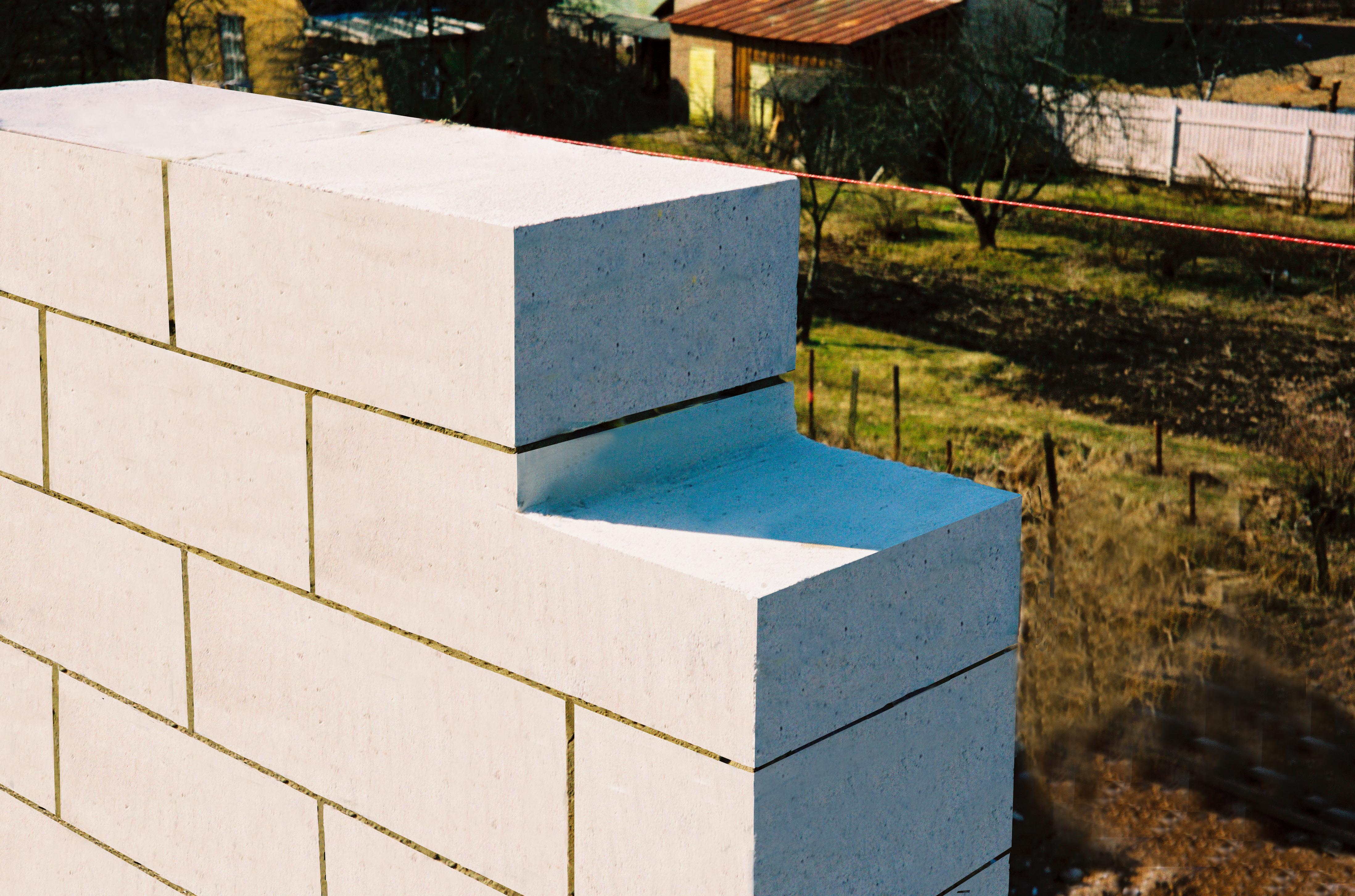
Comparison of characteristics
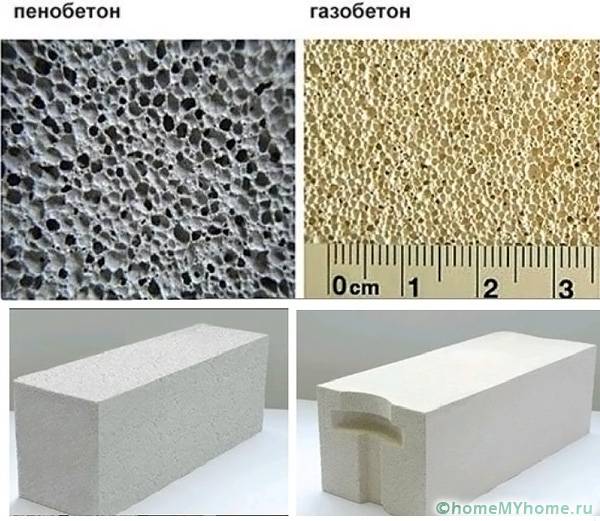
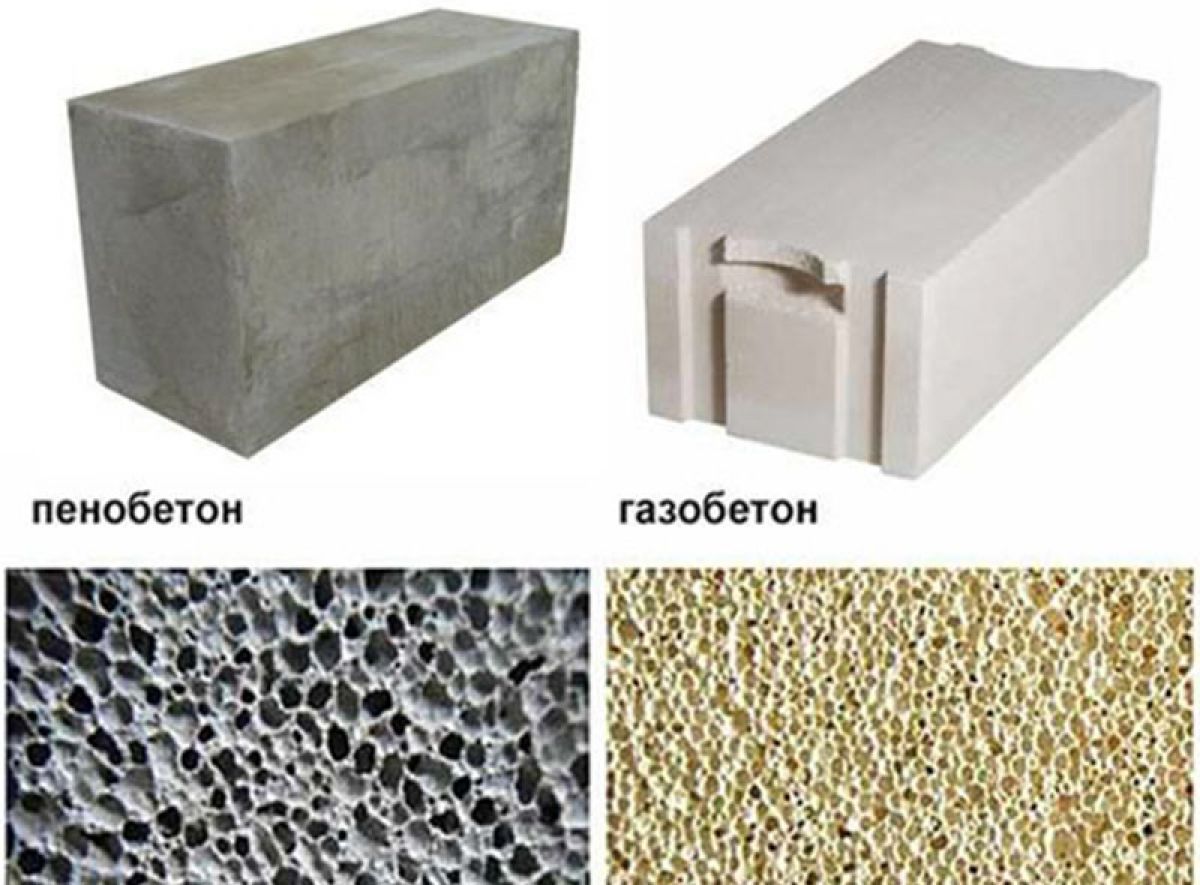
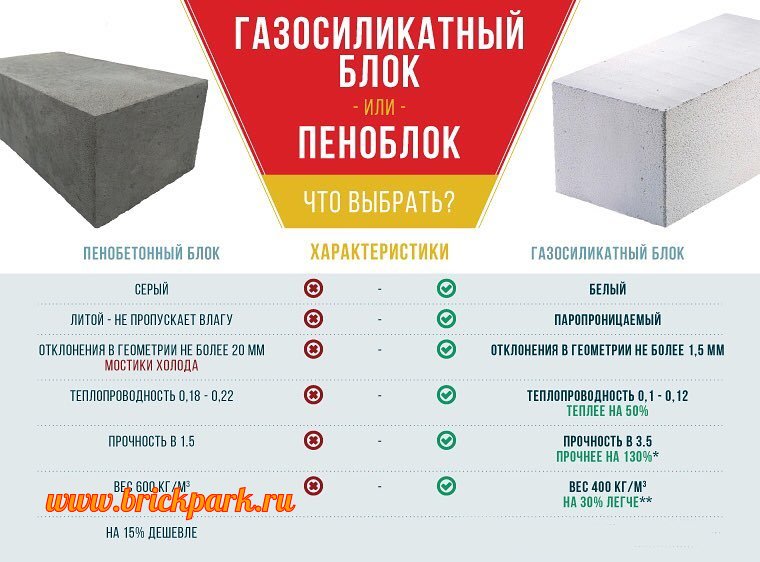
Autoclave gas silicate blocks and autoclave aerated concrete blocks are almost identical in their characteristics. Therefore, we will compare autoclave gas silicate blocks and non-autoclave aerated concrete blocks.
Dimensions (edit)
Gas silicate blocks and aerated concrete blocks do not differ in size according to GOST. The values are as follows, in mm:
250*250*600.
250*400*600.
500*200*300.
600*100*300.
600*200*300
The most commonly used is 600 * 200 * 300.
But, in fact, there are no hard standards, and in practice you can find a variety of sizes. This is especially true of gas blocks produced in small industries.
Strength
The gas silicate block is many times stronger. This is its main advantage over the gas block.
As for the general indicator of strength, it directly depends on the density of the material. The higher the density, the less bubbles are contained in the blocks. It turns out that the stone component of the blocks will be more durable due to the fact that the bridges between the bubbles are thicker. The difference is small - up to 1 mm. But due to the number of these bridges, the effect of strengthening the structure is obtained.
A very important point must be made here. The tensile strength of both blocks is extremely low
Compression performance is better.
Thermal conductivity
It makes little sense to compare the thermal conductivity of aerated concrete or gas silicate blocks, which is better and more reliable. Both keep warm inside the house perfectly.
By the way, there is an inverse dependence of thermal conductivity on the density of the building material. The stronger the block, the denser and heavier it is. And, accordingly, there are fewer voids in it. This suggests that the higher the grade of the block, the worse it retains heat.
Fire resistance
Gas silicate and aerated concrete blocks are non-combustible.
It is not uncommon for manufacturers to publish the results of numerous tests. All of them claim that a 1 cm thick gas silicate plate can survive under the influence of fire for 2 hours. This is before the destruction of the material, that is, before the appearance of cracks. Non-autoclaved aerated concrete has worse performance, but also good enough.
By the way, it is quite possible to hide behind such a wall from the fire. The cavities inside the wall will work like the walls of a thermos, allowing only a small portion of the heat to pass through.
Moisture resistance
The level of water absorption is increased. Both materials absorb moisture. This will lead to the formation of mold and mildew. Strength will also decrease. High-quality waterproofing is required.
Vapor permeability
Present. And that's not bad. It is said that a house made of cellular materials “breathes”, which creates a good microclimate inside.
Frost resistance
The difference between gas silicate and aerated concrete is significant here.
The non-autoclave gas block has a very decent frost resistance, up to 75 cycles.
But in gas silicate, it reaches 150 cycles.
The indicator is more technical, not mundane.
Frost resistance means how many freezing cycles a material can painlessly “survive” and not begin to deteriorate. Ice is the main enemy of the material. The moisture, crystallizing, expands the concrete, because of which the partitions between the bubbles break, thereby weakening the strength of the structure. But, in fact, complete wetting almost never occurs. Only in the event of a flood, perhaps.
Note that the higher the brand of the block, its density, the higher the frost resistance index.
Soundproofing
Aerated concrete and gas silicate - porous structures. And here and there, the sound insulation is excellent. True, there are some differences, in this classification gas silicate is somewhat inferior to aerated concrete. The second has a softer structure, due to which sound vibrations are better damped.
Shrinkage susceptibility
Here the gas block definitely loses to the gas silicate one. If for the first it is about 0.5 mm per meter, then for the second it is about 3 mm per meter.
Environmental friendliness
The blocks are made from natural materials, and after processing they do not emit any substances into the ambient air. Houses built from such building blocks are absolutely environmentally friendly.
Appearance
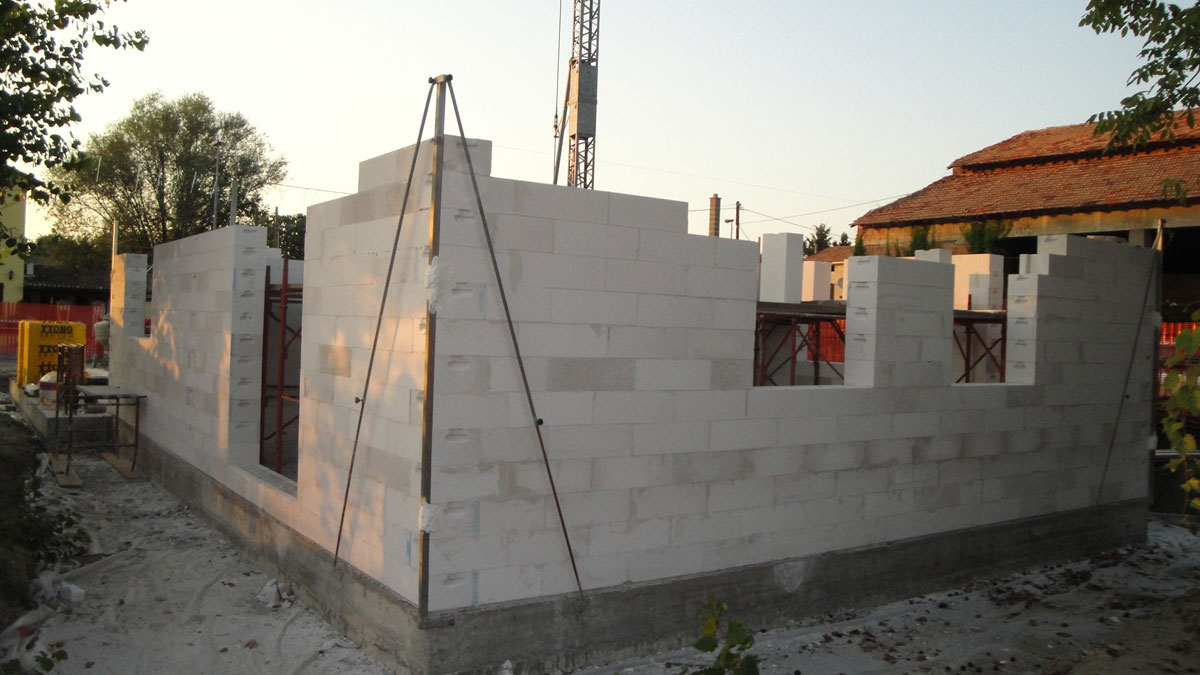
Differences in color. Gas silicate - white, aerated concrete - gray. But that's not the point. Non-autoclaved aerated concrete is almost certainly more uneven. And this can be of great importance during masonry, because imperfect geometry complicates the process and increases the consumption of glue.
Production technology
Foam concrete and aerated concrete are made using different technologies. Let's consider them in more detail.
Aerated concrete blocks are produced as follows:
- First, the necessary materials are prepared in the right proportions (these include sand, lime and cement). When dry, they are mixed using a special technique for 4-5 minutes. After that, a suspension of aluminum powder is added to the mixed composition, the basis of which is water.
- In the course of mixing, lime reacts with aluminum. This produces hydrogen. Due to strong gas formation, air bubbles form in the composition. They are evenly distributed throughout the solution.
- After that, the finished composition is poured into a mold. It should be preheated to the 40 degree mark. Pouring is done by ¼ of the volume of the container.
- When the composition is sent to the molds, they are transferred to a special chamber, where further pore formation of the material is carried out. As a result, the volume of the resulting mass begins to grow gradually and acquires strength properties. In order to activate the desired reactions in the solution, as well as for its optimal distribution in the form, they turn to vibrational action.
- When the resulting composition reaches preliminary hardening, any irregularities must be removed from its surface. This is done with wire strings.
- Further, the composition is taken out of the chamber and transferred to the cutting line.
- The next step in the manufacture of gas blocks will be to send them to an autoclave.
Often, aerated concrete slabs are marked with the designation AGB (meaning autoclaved material). At the same time, the autoclave itself is a kind of "pressure cooker" of impressive dimensions. Under its conditions, a pressure of 12 atm is injected, and then maintained. As for the temperature, it should be 85-190 degrees. In this setting, aerated concrete slabs are prepared within 12 hours.
When the blocks are completely cooked in an autoclave, they are divided additionally, since during preparation in some places they can combine with each other. After that, these materials are placed in a special heat-shrinkable material or polyethylene.
Aerated concrete is produced without the use of an autoclave. In this case, the hardening of the composition takes place in natural conditions - in this case, special equipment does not need to be used.

Foam concrete is made a little easier and easier. There are 2 ways of its production - cassette and sawing.
The cassette method involves pouring the solution into special forms.
The technology, called sawing, involves pouring the solution into one large container, after which it is expected to harden and further cutting into separate elements of the required dimensions is carried out.
For the manufacture of foam concrete blocks, cement of the M400 and M500 brands, clean sand without clay, a foaming agent, potassium chloride and, of course, water are used.

4 Foam blocks or gas silicate blocks - more quality, less hassle. Compare characteristics
To make the right choice and make the right decision, it is necessary to compare the main characteristics of foam concrete and aerated concrete. On the one hand, gas silicate has a higher strength.It withstands external loads well. Therefore, undoubtedly, the building made of it will be stronger. However, the foam block is easier to process. The blocks can be shaped to the desired shape, which allows the construction of complex structures (for example, arches). Therefore, in this situation, the choice should be made on the type of construction and the upcoming decoration.
As for sound insulation, here, of course, the foam block wins simply due to the properties of the material, despite the porous structure that is identical for both varieties. But additional insulation is still required in both cases. Therefore, this property is unlikely to have a large impact on the choice. However, so is energy efficiency. Indeed, despite the fact that gas silicate has a higher thermal insulation, additional heating for buildings will be required when using any of them.
Comparative characteristics of foam blocks and gas silicate blocks
Both materials are not resistant to moisture. They are highly hygroscopic and absorb moisture well. Salvation will be a layer of waterproofing outside and inside the house. But the impact of negative temperatures is easier for foam concrete, but insulation is required again in both cases.
Gas silicate, unlike foam concrete, is a breathable material. That is, in a house built from it, the air will always be fresher. The building does not require any special ventilation. But buildings made of foam concrete must be equipped with a high-quality and branched ventilation system. Windows must be equipped with special valves. Otherwise, fungi and various microbes will quickly begin to develop in the "clogged" space.
For many, before starting construction, the issue of reinforcement remains relevant. Therefore, it should immediately be noted that when erecting a structure, it is necessary to use reinforcing gaskets. For foam blocks, the "step" for a one-story building is 2 rows, and for gas silicate - three. Completing a floor requires an armored belt in both cases.
Cost is not quite a correct value for comparison, but it plays an important role in the choice. In most cases, gas silicate is 15-25% more expensive than foam concrete due to the technological features of its production.
Both materials have impressive advantages and disadvantages. With a completely small difference between themselves, they will become an almost ideal option for budget construction. Being cladded with clinker bricks, they will create the effect of a completely brick house, while being much cheaper, practical, warm solutions. Which is better - gas silicate or foam concrete - you can answer this question correctly only on the basis of the technical requirements that will be imposed on the construction object.
Comparison of characteristics
To know what to give preference to, gas silicate or foam block, it is required to initially conduct a comparative analysis of their technical properties. Unfortunately, despite the rapid technological development, there is still no ideal building material in all respects. For this reason, you have to make a choice based on the analysis and the gas silicate.
To find out which of these materials takes the first place, we need to conduct a comparative analysis according to the following characteristics:
- fortress;
- soundproofing;
- thermal insulation;
- ecological cleanliness;
- price;
- ability to absorb moisture;
- do you need reinforcement;
- the need for decoration or decoration;
- the complexity of installation work;
- the quality of the materials made.
Strength

In the conditions of our country, they are used to building houses so that they stand for more than a dozen years. If we take into account the prices for building materials, it becomes clear that this is not only better, but also simply necessary. Because of this, it becomes clear the desire to choose the most durable material for the construction of walls. It must be remembered that the strength of gas silicate is much better than that of foam concrete.However, due to the reduced strength, such blocks are easily cut into the necessary parts, it is easier to make a hole or protrusions in them.
Gas silicate blocks offer much better resistance against various external loads.
This helps them keep their original shape and do not paint during transportation or unloading. It follows from this that the erected building will come out much stronger.
From this comparison, it becomes clear that it is difficult to make a choice. Everything directly depends on what operations with the block will be performed. If it will be necessary to further process it, then foam concrete is better. If you need a structure with strong and even walls, then gas silicate is the best choice.
Soundproofing
Due to the fact that foam concrete has a special porous structure, the level of sound insulation is higher than that of similar gas silicate blocks. But this does not mean that additional sound insulation will not be needed.
Thermal insulation
All people want to have a warm and comfortable home.
And if we take into account that our winters are not too warm, then the desire not to depend constantly on heating devices becomes understandable. Walls, in the construction of which foam blocks or gas silicate are used, need additional insulation
This especially applies to insulation outside the building. Gas silicate has a much higher thermal insulation, however, insulation work is necessary.
The difference between the blocks is in the ability to absorb moisture
An ideal building must be dry. In this situation, precisely, because they have an almost unique ability not to absorb moisture. Due to such resistance to moisture, experts advise to make waterproofing only outside the house, which is built of cellular materials. There are differences in gas silicate in terms of hygroscopicity, but not too significant. However, this type of material also takes longer to dry.
Installation work

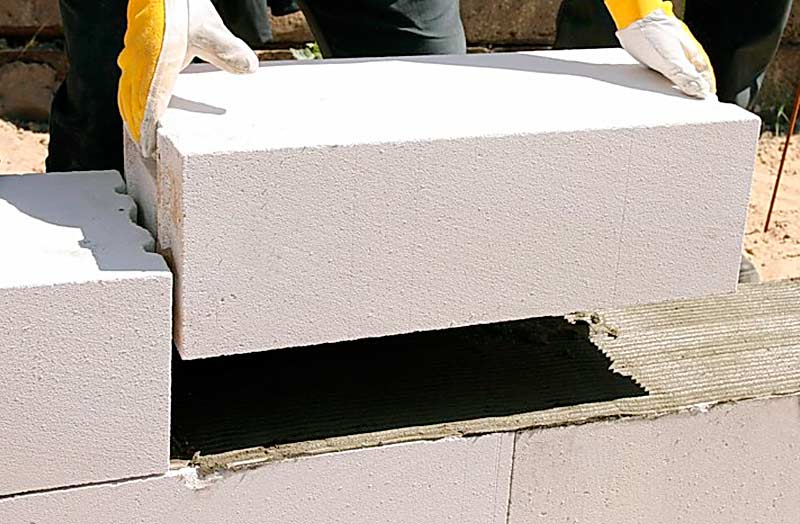
An important factor in construction is the convenience of performing the main technological works. Therefore, the convenience of masonry with these materials is a great advantage. Foam concrete can be laid in any weather, even in the rain, even in the snow, even in the frost.
In addition, they can be applied immediately after production. You can start building as soon as the material is delivered to the desired location.
And since gas silicate absorbs moisture quite strongly, it is used for construction only after the blocks are completely dry. However, plaster works more with them, and this has a beneficial effect on decoration and decoration.
Even experts cannot always tell the buyer which is better - aerated concrete or gas silicate. Increasingly, these building products are used in modern projects to reduce heat loss as materials in the class of cellular heat-insulating concrete.
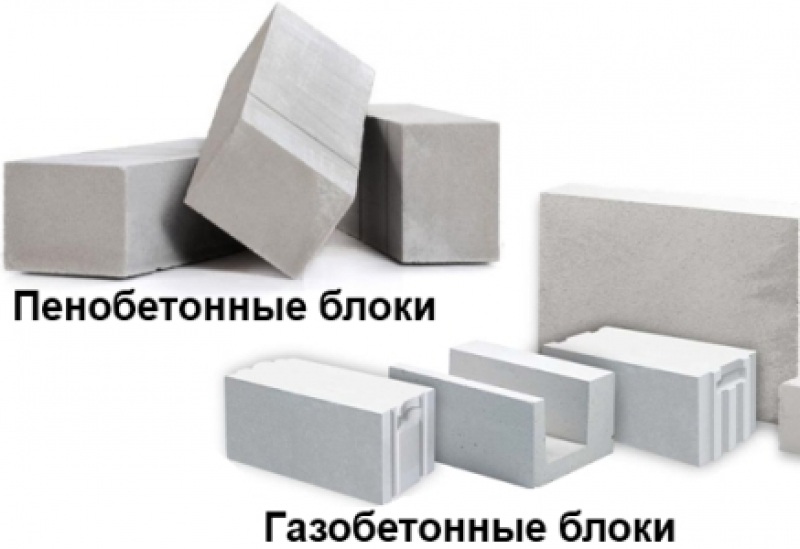
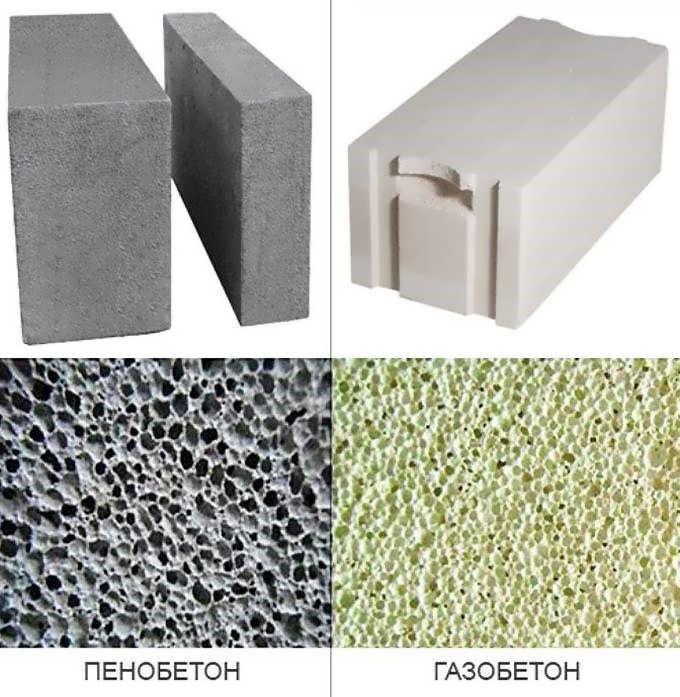
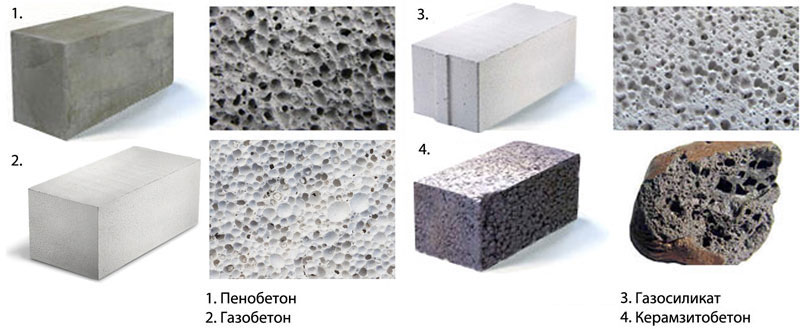
Aerated concrete and gas silicate are often confused due to the same scope of use and general properties. By the method of cell formation, there are:
- aerated concrete;
- foam concrete;
- gas silicate;
- aerated concrete.
How to choose?
To understand which material is better, you should compare the foam block and the gas block in several parameters:
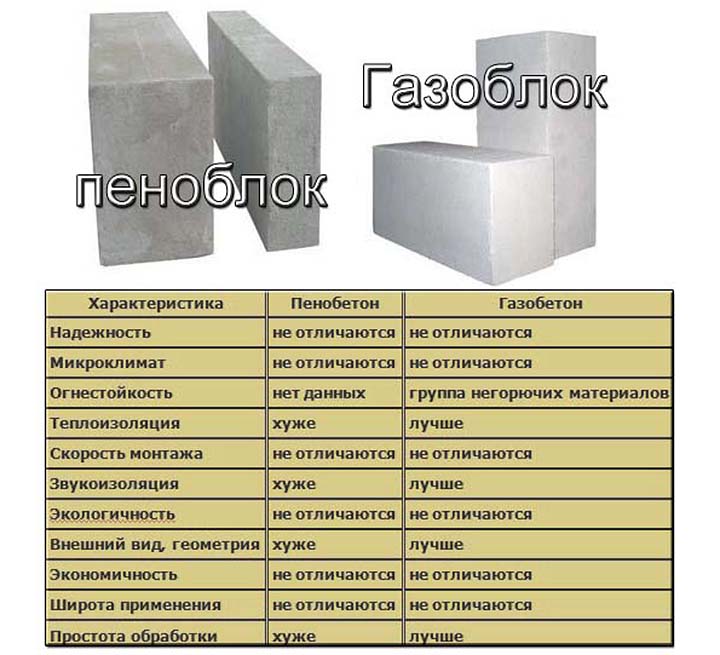
- Structure. Foam blocks have large and closed cells with poor water absorption. Their surface is gray. Gas silicate blocks have smaller pores. They have weaker thermal insulation and require additional finishing.
- Strength characteristics. Aerated concrete blocks are less dense (200-600 kg / cubic meter) than foam concrete blocks (300-1600 kg / cubic meter). Despite this, foam concrete is inferior to aerated concrete, since its structure is heterogeneous.
- Frost resistance. Autoclaved aerated concrete blocks are more frost-resistant and vapor-permeable than other similar materials.
- Features of the application. Cellular foam concrete is used in low-rise construction.It is also used in the construction of monolithic buildings (here it is used as an additional insulating layer). Aerated concrete materials are used as the main structural and thermal insulation materials. They are used to build houses of the most varied complexity.

Production. It is much easier to run into low-quality aerated concrete than bad aerated concrete. This is due to the fact that the former is often made in artisanal conditions, and the process of creating aerated concrete materials is more high-tech and is often carried out in a factory.
Price. Price is the most obvious difference between foam blocks and gas blocks. The latter will be more expensive, since foam concrete blocks are made from cheap raw materials.
Soundproofing. Foam concrete blocks have better sound insulation characteristics than aerated concrete options.
Life time. Foam concrete on average lasts no more than 35 years, and aerated concrete - more than 60 years
This is another important difference to consider when choosing the right material.
Shrinkage. The degree of shrinkage of foam blocks is greater than this parameter of gas silicate materials
It is 2.4 (and aerated concrete - 0.6).


It is not so difficult to distinguish aerated concrete from aerated concrete
It is enough to pay attention to their surfaces. The foam blocks are smooth, and the gas blocks are slightly rough
To say with certainty which building material is better is already more difficult, since both have their pros and cons. However, it is necessary to take into account the opinion of experts who argue that after all, gas blocks are stronger, and their frost-resistant characteristics are better. As for foam blocks, they are warmer and cheaper.
We must not forget that low-quality foam concrete is more common than second-class aerated concrete, as evidenced by the reviews of many consumers. Be that as it may, the choice is up to the buyer.
It is important to decide in advance for yourself exactly what qualities you are looking for in these building materials before you go shopping.


Comparison of the gas block with the foam block is in the next video.
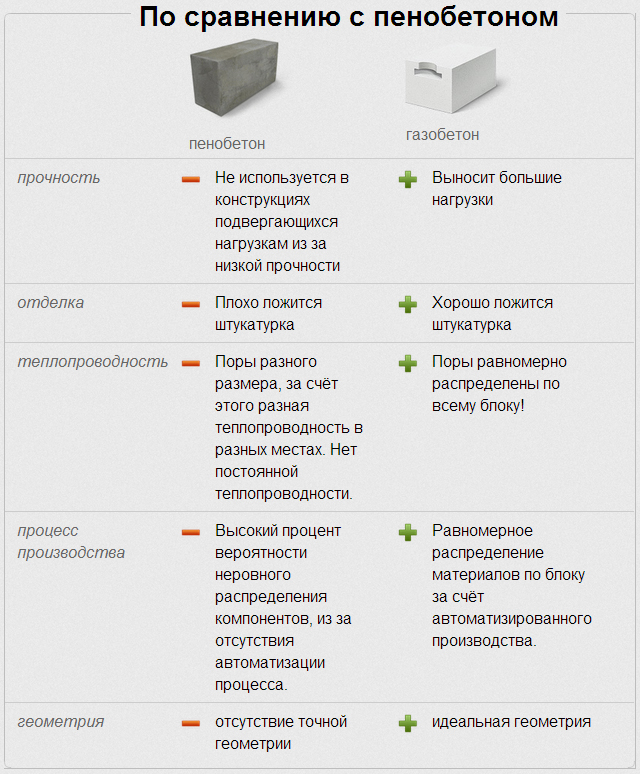
Advantages of aerated concrete over foam concrete
Strength is the main advantage of aerated concrete. With the same density, aerated concrete is much stronger than foam concrete. And if we compare blocks with the same strength, then, naturally, aerated concrete will have a lower density, which means it will be easier and more convenient in construction. By the way, it is believed that foam concrete can shrink and microcracks after construction is completed, so it is useful to wait at least a year after building a house from foam concrete blocks before starting expensive repairs and finishing.
Aerated concrete blocks have better vapor permeability. The whole point, again, in the structure of the material and the method of production. So, in aerated concrete, all the pores are interconnected, which cannot be said about foam concrete, where they are isolated. Therefore, the aerated concrete block allows moisture and air to pass through better, and the microclimate in such a house will be much better than if you use foam concrete, which allows air to pass through much worse. That is why, if you decide to insulate the wall from aerated concrete blocks, it is better to use breathable materials so as not to negate all the benefits of aerated concrete. And foam concrete blocks can be insulated with foam plastic in order to reduce the cost of work.
Now about thermal conductivity. It is believed that aerated concrete and aerated concrete are capable of providing approximately equal thermal insulation performance. But if you look into some of the details, you can understand that the thermal insulation of foam concrete does not always meet the values declared by the manufacturers. The fact is that the pores in foam concrete, as a rule, are of different sizes: they can be 1 mm or 5 mm, while in aerated concrete the size of the pores is usually constant. It follows from this that the value of thermal conductivity may differ in different places of the block.But this is not as scary as the fact that in conditions of high air humidity, the thermal conductivity of foam concrete can significantly increase, which will lead to the fact that the walls simply will not keep the temperature that is comfortable for residents. And you will also have to spend money on more powerful wall insulation. Although there are many experts who can argue with this fact.
Aerated concrete blocks are often called an environmentally friendly material - this is really so, because nothing is used in production except natural materials, which were already mentioned above. In the production of foam concrete blocks, synthetic foaming agents can be used, which cannot be called environmentally friendly. Here we cannot fail to mention the myth that aerated concrete contains aluminum, and it is harmful to our health. It is pointless to argue about the harmfulness of aluminum - it is harmful, but is it available in ready-made aerated concrete blocks? All aluminum goes to react with lime, as a result, oxygen is released and aluminum oxide is formed: oxygen is needed to form pores, and aluminum oxide is harmless and is found in most building materials, even in clay. And the aluminum oxide itself in aerated concrete is less than in foam concrete and in brick. And here not everything is clear: there are opinions that aluminum still remains in the material, not being completely consumed in the reaction, but still we remain with the opinion that aerated concrete is more environmentally friendly.
The shape of aerated concrete blocks is almost perfect, and the error is no more than 2 mm, so it is very easy to work with them, the walls are smooth, and you need a little glue. Foam concrete blocks can have such significant deviations in size that it will be noticeable to the naked eye, and it will be more difficult to fix such irregularities, much more mortar will be needed.
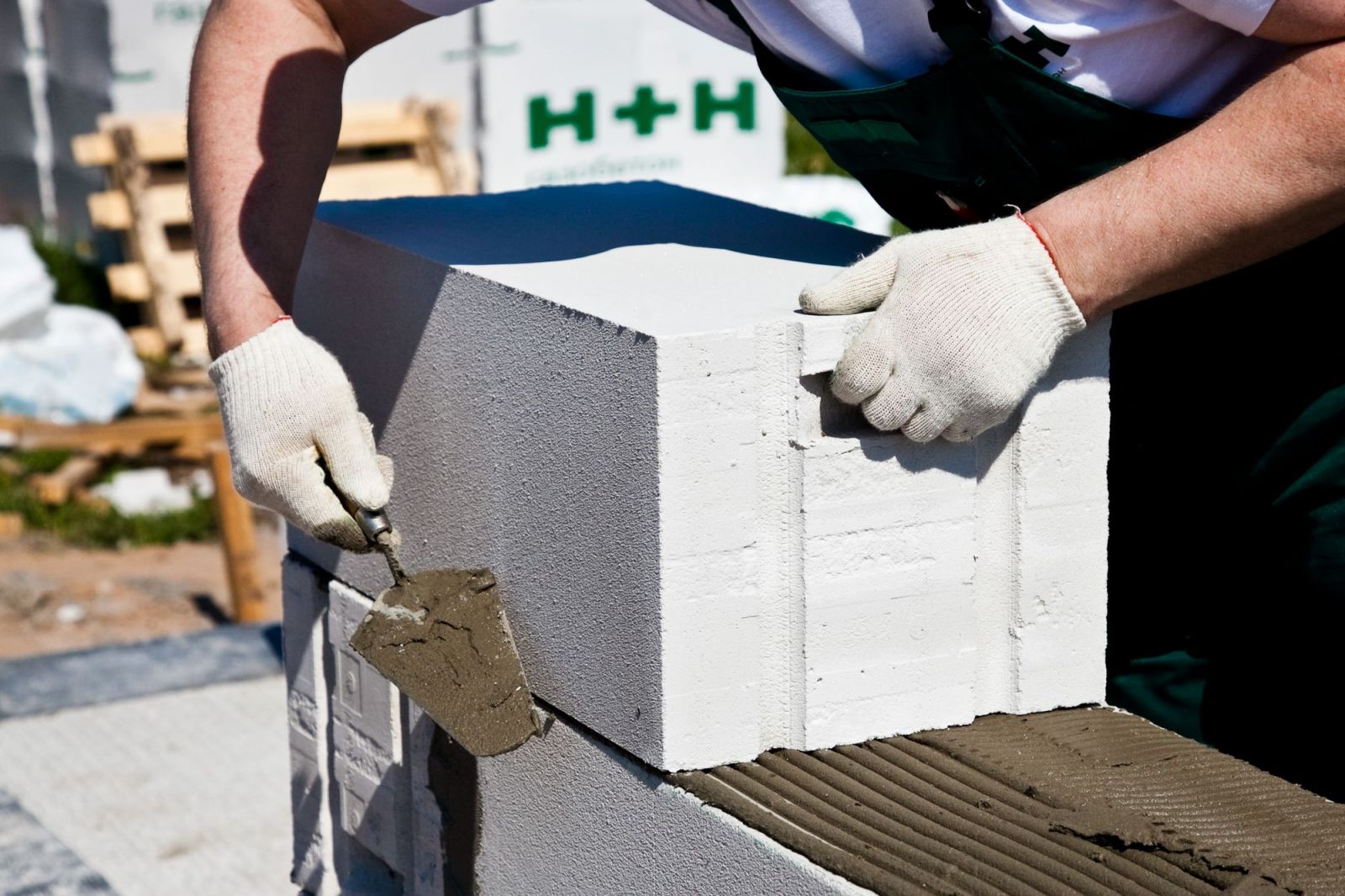
Installation of aerated concrete blocks will cost you relatively less than foam concrete. This is due to the fact that glue is used for laying aerated concrete, and its thickness is much less than the thickness of the cement mortar for foam concrete (2 mm versus 1 cm)
Even taking into account that the glue is 2-3 times more expensive than cement, and its consumption will be about 6 times lower, we get savings, not to mention that when using glue for aerated concrete, there are practically no cold bridges, which makes the house more comfortable and warmer.
Aerated concrete blocks are much easier in subsequent decorative processing, this is largely due to the fact that they have excellent geometry.
Gas silicate blocks: characteristics
Density of gas silicate blocks
The brand and density of gas silicate blocks is indicated in the marking and determines the purpose of the block:
- constructional gas silicate blocks - D1000-1200, have a density from 1000 to 1200 kg / m3;
- structural and heat-insulating blocks - D500-900, have a density of 500-900 kg / cubic meter;
- heat-insulating D300-D500, the density of their materials is 300-500 kg / m3.
Blocks of different density are easy to distinguish from each other visually.
There are several classifications of gas silicate blocks with specific technical characteristics. Today, during construction work, the following grades of this material are used. The best option for low-rise construction is the d500 gas silicate block and d600 gas silicate block.
The numerical designation of the grades listed earlier shows the density of the material. In particular, the d500 gas silicate block has a density of 500 kg / m³.
Gas silicate block d600
Gas silicate block d600 is used in the construction of load-bearing walls of a house. It is also recommended to use it when installing ventilated facades that are well attached to blocks of such density. Gas silicate block d600 has a strength of 2.5-4.5 MPa and has a thermal conductivity of 0.14-0.15 W / (m ° C)
Gas silicate block d500
Gas silicate block d500 is most popular for low-rise (up to 3-storey) construction.This variety is also used in monolithic construction. Its parameters are 2-3 MPa (strength) and 0.12-0.13 W / (m ° C) (thermal conductivity).
When building a house above three floors, preference should be given to gas silicate marked above D600 and additionally insulate the walls. Based on the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient, it can be concluded that the d500 gas silicate block is 15-17% warmer than the d600 gas silicate block.
Gas silicate block d400
This type is used for arranging insulation, for working with openings in the construction of multi-storey buildings using a monolithic method. The D400 brand is also popular in private construction. With high strength, it has great thermal insulation properties. These indicators are in the range of 1 MPa to 1.5 MPa (strength), 0.10-0.11 W / (m ° C) (thermal conductivity).
Gas silicate block d300
D350 brand can only be used as insulation. In the domestic market, this is a rather rare brand due to its fragility. Strength is in the range of 0.7-1.0 MPa. But it differs in thermal conductivity, which is 0.08-0.09 W / (m ° C).
Thermal conductivity of gas silicate blocks
Depending on the proportions of the starting ingredients, a product with different performance characteristics can be obtained. The thermal conductivity coefficient of a gas silicate block depends on its density and is determined by the marking: D300, D400, D500, D600, D700.
The thermal conductivity of gas silicate depends on a number of factors:
- Building block dimensions. The thicker the wall block is, the higher its thermal insulation properties.
- Humidity of the environment. A material that has absorbed moisture reduces the ability to store heat.
- Structure and number of pores. Blocks with a large number of large air cells in their structure have increased thermal insulation performance.
- Density of concrete partitions. Building materials of increased density retain heat worse.
Thermal conductivity table of gas silicate blocks

Composition of materials
To understand the difference between aerated concrete and gas silicate, below we will consider how they are produced:
- The main substance of aerated concrete is Portland cement. In addition, this material includes quartz sand, blast furnace slags, and wastes from various ores. However, the use of an autoclave for mixing is optional.
- The basis for the manufacture of gas silicate are binders - lime or cement, which are combined with fine quartz sand and water. After mixing these components with aluminum powder, which creates a gas-forming effect, a swelling procedure is carried out.

This leads to an even distribution of air bubbles throughout the volume of the mixture. This procedure is carried out in an autoclave, after which the mixture hardens under the influence of high temperatures and pressure.
Arguments in favor of gas silicate
This material also boasts a number of positive qualities:
- environmentally friendly;
- has a low specific gravity;
- low level of thermal conductivity;
- fire safety;
- easy to process;
- tolerates low temperatures.

- Aerated concrete blocks are characterized by a large volume with a relatively low weight, which makes it possible to abandon the use of heavy equipment during installation.
-
The high thermal insulation properties of this type of aerated concrete help to reduce heating costs
... It should be remembered that the instruction recommends using only blocks with a high density (above 400kg / m 3) as a material for walls. If this parameter is lower, it is better to use them as thermal insulation. - Due to its good frost resistance index, aerated concrete can be used in countries of temperate climates, because it can withstand up to 100 freeze / thaw cycles without losing its characteristics.
- Another advantage of this material when used in countries with cold climates is the way it is installed
... The fact is that the use of an aqueous solution of cement of the M400 or M500 grades in conditions of low winter temperatures is unacceptable. But when installing aerated concrete blocks with their own hands, an adhesive mixture is used, which is resistant to frost, which helps to avoid the appearance of the so-called. "Cold bridges".

Technology overview
Gas and foam concrete in construction
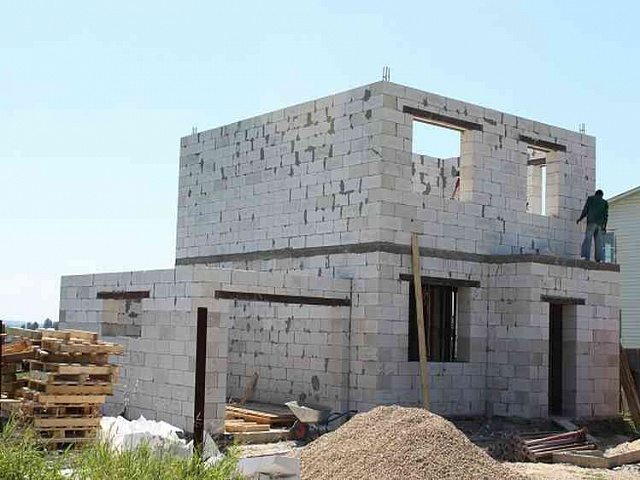
In recent decades, concrete-based porous materials have been widely used in the construction of private houses. They are produced using similar technologies, and only some of the nuances of manufacturing distinguish them from each other (see also the article “Self-tapping screws for concrete: selection options ").
That is why, before deciding which is better - gas silicate or foam concrete - you need to understand the details.
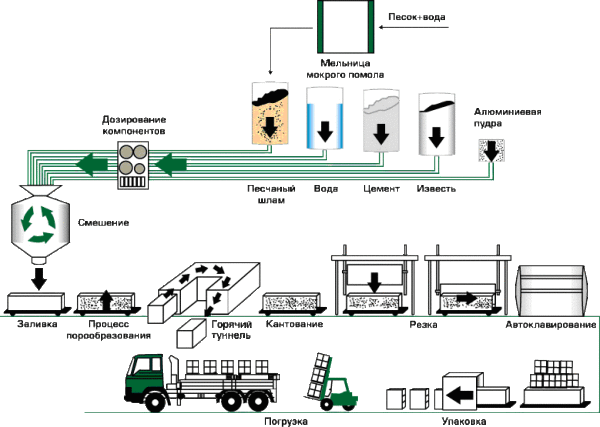
Technological cycle diagram for aerated concrete
- Foam and gas blocks are produced according to the same scheme. High-quality cement is used as raw material, into which special foaming agents are introduced.
- In the process of "ripening", the reagents release a significant amount of gas bubbles, which are evenly distributed in the thickness of the building block.
- Then the nuances that we talked about above begin. The foam block hardens at a temperature of about 15-25C and atmospheric pressure, therefore it is very sensitive both to the composition of the filler and to the drying regime.
- There is often a catch here: the low price of the material may indicate problems with hardening, and as a result, the low strength of foam concrete. That is why you should not save money by purchasing blocks made using “handicraft” technologies.
- Unlike the previous version, the curing of aerated concrete is carried out in special autoclaves or drying chambers with significant heating. That is why the material is more expensive, but its strength is much higher.
And although the advantages of the gas block in this case are obvious, both materials are actively used in construction. They have good thermal insulation properties, relatively low weight and low density. The latter factor greatly facilitates installation: if cutting reinforced concrete with diamond circles is very laborious, then porous modules can be cut with a special hacksaw with your own hands.
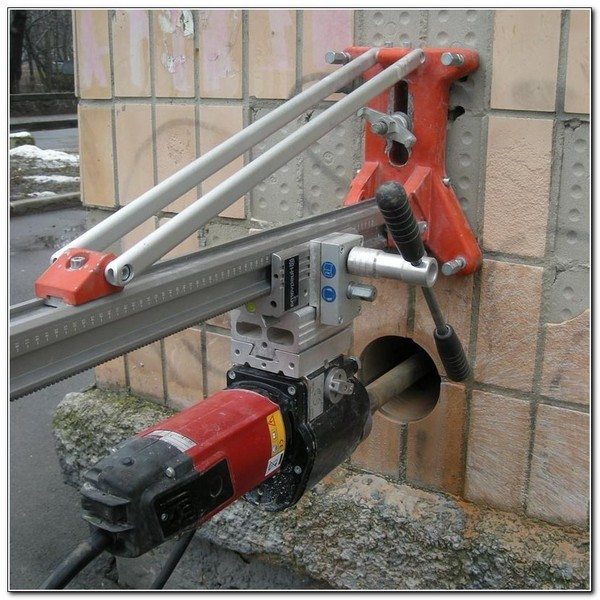

Diamond drilling of holes in concrete, as well as its cutting are very laborious processes.
Production and characteristics of silicate blocks
The difference between gas silicate and foam concrete is easy to see if you analyze the manufacturing technology:
- A mixture of cement, sifted sand and lime is used as a raw material.
- In the process of mixing, pore-forming agents are added to the composition, which are responsible for the formation of microscopic cavities in the thickness of the block.
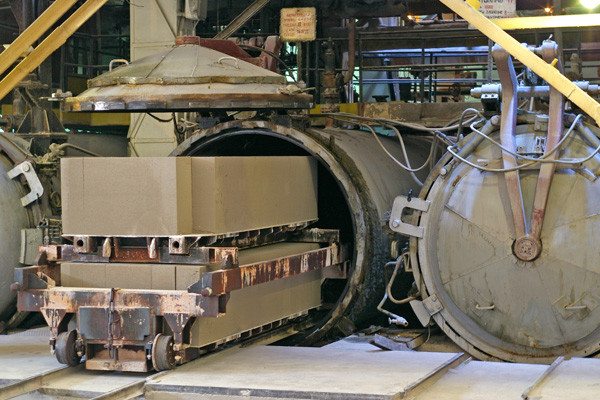

Autoclaving of gas silicate blocks at temperatures up to 20000C
As a result, the answer to the question which is better - gas silicate or expanded clay concrete (foam concrete, aerated concrete), becomes almost obvious. Due to this treatment, building silicate blocks acquire absolutely identical properties throughout the volume, which has a positive effect on their performance characteristics.
The technology of installation and finishing practically does not differ from the method of using other porous concrete. Products are easy enough to cut, have good contact with both mortar and special glue, and have acceptable adhesion to plasters and other finishing materials.

You can saw the material manually
What to look for when buying
Let's list the main things.
Geometry. Extremely important for future construction. Laying is carried out on a thin layer of glue, the thickness of which may not be enough to smooth out irregularities. It will be necessary to either increase the thickness of the adhesive, which is not good, or to grind the protruding parts, which will significantly complicate and lengthen the construction process.Well, indirectly, even blocks are a sign of solid production.
The density of the material. The denser the blocks, the stronger they are. And more expensive, by the way. However, do not forget that an increase in strength entails a decrease in thermal insulation qualities. Therefore, with cellular building materials, as a rule, it is better to play it safe, and choose the most durable one, it does not work very well. We need a middle ground: strong enough and good thermal insulation.
Size and type
It is especially important if you plan to carry out the laying yourself, choose the size that is comfortable for you. And it will be determined whether these will be ordinary blocks or with tongue-and-groove ones.
Manufacturer
Large companies do not cheat. To little-known brands - stricter checks and controls.
How to choose and apply?
All this does not mean, however, that aerated concrete and gas silicate really coincide with each other in all respects. In this case, the difference is already manifested in the composition of the adhesive solutions offered by the manufacturers of certain blocks. The adhesive is a combination of sand and cement, the specific properties of which are determined by additional additives. It is only thanks to such additives that it is possible to compensate for the styling speed. A classic astringent solution, even a very good one, will not help in this case.
When comparing different materials and trying to evaluate which one is better, it is important to understand that all these judgments are relative. The gas silicate blocks improved by pressure will definitely be of high quality, but you will have to pay a lot of additional money for their merits.
Low density gas structures become brittle, but this is "justified" by the increased protection against heat loss. Aerated concrete, obtained without an autoclave, is rather fragile, but it can be obtained independently. These blocks are easy to make on site, saving money. The gas silicate block under identical processing conditions differs from aerated concrete for the better in almost all properties, except for liquid absorption, therefore, gas silicate is used only where the humidity does not exceed 60%. In more severe conditions, the material degrades too quickly.
This means that the facades must be protected from atmospheric moisture.
To solve a similar problem, use tools such as:
- facade paint;
- plaster;
- siding;
- plaster in the form of a thin layer.
A facing brick with a gap for air blowing (the gap is 300-400 mm) can also be used. It is recommended to cover the outside wall with an extended roof overhang. The larger it is, the less dangerous the precipitation is. All finishing materials that are applied over aerated concrete and gas silicate must have a good level of vapor permeability. If this condition is not met, excellent ventilation is required.
The passage of steam through insulation, paint or plaster should be more intense than through structural material. Recommended additional insulation using mineral wool. When finishing or heat protection is performed in several layers, the penetration of steam into each next layer should be more active than into the previous layer. Failure to comply with this requirement may result in condensation. Pockets of mold will soon appear.


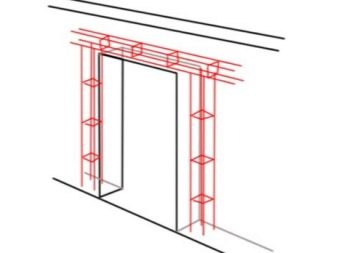
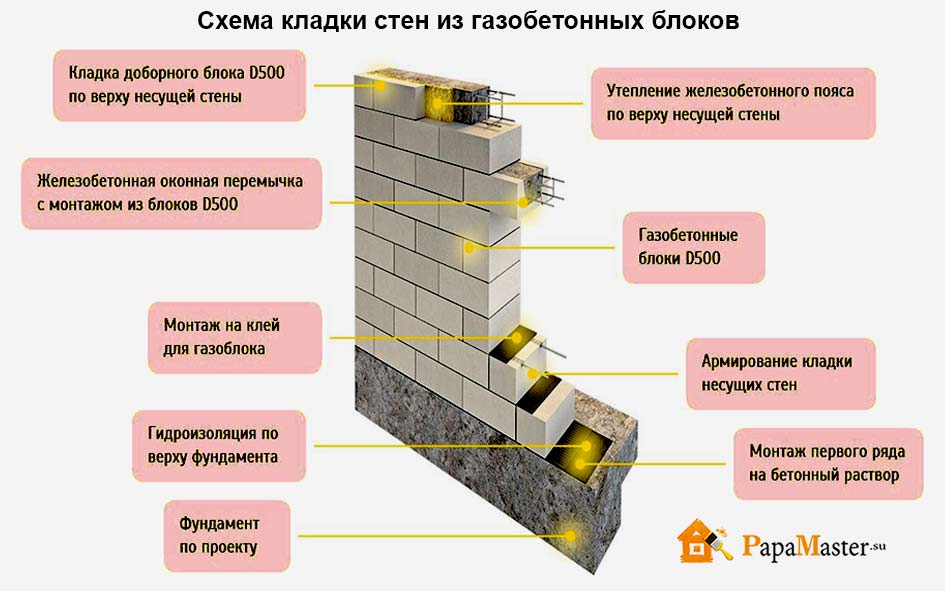
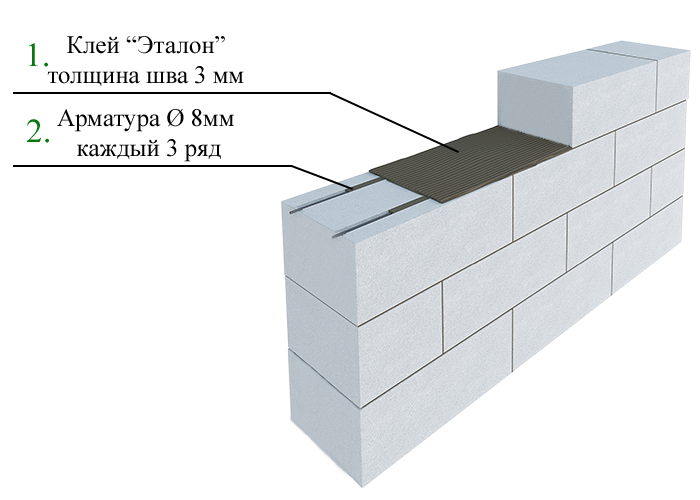
If you have to fix suspended furniture made of gas silicate or aerated concrete, dowels are used. Aerated concrete blocks are additionally fastened using anchor bolts. For both types of structures, foundations with thoroughly calculated parameters and dimensions should be created. It is also advisable to prepare waterproofing. Strengthening is performed on the first and every fourth row. It is also advisable to reinforce the door and window openings.