1 What types of reinforcement are there?
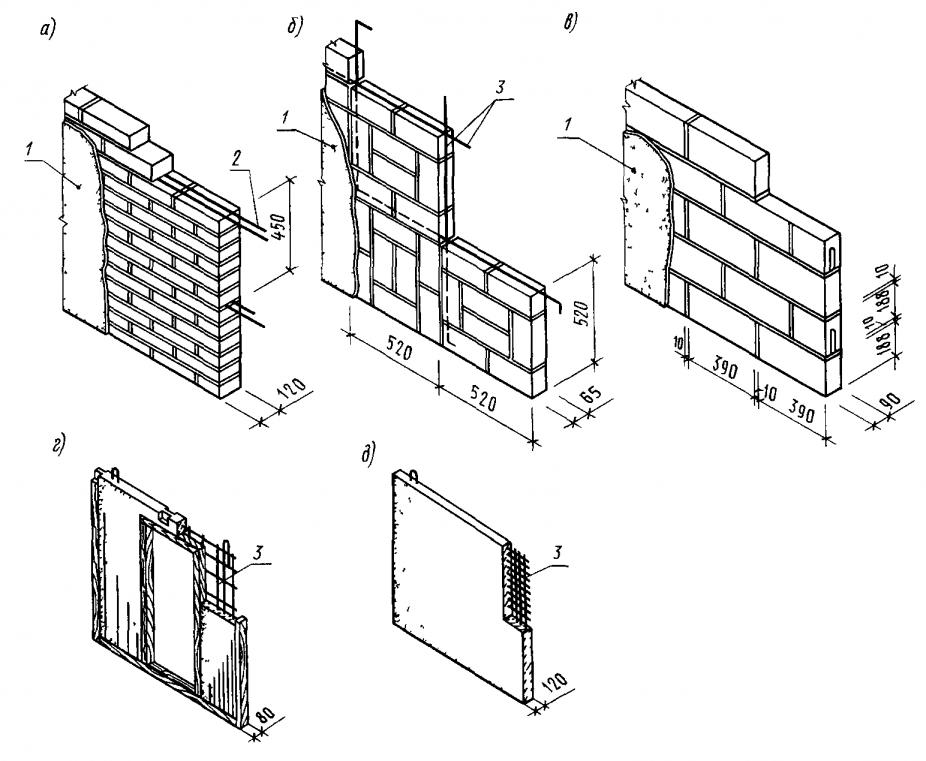
Reinforcement can be used for laying both horizontal and vertical elements, it is especially important for laying in half-brick. It depends on the direction of the load itself, which acts completely on the entire building structure.
After the completion of the work, an appropriate act is drawn up to carry out the work.
So, the reinforcement is of the following types:
- transverse;
- vertical;
- longitudinal.
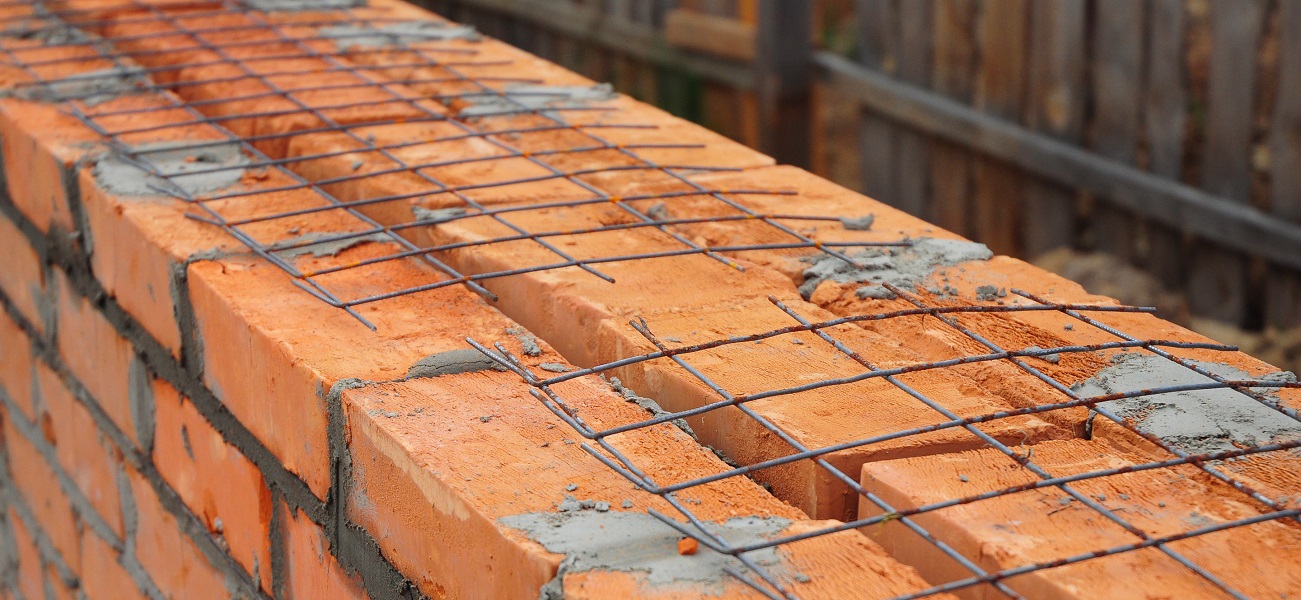
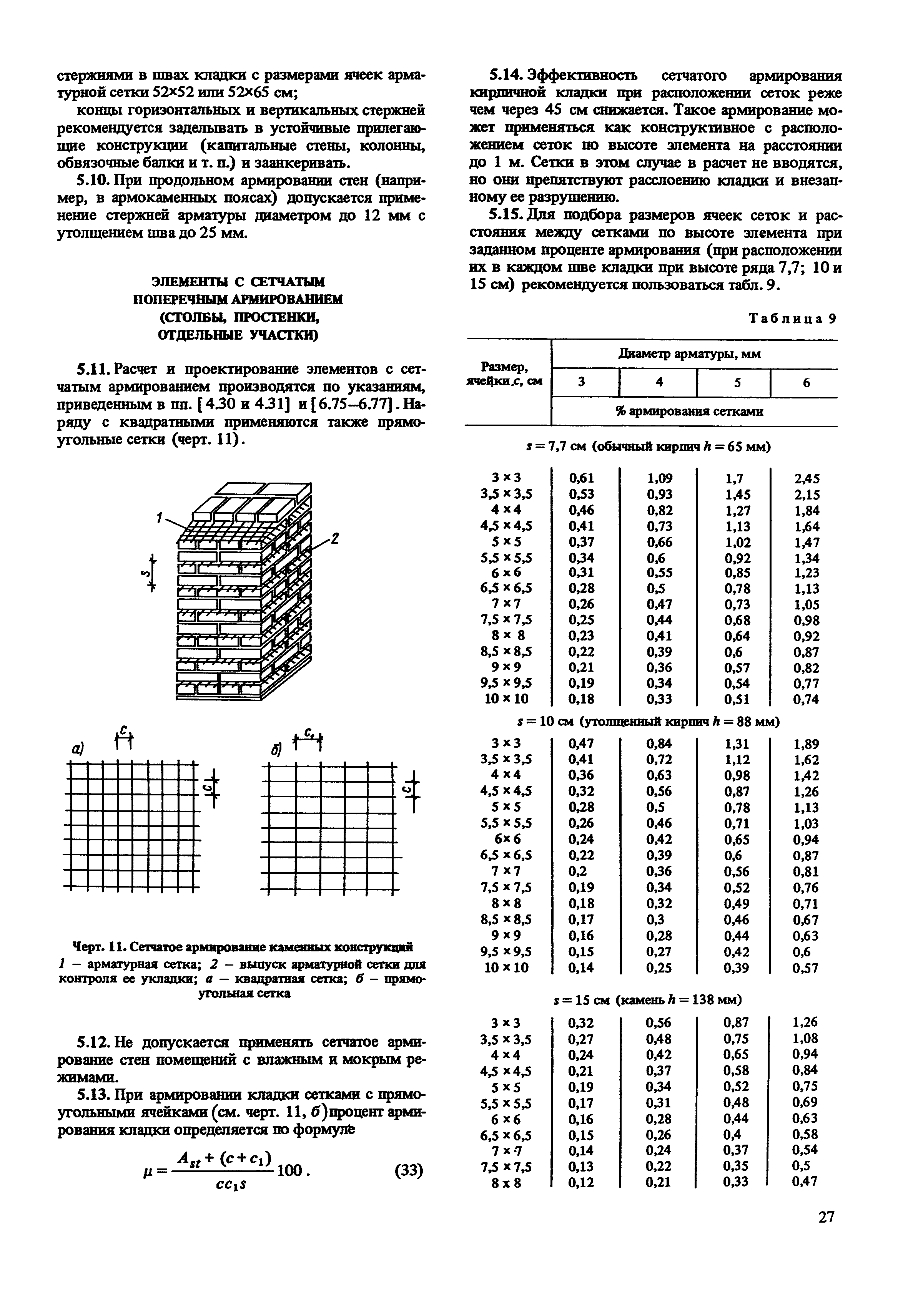
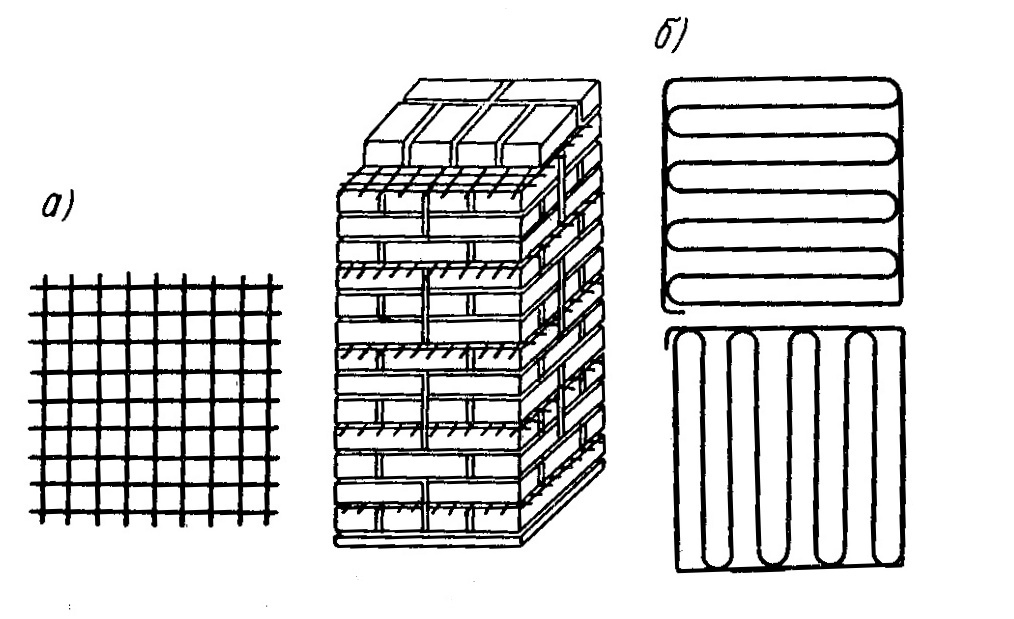
The first type involves the use of a steel post or mesh. The rods are connected to the mesh by welding, with an indent (step) of 30-120 mm. In seams that are adjacent, in no case should any part of the post be inserted.
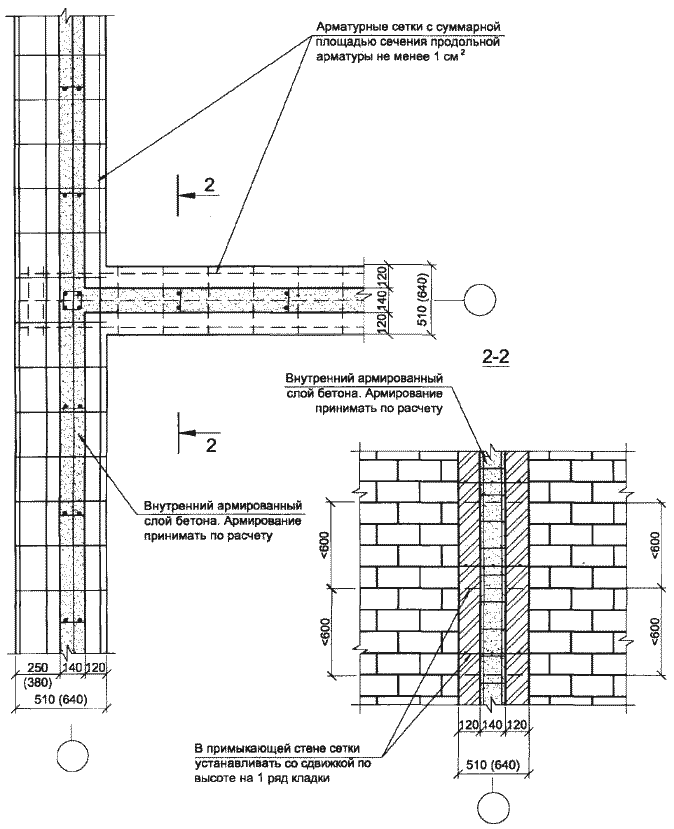
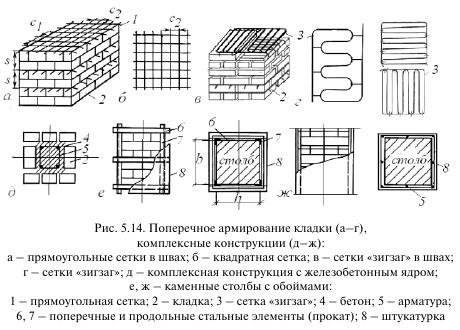
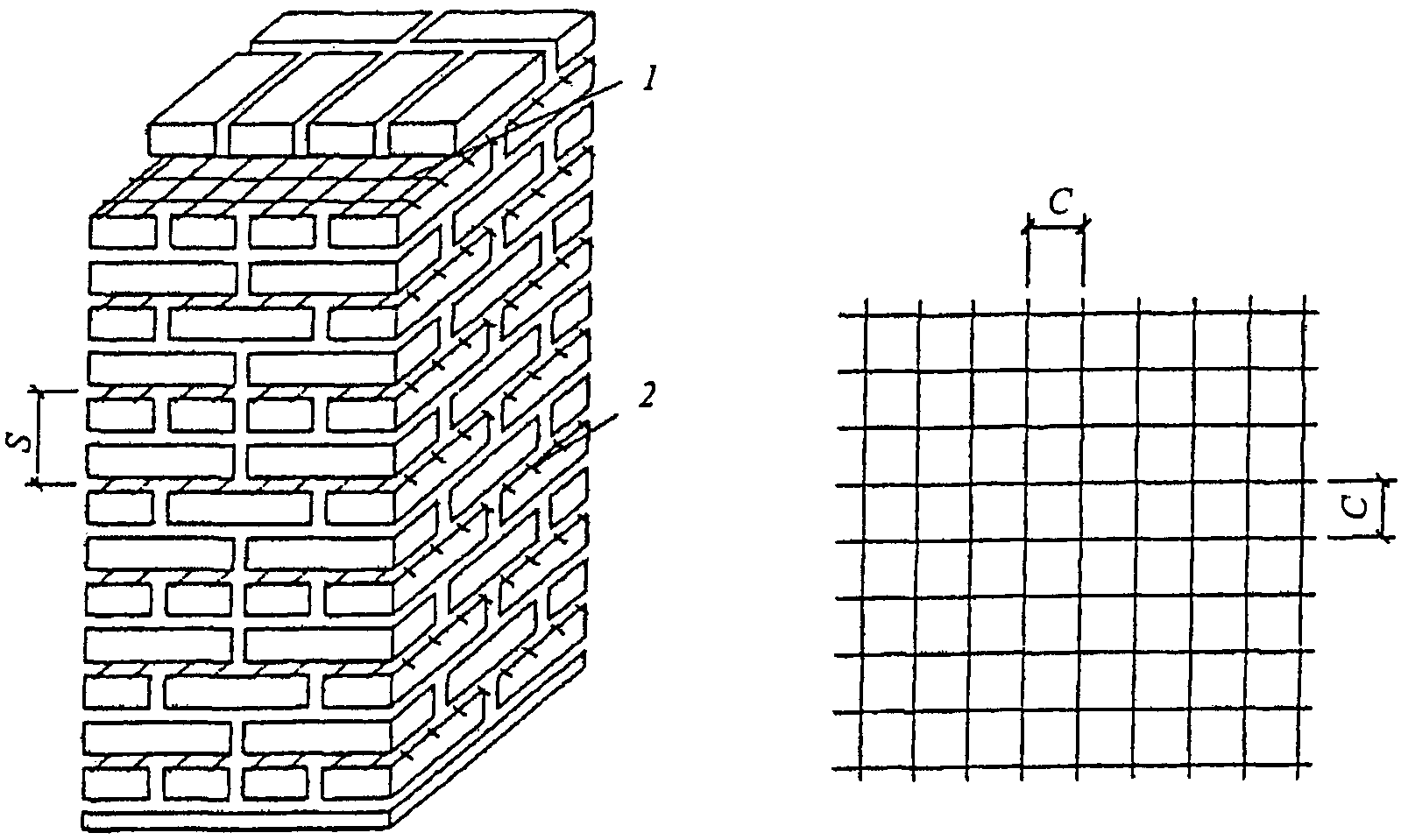
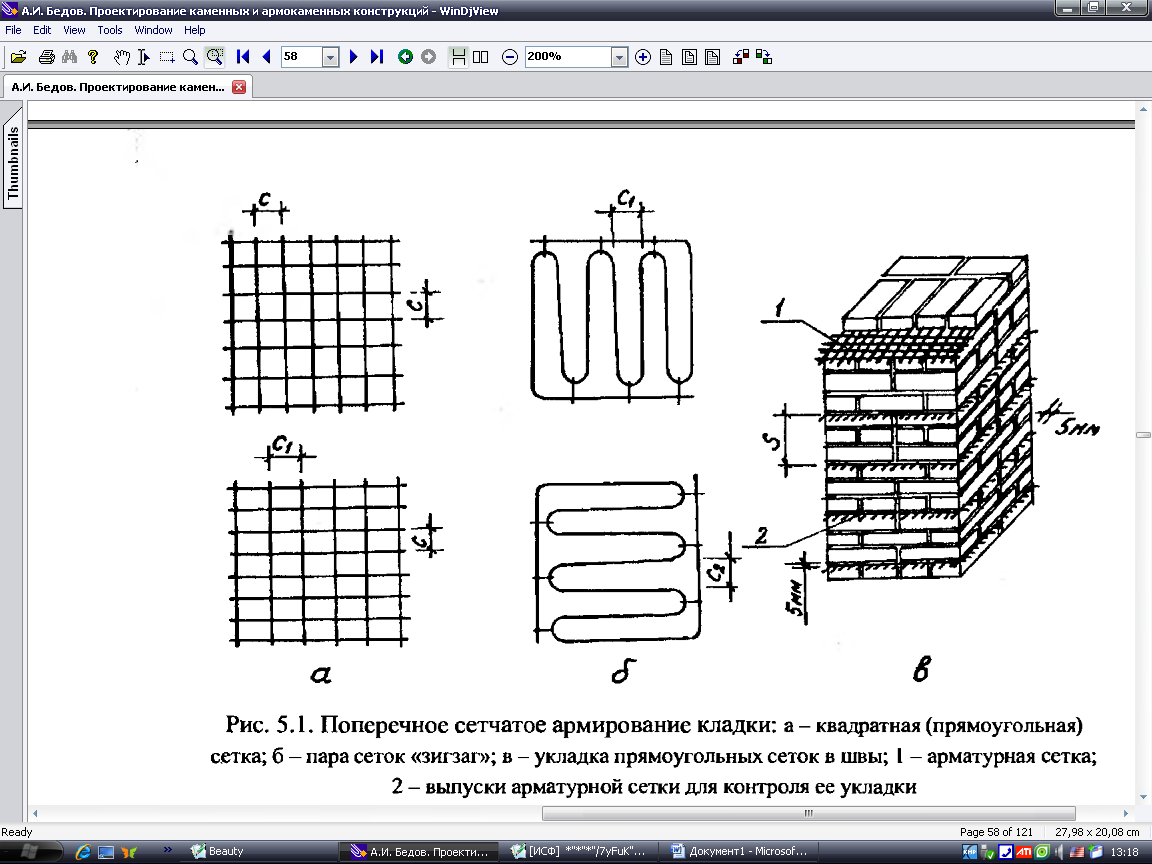
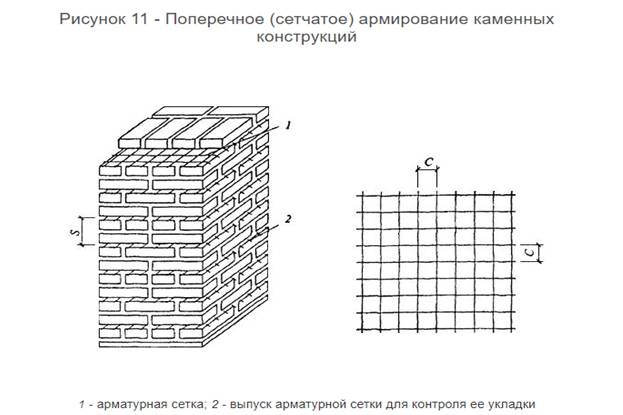
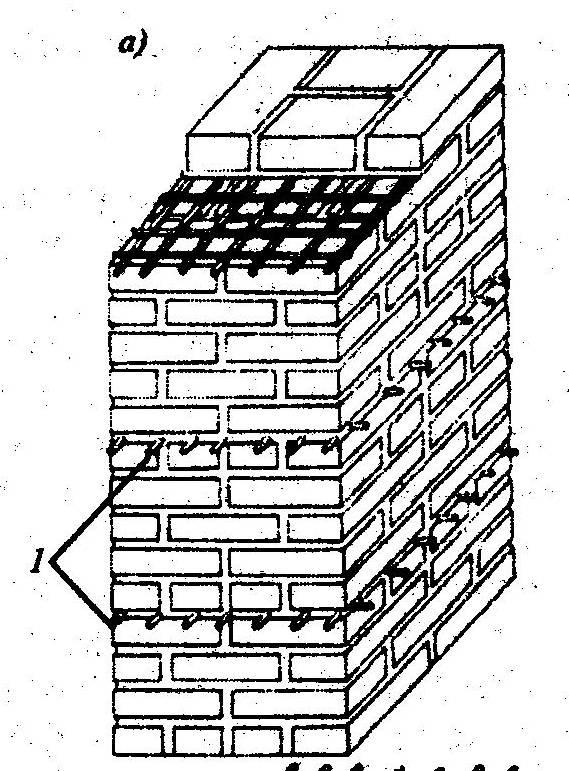
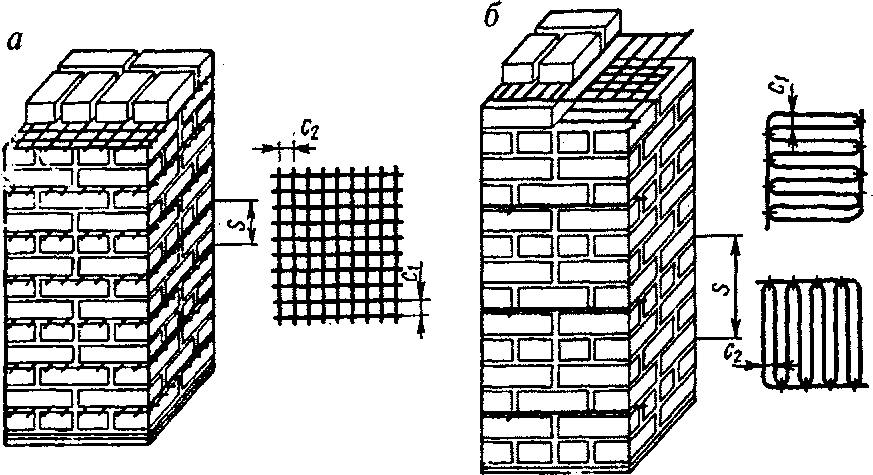
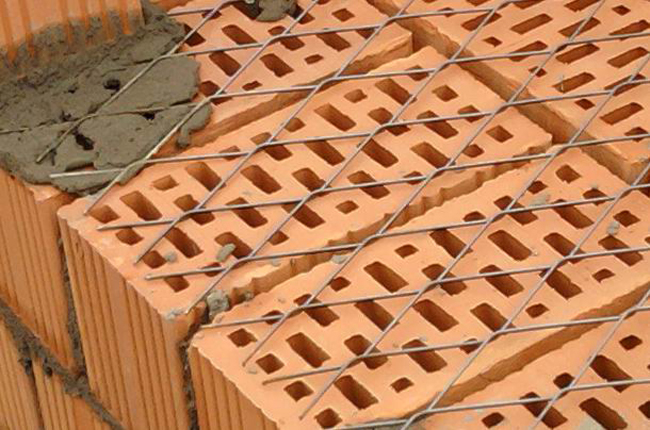
Reinforcing mesh is used to strengthen walls, pillars, half-brick partitions, columns and piers, it can be zigzag, rectangular and square. In order to avoid corrosion, the mesh is installed and immersed in the solution at least 2 mm from all sides. In this case, the seam size will be 14 mm thick.

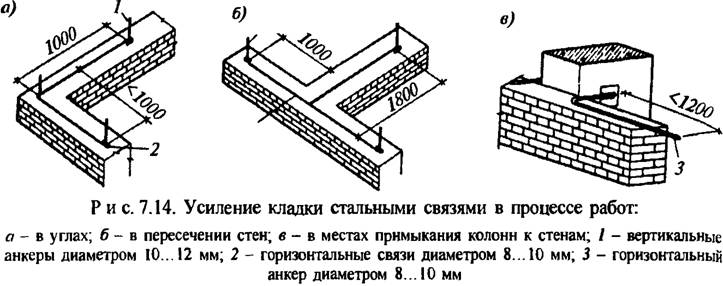
Cross reinforcement of brickwork
The mesh is often inserted through every fifth row of masonry in a half-brick. However, if you chose a rectangular mesh, then it should be laid in four rows. Zigzag meshes are usually made of steel, and each mesh is 50 to 120 mm in size. They are usually laid in pairs every two rows, observing the conditions for the perpendicularity of the direction of the reinforcement.
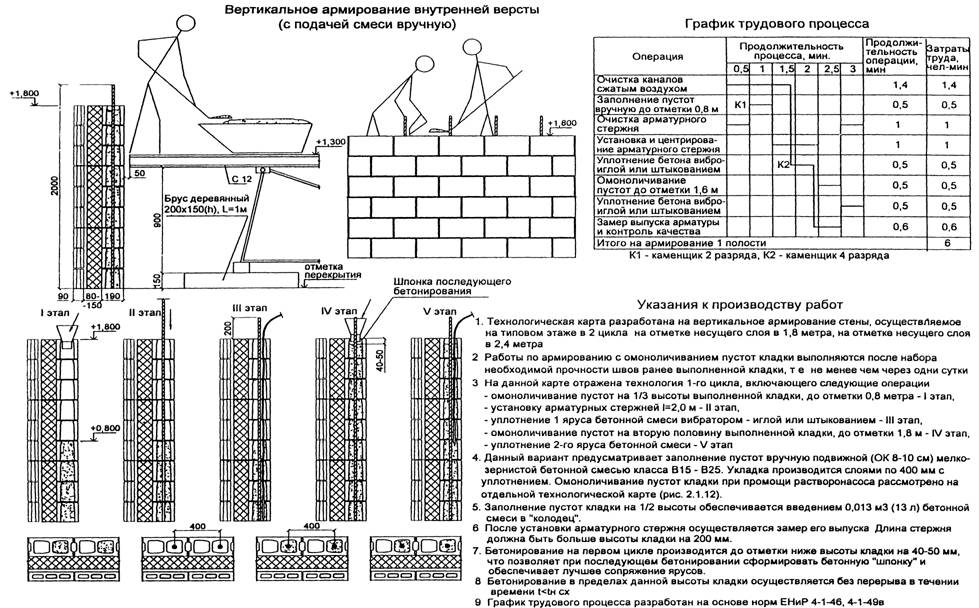
Vertical reinforcement - reinforcement bars are inserted vertically at the base of the brickwork in a half-brick along walls, partitions, pillars or other structures. On average, the diameter of the reinforcement is 10-15 mm, of course, if the building is larger, then the indicator can go off scale and over 30 mm.
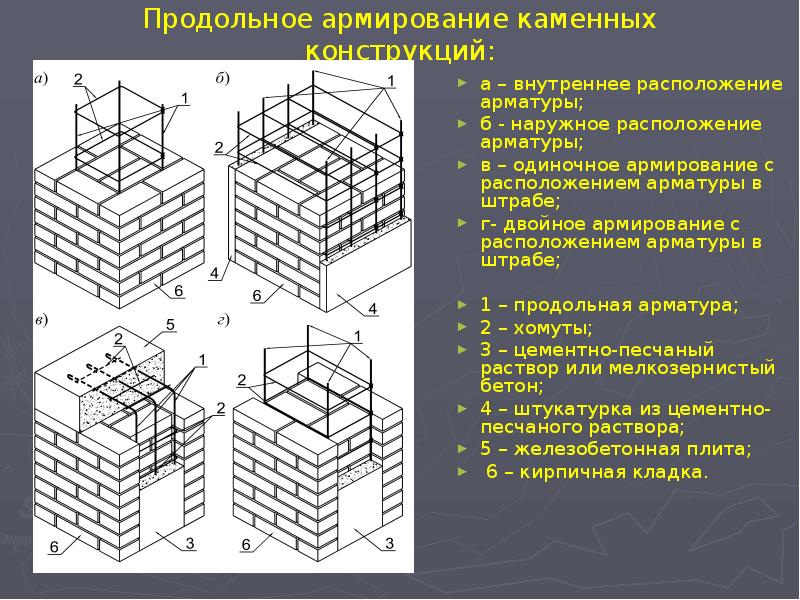
Longitudinal reinforcement can be: external and internal. The use of one type or another depends on which side of the wall the elements will be located on. Most often for longitudinal mounting with a pillar.
Here it is also necessary to observe an indent with a thickness of up to 120 mm, during the installation of reinforcing elements in the facing masonry. This type is used to strengthen the strength of partitions or brick walls at bends. Upon completion, a corresponding act of work is drawn up.
1.1 Recommendations for strengthening the facade
To make a wall in a half-brick more solid and durable, you need to use continuous reinforcement with reinforcement, starting from the bottom to the top at intervals. In the event that the basement is built of brick, then the strengthening must be started with it. When the first row of the foundation (you can read about the calculation of the reinforcement for the foundation separately) is ready, then you should install the finished structure from the reinforcing partitions on top. In the same way, the next five rows are strengthened.
Stages of facade plastering on reinforced insulation
After that, six rows are laid with bricks without reinforcement, and then the strengthening procedure is repeated again
It is very important to follow the sequence
If the pediment is less than 8 m, then the insert is performed after six rows, but if the indicator is higher, then the strengthening of the facing part should be carried out every three rows. Upon completion, a corresponding act of work is drawn up.
Selecting a mesh for a specific width
Here, they rely on the width that the wall has to be finished.
Depending on the specific indicators in a particular case, the results will be as follows:
- When laying two and a half bricks and a width of 630 millimeters, a meter roll of 50 by 50 by 2 mesh is sufficient.Then it will be easier to cut the sheets to the required sizes.
- Two brick masonry, 500 mm thick. The mesh will also be 500mm thick.
- One and a half bricks with a width of 380 mm. The mesh is purchased with a width of 500 millimeters. The partition is made from the pieces that remain after cutting.
- Single-brick masonry, with an indicator of 250 millimeters. The thickness of the mesh should be within the same range.
- Laying in half a brick with a width of 120 mm - then the mesh should have a thickness of 250 millimeters. It is simply cut in half.
Recommended reading:
How is reinforced brickwork done?
- Principles of work
- Brick wall: transverse reinforcement type
- Mesh for transverse reinforcement
- Rod reinforcement of the transverse type
- Longitudinal reinforcement
- Summarizing
In the construction of any structures, the strength characteristics are the most important. Sometimes, huge loads affect the load-bearing masonry of walls and columns, including brick ones. Safety requirements for the operation of such structures lead to the need to strengthen these structural elements. Reinforced brickwork is one of the common ways to increase the strength of buildings.
Types of brickwork.
The technology of reinforcing the structure has been perfected for centuries. In particular, the question: how to reinforce brickwork was decided by our ancestors. The use of this technique is fully justified for critical structures, which are subject to increased strength requirements. In general, the reinforced masonry of the walls, although it complicates the structure, fully fulfills its purpose.
Reinforcement of brickwork: step by step instructions
Masonry mortar
Facade strengthening rules
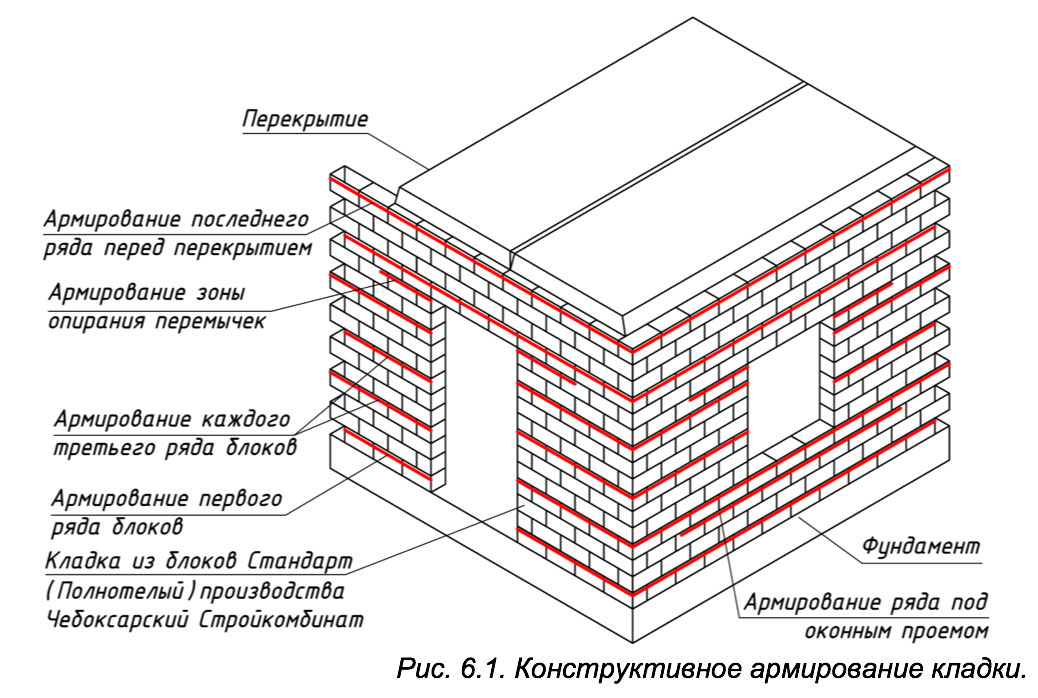
In order to build the most reliable and durable walls, the reinforcement of solid brickwork should be performed from its very bottom. If the basement is supposed to be assembled from brick, this procedure should be carried out in relation to it. Having laid out the first row of bricks on the foundation strip, it is laid on top with ready-made fittings. Thus, the first five rows are strengthened. Next, the wall is raised six rows in the usual manner and the reinforcement is laid again. Then the procedure is repeated.
Important: When assembling a brick pediment with a height of less than 8m, the insert is carried out - as in the construction of walls - every 6 rows. In the pediment, every three rows are laid above
Strengthening openings and problem areas
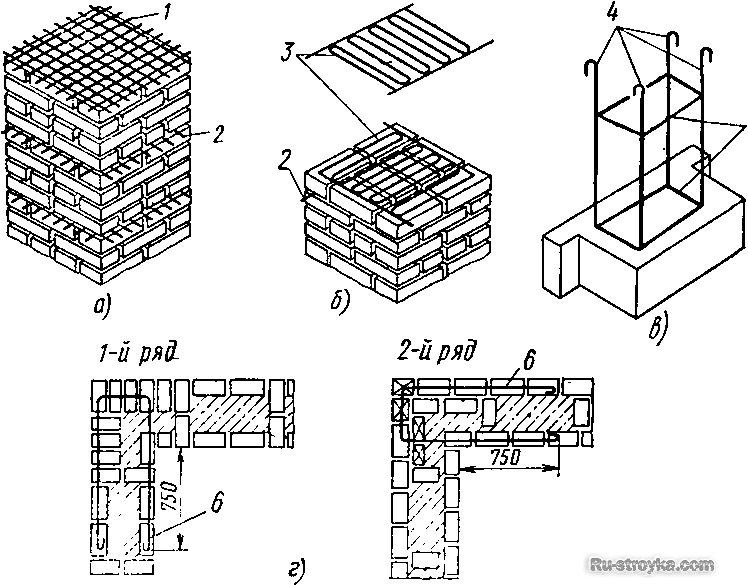
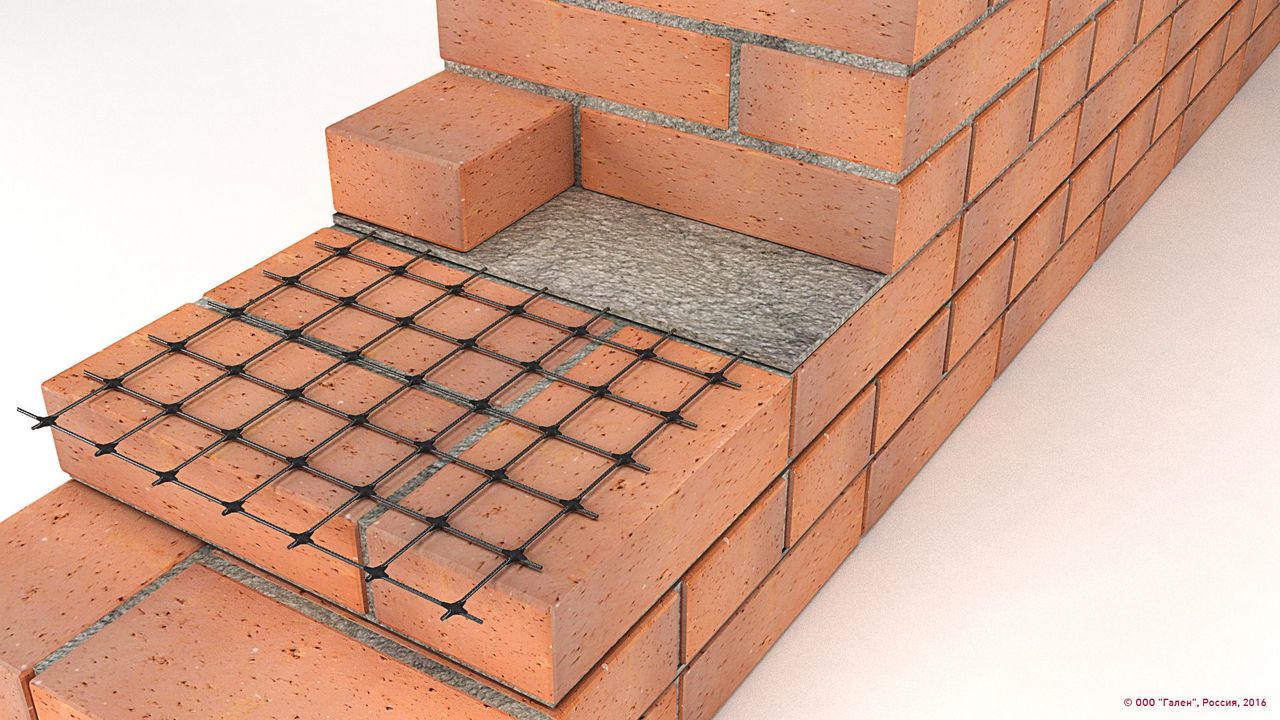
Very often cracks appear in the area of openings. The fact is that a rather serious tension arises in the masonry in this place. It can be compensated by laying fittings. For a doorway, this operation is performed in two rows directly above it. Windows are also reinforced in two rows, but above and below.
A problem area can also be areas of abutment of parts of the house of different heights. For example, where the project envisages joining an extension to one floor to the main structure of two floors. Splits can appear at the junction due to the difference in vertical pressure. In this case, the reinforcement of the brickwork is carried out in the last three rows of the masonry of the low part with its planting into the wall of a higher building so that the center of the grid is horizontally located at the junction.
Laying without bandaging the seams
Sometimes the enclosing structures of buildings are laid out without bandaging the seams. These houses look pretty impressive and stylish. However, the masonry must be reinforced without fail. The mesh is laid in every third row.
Tip: All of the above recommendations apply to Morfor valves. If you will be strengthening with material from another manufacturer, you should first read the instructions for it. The rules for installing other fittings may be different. For example, less reliable material can be used every 4 rows.
Rebar laying rules
When reinforcing brickwork, it is worth observing some standards. In this case, the walls built by your own hands will be as reliable as possible. So:
- The mesh is completely recessed into the solution.
- If you are using ferrous metal fittings, they should be painted before installation.
- The seams should be at least 4mm thicker than the rods.
- When erecting a building, it is allowed to use only reinforcement of the same diameter and other parameters.
- The mesh should be of such a width that the ends of its elements protrude a couple of millimeters on one of the walls of the wall.
- If the mesh will be made independently, its individual elements are tied with a knitting wire. Welding is not recommended.
Sometimes the owners of suburban areas have a question about how to make vertical reinforcement of brickwork. This procedure is usually performed only in seismically hazardous regions. The locations of the rods in this case are determined specifically for this particular project.
Reinforcement methods
In the technology of construction of load-bearing walls and internal partitions, reinforcement is laid in various planes in order to strengthen the critical places of masonry of walls, columns, window and door openings, arched ceilings.
Horizontal and vertical wall reinforcement is applied depending on the nature of the acting loads. In a rather fragile hardened mass of cement mortar, strong elements are laid along the entire length of the masonry. They evenly distribute local loads over the entire structure, preventing cracks from occurring in places of tension.
Taking into account the possible directions of action of critical forces, the reinforcement of brick walls is carried out in 2 planes:
- transverse (deep into the seam);
- longitudinal (along the surface or inside the masonry).
Additionally, the longitudinal reinforcement is divided according to the method of orientation of the element relative to the surface of the walls into vertical and horizontal arrangement.
In certain areas of the masonry, it is important to carry out the correct reinforcement to maintain the integrity of the structure. Which method to choose in a particular case and how to place the reinforcing belts in the walls, through how many rows to lay them, depends on the consideration in the project not only of static weight loads, but also of wind, snow, and seismic components
Which method to choose in a particular case and how to place the reinforcing belts in the walls, through how many rows to lay them, depends on the consideration in the project not only of static weight loads, but also of wind, snow, and seismic components.
Compliance with the rules for the construction of walls and partitions refers to the creation of conditions for the safe operation of buildings and structures, ensuring the service life of individual housing construction not lower than that calculated in the project.
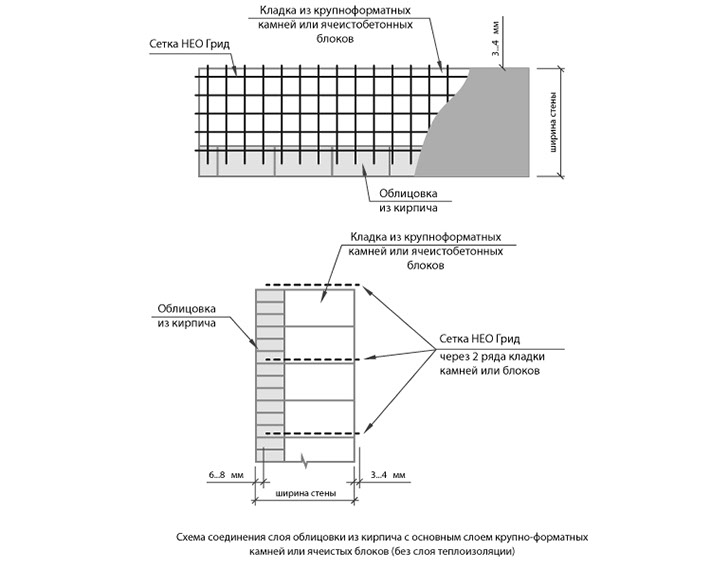
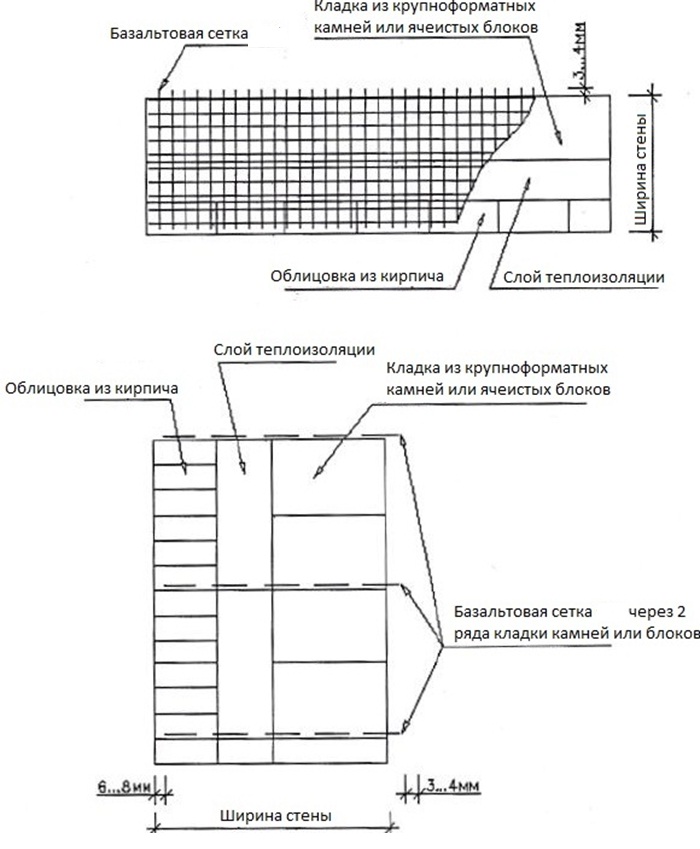
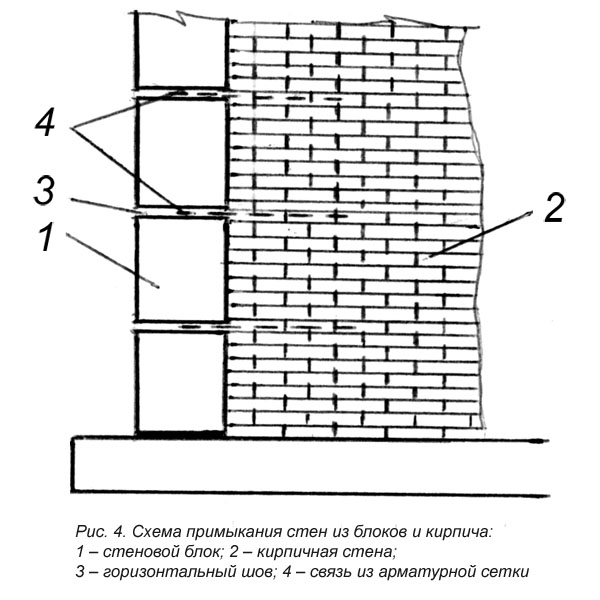
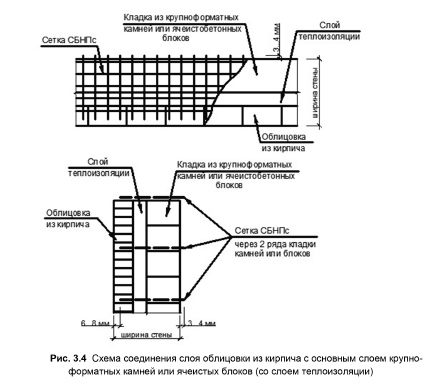
It is possible to increase the bearing capacity of a solid wall or a thinner partition if the brickwork is reinforced in the horizontal plane with a metal mesh or tied with wire. This method is also used to ensure the connection of the facing masonry with the backing wall.
Building codes formulate the requirements for reinforcing brickwork with a grid of horizontal joints as follows:

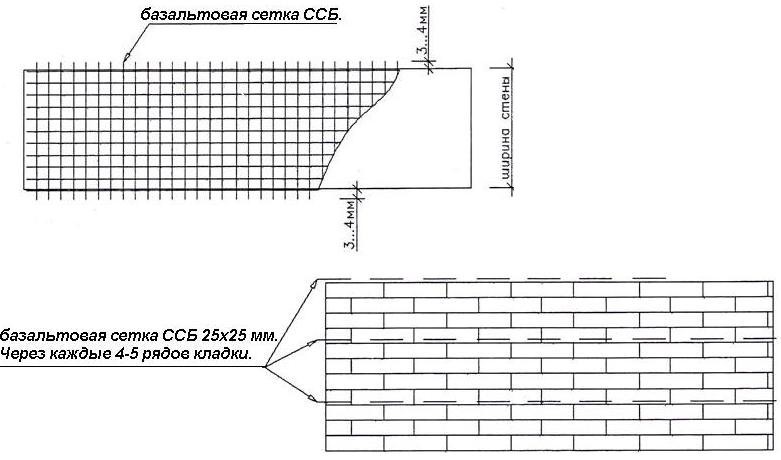
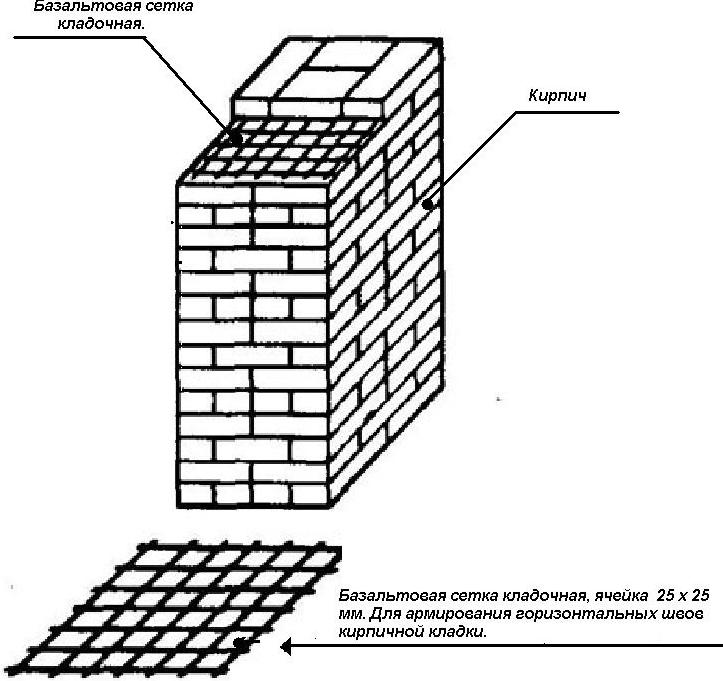
 Basalt reinforcing mesh allows you to reduce the amount of mortar due to the thickness of the seam. In addition, it does not require additional anti-corrosion coating and careful protection from the environment.
Basalt reinforcing mesh allows you to reduce the amount of mortar due to the thickness of the seam. In addition, it does not require additional anti-corrosion coating and careful protection from the environment.
Easily cut to size with regular scissors. When choosing such a material, it should be borne in mind that the ratio of the strength characteristics of steel and composite is 4: 1, therefore, for the same loads, a metal wire needs a smaller section than a basalt one.
The following options are manufactured industrially from a steel bar according to standard cutting formats:
Best in class for individual construction (where large bar diameters are not required for increased strength) is the brickwork mesh. It is produced in rolls, manually cut to the desired size, has an anti-corrosion coating, and reduces the thickness of the seam compared to wire.
General recommendations for reinforcing brick structures
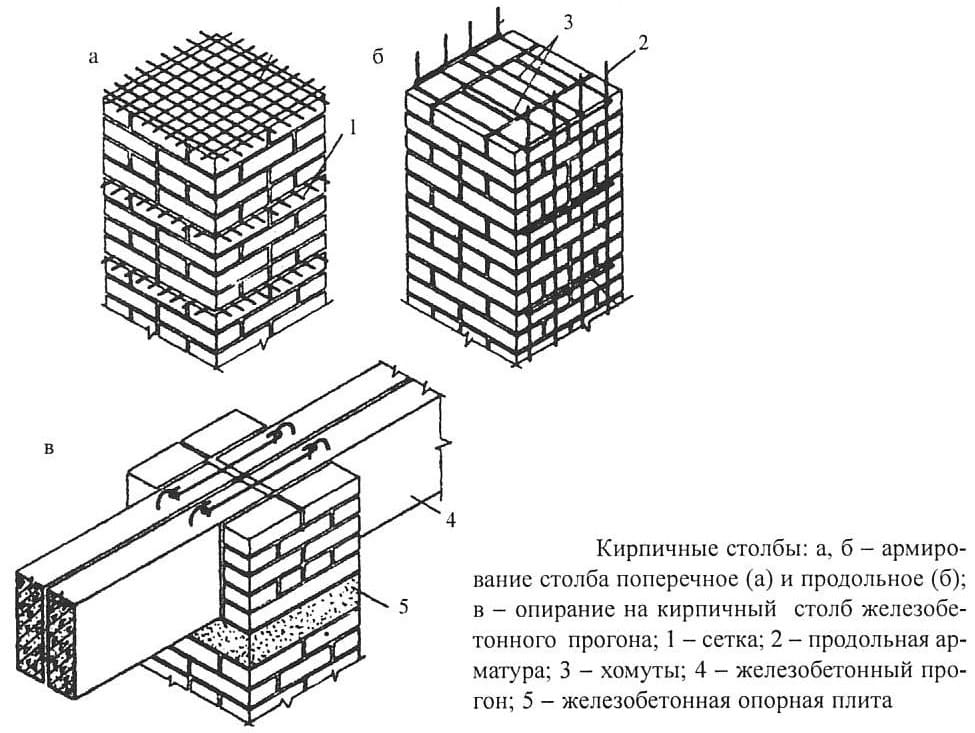
Strengthening brick pillars
There are two main types of brick pillars:
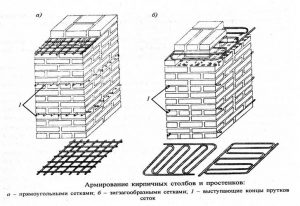
- Carrying out the function of load-bearing columns. Supports are used to evenly distribute the load and maintain the floors placed on them. Such structural elements only experience vertical pressure.
- Semi-decorative fence posts that can both connect sections of the fence and support gates and wickets. Here the main type of load is horizontal.
Due to the small size, the reinforcement of the masonry for the pillars is necessarily carried out by means of a mesh or rods. The scheme for the construction of such pillars is as follows: a foundation containing a reinforcing cage or a built-in metal pillar is lined with bricks. In this case, a reinforcing mesh is used in the horizontal section of the masonry. The construction of hollow columns with minimal strength is dangerous and impractical.
Facade reinforcement
To achieve the maximum effect of strengthening the walls, making them more durable and reliable, perhaps only by making reinforcement from the very foundation. If the foot of the building is brick, then its strengthening is also necessary. Reinforcement of the brick basement begins after the first row is laid out on the foundation. Reinforcing elements are laid out on top of it, the procedure is repeated in each of the next 5 rows. In the future, the wall rises another 6 layers of masonry, after which the reinforcing rods are again laid. Further, the process is repeated cyclically.
Transverse
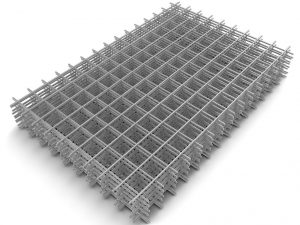
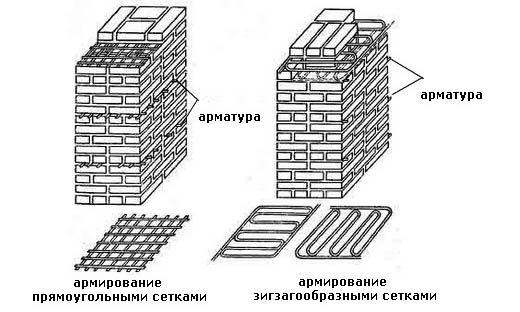
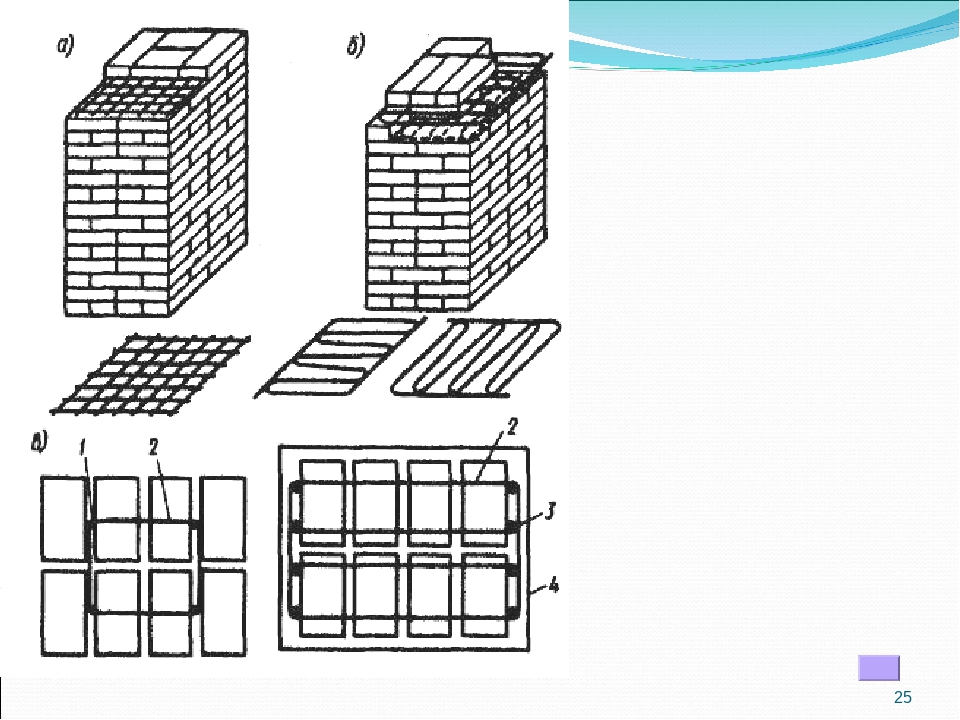
This type of brick wall reinforcement is characterized by the use of a mesh of different materials and steel rods, which protect the brick from deforming tensile and bending stresses. The rods are fastened to the mesh by means of knitting wire or welding. The rules establish the connecting pitch from 30 to 120 mm. Replacing the mesh with single reinforcement in the perpendicular plane does not comply with building codes. For transverse reinforcement, a mesh with cells of three main types is used. It happens:
- rectangular;
- zigzag;
- square.
The masonry is reinforced with a rectangular mesh with a diameter not exceeding 5 mm, while the cell size cannot be wider than 100 mm. Such a grid is laid through 5 rows of bricks. When performing work on strengthening the masonry, the reinforcing elements are positioned so that the edges of the reinforcement and mesh protrude somewhat beyond the front layer of the brick. In the future, they will be deleted.
Zigzag mesh for brickwork is made of wire with a diameter of 5 to 8 millimeters, the size of the cells ranges from 50-120 millimeters. In the horizontal plane, it is laid every 2 layers of bricks and is fastened by reinforcement located in adjacent rows at right angles.
Vertical

Straight and zigzag mesh is used for this type of reinforcement. The rods are laid between each 5th row of bricks. The use of straight rods is recommended for regular brickwork. Along the width, the location of the reinforcing rods is performed with a step of about 100 mm. The rods go deep into the grout-filled joints to a depth of 20 mm.
Longitudinal
This type of wall reinforcement, depending on the placement of reinforcing elements, is divided into internal and external. Reinforcing brickwork in length is taken with rods with a diameter of 10 millimeters or more. With internal reinforcement, reinforcement is placed along the walls, being recessed into the base of the masonry.With external, for fastening reinforcing elements, pillars attached to the wall are used. For small structures, such as a private house, the thickness of the rods does not exceed 15 mm, while for large structures, rods with a diameter of 30 mm and thicker are used. In the front masonry, the pitch of the rods with a thickness of 120 mm must be observed.
additional characteristics
The dimensions of the masonry nets must be selected before purchasing the goods. The latter is made of highly flexible high carbon steel. The rods are coated with PVC or zinc during the production process for more impressive strength. A number of specialists prefer galvanized mesh. However, in recent years, fiberglass coatings have become more common, which give the product the best quality characteristics. In the latter case, the mesh turns out to be lighter, its strength is increased, and the top layer protects against corrosion. If you want the reinforcement to last longer, then you should use a product that is covered with fiberglass.
Types and materials for the manufacture of reinforcing mesh
All building materials used to strengthen masonry are divided into two broad categories:
- light - with a section diameter of less than 10 mm;
- heavy - the thickness of which exceeds 10 mm.
At the same time, the production technology for various types of reinforcing mesh varies: masonry, spot-welded, cold-rolled mesh reinforcement and others. Most often, a masonry mesh less than 5 mm in diameter is used for transverse reinforcement. Also, the meshes differ in the material from which they are made, they are used:

- steel;
- basalt;
- composite: glass and basalt-plastic.
For example, basalt mesh is used to reinforce facing brickwork and wall masonry. Simultaneously with the strengthening of each of the clutches, they are fastened together. Composite meshes are approximately equal to basalt meshes in operational and consumer terms and are superior to metal meshes both in technical characteristics and are more profitable from a financial point of view.
Varieties of execution
In the construction of brick buildings, reinforcement of the following types is used to strengthen walls and partitions:
-
Transverse. Reinforcement of brickwork is carried out with a mesh laid in horizontal seams. The following types of meshes are used:
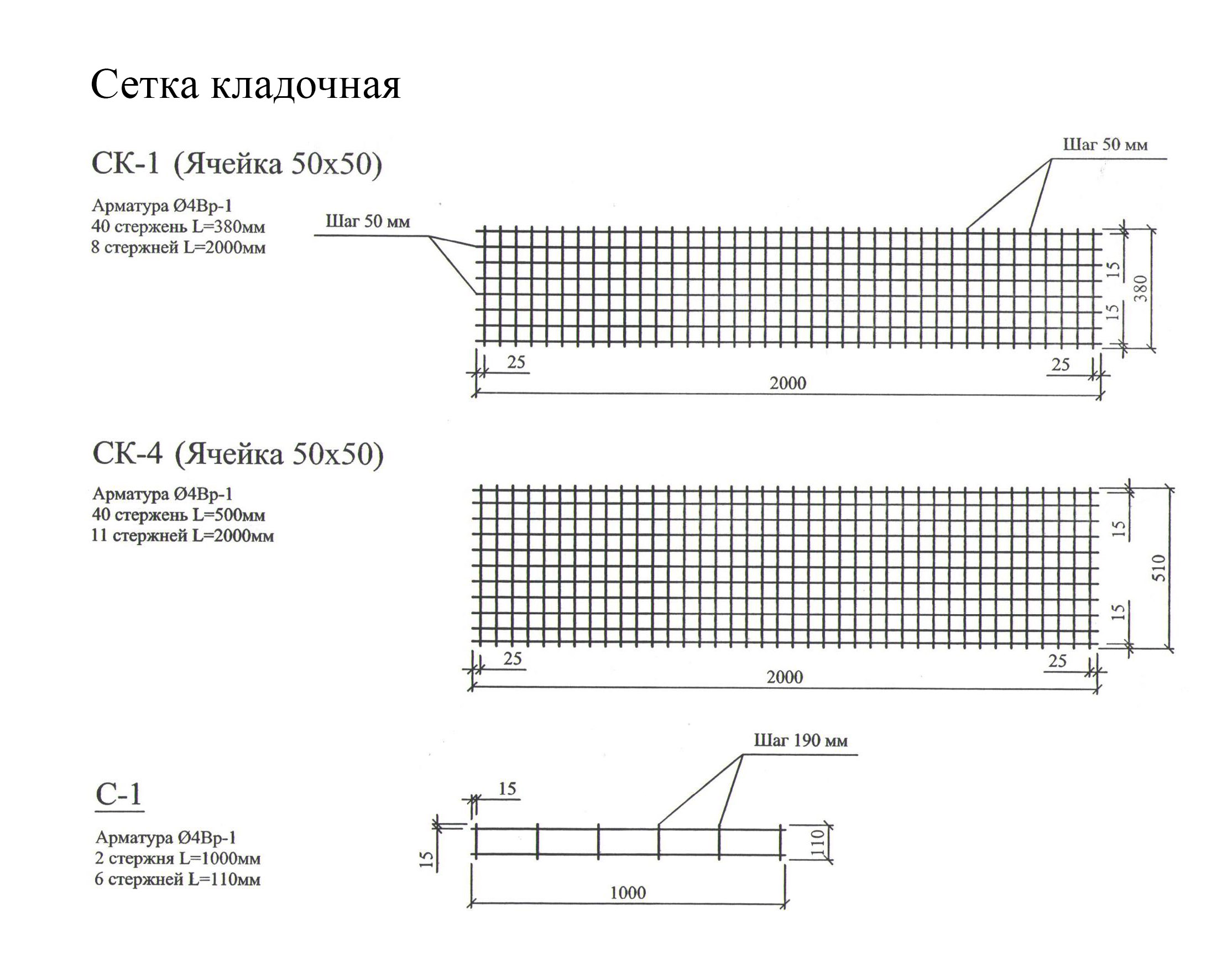
- prefabricated galvanized metal masonry masonry. They are produced in square, rectangular or zigzag form from hot-rolled reinforcing smooth steel А-I and Вр-I with diameters of 3 ... 8 mm with cells from 3 to 12 cm;
- reinforcing bars tied with knitting wire with a diameter of 5 to 8 mm. When using black rods, thorough anti-corrosion painting is imperative;
- all-metal expanded metal meshes (CPVS) are modern reinforcing products manufactured at the factory using expanded metal technologies and have a specific gravity of 2.5 less than traditional welded ones. The undoubted advantage is high strength, reliability and ease of installation;
- polyethylene and PVC nets;
- composite and basalt. Products with low weight are not subject to corrosion and decay, do not conduct electric current, are characterized by high temperature resistance and low thermal conductivity. The use of such products makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the seams due to the possibility of reducing the section of the elements. This saves finances.
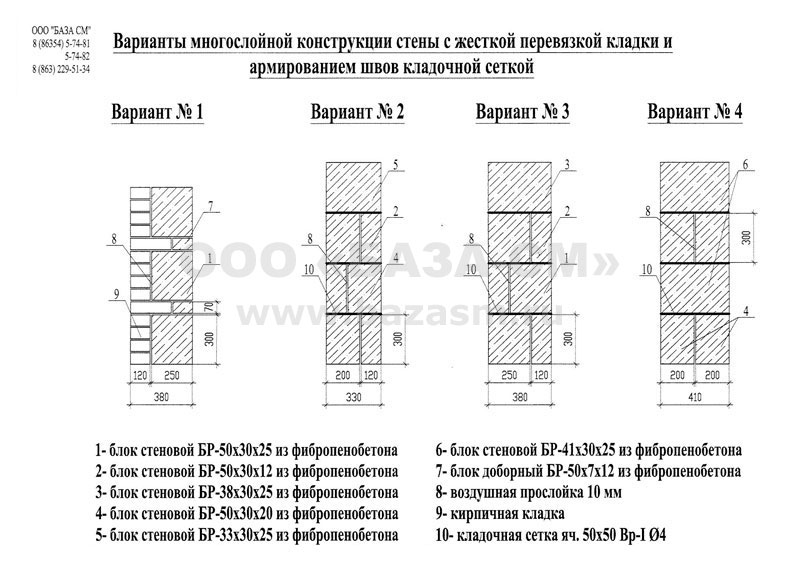
The grids are not laid in every row. How many rows the brickwork is reinforced is determined by the calculation set out in the building codes and regulations. This takes into account the magnitude of the loads acting on the wall, their displacement from the central axes and the height of each row. Most often, the grids are laid at intervals from 2 to 5 rows, and when using thickened bricks, no more than 4.Zigzag ones are stacked in two adjacent rows in pairs, so that the arrangement of the rods in them is mutually perpendicular.
The effect of the use of nets decreases when they are located at a distance of ≥ 45 cm. Structurally, the products are located at intervals of ≤ 1 m. Installation is performed with an overlap of ≥ 15 cm. The mortar layer should be ≥ 2 mm below and above. The ends of the nets should protrude from the inner surface by at least 2 - 3 mm. This makes their location available for visual verification of the correct laying and serves to strengthen the connection with the inner lining. If necessary, the ends can be easily cut with metal scissors.
Reinforcement of the masonry with nets is carried out in combination with a solution of ≥ M 50.
-
Longitudinal. Often used to reinforce brick partitions and main load-bearing walls to increase their flexural strength and resist lateral forces. Reinforcement A-I and A-II with diameters up to 12 mm are used. It can be internal, for which reinforcing bars (less often meshes) welded together with transverse reinforcement are placed in the grooves made in the solution of longitudinal seams. Or external, under a layer of cement mortar. The spacing of the clamps for external reinforcement is taken ≤ 15 diameters of the reinforcement used, and for the internal 25 diameters. The strength of the walls directly depends on the observance of these conditions. Often, basalt grids are laid in every 5th row in non-bearing partitions made in half-brick. Reinforcement of facing masonry can be carried out in the same way for connection to load-bearing walls.
To strengthen the thin partitions, the laying in the seams on both sides of the steel corners connected by metal bridges is also used. Corners can be laid on one side only. At the corners, vertical rods or a mesh are attached, followed by shelter by plastering with cement mortar.
-
Vertical reinforcement of brickwork. Often, brick columns are reinforced in this way, in which it is impossible to place reinforcement in the internal cavity or it is impossible to increase its dimensions to perform external reinforcement. In this case, steel corners of the design section are installed in the corners of the column or pillar, united by welding of metal transverse bridges. Such an operation not only strengthens the masonry, but also partially absorbs the loads acting on the structure. For vertical reinforcement of the walls, reinforcing bars are laid inside the voids in the brick, followed by pouring with cement mortar. For this, the masonry must have voids passing through several rows.
The diameters of rods of classes A-I, A-II, VI are usually taken from 10 to 16 mm, but in high-rise buildings it can increase to 30 mm or more. Especially vertical laying of reinforcement is necessary in areas with high seismic activity.
About additional characteristics
Sizes can be thought over and selected even before the purchase is made. The main production material is high-carbon steel, which is highly flexible. To increase strength, during the production process, the rods are coated with PVC or zinc. Then any masonry mesh will last longer, the sizes of the cells of which are selected individually.
Many professionals prefer to use the so-called galvanized mesh. But recently, fiberglass products have gained recognition on the market. In this case, the performance is really improved. Then the mesh has the following advantages:
- Less weight.
- Increased durability.
- Corrosion-resistant top layer.
The maximum service life is guaranteed by metal-plastic products.
Practical advice
The current SNiPs regulate the requirements for the performance of such work, which must be strictly observed:
the mesh is completely recessed into the mortar mixture;
all metal elements are pre-painted to get additional protection against corrosion;
the thickness of the seam covering the reinforcing bars must be guaranteed to be exceeded;
during construction, the building is reinforced with one of the existing reinforcement options;
choose a grid with the correct mesh configuration;
the edges of the mesh fabric should protrude from the masonry;
use a knitting wire to connect the elements; it is prohibited to use a welding unit;
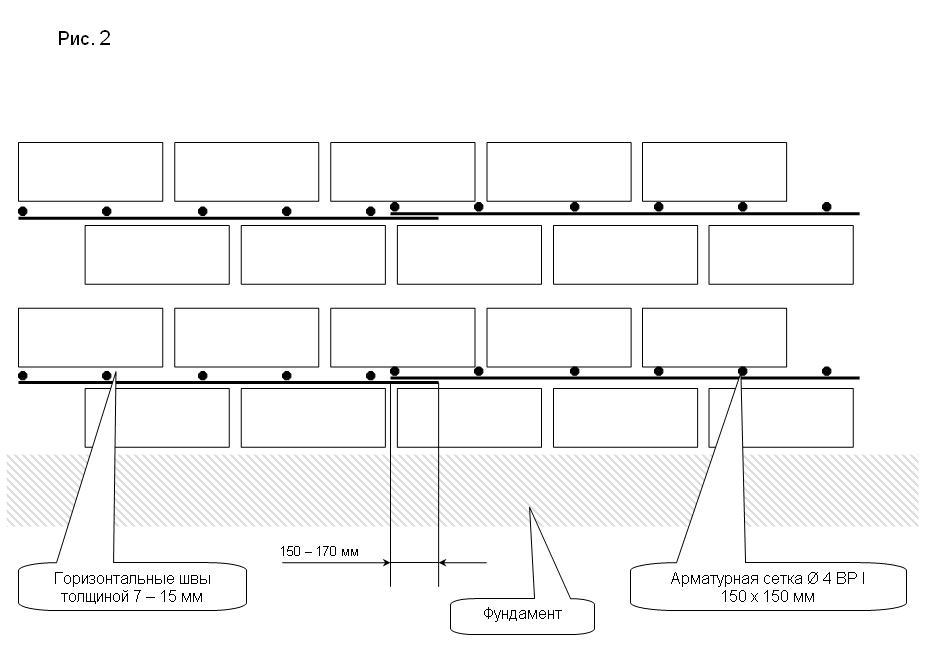
reinforcement begins from the base of the structure, for which a frame made of reinforcement is laid on the first brick row, laid out on the foundation surface. After five rows, the procedure is repeated;
areas and openings that cause alarm in the quality of operation are reinforced without fail
For example, a doorway is reinforced from above by two layers, and for a window block, such a precaution is also provided from below;
if the center of the structure is off-center, it is recommended to reinforce the top contour of the bottom edge of the object.
Cracks often appear around openings, because it is here that the masonry experiences serious stresses, which are compensated by the laid reinforcement.
Problems are created by sections of walls of different heights, adjacent to each other. The difference in vertical pressure contributes to the formation of splits at the joints. Reinforcement in such cases is recommended to be carried out on the last three masonry rows, bringing the reinforcement elements to the higher walls so that the central part of the mesh fits horizontally into the joint.
Some styling tips
The method of using the material is chosen individually by the master. As a general rule of thumb, it is best to use a grid at least every 5 rows. Three rows in the case of low-rise buildings.
Laying usually takes place as follows:
- Decking on the previous rows, forming a bond with concrete.
- The previous and subsequent rows are laid using the same technologies.
- For the next rows, the uniformity of the site is one of the important requirements. The concrete mix completely covers the base.
- 20 centimeters is the minimum thickness of overlapping mesh pieces.
- 12 millimeters is the minimum thickness of the mortar joints, where the reinforcing mesh is added.
They decide in advance the need for a specific type of mesh for bricks at the present time. For example, in the case of a metal reinforcing belt, the thickness must be at least 2 millimeters.
The combination of the following components contributes to the stacking of the individual masonry layers with each other:
- Concrete mortar.
- Reinforcing mesh.
- Friction with pressing effect.
Do not forget about the documents regulating such construction. SNiP recommends using the next belt after a certain number of rows. The size of the cells and other parameters are also strictly controlled.
It will be good to create the most detailed project, its absence in most cases only complicates the implementation. In most cases, the properties of meshes have long been tested in practice.
It is allowed to use different types of reinforcement on the same object. Due to the combination of their properties, the result is positive. The alternation of the grid is quickly solved with competent calculations with drawings.

For what purpose is it carried out?
In the process of shrinkage, the walls are not covered with cracks, load effects are removed from the masonry.
Such work is performed in the following cases:
- large loads are created on the enclosing structures of multi-storey buildings;
- there is a likelihood of cracking on objects erected on weak soil compositions;
- construction is carried out in an earthquake-prone region, and an increase in strength is necessary to create resistance to earthquakes;
- when building arches from bricks or columns, maintaining complex masonry;
- if low quality building materials are used.
What are fittings?
Reinforcement is carried out using long reinforcement rods or special mesh. The mesh or rods are made of metal wire. But modern reinforcing bars are made of PVC or polyethylene.
For such purposes, a rod with a diameter of 3-8 millimeters is suitable. In the construction of small buildings, rods with a thickness of 3-4 millimeters are used. But if it is decided to use reinforcement with a diameter of 6-8 millimeters, then it is not recommended to knit a mesh from it, the mesh at the joints is thicker, which means that the thickness of the seam will also increase. It is best to lay it in a zigzag pattern.
The rods can be spaced 40-100 millimeters apart. Thus, the mesh will have cells from 40x40 to 100x100 millimeters.
The mesh is laid every 3-5 rows. The frequency of laying the mesh depends on the required strength of the wall; at high loads, reinforcement can be laid in 1 row. But the builders do not recommend laying the reinforcement mesh less often than after 5 rows, in this case, the reinforcement's capabilities are greatly reduced and the reinforcement goes wrong.
Reinforcing mesh can be made independently, directly at the construction site. Or you can purchase a ready-made mesh. It is a connection of reinforcement rods at the same distance from each other. The connection is made by welding. If the mesh will be assembled at the construction site, then experts recommend not using welded joints due to the possibility of corrosion, it is better to use a knitting wire.
Reinforcing bar made of ferrous metal must be painted. If this is not done, the metal will corrode and the wire will not be strong. This means that the reinforcement will not perform its main function - to strengthen the masonry.