Concrete strength
Depending on the grade of concrete in terms of compressive strength, the solution will be more or less resistant to loads under various conditions. This parameter is denoted by a beech "M" and a number from 50 to 1000, which indicates what kind of load in kgf / cm2 a certain composition can withstand. The permissible error (coefficient of variation) of this indicator is 13.5%.
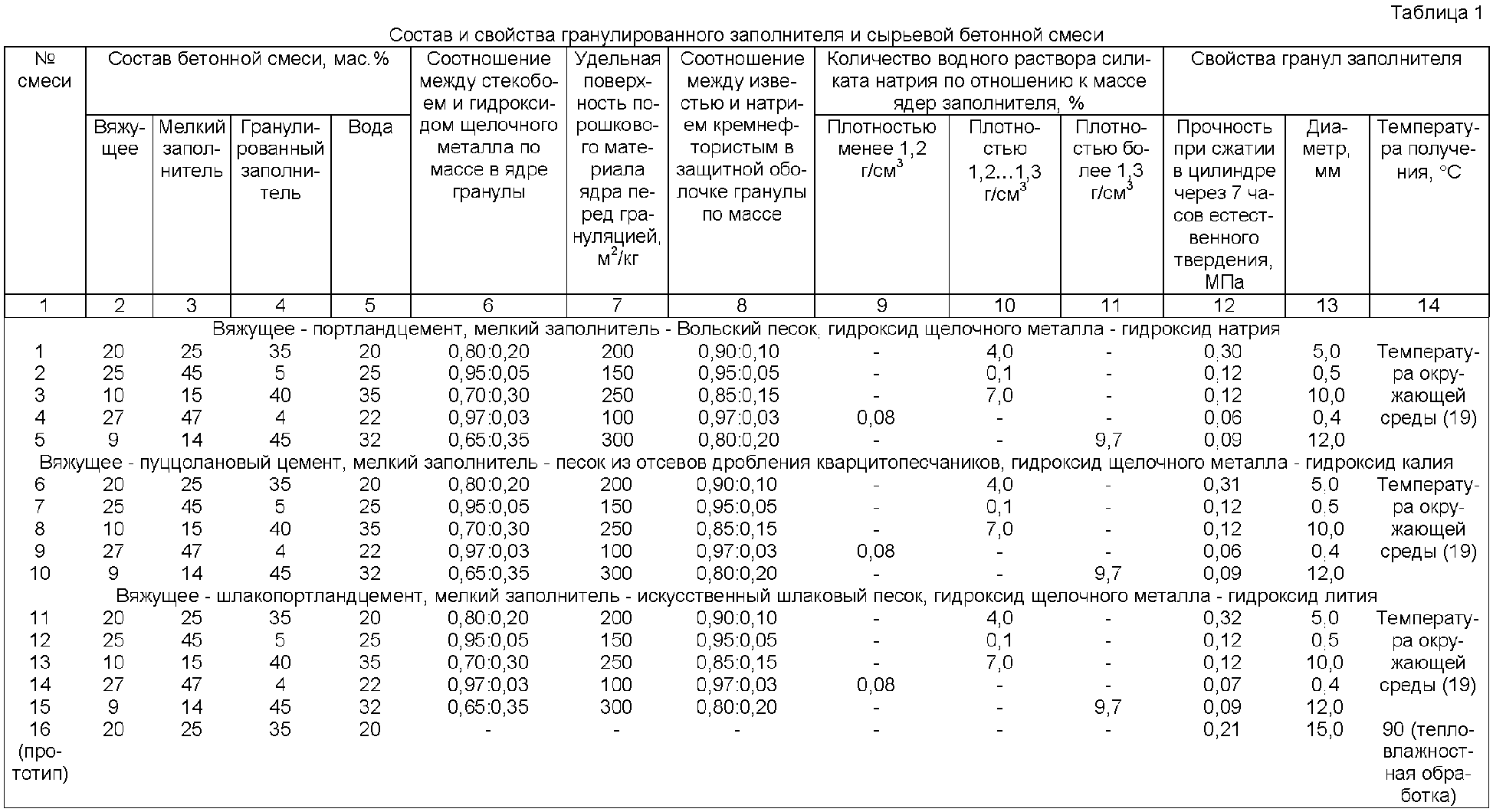
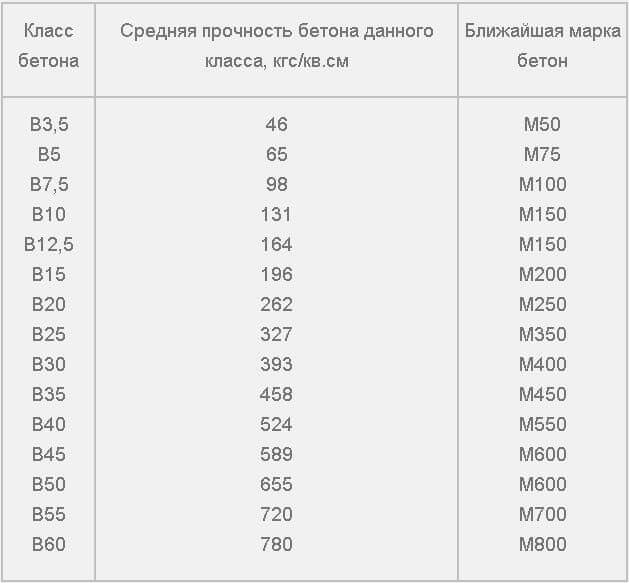
There is also a class of concrete for compression, which is measured in MPa (megapixels) and is denoted by the letter "B", after which there are numbers in the range from 3.5 to 80, indicating what pressure the material can withstand in 95% of cases.
The class of concrete and its brand are inextricably linked, therefore, knowing one of the indicators, you can easily determine the other.
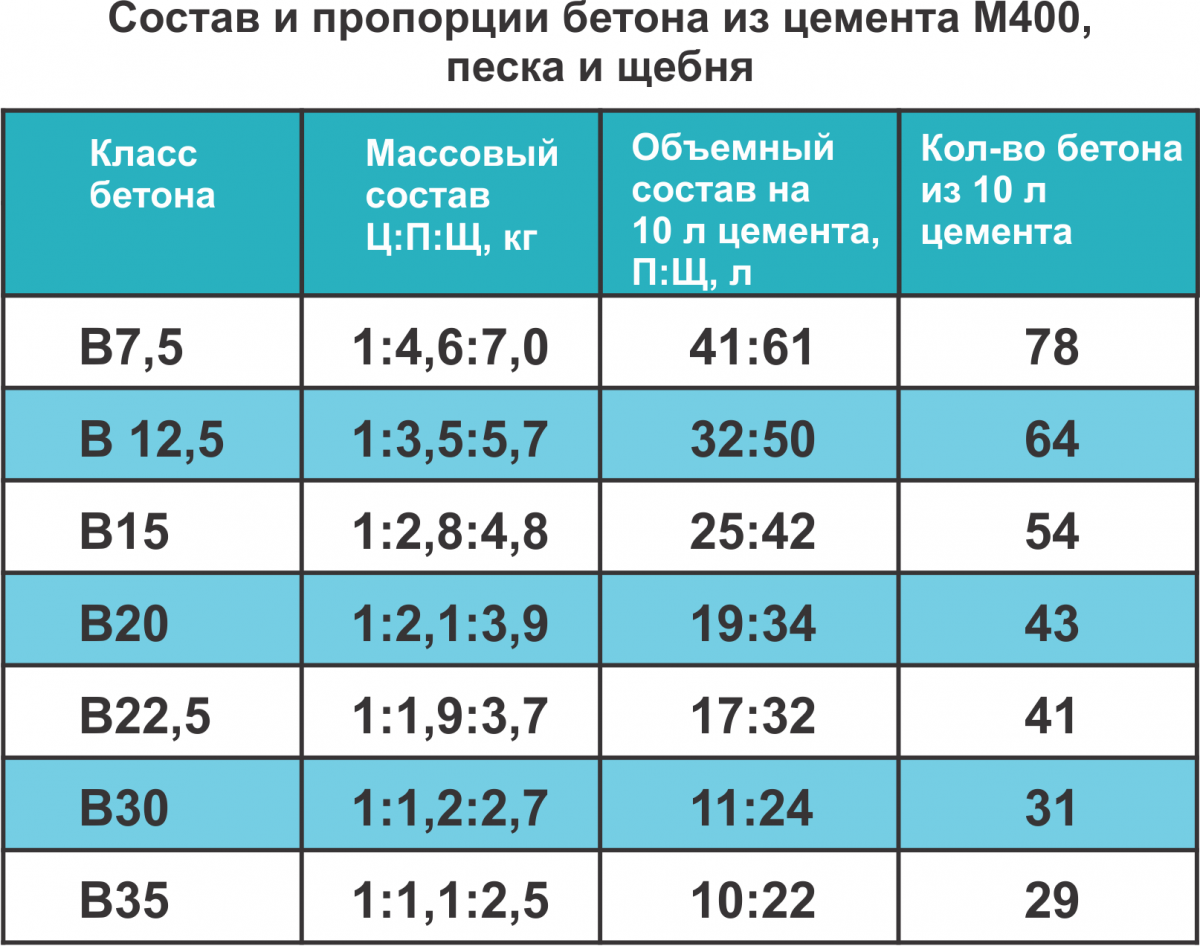
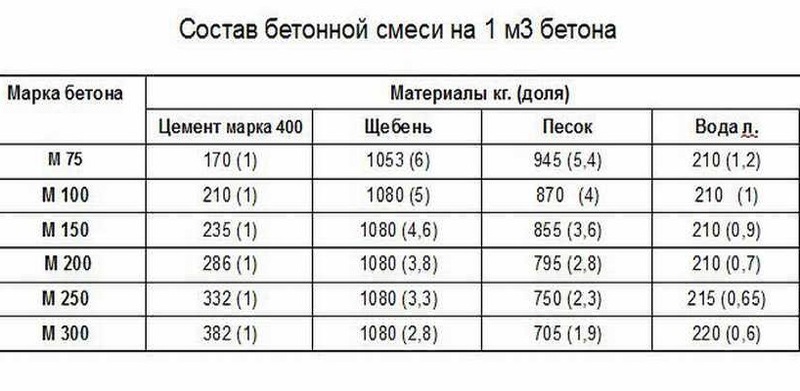
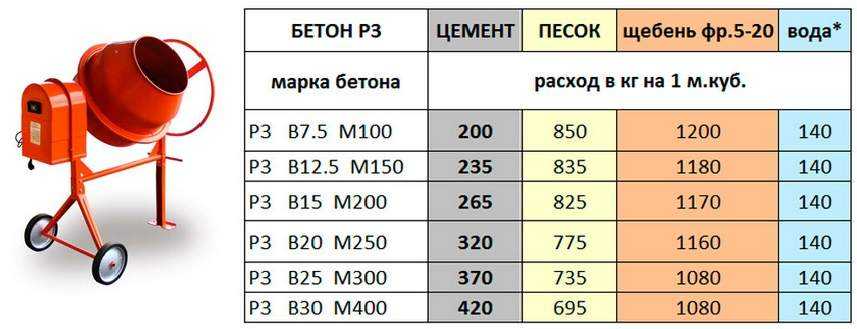
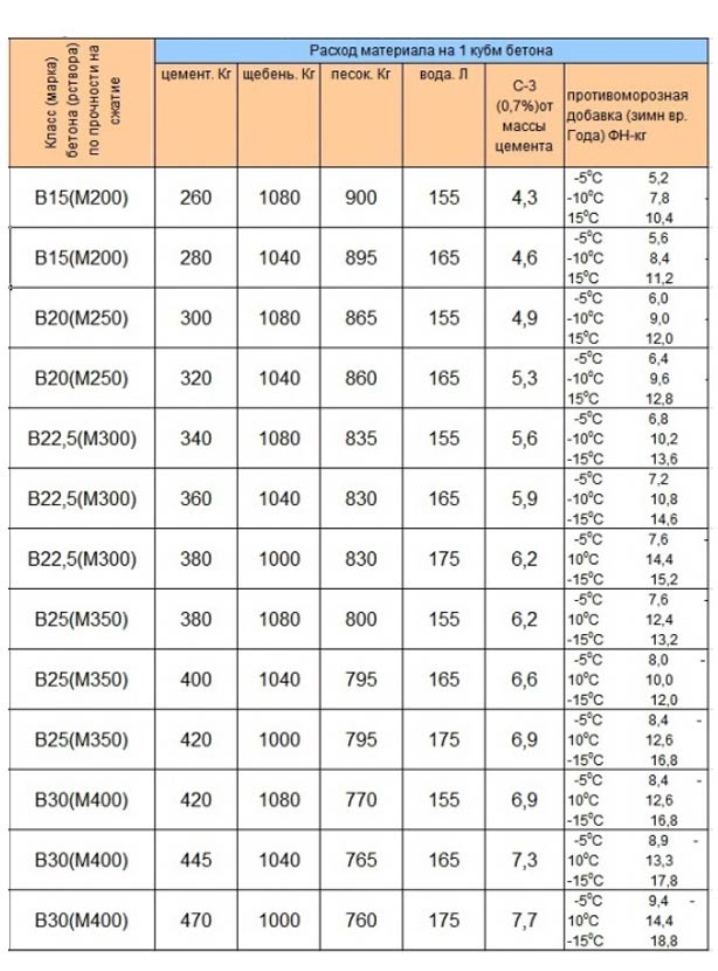
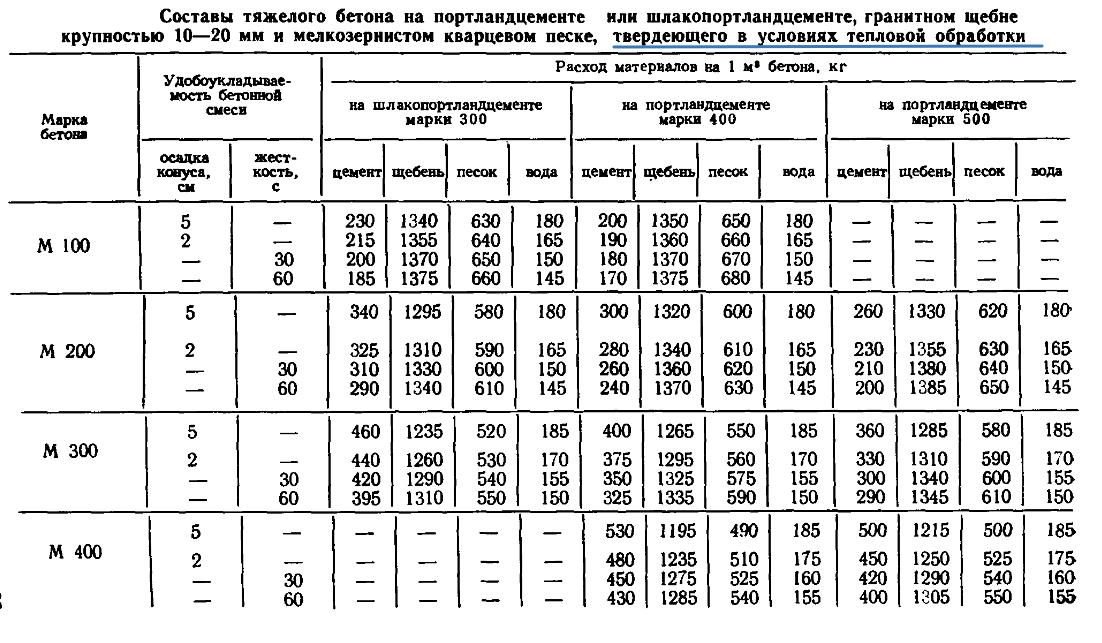
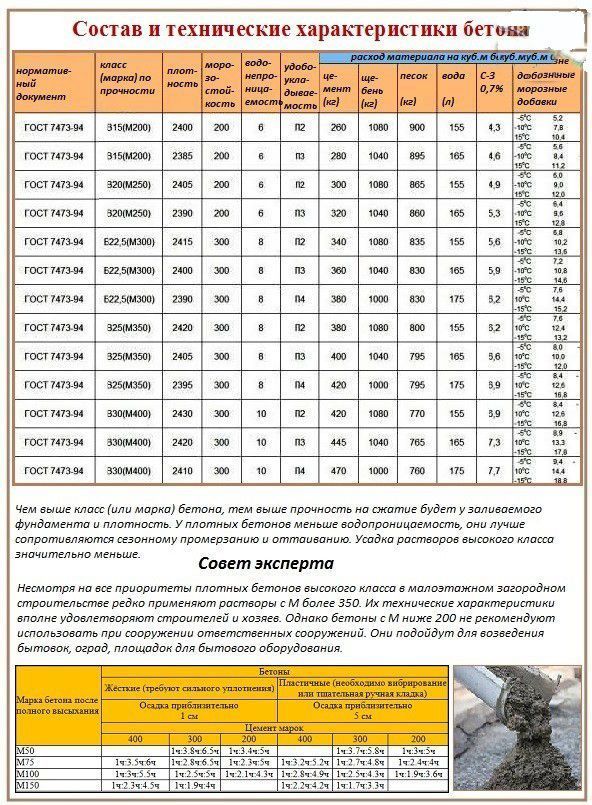
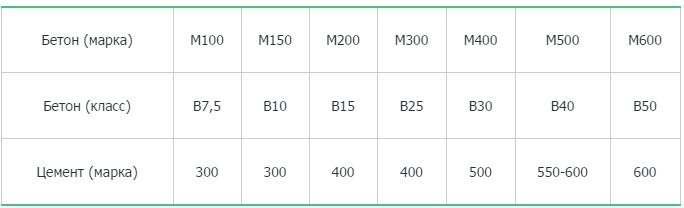
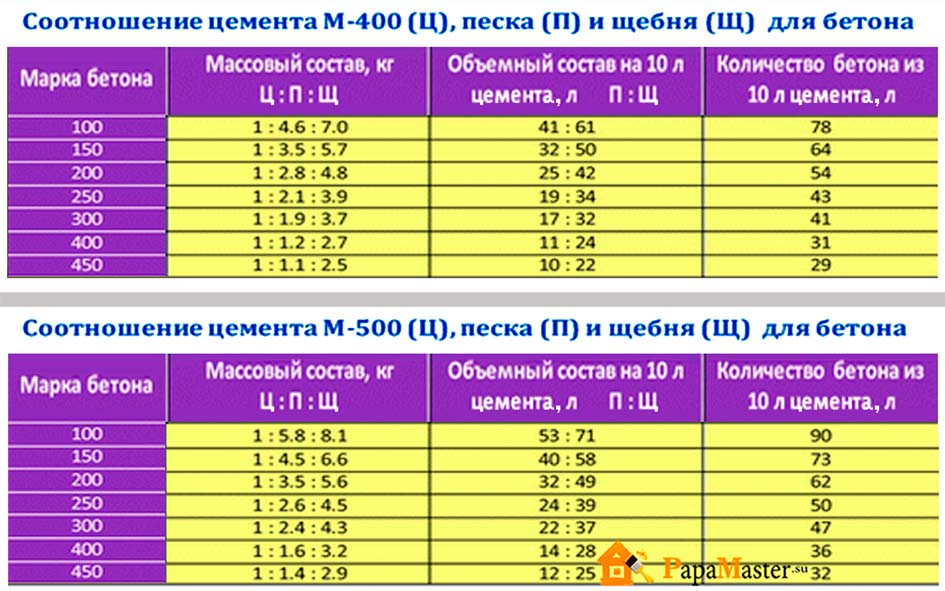
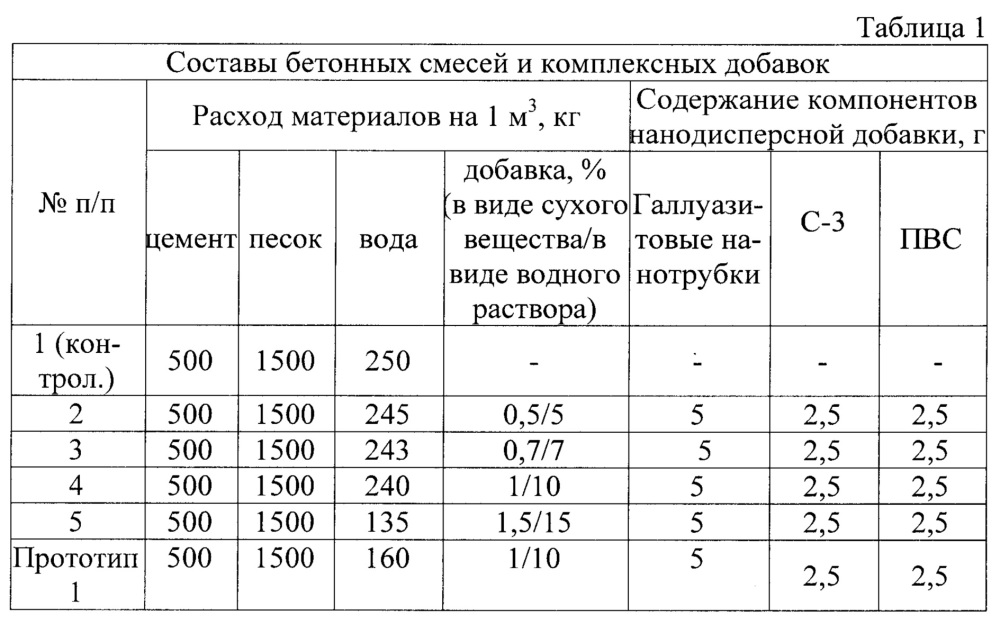
To determine the grade of concrete and the class of concrete, consider the table corresponding to GOST 26633-91.
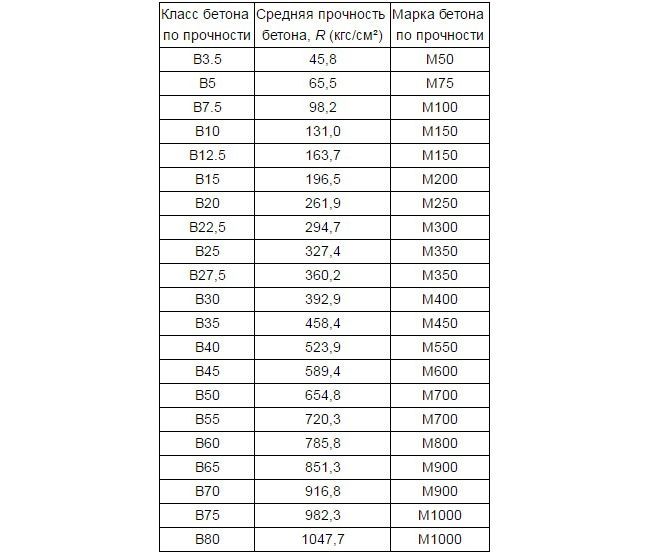
According to these data, the brand and strength class of the concrete solution is determined.
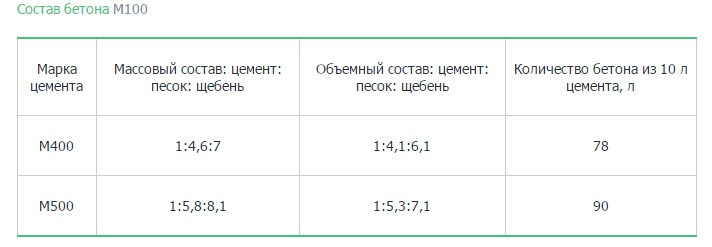
Most often, in the production of building material for fundamental foundations, concrete M 400 is used, but it will not be superfluous to consider and scope of other stamps.
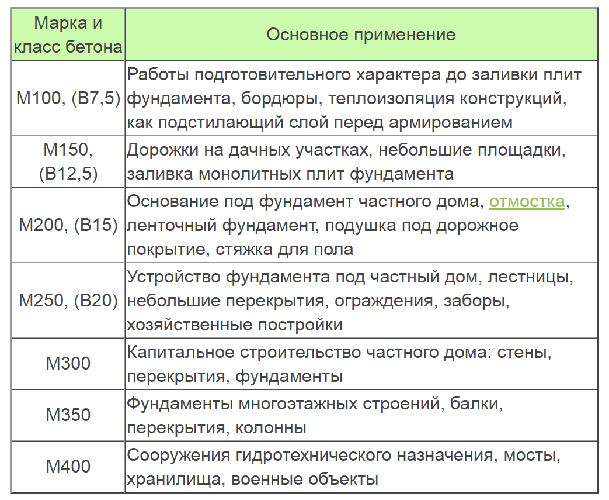
M 50-100
The most fragile and unreliable composition is considered to be marked with 50. Most often it is used when filling voids in structures that do not experience stress. Approximately the same can be said about the mixtures M 75 and M 100. The so-called "thin" concrete was used when pouring the rough layer of the building mixture. These compositions are used in the manufacture of the underlayment (footing) for foundations, screeds and during the installation of road bases.
Based on the fact that the compressive strength class of concrete corresponds to B 7.5, the indicator of such a material does not allow it to be used for serious work.
M 150
Having slightly better strength characteristics, concrete M 150 can also be attributed to lightweight concrete, which should not be chosen for structures experiencing loads. Such mixtures can be used for rough work and when pouring the foundation for small one-story buildings. It can also be used for screeds, garden terraces, paths and areas where people will walk.
M 200-250
With a ratio of grade 200 and concrete class B 15, the composition is more durable. It can be used for the construction of retaining walls, in the manufacture of stairs, platforms, paths, blind areas and curbs. Often, M 200 is poured into tape-type fundamental foundations (only if the soil is stable) and open terraces.
The strength of the concrete is sufficient for the installation of screeds in rooms with low mechanical stress.

Concrete M 250 has practically the same property - it is also often poured as slabs with low load.
M 300
If we consider the grades of concrete and their characteristics, then M 300 today is in rather high demand for the construction of monolithic foundations, due to the optimal ratio of price and quality. Also, mixtures of this type are suitable for pouring platforms and in the manufacture of stairs both outside and inside the house. M 300 concrete has good moisture resistance, so a humid environment does not have a destructive effect on it.
M 350
If you choose a grade of concrete with a class B 27.5, then you will receive a durable material for the construction of structures of both monolithic and overlapping types. Such compositions are used when laying the foundation for multi-storey buildings. Due to the increased strength of the mixture, it is also suitable for more serious buildings: pools, load-bearing columns, airfield slabs and more.

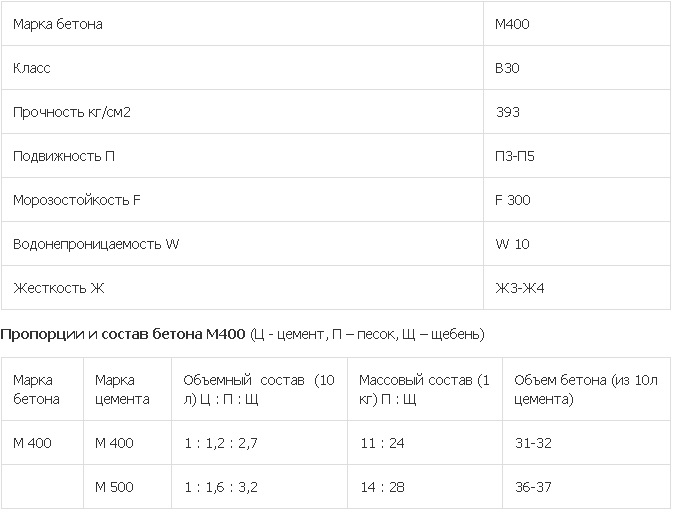
M 400
With such a correspondence between the brand and class of concrete (M 400, B 30), you will have to pay quite a lot for the building material.Due to the high cost, mixtures of this type are not very popular with private developers. Nevertheless, concrete M 400 sets quickly, therefore it is more often used in the construction of large facilities: shopping malls, sports arenas, banks, water parks, and so on. Also, this concrete is suitable for pouring bridges, underwater structures, high-loaded supports and hydraulic structures.
M 500 and above
Such compositions can be classified as highly specialized, since with such a concentration of cement and strength indicators, it is not rational to use M 500 for the construction of residential buildings. Typically, concrete mixes of this class are used for the construction of bank vaults, bridges, dams, dams and strategic facilities.
In addition to the classification of concrete by strength, it is also worth considering other differences.
Description and application
M100 concrete has a low price with a relatively low strength index, therefore it can be used only where there are no large mechanical loads. It corresponds to concrete of strength class B7.5 and is used in the production of reinforced concrete structures that will not be subjected to high pressure and dynamic effects. This material is waterproof enough to create a reliable barrier for the cement laitance of high-grade concretes poured onto an M100 cushion. It has a relatively low density, which reduces the pressure on the ground surface.
When choosing a building mixture, attention is paid to three main parameters: strength, moisture resistance, frost resistance. It is they who determine the scope of application of B7.5 or M100 concrete, which is limited due to reduced performance due to a small amount of cement
This solution is used for such work:
- Arrangement of concrete cushions for bases and foundations on compacted soil or sand. Their purpose is to prevent the binder component from leaving the ground. In addition, such interlayers create an additional waterproofing barrier, protecting structures and reinforcement from corrosion.
- In road construction, a substrate is arranged from this material under the basis of the canvas, in the construction of pedestrian zones, areas for vehicles that are exposed to high loads.
- For casting curbs, small unloaded structures, arranging infrastructure elements, playgrounds and sports grounds.
- For pouring subfloors in utility rooms in private construction, for example, in a barn, workshop or cellar, laid on the ground.

Choosing a grade of concrete: dependence on work
Concrete is classified according to its use for a mixture of various binders. Mortars are asphalt, gypsum, clay, lime, polymer, silicate or cement.
Varieties of concrete
The addition of different fillers makes it possible to obtain mixtures of different types.

- Especially heavy. They contain barite (barium sulfate), iron ore. Such mixtures are used for the construction of nuclear power plants, in military construction.
- Heavy. In this case, the aggregates are better known: they are gravel or crushed stone. These solutions are indispensable for concrete / reinforced concrete structures.
- Lungs. They contain porous aggregates - perlite, expanded clay, pumice (pumicite). They are used to create monoliths, blocks, panels, floor slabs.
- Particularly lightweight - cellular concrete. These include gas and foam concrete. The materials are very popular in low-rise construction.

All types of concrete are divided into waterproof, fire and frost resistant, hard or plastic. The latter characteristics are influenced by the degree of density of the solution.
Classes and grades of concrete
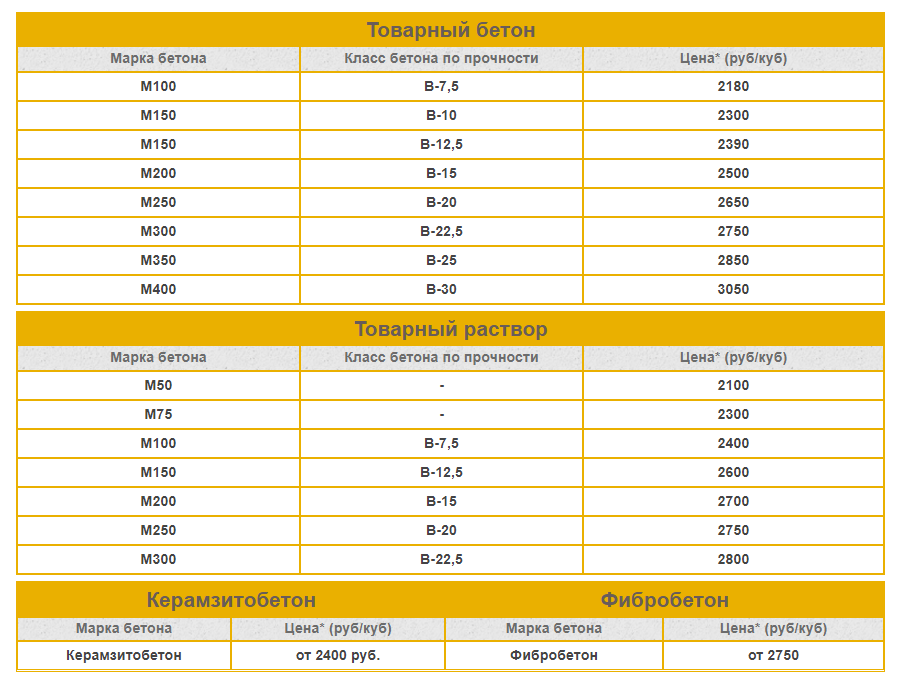
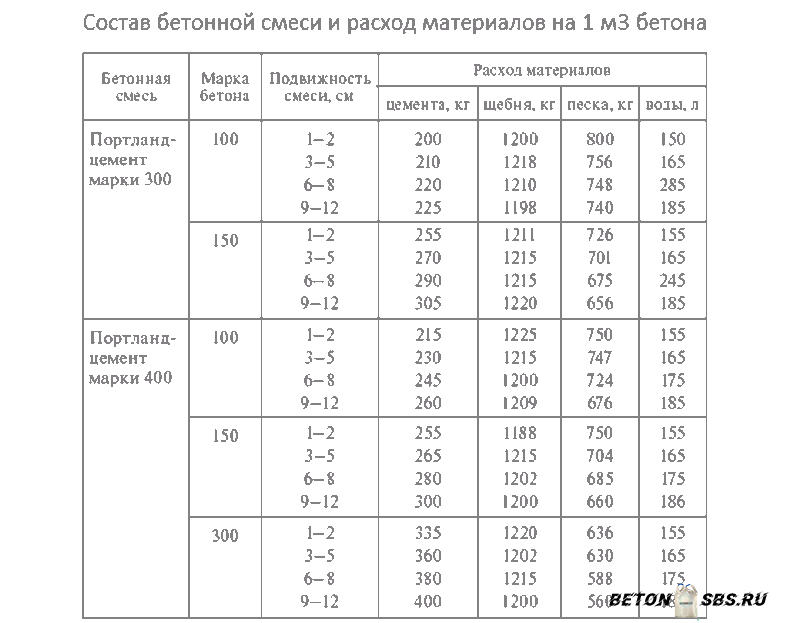
To select the perfect blend, you need to know which grades / grades are needed for a particular job. The most durable concrete used in construction is M500, but not in all cases its use is advisable. To know what to be guided by when choosing, it is better to study the following table:
| Class / grade of concrete | Main areas of application |
| B7.5 or M100 | Construction of concrete foundations in dry soils, curbs, thermal insulation |
| B12.5 or M150 | Floor screed, construction of paths, foundations for small one-story buildings |
| B15 or M200 | Floor screed, foundations for single-storey houses, arrangement of a cesspool |
| B20 or M250 | The foundation of a private house, small floors, stairs, fences, outbuildings |
| M300 | Support structures for private houses, floor slabs, foundations, staircases |
| M350 | Construction of multi-storey buildings: foundations, floors, columns |
| М400-М500 | Construction of industrial buildings, tunnels, bridges, hydraulic engineering, military facilities |
Concrete grades M100, M150 belong to light (lean) mixes, serious loads are prohibited for them. M200 and M250 are in many ways similar: they have a sufficiently high compressive strength, according to the latter type it is more reliable, therefore it is used even for the construction of floor slabs, but only those on which a large load will not be imposed.
M300 "specializes" in all types of foundations for buildings, used for the construction of walls, platforms and fences. M350 already has sufficient strength to be used for arranging slab foundations of multi-storey buildings, for the manufacture of hollow-core floor slabs, bearing columns, basin bowls, road slabs of airfields.

M400 is less popular due to its high price. The scope of his "activity" - the construction of bank vaults, entertainment, shopping centers, indoor pools, water parks. Besides the price, the M450 has one more drawback - it grasps rather quickly, therefore its use is limited, but this brand is used for the same purposes as the M400. Concretes M500 and M550 are very reliable, but they are not used for the construction of buildings. Their "niche" is reinforced concrete products and special purpose structures, hydraulic structures.
If the plans are a small outbuilding, then you can get by with a low grade of concrete - M200. When they "plan" the construction of a residential building with several floors, they acquire a more reliable mixture - M250 or M300.
Secondary qualities
Water resistance, frost resistance - a couple more necessary characteristics, you need to pay attention to them. The first indicator must be taken into account in the construction of underground or hydraulic structures
The second determines the durability of a structure erected in temperate or cold climatic zones. These important parameters depend on the class as well as the grade of concrete. The stronger it is, the higher the stone's ability to withstand moisture and frost.
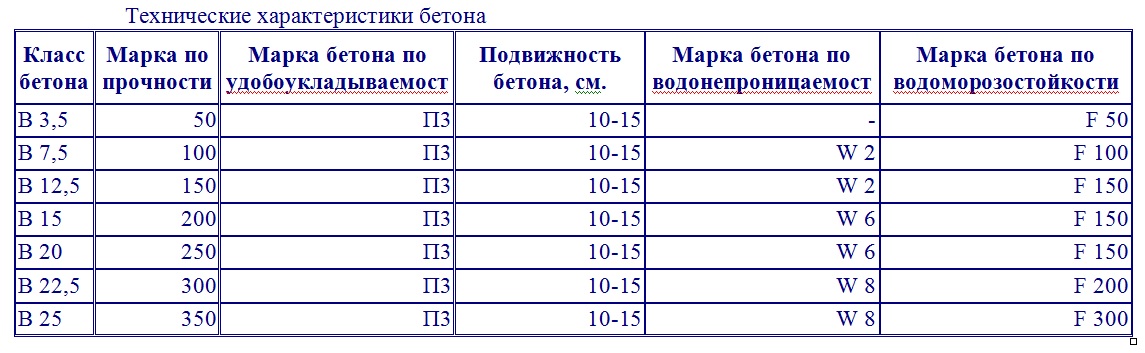
Water resistance is indicated by the letter W (from W2 to W20), it shows the maximum water pressure that the surface of the structure can hold. Frost resistance - F (50-300). The last figures are the number of freeze-thaw cycles after which the material does not lose its properties. Both characteristics can be improved by using special additives.
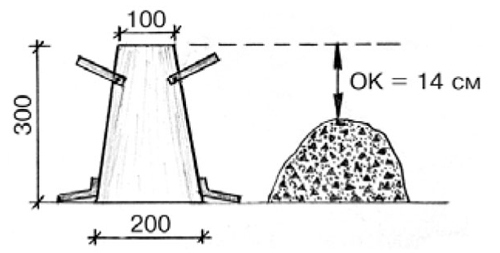
The mobility of concrete (P1-P5), which is checked by the shrinkage of the cone, characterizes the ability of the solution to spread only due to its own weight. This quality depends on the brand of cement, the proportions of the mixture, the fraction, as well as on the shape, purity of fillers, the quality of all components and additives.
Alternative strength test
If the press is not at the construction site, then the manufactured samples are transferred to the laboratory. In this case, you can get absolutely all data on the characteristics of the material. When such a goal is not set, an alternative option is used: this is a special device - Schmidt's hammer, its second name is a sclerometer.
The research method is based on determining the strength of the material using the elastic rebound method. The metal firing pin of the hand tool strikes the specimen with a predetermined force, then bounces upward. The distance is recorded by a sclerometer. As a rule, several checks are carried out, the result is their arithmetic mean.
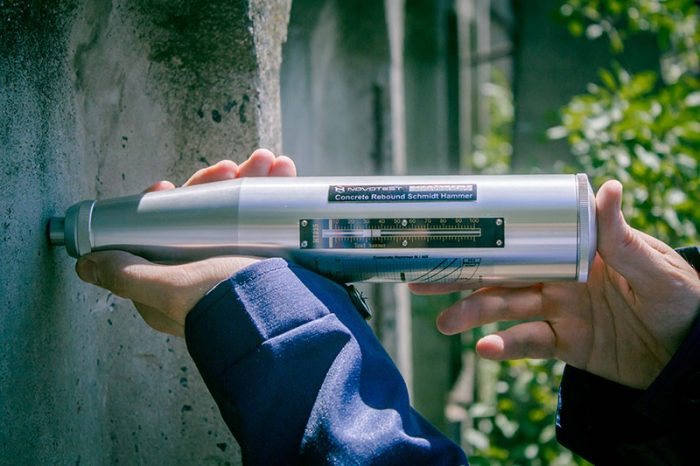

This method cannot argue in full study of characteristics with laboratory work. Accuracy here depends on the quality of the surface, the density of the mass, and the thickness of the sample. However, the instrument allows data to be determined at the production site. If the device is in good working order, then the measurement error does not go beyond 5%.
In private construction, not only the class or grade of concrete is important. In this case, the main thing is strict adherence to the technology for preparing the mixture, a correctly constructed formwork, and the correct laying of mortar into it. However, saving on building materials is far from the best idea: it is always recommended to choose the brand that guarantees the inviolability of the structure.
This popular video will help you finally understand the difference between the class and the brand of concrete:
Application
M200 concrete is lightweight. It is used for filling screeds, leveling various surfaces. It is used for the manufacture of reinforced concrete structures, such as blocks for foundations, floor slabs, flights of stairs.
In low-rise construction, during the construction of outbuildings and brick fences this material is used for construction of shallow foundations.
Manufacturing of paving slabs using concrete grade M200. They are highly reliable, withstand temperature extremes and do not require extra costs.
The use of concrete is determined by the fractions of the rubble included in it. The fine-grained composition is used for products formed in small formwork. This mixture spreads evenly in shape and allows you to get small structures. These are lintels, staircase elements.
The area of application of the coarse-grained composition is the device of strip foundations, walls, reinforced concrete structures.

Concrete and its applications

It is an artificial material consisting of a binder, aggregate, various additives that improve the characteristics of the stone, and water. The scope of application of the universal mixture is incredibly wide: it is used in the construction of buildings - for the construction of various types of foundations, for the construction of walls, ceilings, columns.
The main building material is irreplaceable for the construction of fences, roads and sidewalks, bridges, for the manufacture of the same artificial stones for construction and finishing works. To obtain a material that meets the current standards, all components for the composition are carefully selected, calculated and proportioned, they do not deviate from the manufacturing technology.
In construction, high-quality concrete of high brands is always used, as well as special mixtures that have a whole list of necessary indicators. These include durability, immobility, frost resistance, heat resistance, minimal shrinkage, the ability to resist cracking, moisture attacks.

The main use of concrete is for monolithic or prefabricated concrete (reinforced concrete) structures. Each type of construction work implies its own type of mixture - the corresponding class, brand. The required characteristics of the solution are determined at the design stage of the facility.
Where is the concrete mix M400 used?
The technical characteristics that concrete M400 (B30) have makes it possible to use it for the construction of complex structures and structures with special requirements for strength and resistance to aggressive environments. Today this material is used for the construction of a number of structures:
- Construction of large bridges, including rail and road bridges, with heavy workload.
- Manufacturing of durable reinforced concrete staircases, platforms and curbs.
- Arrangement of bank vaults, other high-strength underground premises, including military ones.
- Construction of supports, columns, arched or beamed ceilings.
- Erection of powerful hydraulic structures.
- Construction of special structures in the field of energy, mining, large-diameter collectors.
This type of heavy concrete is resistant to vibration, therefore it can be used in the construction of transport and industrial infrastructure, for specialized supports, concrete floors and vaults. In private construction, the M400 is rarely used for the following reasons:
- relatively high cost due to the high content of cement in the material;
- excessive density and strength for private construction;
- fast setting, making it difficult to work with the material and complicating delivery.
Nevertheless, in the construction of swimming pools, garden paths, casting monolithic walls, this mortar is still used. It can be made independently, fully withstanding the technology.
Specifications
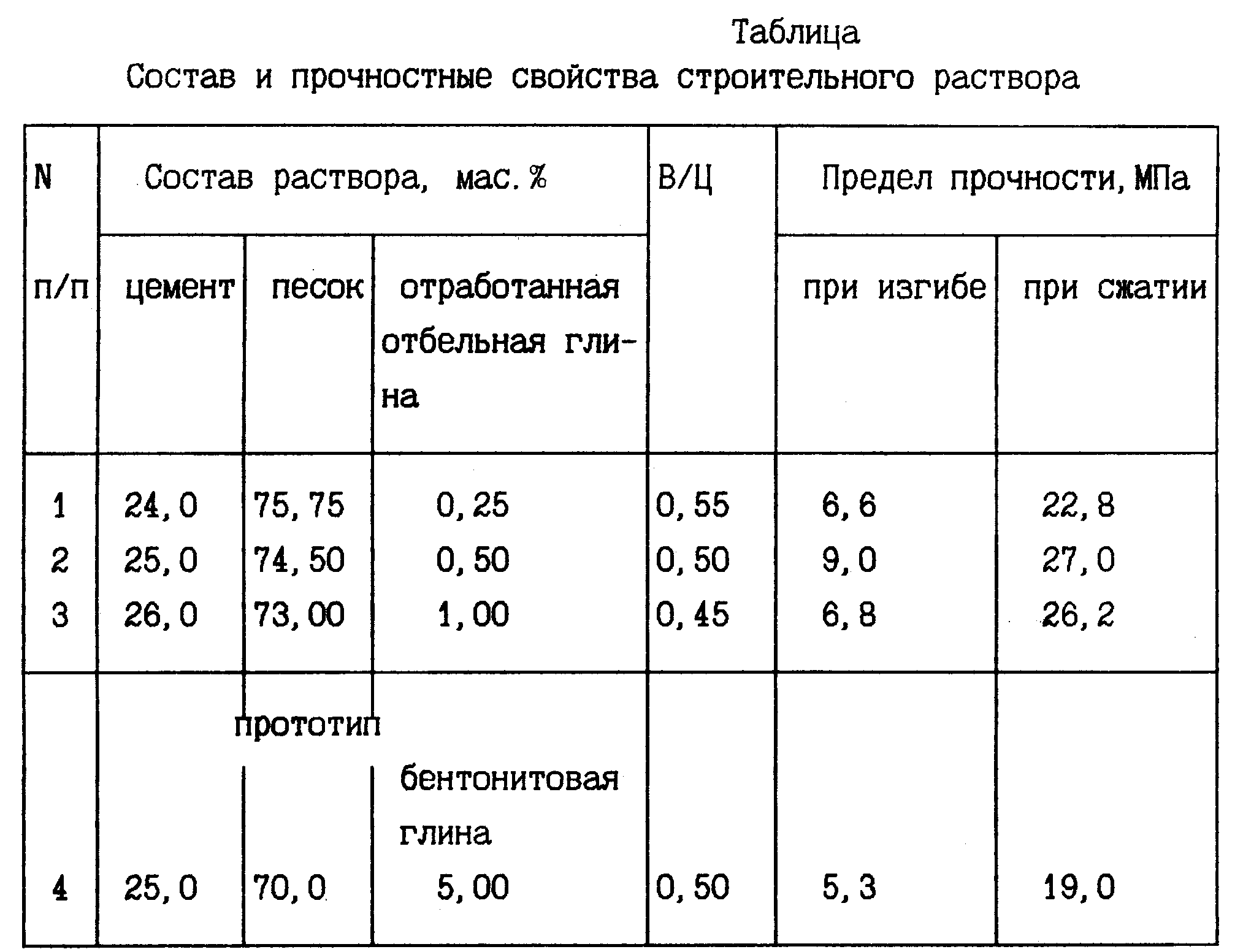
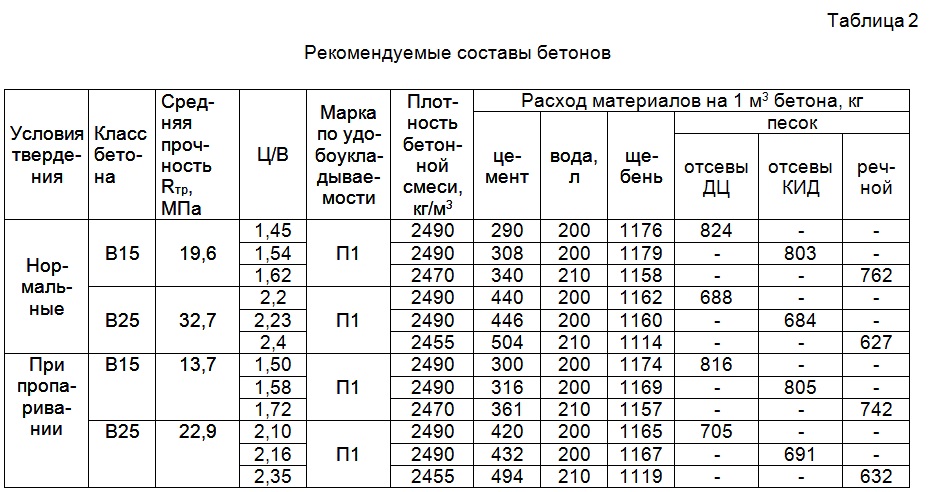
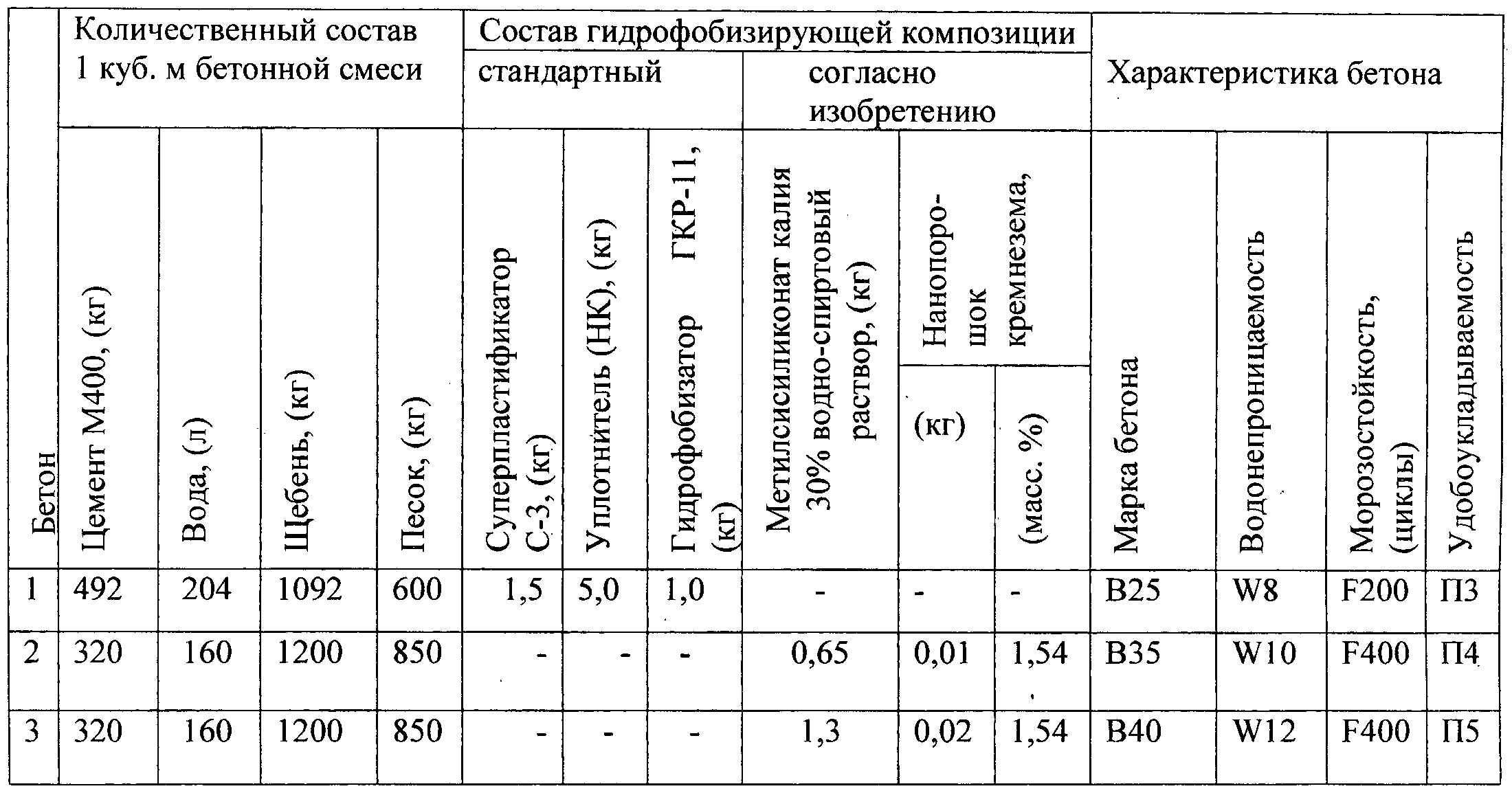
Construction standards are a set of defined rules and requirements for the design and characteristics of materials and structures. Basic technical parameters of B15 concrete according to GOST:

1) Compressive strength. A material of this class is capable of withstanding a load of 200 kg applied to 1 cm² of the surface of a concrete structure.
2) The class of concrete is also an indicator of the strength of concrete, but it comprehensively indicates the guaranteed strength characteristic of the entire structure in MPa (B15). According to SP 27.13330.2011, these markings are valid for designers and builders. To compare the two definitions of strength, class-to-grade conversion tables are used.
3) The density of concrete grade M200 (B15) is 1800-2500 kg per cubic meter. This density class is heavy.
4) Frost resistance and water resistance. These technical characteristics are indicated in the design documentation to ensure the reliability of structures. F50, F75, F100, F150, F200, F300, F400, F500 - the numbers determine the durability of structures operating at negative temperatures. Up to 4 cycles are taken during the year. W2, W4, W6, W8 and W12 - the water resistance of the cylinder is 15 cm at a pressure of 2.4, 6, 8 and 12 kg per cm². For example, concrete B15 F100 with water resistance w4 - class B15, frost resistance 100 cycles and water resistance with a pressure of at least 4 kg.
5) Mobility and stiffness indicators are designated by the letter "P". Values from 1 to 5 indicate the time characteristic of the mix to determine workability. Suitable for narrow formwork - concrete grade (B15, M200) not lower than P3.