Specifications
When producing alumina mixtures, manufacturers are guided by the requirements of GOST:
- GOST 11052-74 regulates expanding gypsum-alumina cement. The technical characteristics of this material depend on the proportion of bauxite, in this case up to 55%;
- Conventional alumina compositions of grades 40, 50 and 60, as well as high-alumina cement, are produced on the basis of GOST 969-91. The bauxite content ranges from 35% for standard types of material and up to 82% for cements with a high bauxite content in the mix.
Depending on the brand of cement, the material must meet the following parameters:
Alumina cement: characteristics, features, application
Alumina cement is a high-strength binder mixture that hardens quickly in water and air, which is mainly used in the manufacture of concrete and heat-resistant mortars.
To obtain this brand, manufacturers take a specialized raw material mixture rich in alumina, burn it in blast furnaces or electric arc furnaces before sintering and finely grind it. In this case, unnecessary raw materials such as iron and silica are removed from the grinding.
General characteristics of alumina cement
The prepared and applied alumina cement begins to harden approximately 45 minutes after application and fully cures within 10 hours. It can be successfully used in a humid environment, humidity does not prevent it from becoming strong enough.
Often, such cement is added to concrete to make the latter waterproof (when building structures located near reservoirs with fresh or sulphate water)
In addition, the alumina grade increases frost resistance and corrosion resistance, which is important for reinforcement
Where is alumina cement used
As a rule, a mixture of this kind is used in industrial construction, in places where one has to deal with aggressive water, high temperatures or gas environments.
An example is heating devices that must operate at temperatures up to 1300C °. Another example is mine construction (aggressive waters and gases), mining, construction of underground structures, and so on.
Builders also use cement during the elimination of accidents (with its help to seal holes in the ships of the sea fleet), in the repair and construction of bridges and industrial buildings. Sometimes the mixture becomes a component in mortars and adhesives for construction chemicals.
Features of the brand. Mixture types and their properties
As for the main difference of this type from other brands, alumina cement is rightfully considered one of the most fire-resistant. When compared with Portland cement, the fire resistance of alumina is slightly higher.
In fact, this mixture can be used in structures operated in temperatures up to 1700C °.
As mentioned above, it can be a part of other compounds (by mixing with such refractory fillers as chromite ore, magnesite and chamotte), which makes it possible to obtain hydraulically hardening refractory mortars and concretes.
There are three types of alumina cement: GC-40, GC-50, GC-60 - which differ in strength parameters:
Peculiarities
The first thing that distinguishes alumina cement from all others is the ability to harden extremely quickly in air or in water. To achieve this effect, the raw materials are processed in a special way, fired, and crushed. So, the initial raw material is necessarily soils enriched with aluminum, and they are supplemented with alumina.It is because of the special raw materials that the second name of alumina cement has gone - aluminate.

As mentioned above, alumina cement has a much shorter setting time than other types. This type is grabbed within 45 minutes after application. The final hardening occurs after 10 hours. In some cases, it becomes necessary to speed up an already fleeting process. Then gypsum is added to the original composition, getting a new variety - the gypsum-alumina version. It is characterized only by a faster setting and hardening period with full preservation of high strength characteristics.

All the positive properties of alumina cement can be combined into a large list.
- Excellent strength characteristics. Even under water, the material will be resistant to chemical and mechanical external influences. It does not corrode, it is not afraid of extremely low temperatures. All this opens up tremendous opportunities for its use.
- High speed of setting and hardening. This is especially true if you want to build any structure as soon as possible (for example, in three days).

- Immunity to aggressive components of the external environment. We are talking about all kinds of chemical compounds that affect the finished cement structure for a long time, for example: hard sulfite-containing water during mining operations, toxic gases, extreme heating.
- Excellent adhesion to all kinds of materials. An example is, for example, metal reinforcement, which is often used to seal blocks of alumina cement.

- Resistant to open fire. There is no need to fear that the cement will dry out and crumble. It perfectly withstands both exposure to high temperatures and a direct fire stream.
- Can be used as an additive to conventional cement. This is important when you need to make the structure frost-resistant, while saving money. On the basis of alumina raw materials, rapidly expanding and non-shrinking cement mixtures are made, which are used in industrial construction or during urgent repair work.

There are alumina options and disadvantages.
The first and foremost is the high cost of producing the material.
It is important here not only equipment, which must be super-strong and have increased capacities, but also strict adherence to technology, maintaining temperature conditions during firing and other nuances

The second disadvantage is associated with the advantage of the mixture. Due to the fact that the alumina variety generates heat when solidifying, it is not suitable for pouring large areas: cement may not solidify properly and collapse, but in one hundred percent of cases it will greatly lose its strength characteristics. You cannot pour such cement even in extreme heat, when the thermometer shows a temperature of over 30 degrees. It is also fraught with loss of strength.

Finally, despite the high resistance of the alumina version to acids, toxic liquids and gases, it is absolutely unable to withstand the negative effects of alkalis, therefore it cannot be used in alkaline environments.

Alumina cement is divided into two large groups: expanding and mixed. The peculiarity of the expanding material is the ability of the raw material to increase during the hardening process. The changes will not be noticeable with the eye, however, this has a positive effect on the resulting density of the monolithic cement block. Expansion occurs within 0.002-0.005% of the original volume.


Mixed samples are made mainly for the purpose of lowering the cost and, accordingly, the price of the product, however, in some cases, additives provide additional characteristics. So, for example, gypsum guarantees a higher setting rate, while the cost of cement increases.Slags and other active mineral additives, on the contrary, increase the setting time, but the price for such a mixed cement is noticeably lower.

Alumina cement: characteristics, features, application
Alumina cement is a high-strength binder mixture that hardens quickly in water and air, which is mainly used in the manufacture of concrete and heat-resistant mortars.
To obtain this brand, manufacturers take a specialized raw material mixture rich in alumina, burn it in blast furnaces or electric arc furnaces before sintering and finely grind it. In this case, unnecessary raw materials such as iron and silica are removed from the grinding.
General characteristics of alumina cement
The prepared and applied alumina cement begins to harden approximately 45 minutes after application and fully cures within 10 hours. It can be successfully used in a humid environment, humidity does not prevent it from becoming strong enough.
Often, such cement is added to concrete to make the latter waterproof (when building structures located near reservoirs with fresh or sulphate water)
Where is alumina cement used
As a rule, a mixture of this kind is used in industrial construction, in places where one has to deal with aggressive water, high temperatures or gas environments.
An example is heating devices that must operate at temperatures up to 1300C °. Another example is mine construction (aggressive waters and gases), mining, construction of underground structures, and so on.
Builders also use cement during the elimination of accidents (with its help to seal holes in the ships of the sea fleet), in the repair and construction of bridges and industrial buildings. Sometimes the mixture becomes a component in mortars and adhesives for construction chemicals.
Features of the brand. Mixture types and their properties
As for the main difference of this type from other brands, alumina cement is rightfully considered one of the most fire-resistant. When compared with Portland cement, the fire resistance of alumina is slightly higher.
In fact, this mixture can be used in structures operated in temperatures up to 1700C °.
As mentioned above, it can be a part of other compounds (by mixing with such refractory fillers as chromite ore, magnesite and chamotte), which makes it possible to obtain hydraulically hardening refractory mortars and concretes.
Specifications
The technical characteristics of alumina cement fluctuate depending on which brand it belongs to. According to GOST 969-91, developed back in the 70s, such cement is subdivided by strength into GC-40, GC-50 and GC-60. Also, the proportions of certain substances in the composition depend on what properties need to be achieved and in what area the cement will be used. It makes no sense to give here the chemical formulas of the substances that make up the cement, but for comparison, it should be said that ordinary alumina cement contains from 35% to 55% of bauxite, while high-alumina refractory cement contains from 75% to 82%. As you can see, the difference is significant.
With regard to technical properties, although alumina cement is a fast-setting option, this should not affect the speed of its setting. According to the rules and regulations, it should be at least 30 minutes, and full curing occurs after 12 hours after application (maximum). Since the material has a special crystalline structure (all crystals in the substance are large), it is not very susceptible to deformation changes, and therefore we can confidently speak of its non-shrinkage and relatively small mass.

Variants differ in characteristics and depending on the method of their production.In total, only two methods are presented: melting and sintering.
Each of them has its own specifics.
Scientifically, the first method is called the method of melting the raw material mixture. It involves several stages, each of which deserves close attention. First you need to prepare the raw materials. After that, the cement raw material mixture is melted and gradually cooled, closely monitoring the temperature indicators to ensure the best strength characteristics. Finally, the obtained high-strength slag is crushed and ground to obtain alumina cement.

With the sintering method, everything happens the other way around: first, the raw materials are crushed and crushed, and only then they are fired. This is fraught with the fact that the cement obtained in this way is not as strong as in the first method of production, but the second option is less laborious.

The technical parameters of the alumina cement composition can vary within a fairly wide range (this also applies to the chemical formulas of the substance), but this should not significantly affect its main characteristics, such as the speed of hardening, strength, moisture resistance, and deformation resistance. If the technology was not followed during the manufacture, and some of the listed characteristics are lost, then the material is considered defective and is not subject to further use.

Types and marking
Depending on the composition and properties, the following varieties are distinguished:
- VRC is a waterproof expanding cement characterized by a high hardening rate and increased resistance to moisture. It is used in the restoration and construction of underground and underwater facilities, waterproofing of mines and tunnels.
- RC is an expanding Portland cement that hardens quickly during steaming.
- NTs - stressing cement, recommended for concreting structures with multidirectional reinforcement, for example, pressure pipes or thin-walled concrete products. This variety, in turn, is divided into NTs 10 (non-shrinking), NTs 20 (straining) and NTs 40 (self-expanding).
- GGRTS - gypsum-alumina, intended for the preparation of waterproofing plasters and concrete.
Main characteristics and properties
All of the above listed types of binder are fast-hardening hydraulic binder, set with water and gaining strength in conditions of high humidity. The technical characteristics of cements with such abilities depend on the composition, the setting time and other indicators differ for different brands:
| Parameter or property name | VRC | RTS (ROC) | NTs | GGRTS |
| Composition, % | Gypsum cement - 70, highly basic calcium hydroaluminates - 10, gypsum - 20 | Portland cement clinker - 58-63, slag - 5-7, gypsum - 7-10, hydraulic additive - 20-25 | Portland cement - 65-70, slag - 16-20, gypsum - 14-16 | High-alumina slags - 70, gypsum - 30 |
| Setting start, min | From 4 | Not earlier than 30 | 2-5, extended by adding sulfite-alcohol stillage | Not less than 20 |
| Final set, strength, h | After 25-28 hours, the structure becomes completely waterproof, but the maximum brand strength is reached after 28 days | 65-80, subject to steaming - 30-35 | Up to 28 days | 70-85 |
| Curing and operating conditions | Internal expansion lasts a long time, the best results are observed when hardening in a highly humid environment | Recommended for steaming at temperatures from +60 ° C | Characteristics are improved upon steaming | They warm up when it is necessary to pour concreting at negative temperatures, when hardened in air, they need intensive moistening for at least 3 days |
| Compressive strength, kgf / cm2 | Up to 500 | 400-600 | Up to 600 at NTs 40 | Up to 500 |
| The value of the relative linear expansion,% | 0,02-1 | 0,3-1 | Until 3 | 0,3-1 |
The positive properties of mortars based on expanding and stressing cement include:
- High adhesion, also with metal fittings and old building materials.
- Accelerated set of strength - most brands reach 80% of the maximum during the first day, they are advised to buy with a limited time frame.
- No shrinkage, crack resistance, uniform distribution of solutions within cavities.
- Resistance to corrosion, aggressive influences, temperature extremes, alkalis and moisture.
- Good compressive strength - up to 600 kgf / cm2.
- Durability.
Alumina fast hardening cement
Currently, cement is deservedly considered one of the most important building materials. It has been widely used for over 160 years. There is also such a variety as aluminous. This type is a highly durable substance that hardens rather quickly both in air and in water. It is obtained by firing to the state of sintering or melting a mixture that is rich in alumina and calcium oxide.
Composition and characteristics
The raw material for this building material is pure limestone and bauxite. The latter are a rock, which consists of alumina hydrates and impurities. Such a component as bauxite is widely used in various industrial sectors: for the manufacture of aluminum, refractories, abrasives, adsorbents.
<?php related_posts(); ?>
Chemical composition as a percentage: CaO (calcium oxide) - 35-45%; А12О3 - 30-50%; SiO2 - 5-15%; Fe2O3 - 0-15%. The mineral composition is dominated by such a component as mono-calcium aluminate, which determines many of the basic properties. Aluminates such as CA2, C12A7 are also present in it.
The main properties include:
- High strength;
- The ability to quickly harden;
- Resistance to aggressive environments;
- Perfect adhesion to fittings;
- Refractoriness.
Manufactured in accordance with GOST 969-91, only three grades, including: GC-400, GC-500, GC-600. The brand is determined, as a rule, at the age of three days from the date of manufacture. Within the framework of the sample under consideration, there are two main groups: mixed and expanding.
Mixed ones are obtained by combining active mineral additives, slags with inorganic binders. The main samples of this group:
Pozzolanic Portland cement. As a rule, it is made using an active mineral additive. Such a sample has long periods of hardening and setting, reduced frost resistance and low exometrium. Produced under the brands 300 and 400.
Slag Portland cement. Usually it is made by grinding clinker, adding gypsum, granulated slag. Available in three grades: GC-300, 400, 500. It has excellent adhesion, both with reinforcement and in reinforced concrete.
It is also important that this option has the lowest cost.
Alumina expanding cement is another variety. The main feature of this type is that during hardening, a certain increase in the volume of the raw material is created. This is due to the fact that calcium hydrosulfoaluminates are formed during the interaction of the initial components.
1. VRC is a waterproof expanding cement. It is quick-hardening because it contains semi-aqueous gypsum and highly basic calcium hydroaluminate. It is produced as alumina cement grade 500. It differs in that it can only be used at positive temperatures, since it has a reduced frost resistance.
2. Non-shrinking cement - VBC - which consists of exactly the same elements, while using slightly different proportions.
Production and application
There are two production methods, which depend on the firing method. It is a sintering method and a melting method. According to the first method, the prepared raw material is sintered. It takes place in rotary kilns or shaft kilns at temperatures no lower than 1300 ° C. This method is quite expensive and, therefore, unpopular.
The second method is cheaper and more convenient.For melting, shaft furnaces with a water-cooled jacket are used. The clinker is crushed immediately after cooling.
It is advisable to use alumina cement:
- in the process of erecting defensive and military transport facilities;
- restoration of the once destroyed military transport buildings;
- when building bridges, highways, artificial structures (especially when there is a lack of time);
- when erecting such structures that may periodically be exposed to the effects of tides - in this case, these can be ports, dams or embankments;
- for work performed at low temperatures;
- for urgent repair work, for the prompt construction of the foundation;
- in urgent cases that may arise in construction practice (repairs after fires, immediate elimination of accidents).
The building materials market offers a wide range. The following prices are presented in Moscow and the region.
Advice
In conclusion, it is necessary to give advice on how to distinguish genuine from fake cement. Alumina and especially high-alumina refractory options are quite expensive, so you can often come across a counterfeit in this market. According to statistics, about 40% of the cement on the Russian market is counterfeit.
There are a number of guidelines to help you spot the catch right away.
The most obvious rule is to buy cement from proven, reliable suppliers. Well-established firms include Gorkal, Secar, Ciment Fondu, Cimsa Icidac and a few others.

To dispel final doubts, you need to ask the seller to show the sanitary and epidemiological conclusion. It states that the material is absolutely safe for human health. Some unscrupulous manufacturers add radioactive substances to cement mixtures. Although present in small quantities, they can cause significant harm to health. The norm for the content of natural radionuclides is up to 370 Bq / kg.


- If, after checking such a conclusion, doubts remain, we advise you to verify the address of the authority that issued the sanitary and epidemiological conclusion. On the packaging and on the conclusion itself, this address must be the same.
- Check the weight of the bag in accordance with GOST. It should be equal to 49-51 kg and in no case go beyond these limits.

Having chosen the composition, first buy one bag for a sample. At home, knead the cement, and if you evaluate it as high-quality, you will not find any extraneous additives in it in the form of crushed stone or sand, then this means that it is of high quality
Finally, pay attention to the expiration date. It is extremely small - only 60 days from the day of packaging
Be sure to take this criterion into account when choosing, otherwise you risk buying a material whose performance will be many times worse than expected.
See below for more details.
Manufacturing features
A raw material such as cement is a product group that includes aluminate and silicate-based hydraulic substances that are formed during the heat treatment of components.
A special place in the line of these products is given to a fast-acting type of construction mixture, the main characteristic of which is the ability of the material to freeze not only in contact with air, but also in water. This product is called alumina cement. In addition, there are other product names such as aluminate cement.


The production of raw materials takes place using a special technology, during which the base components are additionally enriched with alumina. After that, the composition is heat treated in blast furnace or electric arc factory furnaces, and then crushed to the required particle size. The chemical formula and technical characteristics of these products make it possible to use them for the preparation of heat-resistant concrete.The main distinguishing feature of alumina cement from raw materials of other brands is fire resistance, which is several times higher than similar indicators of products of other companies, for example, Portland cement. According to experts, the composition of the mixture allows it to be operated at temperatures reaching 1700C.
Alumina cement is often used as one of the components in various compositions, mixed with magnesite or chamotte, which makes it possible to produce hydraulically set fire-resistant mortars.
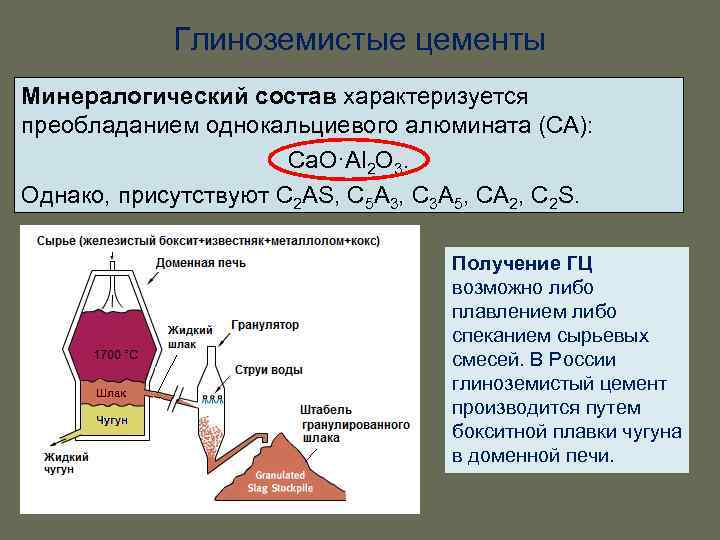
Cement production is carried out on the basis of bauxite and limestone in combination with a number of other substances that are responsible for certain characteristics of the composition. Modern production facilities use two methods of producing the composition in accordance with GOST - sintering and melting. The choice of the production method is based on the specificity of the bauxite composition and the level of content in the elements of various inclusions, for example, iron oxide.


In the course of choosing the latter production method, very high requirements are imposed on the quality of bauxite. The process begins with the immersion of the composition in a water-cooled oven. Hot air, which is supplied through the tuyeres, provides the melting procedure of the composition. At the end of processing, the raw material is cooled and crushed.
Much less often resort to the arc melting method, due to which the highest quality characteristics become inherent in cement.
After production, further preparation of the composition is carried out, which includes mixing all the ingredients. Then they are granulated or briquetted.
When blast furnaces are used for the production of alumina cement, a high-alumina slag is formed as a result of production, in which there is no iron, but there is a large content of silica. Such products have a disadvantage associated with the minimum strength indicators. composition at first solidification. In domestic production, the method of producing a cement mixture by blast-furnace smelting has become very popular.


The sintering process is a method of making alumina cement in conventional factory furnaces with low heating. In the course of the gradual cooling of the raw material, the genelite, which is part of its composition, crystallizes and acquires a glassy structure. Controlling the heating level during this manufacturing process is fundamental, as insufficient heating will promote crystallization of calcium aluminates.
At the exit from the equipment, the composition is granulated. And the quality of the cement obtained in this way will allow the products to stand out with the maximum values of the strength of the raw materials.
In some cases, the method of electrofusion of the composition is used. The advantage of this method is the purification of the composition from silicic acid.


Expanding gypsum-alumina cement GOST 11052-74
Expanding gypsum-alumina cement GOST 11052-74 (GOST 11052-74)
Gypsum expanding cement is a type of alumina cement and is a mixture of finely ground alumina blast furnace slag and gypsum stone in a percentage ratio (70:30)
Chemical composition, %
|
SIO2 |
CaO |
Al2O3 |
SO3 |
MgO |
Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
10-12 |
38-41 |
26-30 |
no more than 17 |
0.9 |
1.5 |
• Tensile strength for 3 days not less than 280 kg / cm.
• Start of setting not earlier than 10 minutes.
• Linear expansion after 3 days from the moment of making the samples should be not less than 0.1% and not more than 0.7%.
• Concretes and mortars prepared on this cement are waterproof at an excess water pressure of 10 atm.
Building properties
• Structures and parts made of concrete and mortars on gypsum-alumina expanding cement can harden both in air and in water. Under water conditions of hardening, concrete on gypsum-alumina expanding cement is non-shrinking, and in air conditions it shrinks 1.5-2 times less than alumina cement.Thus, for gypsum-alumina expanding cement, hardening under high moisture conditions is absolutely necessary.
• Concrete based on gypsum-alumina expanding cement is sufficiently stable and durable in strength.
• Expandable cement mortars and concretes can be successfully steamed, but should not be used above 100 degrees.
• Concretes based on gypsum-alumina expanding cement harden even faster than concretes based on original alumina cement (at three days of age, having 85% of the 28-day strength).
• Possess high weather resistance, frost resistance, sulfate resistance.
• They have an advantage over Portland cement-based concretes in monolithic massive structures and foundation bolt pouring.
• Fire resistance of gypsum-alumina expanding cement is higher than that of Portland cement, but significantly lower than that of alumina cement.
Application
Gypsum-alumina expanding cement is intended for the production of non-shrinking and expanding waterproof concrete and waterproofing plasters:
• In metro construction, it provides watertightness of metro tunnels, allows for caulking of seams between tubing, for cementing and reinforcing old structures.
• In industrial and civil construction, it is used in the construction of tanks for storing liquid fuel and other similar purposes, for caulking the seams of water lines at an operating pressure of up to 10 atm.
• In municipal services for waterproofing coatings of treatment facilities, when monolithing joints of various liquids, construction of swimming pools, during the repair of showers and other structures.
Consumers
The main consumers of gypsum-alumina expanding cement are:
• Construction organizations of the metro.
• Utilities enterprises.
• Construction organizations erecting tanks for various liquids.
It is shipped in paper bags (45 kg), containers (MKR-1, OS) to all regions of Russia.
Structure and types
Depending on the volume of impurities in the substance, cement of this type is divided into two main types: ordinary composition and high-alumina. Determination of the cement grade is carried out after 72 hours. The composition is usually imported to Moscow and the region, other regions in small volumes, sold in special bags or containers of 40-50 kilograms. Depending on the volume of iron in the total composition and the oxidation rate of the components, alumina cement can be green, yellow, brown, black in color.
Products are marked with GOST. There are three main types of alumina cement, which differ in their ability to withstand compressive loads: grades GC-40, GC-50 and GC-60. After 72 hours after pouring, the GC-40 mixture gains strength from 22.5 (MPa every other day) to 40 MPa. This is the most popular brand, relevant for various construction work. The strength index of GC-50 reaches 50 MPa, respectively, cement is used in the field of fuel and energy. The strength of GC-60 reaches 60 MPa; this mixture is used in the defense sector and metallurgy.
Alumina cement is a material that requires proper operation. It is advisable to entrust the work with the mixture to the masters. Cement has a high viscosity, it is harder and longer to mix (when compared with ordinary Portland cement, for example), but the homogeneity and resistance of the concrete depend on the correct mixing.
The mixture is usually prepared in small portions, since it will not be possible to slow down the hardening process, and it is almost impossible to quickly use large volumes of concrete. When the composition begins to set immediately after preparation, it is very difficult to work with it, and this can affect the quality of the final design.
Alumina cement is often used for the preparation of various types of expanding mixtures, fast-hardening compositions.For any such solution, the ratio of the components and the composition are subtracted separately. Usually, the mixture increases in volume during hardening, balancing shrinkage, and also self-compacting. To obtain these mixtures, alumina cement is mixed with various additives.
Special types of HC:
- with gypsum and crushed slag - sets quickly, expands in water.
- Waterproof mixture with minimal shrinkage - gypsum hemihydrate and slaked lime are added to the cement, which makes it possible to obtain a material that is relevant for use in waterproofing works.
- Expanding Waterproof Cement - rapidly gaining strength, used for waterproofing shipping locks, tunnels, pipelines, swimming pools, etc.
Alumina cement GC-40, GC-50, GC-60 GOST 969-91
Alumina cement GC-40, GC-50, GC-60 GOST 969-91 (GOST 969-91)
Alumina cement is a high-strength binder that quickly hardens in water and in air, intended for the manufacture of building and heat-resistant mortars and concretes.
Produced in accordance with GOST 969-91 in three grades: GC-40, GC-50, GC-60. It differs from other cements in its high strength achieved at an early age.
|
The beginning of setting - not earlier than 45 minutes |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
End of setting - no later than 10 hours |
|||
|
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH AT AGE |
1 DAY |
3 DAYS |
|
|
GC-40 |
MPa |
22,5 |
40,0 |
|
GC-50 |
MPa |
27,4 |
50,0 |
|
GC-60 |
MPa |
32,4 |
60,0 |
The setting time can be changed by the introduction of retarders (boric acid, borax, calcium chloride, etc.) or accelerators (lime, Portland cement, gypsum, etc.).
Special properties include
• rapid build-up of strength at an early age;
• when concrete hardens on alumina cement, a large amount of heat is released, which makes it possible to use these concretes at negative temperatures down to -10 degrees without heating;
• alumina cement has an increased density of cement stone, which determines the greater resistance of concrete against all types of aggressive liquids and gases in comparison with concrete based on Portland cement;
• Alumina cement is more fire-resistant and thermally stable than Portland cement. In a mixture with refractory aggregates: chamotte, chromite ore, magnesite, etc., alumina cement can be used to obtain hydraulically hardening refractory mortars and concretes.
Application
• For the manufacture of concrete and reinforced concrete structures, when the design strength of concrete must be achieved within 1, 2, or 7 days.
• For the construction of offshore and underground structures where increased sulfate resistance is required.
• For plugging cold oil wells, plugging cracks in rocks at high water flow rates.
• For sealing holes in ships of maritime transport.
• For quick installation of foundations for machines, pouring anchor bolts, rebuilding damaged buildings and bridges.
• For the manufacture of precast concrete products at precast concrete factories and construction sites, where alumina cement plays the role of a concrete hardening accelerator.
• For the manufacture of containers and other structures, where alumina cement gives increased resistance against organic acids, sulfur compounds, sulfuric acid, lactic acid, brine, starch.
• For the manufacture of refractory concrete and piece products with refractoriness up to 1700 gr. C.
Consumers
The main consumers of alumina cement are enterprises of the fuel and energy complex, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, and construction complexes of defense significance.
The cement is certified, it is shipped in paper bags (45 kg), containers (MKR-1, OS) to all regions of Russia and the CIS countries.