Forming and casting. Application of quartz sand
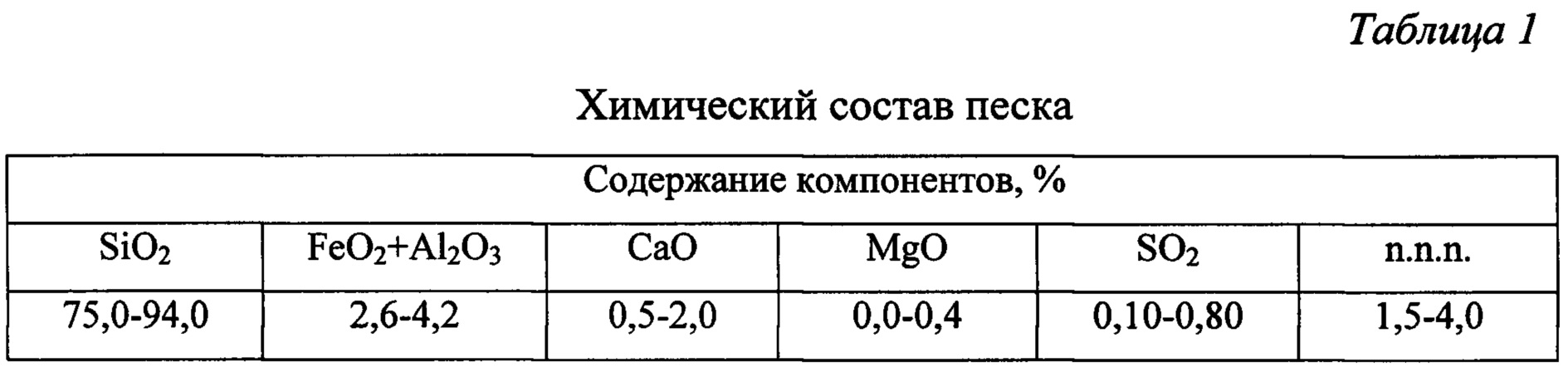
Quartz sand is widely used in the production of molding sands for molds and cores in the iron foundry, steel and other types of metallurgical industries. Molding mixtures based on quartz sand must have certain properties:
-
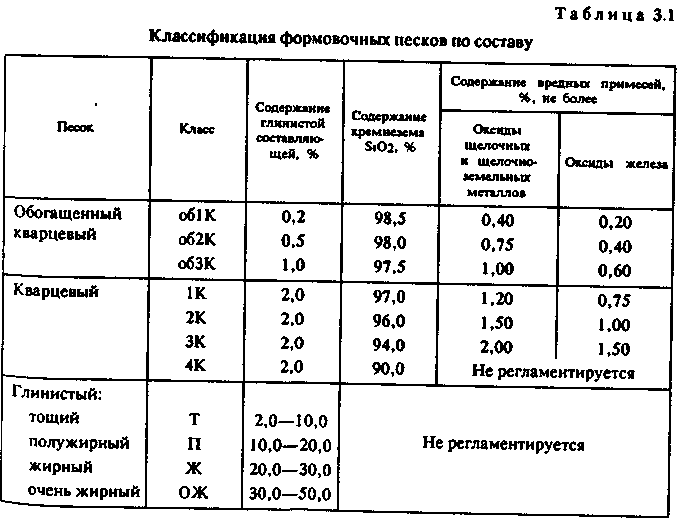
silica content (SiO2) up to 98%,
-
the minimum percentage of impurities of alkali and metal oxides,
-
clearly normalized percentage of clay impurities (depending on the brand of molding sand),
-
rounded sand shape.
Molding sand from the group of companies "Khokholsky sand pit" grades 5K3O403.5K3O3025 and 1T1O302-03 enriched molding sands of fractions 0.1-0.4; 0.16-0.63; 0.16-0.8; 0,63-1,0 meet all the standards and requirements of GOST 2138-91 "Molding sands" The presence of certain grades of molding sands, check with our consultants.
Currently, the issue of supply and launch of equipment for the beneficiation of sands to grades 1K2O303, 1K2O2025 and 1K2O202 is being considered.
Quality quartz molding sand
This type of sand is mined in an open way. In addition to quartz grains, sand contains particles of clay, various minerals, mica, iron oxides, and feldspars. In places of extraction, sand is enriched, freeing it from foreign impurities, which increases the quality and value of the foundry sand. Then the sand is divided into fractions according to the grain size.
Foundry sands are used as a refractory material in foundries in the manufacture of casting molds and cores, and are also the main constituent material for the preparation of cement, bentonite, synthetic resin and others.
The choice of high-quality, enriched molding sand makes it possible to save on expensive binder material and at the same time ensure the necessary physical and mechanical properties of the mixtures.
The main qualitative indicator of the chemical composition of foundry sands is the content of silica SiO2... The higher the amount, the higher the quality of the sand.
The peculiarity of quartz grains is that they are very hard, have great refractoriness and transparency.
That is why quartz sands are light in color. Various color shades are imparted to the molding sand by impurities. The less impurities are contained in the sand, the lighter it is and the higher its refractory properties.
Depending on the content of silica, clay component, and harmful impurities in accordance with GOST 2138-91 “Molding sands. General technical conditions ”distinguish several classes of molding sands: enriched (Ob1K, Ob2K, Ob3K), quartz (1K, 2K, 3K, 4K), semi-bold (P), oily (F), very fat (OZh).
The fractional composition of sand is determined by sieving through a set of sieves with mesh sizes ranging from 2.5 to 0.005 mm. The remainder of the sand, located on three adjacent sieves, is called the main sand fraction. Its content should not be less than 70%.
By grain size, quartz foundry sands are classified into the following groups:
|
Sand class |
Group no. |
Quartz grain size |
|
Dusty |
005 |
0.063 mm. and less |
|
Thin |
0063 |
0.100 - 0.005 mm. |
|
Very small |
01 |
0.160 - 0.063 mm. |
|
Small |
016 |
0.200 - 0.100 mm. |
|
Average |
02 |
0.315 - 0.160 mm. |
|
Large |
0315 |
0.400 - 0.200 mm. |
|
Very rude |
04 |
0.630 - 0.315 mm. |
|
Rude |
063 |
1,000-0,400 |
Foundry sand categories
According to the distribution of the main fractions of sand on three adjacent sieves, there are two categories of sands: A and B. Category A includes sands with the remains of the main fraction on the uppermost sieve, greater than on the extreme lower sieve; to category B - sands with the remainder of the main fraction on the extreme lower sieve, more than on the extreme upper one.
In the marking of sand, the designation of the class is in the first place, the grain group is in the second, and the category is in the third. For example, marking about 1K02A means: enriched quartz sand of enrichment class 1K of grain group 0.2 of category A.
MOLDING SANDS

Types of sand forms
The variety of sand molds for casting made it possible to divide them into several groups designed to obtain castings with different characteristics.

Sand casting molds
In total, there are 7 groups of casting technological equipment or model kits.
- A model set made of metal, which includes accessories for machine forming.
- The set, made of metal, includes additional accessories that are designed for machine and hand molding.
- Model set used for machine and hand molding. The models themselves are made of metal, and some parts, for example, the rods for the formation of cavities, are made of wood of different species.
- Set for the production of hand and machine molding. Models and rods subject to heavy wear are made of metal.
- Set for molding hardwood castings.
- A set for forming castings made of soft woods.
- Sets for making manual casting.
Raw sand mold
For the production of molding equipment, mixtures consisting of sand, water, clay and some kind of binder are used. A typical recipe looks like this:
- 90% sand;
- 3% water;
- 7% clay.

Raw sand mold
Rigging of this type is considered to be very economical and widely used.
Dried sand mold
The production of such a tooling is similar to the production of a raw form, but additional materials are introduced into the formulation to bind the components of the mixture.

Dried sand mold
The working surfaces of the equipment are dried by heating. This approach to the manufacture of molds leads to an increase in the accuracy of the dimensions of the workpieces and their quality. The production of such molds is time-consuming and as a result, their cost increases and the production of parts decreases.
Dry sand mold
In this type of tooling, organic type additives are used. Their task is to link the components of the mixture into a single whole. The final processing is carried out in an oven. The clear advantages of these products include the accuracy of the casting. But it should be understood that these molds have a high manufacturing cost and low casting performance.
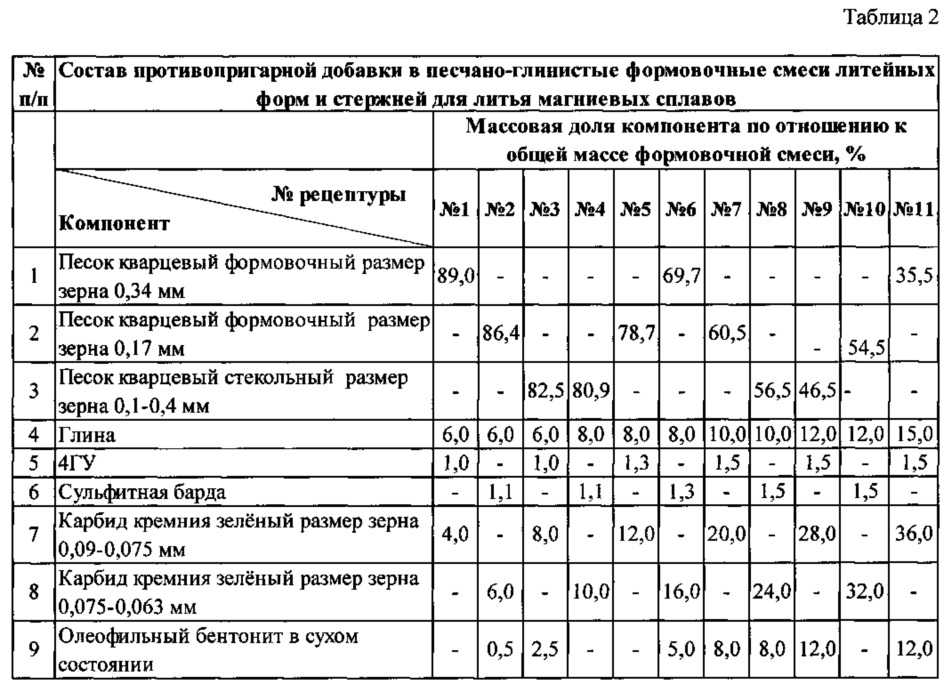
Chemically hardening sand mold
Resins are added to the molding composition of the chemically hardening tooling. They ensure the formation of the model in the open air without the use of heat treatment.
Chemically hardening sand mold
The mixture is based on quartz sand. In addition to sand, the mixture includes liquid glass and caustic soda. The addition of this chemical affects the processing properties of the mold. In particular, its service life will be extended. After hardening, its strength will be higher than that of other types of mixtures.
Appointment
Sedimentary rock is widely used:
- when casting into the ground;
- in the production of molding and core sands (pure quartz sand);
- for sandblasting;
- in the sandboxes of railway locomotives (fraction 0.2–0.5 mm).
Coarse sand is suitable for making large and thick-walled castings with good refractory and gas permeability properties. Fine-grained is in demand for thin castings in non-ferrous and artistic casting in order to obtain a better surface.
Quartz sand with a minimum amount of harmful impurities is used for steel casting.
Skinny or oily - with a high clay content - for the manufacture of cast iron and non-ferrous alloys.
Using the earth-casting method, many simple and complex geometries can be produced using foundry sand. Among them are simple rings, wheels, fittings, blanks for gears, complex body parts and beds.
 The quality of casting when casting into earth depends on the size and purity of the foundry sand.
The quality of casting when casting into earth depends on the size and purity of the foundry sand.
Properties
The main characteristics of this building material include:
- strength - the mixture has a high density and is practically indestructible;
- plasticity - the mass has a tendency to deformation, this is due to the presence of clay inclusions;
- fluidity - the mixture has the ability to evenly distribute inside a container or casting box;
- gas permeability - the material is able to "get rid" of excess air and gases that are formed during pouring;
- fire resistance - foundry sand has increased resistance to high temperatures.


In addition, its main properties include:
- uniformity;
- high sorption capacity;
- chemical resistance;
- increased flowability and porosity of the structure.

In addition, the molding material is divided into two types (designated by the letters A and B). The first includes a variety with a large residue on the uppermost sieve, on the lower one - to category B. Natural and enriched sands also differ. The latter are obtained by special processing, removing clay and unnecessary impurities from natural sand.

Foundry models
Models for this form of sand casting must withstand a fairly high pressure that occurs when the flask is filled with casting earth. That is why metal and hard wood are used for the manufacture of injection molds. All materials that can be used for the manufacture of injection molds can be combined. That is, they can be assembled on threaded joints, glued, etc. To eliminate pores on the wooden parts of the models, they are carefully treated with abrasive paper. Then, it is varnished. In the manufacture of casting molds, it is necessary to take into account the fact that it is necessary to maintain the angles of inclination of the vertical planes. The presence of these corners will subsequently facilitate the removal of the finished casting from the mold.
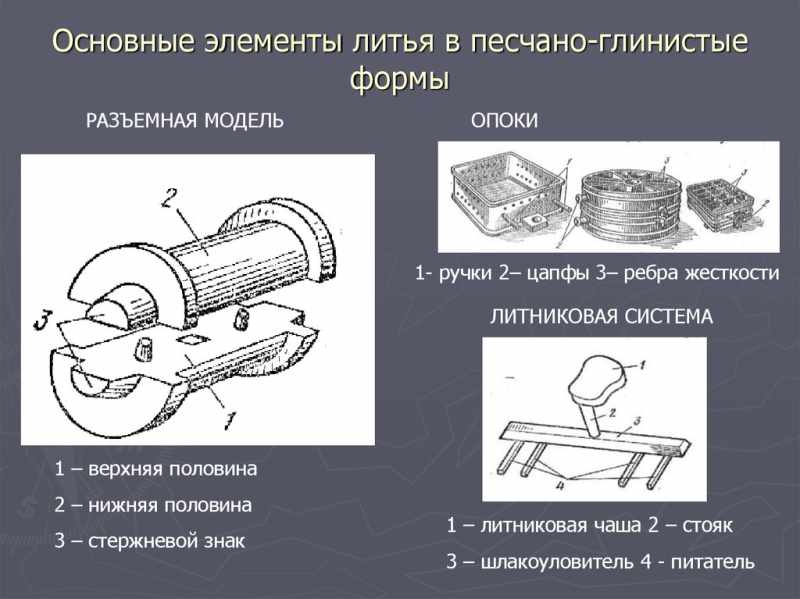
The main elements of casting in sand and clay molds
One of the key factors determining the quality of casting is the properties of the sand (earth) used to obtain the casting equipment. Practice shows that the finer and cleaner the sand, the higher the quality of the resulting casting will be. We must not forget about the rods, which can be reusable or disposable.
General classification of sandy molding sands
Depending on the application, the mixture can be divided into the following subspecies:
- facing them are used to create the working surface of the form;
- dyne (filling), they are used directly to create a form.
General classification of sandy molding sands
Facing materials have a thickness that is determined by the thickness of the future casting, it can be 20 - 100 mm. A filling mixture can be poured on top of the mixture used for facing. The filling mixture or a single mixture is used for filling the entire mold and is used for the production of tooling in all types of production, from single products to mass production.
Making a casting sand mold
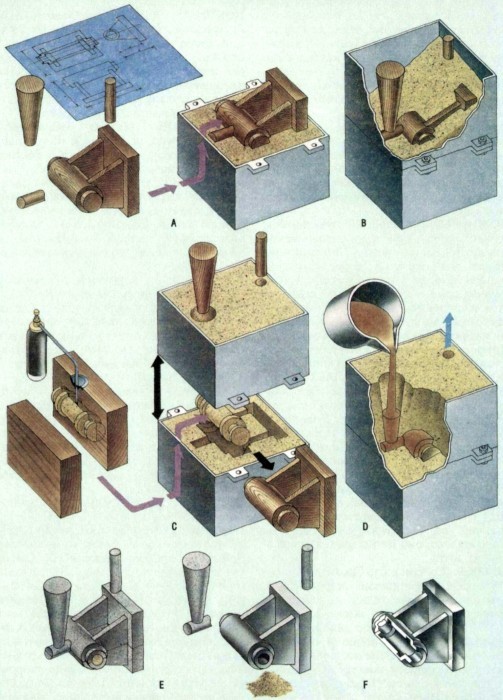
Sand casting begins with its creation. A distinctive feature of sandy equipment is that they can be used only once and to obtain a new part it is necessary to make a new one.
The tooling is made with a model of the future part in hand. It is installed in a flask (wooden or metal box for molding sand), and the earth is poured. Then it is necessary to compact the backfilled sand mixture. To do this, use a manual or mechanized percussion tool and device. When the mixture reaches the required condition, that is, the required density, the model is removed and the foundry staff will have ready-made technological equipment at their disposal.
To obtain cavities located inside the future casting, rods are used. They are usually made from the same material as the tooling itself. The process of making a sand casting mold includes the following main stages.
- installation of the model in the flask;
- compaction of the sand mixture;
- removal of the model from the investment box.
The labor intensity and technology for the production of foundry equipment largely depends on the following parameters:
- the size of the future casting;
- the number of cavities;
- type of snap.
Sand casting mold assembly
After the casting tooling is made, it is prepared for pouring the melt.The working surfaces must be lubricated with a special compound that facilitates the free extraction of the finished casting. After the preparation of the working surfaces, the casting cores are installed.

Mold making process
At the final stage, the half-molds are connected together and securely fastened. Assembly reliability will not allow the melt to flow out of the mold.
Scope of application
Possessing unique characteristics, quartz sand has found wide application in human life and is used in the following areas:
- used in construction for the manufacture of various types of decorative plasters, dry mixes, as well as for the creation of self-leveling floors;
- for injection heat-resistant forms in the metallurgical industry;
- for the pool as a filter material;
- for football fields as a covering;
- in the production of glass, fiberglass;
- in the production of building materials - for the manufacture of sand-lime bricks, paving stones, refractory concrete;
- in the agro-industrial sphere as an additive in animal feed;
- in the manufacture of electrical fuses, since quartz is a dielectric material;
- for creativity and drawing, in landscape design;
- when composing mixtures for the production of reinforced concrete with increased strength.
Quartz sand is a part of modern road surfaces, since silicon dioxide is strong and resistant to abrasion, which allows the asphalt road to be durable and reliable, despite the huge weight load and high cross-country traffic. Most of the tableware on the shelves is made using quartz sand. A mineral additive from fine-grained quartz allows it to be added to porcelain, earthenware and ordinary glass, which gives these materials increased strength and shine. Quartz is also added in the manufacture of technical glasses, as well as window, automobile varieties, with its use, laboratory glassware that is resistant to heat and chemical environments is produced, and is also added to the composition of the mass intended for the production of ceramic finishing tiles.
But that's not all. Quartz sand is an essential component used in the production of optical lenses, making these products smooth, transparent and durable in use. Due to its ability to retain heat, quartz sand is used for industrial and domestic needs. With his participation, electric heating devices are made - quartz is included with an incandescent spiral system, which heats up quickly and maintains the required temperature for a long time.
Engraving and grinding surfaces, as well as processing stone, metal or durable polymers, are not complete without the use of quartz sand, which is used in sandblasting materials. The essence of the process lies in the fact that acute-angled rock particles, mixing with the air flow, are supplied under a certain pressure to the surface to be treated, which is polished and becomes perfectly clean and smooth.
The well-known ability of quartz sand to absorb various substances is used to filter water in hydraulic structures of various types and purposes. In addition, the adsorbing properties are used in the food industry, as well as in the production of filter technology.
For information on how to choose the right quartz sand for your pool, see the next video.
Definitions
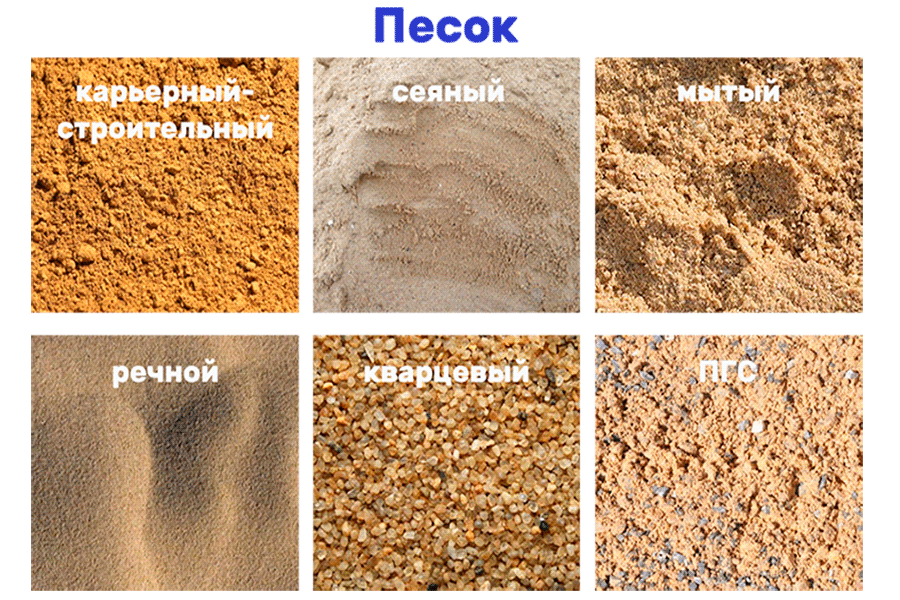
There are several types of sand, for a qualitative understanding of the essence of the issue, you need to familiarize yourself with the main differences:
natural sand. A material that has a free-flowing state, while it is inorganic. The grains reach a size of 5 mm. Sand is produced by the natural crushing of rocks. It is obtained by mining from sandy deposits or mixed with gravel;

Natural
- special enrichment equipment can be used;
- crushed.The grain size does not differ and is less than 5 mm. It is made by man using special equipment of crushing and grinding type. Received by crushing rocks;

Crushed
fractional. This is a homogeneous sand that has been previously divided into 2 or more fractions. For this, special equipment for sifting is used;

Fractional
screenings from crushing. Product of inorganic origin, grain size up to 5 mm. It is obtained by sifting out the destroyed rocks of the mountains. It is a minor product in the production of crushed stone and some types of metals. Also obtained from some non-metallic minerals.
BRANDS
1.1. Molding sands, depending on the mass fraction of the clay component (particles of clay materials and fragments of grains of quartz and other minerals less than 0.02 mm in size) are subdivided into quartz (K), lean (T) and fatty (F).
Quartz and lean molding sands are subdivided into groups depending on the mass fraction of the clay component, silicon dioxide, uniformity coefficient and average grain size, oily - on the ultimate compressive strength in a wet state and the average grain size.
1.2. Quartz sands contain up to 2.0% of a clay component.
Groups of quartz sands are given in table. -.
Table 1
|
Mass fraction of clay component,%, no more |
|
|
1 |
0,2 |
|
2 |
0,5 |
|
3 |
1,0 |
|
4 |
1,5 |
|
5 |
2,0 |
table 2
|
Mass fraction of silicon dioxide,%, not less |
|
|
TO1 |
99,0 |
|
TO2 |
98,0 |
|
TO3 |
97,0 |
|
TO4 |
95,0 |
|
TO5 |
93,0 |
Table 3
|
Uniformity coefficient, % |
|
|
O1 |
St. 80.0 |
|
O2 |
70.0 to 80.0 |
|
O3 |
» 60,0 » 70,0 |
|
O4 |
» 50,0 » 60,0 |
|
O5 |
Up to 50.0 |
Table 4
|
Average grain size, mm |
|
|
01 |
Up to 0.14 |
|
016 |
0.14 to 0.18 |
|
02 |
» 0,19 » 0,23 |
|
025 |
» 0,24 » 0,28 |
|
03 |
Over 0.28 |
1.3. Skinny sands contain from 2.0% to 12.0% of a clay component.
The groups of lean sands are given in table. -.
Table 5
|
Group |
Mass fraction of clay component,%, no more |
|
1 |
4,0 |
|
2 |
8,0 |
|
3 |
12,0 |
Table 6
|
Mass fraction of silicon dioxide,%, not less |
|
|
T1 |
96,0 |
|
T2 |
93,0 |
|
T3 |
90,0 |
Table 7
|
Wet compressive strength, MPa |
|
|
F1 |
Over 0.08 |
|
F2 |
0.05 to 0.08 |
|
F3 |
» 0,05 |
1.4. Fatty sands contain from 12.0% to 50.0% of the clay component.
Groups of oily sands are given in table. and .
1.5. The designation of grades of quartz and lean sands consists of designations of groups according to the mass fraction of the clay component, the mass fraction of silicon dioxide, the uniformity coefficient and the average grain size.
Example. 2K1O302 - quartz molding sand with a mass fraction of a clay component from 0.2% to 0.5%, a mass fraction of silicon dioxide not less than 99.0%, a homogeneity coefficient from 60.0% to 70.0% and an average grain size from 0 , 19 to 0.23 mm.
(Amendment).
1.6. The designation of grades of fatty sands consists of the designations of the groups according to the ultimate compressive strength in a wet state and the average grain size.
Example. F2016 - oily foundry sand with a wet compressive strength of 0.05 to 0.08 MPa and an average grain size of 0.14 to 0.18 mm.
ACCEPTANCE
3.1. Molding sands are accepted in batches.
A batch is considered to be the amount of sand of one grade weighing at least 50 tons, drawn up by a quality document containing:
the name of the manufacturer or its trademark;
product name and designation;
number and date of issue of the document;
net weight of the batch;
batch number;
date of shipment;
test results;
designation of this standard.
3.2. To check the conformity of the quality of molding sands to the requirements of this standard, acceptance tests are carried out for each batch according to the indicators specified in table. -.
For quartz sands, tests are additionally carried out on the mass fraction of moisture and concentration of hydrogen ions.
3.3. Tests of molding sands according to the indicators of table. spend with the supplier at least twice a week.
Tests of molding sands according to the indicators of table. - carried out periodically with the supplier at least once a quarter.
3.4. To check the conformity of the quality of foundry sands to the requirements of this standard, at least 8 point samples with a mass of at least 0.5 kg are taken from each batch.
The mass of the combined sample must be at least 4 kg.
3.5. When unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests for this indicator are carried out on a combined sample of a doubled mass taken from the same batch.
The results of repeated tests are valid for the entire batch.
TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. Molding sands are transported in accordance with the rules for the carriage of goods in force for this type of transport, technical conditions for loading and securing goods, approved by the Ministry of Railways and GOST 22235.
Bags are packed in accordance with GOST 26663, GOST 24597, GOST 21650 and GOST 22477.
5.3. It is allowed, by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, to transport molding sands with a mass fraction of moisture less than 0.5% in hopper cement trucks and cement tank cars.
5.4. The frozen foundry sands are discharged using thermal and mechanical means for restoring flowability.
5.5. Molding sands with a mass fraction of moisture over 0.5% are stored separately by brands, with a mass fraction of moisture up to 0.5% - separately by brands in covered warehouses or bunkers.
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED TC 252 "Foundry"
2. APPROVED AND INTRODUCED INTO EFFECT by the Decree of the Committee for Standardization and Metrology of the USSR No. 2263 dated 28.12.91
3. REPLACE GOST 2138-84
4. REFERENCE REGULATORY AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
|
Designation of NTD referenced |
Item number |
5. REPUBLICATION. July 2005
Foundry sand characteristics
When casting in sand equipment, one must understand that the quality of the casting directly depends on the composition and properties of the foundry sand. Foundry practice has identified five key parameters that determine the quality of foundry sand.

Physical characteristics of sand
- strength;
- gas permeability;
- stability when exposed to temperature;
- the ability to drawdown;
- the possibility of repeated use.
Strength
Strength is the ability of the mixture to maintain the specified parameters during the casting operation and transportation of the investment ring inside the production room.
Gas permeability
Gas permeability is the ability of sand to pass through itself gases formed during the solidification of the melt. If the mixture is highly permeable, the porosity of the casting will be reduced. If the permeability is low, the surface quality will be much better. Gas permeability directly depends on the composition and fraction of the sand mixture.
Thermal stability
The ability of a tooling to maintain a given shape when exposed to temperature, to resist cracking and the appearance of other defects that appear when exposed to a high temperature of the molten metal is called thermal stability.
Drawdown ability
The ability of the sand to compress tightly during the solidification of the molded part. If sand did not have this property, then the cast billet would not have the ability to change dimensions within the mold. As a result, this would lead to cracking of the workpiece and the manifestation of other defects arising from the pouring of molten metal.
Reapplication
This means the possibility of using the molding mixture for the production of tooling intended for the formation of a new batch of castings.
Rules for the reception of quartz, river and alluvial sand
Quartz, river, alluvial sand and screenings during crushing must be assessed before shipment to the consumer and additional samples are taken upon delivery of the cargo. For this, special tests are carried out, the technical control service is responsible for the reception.
So samples are taken from each production line, then it is confirmed whether the sand is suitable for construction or whether the sand is suitable for sandblasting or there are any deviations from the norm.
During the control, it is revealed:
- the composition of the grains;
- the presence of clay and its amount in pieces;
- the amount of dusty residues and clay components;
- lack of third-party impurities and debris.
Periodic monitoring is carried out in order to determine changes in rocks over a certain period of time:
- once every 3 months - the density of the embankment is determined, if necessary, a test is possible under certain humidity conditions. The presence of harmful, organic additives and their quantity are revealed;
- once a year or with a changing composition of the rock, it is necessary to check the density of the grains, the amount of minerals contained, mainly harmful. The strength grade and efficiency of radionuclides are determined.
Research on radionuclides cannot be carried out within the enterprise, so the samples are taken to specialized research institutions. They must be accredited by supervisors.
If geological analysis data are not available, then an assessment of the radioactivity can be carried out immediately after extraction. An expressive version is used, based on the alluvium map. Sample preparation for examination is carried out on the basis of GOST 8735.
When delivered by rail or sea, the consignment is the simultaneous quantity of the shipped cargo. Upon delivery, all material brought in a day is taken into account.
Why do you need a passport for sand GOST 8736 93
The consumer may require a passport for sand GOST 8736 93 issued to the enterprise and technical documentation for the batch. To obtain information about the quality of the goods, samples should be taken, their quantity depends on the order:
- for a batch up to 350 m3, the number of samples is 10;
- orders of 350 - 700 m3 can be sampled 15 times;
- over 700 m3 should be sampled from 20 different locations.
The price per m3 of sand GOST 8736 93 is approximately 500 rubles, but the cost varies greatly in accordance with the quality of the product, the distance of the quarry and the manufacturer's or intermediary's premium. So river sand GOST 8736 93 is somewhat more expensive than screening after crushing.
Also, coarse sand is somewhat cheaper than the fine fraction and not every manufacturer divides the fraction.
Choice
The choice of this or that type of sand is determined by its purpose, economic feasibility. For example, river sand is more suitable for making concrete. The material does not require thorough rinsing. Provides resistance to moisture, temperature extremes. However, it should be understood that determining the type of bulk substance is not enough to obtain the desired result.
In this case, it is also important to pay attention to the concrete grade. For each brand, there are acceptable grain size indicators. For example, for concrete grade M200 and below, fractions from 1 to 2.5 are suitable.
Fractions from 2.5 to 3.5 are suitable for grades M350 and higher. When laying the foundation, fractions from 1.5 to 3.5 are used
For example, for concrete grade M200 and below, fractions from 1 to 2.5 are suitable. Fractions from 2.5 to 3.5 are suitable for grades M350 and higher. When laying the foundation, fractions from 1.5 to 3.5 are used.


Quarry sand can also be used, but only after thorough washing. As a rule, it is used in order to save money when there are no high requirements for the result. Due to the presence of a large amount of additional impurities, the material is not able to provide sufficient structural strength. Therefore, it can only be selected if heavy loads are not expected.
Quartz or gravelly types of material are obtained artificially. This requires significant financial, labor and time costs, therefore, from an economic point of view, it is unprofitable. This type of sand is often preferred in landscape design. This is due to the uniformity, evenness of the surface of the grains.


For any finishing work, production of industrial mixes, brickwork, tiles, it is recommended to choose a material with a minimum amount of impurities. River sand is suitable for this. The use of a quarry type of material is allowed in industrial production or where there are no strict requirements for the strength and stability of the final product.
When choosing sand on your own, you should carefully study the composition, characteristics, compatibility with other components of the mixture.