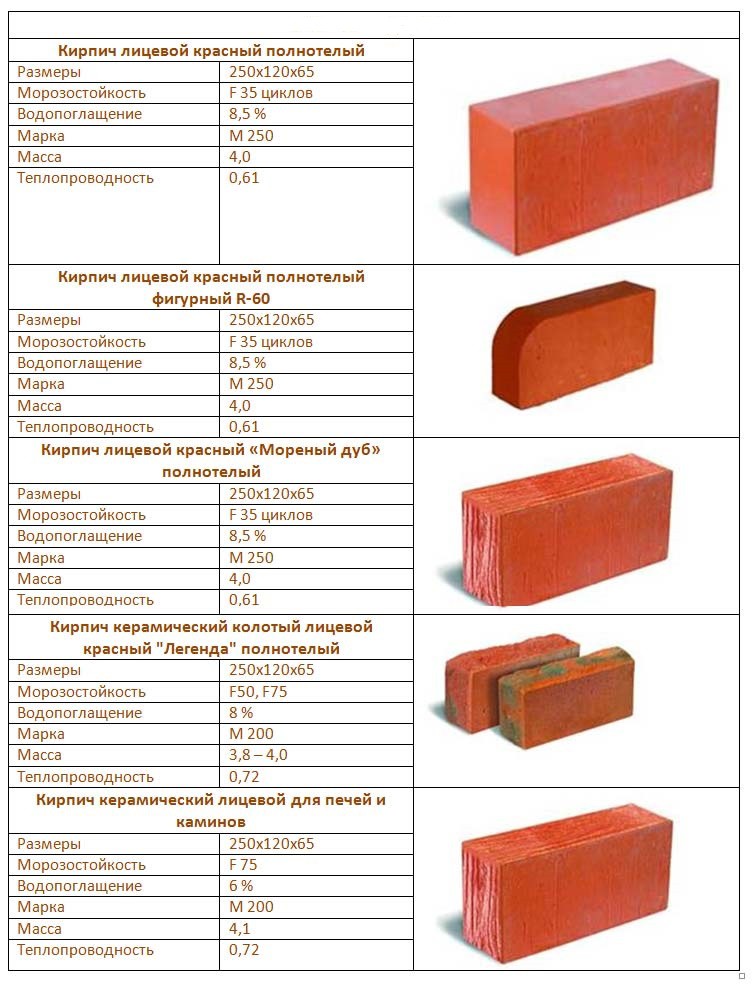
Red brick size.
The standard size of a red brick product was introduced at the beginning of the 19th century, and finally established itself relatively recently, in 1927, and is 250x120x65 mm.
Often such dimensions of single ceramic bricks are called normal or basic format. It is a product of this size that is considered the most convenient for the production of wall masonry work, more precisely, for alternating the arrangement of bricks when bandaging the masonry.
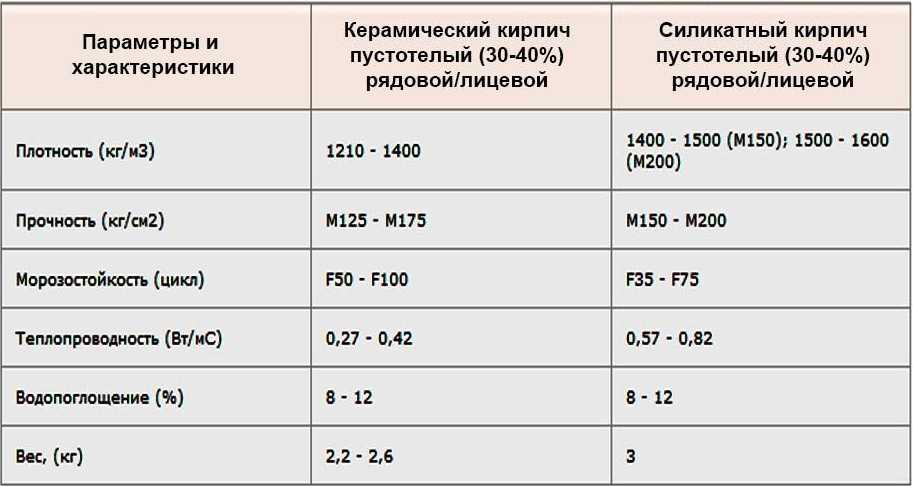
The size of the silicate brick.
SC is used in many cases when high strength is required from the building.
A brick is produced with the following dimensions:
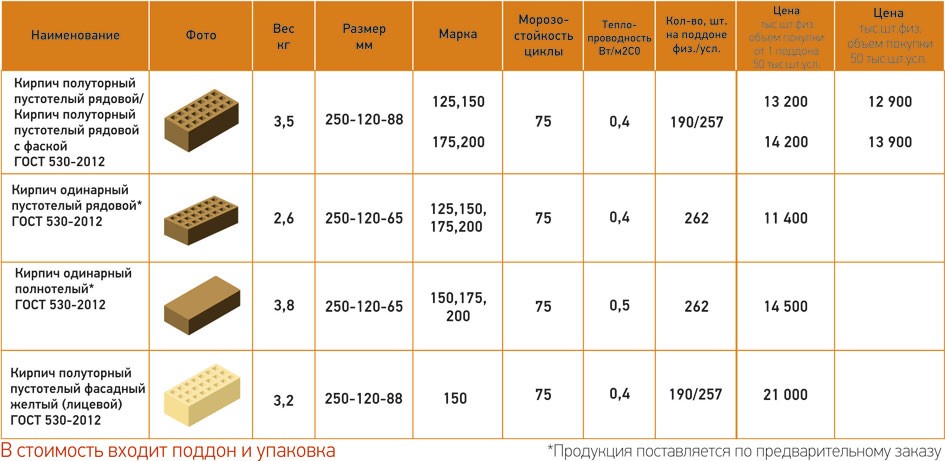
- single - 250 mm long, 120 mm wide and 65 mm thick. The weight of the product depends on its type - hollow or corpulent;
- one and a half - or thickened, with the same length and width, the thickness of the product is 88 mm;
- double - or silicate stone, has a thickness of 138 mm.
There is a whole category of SC of non-standard size and shape rather far from a parallelepiped. These products are designed to form various architectural elements: arches, rounded corners, vaults, and so on. Their dimensions are regulated by TU and annexes to GOST.
The size of the facing brick.
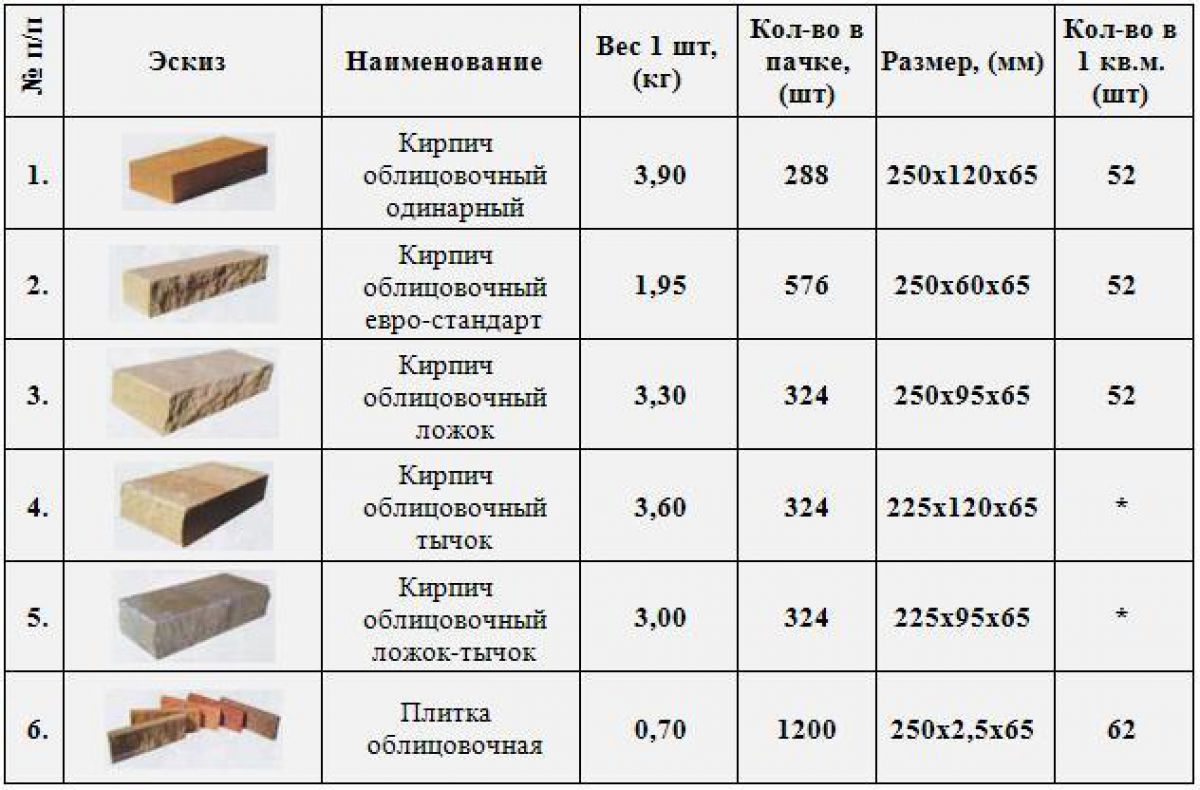
The usual size of decorative bricks can have the following parameters - 250x120x65 mm, 250x90x65 mm and 250x60x65 mm.
As you can see, the height can change, but the length and width of the brick remain unchanged. The only exceptions are the elongated elements, the parameters of which are 528x108x37 mm.
Dimensions of ceramic bricks.
KK is full-bodied, hollow, porous. The first modifications are made using a similar technology in various forms, into which the clay is filled. A unique technology is used in the production of porous ceramics.
The dimensions of the KK are as follows:
- single, perhaps the most common type. The standard dimensions of a single ceramic brick are 250 × 120 × 65, as you know, the dimensions of building materials are indicated in millimeters;
- the size of a one-and-a-half ceramic brick differs from a single one only in height, it is 88 millimeters, and the length and width remain unchanged.
- double, also higher than the standard, single, its height is 138 millimeters with the same length and width.
What are the markings of bricks.
Each batch of bricks is marked by the manufacturer, all information about the product is indicated on the marking in an alphanumeric code. It is not difficult to decipher the marking, it consists of: marking the name of the product, letters P - for privates, L - for obverse; size designations and designations: Po - for corpulent, Pu - for hollow; grades for strength and frost resistance; medium density class and designation of GOST.
For example: Brick KORPu 1NF / 100 / 1.4 / 50 / GOST 530-2007.
Marking of ordinary ceramic bricks, hollow, thickened, size 1.4NF, strength grade M150, average density class 1.4, frost resistance grade F50.
Or: Single silicate brick, ordinary grade for strength 150, grade for frost resistance F15 will be marked: Brick COP-150/15, GOST 379-95.
Definition and labeling
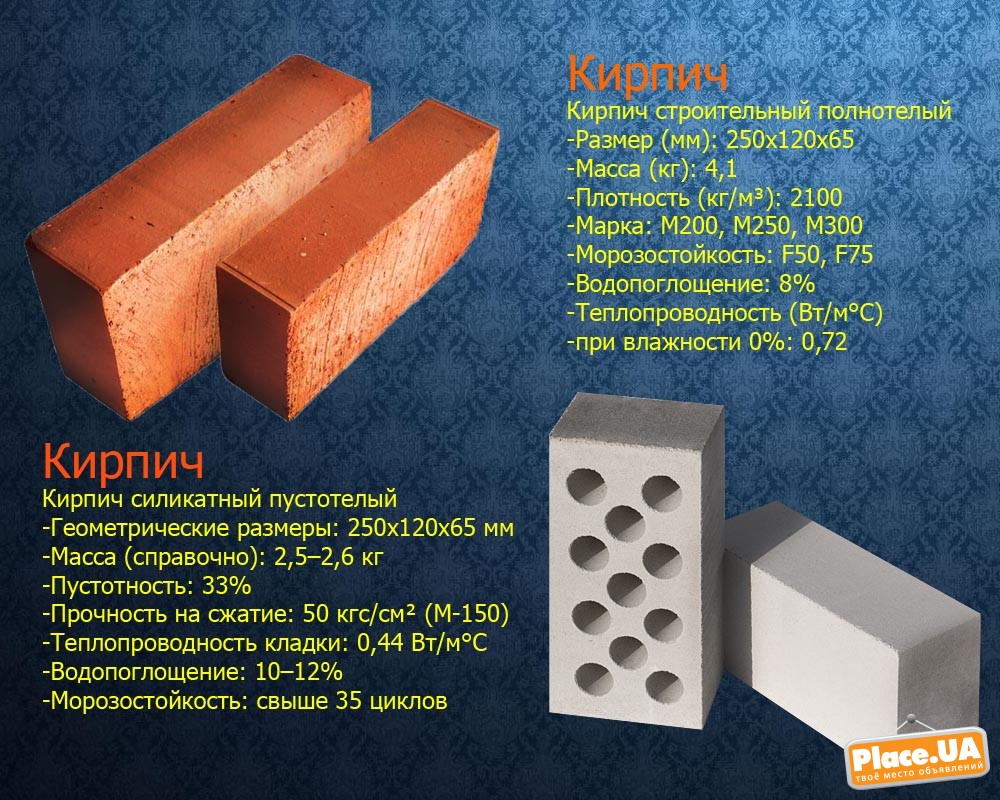
Brick is a ceramic material, as it is made from clay and then fired. Usually it has the shape of a parallelepiped with right angles, and its standard dimensions are 250x120x65 mm. Also, bricks are additionally marked in accordance with the strength, which is indicated by the letter "M".
For facing materials, not only quality, strength and compliance with standards are important, but also a beautiful appearance.Therefore, such products may have the following side surfaces: textured, glazed, with a relief
Such requirements are not imposed on ordinary bricks, and therefore they usually have smooth surfaces, and the color can be different, depending on the type of additives used.
Composition of ceramic bricks
The best ceramic bricks are made from clay of fine fractions and constant composition. The process of extracting raw materials in this case takes place using a single-bucket excavator that does not mix layers of clay. But there are very few such quarries left. Rotary excavators mix all layers of clay and grind them, therefore, in order to produce high-quality ceramic bricks from such raw materials, the firing technology must be strictly followed.
Clay is a mixture of low-melting and refractory elements. With proper firing, low-melting components bind and dissolve their more refractory analogs; the structural composition of the brick depends on the ratio of these ingredients. The technology of correct molding and drying of raw materials is aimed at giving it maximum strength while maintaining a given shape. The shape and technical characteristics of ceramic bricks are regulated by GOST 530-2007.

Classification and subspecies of ceramic bricks.
Ceramic bricks differ in manufacturing technology: fired and unfired.
- Unfired ceramic bricks (adoba) are made by drying in the open air, thus a material with low technical characteristics is obtained and is practically not used in modern construction.
- Fired brick is thermally exposed in special kilns and tunnels, which gives it high strength and low moisture permeability.
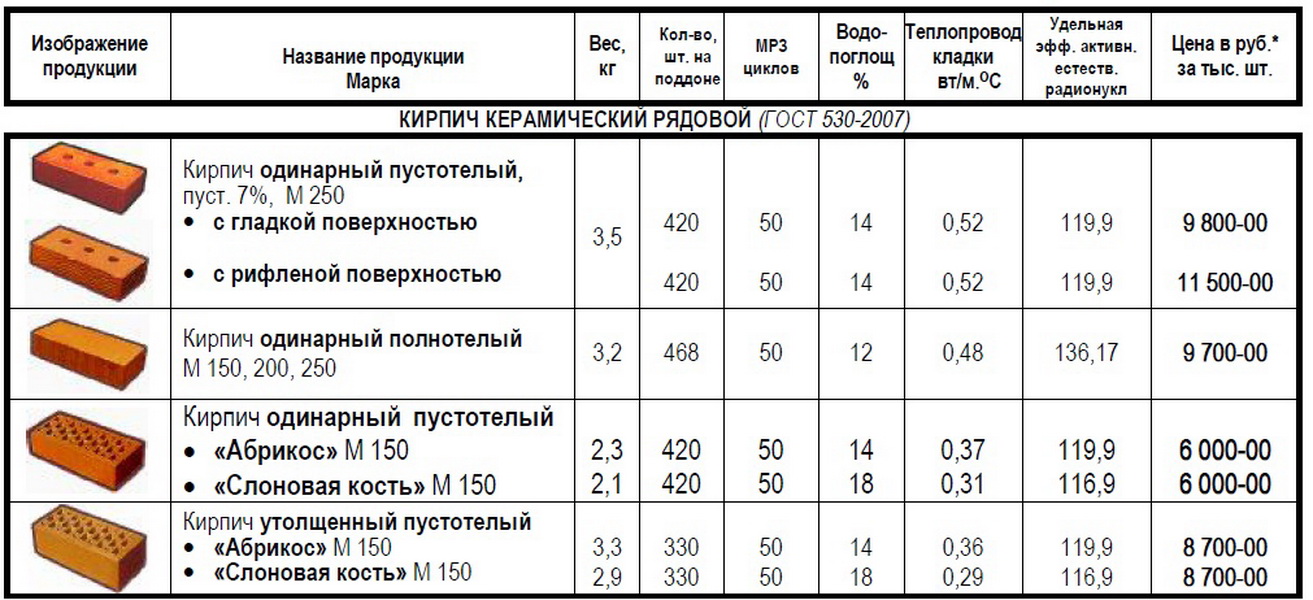
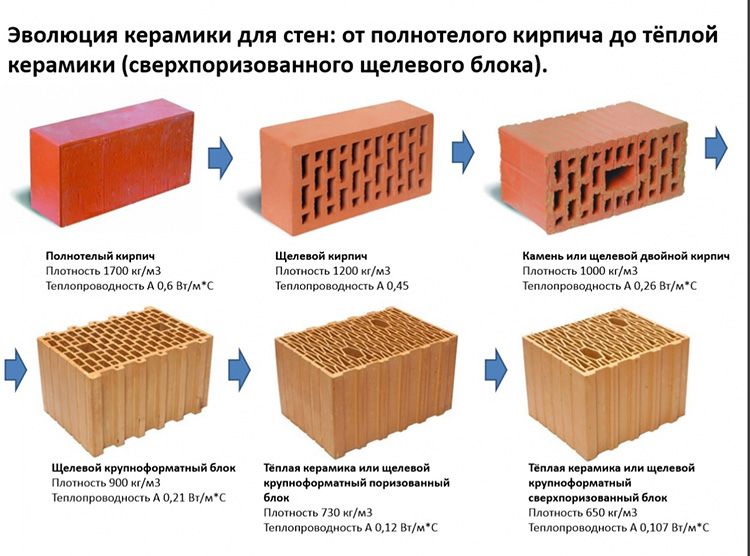
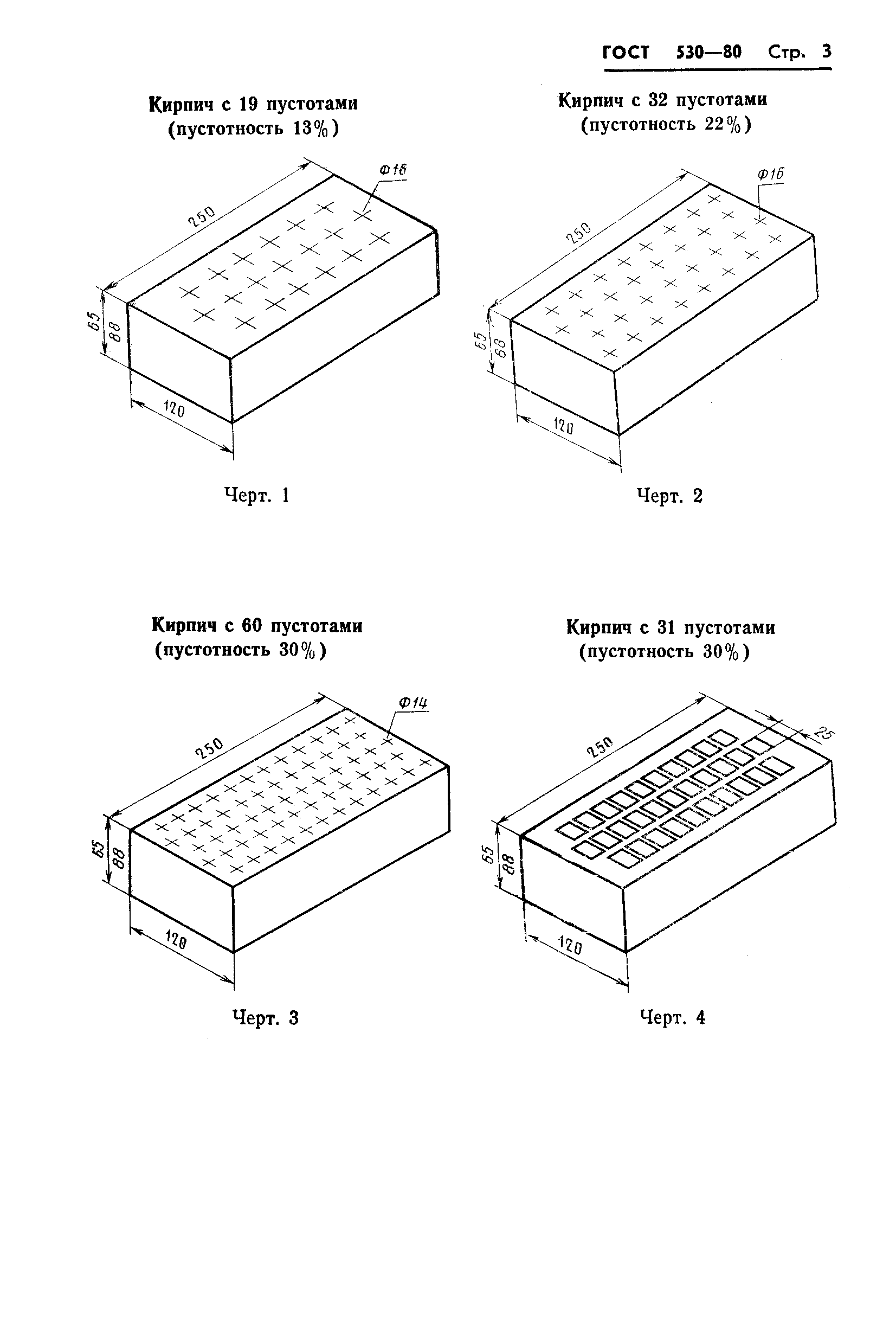
Ceramic bricks are made in solid and hollow versions.
- Solid brick is heavier and has increased thermal conductivity, therefore it is gradually replaced by hollow material.
- Hollow bricks are made with the creation of internal cavities of various shapes and sizes. The volume of the cavities can be up to 55% of the total volume of the product. Cavities reduce the thermal conductivity of the material, allowing thinner walls to be laid.
According to the quality of workmanship, the brick is divided into ordinary and front.
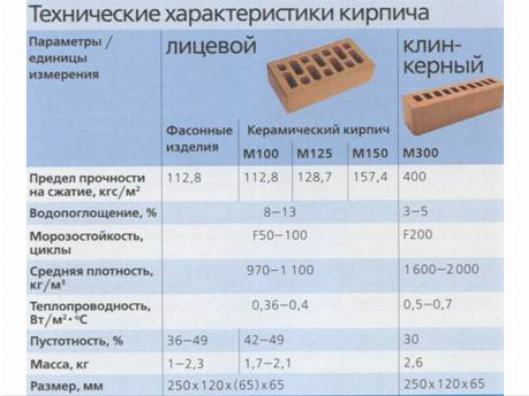
The strength characteristics of ceramic bricks are determined by its brand: from M100 to M300. The numerical value of the brand indicates the maximum pressure that the material can take, measured in kg / cm 2.
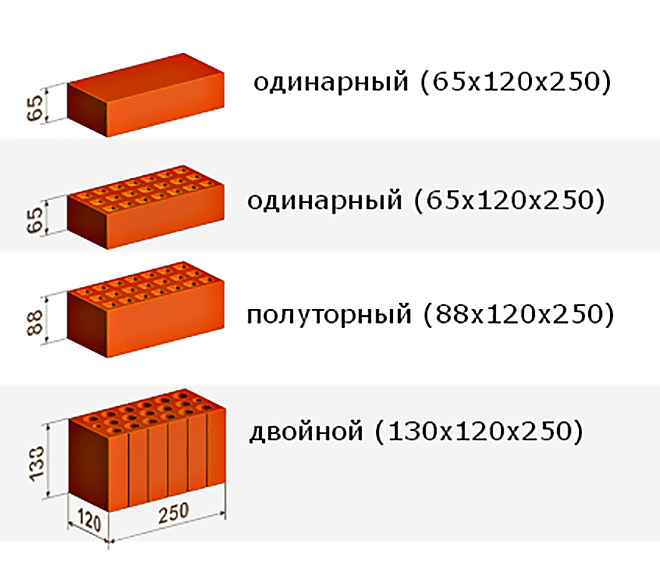
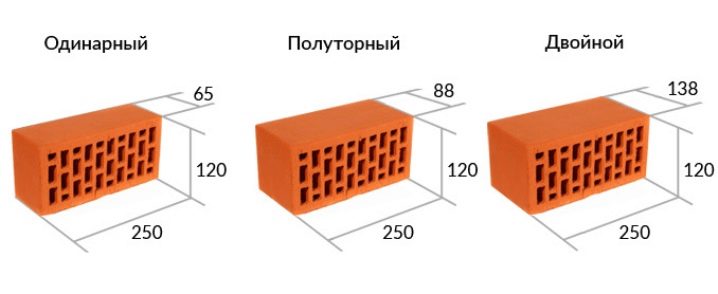
In terms of size, ceramic bricks are divided into three main groups:
- Single brick - 250 x 120 x 65 mm;
- One and a half brick - 250 x 120 x 88 mm;
- Double brick - 250 x 120 x 140 mm.
Also in our country a different standard is used:
- 0.7 NF (Euro) - 250 x 85 x 65 mm;
- 1.3 NF (modular single) - 288 x 138 x 65 mm.
The size of the brick is carefully thought out as its width is half the length with a 10mm tolerance for the mortar joint. A solid double brick in accordance with GOST is called a ceramic stone and is the most economical of the above materials.
Bricks vary in color: from light yellow to dark brown, depending on the raw materials used. Currently, the pigmentation of ceramic bricks is actively used, giving the material various color shades.
Facing brick: sizes and types of material
The requirements for the inner surface of the walls of the house are several times less than the requirements for facing the outer part of the house. And if in the first case you can use ordinary clay or sand-lime bricks, as well as foam concrete or aerated concrete blocks, then you can provide a really attractive appearance for the outside of the house only by using facing bricks for the facade.

Facing bricks for the facade of a house can have a variety of textures and vary in size and thickness.
But even in the case when the choice is made in favor of facing bricks, the owner of the house still has to make a difficult choice, and give preference to one or another of its options.
Consider what types of this material are, and what you should pay attention to when choosing
The parameters of a brick are directly determined by the technology of its production, so that, depending on the features used for the production of materials and related processes, there are 4 types of finishing bricks:
- ceramic;
- clinker;
- concrete (hyper-pressed);
- silicate.
Moreover, each of the listed options is also available in 2 types - hollow and full-bodied, so the choice is really wide. Let's briefly consider the characteristics of each of the options, as well as its features and advantages.

The choice of facing bricks is quite wide, which makes it possible to use it to implement various design ideas.
Helpful advice! In addition to the fact that hollow bricks have a significantly lower weight (the difference is about 25-35%), they also resist heat loss more efficiently, surpassing solid bricks by 10-15%.
Another interesting question - how much does one brick for facade cladding weigh? The weight of the facing brick is determined by the material it was made from. For example, a solid silicate (white) brick, the size of which corresponds to the standard, weighs on average 4.6 kg, and an ordinary ceramic brick intended for cladding will weigh only 1.45 kg.
Basic standards GOST 530 2012
Here are the main provisions of the GOST characteristics for bricks.
The density of the stone largely depends on the density of the class to which the building material belongs.
- 0.7 - up to 700kg / m3;
- 0.8 - up to 800kg / m3;
- 1.0 - up to 1000k / hm3;
- 1.2 - up to 1200 kg / m3;
- 1.4 - up to 1400kg / m3;
- 2.0 - up to 2000kg / m3;
- 2.4 - up to 2400kg / m3.
Permissible deviations in the density of products for the class: 0.7, 0.8, 1.0, no more than 50 kg / m3. For other classes, no more than 100k / m3. As for the characteristics of thermal conductivity, they are estimated by the coefficients of masonry in dry mode. The strength grade of the brick depends on the possible compression and bending of the product.
Specifications
The moisture absorption of ceramic bricks can only be within the appropriate limits - no more than 6%. The initial water absorption of the product should be between 0.10 kg (m2 * min) - 3.00 kg (m2 * min). As for the facing bricks for the facade of the building, there are no restrictions.
There should be no damage such as cracking, crumbling, flaking and chips.
The coefficient depends on the values indicated by the manufacturer from 25 to 300. Ceramics is recognized as a non-combustible material, therefore, it must comply with this. The value of the specific radionuclide activity should not exceed 370Bkkg
With regard to the methods of testing the quality of ceramic bricks, they are also spelled out in the GOST standards, and take into account a number of requirements that the test specimen must withstand in order to meet the quality.
All test results are indicated in the relevant documents, which are submitted for making an opinion on the quality of the brick under study.
Here are some points:
- compliance with the declared size: length, thickness, height;
- if the product is hollow, then the conformity of the dimensions of the voids is acceptable during production. To determine the size of the voids, at least three cavities are measured and the largest value is recorded.
Specifications
The standard defines strength grades, frost resistance and density class. Strength grades represent the load that a material can bear. It is easy to decipher this value. The number that follows the letter "M" is the number of kilograms per square centimeter that the material can withstand without destruction. Example: M150 means that ceramic bricks of this batch will withstand a load of 150 kg / cm².
| Strength grades | Ceramic bricks | M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300 |
| Ceramic stone | M300, M400, M500, M600, M800, M1000 | |
| Clinker bricks | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100, M125, M150, M175, M200, M250, M300; | |
| Brick and stone with horizontal voids | M25, M35, M50, M75, M100 | |
| Frost resistance | F25, F35, F50, F75, F100, F200, F300. |
Strength and frost resistance grades for ceramic stone and bricks are indicated.
Frost resistance is indicated by the letter F and a number. The figure shows the number of freeze / thaw cycles that do not change characteristics and appearance. For example F50 - 50 frost and defrost cycles. For internal partitions in heated buildings, frost resistance can be taken low - a positive temperature will still be maintained.
Thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal resistance
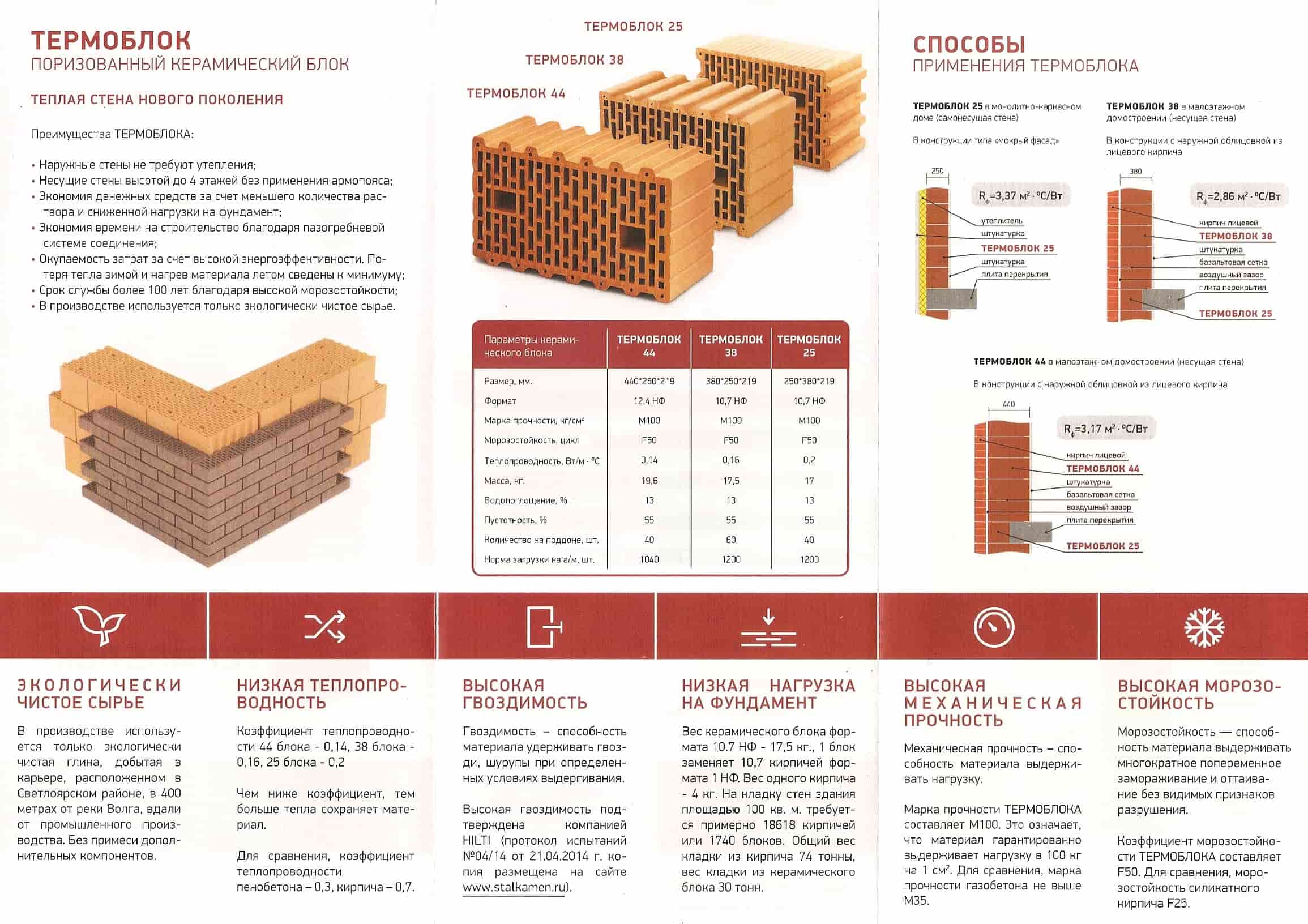
The density class corresponds to the average density of the material, but the energy efficiency of the material also depends on the density. The lower the density, the better the thermal insulation properties. But it will not be possible to significantly reduce the density for external walls. They must carry a certain level of stress. Therefore, in recent years, a brick house has been made with insulation.
The ratio of the average density of the product and the density class
How to work with the last two tables? The density class is indicated in the marking. By this characteristic, you can find out the mass of a ceramic brick cube. It is listed in the first table. The second table helps to compare the density of the material and the coefficient of thermal conductivity of masonry from it. For example, the density class of ceramic bricks is specified as 1.0. This means that the cube should weigh 810-1000 kg, and the masonry on a minimum layer of glue after drying will have a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.20-0.24 W / (m * ° C).
Groups of ceramic bricks and blocks according to the thermal characteristics of masonry (with a minimum amount of mortar)
It is worth saying that according to modern standards, none of the types of bricks gives the necessary thermal resistance. Unless the thickness of the wall will be more than a meter.
Masonry made of ceramic bricks of one and a half or two bricks does not meet modern requirements for thermal conductivity of external walls
In this case, a hollow brick or a building ceramic block wins, since they have the best thermal conductivity characteristics. The wall will be a couple of tens of centimeters already - not 147 cm, for example, but only 105. So, in any case, it is worth considering additional insulation of the outer walls.
Ceramic brick weight
The weight of ceramic bricks depends on the density and the presence / number of voids. The exact figure is recognized in the accompanying documents, and then, the spread within one batch is up to 10%.
The characteristics indicate the weight of different types of bricks: masonry, finishing, with and without voids
Using the old terminology, the approximate weight of ceramic bricks will be as follows:
- Single (type 1 NF, size 250 * 120 * 65 mm):
- corpulent (private, masonry, construction) 3.3-3.6 kg / piece;
- worker (private, masonry) hollow - 2.3-2.5 kg / piece;
- facing (front, finishing) hollow - 1.32-1.6 kg / pc.
- One and a half has a mass (type 1.4 NF, dimensions 250 * 120 * 88 mm):
- full-bodied private - 4.0-4.3 kg / piece;
- hollow private - 3.0-3.3 kg / piece;
- facial hollow - 2.7-3.2 kg / pc.
- Double weighs (1.8 NF 288 * 138 * 88 mm.):
- ordinary corpulent - 6.6-7.2 kg / piece;
- ordinary hollow - 4.6-5.0 kg / pc.
Comparison of the characteristics of ceramic bricks - hollow, different density, solid
We will give an approximate weight, since the density and number of voids for each plant can differ significantly. The number of voids is not regulated, so the finishing materials can be lightweight.
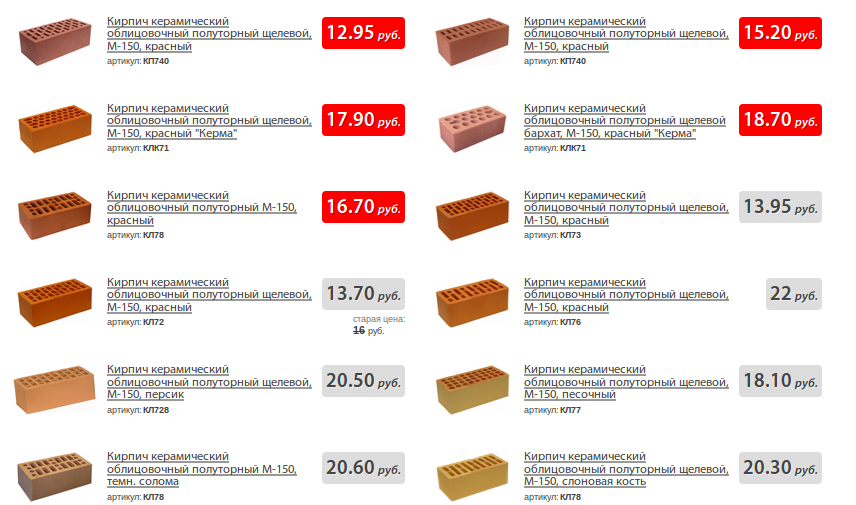
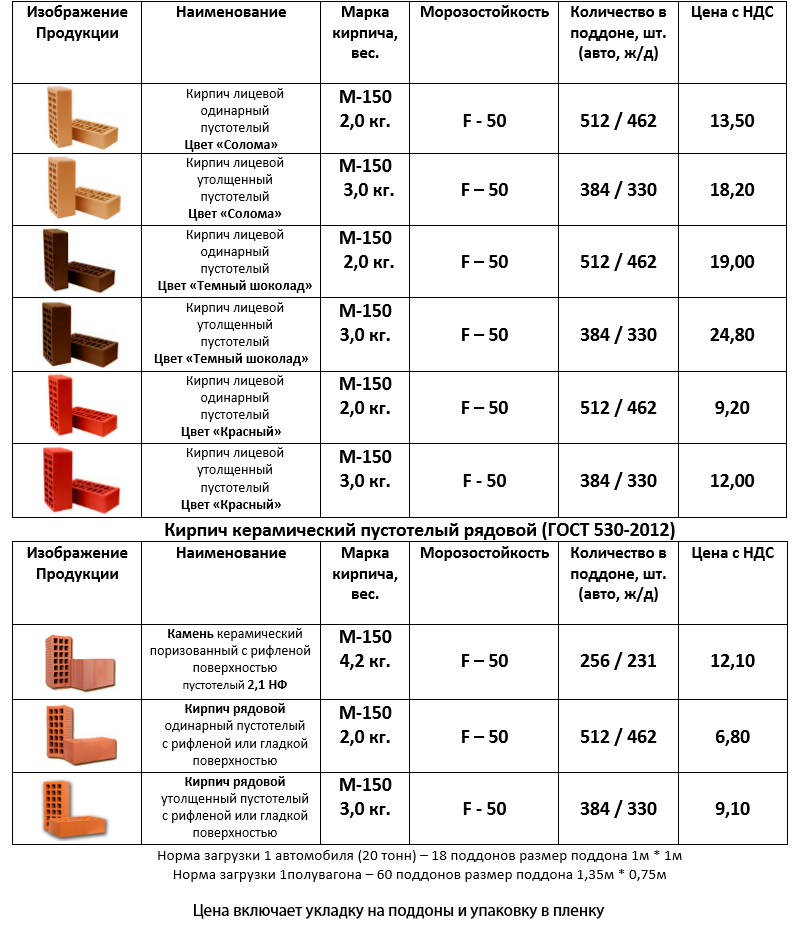
Price offer
The availability of brick products makes this material more popular in the market than others. Many brick factories offer their products, so if you need to purchase a large batch of goods, you can contact the factory closest to you and place an order.
When a large batch of bricks is purchased, the factory may provide free shipping, check this moment before buying.
The price of products depends on the type of ceramic bricks you need. So, for example, facing material will cost significantly more than ordinary ordinary brick. Here is the size of the facing brick. The brand of brick also affects the cost, so high-quality products are more expensive than low-quality ones, by 30% on average.
The cost of the most inexpensive standard brick starts at 6 rubles. per unit, but it can vary from region to region. Here's its size. The price for facing will be from 15 rubles, if you buy the most expensive imported production, then the cost will be from 40 rubles per piece.