Varieties and labeling
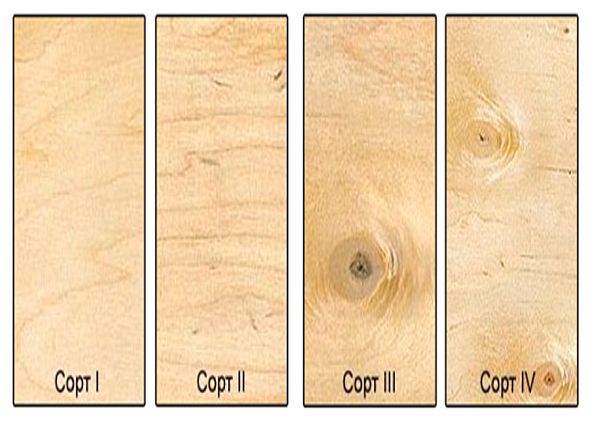
There are five grades of plywood. The highest is E (Elite), and further, as it deteriorates, from I to IV. The grade is determined by the state of the upper - front layers. Moreover, the quality of both surfaces is assessed separately and written through a forward slash (slash). For example, I / II or III / IV.
In GOST, it is described in detail for which grade which surface errors are permissible, there are special tables by which this grade is determined. If at least one parameter is worse than the permissible value, the grade is reduced.
Varieties differ in the presence and size of certain defects
These are the features on the front surface of different grades of plywood.
-
Elite. For this brand of plywood, the veneer must be perfect. There can be only minor changes in the wood (no eyes). Everything. There shouldn't be any other drawbacks.
-
I grade. May be
- Knots:
- pin, no more than 3 pcs per square meter;
- healthy, intergrown, dark and light with a diameter of 15 mm, no more than 10 pcs / m², they can have cracks no more than 0.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 3 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks no more than 200 mm long and no more than 1 mm of the sheet width.
-
Healthy discoloration - no more than 5% of the area.
- Knots:
-
II grade. Allowed:
- Knots:
- pin without restrictions;
- healthy, intergrown, dark and light with a diameter of 25 mm, no more than 5 pcs / m², they may have cracks no more than 0.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 6 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks no more than 200 mm long and no more than 1 mm of the sheet width.
- Open cracks no more than 200 mm long, no more than 2 mm wide in an amount of no more than 2 pcs when covering with putty.
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- The overlap in the outer layers is not more than 100 mm in length, in the amount of not more than 1 piece per 1 m of the sheet.
- Leakage of glue no more than 2% of the sheet area.
- Torn fibers no more than 5% of the sheet area.
- Scratches, dents are allowed in depth (height) within the limits of the maximum deviations in thickness.
- The gap in joints with a width of not more than 1 mm is not more than 1 piece per sheet.
- Wood inserts no more than 8 pcs per 1 m².
-
Double insert - no more than 2 pcs per m².
- Knots:
-
III grade.
- Knots:
- pin without restrictions;
- healthy, fused, dark and light with cracks no more than 1.5 mm wide;
-
partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 10 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks without limits.
- Open cracks
- length no more than 300 mm no more than 2 pieces,
- no more than 600 mm long, no more than 5 mm wide in an amount of no more than 2 pieces when covering with putty;
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- The overlap in the outer layers is no more than 200 mm in length, no more than 2 pcs per 1 m of the sheet.
- Leakage of glue no more than 2% of the sheet area.
-
Torn fibers no more than 15% of the sheet area.
- Scratches, dents are allowed in depth (height) within the limits of the maximum deviations in thickness.
- The gap in joints with a width of no more than 2 mm is no more than 1 piece per meter of sheet.
- Wood inserts and double insert - no limit.
- Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed.
- Knots:
-
Class IV may have such defects.
- Knots:
- pin;
- healthy, fused, dark and light without limits;
- partially fused, not fused, falling out with a diameter of no more than 40 mm without restrictions;
- Closed cracks without limits.
- Open cracks
- no more than 300 mm in length without restrictions;
-
no more than 600 mm long and no more than 10 mm wide without restrictions;
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- Overlap in outer layers is allowed.
- Leakage of glue is allowed.
- Torn fibers are allowed.
- Joint clearance is allowed.
- Scratches, dents are allowed.
- Wood inserts and double insert - no limit.
- Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed.
- Knots:
Compliance with the designations of plywood grades according to various standards: GOST 3916.1-96, TU 5512-002-00255214-2000, GOST 10.55-71
If there are defects that are not listed in the GOST, the product is considered off-grade. It is also considered off-grade when the maximum permissible size of defects is exceeded. Sometimes they try to sell such products as the fourth grade, but this is a re-grading and the price for it should be much lower.
By the way, if there are no obvious cracks and fallen out knots, the third grade can be used for interior decoration. In certain interiors, it looks even more interesting than E or the first, which are just a flat sheet without any peculiarities inherent in wood.
How to choose?
When building a house, plywood is most often used, consisting of 3-5 layers of glued veneer. The veneer layers can be located in the sheet material in different ways, they are evaluated according to the outer layers of the sheet. If the wood grains are located in the direction of the length of the sheet, then such plywood is called longitudinal. If the fibers are located in the direction of the sheet width, then such plywood is considered to be transverse. Longitudinal sheet plywood is used wherever high flexibility of the sheet is required when performing work. Cross plywood is used when good bending stiffness is required.

Due to the impregnation of the layers with glue, plywood sheets are highly resistant to moisture and water. Several brands are most common.
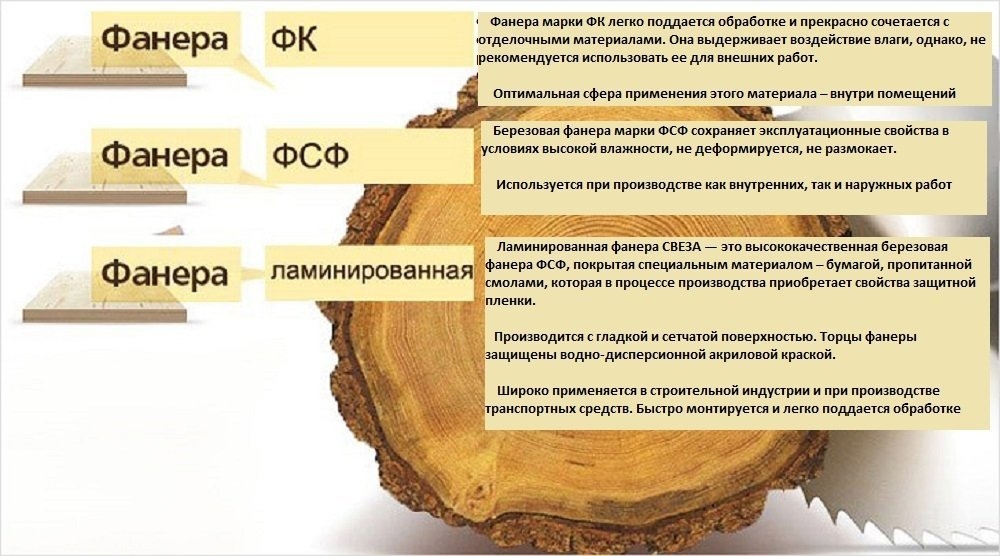
FC - is a moisture-resistant sheet, the veneer inside which is impregnated with glue, consisting of a mixture of resin and formaldehyde. If plywood has an E1 impregnation class, it means that the degree of emission of formaldehyde vapors into the external environment is low, and such material can be used in residential premises.
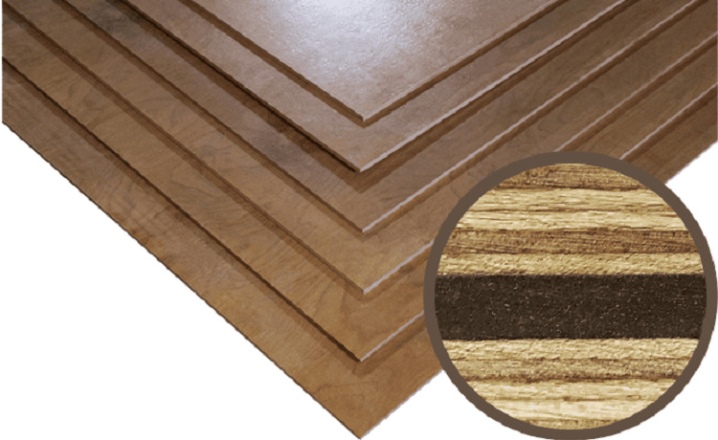







Finished pressed plywood sheets are sanded.
There are two types of plywood products.
Sanded - if only one side of the sheet is sanded, then the Sh1 code is added to the plywood brand nomenclature. If both sides are ground, then the products are marked with the Sh2 code.


Plywood, sanded on both sides, is used for the production of furniture products. If you choose a material for construction work, then it makes no sense to overpay for sanded sheets - you can get by with a cheaper unpolished option.
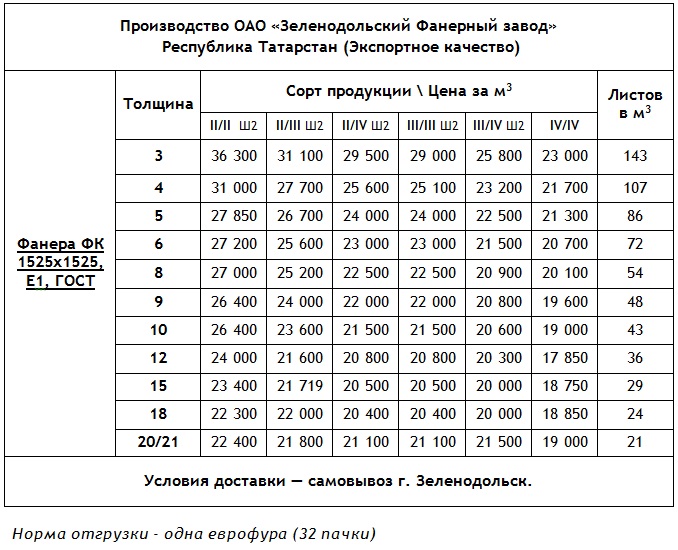
Plywood sheets are divided into 5 grades. The best grade is marked with the letter E, which denotes an elite and high quality product. Then, as they deteriorate, the varieties are divided into I, II, III and IV. The grade is determined by the appearance and quality of the front sides of the material. Each side is evaluated separately, and the result in the nomenclature is written with a fraction sign. For example, plywood marked I / II will indicate that one side of this material corresponds to I grade, and the other side of the sheet is only of II grade quality.

To correctly determine the amount of material required for work, you need to make preliminary calculations before buying:
- determine the area of the plywood sheet;
- calculate the area of the working surface;
- divide the area of the working surface by the area of the plywood sheet, round the result up to whole numbers.
When buying material, you need to take a small stock, which will be needed in the event of an incorrect cut.
Experienced experts recommend considering the following important nuances when buying plywood material:
determine the purpose of plywood and select the appropriate grade of material for this purpose, as well as take into account the composition of the adhesive base;
check with the seller what material the plywood sheets are made of - birch and pine wood are considered the most suitable for indoor and outdoor work;
pay attention to the quality of the surface of the sheet - there should be no chips, bubbles and foreign inclusions on it.
For the manufacture of furniture products, plywood sheets are used, the thickness of which does not exceed 9-10 mm, while for construction purposes they take material with a thickness of at least 12 mm. Finishing works are performed with sanded plywood of grade E or category I with obligatory sanding of the outer side. For other works, the appropriate class of material is also individually selected and the need for grinding is determined. The cost of a plywood sheet directly depends on its grade, size and thickness. The larger the dimensions of the sheet and its thickness, the more expensive the material is.
Which plywood is better, see below.
Moisture resistance
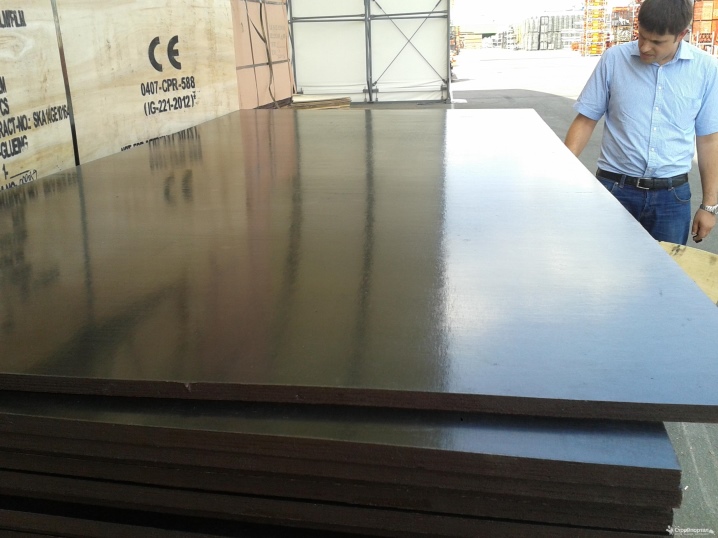
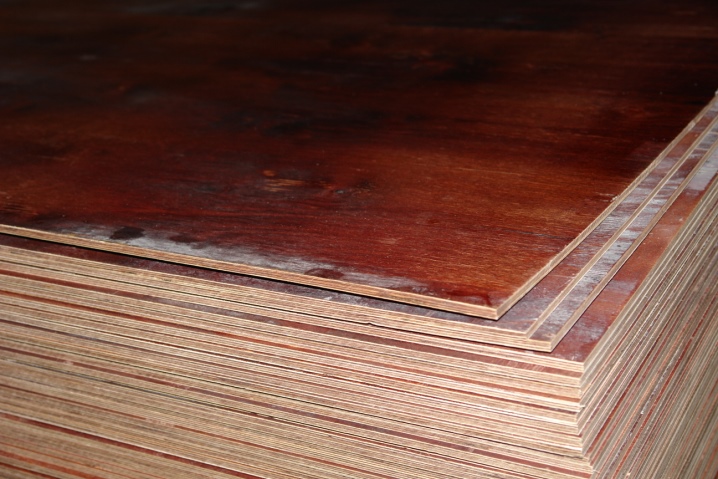
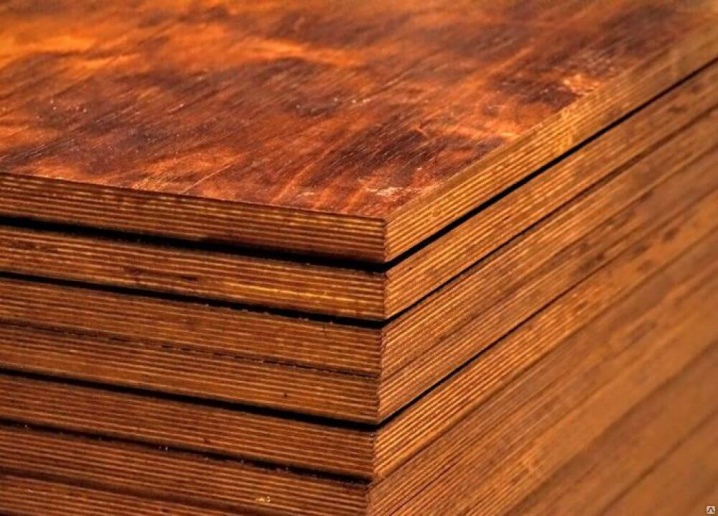
There are several types of plywood in relation to the indicator of its moisture resistance. They have a specific designation, which is indicated in the marking. The material of the FSF type is moisture resistant. This plywood is resin formaldehyde. Moisture-resistant film faced plywood FSF, unlike other types (FP, FBA), is resistant to such influences. It can be used outdoors. This is due to the peculiarities of its production.
The composition of the material includes an adhesive based on a phenolic component. It is he who endows plywood with its moisture-resistant qualities. However, phenol-formaldehyde glue also has a number of disadvantages. It is not a safe substance. Phenol formaldehyde can be harmful to human health.
It should be noted that in the production of waterproof plywood covered with a layer of a special film, glue with a safety class of at least E1 is used. This allows the presented type of plywood to be used even indoors. It is allowed to make furniture from such material, including for children's rooms. At the same time, the content of formaldehyde components in the composition is minimal.
When purchasing moisture-resistant film faced plywood for flooring, creating furniture or products from similar materials, you need to give preference to products from trusted brands. Only such manufacturers fulfill all the requirements of GOST. Their products are safe for human health. Little-known manufacturers can save on quality, which results in plywood with a persistent chemical odor. If an unpleasant, strong formaldehyde aroma is felt, these products should not be purchased for indoor use.
Plywood such as FOF, FBS, FK also belongs to waterproof materials.
Plywood grades - classification by type of adhesive
The performance properties of plywood largely depend on the substance used for gluing the sheets. The quality of the impregnation affects the moisture resistance and environmental friendliness of plywood, as well as its ability to withstand temperature fluctuations, humidity and other external influences. Many types of plywood are distinguished on the basis of the adhesive components used in the production.
Plywood FBA
FBA is the least resistant material to a humid environment. However, the use of albuminocasein glue makes it absolutely safe from an environmental point of view. This plywood is only suitable for rooms with low humidity levels. In particular, it has found its application in the manufacture of pieces of furniture, and is also used to create all kinds of decorative elements of the interior.
Plywood FC
FC is a material with rather low moisture resistance. In this case, the function of a binder is performed by urea glue, which does not emit harmful substances, which makes it possible to use this type of plywood for finishing work inside residential premises. At the same time, a moderate level of humidity is allowed.
Plywood FKM
FKM - veneer sheets connected with melamine glue. According to the degree of moisture resistance, the material has average indicators.
Plywood FSF
FSF - especially durable wood-based panels, the layers of which are impregnated with phenol-formaldehyde resin. The material is able to withstand significant loads and resist moisture.However, the amount of toxins contained in the adhesive makes it possible to use such plywood exclusively outside the premises. In particular, it is ideal for cladding exterior walls in frame house building, erection of enclosing structures, and the manufacture of outdoor furniture.
Plywood FB
FB is a material in the production process of which bakelite glue is used. Sheets impregnated with such a composition are characterized by increased moisture resistance and are able to withstand almost any temperature conditions. The impregnation reliably protects wood from negative environmental influences, which makes it possible to use this type of plywood in almost any area.
At the same time, plates of the FB type may have characteristic differences, depending on the composition of the adhesive and the gluing technology that affects their characteristics.
Materials treated with alcohol-soluble impregnations are moisture resistant and are divided into three types:
- FBS - plywood of the highest quality, each sheet of which is impregnated as thoroughly as possible;
- FBS1 - plywood boards, in the manufacturing process of which the method of smearing veneer sheets is used, due to which the quality indicators of the material are reduced;
- FBS1A - belonging to the lowest class of bakelite plywood, in the production of which the amount of applied alcohol-soluble substance is limited, which implies the processing of exclusively longitudinally arranged sheets.
Another type is plywood FBV, in the manufacture of which water-soluble adhesives are used.
There are two types of such plywood:
- Plywood with coated inner layers but impregnated outer sheets.
- Plywood boards with the FBV1 marking, for all layers of which only the coating method is assumed.
Thickness of sheets
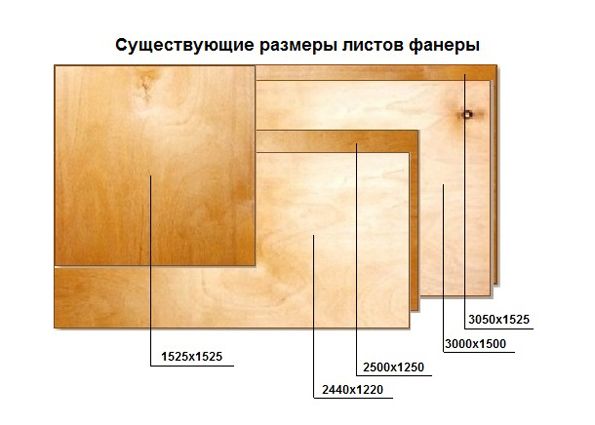
Since the field of application of premium sheets is very wide, one or another material thickness is better suited for each type of work. There are three types of products in accordance with the thickness - it can be thick, medium or thin. With a material thickness of 18 mm, it is classified as a thick product, if the sheets are 8-15 mm, then the thickness is average, products up to 6 mm are classified as thin types.
Thin sheets, called aviation or Finnish, are highly durable and flexible. This material has a thickness of 0.4-6 mm. The scope of these products is determined by its name. This is the design of aircraft, amateur aircraft modeling. Such material is used for the manufacture of souvenirs, appliances and musical instruments.
Consider where material is used with a thickness of 3 mm to 6 mm (grades FSF and FK). Plywood 3 mm grade 1 is used for the manufacture of souvenirs and decorative items. Such products are distinguished by a high level of flexibility and strength, this is due to the high quality of the products. At the same time, products with a thickness of 3 mm are used somewhat less often than 4 mm sheets. This fact is determined by the lower price of the latter.
The thin material of 3 mm has a high cost, which is compensated by the small amount required for the manufacture of each item. In addition, due to the high quality, labor productivity is increased.
Sanded plywood of medium thickness, marked 1/1, 1/2 and 1/3, is distinguished by a beautiful texture of the front side and aesthetic appearance. Products are used for interior decoration, front sides of the floor and walls.
Thick first-class sheets are used less often, they can be used in the construction of playgrounds, wall cladding, partitions, in mechanical engineering and furniture production, in construction for the manufacture of formwork.
Plywood FK GOST
Application of plywood FC
- shelving systems in warehouses;
- finishing of ceilings and walls;
- for the construction of internal walls;
- for the manufacture of shelves and other various decor details;
- for the manufacture of cabinet furniture for a home or office;
- for finishing bodies in transport, for finishing bodies and cargo containers;
- in the advertising business;
- cinema;
- industrial modeling;
- art;
- in the manufacture of decorations;
- advertising models and objects;
- souvenirs, toys, household items;
- in acoustics and sound engineering;
- for the manufacture of bodies for musical instruments;
- containers, packages, boxes, packing boxes;
- partitions for transportation;
- as a base for parquet or laminate;
- for the preparation of signboards and stands intended for indoor use;
- some parts of sofas, armchairs;
- to create balcony ceilings and partitions;
- combined thermal insulation device;
- creation of insulating products in electrical engineering;
- models of ships, aircraft;
Types of plywood
The veneer is cut from logs of various types of wood, which determines the types of plywood obtained. Larch plywood sheets have a homogeneous structure, but this does not interfere with the use of the material for finishing work. Sheets are made of linden, aspen, alder, maple. But more often on the market you can find products made of birch, therefore the deciduous variety was so called birch. Softwood plywood has a beautiful texture, which allows the sheets to be used as a finishing. Enough varnishing is enough to express the nature conceived drawing. The following tree species are selected as raw materials for making sheets: spruce, pine, fir, cedar.
• Urea glue is a bonding agent for FC plywood. The adhesive is environmentally friendly, so the finished material can be safely used to decorate bedrooms, children's and other living quarters. For the production of this type, birch veneer is more often used. The products are in great demand in the furniture industry and construction.
• Phenol-formaldehyde resin is used for the manufacture of moisture-resistant plywood FSF. Experts recommend using this type exclusively for outdoor work due to the toxicity of the material. In the furniture industry, the sheets undergo additional processing (the surface is covered with finishing), which makes them safe for indoor use. Moisture-resistant plywood is in demand in various spheres of economic activity: construction, furniture industry, shipbuilding, etc.
• Melamine resin is safe for human health, but this does not prevent it from imparting high moisture resistance to plywood sheets. The type of products FKM represents an averaged version between FK and FSF. In appearance, the material is identical to FC, but differs in light ends. In terms of moisture resistance, it is not inferior to the phenol-formaldehyde type, but due to the safety of the glue, the use of plywood indoors is allowed.

• Bakelite resin gives the sheets strength and high resistance to various types of media. Plywood is used in shipbuilding, automotive and construction, especially in areas with high humidity. The methods of applying the glue determine the varieties produced:
- FBS provides for the impregnation of the upper layers with alcohol-soluble resin, which gives them extra strength;
- FBV has the upper layers impregnated with a water-soluble resin, which reduces moisture resistance, but significantly affects the pricing;
- FBS-1 is made on condition that all veneer layers are impregnated with alcohol-soluble resin, this gives strength from prolonged contact with water and exposure to aggressive media;
- FBS-1A provides for impregnation of all layers with alcohol-soluble glue, except for perpendicularly laid; this slightly reduces strength, but makes the material more accessible.

Selection rules
The main rule of choice is that you should delve into all the existing parameters of plywood in as much detail as possible, know the various markings, and clearly understand what they mean.Considering that this is not only a finishing, but sometimes a building material, which, moreover, is not always 100% environmentally friendly, one must be sure that no potentially dangerous properties of plywood have remained behind the scenes. Avoid making a choice in favor of the plywood that differs from the one you need "by only one or two points", while being cheaper.
Before purchasing, think carefully about what the ideal plywood should beat to solve the task, and do not deviate from the requirements a single step. Agree, it would be strange to use theoretically toxic plywood in a nursery simply because such material costs a little less. Saving is also inappropriate if the moisture resistance class of the material is lower than required, or if the product turns out to be so rough that it loses its aesthetics and can become a source of splinters.