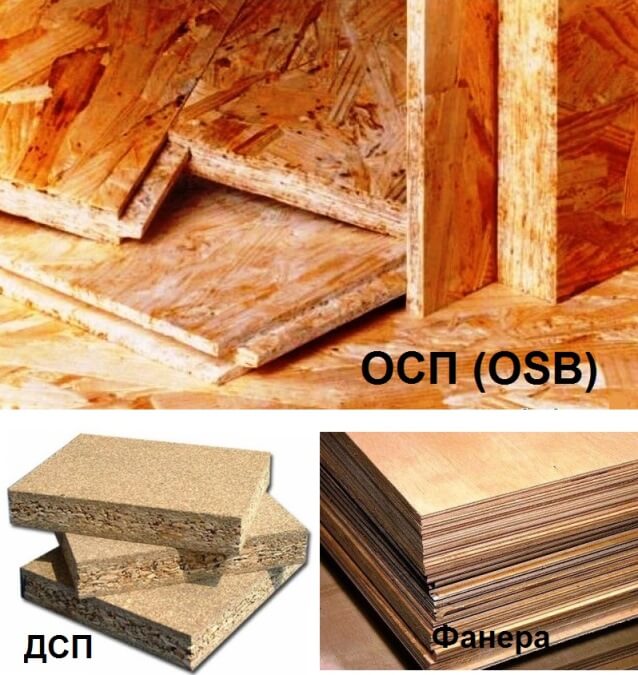
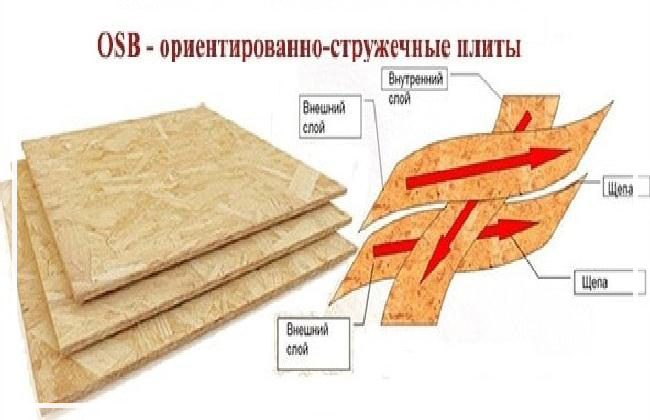
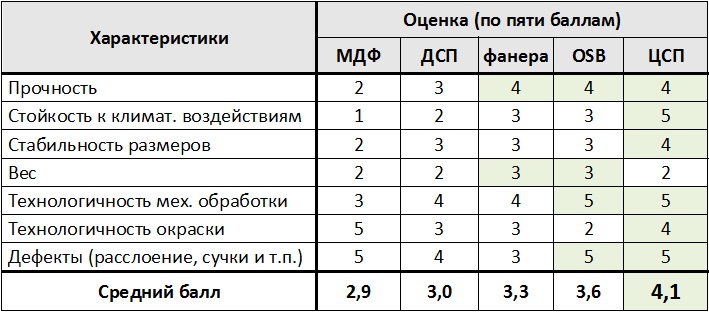
Comparison by characteristics
Most often, either plywood or OSB is placed on the floor. But which is better? Most will say that plywood is stronger in bending and therefore it is better to lay it on the floor. It is stronger. That's for sure. But if the material is laid on a concrete base or floating flooring is made from it, or it is placed on a rough floor by logs - why is high bending strength needed here? More important is the tendency to delamination and warping, and these are precisely the problems of plywood. In general, it's up to you to decide which is better - plywood or OSB. Below is information for an informed decision.
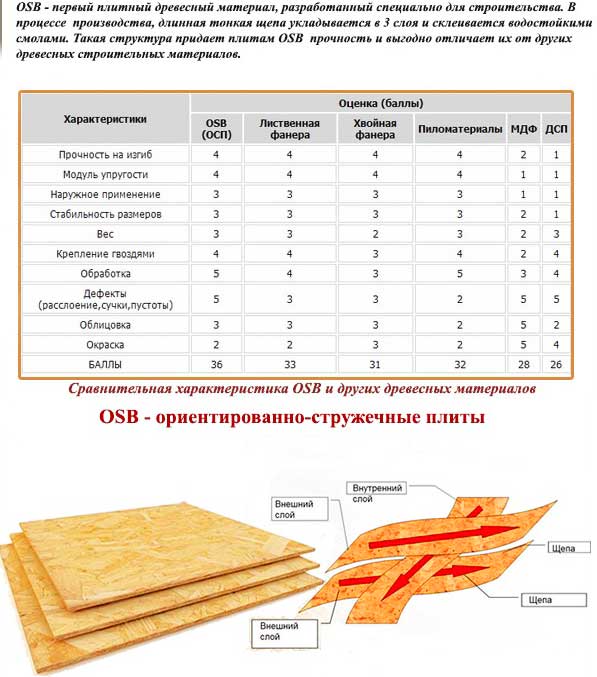
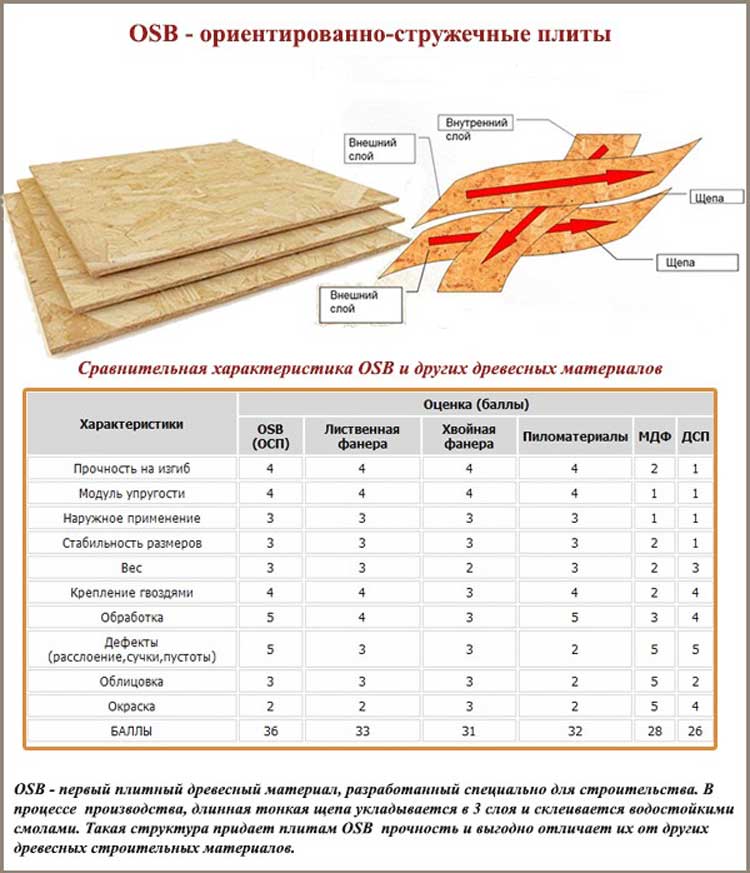
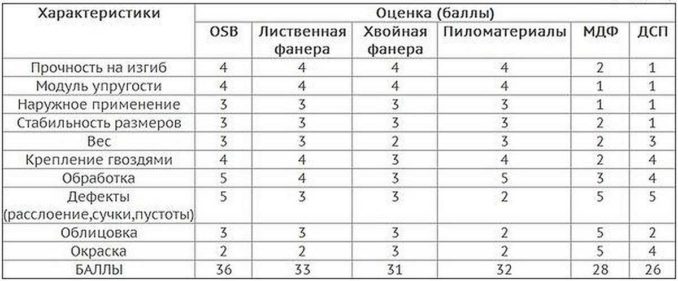 The comparison is given in points and it is difficult to judge objectivity, but ...
The comparison is given in points and it is difficult to judge objectivity, but ...
Moisture resistance and environmental friendliness
Oddly enough, moisture resistance is directly related to environmental safety. The fact is that a synthetic binder is used in the production of materials, and it is possible to say which is more environmentally friendly - OSB or plywood, specifically for each material. Although, in general, plywood is safer: there are brands in the production of which safe substances are used. But not all. For example, FSF is one of the cheapest types. It is made using a phenol-formaldehyde binder. So this brand does not differ from OSB in terms of environmental friendliness.
 The most reliable self-test with materials intended for purchase
The most reliable self-test with materials intended for purchase
In the case of oriented strand board, phenolic resins are always used. They give the material high strength and moisture resistance. But it is phenol that is a substance hazardous to health. Its release is controlled by a sanitary station. A special classification has been introduced - formaldehyde emission. Each batch must be checked and an emission class must be assigned based on the measurement results. Safe are E0 or E1. And E2 and E3 can only be used outdoors. By the way, the same characteristic should be indicated in the technical parameters for FSF plywood.
OSB water resistance
Oriented strand boards are available in four water resistance categories:
- OSB1 and OSB2 - not moisture resistant, for use in rooms with normal operating conditions;
- OSB3 and OSB4 are waterproof, for use in high humidity conditions.
 It's not easy to make a choice - plywood or OSB
It's not easy to make a choice - plywood or OSB
If they make the floor, they usually take OSB3. Its water resistance is sufficient for use in any floor cake, so the material is versatile. If significant strength is required, a higher grade can be taken.
Waterproof plywood
Plywood is a little more complicated. In its production, various glue is used and it is he who affects the properties of the material. The following types are used in construction:
- FC - on urea glue. Good environmental performance, but average moisture resistance. If you lay it on the floor, then in dry rooms where moisture is unlikely to come in. There is a waterproof plywood of this brand. The letter V is added to the marking - FKV, sometimes the letter G is added - hydro-resistant. But moisture resistance is achieved not due to glue, but due to additives / impregnations for wood.
-
FSF - on phenolic glue. This type has high moisture resistance, but the phenolic glue gives off formaldehyde. So you need to be sure of the safety of the material. This is one of the cheapest types, often called construction. They are used more often for temporary structures - formwork.
- FKM - on melamine glue. Waterproof but expensive.
- FB - bakelite on a water-soluble composition, BS - on alcohol-soluble glue. BS plywood is most often called aviation. Lightweight and durable, waterproof, expensive.The FB subtype is used more often in the construction of ships and railway cars, where there is less weight requirement.
So it is difficult to compare plywood and OSB in terms of water resistance. There are different brands and the matter is in a specific choice. It's just that in terms of water resistance, OSB is more reliable, since the chips are in a layer of glue, which simply does not let moisture to the wood. With plywood it is more difficult: the outer layers are wood veneer, the veneer cuts at the edges of the sheet also remain open. So even moisture-resistant plywood often begins to warp - the top / bottom layer swells, the edges swell.
Types of plywood
Plywood is divided into classes by means of letter marking - below we will consider the most common abbreviations.
FSF
 FSF products
FSF products
One of the most popular types of plywood, in view of the ratio of cost and quality characteristics. It can be used for both internal and external work, for example for making plywood formwork.
As an adhesive composition, it uses resinous phenol-formaldehyde glue, by means of which both the gluing of veneer sheets and their impregnation are carried out.
A distinctive feature of FSF plywood is the color of the internal structure, which contains a red-brown tint - the color of the composition used for impregnation.
It has good strength, durability and moisture resistance characteristics for its price range. The optimal combination of the above parameters for a completely affordable price is the main advantage of this product.
However, for all its advantages, the phenol-formaldehyde component makes its use in a residential building undesirable, since under certain conditions toxic formaldehyde compounds are released. Even under normal operating conditions, toxic fumes still occur, which ultimately can adversely affect human health.
FBA
 FBA products
FBA products
Veneer in this type of product is glued with albuminocase glue, which is a completely natural material. This is the most environmentally friendly plywood that is produced at the moment - it is made from completely natural materials that do not cause allergies and do not pose a danger to the human body.
The only drawback of this product is its low strength and high degree of moisture absorption, which allows it to be used only indoors.
FBA plywood belongs to the materials of the middle price category, which makes it the best choice for those who prefer environmental friendliness and safety. Most often it is used in rooms such as a nursery, bedroom, etc.
FC
Urea glue is used for impregnation and gluing of layers. This type of plywood is less environmentally friendly than FBA analogs, however, its strength characteristics are slightly higher.
The level of moisture absorption and wear resistance is practically the same as that of FBA plywood - mechanical effects of moderate severity leave scratches and dents on the surface, and prolonged exposure to moisture leads to swelling. The color of the chip has a yellowish tint.
FB
 FB plywood
FB plywood
The veneer is impregnated and glued with a water-based bakelite varnish - polyoxybenzylmethylene glycol anhydride, which is a derivative of the interaction of phenol and formaldehyde.
This is the most resistant plywood to external influences - it is quite difficult to scratch it, and boards coated with an alcohol-soluble bakelite composition (BS plywood) are absolutely moisture-proof.
The main difference from other types of plywood is its heavy weight - bakelite counterparts sink in water. This is the least environmentally friendly material of all the above-mentioned analogs.
Its use for the decoration of residential premises is strongly discouraged, since in addition to methanol and formaldehyde, toxic phenol fumes are also emitted into the room.
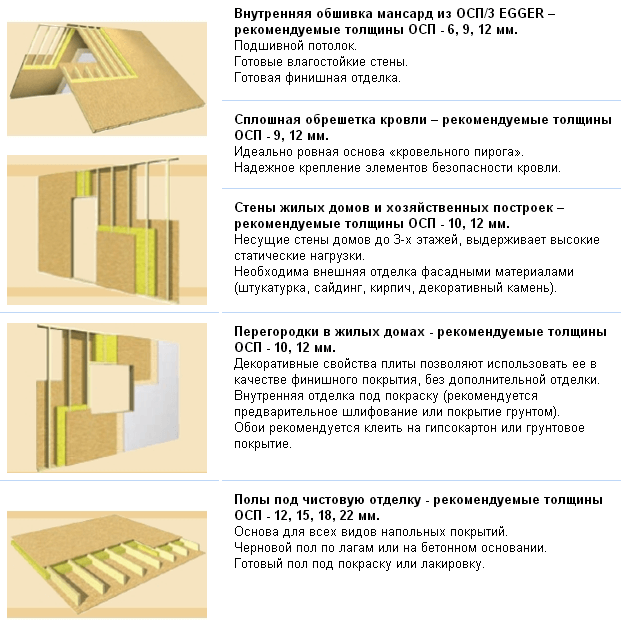
Appointment of plates and their varieties
Before disassembling the types of panels, let's figure out what is a sb stove? So, osb is a material consisting of three pressed layers. It consists of elongated chips, which are waste from aspen or pine. The strength of the panel lies precisely in the fact that in the middle layer the chips are located at right angles to the upper and lower layers, and in the covering ones, on the contrary, along. All layers can withstand the press at high temperatures, and resins and waxes are used as waterproof impregnation binders.
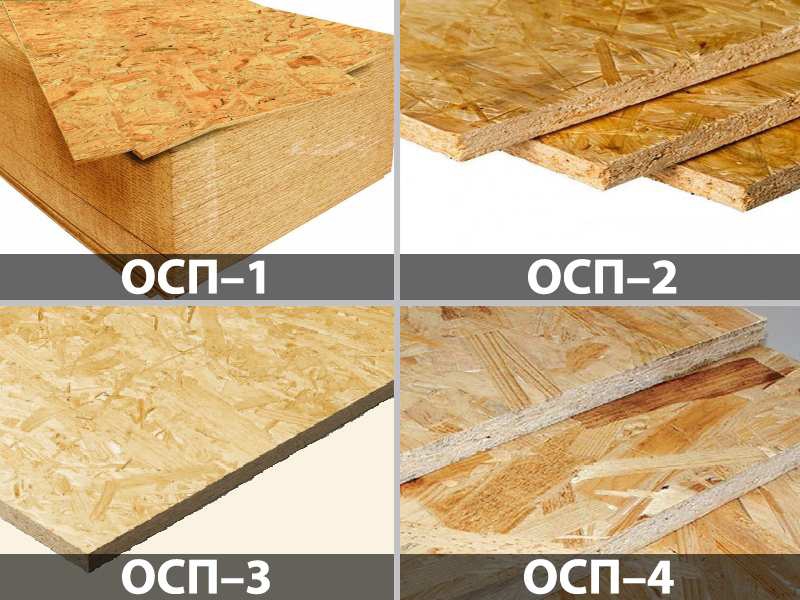
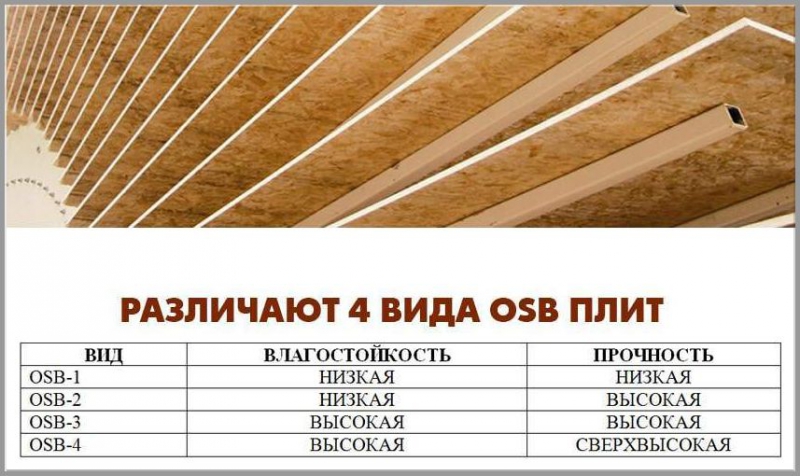
There are four types of osb boards. Let's take a look at each of them:
- OSB1 - used for the production of furniture products. Wall and floor paneling is discouraged due to its low density and fear of moisture.
- OSB2 are denser than the first type, but they are also susceptible to moisture. The characteristics of the panels allow their use for cladding indoors with medium humidity levels.
- OSB3 is the most popular type due to its excellent moisture resistance. Under the prolonged influence of water, it nevertheless begins to deform and if it is used for outdoor work, then mandatory painting of the material is required.
- OSB4 - has the best characteristics and is absolutely not afraid of moisture. The casing does not deform even after prolonged contact with water.
Let's take a look at a small table and take a look at the strength and moisture resistance that osb boards have:
| Classification | Strength | Moisture resistant | % maximum swell | Yellow is low, green is high, red is super high. |
| OSB 1 | 25 | |||
| OSB 2 | 20 | |||
| OSB 3 | 15 | |||
| OSB 4 | 12 |
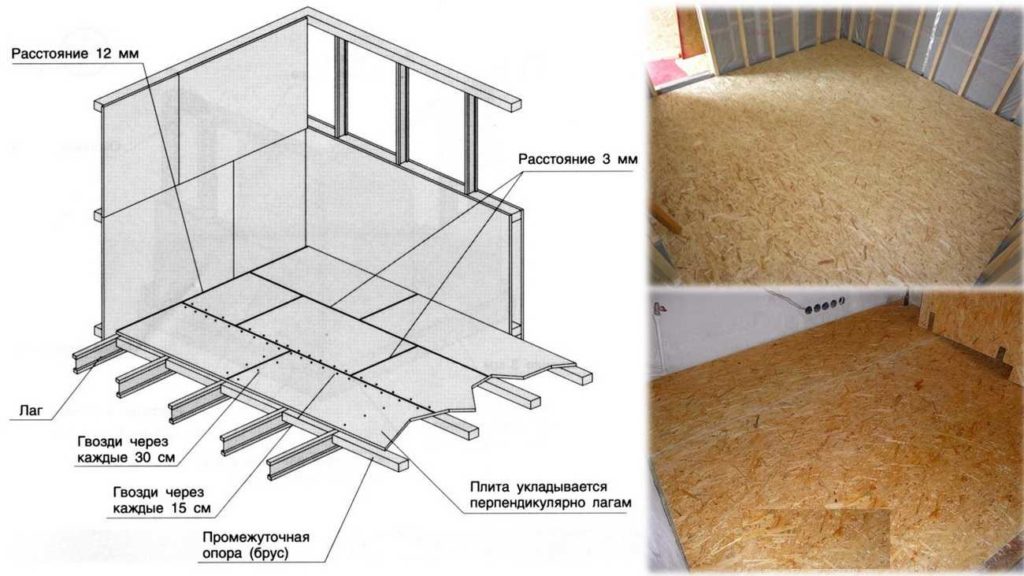
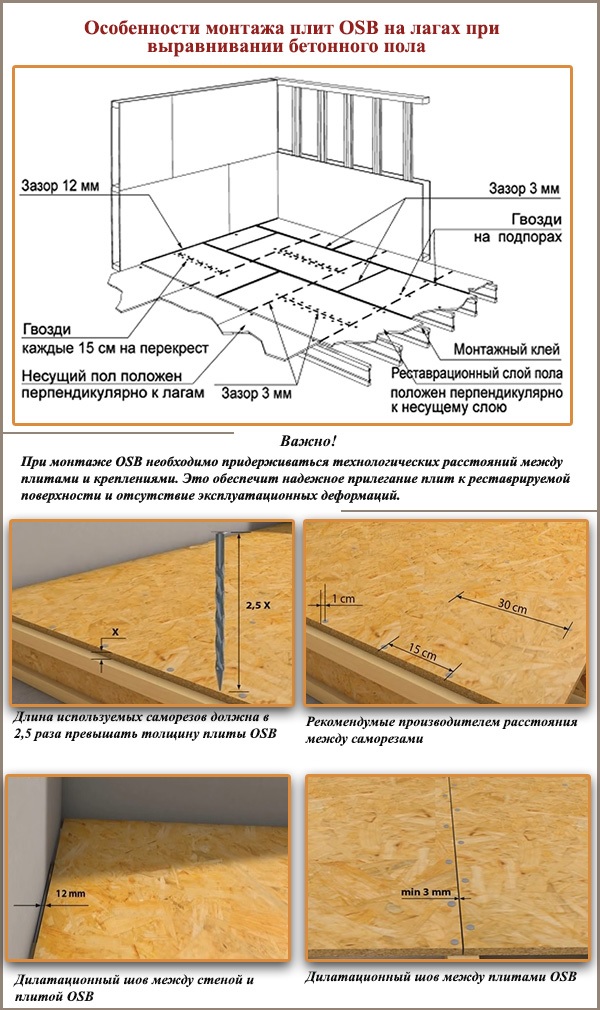
Main characteristics
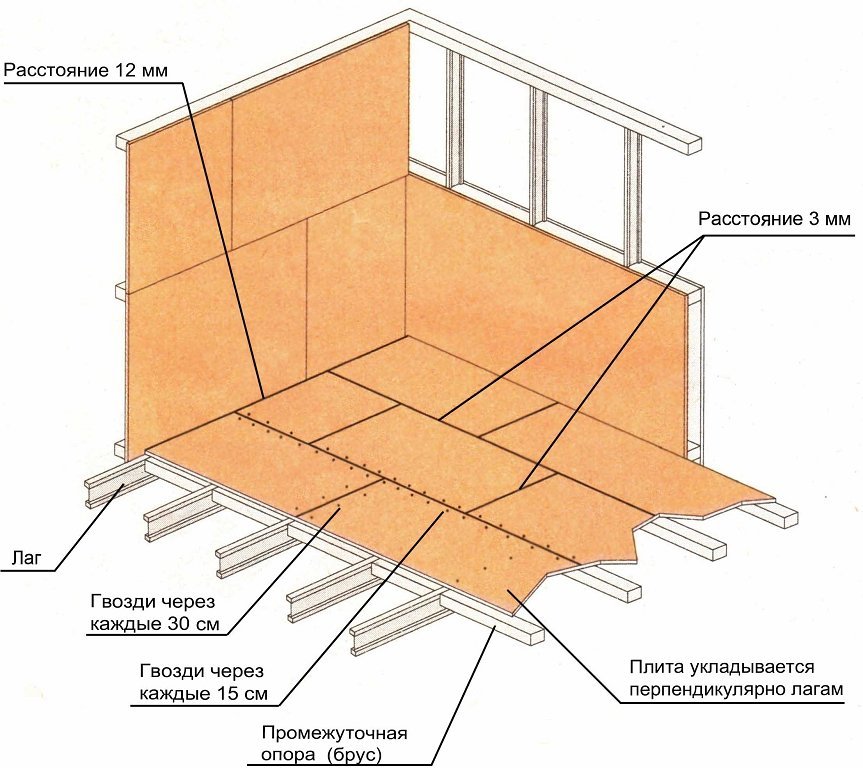
Gap parameters for laying OSB-3 boards on the floor.
In order to form a complete opinion about this material, you need to consider the following indicators:
- Biological resistance. Plywood layers are glued using glue containing phenol-formaldehyde. Such a substance protects the slab well from the effects of various fungi and other harmful microorganisms. During production, the ends of plywood boards are laminated, which leads to protection from adverse weather effects, and it is for this indicator that plywood can be used as a building material for streets. In addition, it is not afraid of direct sunlight, which means that the plates will not lose their color, and cracks will not form on them.
But during operation, it must be remembered that the humidity of the ambient air should not exceed 20%, and so that the plywood does not rot, it needs oxygen with air with a temperature of 20 to 30 degrees Celsius. If such a board is damaged by the covering film or the lamination, then, accordingly, it loses the quality of resistance.
OSB production process.
To prevent decay, manufacturers impregnate their products with special antifungal solutions. They also protect the plywood from the appearance of blue. And additional additives contribute to longer color retention and protect against harmful insects.
- Chemical properties. Plywood is a material that resists exposure to weak acids, acid-salt solutions and flammable oils. But if a valence solution gets on such a sheet, this will lead to softening and swelling of the wood. The ingress of concentrated acidic substances entails destruction.
Substances such as chlorine, hypochlorite and various nitrates are also undesirable for contact. In order to maintain the strength of the coating, it is not recommended to use acetone, gasoline and alcohol for any purpose, since they, in turn, destroy the wax coating, which means that they reduce the level of strength of the product.
Places of application of OSB boards.
In order for plywood to be more resistant to such influences, its lamination is necessary.
- Thermal conductivity. The more moisture in the plywood slab, the faster it heats up, because water heats up three times faster than wood.Accordingly, if the moisture level rises, then the thermal conductivity also increases.
If the ambient temperature is about +20 degrees, then even with insignificant temperature drops, the tree will not lose its properties. But with an increase to 100 degrees, plywood boards lose their strength by half. It should be noted that at subzero temperatures, such material has even better elasticity and strength compared to the room range.
- Refractoriness. Like any other wood, plywood ignites easily. The temperature at which it ignites is 270 ° C. The stove just won't catch fire, for this it is necessary that the temperature in the heat affected zone reaches 400 ° C. In order to minimize the harm from burning plywood, such plates in the stage of charring slow down the burning process itself.
To improve the refractory properties, manufacturers are trying to treat their products with various chemical impregnations.
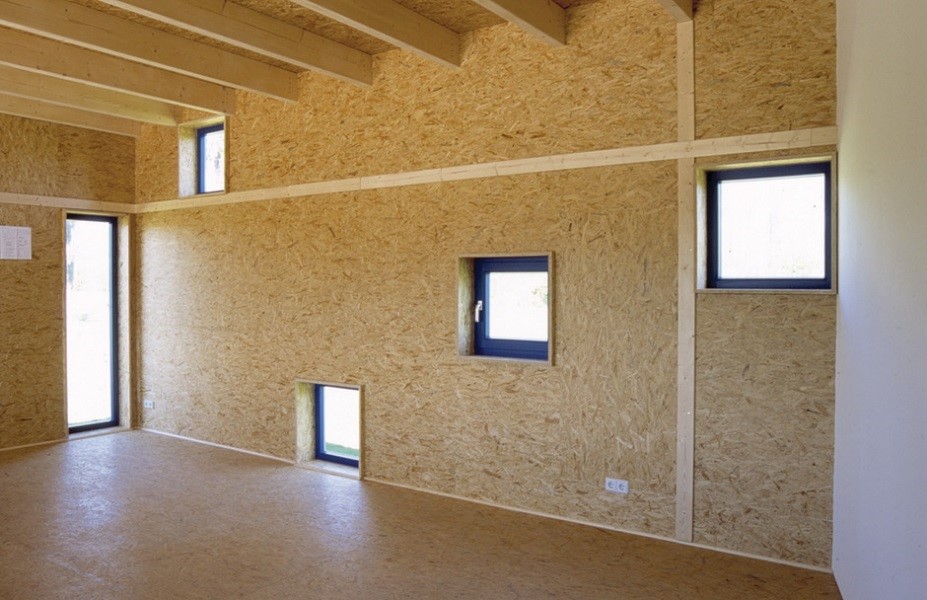
Features of materials
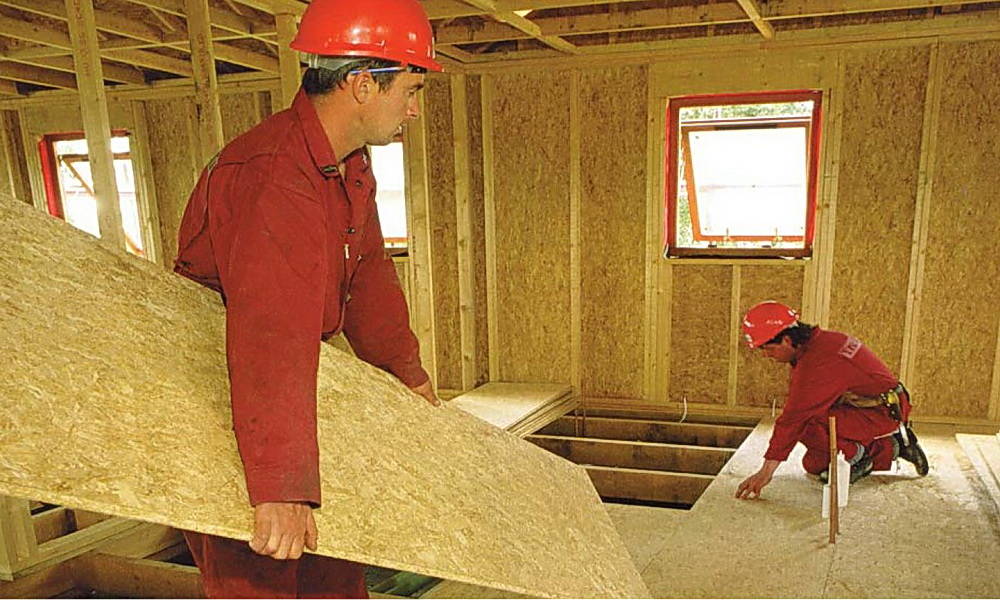
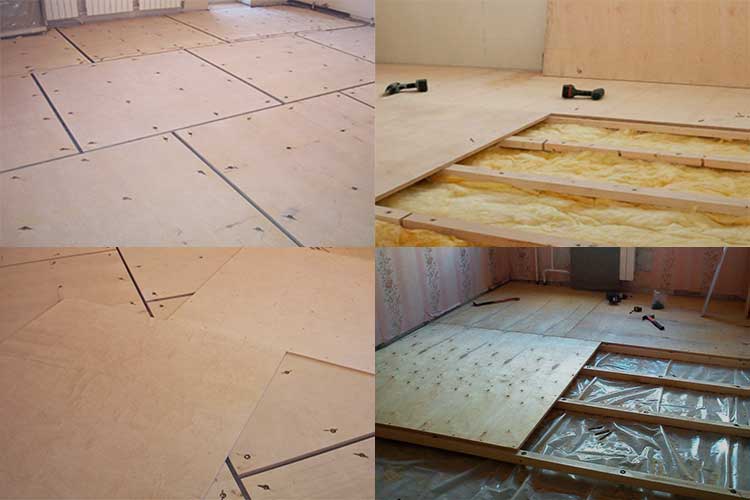
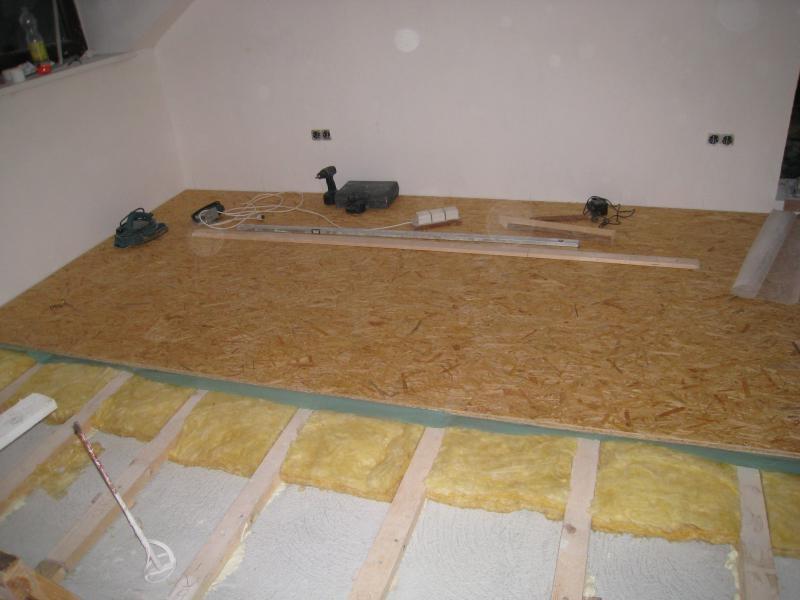
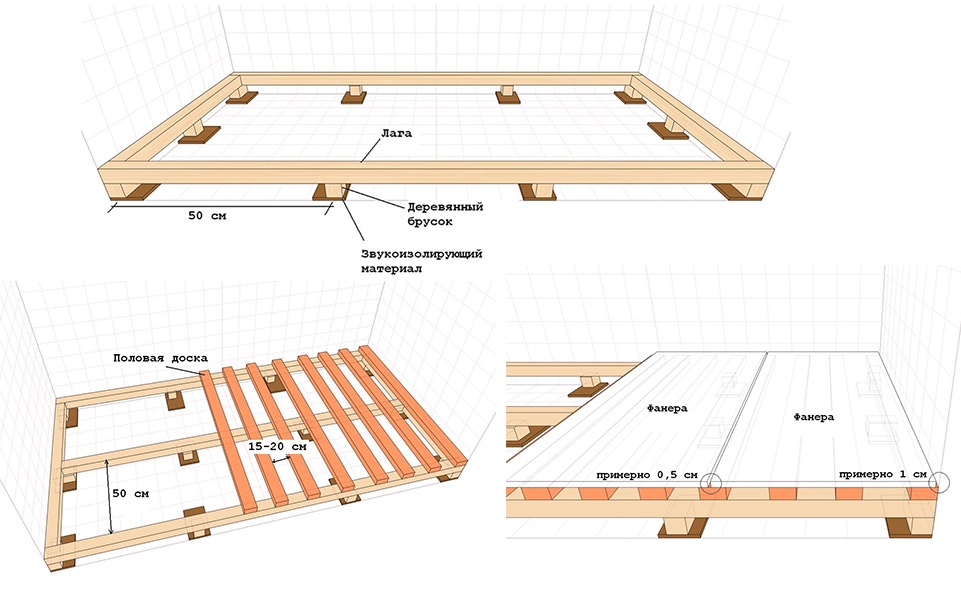
Plywood and OSB are often used to level wall and floor bases before facing work. They are installed on top of obsolete wooden floors, logs or concrete screed.
Plywood board is made from wood veneer. During the manufacturing process, the strips are covered with glue, connected and pressed on hydraulic equipment. This creates a solid and durable slab. Its technical parameters depend on the number of layers, type of glue, wood species. The more planks used in production, the thicker and stronger the product will be.

Plywood sheets come in several varieties:
- 1 - expensive and of high quality without visible external defects;
- 2 - with a minimum of scrap (small cracks, amenable to grinding);
- 3 - with visible "flaws": knots, roughness, wormholes;
- 4 - cheap with a lot of external damage.
Plywood boards are classified depending on the type of impregnation used in production. There are 4 types of plywood on sale:
- FC - characterized by low moisture resistance, urea glue acts as a binding base;
- FSF - (product with phenol-formaldehyde glue) is recommended for outdoor work;
- FB - with bakelite varnish, designed for use in aggressive environmental conditions;
- FOF is an abbreviation indicating a laminated surface.
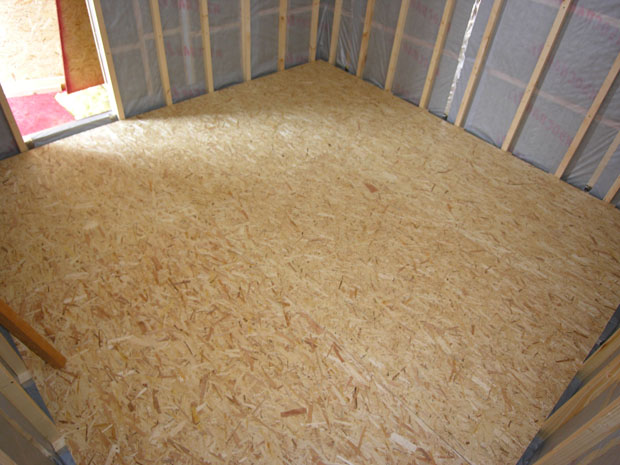
Oriented strand board is made from wood chips and glue. During production, the components are mixed, pressed under high pressure, forming a one-piece structure. There are 4 types of such a board:
- 1 - a fragile base, more than others exposed to moisture;
- 2 - solid bar, unstable to high humidity;
- 3 - product with increased reliability and moisture resistance;
- 4 - a board that is not afraid of moisture, it is able to retain its properties even when used in extreme conditions.
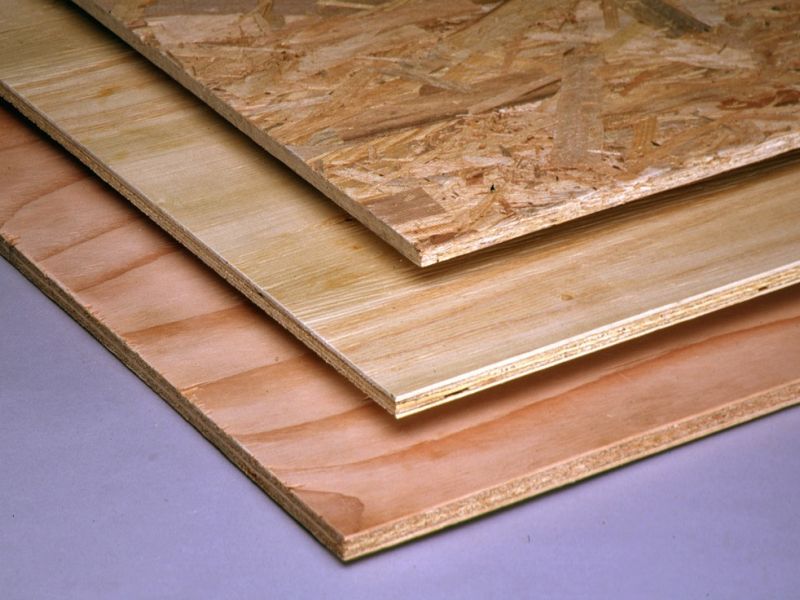
The two compared materials have different sheet sizes - they come in small, medium and large sizes.
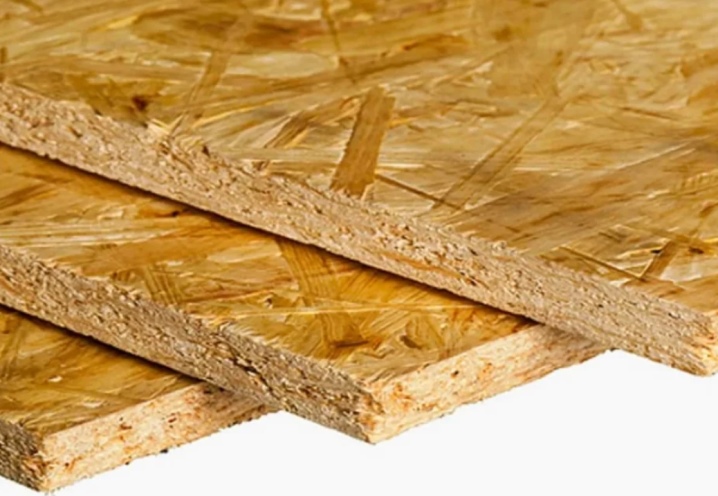

Comparative characteristics
Now let's compare these two materials on separate parameters to find out which one is better, OSB or plywood.
Strength
Plywood is more flexible and resilient, due to the solidity of its structure, it is several times higher than OSB in bending strength, tensile strength and resistance to shock loads.
Water resistance
The OSB board resists short-term exposure to moisture, but in constantly humid conditions it changes its shape. Despite the higher content of phenol-formaldehyde resin, it swells strongly and unevenly, plywood behaves much more stable. In terms of moisture resistance, even OSB-4 will be inferior to the FC and FSF brands.
Environmental friendliness
Manufacturers of these materials are constantly trying to find a compromise between environmental friendliness and moisture resistance, since an increase in one indicator usually leads to a decrease in another.
Formaldehyde emission from FSF and OSB plywood used for flooring is approximately the same and corresponds to class E2.The FK brand has a higher environmental friendliness due to the absence of phenol-formaldehyde resins in the production.
Fire resistance
Plywood burns well, OSB does not support combustion. This property is unlikely to affect the safety of the house in case of fire, but it will certainly affect the speed of fire propagation.
Sheet sizes and geometric shape
The material is laid on logs or directly on the base if it is even. OSB of the standard size 1220x2440 mm is specially sharpened for the step between the lags. The optimal step size is 0.3 m for subfloor and 0.4 or 0.6 m for finishing, depending on the thickness of the material. Plywood of the 1220x2440 mm format is less common, the size of 1525x1525 mm is more common. When using it, you will have to reduce the step or cut the sheet, which is associated with additional costs.
OSB has an ideal geometric shape, diagonals do not walk. Some slabs are made with a groove-tongue connection on two or four sides, allowing for a clearer and more reliable joint.
Ease of use
It is easy to saw both OSB and plywood with a hacksaw, you can fasten it with nails. The weight of these materials is about the same. Plywood sheets with dimensions of 1525x1525 mm have an advantage over OSB when lifting into an apartment.
Appearance
For subfloors, this criterion is not so important, with the exception of grade IV plywood, which is not suitable for soft floor coverings. OSB is more suitable for finishing floors, it has no surface defects and a more beautiful texture, especially after painting or varnishing.
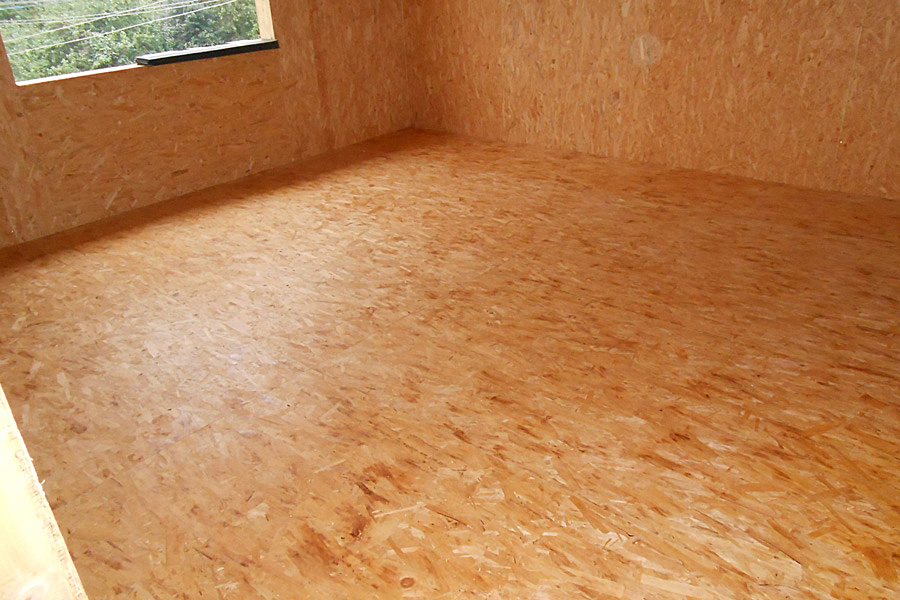
 Finishing floor from OSB boards
Finishing floor from OSB boards
Price
Plywood is a more expensive and quality material, OSB is much cheaper (by 30–40%). From the point of view of the preservation of forest resources, the use of oriented strand board is preferable, since less valuable wood is used in its manufacture. This is one of the reasons for the popularity of OSB abroad, in particular, in the USA and Canada.
Is fiberboard material harmful?
Many people know that chips are used for the basis of a fiberboard, less often cellulose waste and stalks of a rough plant, cotton or corn. As we can see, natural materials are used as basic raw materials. But in this case, binder hygroscopic and antiseptic substances should also be considered. What can be added to the wood pulp in the manufacture of fiberboard? First of all, it is paraffin, it is a substance that consists of a mixture of a saturated hydrocarbon. Next comes the emulsion of a non-aggressive synthetic resin. Rosin is also added, which is produced from coniferous wood. Bitumen is also present - it is a mixture of hydrocarbon and its derivatives. Pectol is a tall oil processing product. Finally, gypsum, which is a sulfate mineral.
All of the above substances do not emit any harmful fumes. Phenol-formaldehyde, which has spoiled the reputation of the board as such, can only be found in chipboard, and in the "pirated" version of production. In our country, the use of phenol-formaldehyde has long been prohibited on the basis of relevant regulations.

Drawing a conclusion from all that has been said previously, it can be assumed that, despite the class, not the characteristics, completely safe plywood does not exist. But, according to all the studies carried out, we can say that ordinary plywood is the least harmful. This is not a shortage, it can be found in any hardware store, but it is not always suitable for a particular job. As for the USB cooker, most stores sell far from environmentally friendly options that will certainly help solve construction problems, but they should be used very carefully.
Comparison of plywood and OSB
Plywood grades.
The raw material for the production of OSB boards is chips, and in the case of plywood, veneer. The profitability of osb boards is immediately apparent, since even wood waste, that is, shavings, can be used for their production. Their technology does not require the use of toxic hazardous substances.In addition, such a board can be re-processed, and the production process itself does not have strict standards. Due to this, OSB boards do not have clear dimensions and thickness, which has led to a very wide range of them in the modern construction market.
The tree from which OSB boards are made is needles, and birch is also used for plywood. In this case, the OSB board is made three to four layers, and the plywood has a greater number of layers.
But in the first slabs it is very important to observe the principle of fiber orientation, when in the second product it is not so significant.
If we compare the one and the other plate, then osb has a formaldehyde level lower than plywood. Despite the fact that these two types of material are quite strong, plywood sheets are still inferior in shear strength. And with the same strength indicators, the OSB board is much lighter than plywood.
Layout of plywood in the room.
A special plus is that the OSB board is absolutely not afraid of moisture and does not deform at an increased level. When working with such material, there are no special difficulties. It is easily drilled, cut, milled, ground, easily painted and varnished. If desired, they are easily processed with protective solutions, and there is no difficulty in installing with them. The main thing is that all this is easy to accomplish with the help of automatic equipment. But plywood requires careful manual processing.
In addition, insects "prefer" plywood rather than OSB. But it should be noted that the plywood slab is more difficult to deform, and the service life does not affect its shrinkage. The best aesthetic appearance of the product is from plywood sheets, but if the OSB board has a coating, then it easily becomes one level.
It is very important to note that if one or another product is treated with varnish or special impregnation, then it becomes difficult to argue about the strength of plywood or osb. What to opt for? In order to decide which is better plywood or OSB, you must initially understand the characteristics of each material separately
What to choose for? In order to decide which is better plywood or OSB, you must initially understand the characteristics of each material separately.
What is the danger of formaldehyde and what are the standards for its concentration in the air
What is formaldehyde, and is it really that bad for human health, or is it just another horror story of competing marketers?
Formaldehyde (aka formic aldehyde) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor, relatively stable at 80-100 ° C and slowly polymerizing at temperatures below 80 ° C. It has found wide application in various areas of the national economy: in the chemical industry - for the production of plastics and artificial fibers, in the construction industry - for the production of varnishes, paints, polyurethane foam, linoleum, various chipboards (chipboard, OSB, MDF, plywood) and as an antiseptic for wood processing, in the tanning industry - as a tanning agent, in agriculture - as a fumigator during grain storage, etc.
With short-term exposure to high concentrations of formaldehyde vapors (1.2 mg per cubic meter of air), irritation of the upper respiratory tract, skin, mucous membranes of the eyes is observed, the first signs of damage to the central nervous system appear (headaches, dizziness, weakness). Daily exposure to small concentrations of formaldehyde on the human body for a long time is the cause of chronic rhinitis, chronic bronchitis, obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma. In addition, formaldehyde is a carcinogen: with prolonged contact with its vapors, the risk of developing cancerous tumors of the nasopharynx significantly increases.
In accordance with the sanitary and hygienic standards SanPiN 2.1.2.1002–00 and GN 2.1.6.1338–03, approved by Russian legislation, the maximum permissible concentrations of formaldehyde in indoor air are:
- maximum one-time (MPCmr) - 0.05 mg / m³ (exposure 30 minutes),
- average daily (MPCss) - 0.01 mg / m³.
The value of one-time MPC (MPCmr) corresponds to the maximum concentration of a substance in the air, at which there are still no reflex reactions of the human body to contact with this substance. The value of the average daily MPC (MPCss) denotes the concentration limits within which a substance does not cause direct or indirect harm to human health under conditions of constant inhalation for an indefinite period of time. At concentrations of formaldehyde vapors below the MPCss you can not be afraid of the appearance of any pathological changes in the body. The substance has no general toxic, carcinogenic or mutagenic effect at such concentrations.