Application of plywood products for general purposes
General purpose plywood is used in the furniture industry, in construction - as a finishing material and as structural or auxiliary products. The grade of products does not affect their strength. For finishing works, sheets of grade E or 1 are used as front panels: the ideal pattern makes these products suitable for wall cladding "imitating a tree"; with the help of stains and varnishes, the surface of high-quality veneer can be given the appearance of valuable types of wood.
Plywood 4 mm 2/2 - products of the second grade, the front and back surfaces of which are distinguished by a minimum amount of damage, cracks, knots. In most cases, knots and obvious wormholes are sealed with veneer inserts, which makes it possible to use this material as a front finish. Plywood 4 mm grade 2, covered with decorative paints and varnishes is used for wall cladding in modular houses; furniture cases and panels are made from it.

Plywood 3 mm 2/2 is the thinnest material offered by the industry; is one of the most common. Possesses high elasticity, low weight and sufficient decorative properties. The sheets are used to make substrates for decorative sandwich panels - floor and wall coverings. In the furniture industry, three-millimeter sheets are used as back panels, cases of sliding drawers, and adhesive bases. Often this plywood is used for the manufacture of container products - mailing boxes, suitcases, travel bags.

Slim, strong or Finnish
A separate GOST - 102-75 provides for a special category of plywood - aviation, popularly - Finnish. For the manufacture of this material, it is allowed to use only the birch veneer that is able to withstand the tensile force along the fibers - 950 kgf / cm2. The mechanical characteristics of aircraft plywood are 1.5–2 times superior to those of general-purpose glued panels: if the tensile strength for ordinary plywood is 30–40 MPa, then for aviation (depending on the grade) it is 49–95.
The specific strength of thin plywood increases with decreasing thickness. The minimum section of a sheet of domestic plywood grades BP-A, BP-V is 1 mm. The material consists of three layers of birch veneer, located at right angles to each other and glued with a bakelite film of grade A or B. According to GOST, the step size of sections up to 3 mm is 0.5 mm.
In addition to domestic thin plywood, export types of products from Finland are presented on the market. The cross-sectional step of Finnish products is different:
- group up to 2 mm: 0.4 mm; 0.6 mm; 0.8; 1 mm; 1.2mm, 1.5mm;
- group 2 mm and more: 2 mm; 2.5 mm; 3 mm;
- group from 3 mm: 4 mm; 5 mm; 6 mm; 8 mm; 10 mm.
Plywood 1.2 mm can be made according to a separate order by a domestic manufacturer. In this case, the difficulty is the development of a separate estimate.
The BPS-1V brand is particularly durable and lightweight. Plywood with a thickness of 2 mm is provided by 5 layers of veneer, and the veneer center is made of three mutually perpendicular sheets, and the outer surfaces on both sides are faced with a pair of veneer sheets, the fibers of which are directed parallel to each other. The grade of thin plywood determines its strength. GOST provides for two types of products, and five-layer sheets BPS-1V can only be of the first grade.

During the first half of the last century, aircraft fuselages were sheathed with 2 mm sheets. The versatility of this material is due to the combination of high strength and minimum density.In addition to the aircraft industry, 2 mm plywood has found application in instrumentation, yacht building, the manufacture of string and plucked musical instruments, modeling and applied art. For crafts and souvenirs, sheets with a thickness of 1.2 mm - 2.5 mm are most often used. Moreover, if a material with a thickness of 1.2 mm is considered a shortage, five-layer plywood with a thickness of 2.5 mm from a national manufacturer is widely represented.
BS-1 plywood is made of an odd number of layers of birch veneer glued with hot curing phenol-formaldehyde resin SFZh-3011. The minimum cross-section of this three-layer material is 3 mm. Popular plywood products from sheets with combined joints.
Of the special types of plywood, laminated, metallized, bakelized and shaped plywood can be distinguished. Modern industry every ten years produces new types of products, taking into account the latest achievements of science.
Plywood specifications
Strength and density of plywood
The strength of the plywood depends on the characteristics of the original wood and the bond strength. Strength is indirectly indicated by the density of the material. As a rule, the density of plywood ranges from 550-750 kg / m3, that is, it roughly corresponds to the density of wood or slightly exceeds it due to the higher density of the resin with which the veneer is held together.
In GOST, for ordinary plywood, different density levels are provided - from 300 to 1000 kg. Low specific gravity is possible when using light wood and "loose" veneer. Weighting occurs due to the use of denser resins and other features of the manufacture of a particular type of material. For example, bakelized plywood can have a density of up to 1200 kg / m3. It is also distinguished by the greatest strength.
The main, most important indicators of the strength of plywood are the ultimate strength in bending, the holding strength of the fasteners. The flexural strength of plywood grades FSF and FK is approximately 3-4 times lower than that of solid wood. FBS and FBV grades are superior in strength to the original wood. The resistance of screws to pulling out is quite high due to the pronounced layered structure (when installed in the face) and reaches 6-8 kg for each millimeter of fastener length.
Environmental friendliness
The ecological properties of plywood are characterized by their emission class. The best brand in this respect is FBA. There are no synthetic materials in it at all.
All other plywood grades are sources of volatile formaldehyde to one degree or another. For residential use, materials with emission class E1 and lower should be selected. It is interesting that in GOST only class E1 is provided for film faced plywood.
Biological resistance
Plywood is not insured against rot, blue (for conifers), mold. However, the resistance of plywood to biological damage and damage is higher than that of ordinary wood. This is due to the fact that the veneer is in direct contact with phenolic or urea resins, which partially function as an antiseptic. Coniferous veneer has a higher resistance due to the characteristics of wood. Bakelized plywood has the greatest durability.
In any case, you should take into account the operating conditions of the material and choose the right one for them or carry out additional antiseptic treatment.
Flammability
Plywood is a highly flammable material. This must be taken into account when applying it. It is possible to increase the fire resistance of structures and products from it by special processing. There is also a special, difficult-to-combustible type of plywood - FSF-TV.
Moisture resistance
The moisture resistance of the most popular FSF and FK varieties is demonstrated by the leaf delamination test, which is carried out after strong moisture. Before testing, FC plywood is soaked in water for 24 hours, the FSF brand is boiled for an hour, and upon agreement with the customer, within 6 hours. FBS and FBV brands are also boiled for an hour.
After water treatment and drying, the shear strength on the adhesive layer for different brands is:
- FC and PSF - from 2 to 10 kgf / cm2 (0.2-1 MPa);
- FBV - 14.7 kg / cm2;
- FBS - 17.6 kg / cm2.
FBS grade is suitable for tropical climates and other difficult conditions.
Insulating properties
Plywood can be used as part of external enclosing structures. In this application, its insulating qualities are taken into account.
Moisture permeability.
Any plywood is capable of absorbing water, and therefore is permeable to moisture. However, the moisture permeability of the material is capillary and depends on the type of impregnation. In any case, when one side is moistened, moisture will penetrate to the opposite side and can be transmitted to adjacent layers of the enclosing structure.
Thermal conductivity.
The thermal conductivity of plywood depends on its density and can range from 0.09 to 0.25 W / (m ∙ K). For the most used brands, the thermal conductivity of the material is close to that of wood.
Water vapor permeability.
Water vapor permeability is an important parameter that is taken into account when calculating multilayer structures that enclose rooms with an artificial microclimate.
The vapor permeability of plywood is approximately three times lower than the permeability of wood in the direction across the grain, and five times lower than the permeability of brickwork. In some cases, this property can be used for vapor barrier walls from the inside, and must be taken into account when using plywood for external cladding.
General information about plywood and rotary cut veneer
Plywood is a material obtained by gluing at least three sheets of peeled veneer with mutually perpendicular direction of fibers in adjacent layers
Construction of three-layer plywood sheet
When designing plywood, the following rules are observed:
- The plywood sheet should be symmetrical about the middle layer.
- The number of veneer layers in plywood is usually an odd number (3, 5, 7, 9, etc.), although 4-ply plywood is also produced in which the two inner layers have parallel grain direction.
Distinguish between equal-layer plywood (the thickness of all veneer sheets is the same) and uneven plywood. For uneven plywood, it is desirable to have a thicker, low quality veneer middle layer and thin, high quality veneer outer layers. The outer layers are divided into front and back, the quality of which determines the quality of the plywood sheet. Peeled veneer also has a front and a reverse side, while the quality of the front side of the veneer is higher than the reverse side, facing the center of the block during its peeling and having more cracks. When assembling a plywood sheet (package), the reverse side of the veneer must face the glue line.
Schematically, the construction of plywood is indicated with an indication of the thickness of the veneer, for example, the entry 1.15 x 2 + 2.20 denotes three-ply plywood with an outer layer thickness of 1.15 mm and an inner layer thickness of 2.2 mm.
Rotary cut veneer is not only a semi-finished product for the manufacture of plywood and plywood products, but also an independent commercial product, usually used in the furniture industry for facing panels and obtaining glued parts, as well as in a number of other industries, providing a more rational use of raw materials than when using sawn timber:
Specifications for rotary cut veneer are specified in GOST 99 - 96. The length of veneer sheets ranges from 0.8 to 2.5 m, width - from 0.15 to 2.5 m, veneer thicknesses are indicated in the table
Rows of rotary cut veneer thicknesses
|
Wood species |
Range of thicknesses, mm |
Limit deviation, mm |
|
Deciduous |
0,55; 0,75; 0,95; 1,15 |
± 0,05 |
|
1.25 - 4.0 in 0.25 steps |
± 0,10 |
|
|
Conifers |
1.2 - 4.0 in increments of 0.4 |
± 0,15 |
|
4.0 -.6.5 in 0.5 steps |
± 0,20 |
The quality of veneer sheets can be very varied due to the variety of wood defects and processing defects. According to the standard (effective from 1.01.98), the designation of varieties has undergone changes
Designation of grades of rotary cut veneer according to various standards
|
Hardwood |
Conifers |
|||
|
according to GOST 3916.1-96 |
For export plywood |
according to GOST 3916.1-89 |
according to GOST 3916.2-96 |
according to GOST 3916.2-89 |
|
E |
— |
A |
Ex |
— |
|
I |
B |
AB |
Ix |
AX |
|
II |
BB |
B |
IIx |
ABX |
|
III |
CP |
BB |
IIIx |
Bx |
|
IV |
C |
C |
IVx |
CX |
The moisture content of the commercial veneer should be 8 ± 2%. Veneer is made of birch, alder, maple, ash, elm, oak, beech, linden, aspen, poplar, spruce, pine, fir, cedar and larch wood. The following directions of use of veneer grades of external surfaces of plywood are recommended
Recommended directions of use of rotary cut veneer of various grades
|
Variety |
Direction of use |
| E, Ex, I, Ix | For front surfaces under a transparent finish |
| II, IIx | For surfaces of various purposes for all types of finishes |
| III, IIIx | For product surfaces predominantly for structural purposes for an opaque finish |
| IV, IVx | No requirements for the appearance of products |
Grade of material
The strength of the material is also influenced by the dirtiness of the wood. In the manufacture of plywood, veneer is used in different grades - from elite to grade 4. It is clear that grade 1 is used for thin aviation plywood, and all veneer layers are classified as grade 1.

FC as a material where strength is not so critical, and there is no need to achieve such a great fineness as a sheet of 1 mm or 1.2 mm, grade 1 can only be used for the front layer, while grade 3 or 4. The product is marked as FSF 1/4. This means that premium veneer is used for the top layer and grade 4 for the bottom. In the photo - plywood 3 mm grade 1.
In addition, grinding information is indicated in the marking.
- NSh - unpolished.
- Ш1 - ground on one side.
- Ш2 - material ground on both sides. This option is required for modeling.
Plywood marking
Plywood, like any other building material, has markings based on its various properties.
The following parameters are used for marking:
- by type of adhesive
- for processing the top layer
- by formaldehyde content
- decorative plywood marking
Let us examine these designations in more detail.
By type of adhesive
The moisture resistance of plywood is determined primarily by the composition of the adhesive. Depending on it, the following brands of plywood are distinguished.
| Designation | Adhesive composition | Moisture resistance | Application |
| FC | Urea adhesive with the addition of formaldehyde resins | Yes | It can be used both indoors and outdoors. belongs to a high class of environmental friendliness. |
| FSF | Phenol formaldehyde adhesive | Yes | It can only be used outdoors, since the binding components are hazardous to health. It is used for the manufacture of film faced plywood, which is used in the construction of external structures. |
| FBA | Albumocasein glue | No | It can be used indoors. |
| FB | Bakelite varnish | Yes | It can be used in any climatic conditions and at maximum humidity. Withstands exposure to sea water. |
| BS | Alcohol-based bakelite glue | Yes | The characteristics are even better than those of "FB". It is often used in aircraft and shipbuilding, therefore it is also called "aviation". |
| BV | Bakelite composition | No | Since water-soluble bakelite is used in the production, there is no moisture resistance of plywood. Nevertheless, plywood is quite durable. |
By processing the top layer
An important parameter of plywood is the quality of the plywood top layer and its processing. A special label has been defined for this parameter.
| Designation | Description |
| Ш1 | The veneer is sanded on only one side of the plywood |
| W2 | Veneer sanded on both sides of the plywood |
| NSh | The veneer of the top layers of plywood is not sanded |
Formaldehyde content
Since formaldehyde is very harmful to human health, the amount contained in plywood is important and affects the environmental friendliness of the material.
| Designation | Formaldehyde content in 100 g of material |
| E1 | does not reach 10 mg |
| E2 | from 10 to 30 mg |
| E3 | from 30 to 60 mg |
Decorative plywood marking
Decorative plywood (DF) can be faced with various film coatings and paper, which give it a unique appearance and additional enhanced characteristics. The following brands are distinguished.
| Designation | Facing coatings | Resins |
| DF-1 | Transparent, does not hide the texture of natural wood | Urea-melamine-maldehyde |
| DF-2 | Opaque with decorative paper to simulate the texture of precious woods. Any drawing is possible. | |
| DF-3 | Increased water resistance. Transparent, does not hide the texture of natural wood | Melamine-maldehyde |
| DF-4 | Increased water resistance. Opaque with decorative paper that imitates the texture of precious woods. Any drawing is possible. |
Peculiarities
There are many options for such a material, they all differ in their width, coating and manufacturing features.
In order to choose the optimal product, you need to pay close attention to the study of the characteristics. Plywood is an ordinary sheet that is created using wood
In turn, it goes through several stages of processing, which gives the product its unique properties.
The process of gluing the layers is due to the use of special compounds, which are usually obtained on the basis of resins. The result is a lightweight material that can also boast of its resistance to temperature extremes.
Among the main advantages of such a product are the following.
- Resistant to moisture, so the material can even be used to decorate a bathroom. This can be achieved due to the fact that upon contact with water, the plywood sheets do not delaminate and do not lose their shape.
- Ease of processing and installation. This material is famous for its strength, so you can use any tools for processing without fear. Plywood can be easily cut, sawn or drilled, which favorably distinguishes it from the background of other materials.
- The ability to combine with other materials. It should be noted that film faced plywood is very often used as an additional material, therefore it is perfect for finishing the ceiling, floor or roof. Most experts use this plywood in combination with natural wood.
- Huge scope of application. Film faced plywood can boast of its unique performance characteristics, which makes it possible to use it in the process of finishing works, in the production of furniture and decorations.
A distinctive feature of moisture-resistant film faced plywood is that it takes much longer to process during the manufacturing process, and is also covered with thicker paper. This paper is impregnated with a special composition, which makes the finished product durable and allows it not to lose its properties for a long time. In addition, it provides water resistance.
Film faced plywood differs from other materials in that it is almost not susceptible to temperature changes, therefore it can be used even in a bath. The special layer also protects against the effects of cleaning agents, including aggressive abrasives. Another feature of such plywood is that it contains a minimum amount of phenol. As a result, a more elastic and durable material is obtained, which also has a varnished protective polymer layer.
Bakelized plywood
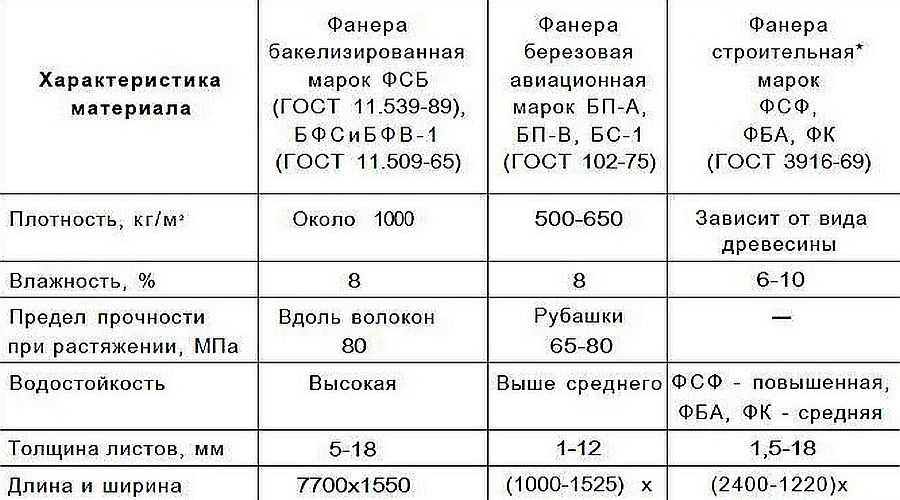
Bakelized plywood is called high-pressure glued birch veneer, pre-impregnated with phenolic (bakelite) resin. The main differences between bakelized plywood and general-purpose plywood are its higher density (up to 1200 kg / m3), longer sheet length and a darker color - usually a red-brown hue. Plywood is a high strength, resilient, waterproof and wear resistant material that can compete with many materials, including low alloy steels.Bakelized plywood can work for 10-15 years at temperatures from -50 to +50 0С, as well as in water and in tropical climates.
Buckfaner is used in the automotive industry for flooring in buses, trolleybuses, trams, for the manufacture of trailers, containers, trailers, bodies, etc .; in shipbuilding as a cladding material for boats, yachts, small ships; in construction as a formwork material, in the manufacture of warehouses, awnings, partitions, counters; in hydraulic engineering, as well as in mechanical engineering as a structural material.
The following plywood grades are produced:
- FBS - for the manufacture of structures in machine, auto and shipbuilding, in construction, operating in atmospheric conditions. An alcohol-soluble resin is used. For the inner layers, it is allowed to use not impregnation, but the application of resin to the veneer,
- FBV - for the manufacture of internal structures in mechanical engineering and construction. A water-soluble phenolic resin is used as a binder.
The dimensions of plywood are 7700, 5700, 5600, 4900, 4400 and 1500 mm in length, and 1550, 1500 and 1250 mm in width; a range of thicknesses - 5, 7, 10, 12, 14, 16 and 18 mm. For manufacturing, peeled birch veneer of grades B and BB is used. For bakelized plywood, the standard regulates not only the ultimate shear strength along the adhesive layer after boiling the samples in water, but also the tensile and bending strengths (see Chapter 7). According to these indicators, plywood of the FBS brand can be attributed to the highest or first quality category. When marking products, a paper label is glued to each plywood sheet with an indication of the manufacturer, brand, sheet thickness, press-fit numbers and GOST 11539 - 83.
Bakelized plywood of the FBS-S brand (TU OP 13-5747575-16-87) is produced especially for formwork in industrial and civil construction. The arrangement of fibers in adjacent layers is mutually perpendicular, plywood thickness is 10-12 mm, length - up to 5600 mm. When assembling, veneer sheets with applied resin and sheets without resin are alternated, which reduces the consumption of glue by 1.5 - 2 times. The turnover of new material is up to 100 times.
Material features
The difference between the types of products, depending on the species of wood, concerns the facing layers: in deciduous species, the outer sheet is made of birch, aspen or beech, and the inner sheet is made of spruce, larch or pine. If both the veneer and the core are made of resinous wood, the entire material is considered coniferous.
Most of the quality parameters of plywood, including the type of wood, depend on the characteristics of the outer layers. These include:
- Grade - determined by the appearance of the front layer and back. The variety depends on the number of decorative defects per 1 m2 of area;
- The type of processing is non-sanded, with a sanded front surface or sanded on both sides, indicated by the abbreviation: nsh, sh1, sh2.

The grade of plywood is determined by the degree of its moisture resistance:
- waterproof - with sheets glued with phenol-formaldehyde resins (FSF);
- glued moisture resistant, the sheets of which are connected using farbamide-formaldehyde resins.
General purpose plywood
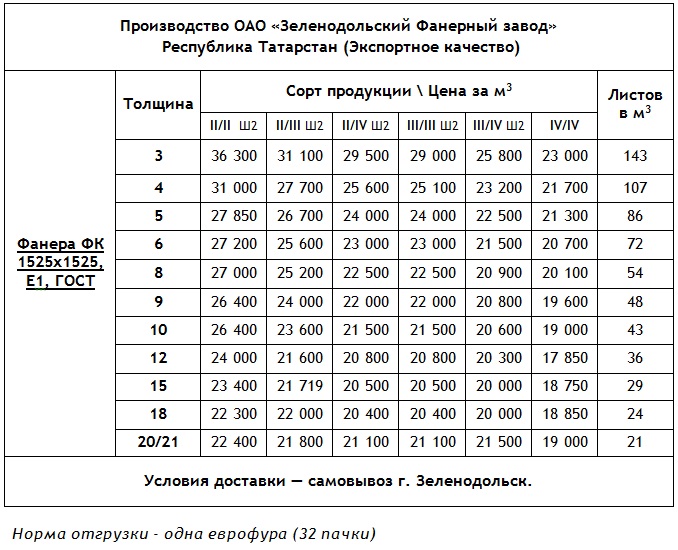
General-purpose plywood is called plywood that does not belong to special types - aviation, decorative, bakelized. GOST 30427 - 96 establishes general rules for the classification of such plywood by appearance. Depending on the appearance, plywood is divided into grades E (elite), I, II, III, IV for hardwood and grades Ex, Ix, IIx, IIIx, IVx for softwood. When designating a variety, first indicate the variety of the front layer, then - the reverse layer. Such combinations are possible
General Purpose Plywood Grade Options
|
For hardwood |
For conifers |
||||||||
|
E / E |
Ex / Ex |
||||||||
|
E / I |
I / I |
Ex / Ix |
Ix / Ix |
||||||
|
E / II |
I / II |
II / II |
Ex / IIx |
Ix / IIx |
IIx / IIx |
||||
|
E / III |
I / III |
II / III |
III / III |
Ex / IIIx |
Ix / IIIx |
IIx / IIIx |
IIIx / IIIx |
||
|
I / IV |
II / IV |
III / IV |
IV / IV |
Ix / IVx |
IIx / IVx |
IIIx / IVx |
IVx / IVx |
The standard indicates wood defects (32 items in total) and processing defects (23 varieties) that must be taken into account when assessing the quality of general-purpose plywood. The veneer grades of the inner layers are not regulated, but it is indicated that possible wood defects and processing defects should not affect the performance properties of the product.
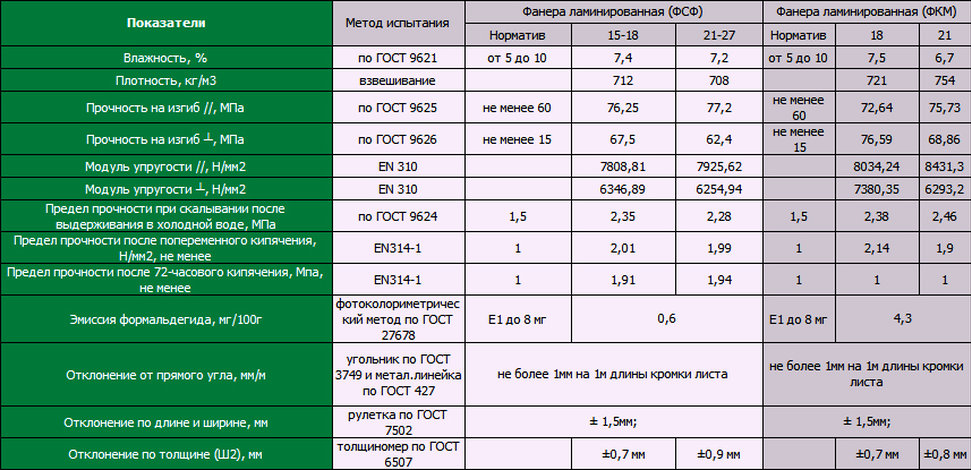
GOST 3916.1 - 96 and 3916.2 - 96 establish technical requirements for general-purpose plywood with outer layers of deciduous and coniferous wood, respectively.According to the degree of water resistance, plywood can be of the FSF grade (increased water resistance) and the FC grade (water resistant). Previously produced plywood based on protein adhesives of the FBA brand is not provided for by the new standards. According to the degree of surface treatment, plywood is distinguished unpolished (NSh), sanded on one side (1SH) and sanded on both sides (2SH). In addition, for all materials, it is mandatory to indicate the emission class of free formaldehyde E1 or E2 (respectively, up to 10 or from 10 to 30 mg / 100 g of absolutely dry product)
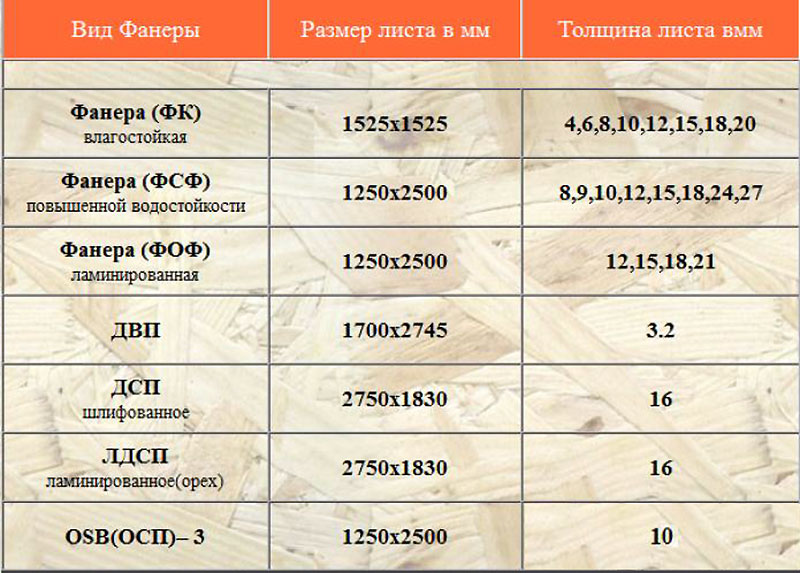
Standard product sizes are shown in the table
Dimensions of plywood sheets, mm
|
Length (width) of plywood sheets |
Limit deviation |
|
1200, 1220, 1250 |
± 3,0 |
|
1500, 1525, 1800, 1830, 2100, 2135, 2440, 2500 |
± 4,0 |
|
2700, 2745, 3050, 3600, 3660 |
± 5,0 |
Thickness (mm) and ply of general purpose plywood
|
Nominal thickness |
Layering of plywood, not less |
Sanded plywood |
Unsanded plywood |
|||
|
Deciduous |
Coniferous |
Limit deviation |
Difference in thickness |
Limit deviation |
Thickness difference |
|
|
3 |
3 |
— |
+0.3 / -0.4 |
0.6 |
+0.4 / -0.3 |
0.6 |
|
4 |
3 |
3 |
+0.3 / -0.5 |
0.6 |
+0.8 / -0.4 |
1.0 |
|
6.5 |
5 |
3 |
+0.4 / -0.5 |
0.6 |
-0.9 / -0.4 |
1.0 |
|
9 |
7 |
5 |
+0.4 / -0.6 |
0.6 |
+ 1.0 / -0.5 |
1.0 |
|
12 |
9 |
5 |
+0.5 / -0.7 |
0.6 |
+1.1 /-0.6 |
1.0 |
|
15 |
11 |
7 |
+0.6 / -0.8 |
0.6 |
+1.2 / -0,7 |
1.5 |
|
18 |
13 |
9 |
+0.7 / -0.9 |
0.6 |
+1.3 / -0,8 |
1.5 |
|
21 |
15 |
9 |
+0.8 / -1.0 |
0.6 |
+1.4 / -0.9 |
1.5 |
|
24 |
17 |
11 |
+0.9 / -1.1 |
0.6 |
+1.5 / -1.0 |
1.5 |
|
27 |
19 |
11 |
+1.0 / -1.2 |
1.0 |
+1.6 / -1.1 |
2.0 |
|
30 |
21 |
13 |
+1.1 / -1.3 |
1.0 |
+1.7 / -1,2 |
2.0 |
It is allowed to make plywood of other sizes, thicknesses and layers according to the terms of the contract. For non-standard thicknesses, the maximum deviations are:
for sanded plywood:
for unpolished:
where Sf - plywood thickness, mm.
Plywood is considered to be made from the same type of material from which its outer layers are made. The plywood symbol contains the name of the product, the brand, the combination of external grades of veneer, the emission class, the type of surface treatment, the dimensions and the designation of the standard. For example, the designation Birch / birch plywood FC, II / III, E1, Ш2, 2440 x 1220 x 12 GOST 3916.1-96 refers to birch plywood with birch inner layers, grade FC with face layer grade II and reverse layer grade III, emission class E1, ground on both sides, 2440 mm long, 1220 mm wide, 12 mm thick.
The new standards also limit the maximum permissible veneer thickness. For hardwood plywood, the outer layers should be no thicker than 3.5 mm and the inner layers should be 4 mm thick. For softwood plywood, the thickness of the outer and inner layers should not exceed 6.5 mm.
The quality of plywood is also assessed by the ultimate shear strength, static bending and tensile strength of samples cut from the finished product. For FSF plywood, tests are carried out after boiling in water for 1 hour, for FC - after soaking in water for 24 hours. The normalized strength indicators depend on the type of wood. The moisture content of FSF and FK plywood should be from 5 to 10%. Plywood is counted both in m3 and m2. On the plywood package, the name of the manufacturer, its trademark and the number of plywood sheets in the package are additionally indicated.
Specifications
BP combines unique properties:
- strength - one might even say super strength;
- moisture resistance - or rather, water resistance, parts from the power supply unit can be used under water;
- flexibility - a sheet of 1 mm can be bent at an angle of 180 degrees or more;
- resistance to aggressive environments - products withstand both urban smog and tropical climates;
- products made of 1 mm BP do not rot and are not susceptible to fungi, even in high humidity conditions.

Application
Plywood FC 1 mm is not provided for by GOST, as well as 1.2 mm or 1.5 mm. Its minimum thickness starts from 3 mm. The most popular is the parameter of 10-12 mm, suitable for a variety of substrates, as a finishing material, and so on.
A power supply unit in 1mm or 1.2mm is distinguished by its minimum weight and exceptional strength with such parameters. This type of plywood was used in aircraft construction until it was replaced by aluminum alloys. Today BP of 1 mm is the main material for aircraft modeling. Its aerodynamic load capacity is excellent.

- At the same time, the material is distinguished by high moisture resistance, so it has become a "favorite" in ship modeling as well.
- A 1 mm power supply unit is also used in furniture making - in the manufacture of units where there is an increased load.
- Architectural projects are often also erected from 1 mm plywood: the flexibility and thinness of the sheet allows you to reproduce exactly all the architectural features of the future building, but in miniature.
- Plywood 1.5 mm and 1 mm is used in the manufacture of musical instruments. In this case, only “pure” material is suitable, and not composite with plastic, since the latter's admixture has a fatal effect on the sound.
It should be noted that the technology for making real delta wood, which was used in aircraft construction, has been lost. Therefore, for example, the Mi-10 helicopter and the like, where the propellers were made from this material, were discontinued.