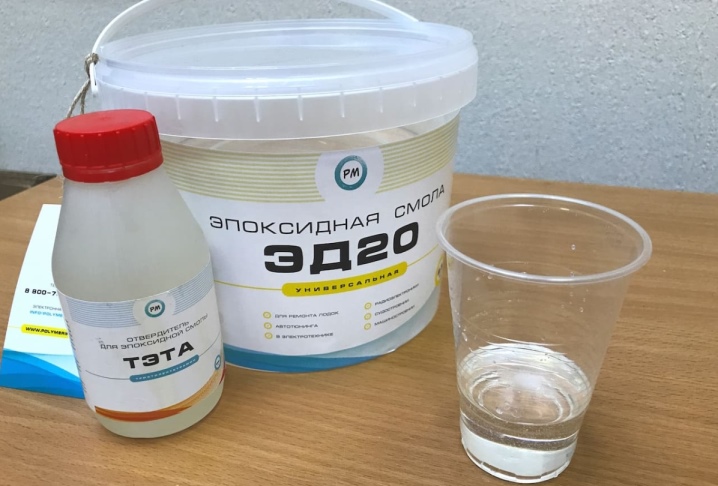
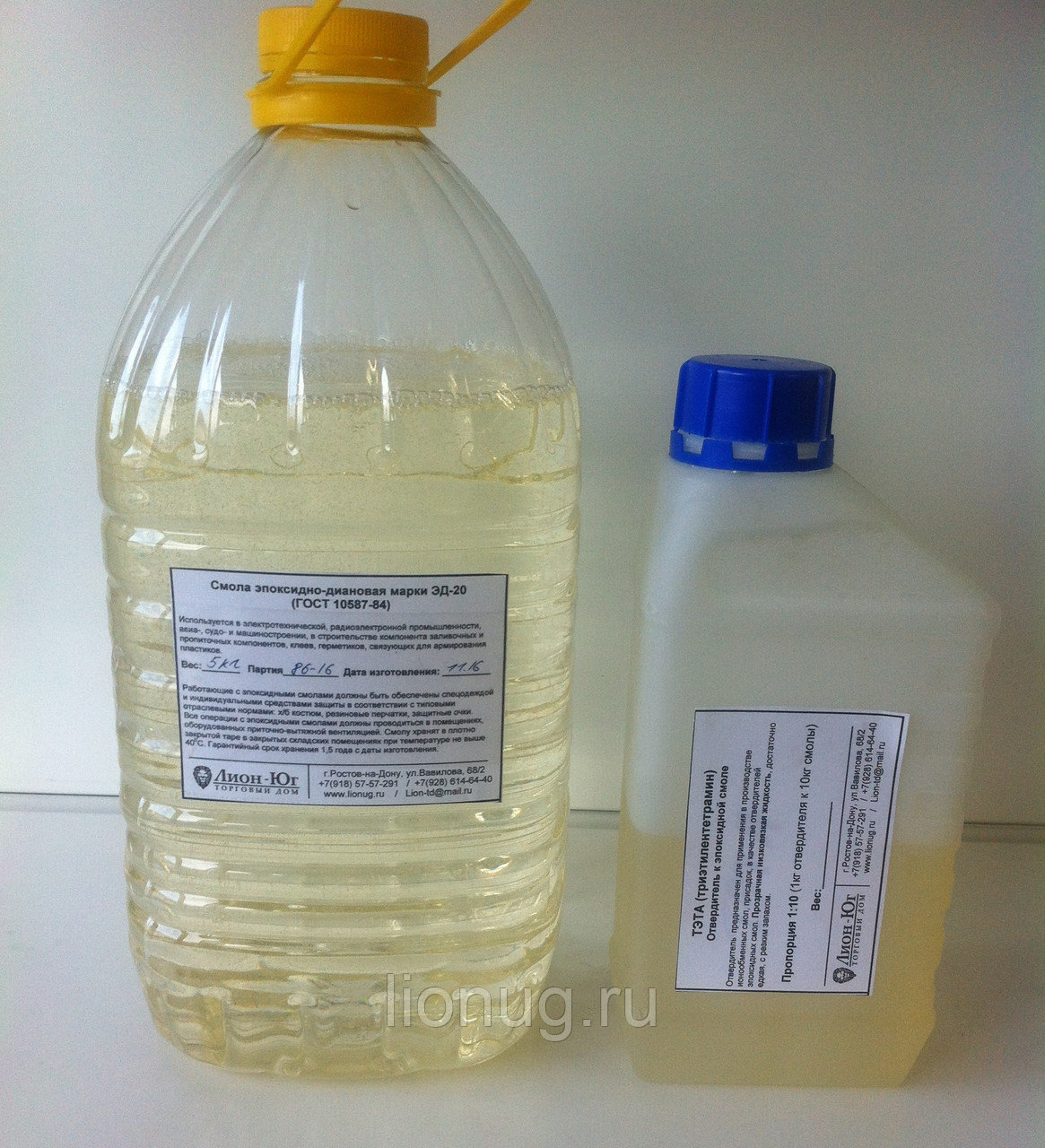
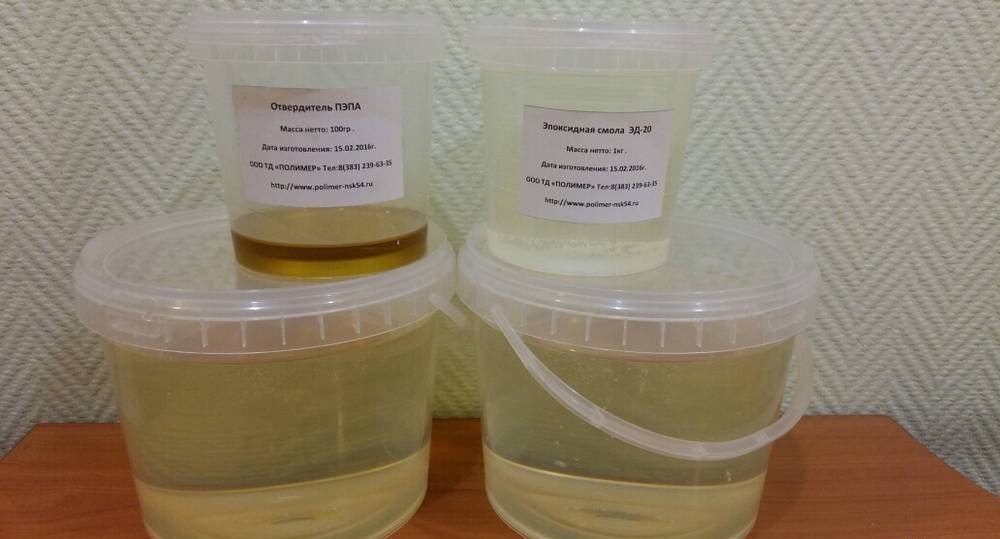
Curing of epoxy resin ED-20
Uncured diane epoxy resin ED-20 can be converted to infusible and insoluble
condition by the action of curing agents (hardeners) of various types - aliphatic and aromatic di- and polyamines,
low molecular weight polyamides, di- and polycarboxylic acids and their anhydrides,
phenol-formaldehyde resins and other compounds.
Depending on the hardener used, the properties of the cured ED-20 epoxy resin can
vary over the widest range.
ED-20 is used in industry in its pure form,
or as components of composite materials - potting and impregnating compounds, adhesives, sealants,
binders for reinforced plastics, protective coatings.
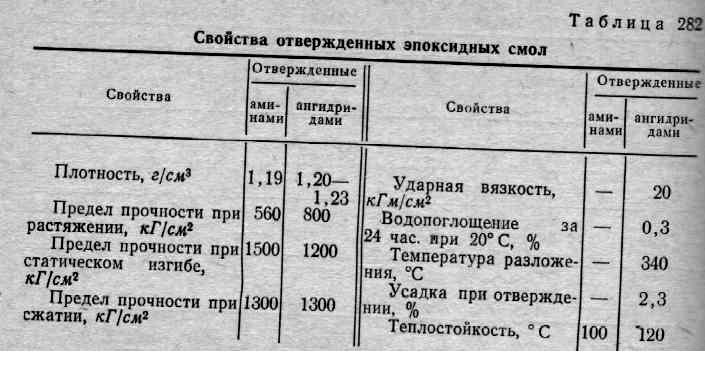
Characteristics of ED-20 resin
Epoxy resin ED-20 is not explosive, but it burns when introduced into a fire source. Volatile components (toluene and epichlorohydrin) are found in
resin in quantities determined exclusively by analytical methods,
and refer to substances of the 2nd hazard class according to the degree of impact on the human body.
Resin ED-20 is stored in a tightly closed container in closed warehouses at a temperature not exceeding 40 ° C.
The guaranteed shelf life of ED-20 epoxy resin is 1 year from the date of manufacture.
Epoxy can be supplied with hardeners
cold and wet hardening.
Qualitative indicators of ED-20 epoxy resin according to GOST 10587-84:
| № | Indicator name | Standard according to GOST | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top grade | First grade | ||
| 1 | Appearance | Highly viscous transparent without visible mechanical impurities and traces of water | |
| 2 | Color on iron-cobalt scale, no more | 3 | 8 |
| 3 | Mass fraction of epoxy groups,% | 20,0-22,5 | 20,0-22,5 |
| 4 | Chlorine ion mass fraction,%, no more | 0,001 | 0,005 |
| 5 | Mass fraction of saponified chlorine,%, no more | 0,3 | 0,8 |
| 6 | Mass fraction of hydroxyl groups,%, no more | 1,7 | — |
| 7 | Mass fraction of volatile substances,%, no more | 0,2 | 0,8 |
| 8 | Dynamic viscosity, Pa * s at 20 ° С | 13-20 | 12-25 |
| 9 | Gelatinization time with hardener, h, not less | 8,0 | 4,0 |
Additional information about ED-20 resin
Precautions: Working with epoxy resins must be provided with protective clothing and personal protective equipment. All operations when working with epoxy resins should be carried out in rooms equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation
Storage: Epoxy-diane resin is stored in a tightly closed container in a closed warehouse at a temperature not exceeding 40 ° C.
Packaging: Epoxy resins are shipped in steel buckets, drums, barrels. See the price table for packaging availability.
The guaranteed shelf life is 12 months from the date of manufacture.
Epoxy resin code type ED-20 CAS No.25068-38-6. English name - Poly (bisphenol-A-co-epichlorohydrin)
Liquid Epoxy resin (Biphend A type), Epoxy Equiv: 184-194 g / eq.
Base resin ED-20 in the production of glass and carbon fiber reinforced plastics
Application of basic epoxy resin ED-20 in the production of composites, using as a reinforcing filler
rovings and fabrics made of glass and carbon, methods of manual laying of impregnation under vacuum, winding, pouring, etc. are not technological and
can only be justified by economic considerations.
Our company offers a number of ED-20 analogues:
epoxy liquid resin KER-828,
, resin BE-188,
NPEL-128,
DER-331,
DER-330,
EPOTEC YD-128,
YD-128,
Eposir-7120.
For good results, experts usually recommend
use epoxy resins modified with active thinners, for example from our range:
- Choosing a Modified Epoxy Resin
- Modified epoxy resin Etal-370
- Modified epoxy resin Etal-245
- Modified epoxy resin Etal-247
- Modified epoxy resin Etal-249
- Epoxy compound К-115
- Epoxy compound K-153
- Epoxy compound K-153A (resin)
- Epoxy compound KDA
- Low-temperature transparent epoxy compound Etal-27NT / 12NT
- Modified epoxy resin Etal-148 for elastic compositions
- Modified epoxy resin Etal-200M
How to dilute correctly
The attached instructions from the manufacturer indicate the description of the proportions that should be observed when preparing the solution, and also indicate the terms and conditions for the polymerization of the layer. But the very actions required to obtain the desired composition are usually not described. All specified data must be strictly observed, the types of hardeners must not be replaced, otherwise the epoxy may turn out to be completely different, and it will not be of high quality.
If a large amount of resin is to be prepared, it is necessary to prepare a container in which it can be heated. It is heated in a water bath for 10-15 minutes, the temperature is brought to about 50 degrees.
When choosing a hot cure method, proceed as follows:
Measure the amount of composition that will be heated
It is better to do this in portions, because the composition freezes quickly.
A water bath is heated, a container is placed in it, into which the resin is poured, it is important to ensure that no liquid gets into it.
The temperature indicators of the bath must be monitored, overheating can lead to deterioration of the material.
When heating occurs, thorough stirring should be done, the introduction of the hardener occurs gradually, a large amount cannot be injected immediately. The attached instructions from the manufacturer indicate the description of the proportions that should be observed when preparing the solution.
 The attached instructions from the manufacturer indicate the description of the proportions that should be observed when preparing the solution.
The attached instructions from the manufacturer indicate the description of the proportions that should be observed when preparing the solution.
You can use the following options:
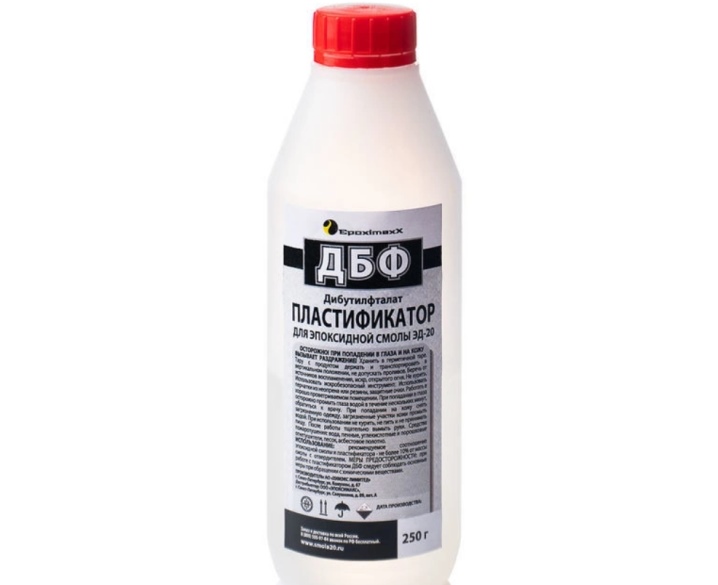
- DBP, added in a small amount, a maximum of 5% of the total can be infused. Helps to improve the performance of protection against cracks, low temperatures and mechanical stress;
- DEG-1. Active diluent for resins. An increase in the amount of it in the composition makes it possible to reduce the similarity of epoxy to rubber. The allowable amount ranges from 3% to 10%. Cannot be used to obtain transparent products;
- TEG-1. Has similar characteristics to the previous type, but more viscous. It dissolves in water.
 To give elasticity to the epoxy, plasticizers are added to it.
To give elasticity to the epoxy, plasticizers are added to it.
Appointment of hardeners
The role of the hardener is that it is not only a catalyst for the reaction, but also a full-fledged participant in it. The result is a compound of a certain consistency, suitable for work. And the resulting product after solidification will be distinguished by reliability, strength and durability.
The composition of modern compounds includes substances that affect the acceleration of the hardening process, which depends on the temperature of the solution and the type of hardener used. Solutions are commercially available that solidify even at low temperatures. Polymerization of some compounds is possible in high humidity conditions.
 Hardener types
Hardener types
For household needs, a resin that hardens at normal temperature is used, it is also called "cold hardening". However, the most durable, chemically and mechanically resistant are products made from hot-cured formulations.
The degree of homogeneity, hardness, durability and transparency of the composition depends on how accurately the proportion of the hardener is selected. An incorrectly selected amount and mixing of components reduces the quality characteristics, affects the reduction in the service life of the solution and the resulting product.
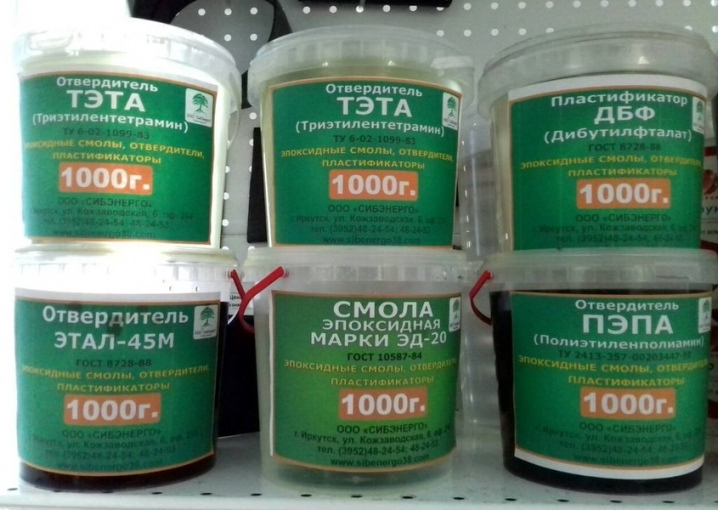
Varieties
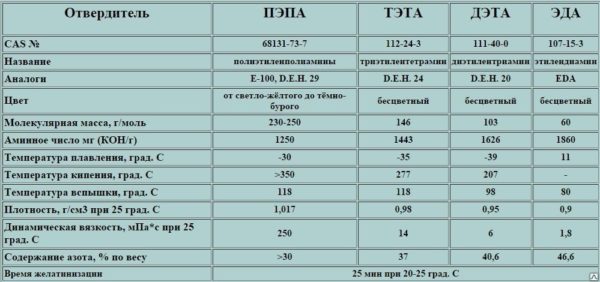
The quality of the result is primarily influenced by the type of hardener, not the resin. The most common low-cost versions are PEPA and TETA hardeners.However, their quality is significantly lower than that of the modified formulations.
 Set with PEPA hardener
Set with PEPA hardener
The main disadvantages of cheap formulations include the following:
- The temperature at which curing occurs for TETA is at least 30 degrees, for PEPA - 15 degrees.
- The compositions are vulnerable to moisture - this is a significant disadvantage when carrying out waterproofing work or when pouring a floor.
- Polymerization occurs quickly, so creating a thick layer is problematic.
As for the modified compounds, these disadvantages are not inherent in them. The only drawback is the high cost.
 Set with hardener TETA for obtaining a clear solution
Set with hardener TETA for obtaining a clear solution
If we compare these two types of hardener, then it is easier to work with PEPA, since it allows a slight deviation from the proportions and behaves perfectly at room temperature.
 Characteristics of different brands of hardener
Characteristics of different brands of hardener
Characteristics and properties
ES is characterized by resistance to halogens, as well as caustic alkalis and acids. It dissolves in acetone and some esters without forming a film. Let's take a closer look at the parameters of epoxy resin.
The hardened ES retains its shape and volume. This property allows the production of molds and other products. After hardening, the resin hardly shrinks, so the volume of the workpiece remains unchanged.
Most resins are resistant to abrasives and aggressive solutions. This allows you to use any detergent compositions when working with epoxy products. Even if small defects appear on the coating, with a small supply of epoxy, they can be easily and quickly eliminated.


ES is waterproof, this property plays a major role in the choice of finishing materials in rooms with high humidity. For example, kitchen countertops made of epoxy have a long period of use, while furniture modules made of fiberboard, due to frequent exposure to moisture, deteriorate very quickly.
Possessing increased heat resistance, the composition boils at +155 degrees, with more "hot" exposure it begins to melt. The substance belongs to the II class of danger, does not ignite even if it is brought into an open fire. These characteristics are typical for all types of ES. However, they can manifest themselves to varying degrees depending on the additives used in the preparation of the epoxy.

3 Technical requirements
3.1 Epoxy-diane resins are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to the technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
3.2 Depending on the physical and chemical properties, the following grades of epoxy-diane resins are established: ED-22, ED-20, ED-16, ED-14, ED-10, ED-8. The designation of grades consists of blocks of letters and numbers: - the first block - designation of resins "ED" (E - epoxy; D - diphenylolpropane); - the second block - numbers corresponding to the lower value of the norm in terms of "mass fraction of epoxy groups".
3.3 Features
3.3.1 In terms of physical and chemical parameters, epoxy-diane resins must comply with the requirements and standards specified in table 1.
3.4 Requirements for raw materialsOnly premium grade epichlorohydrin should be used for the production of epoxy-diane resins.
|
Indicator name |
Norm for the brand |
Test Method |
|||||||||
|
ED-22 |
ED-20 |
ED-16 |
ED-14 |
ED-10 |
ED-8 |
||||||
|
top grade |
first grade |
top grade |
first grade |
top grade |
first grade |
top grade |
first grade |
||||
|
1 Appearance |
Viscous transparent |
High viscosity transparent |
Highly viscous transparent |
Solid transparent |
According to 7.3 of this standard |
||||||
|
Free from visible mechanical impurities and traces of water |
|||||||||||
|
2 Color according to iron-cobalt scale, reference solution number *, not darker |
3 |
5 |
3 |
8 |
3 |
8 |
10 |
6 |
2 |
6 |
According to 7.4 of this standard |
|
_______________ * The text of the document corresponds to the original. -. |
|||||||||||
|
3 Mass fraction of epoxy groups,% |
p 22.1-23.6 |
20,0-22,5 |
16,0-18,0 |
13,9-15,9 |
10,0-13,0 |
8,5-10,0 |
8,0-10,0 |
According to GOST 12497 and 7.5 of this standard |
|||
|
4 Mass fraction of chlorine ion,%, no more |
0,001 |
0,003 |
0,001 |
0,005 |
0,002 |
0,004 |
0,006 |
0,006 |
0,001 |
0,003 |
According to GOST R 52021, section 8 |
|
5 Mass fraction of saponifiable chlorine,%, no more |
0,2 |
0,5 |
0,3 |
0,8 |
0,3 |
0,5 |
0,6 |
0,6 |
0,2 |
0,3 |
Also |
|
6 Mass fraction of hydroxyl groups,%, no more |
1,0 |
Do not define |
1,7 |
Do not define |
2,5 |
Do not define |
According to GOST 17555 and 7.6 of this standard |
||||
|
7 Mass fraction of volatile substances,%, no more |
0,1 |
0,4 |
0,2 |
0,8 |
0,2 |
0,4 |
0,6 |
0,6 |
0,2 |
0,3 |
According to GOST 22456 and 7.7 of this standard |
|
8 Dynamic viscosity, Pa s, at (25.0 ± 0.1) ° С (50.0 ± 0.1) ° С |
8-12 |
7-12 |
13-20 |
12-25 |
Do not define |
According to 7.8 of this standard |
|||||
|
Do not define |
5-18 |
5-20 |
20-40 |
Do not define |
|||||||
|
9 Softening temperature according to the "ring and ball" method, ° С, no more |
Do not define |
65 |
65 |
According to GOST 11506 |
|||||||
|
10 Gelatinization time, h, not less |
18,0 |
9,0 |
8,0 |
4,0 |
4,0 |
3,0 |
2,5 |
2,0 |
3,0 |
2,0 |
According to 7.9 of this standard |
3.5 Marking
3.5.1 Transport marking - in accordance with GOST 14192 with the application of handling signs: "Keep away from moisture", "Up." liquid epoxy-diane resins) or 3077 (for solid epoxy-diane resins).
3.5.2 The marking characterizing the packaged product must contain: - the name of the manufacturer, its trademark and legal address; - the name of the product, its brand and grade; - batch number; - batch weight; - date of manufacture; - designation of this standard .Method of applying marking data and handling signs - according to GOST 14192.
3.5.3 Labeling of products supplied for export must comply with the requirements of the supply agreement or the terms of the foreign economic contract, taking into account the requirements of this standard.
3.6 PackagingEpoxy-diane resins are packed in barrels in accordance with GOST 13950 and in drums in accordance with GOST 5044.
Refractory resins
There are refractory resins, these are, first of all, halogen-free KDP-555MC80, KDP-540MC75, KDP-550MC65. The first numbers in the index after the letter combination KDP indicate the critical temperature that this resin can withstand when used as a bonding agent for some composites. The main field of application of such refractory resins is in the aviation and space industries, where materials made with KDP are used in the manufacture of outer contours of wings, fairings that can withstand high dynamic loads of flight control stabilizers, ailerons and spars.
Carbon fiber reinforced plastics, which are able to withstand multiple high temperatures, contribute a significant share to the fire resistance of such materials. But the base itself acquires refractory properties, first of all, due to the additives introduced into it in the course of polymerization in the form of organoelement compounds. First of all - organosilicons.
During the modification of an epoxy resin with these elements, many properties of such a resin change, and often quite significant. Changes are not in vain; while maintaining the main parameter in the form of heat resistance, one more is usually required. For example, maintaining some plasticity or stability of the properties of the resin as a dielectric, moreover, over a wide temperature range. This is usually achieved by including acyclic diepoxides in the polymer chain instead of the base of diane resins, but then the fragility of products made of such resin increases.
Usually, the higher the numerical index of epoxy resins (ED 16, 20, 22), the more likely, under the influence of extremely high temperatures, the transition of the solidified, polymerized form of the resin will take place immediately into a destructive crystalline state, with preliminary cracking of the monolith. The transition to some kind of liquid state of aggregation in the behavior of the resin is not provided. Perhaps only some preliminary softening, the resins are deformed.
Resins with numeric indexes ED-6 and ED-15 are more resistant to high temperatures. When exposed to relatively low temperatures in the range of 200-250 ° C degrees, products from such a resin begin to emit gaseous products and a colorless viscous liquid. This is a consequence of processes that reverse the polymerization that occurred during the curing of the product.Of course, there is no question of a full-fledged reverse reaction, the processes of destruction prevail over the "joining" of molecules, and the indicated temperature in its upper limit is critical and predisposing. With a duration of its exposure for more than an hour, and even more so with its increase, the processes of decomposition of epoxy components become irreversible, with a sharp drop in all properties inherent in the material.
The most heat-resistant epoxy materials are obtained by the synthesis of fluorinated diphenylolpropanes. These substances play the role of latent, or latent, hardeners, chemically neutral to the resin at room temperature, but beginning to actively work on resin polymerization when exposed to temperatures of 100 ° C or more, when its chemical and physical properties begin to change. These include dicyandiamide, melamine, isophthalyldihydrazide.
Exactly products from these epoxy resins, with introduced in them organosilicon plasticizers, are placed as fairing heads for ships launched into orbit, and are launched onto the elements of dynamic control of launch vehicles and supersonic aircraft reinforced with carbon fiber.
In the future, the development of elements of the load-bearing frame of the control elements of hypersonic vehicles. The upper temperature limit for them currently exceeds 550 ° C degrees. Although this, of course, is not enough, but chemists do not stand still, new methods are being developed to improve the physical properties of oligomers. A promising trend is the introduction of fine powders from refractory metals or their carbides, for example, tungsten carbide, into the composition of epoxy polymers.
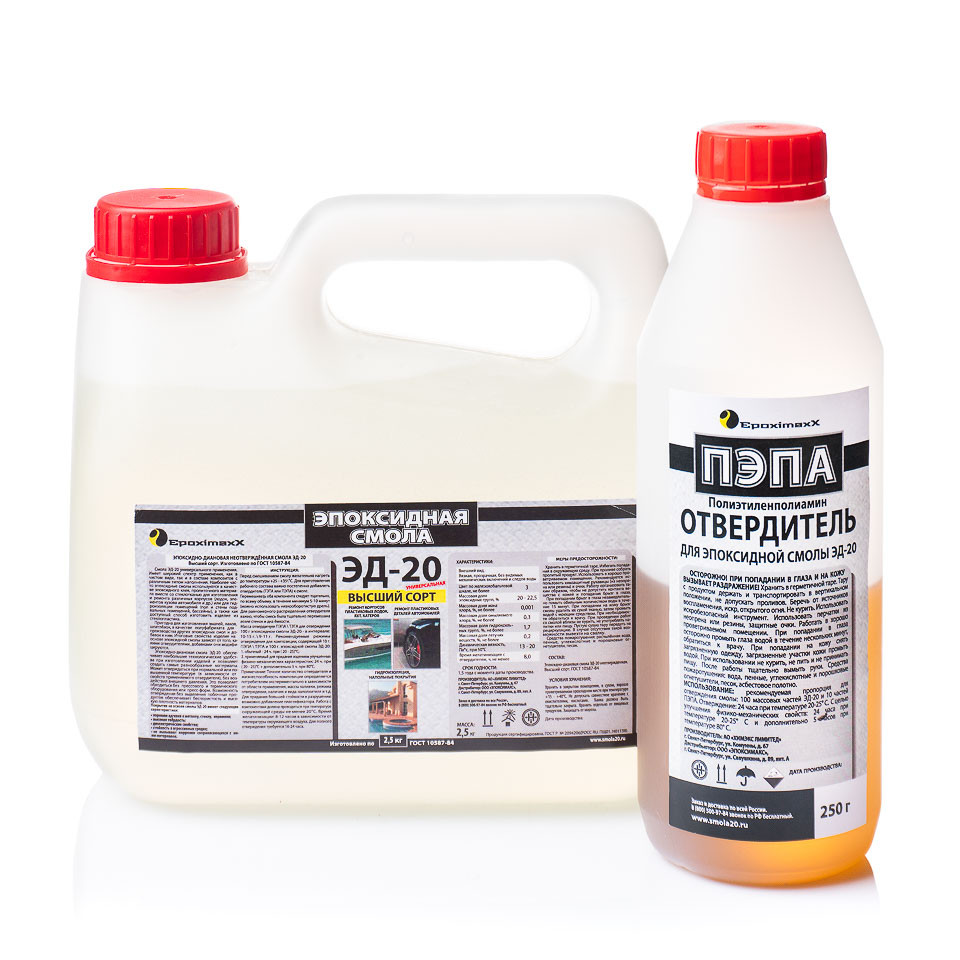
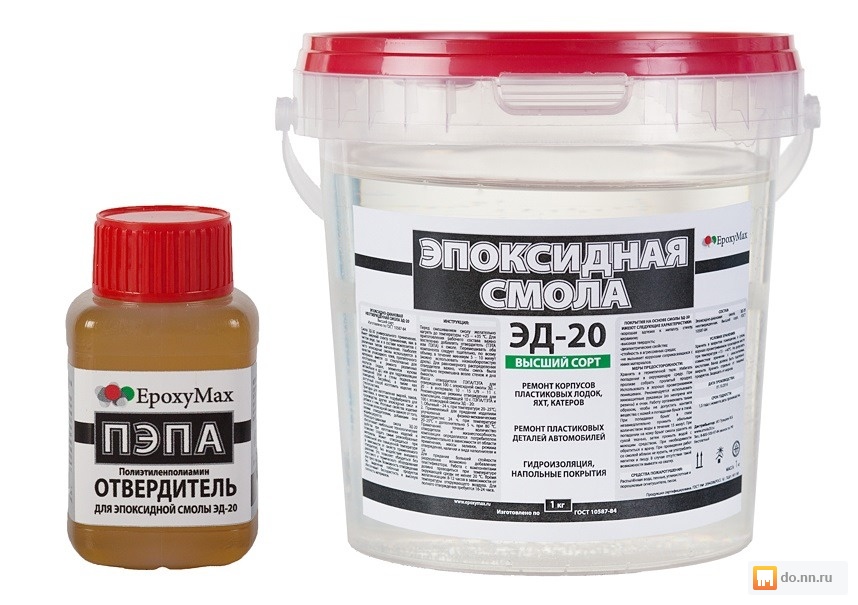
Resin ED-20 (ED-16) and its mixing rate with hardener (PEPA) (Glue EDP)
Previously, the well-known two-component adhesive of the EDP brand sold in stores has become widely known among Russian citizens. In fact, EDP glue is nothing more than a resin (most often of the ED-20 brand) and a hardener for epoxy-diode resins - PEPA brand (polyethylene polyamines).
When buying an EDP glue, which consisted of two bottles, the contents of the bottles were mixed and a full-fledged glue was obtained. The curing time for this glue varied from 30 minutes to 2 hours, and the time for complete drying - up to two days.
Mixing rates for ED-20 (ED-16) GOST 10587-84 resin and hardener for glue production.
Resin ED-20 (ED-16) GOST 10587-84 (as well as campaigns based on them, such as K-153 and the like) are mixed with PEPA hardener (Polyethylene polyamines) in a ratio of 10: 1 (optimal ratio for cold curing). That is, for 10 units of resin, 1 unit of hardener is added. Or, in other words, the percentage of the hardener is 10%. Depending on the needs or the technological process, the percentage of the hardener can vary from 8% to 20%. But it must be clearly understood that at 20% of the hardener, the polymerization process occurs with a large release of heat. Also, with a large amount of hardener, the curing time decreases (significantly), but the strength characteristics also deteriorate.
Mixing rules
The resin, as well as the hardener, subject to the use of cold conditions - before mixing must be warmed up in a warm room (18 ... 25C) for at least a day. Forced heating on heating installations is prohibited.
After warming up indoors, stir the resin well and add the hardener in small portions, stirring the added hardener well. After complete introduction of the hardener into the resin, it is recommended to mix the composition thoroughly to a homogeneous consistency. Then pour into another (clean) container and mix everything again. The adhesive is ready to use.
How else to add glue?
Cured ED-20 resin is a completely insoluble substance. Despite this, the resin is very fragile, which limits its use.
In order for the resin to become more plastic (see GOST 10587-84), DBP plasticizer (dibutyl phthalate) is added to the resin composition.The percentage of plasticizer in the resin is also 10% by weight of the resin.
It should be noted that the order of mixing the resin with the plasticizer and hardener is strict: First, the resin is mixed with the plasticizer until smooth. The plasticizer should also be served in small portions, mixing the composition well. After mixing the composition (ED-20 resin and DBP plasticizer), the PEPA hardener (polyethylene polyamines) is introduced according to the section "Mixing rules".
To mix 100 kg of ED-20 resin, we need:
- 100 kg of ED-20 resin
- 10 kg of DBF plasticizer
- ~ 10 kg PEPA hardener
For additional advice, purchase and other questions, please call in Dzerzhinsk: +7 (8313) 36-08-70, 36-56-34.
Best Answers
... my name is Vovka ...:
Epoxy resins are soluble and fusible reactive oligomeric products based on epichlorohydrin and diphenylolpropane, which can be transformed into an infusible and insoluble state under the action of various types of curing agents.
Epoxy resins are used as a component of potting and impregnating compounds, adhesives, sealants, binders for reinforced plastics in the radio-electronic, electrical, aircraft, ship and machine building industries, as well as in construction. Epoxy resins are used to repair products made of various materials and reliably bond porcelain, faience, ceramics, fiberglass, marble, stone, concrete, brick, wood, metals, hard polyvinyl chloride, and other plastics. But with the exception of polyethylene, polypropylene and teflon. Resins are especially suitable for the restoration of natural and artificial stones, concrete and all types of building materials. Also ideal for repairing missing parts. Seals, glues and fills.
Specifications:
The epoxy is fully cured after 24 hours, but by increasing the temperature to 70 ° C, the cure can be accelerated. The cure rate is reduced at temperatures below 15 ° C. Does not shrink and expands when cured. The product can be machined after the epoxy is completely cured (cleaned, polished, drilled, ground, and painted). Operating temperature of the glued products: from -50 ° С to + 150 ° С. The temperature under heavy load on the glued parts should not exceed 80 ° C. Epoxy resin is resistant to water, oil, solvents. Guaranteed shelf life of epoxy resin: 1.5 years
metcvetobrabotka ›epoksidnye_smoly logosib› epoxy_resin / akiv ›ru9-epoksidnaya / smola-epoksidnaya ... referatec m› referat_83862_str_5 souztechmet ›epoks techno.x51› index.php-sibompozit ›ruptured. wikipedia ›wiki / epoxy_epoksid› Working with epoxy resins
Irish McClaud:
-40 to +120 ° C (continuous) -40 to +150 ° C (maximum)
Found here, for example, mirsmazok / catalog / auto-smazki / category38790 / 10955
In general, here's another small article about them - mirsmazok /blogs/modules.php?name=articles&id=523
Nadezhda Stepanova:
"Extreme" values: + 350 ° С 20 min for epoxy glue PEO-490K (JSC "LZOS", Lytkarino); -196 ° С for epoxy glue PEO-13K (LLC "LUMEX", St. Petersburg); rapid temperature change from -60 to + 125 ° С 20 cycles for the epoxy compound PEO-28M (JSC PLANET, Veliky Novgorod); single-action mechanical shock 80000g and linear acceleration of 1300 rev / s for epoxy glue PEO-110K (ZAO NPP REF-Optoelektronika, Saratov).
How to work with resin?
When working with resin, the main thing is to carefully observe the proportions, since an insufficient or, conversely, too large amount of hardener has the most negative effect on the functionality of the final composition. With an excess volume of the hardener, the composition loses its strength. In addition, excess can be released to the surface as it hardens. With a lack of hardener, some of the polymers remain unbound, such a composition becomes sticky.
Modern formulations are usually diluted in the proportion: for 1 part of the curing agent - 2 parts of ES, the use of equal proportions is allowed. Stir the epoxy and hardener thoroughly so that the consistency is uniform. Stirring is performed slowly, if the movements are sharp, bubbles will appear.
After pouring, wait until the resin hardens.In the course of polymerization, ES goes through several stages.
- Liquid state. The mixture of the main components easily drains from the stirring rod, this moment is optimal to pour the composition into the mold.
- Thick honey. In this state, the mass does not lie down in a thin, even layer, but easily fills a small volume.
- Candied honey. At this stage, it is not possible to carry out any actions with the resin, the only possibility of use is gluing surfaces.
- The transition from honey to rubber. At this point, the resin does not need to be touched, otherwise the formation of polymer chains can be disrupted.
- Rubber. The mass of the components has already entered into interaction and has ceased to stick to the palms, however, its hardness is not enough yet. In this state, the workpiece can be twisted and deformed.
- Solid. This resin does not bend, twist, or pick out.
Epoxy from different manufacturers has a different cure period, it is determined only empirically.
However, even without varnish, its surface looks glossy and shimmery.
Security measures
Working with chemical polymer substances that react with each other requires careful and careful handling from the user. Safety precautions must be followed to protect your own health and preserve the well-being of the environment. The fact is that the components of epoxy resin do not affect people, animals and wildlife only in the case of complete polymerization. In other cases (being in liquid form, separately, as well as during mixing of these substances), chemical elements that are harmful to health are released into the environment.


Epoxy resin has been assigned a hazard class 2 when exposed to the body of humans and animals. If, during the preparation of the mixture, the components of the resin get on the skin, they will cause allergic reactions. To prevent this, the skin must be washed under running water with the addition of soap, and then wiped with a swab dipped in alcohol. After completing these steps, petroleum jelly, castor oil or an emollient cream are applied to the skin.
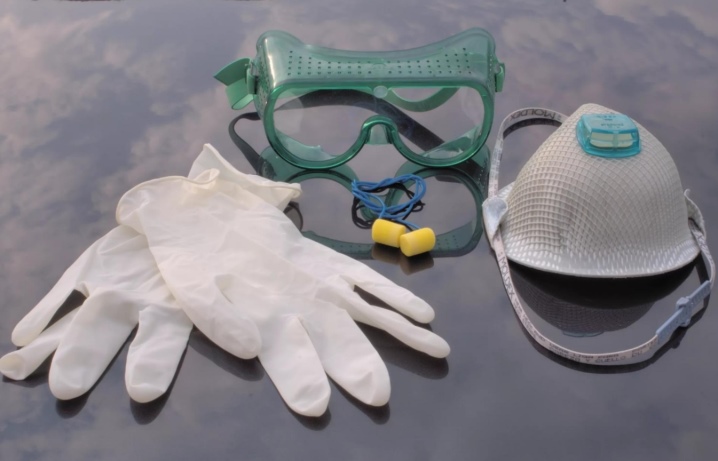
When working with epoxy-diane resin, it is necessary to protect the organs of vision and breathing. To do this, wear protective goggles, rubber gloves and a respirator. The larger the working area of the resin coating, the more effective personal protection should be. To quickly neutralize chemical components, you should have clean water, alcohol and emollient cream on hand.
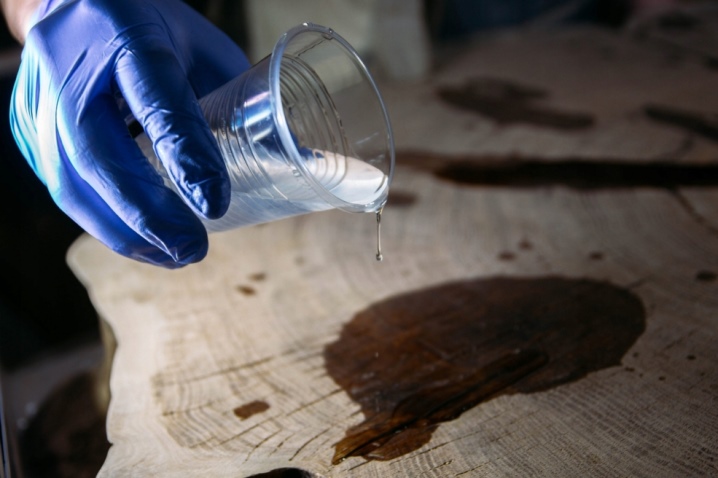


Resin hazard class ED-20
This substance is not capable of provoking combustion or ignition, therefore it is classified as hazard class 2. Epoxy does not ignite even when brought into an open flame. But when working with such material, you must adhere to safety rules.
People who work directly with such substances must have protective equipment. Such means are considered: respirator and overalls. Rooms where epoxy resins are produced must be ventilated. If this substance comes into contact with the skin, it can cause skin inflammation and dermatitis. You may also experience an allergic reaction to the resin components.
Epoxy Creative Applications
Epoxy resin is a versatile material that allows you to make beautiful products in various fields of use: jewelry and bijouterie, interior decoration elements and furniture. For different purposes, different types of epoxy are used - transparent or colored, differing in the type of filler added to the composition before use.
Transparent
Transparent epoxy resin is used in the production of advertising and souvenir, decorative and jewelry items, as well as in the creation of polymer floors with a 3D effect.
In addition, transparent epoxy is used at different stages of construction and installation work in the construction of objects of various types.The industry produces epoxy resin in a liquid and solid state, which determines the sequence of work with its use.

"Magic Crystal-3D" ideal for creating jewelry and bijouterie
The most popular among users are the following grades of transparent epoxy:
-
"Magic Crystal-3D" - used for making jewelry and bijouterie, as well as for pouring glossy and 3D coatings;
Magic Crystal-3D -
"Epoxy CR 100" - used in the manufacture of polymer floors;
Epoxy CR 100 -
"ED-20" - is one of the types of epoxy-diane resins used in the creation of potting and impregnating compositions for construction work, as well as in the production of sealants and adhesives.
ED-20
Colored
This type of epoxy resin differs from transparent only in that during its preparation, special fillers are used, which give the final product a certain color.

Colored epoxy for jewelry making
Fillers (surfactants) can be sold separately from the epoxy, allowing you to choose a colorant according to the desired color or be factory-ready for further use.