Types and features of material
Depending on the manufacturer, polypropylene agrotechnical fabric is available in 3 different colors:
- black;
- white;
- green.
Most often, it is black agrotechnical fabric that is found on sale. Since black is the least exposed to UV rays, weed growth will be less under the black fabric.
White agrotextile is most often used to cover the soil in greenhouses and greenhouses. White color reflects sunlight better than others, which contributes to faster ripening of fruits.
In addition to its main function - protection against the germination of unnecessary weeds, agrotextile has other useful properties.
- It is able to pass air, water and mineral fertilizers due to its porous structure.
- It makes it possible to reduce the number of waterings.
- Prevents moisture from evaporating too quickly from the soil surface in dry weather.
- Protects the root system of plants from overheating or hypothermia through air circulation.
- Due to the fact that when laying agrotextile there is no need for weeding, all useful minerals remain in the soil, and its fertility increases.
- Protection of fruits from rotting due to the fact that the coating does not allow them to come into contact with the ground.
- Protection against pests such as slugs, worms, stick insects. Solid flooring will not allow parasites to penetrate the fruit.
- Frost protection for roots. With the onset of frosty weather and insufficient snow cover due to agrotechnical, an additional layer for insulation is created.
- Ability to withstand temperature extremes. Thanks to this property, it will be enough to cover the dense polypropylene fabric once; it does not need to be removed for the winter period.
Another distinctive feature of dense agrofibre, as opposed to thinner agrofibre, is its high cost. The prices for agrotechnical fabric are 3-4 times higher compared to the prices for film or covering nonwoven fabric. But the service life of durable agrotechnical fabric is several times longer than the service life of cheaper materials and ranges from 10 to 15 years. Therefore, you should not save money when buying, since agrotechnical fabric will pay off the costs after 3-4 years of its use.
Mulching agro-fabric: on the disadvantages and features
Apart from the high price of agrotechnical fabric as a disadvantage, there are not so many of the latter. But something needs to be said.
- pay attention to the quality and availability of a UV stabilizer. Any agrotextile is destroyed under the influence of sunlight
To avoid this, good manufacturers also add an ultraviolet stabilizer to its composition. If you purchased a cut on the market, and after 3-4 years weeds began to break through it - alas, it's all about the quality of the material. For reliability, it is possible to pickle the soil with a herbicide before covering agricultural fabric, but not everyone is ready to pickle their land. By the way, a UV stabilizer is added (or not added) to all types of covering materials - agricultural, film, geo-fabric.
- problems with mulch. Imagine: you covered your tree with agrotechnical cloth, poured beautiful bark or pebbles on top as decorative mulch and rightfully admire your creation. But the fallen leaves begin to pollute the mulch, the wind causes litter and sand. To prevent a beautiful mulch from turning into a compost heap after a year or two, it must be cleaned regularly. As an option - to change it annually, but oh, how expensive it is. Therefore, be sure to take this factor into account when planning a site.As for fruit trees, you should not use any mulch besides agrotex.

- mice, moles, goosebumps - what else do you have? It is warm, dark under the agro-fabric, no one bothers - a paradise for animals and insects. Of course, a lot depends on the area, on the soil and on the type of crop grown. But with the problem, one way or another, you will have to fight: take out ants, put nets from moles, brave mice.
And now we bring to your attention a video from which you will learn how to properly lay agrotextile under the trees:
Tatiana Kuzmenko, member of the editorial board Sobcor of the Internet edition “AtmAgro. Agroindustrial Bulletin "
Features of agrofibre
One of the main characteristics of a garden protective film is the density of the material. It is on this that the weight and performance of the coating depend. The denser the geotextile, the better it protects plants and soil from low temperatures.
Several varieties of agrofibre can be found on sale:
- Universal.
- Black.
- White.
 Agrofibre for a greenhouse allows moisture, air, and sunlight to pass through, while retaining heat, protecting plantings from ultraviolet radiation and cold.
Agrofibre for a greenhouse allows moisture, air, and sunlight to pass through, while retaining heat, protecting plantings from ultraviolet radiation and cold.
White and double-sided spunbond can be spread on different sides, which makes it easier to use the material.
Black agrofibre is intended for laying material on the ground. Such a protective coating does not allow sunlight and ultraviolet light to pass through. Due to the property of retaining heat under agrofibre, the soil quickly warms up, creating optimal conditions for the development of the root system of grown vegetables and fruits.
A high-quality durable spunbond can last at least 5 years, such a coating is not afraid of significant temperature changes, therefore, it does not need to be removed from the garden before the onset of cold weather. Subsequently, the gardener in the spring only needs to plant the seedlings prepared by him under the film. All this makes it possible to simplify the care of the plantings, eliminating the need to dig up the garden, and subsequently carry out weeding, clearing the beds from various weeds.
Growing onions in the open field and caring for them
How to use?
If you want to use agrotextile in your summer cottage, garden or flower bed, then you should know about the different methods of application and select the most suitable one for your situation.
The first option is to wrap up the plant. If you are going to do this using rolled geotextiles, then you need to wrap the material around the plant with allowances for the possible growth of the plant, fix it from below and from above. For convenience, it is recommended to use special ready-made bags that are made for these purposes. You only need to select the size and secure the canvas from the bottom.

The second option is to cover the soil. In this case, there are two possible outcomes of events.
- You can cover the beds and create what is called a greenhouse. To do this, you need to install additional structures and supports. This is suitable for insulating beds with cucumbers, tomatoes and other vegetables.
- You can also apply agrotextile before directly planting plants in the garden. To do this, you need to clear the area for the garden bed and cover it with a canvas, securing it with special nails or homemade wire staples. Next, you need to cut holes where you will plant the plants.
This method is ideal for planting strawberries. After all, a few decades ago, straw was placed under the strawberry bushes so that the berries did not touch the ground and did not start to rot ahead of time.
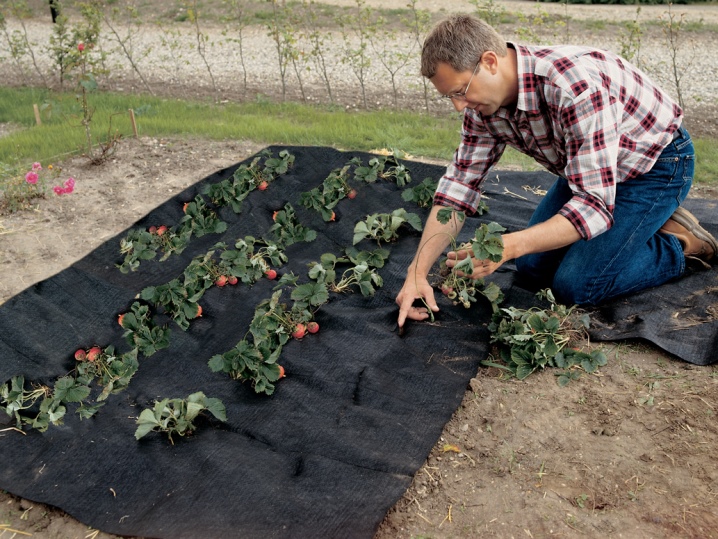

You can see how to use agrotextile for growing strawberries in this video.
Agrofibre: application for all seasons
The need to use agrofibre is justified at any time of the year. It is a durable homogeneous material that does not pollute the environment and does not harm the plants.The color and thickness of the spunbond may vary depending on the application and the season.
Spring

222
Before sowing, it is laid out on a bed, X-shaped or O-shaped cuts are made in it, where seeds are sown or seedlings are planted.
For planting tree seedlings, some manufacturers (Agrotex) offer ready-made trunks made of black thick fiber.
Thinner material (17 g / m2 and 30 g / m2) can be used to cover crops. The material is spread on the bed and pressed along the edges with the ground.
As the shoots grow, the plants themselves lift up light material, which does not interfere with their proper development at all. Planting under an agricultural canvas with a density of 60 g / m2 allows you to protect seedlings from spring frosts. Seedlings of some crops under it can withstand frosts down to -7⁰C - 9⁰C.
Summer
The main role of white spunbond in summer is shading, moisture retention, protection from winds and pests. Spunbond black covering nonwoven fabric (60 g / m2) is used to protect berries and vegetables from rotting and contamination. It is spread on the surface of the soil to exclude contact of the fruit with moist soil. This method is also effective in weed control.
Autumn
The first autumn frosts destroy crops that are still capable of producing crops. On the eve of the onset of cold weather, you can use a covering canvas to save fruiting crops from early cold weather. At this time, it is also time to mulch the soil with agrofibre to protect the roots of wintering plants.
Winter
A dense canvas will protect shrubs, berry crops and winter crops in winters with little snow. Agrofibre is frost-resistant, and also capable of withstanding a significant weight of snow cover. Heat-loving crops, such as grapes, are best covered for the winter with spunbond, and then covered with sawdust or earth. This will reliably protect the plants, and it will be easier to open them in the spring.
Lutrasil and its types
Thin lustrasil looks like a spider web, which reliably protects plantings from negative factors
Lutrasil is one of the most common covering materials, as it well protects the beds from atmospheric phenomena.
The material is divided into 4 types, depending on its density. Each of them has its own characteristics that determine the method and features of its application.
Table 1. Varieties of lutrasil and their use.
Density
Features and Applications
17 g / sq.m
Thin, light agricultural canvas used to cover sown plantings. It is laid directly on the ground, does not require fixation or installation of supports - so that the material is not blown away by the wind, it is enough to press it down with stones or boards. It helps to warm up the soil, protects against a drop in temperature to -3 degrees. Thin lutrasil does not break plants, but rises with them, continuing to perform its functions. You can water the plantings on top of the shelter, since it passes water well and keeps it in the soil. Due to its low density, it is not able to protect plants from heavy rainfall (for example, hail), and crops with thick branches can break through the material
30 g / sq.m
A fairly dense agrotextile, which is used not only to cover plantings, but also to organize small greenhouses. The material protects plants from frost down to -5 degrees, overheating in the hot season, birds, harmful insects, heavy rain. Can be used to protect large crops - shrubs, fruit tree seedlings
42 g / sq.m
Durable yet soft material suitable for covering large areas
Well imitates snow cover, which is especially important in late autumn and early spring, when plants need natural protection. Protects plantings from frost down to -7 degrees, transmits sunlight, air and moisture
This type of lutrasil is most often used for greenhouses with a frame or tunnel structure that can be easily disassembled.Due to the operational properties under the shelter, a microclimate favorable for photosynthesis is formed, but condensation does not accumulate. The material is able to withstand heavy rain and hail, but in case of prolonged precipitation, it is recommended to additionally cover it with a film
60 g / sq. m
The thickest, most durable canvas, which is used to organize greenhouses and greenhouses. The material contains carbon black, which gives it a black hue, elasticity and impermeability to sunlight, and prevents weeds. Withstands long-term frosts, but it is best to use the canvas in combination with the film
Improper use of black lutrasil contributes to overheating of plants
Lutrasil is produced in white or black, which also affects the characteristics of its use. A white canvas is used to protect plants from negative factors or to equip greenhouses, and a black one is used for mulching the soil.
When choosing a material, one should take into account its characteristics, the characteristics of the crops that are supposed to be grown in a sheltered area, the climatic conditions of the region. In warm climates, it is better to use a thin white material - black agrotextiles with a high density attract heat, so there is a risk of overheating the plants in intense heat.
Lutrasil can be laid directly on the beds without additional supports
In addition to density, the following material characteristics are indicated on the packages of lutrasil:
- light transmission;
- tensile or tensile strength;
- additional qualities (foiling, reinforcement);
- moisture permeability;
- life time.
If there is little data, it is better to contact the manufacturer and clarify the characteristics of the material, since the wrong choice will give the opposite result.
Agrotextile, agrofibre, geo-fabric: what's the difference?
Oh, this terminology. All kinds of combinations "geo", "agro", "fabric" and "textiles" as a result form such a jumble of similar words that it is no longer clear - who is synonymous with whom, who is whose subspecies, and who is not used at all in gardening.
For your convenience and understanding, we provide a small diagram that will dot at least some of the "i" s.
Difference between agrofiber, agrofibre and geo-fabric:
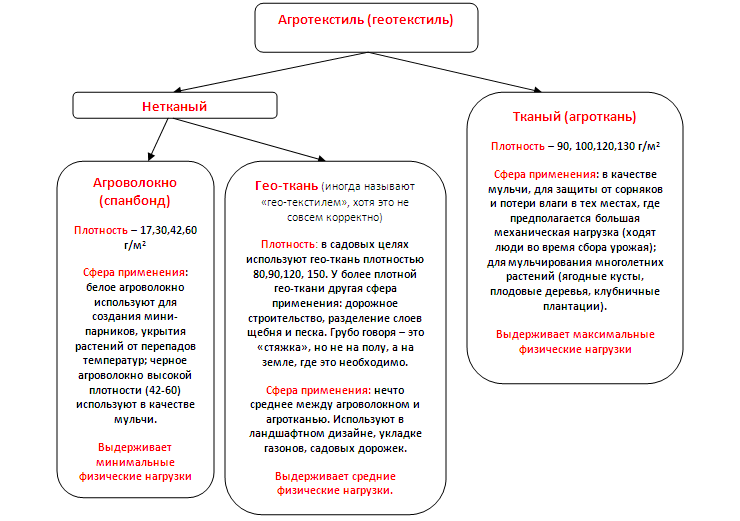
All these materials are made from the same raw material - polypropylene, but in different ways. And all these materials can mulch the soil, they are all black, inhibit the growth of weeds, etc. What distinguishes agro-fabric among others, in which case should you give preference to it, and in which - agrofibre or geo-fabric?
Varieties of covering material
Covering material for plantings are presented in several varieties, which differ in the method of manufacture and use.
Spunbond
 Spunbond is considered the most common covering material among gardeners.
Spunbond is considered the most common covering material among gardeners.
One of the most popular covering materials in the gardening business. It is a white or black non-adhesive non-woven liner used for mulching or covering the beds. It is made of fiber-forming polymeric materials that are held together using needles or exposure to high temperatures. It has elasticity, resistance to mechanical damage, negative factors. It can be used at any time of the year to cover plantings, accelerate germination, warm the soil, and create greenhouses.
Agril
 Agril creates the most favorable microclimate for plants under cover
Agril creates the most favorable microclimate for plants under cover
The material is made in a similar way to spunbond, has a high permeability to sunlight, but at the same time it scatters ultraviolet radiation well. Due to this, in the cold season, the plants are protected from hypothermia, and in the hot season they are not exposed to high temperatures. It is easy to use, durable and suppresses weed growth, which reduces the need for frequent weeding.
Agrospan
 In appearance, Agrospan resembles a durable, dense non-woven
In appearance, Agrospan resembles a durable, dense non-woven
Nonwoven fabric combining the performance of other product varieties. This is a synthetic fiber, bonded together in a special way, outwardly resembling non-woven fabric. Agrospan creates a special microclimate, protects plantings from weeds, pests and insects, retains moisture in the soil, thereby reducing the need for frequent watering. The lack of material is a low level of thermal insulation, which negatively affects the development of thermophilic crops.
Agrosuf
 Agrosuf is especially popular among strawberry gardeners.
Agrosuf is especially popular among strawberry gardeners.
Used to equip greenhouses and protect plantings from low temperatures. Provides ventilation of plants and the flow of moisture, which has a beneficial effect on the development of plants. The material is distinguished by its high strength and long service life - in the difficult climatic conditions of central Russia, it can be used for 3 seasons in a row. It is especially often used by gardeners who grow strawberries. Under a layer of agrosuf, the bushes can survive the cold season without loss, do not grow too much, and give a good harvest.
What it is?
Agrotextile is a material based on polypropylene fiber. It is characterized by lightness, harmlessness, durability and reliability, safety in relation to the environment. It is widely used in agriculture, in summer cottages to protect beds from cold weather, weeds, and pests.

This canvas successfully replaces ordinary plastic wrap for summer residents, because it has a number of advantages.
- The service life of agrotextile is longer, it is much stronger and more resistant to ultraviolet rays and mechanical stress. With careful storage, the material can last 5-6 years, or even more.
- The canvas allows air, light and moisture to pass through itself. If you cover a garden with it, it will not negatively affect the plants. On the contrary, they will not "cook" and will not dry out.
- Agrotextiles are resistant to mold and bacteria. Since it is air and moisture permeable, moss will not form on the soil.
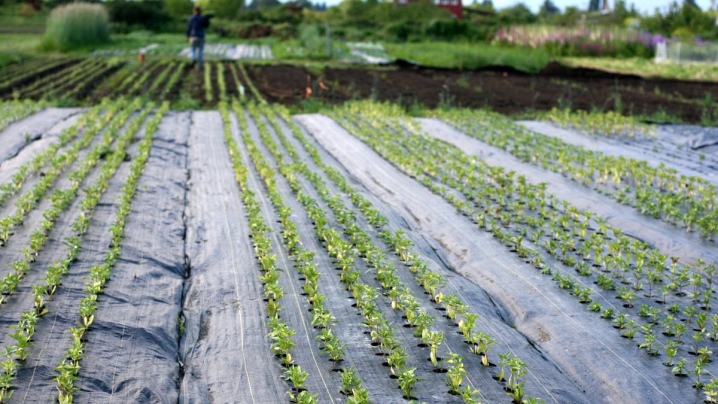

Agrotextile: application
Agrotextile is the most durable geotextile in horticulture. Outwardly, it resembles a bag of sugar, only black and usually marked with squares (usually green or red). This is useful when you want to cut the fabric evenly or make holes at the same distance. Also, the fabric does not "crumble" along these lines.
Most often, black agrotextile is produced, since the main function of agrotextile is mulching from weeds (without light, weeds germinate much more slowly, or do not germinate at all). White or colored (brown, green) agrotechnics are much less common.
The use of agrotechnical fabric is convenient because this material allows water, air, and solutions of mineral substances (mineral dressings) to pass through. At the same time, moisture evaporation decreases, the temperature regime of the soil improves, and due to the fact that the agro-fabric does not transmit light, the weeds will not get a chance to germinate. Moreover, agrotextile does not decompose in the soil and is resistant to chemicals.
What is the main difference between agrotextile and agrofibre? It is stronger, denser, and can withstand significant physical stress. More UV stabilizer is added to the agro-fabric, so it will last longer (7-10 years, depending on density and quality). But agro-fabric is three times more expensive than agrofibre. Therefore, it is impractical to lay it everywhere.
And where is agrotechnical used in gardening?
- when growing strawberry plantations. It is in large areas, as a rule - in farms, where strawberries are repeatedly processed, and then harvested, where tens or hundreds of human legs pass, agrotechnical for strawberries will be the best option.At the dacha, where there are three rows of strawberries, it is much cheaper to lay a high-quality black spunbond with a density of 60 g / m2. Yes, spunbond is not intended for walking on it - at least often. But nothing prevents you from working neatly, and put, for example, boards in the aisles. That is, the whole point is in your personal benefit, since agrofibre is much cheaper than agrofibre.
- agrotechnical weed control (mulching agrotechnical). If you mulch vegetables, grapes, melons and gourds - here agrotechnical is really the best choice. Black agrofibre will also protect well from weeds, moisture evaporation, but if in the case of strawberries you do not tread around each bush, then there is always work around cucumbers, melons, peppers, grapes, and agrofibre will "burst" under your feet in a season. That is, the point, again, is the ability to withstand physical exertion. To save money, you can think about this option: put spunbond directly under the plants, and line the paths with agrotechnical fabric.
- agricultural fabric for shrubs and fruit trees. Another advantage of agrotextile over agrofibre is that you can lay it down once and never rewrite it (spunbond is hidden for the winter, it quickly deteriorates from frost). Therefore, under fruit trees and shrubs, agricultural fabric is very even shown: spring and autumn pruning, scions, treatments against pests and diseases, harvesting - it will withstand all this, and even retain moisture for plants, protect young trees from freezing of roots, prevent overgrowth weeds. As for decorative trees, under which you rarely walk, you can get by with a cheaper geo-fabric. Its service life is approximately the same as that of agrotechnical, but it is designed for less mechanical stress.
- agrotechnical fabric for flower beds. As in the case of decorative trees, it will be cheaper for flower beds to get non-woven geo-fabric. Dense agrofibre is also permissible to use, but for the winter it will have to be removed so that the covering material does not become unusable.
- agrotechnical fabric in landscape design, arrangement of lawns and paths. Here you need to look at what kind of design is expected. Geo-fabric was created just for landscape design, this is purely its profile. But if you plan to use large, very heavy decor items (load more than a centner per square meter), you should give preference to agrotechnical fabric. Agrofibre in this case is not considered at all.
Material description
Agrofibre is a durable and lightweight material that is made from stabilized environmentally friendly polypropylene, has a thin structure that allows moisture to pass through. The film provides high-quality insulation of the earth, completely solving weed problems. Agrofibre, or, as it is also called, spunbond, is a non-toxic material that is resistant to ultraviolet rays and resembles ordinary woven fabric in appearance. Due to the presence of carbon black in stabilized polypropylene, such a film is able to accumulate heat, providing rapid heating of the soil.
The use of geotextiles is an excellent alternative to mulching the soil, while completely solving the problems with weeds, which, without receiving sunlight, cannot grow in the beds. Vegetables and fruits covered with such a protective film grow well and bear fruit well. The gardener gets the opportunity to grow heat-loving crops in the open field, which, without using this technology, could previously be planted exclusively in greenhouses and greenhouses.
Agrofibre or agrotextile, which is better?
Based on the information received, it is impossible to say what is better than agrofibre or agro-fabric. Because it is one and the same material at its base, which has different properties due to the manufacturing technology, and, therefore, different applications.
Agrofibre and agro-fabric have the following characteristics:
- density;
- stretching the surface;
- colors;
- breathability;
- water permeability.
Geotextile has a density of 17 to 600 g / m2. In agriculture, and, accordingly, in the country, and in your own garden, woven and non-woven agrotextiles with a density of up to 130 g / m2 are used for growing plants.
More dense geotextiles are used in construction and landscape design as a reinforcing and reinforcing material. In addition, woven and non-woven geotextiles are used to reinforce slopes, when constructing drainage systems, or used as a reinforcing layer for constructing artificial reservoirs, when strengthening banks. Geotextiles can be elastic and strongly stretch at break points, which is typical for agrofiber. Agrotechnical fabric has less surface stretch, because it is denser due to the interlacing of the fibers.
In gardening stores, you can find woven and non-woven agrotextiles in different colors. Brown, green and black agrotextiles are mainly used for mulching or landscaping.
White agrotextiles are commonly used to shelter plants in winter, to protect against flying insects and heat in summer, to germinate seedlings under agrofibre or to cover greenhouses, or for mulching in greenhouses where it is important not to overheat the soil. Agrofibre and agrotextile are supplied in rolls of standard widths: 525, 420, 330, 210, 105 cm
This brings a certain convenience when dividing the site into even, neat beds.
Agrofibre and agrotextile are supplied in rolls of standard widths: 525, 420, 330, 210, 105 cm. This brings a certain convenience when dividing the site into even, neat beds.
Agrofibre is a highly permeable and breathable fiber, but agrotextile is breathable, but poorly permeable to water, although it retains it well in the soil, contributing to less evaporation.
Both types of material are UV protected, which reduces the effect of ultraviolet radiation on the protected or coated surfaces
It is also very important to remember that all geotextiles are resistant to mold, the development of bacteria, etc.
Also, geotextiles are resistant to deformations, vibrations, aggressive substances and temperature influences, withstanding temperatures from - 5 to 100 ° C, without changing their properties.
If we talk about durability, then with careful use in agriculture, agrotechnical fabric can last up to 25 years, which depends on the density of the material itself. Agrofibre, on the other hand, does an excellent job with its tasks within one year and can last up to 3 years. Which also depends on the density of the material.
At the same time, it is important to point out that geotextiles do not affect the change in soil acidity and do not allow fertilizers to penetrate to the surface, and, creating favorable conditions, in a sense, even helps to preserve beneficial microflora in the soil. Summing up, we can highlight the general characteristic advantages of agrofibre and agrotechnical, which are used as a mulching material:
Summing up, we can highlight the general characteristic advantages of agrofibre and agrotechnical, which are used as a mulching material:
- do not let in sunlight, weakening the process of photosynthesis, preventing the appearance of weeds;
- reduce the use of herbicides;
- reduce the rate of evaporation of water, keeping the soil moist even in dry weather;
- pass water and air;
- reduce the time for spring crops to emerge;
- reduce the time of caring for seasonal plants;
- resistant to mold, bacteria and UV radiation.
