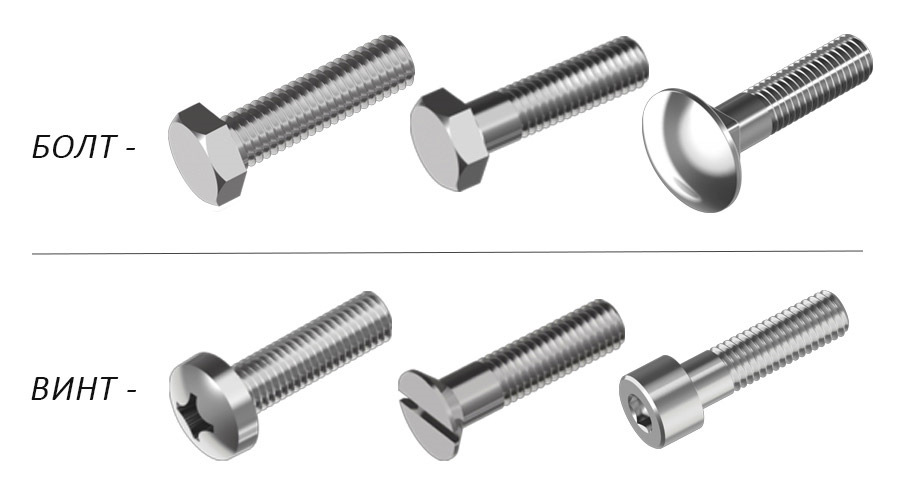
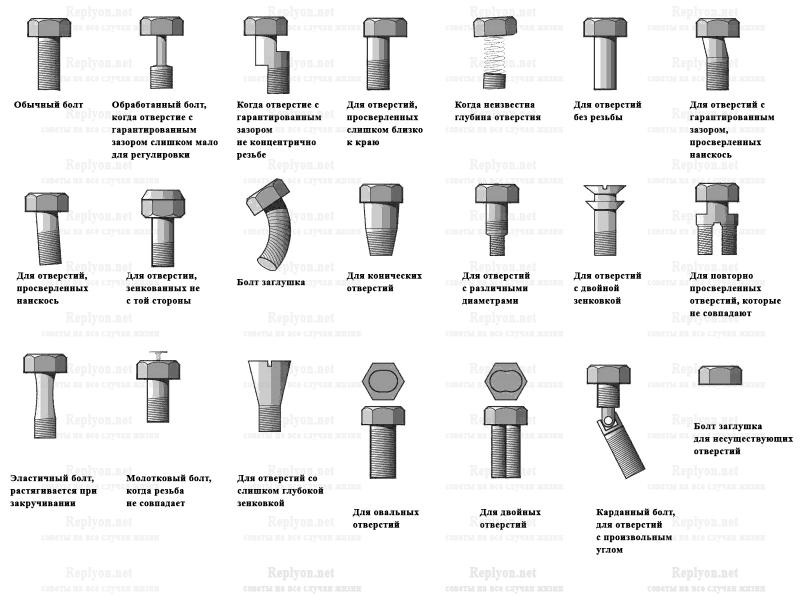
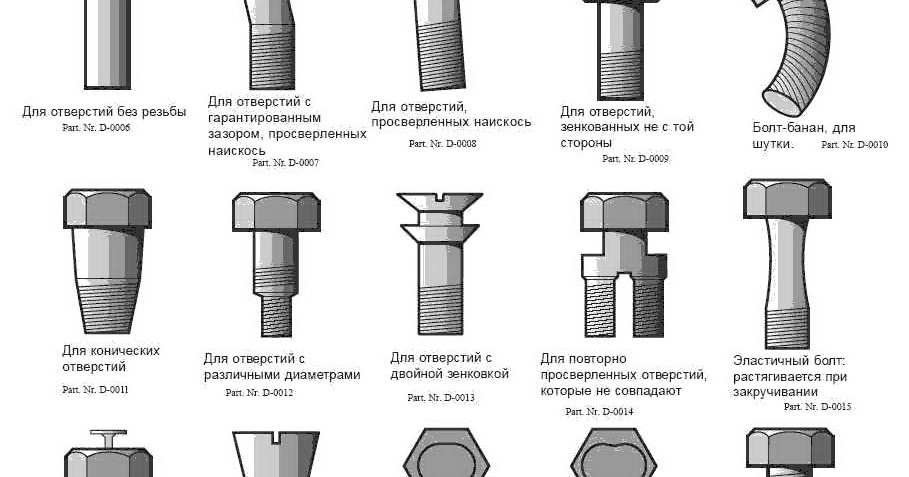
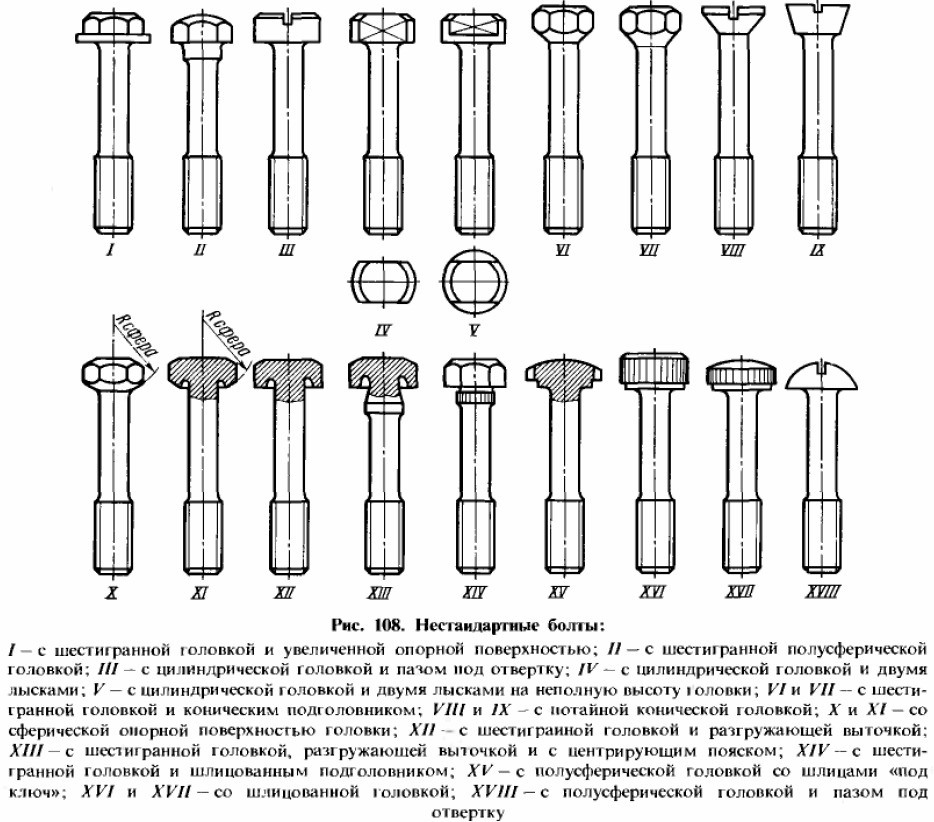
Comparison of bolt and screw
So, the screw differs from the bolt in the way of connection. The screw and bolt are used in different loading schemes. The bolt is calculated for shear (a large load falls on the place perpendicular to the parts to be joined). The calculation of the screw is for non-opening of the joint (the main load falls on the place located along or parallel to the axis of the fastened parts).
The design of the screw is very similar to the bolt. However, their main difference lies in their application: the bolt goes through the parts to be connected through, a nut is screwed onto it, and the screw is screwed into one of the connected parts with a thread using a screwdriver.
The screw can be tightened or unscrewed with a screwdriver or socket wrench inserted into the slot of its head. The bolt is tightened with a wrench or nut. Therefore, the heads have different slots. A bolt cannot rotate as a result of the connection of two parts, like some types of screws used in movable, moving machine mechanisms.
When screwing in, the head of the screw is often deepened into the part to be connected; when bolted, it remains on the surface. The very concept of a screw as a geometrical figure corresponds to the word "thread". For the sake of an example, we can give a lead screw in a jack and a lathe that is familiar to everyone. The bolt stands for "pivot". Screws, unlike bolts, are often made very small. For example, screws are common for fastening the clockwork and other micro-sized devices. The bolted connection is disconnected by shearing the bolt, and the screw connection by cutting the screw thread.
Definition and scope

To create a strong fastener connection, you need to know the exact dimensions of the connecting parts. The length, width of the fastener, as well as the length, thread diameter, head height, turnkey height - all these data are important.
Bolts

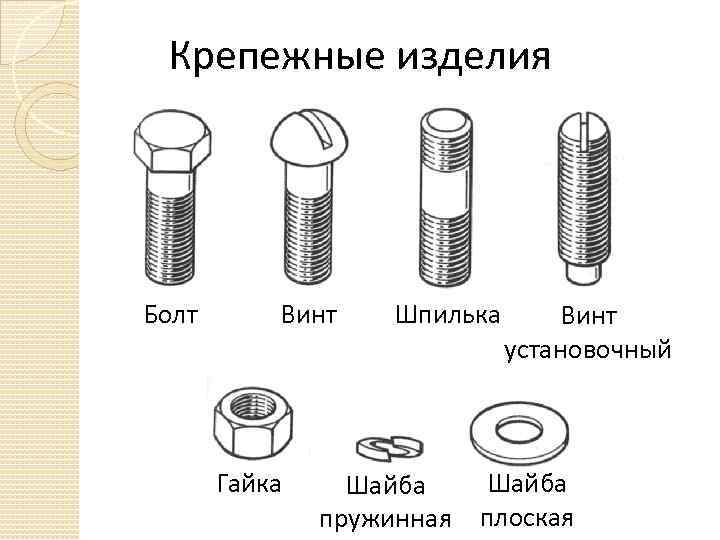
The fastener is a hardware product - a rod with an external thread applied to it. The head can be of various shapes, but more often in the form of a hexagon, under a wrench. Connection and fastening is done by screwing on a nut of the appropriate size. Washers are used to evenly distribute the load and protect the material from punching.
Bolts are used to strengthen various structures. They are irreplaceable in construction, mechanical engineering, machine tool building, furniture manufacturing. But it happens that the use of a bolted connection becomes irrational, especially if the parts to be fastened periodically need to be disassembled. Then choose an alternative fastener.
Hairpins

The hairpin also looks like a rod with a thread applied to it on the outside, but does not have a head. It forms a connection with additional elements and a threaded hole. This type of fastener is designed to connect various modules with threaded or plain holes. Most often used in mechanical engineering, furniture, road industry. The high strength class makes the studs indispensable and widely demanded.
What is a screw
From the German gewinde comes the word "screw", it means "cutting, threading". According to GOST 27017-86:
The slotted head for transmitting torque can be a structural element.

Each screw is marked with two numbers, for example, 4x30. The first number informs about the diameter of the screw under the head, measured in millimeters, the second - the length of the screw section (mm). For mechanical or metric screws, which are used for metal, the diameter of the rod along the length is constant.The screw can be screwed into a threaded hole drilled in the metal, or it can be passed in a package of fastened parts into a through hole, after which a flat or spring washer is put on its end and a nut is screwed so that the parts are tightly compressed together.
The nut is designated by the letter M and marked with a number (from M1 to M68). The number denotes the diameter of the screw onto which the nut intended for it will be screwed: for example, a nut marked M4 will only fit a screw with a diameter of 4 millimeters. Although it also happens that even if their diameter is the same, the nut cannot always be screwed onto the screw. This can be due to the fact that they have a different thread profile and pitch.

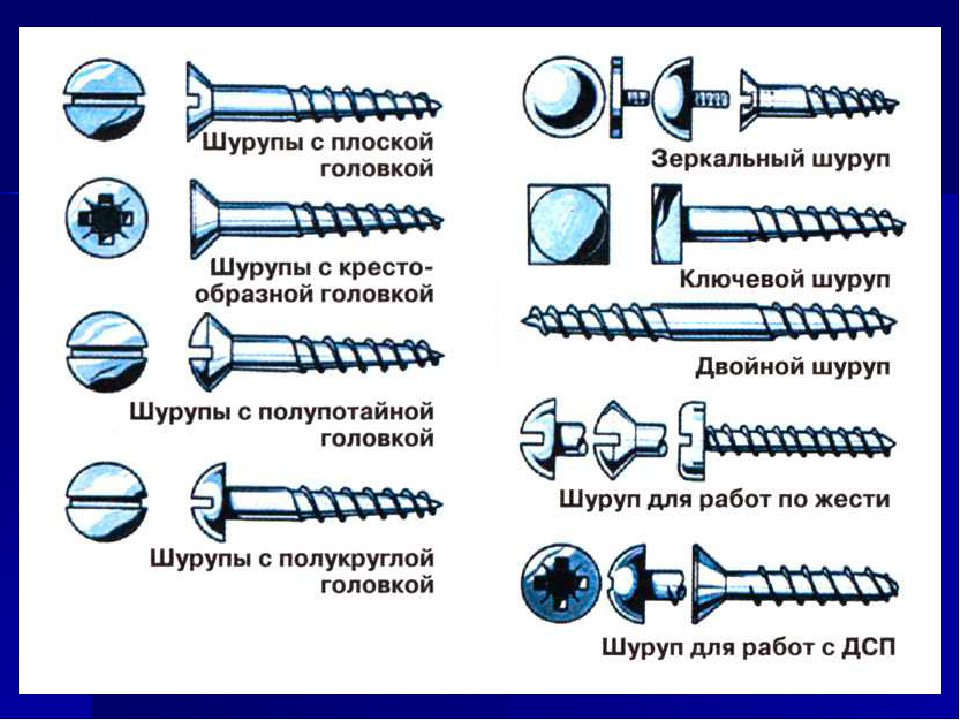
What is the difference between a screw and a self-tapping screw: comparison, photo
The self-tapping screw itself is a type of screw, but it differs in some features. The fact is that the technology for making self-tapping screws is somewhat more complicated. Since harder, stronger materials are used for manufacturing, which can destroy the surface with a certain effort. For example, a self-tapping screw can be screwed in without making a separate hole, it is enough to make an effort. Screwed in from a certain force. Thus, the self-tapping screw will fit tightly into the surface of a tree or other material. In order to insert a screw, you must first make a hole on the surface.

Screw
That is, the screw itself cannot be screwed in without making an additional hole. Since the material is quite fragile and not as strong an edge. They are not so sharp, so it is rather difficult to screw without an additional hole. In addition, the screw has a smaller height and a smaller thread pitch. In this case, the tip of the screw is sharper than that of the screw.

Self-tapping screws
Comparison of competitors
To understand what is better, what kind of hardware needs to be used in a particular situation, you need to understand all the differences, advantages and disadvantages. The dimensions of the parts, the frequency of disassembly / assembly of structures are also recommended to be taken into account.
Key features
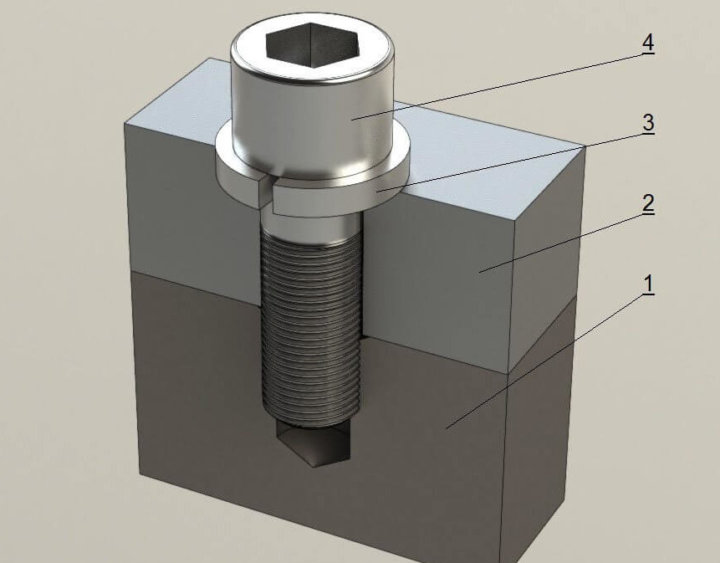
A bolt is a universal fastener in the form of a rod with an external thread, which fundamentally differs from the competitor with a faceted head.
A hairpin is a cylindrical rod that has an external thread at both ends or along its entire length. It is used where it is impossible to use a bolted connection - parts are too wide, there is no room for a bolt head, or where it is necessary to obtain a compact connection. The hairpin is also used if it is necessary to connect the parts so that there is space between them.
Advantages

Each type of fastener has advantages and preferred applications.
The advantages of a bolted connection are as follows:
- Detachable, possibility of multiple assembly / disassembly.
- Simplicity, precision in manufacturing, a wide variety of hardware - from general purpose to specialized.
- Small forces when connecting a bolt with a nut give a strong tightening of the elements, which can be compared with welding in terms of reliability and service life.
- A bolted connection is used when the thickness of the parts to be joined is relatively small, or when the material of the part is not strong enough for the thread.
- With a wide variety of component arrangements, assembly is easy.
Low cost combined with effective and reliable fastening makes the bolt a popular fastening option.
One of the main advantages of a bolted connection is that there is no need for threads on the parts to be joined.

Pluses of stud connections:
- This fastener is indispensable where the body of the parts is large, and it is impossible to make a through hole for the bolt.
- The element is in demand if there are weight restrictions for the entire structure.
- It can be used if frequent assembly / disassembly of the structure is required.
- It is used instead of screws when the material strength of the entire threaded part is insufficient. An example is aluminum alloys.
- Easy to install in hard-to-reach places.

Fastener tightening stress is distributed more evenly than bolt tightening.
disadvantages
In addition to the advantages, the disadvantages of the fasteners must also be taken into account.
Bolts have the following disadvantages:
- Usually it is necessary to use several pieces at once, which significantly makes the structure heavier.
- When tightening, an increased stress occurs at the point where the head meets the rod.
- Since an ideal tandem of a bolt and a nut is required for fastening, and it is also possible to use a third element - a washer, the correct choice of hardware is required. With the wrong selection of fasteners, docking and fastening of parts becomes impossible. But if fixing the parts succeeds, then imperfect dimensions lead to early failure of the entire structure.
Disadvantages of studs:
- can bend, which means they lose strength;
- the thread breaks off from extremely heavy loads, for example, on the wheel parts of a car.
In both cases, it is necessary to urgently replace the damaged elements with new ones.
General concepts

Screw and bolt
Bolt and screw - GOST 7798 gives a clear definition to each of the elements.
Everything about fasteners with terms and names, manufacturing standards, are specified in GOST 27017-86.
It is not always clear why the developers have shared the terminology of two largely similar hardware.
Standardization science is exact, it shows why such distinctions occurred.
A fastener with an external thread designed to fix objects in a certain place is called a bolt.
Visually, it is represented by a solid threaded rod, the end of which is a cylindrical or hexagonal head. With the help of bolts, various structural panels are fastened in construction, and detachable mechanisms in equipment, equipment, and machines are connected. The use of this or that hardware occurs after the definition of the working object.
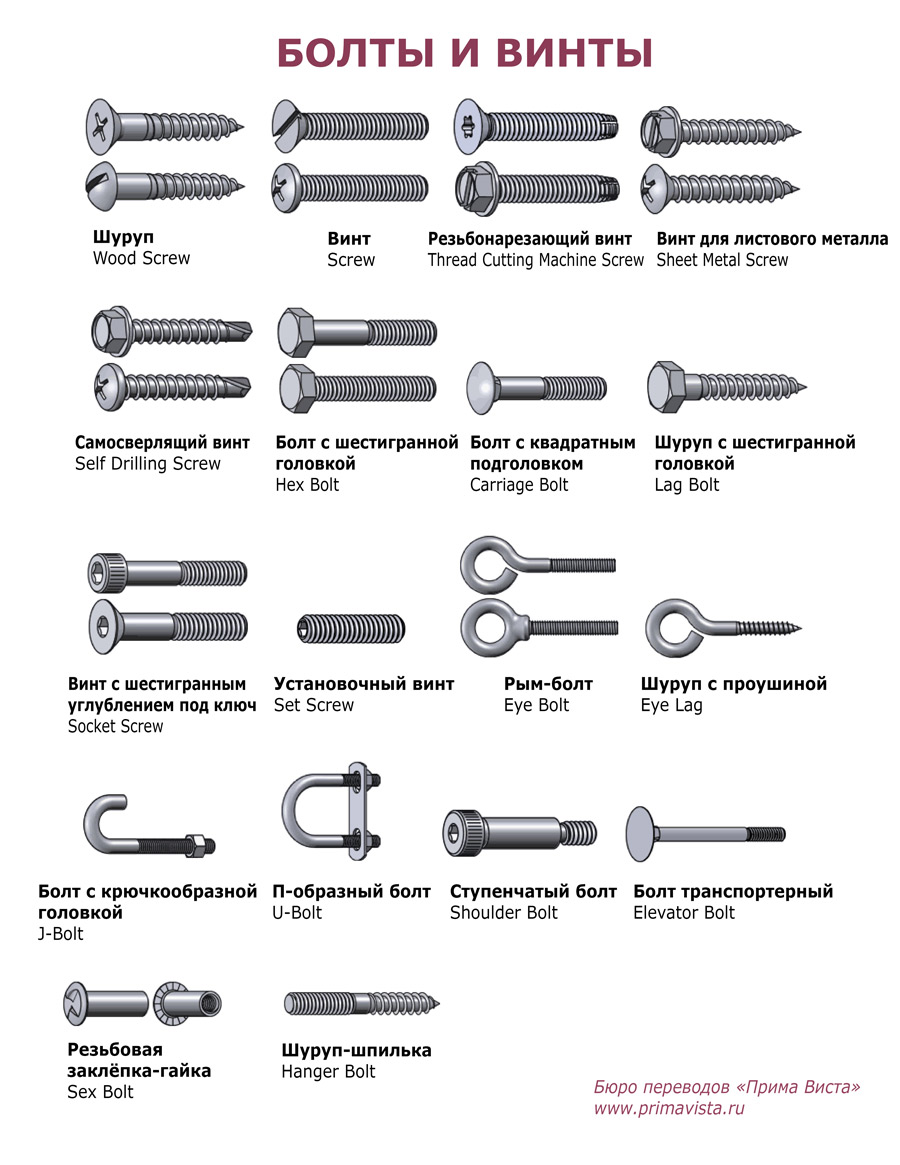
Screws belong to the same group of items in terms of their functionality. They are popular in bonding technical materials, various types of industrial products. Assembly of furniture, for example, cannot be done without screws.
For the production of this hardware they use:
- acid resistant steel
- zinc-nickel alloys
- brass substance
- bronze
- copper
Screws are good conductors of electrical current when they are used to secure electrical parts in equipment.
One end of a straight rod ends in a peculiar shape:
- cylindrical
- hemispherical
- conical
- multifaceted
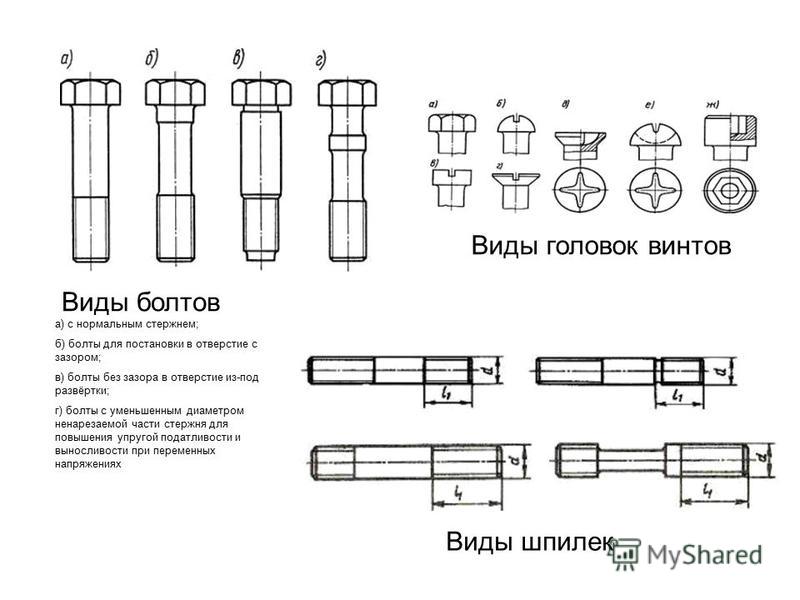
This hardware can be both small and large (for mechanical engineering). The head covering the rod is divided by a slot, a slot. This section determines which screwdriver to use a flat or Phillips screwdriver, the cuts are made especially for them.
Special features in comparison
How the bolt and the screw differ from each other will answer the way of fixing objects. When screwing in, the perpendicular load is directed to the cut.

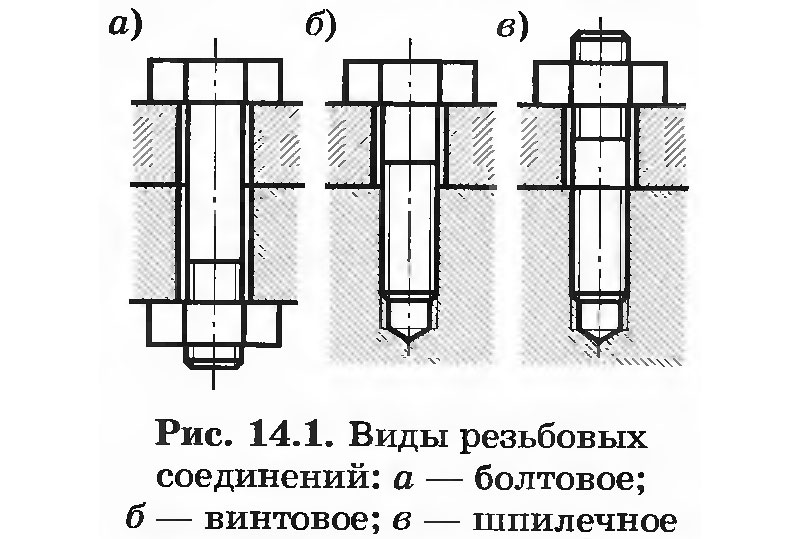
Bolted connection
When the screws are screwed in, they rest on the axis of the interlocking parts. The installation of these items is also different. A constructive, aligned element is pierced with a bolt, through a pre-prepared hole, the connection is fixed with a nut screwed to the rod. The nut requires a special wrench that is suitable for its size.
The screws are tightened with screwdrivers, socket wrenches suitable for the slot. Bolted connections are considered stronger, they do not allow the fastened objects to scroll. With screw fastening, movable mechanisms can be moved.
Screw connection
The form protruding above the core brings its functions. The screws are screwed in flush with the surface, they are often not noticeable. The bolt is visible by its head, it is unscrewed or cut to disconnect it. The screw is removed with a screwdriver, there are a large assortment of different sizes.
Which is better: a bolt or a stud
To choose the appropriate fastener, use studs instead of bolts or a bolt instead of a screw, screw, carefully read the recommendations and watch the video:
If you need to connect two parts with an existing through hole, then you should choose bolted fasteners. The hairpin is chosen when it is required to fix parts without holes - it is screwed in to the desired depth.
The bolt and stud are used for different purposes. Replacing the bolt with a hairpin, and vice versa, experts do not advise. And if this can be done, then it is unlikely that the fasteners will last long.
Previous post Mounts for navigators in the car
Next post How to disassemble a mouse without bolts
The purpose of other similar hardware
Attach items for various purposes and other hardware, among the most popular are self-tapping screws with screws. Self-tapping screws are confused with screws due to their similarity in many respects. They have a sharp thread and a pointed end.
They themselves cut the threads inside the bonded materials, they are divided according to the type of work:
- wooden
- metal
These tools are durable, unlike screws, for the latter a hole is drilled to screw the connected part. They refer to the screw type of fasteners. They are different by the type of threaded step. The screw can be used with a dowel for greater stability in a material that can crumble.
As a result, we can conclude:
- bolts and screws belong to the variety of hardware
- the bolt ends with a cylindrical head, the screw is streamlined
- screws are conical or cylindrical
- the screw does not protrude beyond the part, the bolts penetrate through it
- the shapes that end the bar with one connection remain on top of the attachment, with the other they are compared with the surface
Buyers, purchasing hardware, usually focus on the size and availability of a nut to determine what do they still need ask the seller for a bolt or screw. The self-tapping screws by the name speak of their reassignment and the presence of a rod similar to a drill, the base of the screw does not have a sharp end.
What is the difference between a bolt, a screw and a screw - in the video:
Fastening systems
Attachment classification

All fasteners are manufactured according to approved standards and technologies. Bolts are classified by type:
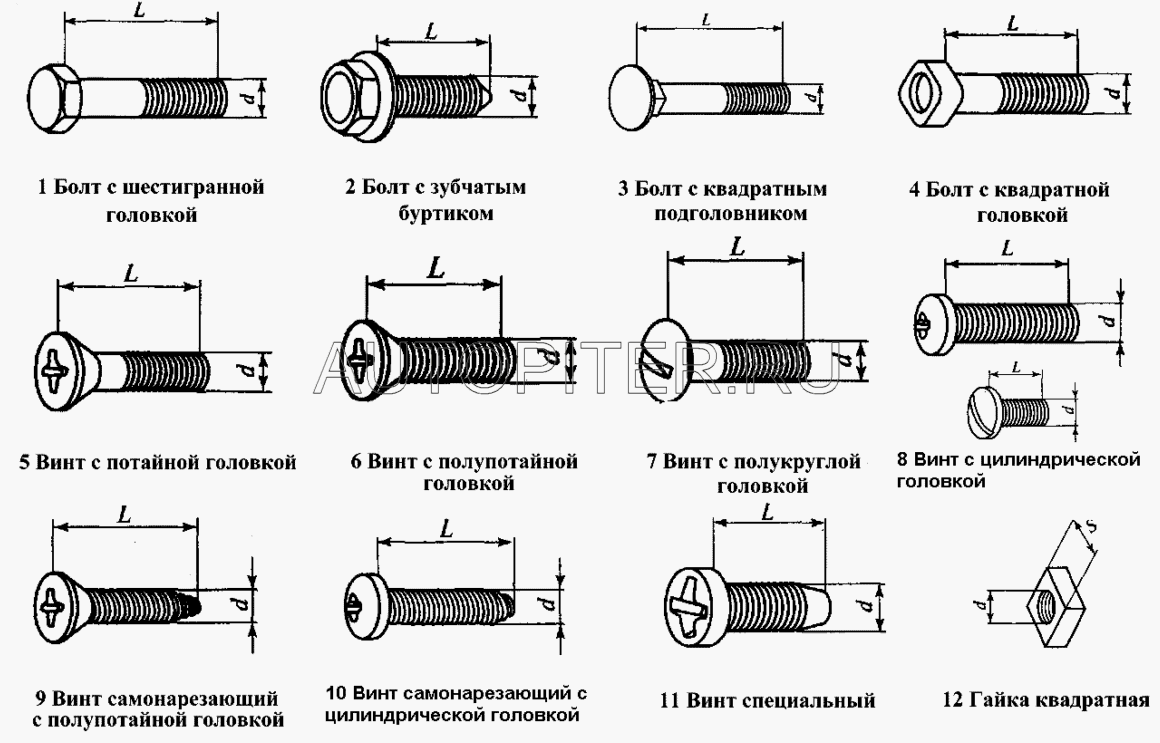
- Shape - depending on which elements need to be connected, the bolts are classic - folding, anchor or eye. Distinguish between hexagonal, countersunk, semicircular head shape or with a flange.
- Type - size (rod length) from small diameter M6 (10-90 mm) to large diameter M14 (22 - 300 mm).
- Manufacturing material - high-strength carbon, alloyed, unalloyed steel alloys in accordance with GOST.
- Purpose - for use in fastening agricultural machinery (plowshares), as well as in mechanical engineering, furniture industry, road structures.
- Strength class, top layer coating - 11 classes are distinguished from 3.6 to 12.9. A high strength class (from 6.8 to 12.9) is achieved thanks to modern manufacturing technologies (hot - cold heading), including special heat treatment and the application of special coatings.

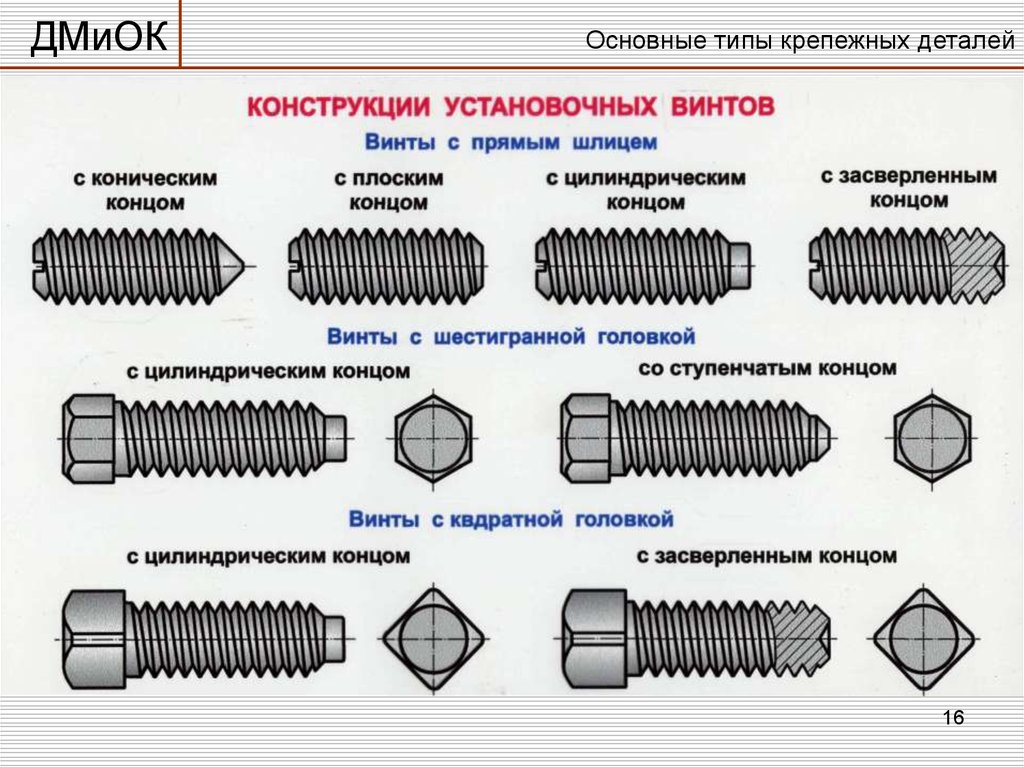
Studs are strictly standardized in size and design. Sizes from minimum (2 mm) to large (52 mm), with different threads. They can be threaded:
- the same along the entire length;
- different on the sides - from one end for wood products, on the other hand - for metal (for joining parts made of different materials).
There are varieties of anchor rod, consisting of:
- element with a tapered end;
- anchor sleeve;
- hex nut and washer.
The material of manufacture of this fastener, strength class with coating, the purpose corresponds to the bolt. Manufacturing is carried out on automatic machines.
Bolt, stud, screw
For clarification, it is worth referring to the official document, which is GOST 27017-86 “Fasteners. Terms and Definitions". It contains all the main characteristics for each specific hardware.
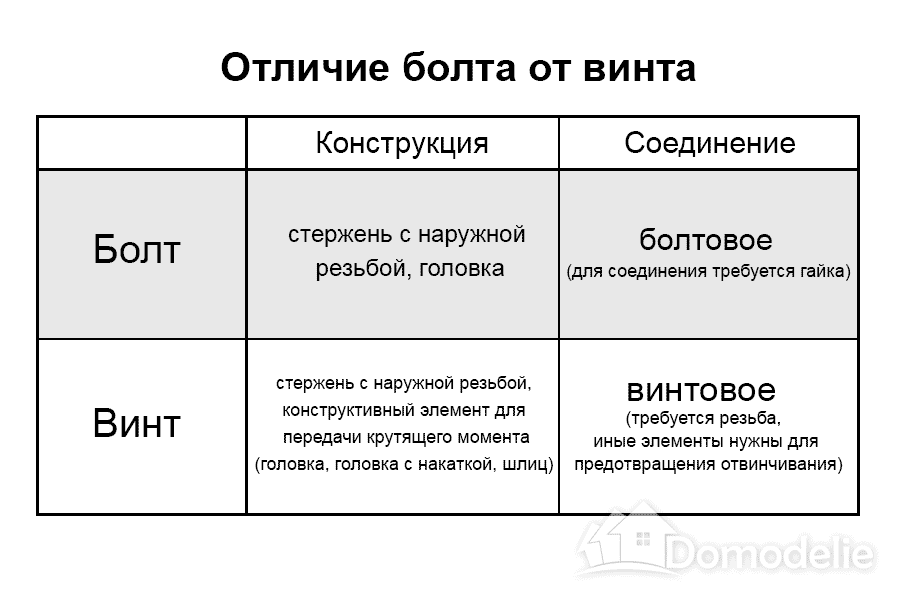
According to this vocabulary, both a screw and a bolt are fasteners that have a rod with an external thread. This, in principle, does not tell us anything, because almost all major hardware must consist of a core. However, in the text of GOST there is something that deciphers, in fact, how the screw differs from the bolt. There are two such characteristics.
The bolt has a head, while its congener has some kind of "structural element for transmitting torque", and this is not always the same hex or semicircular head. An “element” can also be just a slot applied to one of the ends of the screw body.

Another difference is the connection method. Bolt (it is called that) is distinguished by the obligatory presence of additional fastening - a nut, while screw fastening requires only the presence of a thread, and it is bypassed.
We will not stop and compare other fasteners, because a bolt, hairpin, screw, and also a screw and a self-tapping screw often mimic each other.
A hairpin is a fastener very similar to a screw and a bolt, the differences are true only in one part, namely in a threaded rod. Actually, it is this - a cylindrical body with a thread at both ends or along the entire length - that is a hairpin. It is used when it becomes necessary to bond two surfaces, sometimes leaving a gap between them.


Screw - The distinguishing feature of this fastener is the tip feature. It, as a rule, has a conical shape, which allows this hardware to create a thread on its own inside the surface into which it is screwed. However, the screws are so intelligent that they require preliminary processing in the form of a hole, because they are most often used in joints of rather soft materials - plastic or wood.
The more brutal older brother of the screw is a self-tapping screw or a self-tapping screw. And here a snag occurs with the terms. Bolt, hairpin, screw - here the differences seem to be relatively clear. As for the screw and self-tapping screw, GOST 27017-86 does not consider them either equal types of fasteners, or even subspecies. The official version is as follows: a screw - hardware in the form of a rod with a special thread and a tapered end, which forms a thread in the hole of the working surface.

Bolt and screw differences
But what we used to call a self-tapping screw is not a screw, although in design it is almost identical to it, but a self-tapping screw, the difference of which is the tip in the form of a cone and the ability to independently form a thread just right into the part. Well, if it ends with a drill, the correct official name for such a fastener will be a self-drilling self-tapping screw. Quite a tricky name, especially for identifying fasteners in stores.
In order not to confuse potential buyers, manufacturers themselves often move away from official, standardized names. The dimensions and quality characteristics of fasteners correspond to GOST, but the names are simplified. Screw and bolt differences mean themselves, if the first is small, and the second comes immediately with a nut. A screw is called a product with a tapered non-pointed tip, but self-tapping screws most often mean fasteners with a drill. It's definitely hard to make a mistake here.