Advantages and disadvantages of the insulated Finnish plate (UWP) in comparison with the insulated Swedish plate (USHP)
Of course, the Finnish insulated foundation is not a panacea for all problems and has not only strengths, but also weaknesses. Of the advantages, they note:
- Profitability. For the installation of this type of foundation, a minimum amount of building materials is required.
- Plates are convenient to use.
- The pressure transfers to the strip part of the foundation, the base screed does not participate in this.
- It is possible to equip the floor with several options, for example, make it electric or water.
- The foundation is laid as simply and quickly as possible.
- Great for difficult terrain, even on uneven ground with gradients and slopes.
- Accumulates and retains heat.
Weaknesses include:
- The need to dig a pit for the tape.
- The procedure for filling the trenches and the building perimeter cannot be circumvented.
- Non-metallic materials are used.
- The help of special equipment is needed.
If we compare the UFF with the Insulated Swedish Slab, then the main difference between them is the use of a strip foundation in the Finns in the form of an auxiliary support along the entire perimeter of the building.

The insulated Swedish slab is an ordinary concrete slab, which is cast in a special polystyrene foam tray. In fact, this is a one-piece structure, to which a blind area is attached, which serves as a drainage system. The Swedish slab is placed on a cushion of sand and gravel, followed by the installation of a frame mesh made of reinforcement and laying of communication lines for the future home. Upon completion, the reinforcement is poured with concrete, and the resulting surface is carefully sanded.
It follows that the UVF installation does not need to be carried out on a perfectly flat surface, therefore, there is no need to be afraid of sites with a slight slope.
Since there is no rigid connection between the floor platform and the strip foundation, the structure becomes stable, is not afraid of fracture and increases resistance to loads and pressure on problematic unstable soils. The UVF installation technology allows the slab to be poured after the walls have been erected and the roof has been installed. Therefore, this method is ideal for construction in winter, without interrupting the process due to frost.
However, the cost of installing an insulated Finnish foundation is more expensive than using insulated Swedish slabs. The final cost is influenced by the height of the base and at what level the base tape will be laid.
The advantages of a Finnish foundation
An ordinary shallow tape experiences the action of frost heaving forces. Theoretically, it should rise evenly in winter, and after thawing the soil, it should also lower evenly. Here are just small differences in the load (for example, if one part of the building is lower and, accordingly, lighter than the other), as well as quicksands often lead to the fact that the tape settles into the ground with a bias or deforms (if the reinforced frame cannot withstand). As a result, the building tilts or cracks appear in the masonry above the openings. In the Finnish version, the insulated blind area does not allow the ground to freeze and the foundation does not "float", therefore distortions are excluded.
With a conventional strip foundation, as a rule, a beam ceiling of the first floor is erected. Even with good ventilation of the underground, it decays rather quickly. The service life of the structure usually does not exceed 30 years. In the Finnish version, concrete floors are arranged on the ground - they are practically eternal.
The concrete base of the floor simplifies the installation of a water underfloor heating.This system, in combination with a massive slab with significant thermal inertia, ensures maximum comfort in winter, while in summer such floors keep you cool and save on air conditioning.
Design features
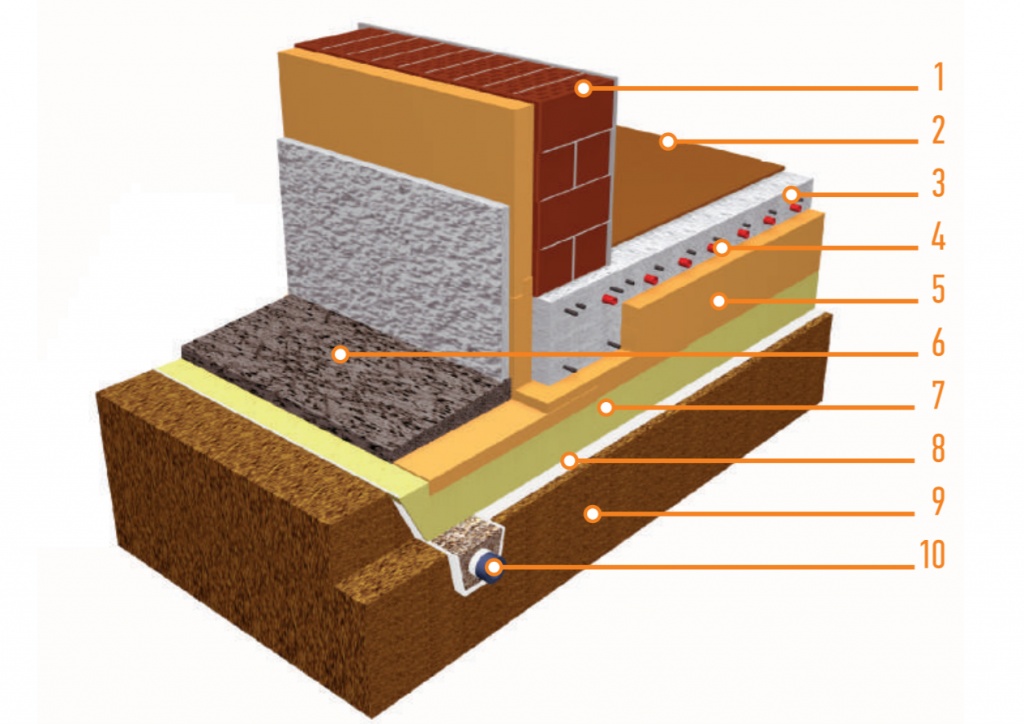
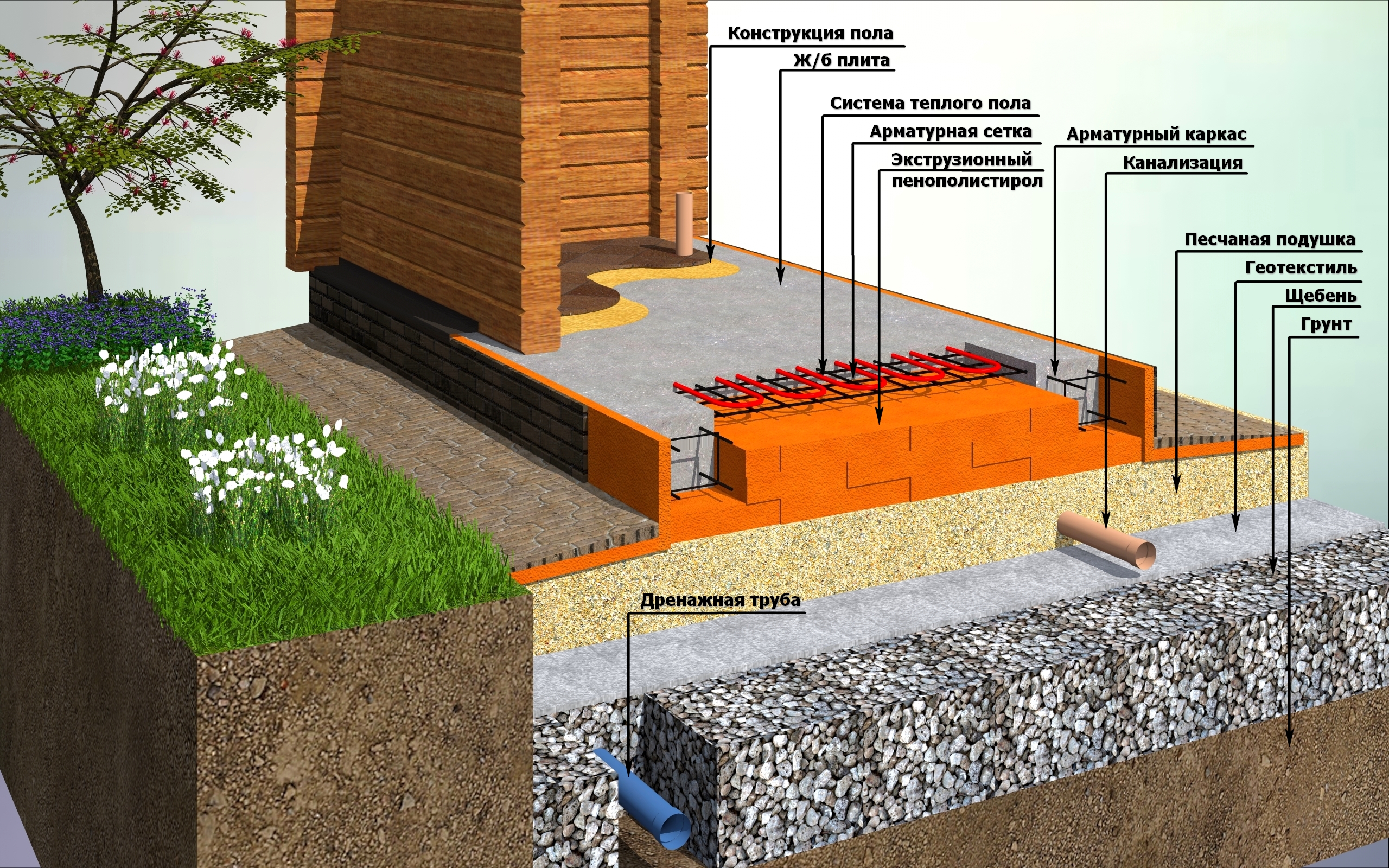
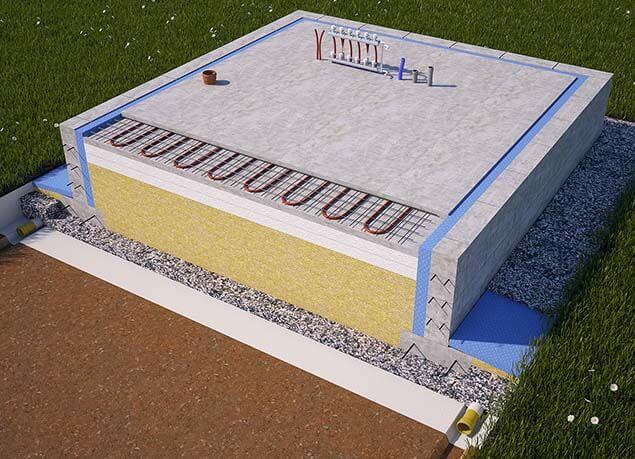
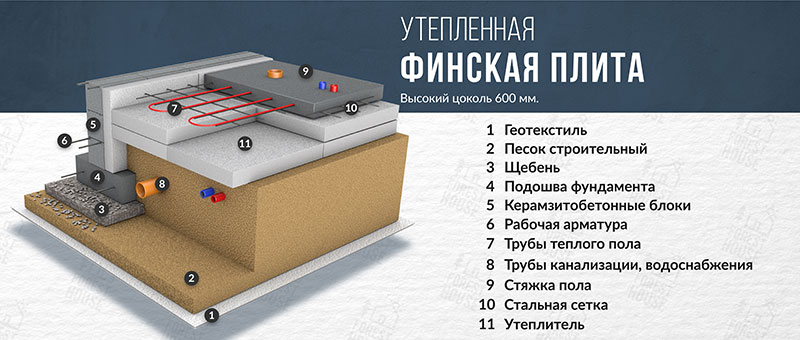
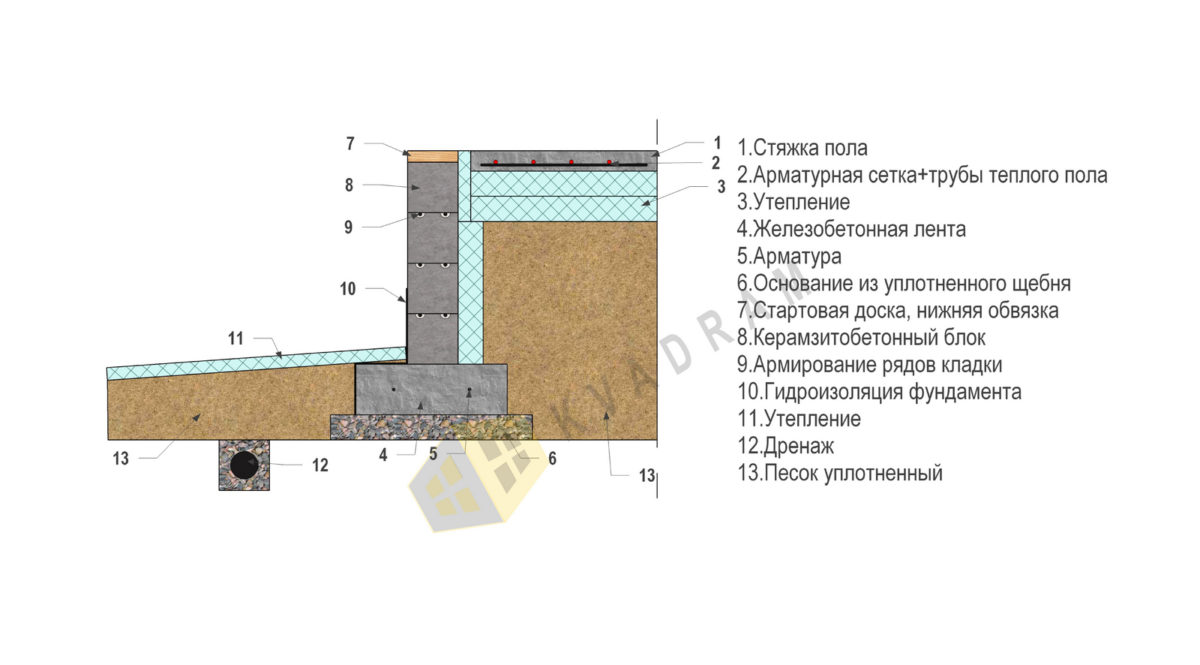
The general construction of the UVP consists of layers:
- Foundations, erected over the entire area of the house and equipped with stiffening ribs.
- Insulation, which is laid on top of this base.
- Underfloor heating systems and communications.
- Cement screed.
Structurally, a kind of Finnish foundation slab is a cold contour.
The insulation material should be laid on the base plate, while the thickness of the insulation layer should not be less than 150 millimeters.
UVP is often used in frame-type houses, but it can also become the basis for other houses equipped with a warm floor system. The peculiarity of such a structure is the high speed of its construction, since the slab is poured at one time, however, its cost, as a rule, is higher in comparison with other foundation varieties. When erecting such a slab, the presence of a reinforced screed is a prerequisite.
Attention: the use of insulation on the first floor of the building eliminates direct contact with the cold foundation, therefore, for a warm floor, a reinforced screed with a thickness of at least 80 millimeters is constructed. The insulated foundation, like the Finnish variety, is suitable in the following cases:
The insulated foundation, like the Finnish variety, is suitable in the following cases:
- when it is necessary to spend a minimum of time on the construction of a building;
- when the main condition for the foundation is its durability;
- if in the future building the structure provides for the creation of a warm floor system;
- if the soil on which the house will be built has a high degree of freezing.
Device technology
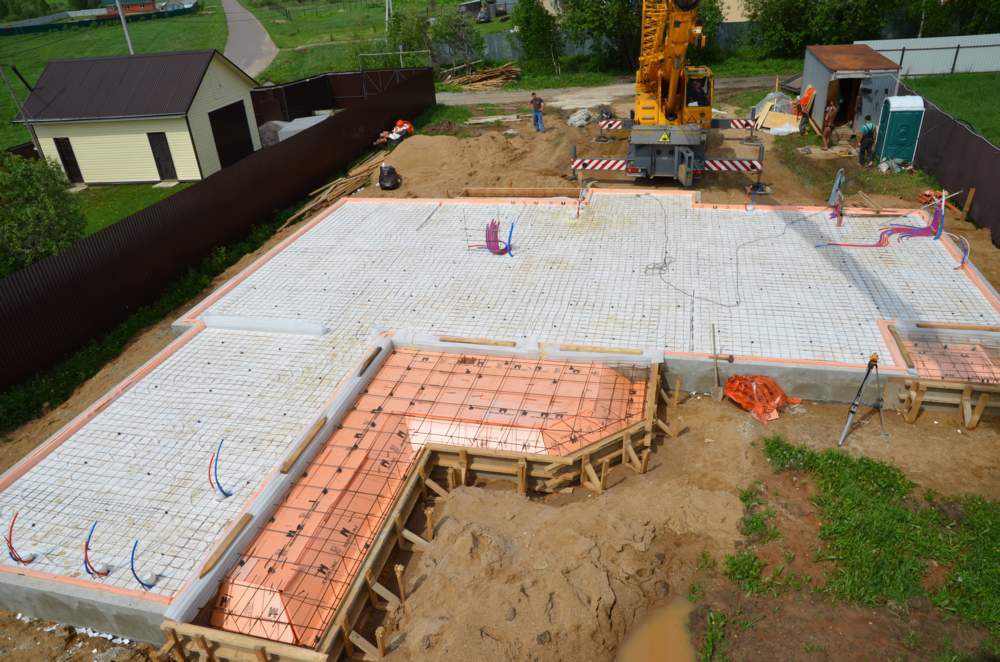
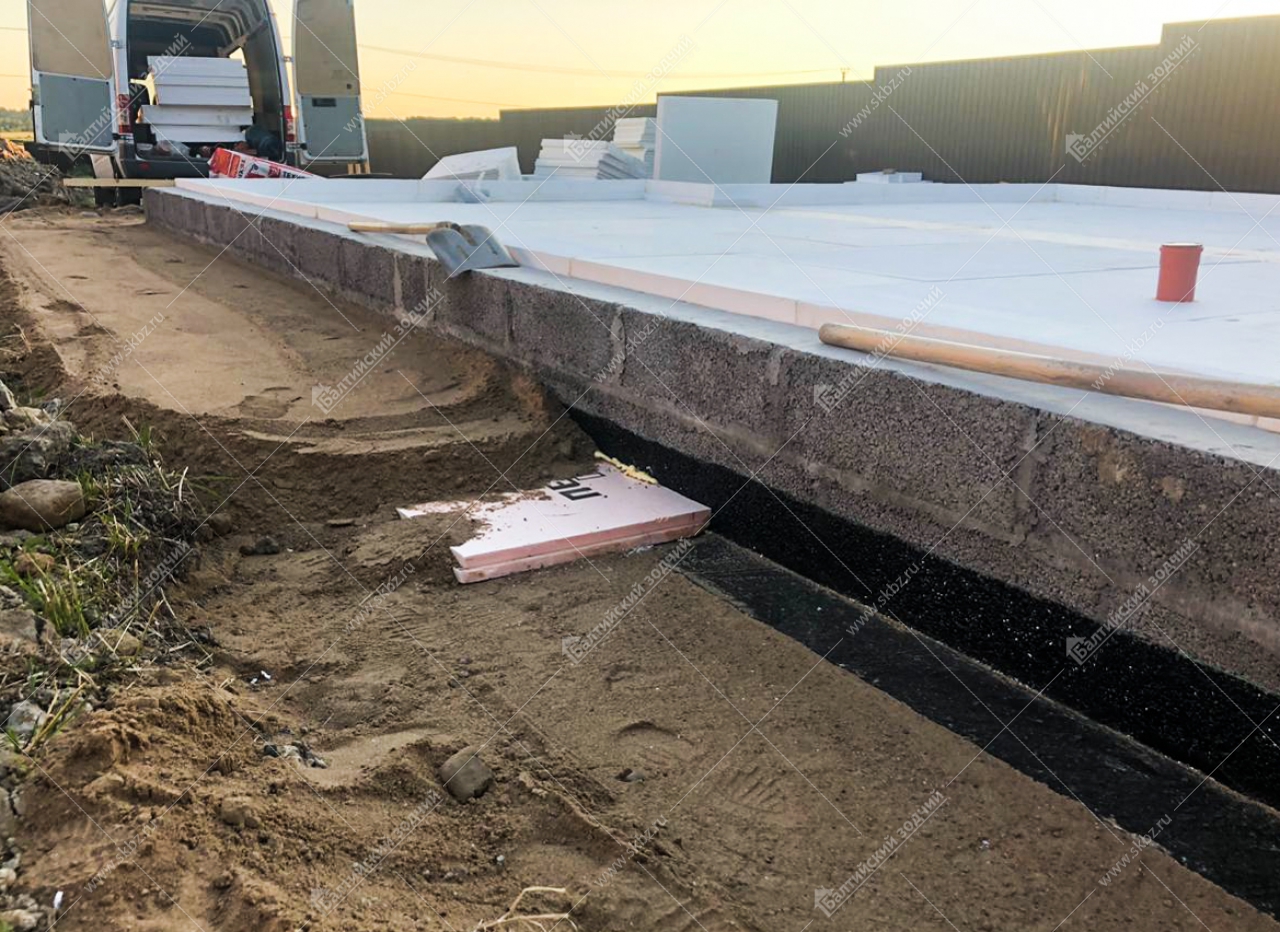
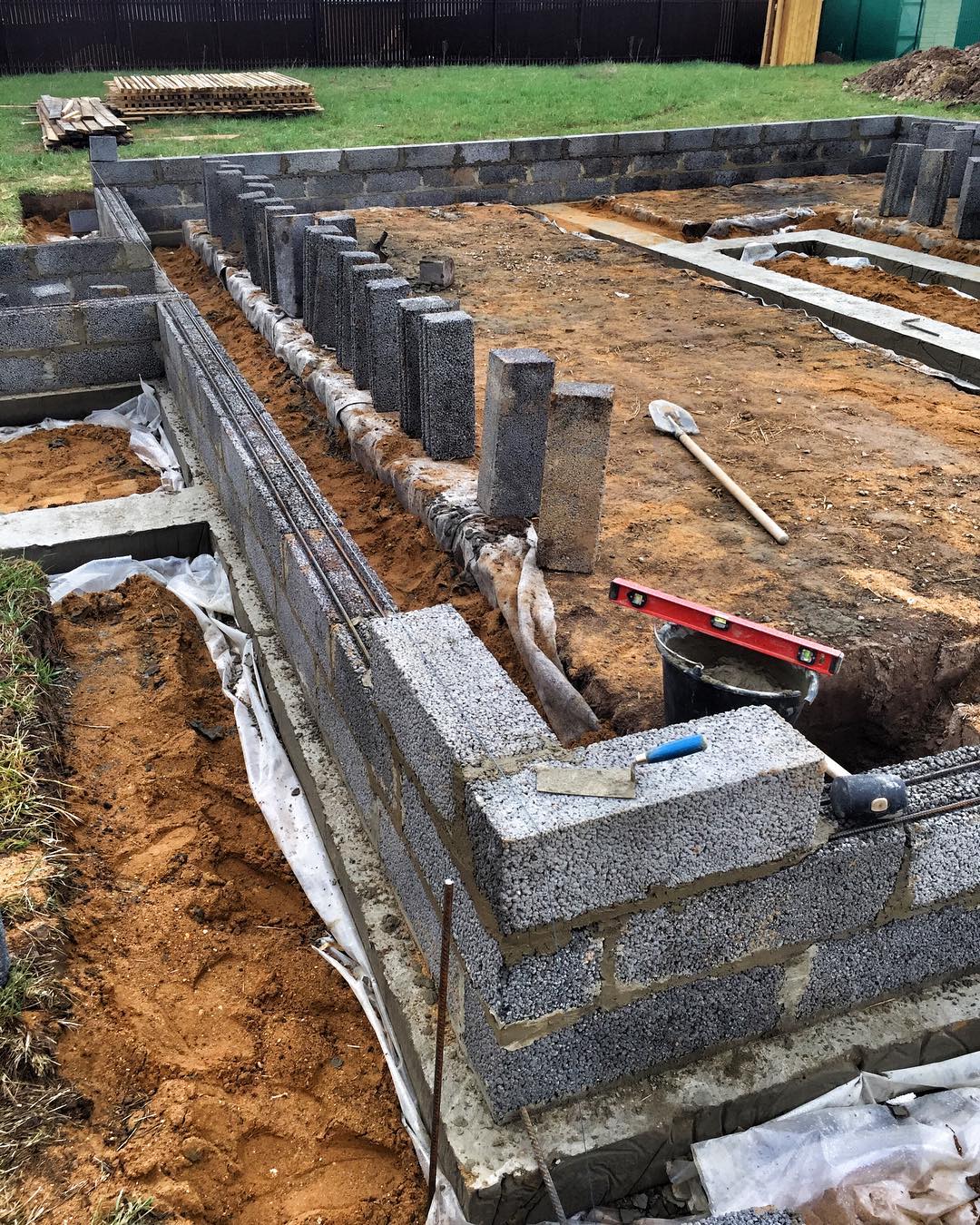
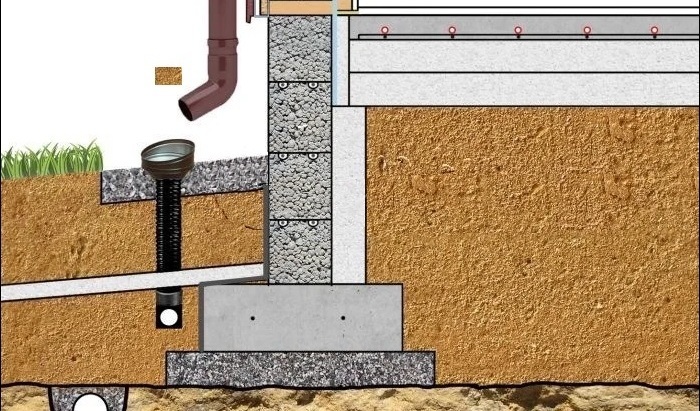
First (of course, after removing the sod and leveling the construction site), they dig a trench no more than 40 cm deep and pour 15-20 cm of sand gravel onto its bottom. Next, a reinforced concrete tape is poured with a total height of about 600 mm and a width of 300-400 mm (depending on the design wall thickness). On very "safe" soils (dry sand), the tape is laid out from the foundation blocks.
After that, a thick sand or sand gravel pillow is arranged in the space bounded by the tape. It is laid in layers, each of which is carefully tamped. Then a slab (in this case it is often called a screed) is poured with a thickness of usually 120 mm, reinforced with a single-level frame made of a rod with a diameter of 12-14 mm. Usually in this slab, which is displayed at the zero level of the building, pipes of a water-heated floor are monolithic.
The final stage is the installation of a blind area more than about 1.5 m wide, insulated with extruded polystyrene foam plates and a reinforced road mesh.
IZBA De Luxe
When pouring the tape, it is convenient to use a prefabricated blind area
IZBA De Luxe
Sand cushion is rammed by machine
IZBA De Luxe
With a large area and a complex configuration of the house, the slab is reinforced with a two-level frame
IZBA De Luxe
A slab of concrete with winter additives gains 70% strength in about a month
Range of application and features of the scheme
Each project requires an individual calculation of the foundation, depending on the characteristics of the soil, the weight of the house, the ratio of the building area to the length of the perimeter, the characteristics of the climatic zone and other factors.
If to generalize as much as possible, then the Finnish foundation of the considered structure can be recommended for use in all climatic zones of the Russian Federation for all categories of soils with an approximate load of 1 - 3 tons per linear meter of MZLF.
The specified load range corresponds to most projects of frame houses with 1 - 2 storeys and one-storey cottages without limiting the type of their construction. However, the adaptation of the UVF for heavier houses is not a problem: the design change in this case is by increasing the sections of the pillow and the basement of the strip foundation.
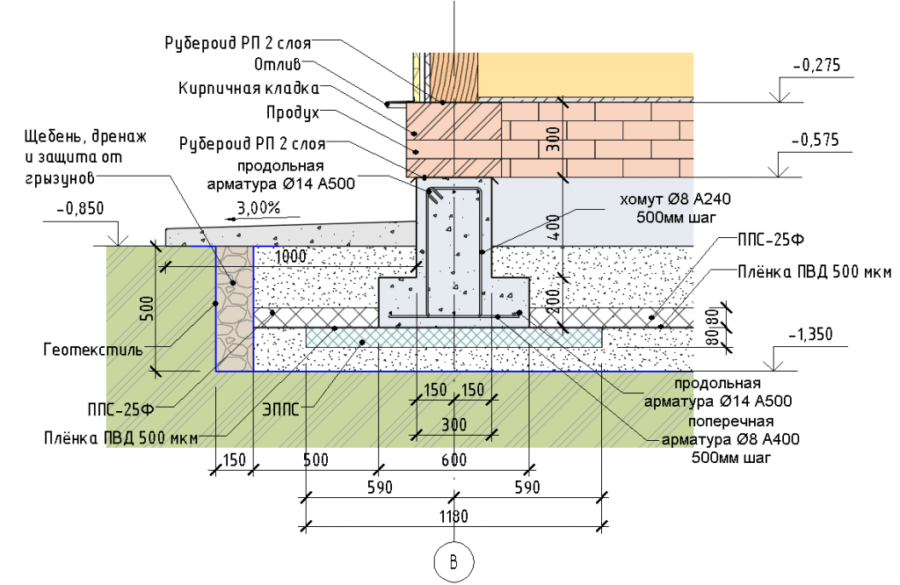
Typical design of MZLF - shallow strip foundation
In economic terms, the scheme is suitable only for buildings without basements.
Among the advantages of UVF are:
- Sleek and simple anti-frost protection solution
- High energy efficiency indicators, only slightly inferior to the scheme of the type of insulated Swedish plate (USHP).
- Good adaptive ability to change projects in terms of loads, basement height, sequence of implementation of individual stages, maintainability of laid communications.
- Opportunities to carry out work with small forces and small funds, taking significant breaks in time (for example, you can do without formwork, and it is permissible to engage in heating distribution and cast the floor slab after the roof has been installed).
- The option better than the UWB adapts to the slopes of the site.
- The scheme can be used with a high level of groundwater
material on the link
Disadvantages (in many respects, conditional) of this type of foundation are associated with insufficient energy efficiency in relation to the concept of a "passive house" and a significant amount of earthworks. The cost of the cycle for the implementation of schemes close to the Omatalo technology is 100 - 120 $ / m² of the construction plan.
The option is more expensive than the standard zero cycle. However, if we take into account the insulation and wiring of communications, the Finnish scheme comes out a little cheaper.
A technical and economic comparison with the USHP gives the following results: with a basement height of 80 cm and higher, the option is 10% - 15% more expensive than an insulated Swedish plate. The height of the basement has a significant impact on costs, as it is directly proportional to the volume of backfill materials delivered to the facility.
It should be noted that the replacement of extruded polystyrene foam with foam (while maintaining the thickness of the insulating layer) does not give a tangible reduction in the cost of the project (the total amount is reduced by no more than 2% - 3%). If we proceed from the same level of energy efficiency, taking into account moisture absorption, then floor insulation with PSB-S plates is more expensive than using EPS.
UVF device technology
Let us consider step by step a set of works, based on the optimization (reduction) of the time for their implementation.
- The location of the construction on the site is determined (if this was not determined by the individual project of the house). All natural barriers, external communications, site boundaries, access roads, etc. are taken into account.
- The marking of the pit with castoffs (pegs with strips attached to them) is made taking into account the margin (0.3 - 0.5 m) relative to the outer perimeter of the insulated blind area.
- The fertile layer is completely removed.
-
A trench is dug under the load-bearing walls according to the depth of the pillow and the required height of the backfill layer.
- The removed heaving soils are removed from the construction site, unless otherwise provided by the landscape design plans.
- A drainage slope is created, drainage backfill is performed on the geotextile and compacted with a vibrating plate.
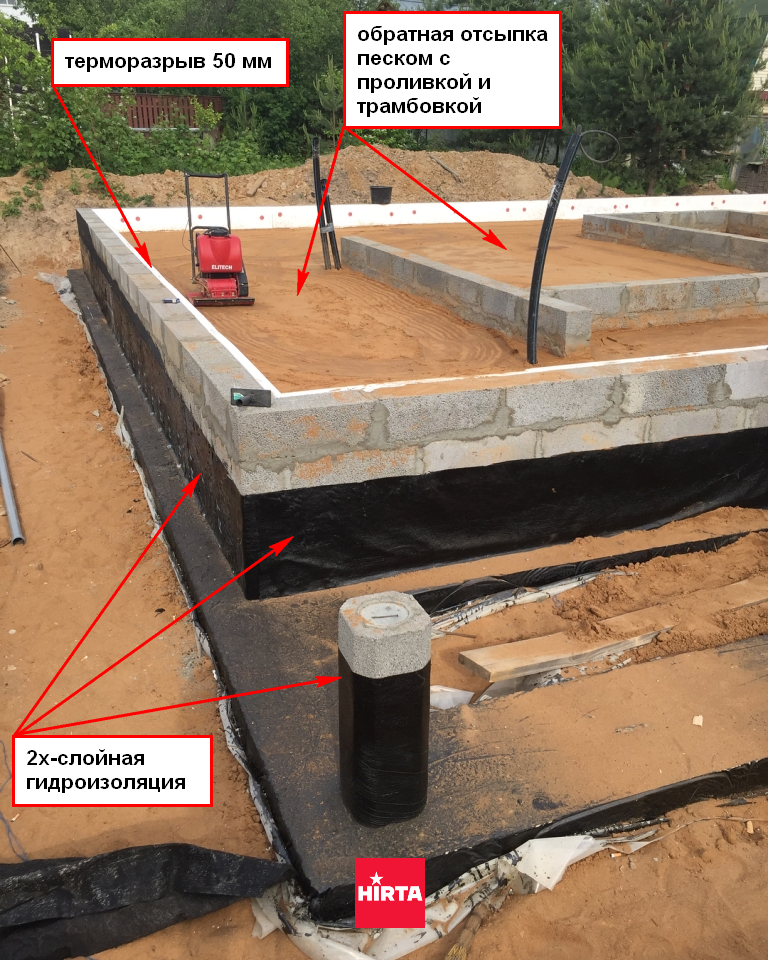
- Under the cushion of the tape, a roll of waterproofing is laid out in 2 - 3 layers with a margin that allows the material to bend up to adjoining the side surfaces of the base. The outer surface of the plinth can be waterproofed later (if necessary). Then the pillow is insulated with slab material (if provided by the project).
- The cushion is reinforced. Reinforcement of periodic section with a diameter of 8 - 14 mm is used. With a pillow thickness of no more than 25 cm, as a rule, two reinforcement belts are dispensed with. If otherwise is necessary by calculation, or the thickness reaches 30 cm, the third reinforcement belt is performed.The belts are connected with vertical bridges. The lower belt is laid on polymer or concrete pads.
-
Formwork is being mounted and concrete is being poured. Dismantling of the formwork is carried out after 50% strength gain (depending on weather conditions and concrete grade, the period is 2 - 7 days).
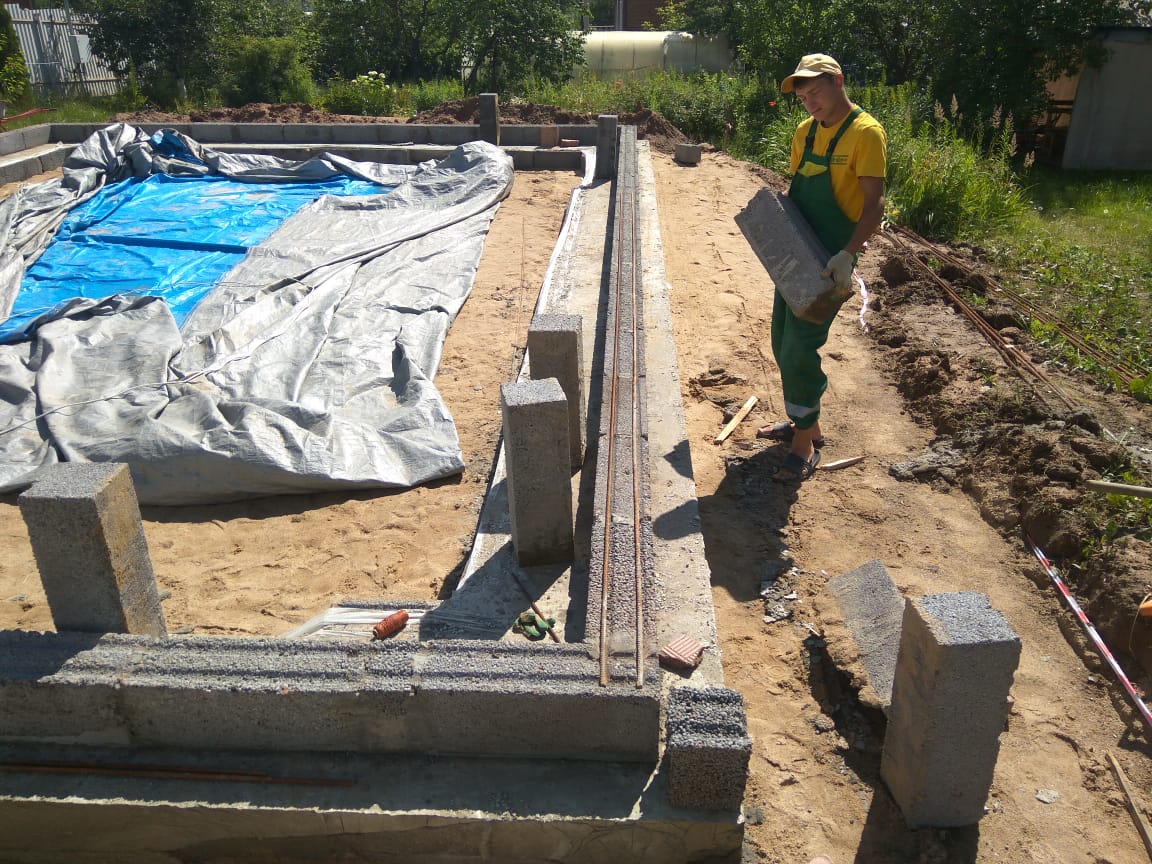
- A tape of foundation blocks is laid out.
-
The inner surface of the tape is insulated with EPS or PSB-S plates. Insulation of the scaffold and its backfill does not have to be coordinated in time with other types of work.
- After the tape is insulated, the inner part is backfilled. Used sand and fine gravel. Compaction with a vibrating plate is performed every 10 cm of height. To exclude mixing of dissimilar layers, geotextiles are used.
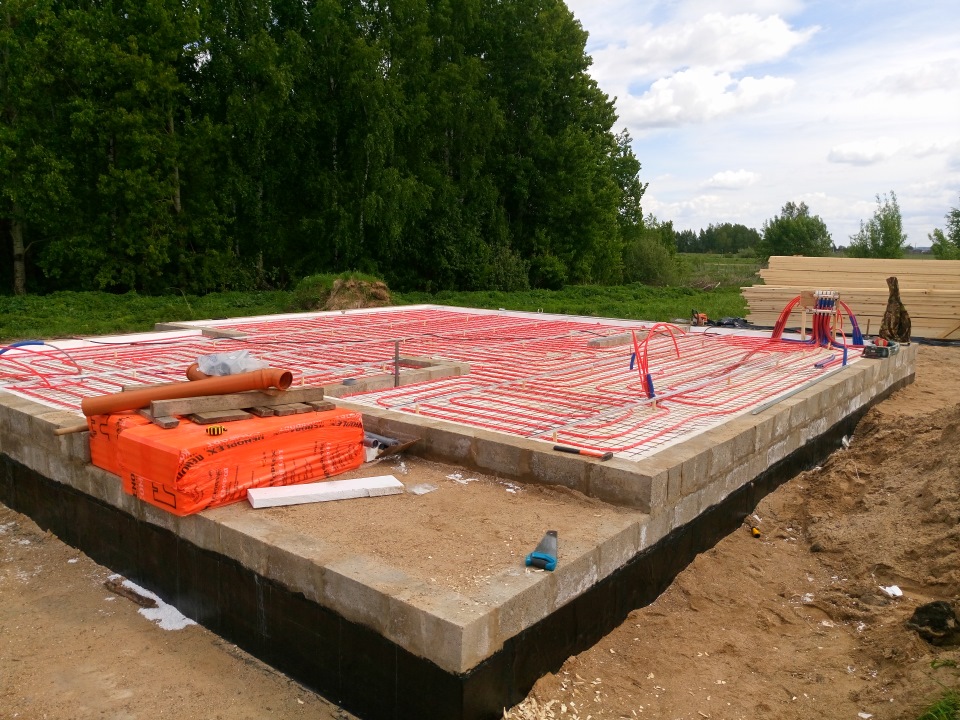
- Floor insulation is laid out. If provided by the project, foil-clad insulation is laid on top of the slabs.
-
Installation of water floor heating pipes or electric cable mats is in progress. Installation of mortgages is carried out for all provided communications.
-
The screed is poured using a metal mesh in accordance with all standards of this type of work.
UFF advantages
 Finnish insulated slabs
Finnish insulated slabs
Despite the fact that insulated Finnish plates may be several times more expensive than "Swedish" ones, it is still recommended to give preference to the first. So, with UFF there is the possibility of "installment" payment, the presence of a high base, which is more acceptable for Russia. It is also possible to erect on an uneven surface with various slopes. This is true for areas that are closer to the mountains.
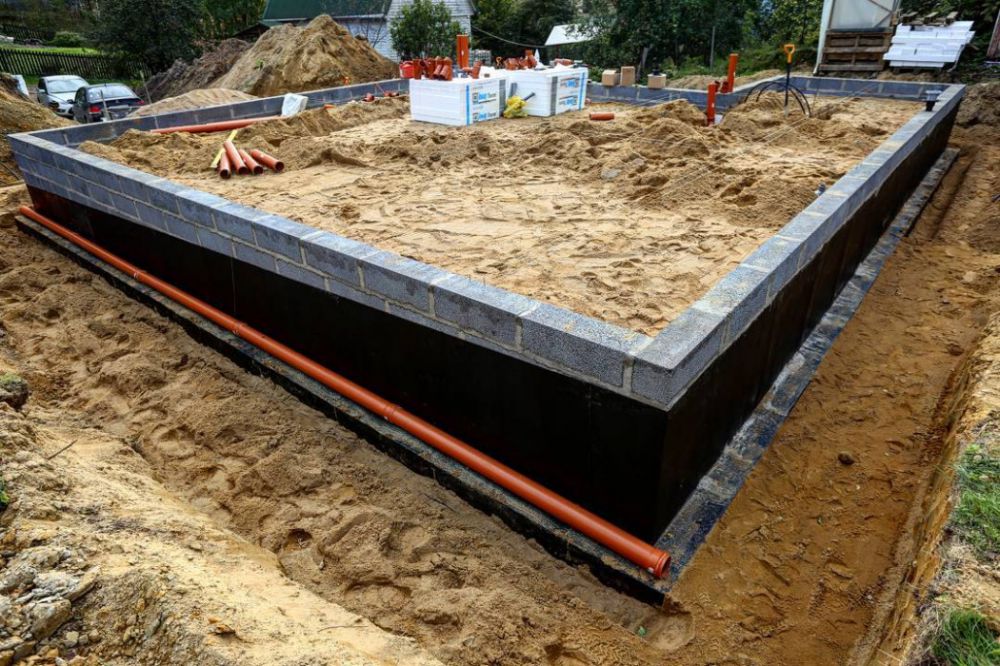
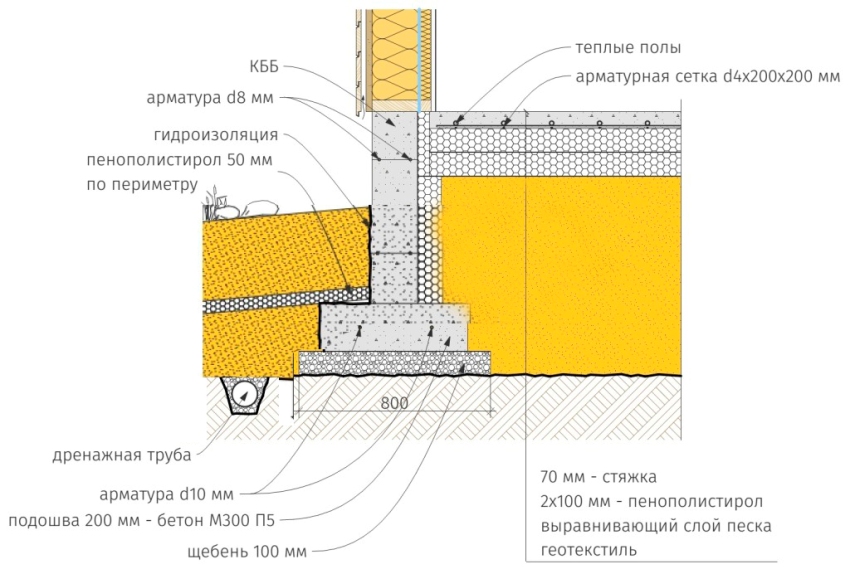
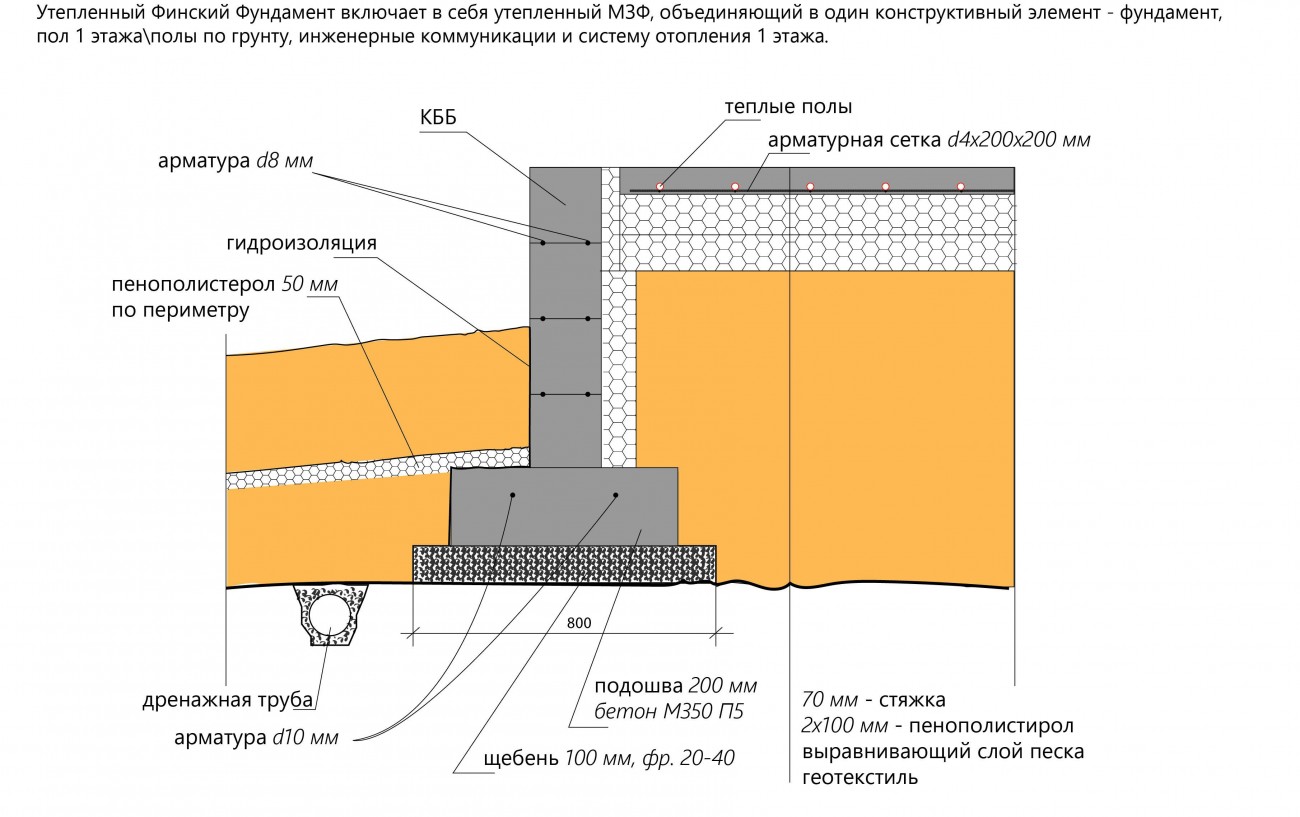
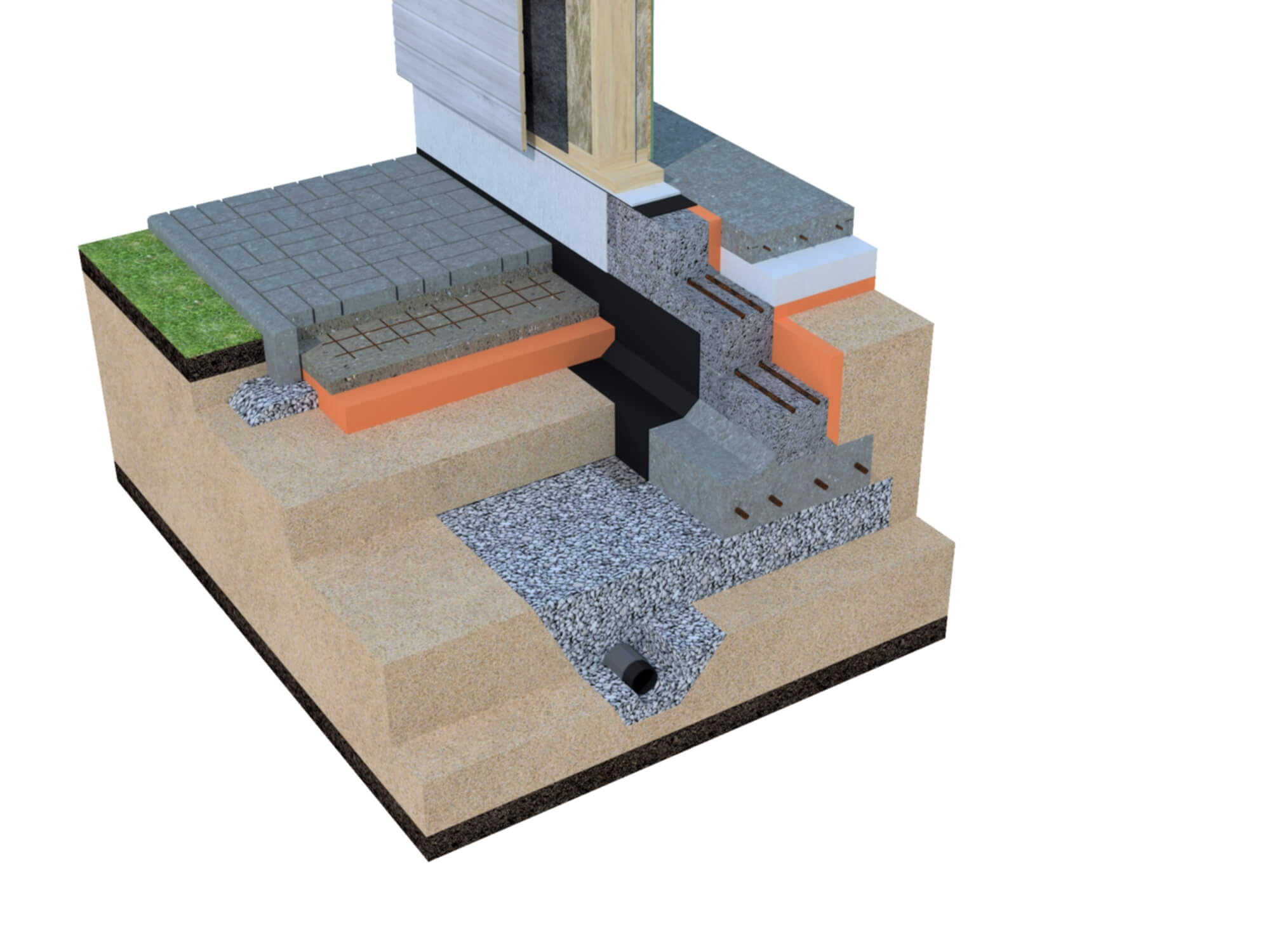
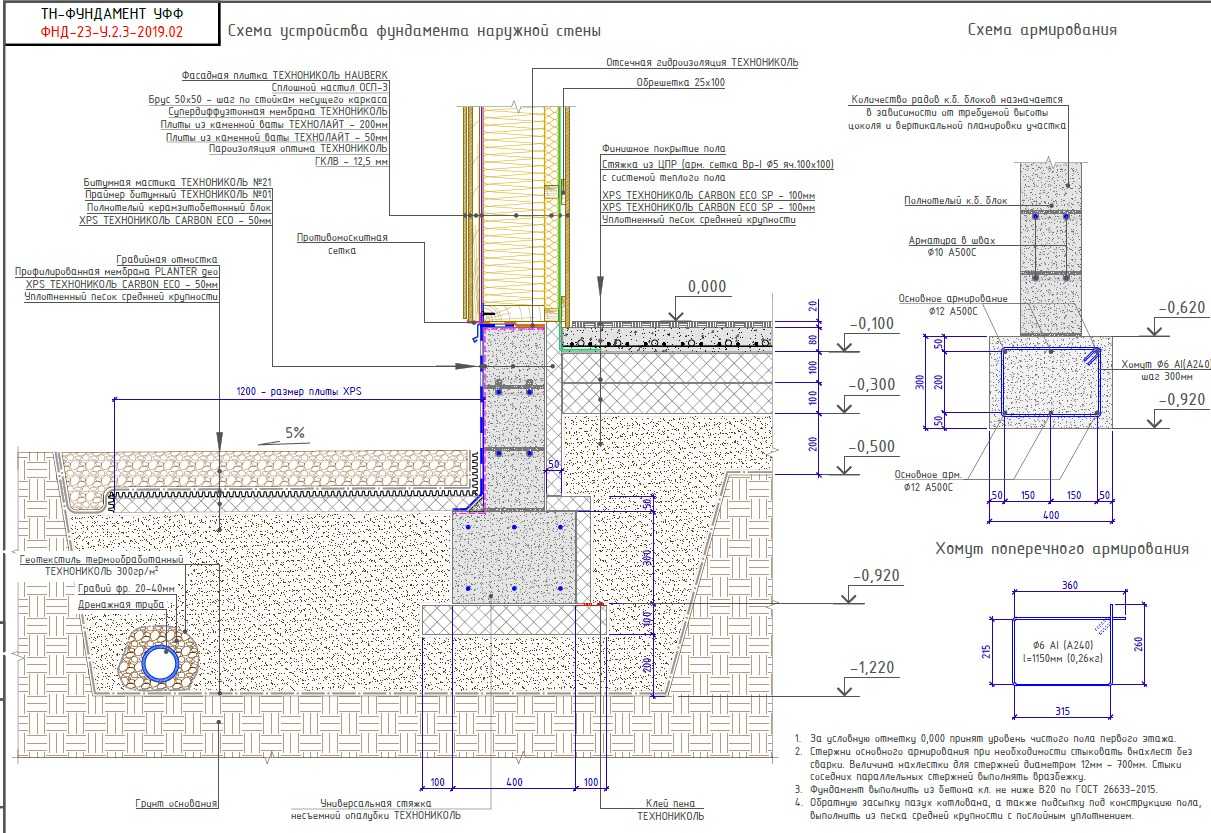
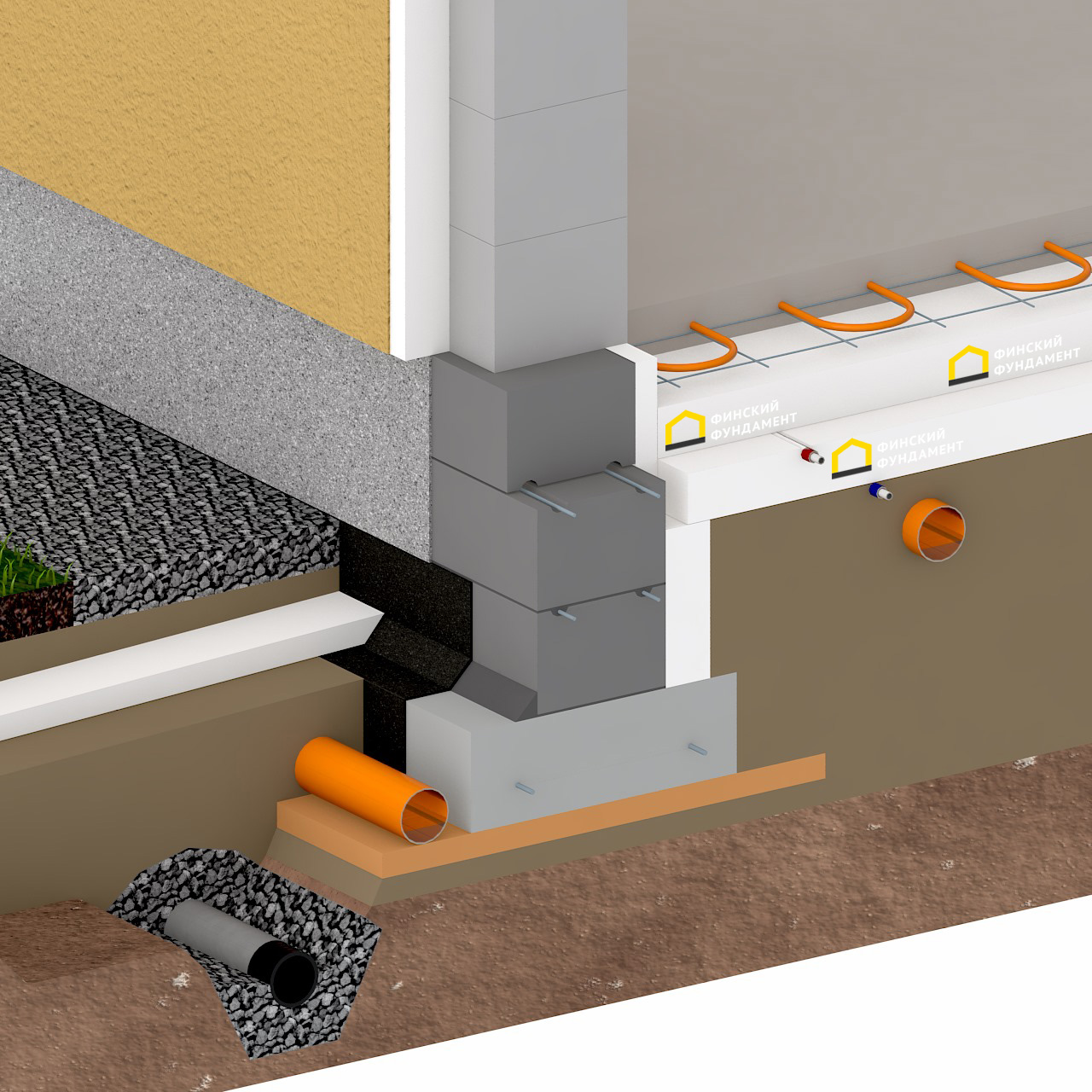
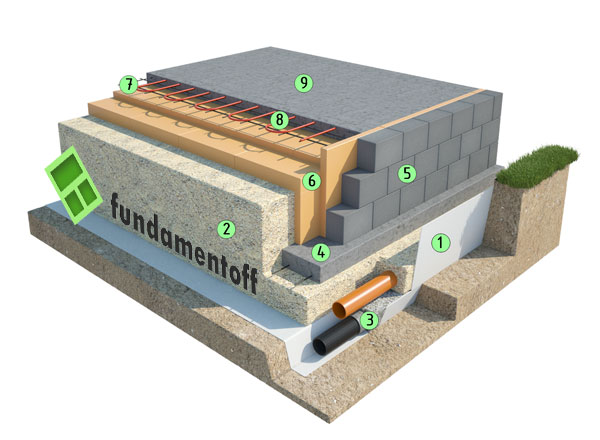
The Finnish slab in its classical form has the form of a prefabricated strip foundation, which can be folded into several rows of KBB (expanded clay concrete blocks). The tape reaches up to 800 mm in height and 200 mm in width. All rows are reinforced with each other using 2 steel bars. The foundation is insulated with expanded polystyrene. Further, it is covered with sand and compacted, the laying of engineering networks is carried out.
The construction of a house, building or any structure is always a responsible and costly process. When erecting them, it is necessary to follow the calculation technique and correctly draw up a drawing of the future structure. With the right approach, you can significantly save at the initial stage of construction.
Video:
When considering the question - with which technology to start installation work, it all depends on the personal preferences of both the customer and the contractor. However, it is recommended to use UFF boards, since, despite their high cost, they have a number of useful properties, which justifies their price.
What is UVF?
The term became famous thanks to construction forums, but is not official. In accordance with the SNiP categories, we are talking about a combination of MZLF and a floor on the ground, for the construction of which external thermal insulation is used.
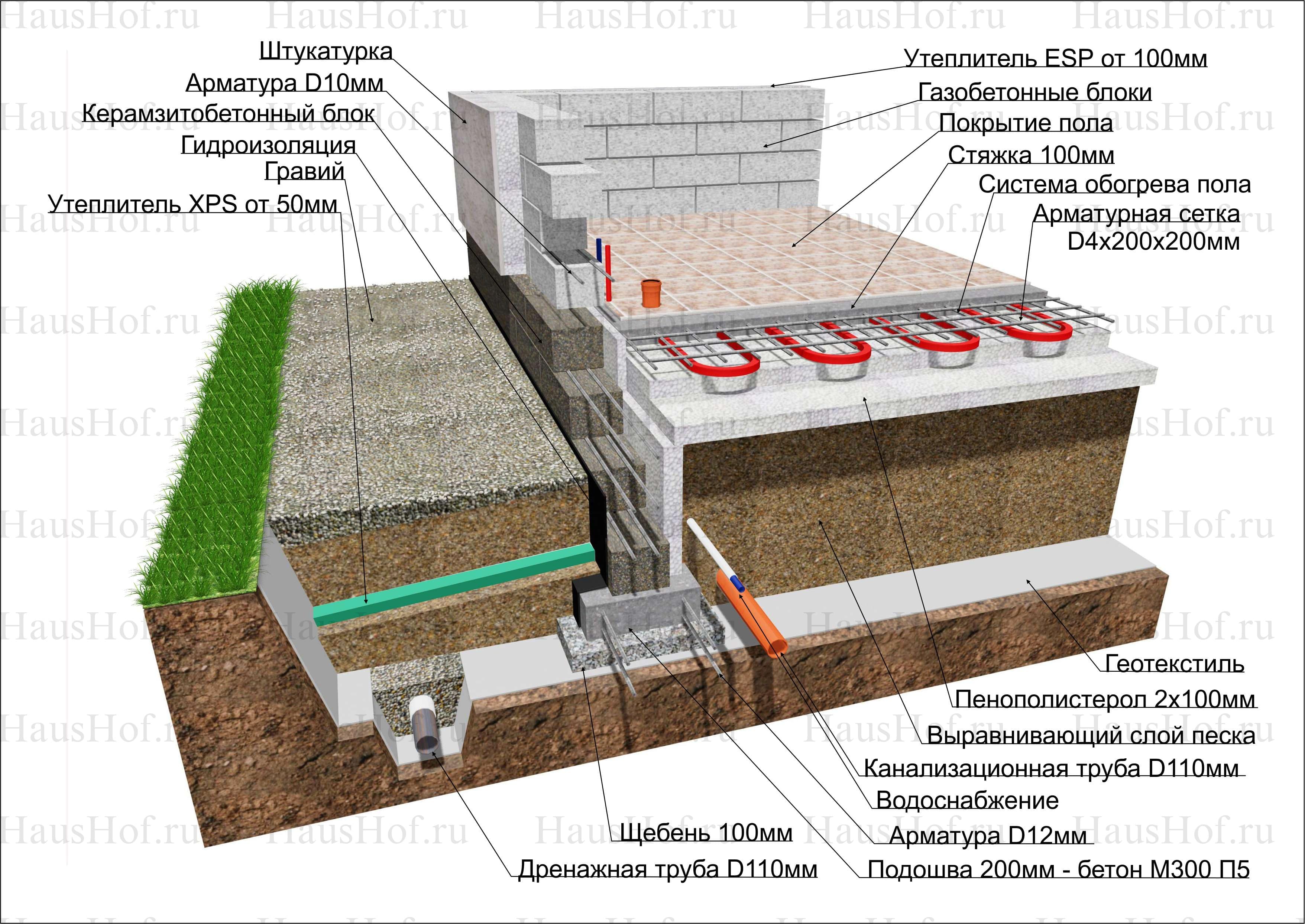
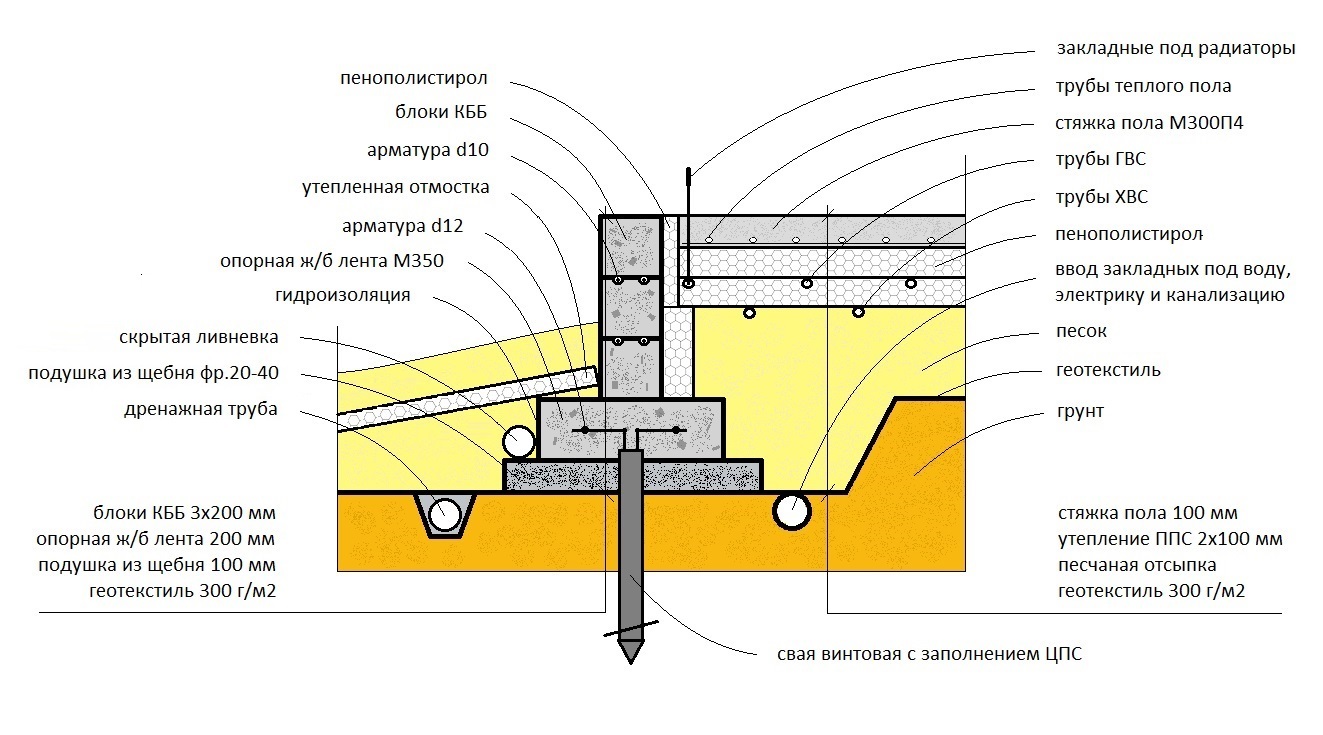
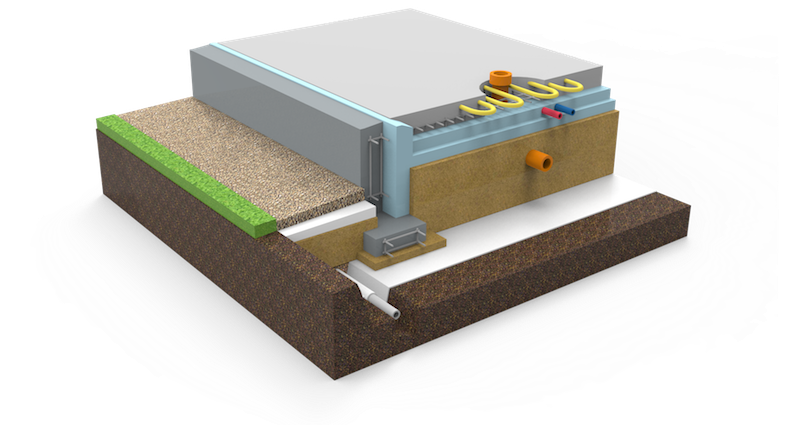
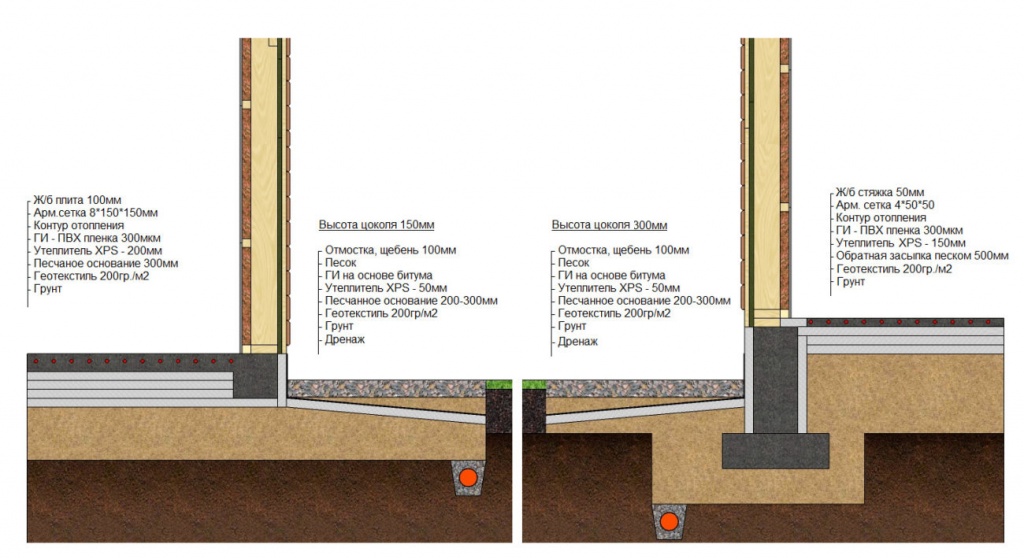
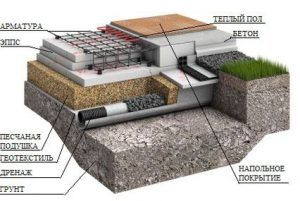
The foundation scheme, which is gaining popularity in the Russian Federation, from the Finnish construction company Omatalo provides:
- Shallow tape foundation, consisting of a concrete base with a section of 600 × 200 and foundation blocks 200 mm thick, making up the base of the required height. Thorough compaction of backfill soil is mandatory.
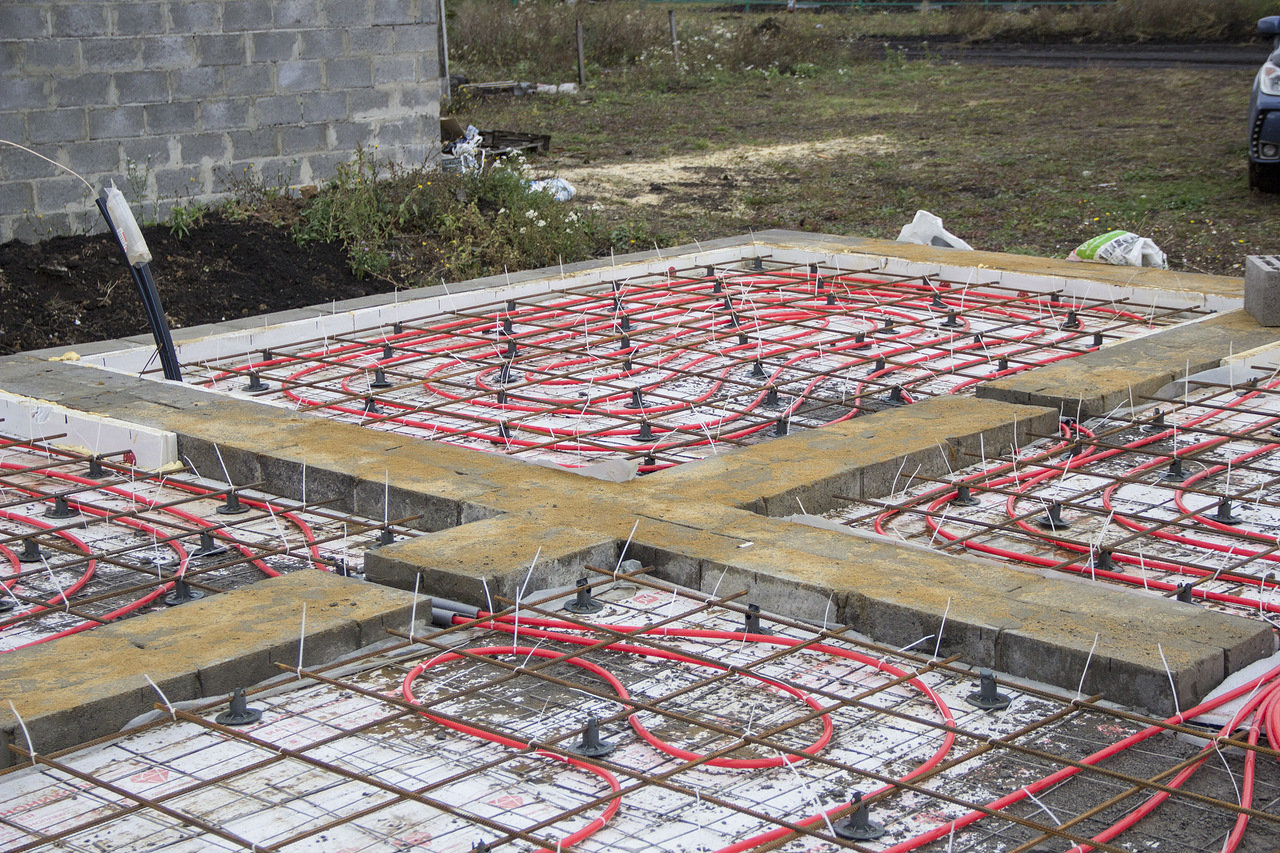
- Reinforced cement-sand screed, 80 mm thick, cast over a 150 mm layer of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). Before pouring, the wiring of the pipes of the water heated floor is laid. The insulating boards rest on fine-grained anti-capillary rubble. Sand filling is located under the rubble.
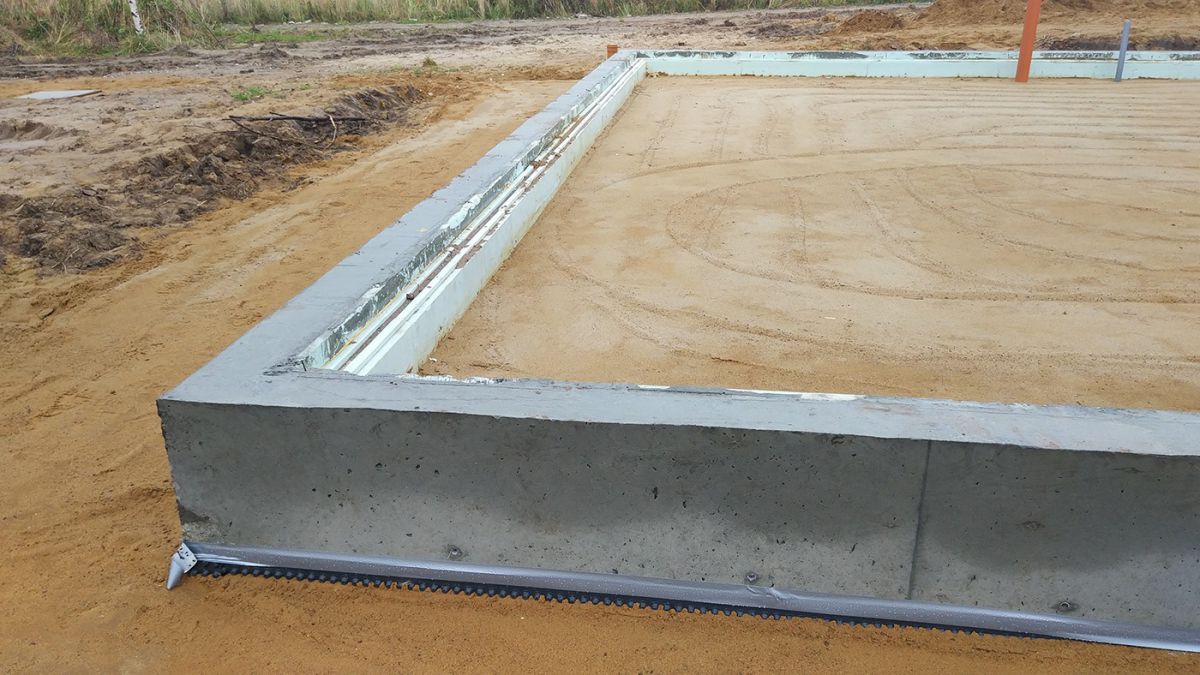
- Structural separation of the plinth and floor slab with an EPPS layer. A slab with a thickness of 50 - 70 mm adjoins the inner side of the plinth and is located at its entire height, resting against the bottom of the foundation cushion.
- Arrangement of the insulated scaffold using 120 mm EPS plates installed along the outer perimeter of the basement at the depth of the top of the foundation cushion.

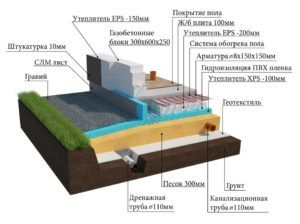
Schematic diagram of the UFF device - insulated Finnish foundation
Developers vary this pattern by varying layer thicknesses, insulation materials, and some other components. For example, instead of EPSP, PSB-S plates (the most durable types of foam plastic) can be installed under the screed, and when installing a warm floor, in some cases, preference is given to electrical systems. In climatic zones with a frost index of more than 70,000, the plinth is preferred to be cast into a fixed formwork made of extruded polystyrene. The common thing for all modifications of uff is the observance of three principles:
- MZLF is located in a trench with compacted backfill soil;
- thermal insulation layers are located under the floor screed, as well as between the base and the screed;
- it is obligatory to install an insulated scaffold with an abutment to the base of the foundation tape.
In European and North American practice, this scheme is not allocated to a special category, but is included in the group of anti-frost or insulated MZLF. Basically, there are two terms:
- Frost Protected Shallow footing / foundations (FPSF) and
- Insulated Shallow footing.
UFF (insulated foundation)
A less popular type of building the foundation of a house, which is gaining strength and differs from the one described above in that it is an insulated tape with a small threshold, which acts as a support and supporting base - UFF. This uff-technology is implemented by using blocks or solid concrete as a tape, placed on a non-removable foam formwork.
Distinctive features of UFF boards
 The differences between the UFF foundation are as follows:
The differences between the UFF foundation are as follows:
- manufacturing of a slab structure that is not connected to the basement and only accepts operational loads;
- the depth of occurrence is from 0.5 to 0.8 m, in contrast to the USHP, where this indicator varies in the range from 0.1 to 0.3 m;
- all communication systems are carried out at the stage of final finishing;
- execution of both external and internal formwork.
Dignity
Having added up all the listed advantages of USWB, a number of individual characteristics should be added that significantly increase the significance of this material:
- the ability to use on soils with a steep slope;
- high basement equipment;
- systematic implementation of warm floors and communications, as well as their affordable repair.
Price policy
Not a significant increase in value in comparison with the previous type. So, the use of UFF will cost the customer 15-20% more expensive with the same quadrature.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using UVF
Let's consider what are the advantages of the foundation, poured according to the Finnish slab technology:
- a profitable and less costly solution for areas with a sloping surface;
- the ability to equip a high basement part;
- ease of adaptation to heavy objects by increasing the size of the heel and tape section, as well as the configuration of the tape itself;
- the option of using block material creates an opportunity for a complete rejection of the arrangement of the Finnish formwork;
- the device of such a foundation does not cause difficulties, the work is performed by a small team of builders;
- since the bearing capacity is performed by the base and the heel under it, in the future you will be able to easily repair the communication lines, because the screed poured over them is "not connected" relative to the foundation tape;

- even after the completion of the construction of the house, it is possible to arrange a "warm floor" system, to lay communications;
- used building materials and technological methods can significantly reduce the total weight of the facility under construction;
- Finnish stoves are excellently used, maintain a comfortable microclimate, save energy resources;
- the structure can be installed on any type of soil composition, even with shallow groundwater.
For all the merits, it's fair to talk a little about the downsides. The main disadvantage is a lot of earthwork, which increases the cost of the structure. But this problem can be compensated for by the size of the base.
Differences between the Finnish slab and other technologies
In the special literature, the codes of the joint venture, the remaining SNiP, there is no differentiation of construction technologies on a national basis. Therefore, both "Swedish" and "Finnish" slabs are rather professional construction slang. The main differences between the Finnish slab foundation and Swedish technology are:
- structure - the slab is not connected to the basement / foundation part, it only perceives operational loads (sometimes the weight of the partitions is added, therefore reinforcement is necessary);
- burial depth - if in the USH the stiffeners have a height of 10 - 20 cm, in the UVF the tape can be buried at any level (0.4 - 0.7 m);
- lack of communications - the warm floor is integrated at the finishing stage, and not at the time of pouring;
- scope of work - more excavation, backfilling;
- formwork - in the USHP only outside, in the UFF an internal one is added, which increases the construction budget.
Insulation of the blind area is similar in both versions, the heat insulator is laid along the perimeter at a depth of 30 - 40 cm.Drainage traditionally takes place at the level of the basement base, the cost of communications is the same.
UFF - Insulated Finnish Foundation
This foundation is not yet as popular as UWB, but I am sure that it will take its course. Strictly speaking, the abbreviation UFF appeared on the same Forum House, when this type had to be somehow distinguished from all others. We tried to call it an insulated Finnish plate (UFP) and something else, but UFF is not really a plate.
In general, such a construction has been well used in Russia for a long time and is known as a “tape with floors on the ground”. True, the differences between the UFF and the simplest floors on the ground are practically the same as that of the USP from a “simple” reinforced concrete slab.
The UFF owes its appearance to another active member of the forumhouse, known under the nickname Tim1313, who decided to "remodel" it for his house, using information from his brother, who built houses in Finland and is well acquainted with this technology.
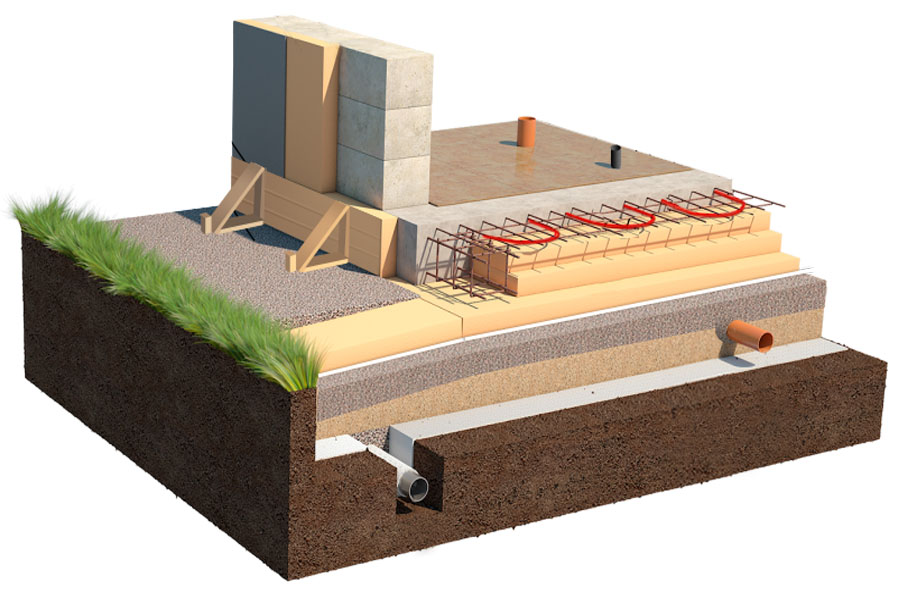
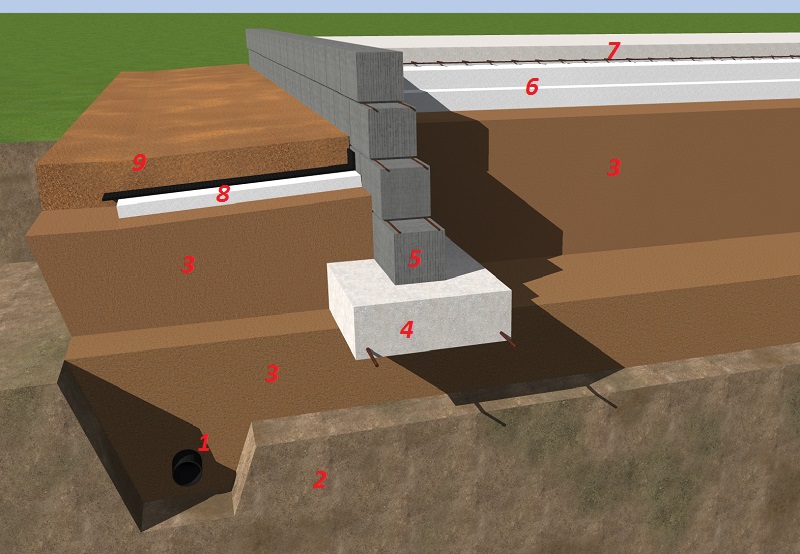
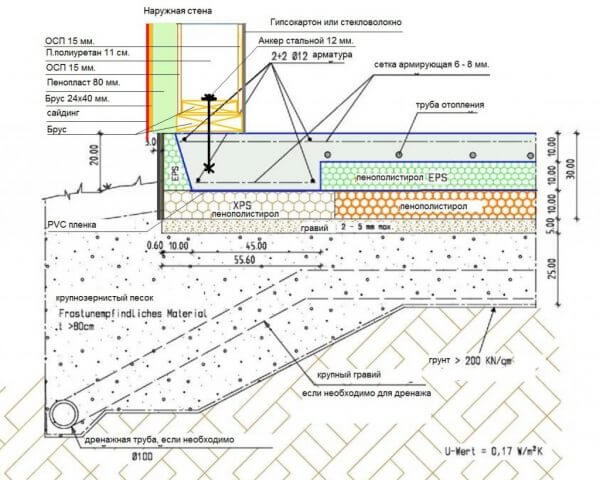
If we have a USHP, this is a trough with foam concrete and underfloor heating, then UFF is an insulated tape with a “heel” that plays a supporting and load-bearing role, backfilled with well-compacted soil, and a well-insulated screed with warm floors. There are many options for such tapes, I will give a diagram from the Finnish house-building concern Omatalo (Finndomo)
The original scheme of the Finnish foundation from the company Omatalo (finndomo)
Simplified but working circuit by Tim1313
The same Scandinavians can have many implementations of UFF construction - both blocks and monolithic concrete can be used as a "tape", and in a fixed formwork made of foam. With large slopes and in some other cases, they can refuse backfilling and overlap with reinforced concrete slabs, with the further arrangement of an insulated screed along them. Different schemes of tape and perimeter insulation can be used. In Norway, due to the nature of rocky soils, they often make a tape without a heel, on a crushed stone pillow.
Benefits of UVF
Actually, all the same advantages as that of UWB, only to them you can add something that removes some of the disadvantages of UWB
- May be more profitable and less labor-intensive on sloped areas
- The ability to make a "high base" - the actual height of the base is limited only by your finances.
- Easier to adapt for heavy houses (the size of the heel and the cross-section of the tape increases, the configuration of the tape under load-bearing walls)
- The option with a base of blocks allows you to abandon the use of formwork almost 100% - which saves both time and money.
- Oddly enough, this type of foundation is "clearer" for domestic builders and, accordingly, it is easier to find performers.
- Potentially better maintainability of communications in the distant future, since, in contrast to the USHP, the base and the heel under it play a bearing role, and the tie with communications is “untied” relative to the tape.
- The ability to carry out communications, to make a warm floor and a screed after the house is "under the roof" - by the way, a very popular option in Scandinavia
Disadvantages and cost of UVF
It makes no sense to describe separately the cost of UFF and its shortcomings, since these are interrelated things. The main disadvantage of the UFF is the large number of works, including earthen and a large amount of "loose" for backfilling. Accordingly, this leads to an increase in the cost of UWF relative to UWB. The rest of the drawbacks are the same as those of the “Swedish” plate, with the exception of those solved by the UFF.
But the increase in value isn't dramatic. In general, UWF will cost 10-15 percent more than USP. Although in some cases, it may be comparable, if not cheaper. Moreover, the cost of the UFF will directly depend on the height of the base that you wish. The higher - the more expensive.
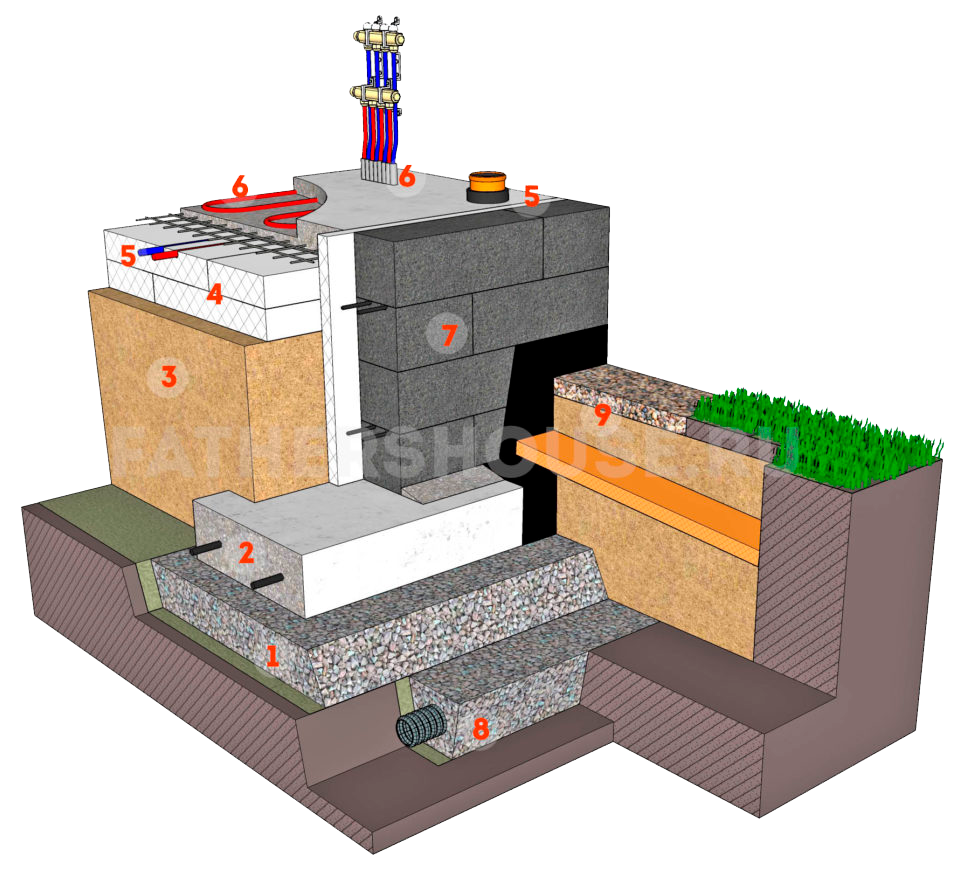
Support heel and block plinth
Backfill with internal insulation
Underfloor heating layout and screed filling
EPPS formwork for a monolithic plinth, also a popular option in Scandinavia
(Visited 56 813 times, 1 visits today)
Pros and cons of UVF
Like most building structures, the insulated Finnish foundation has advantages and disadvantages. Among the main advantages, experts call:
- the possibility of installing the base on any type of soil, except for weak peatlands with a high level of groundwater;
- economical consumption of materials in comparison with other types of bases, except for the Swedish plate, where the cost is approximately the same;
- the floor screed is not load-bearing and the entire weight load from the enclosing structures is transferred to the strip part of the foundation;
- the presence of a built-in underfloor heating reduces the cost of heating installation;
- filling the insulated floor is possible at any time of the year;
- the possibility of constructing a supporting base on small slopes and with differences in relief heights.
The disadvantages of the Finnish slab foundation technology include:
- the need for earthworks with digging a trench and foundation pit, which may require the involvement of special equipment;
- backfilling with non-metallic materials after installation of the tape part, followed by mechanical ramming;
- low bearing capacity of a shallow tape that limits the number of storeys in buildings.
As you can see, for a light one-story individual construction, the insulated Finnish foundation is a technically and economically feasible option.
Description of construction technology
The construction of the insulated Finnish foundation consists of several successive stages:
- determination of the construction site, performance of design calculations and development of the graphic part;
- pit marking;
- complete removal of the fertile layer;
- development of a trench for a shallow strip foundation;
- crushed stone drainage layer;
- laying a waterproofing layer;
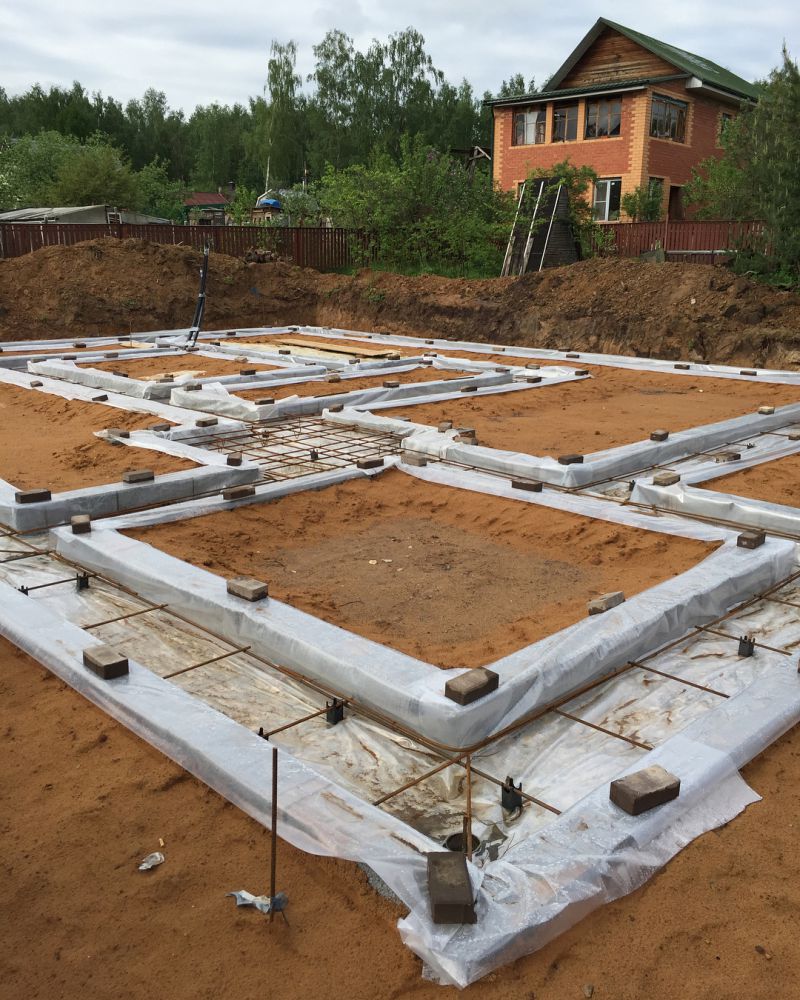
- installation of a reinforced support cushion MZLF;
- laying of a foundation tape from building blocks;
- internal insulation of the strip foundation with polystyrene foam plates;
- backfilling of the inner part of the pit with fine gravel and sand;
- laying floor insulation slabs and reinforcing mesh;
- installation of floor heating pipes;
- pouring concrete for the device of the slab;
- laying the blind area insulation around the perimeter of the building.
At the final stage, a blind area is installed and unused soil is removed.
Layout and excavation
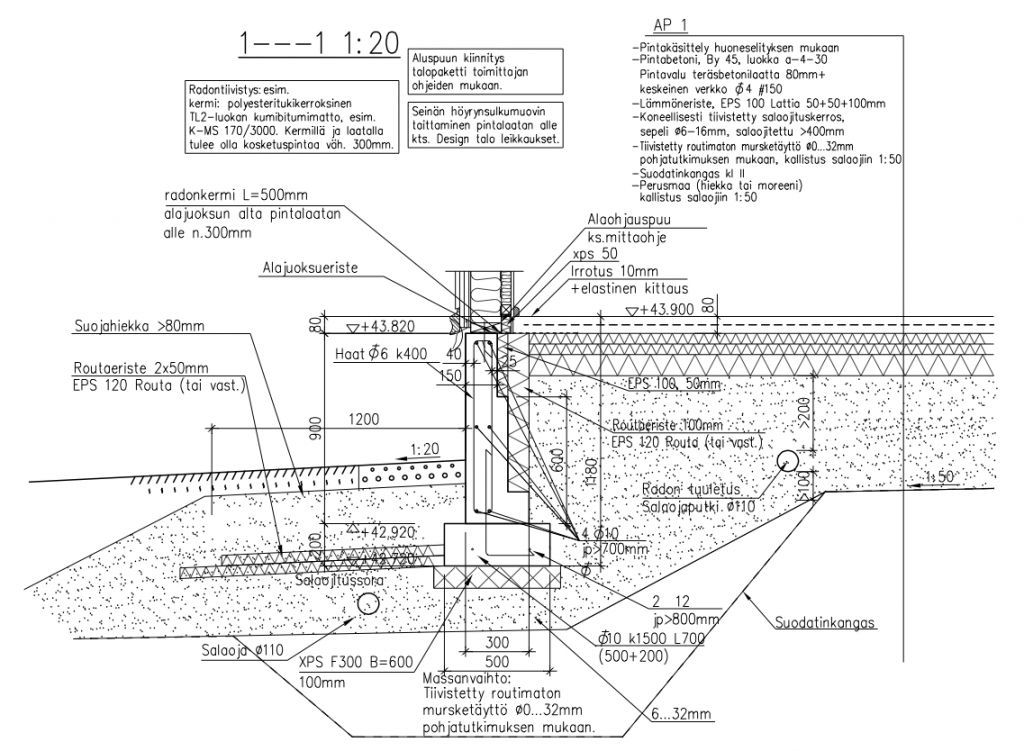
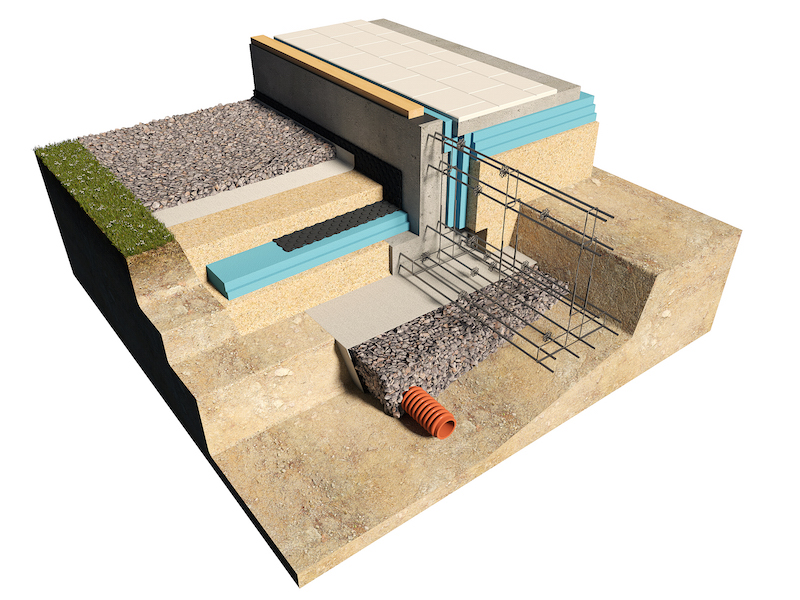
The marking of the future foundation should be carried out in strict accordance with the adopted design decisions.In this case, the existing external communications, access roads, the boundaries of the building site and other factors should be taken into account. The working axes are marked with a cord stretched along the horizontal strips with a margin of 500 mm from the outer perimeter of the building.
After that, the fertile layer must be removed to the depth of germination of the plant root system. Under all load-bearing walls, a trench should be dug to the design depth of the strip foundation with a margin for the installation of a bulk drainage layer.
 Excavation and cushion laying.
Excavation and cushion laying.
Drainage, underlayment and installation of the foundation tape
A layer of crushed stone 200 mm thick is poured into the trenches for the MZLF device, compacted and covered with a layer of geotextile.
 Next, the underlying sand cushion is poured and the formwork is installed to fill the base plate of the tape.
Next, the underlying sand cushion is poured and the formwork is installed to fill the base plate of the tape.
The reinforcement cage is knitted, laid inside the formwork and poured with concrete.
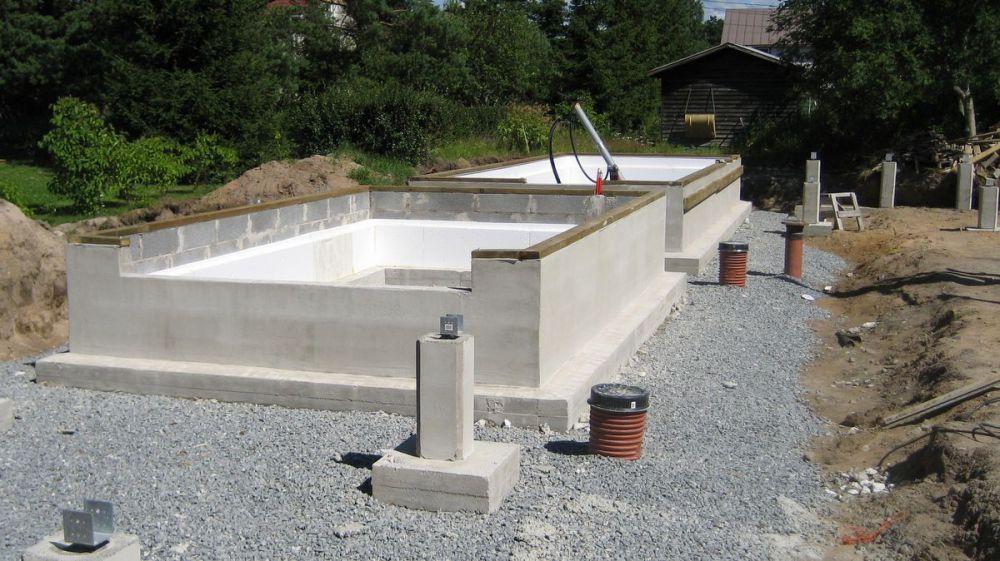
During the hardening of concrete, it is possible to carry out work on the removal or leveling of the soil taken out of the pit and trenches. After the concrete mixture has set, it is possible to lay building blocks to the calculated height of the basement. For high base / plinth heights, it is recommended to lay a reinforcing mesh every 3 rows of blocks.
The outer and inner surface of the plinth must be insulated from moisture. To do this, it is necessary to use gluing waterproofing materials for the outer surface, and coating materials for the inner side (more about their types - here).
Waterproofing.
Backfilling of underlying layers and laying of insulation
Install polystyrene foam boards vertically along the inner surface of the base to a thickness of at least 100 mm and fix them. Lay geotextile fabric at the bottom of the pit and fill in rubble for the device of the drainage layer. The backfill must be carefully compacted with a vibrating plate.
Lay 3 layers of roll hydraulic insulation on the crushed stone layer with gluing all strips and layers together. In this case, it is necessary to provide a margin of waterproofing for wrapping it on the vertical wall of the basement part of the strip foundation.
Lay insulation plates over the entire area of the pit to create a layer 200 or more millimeters thick.
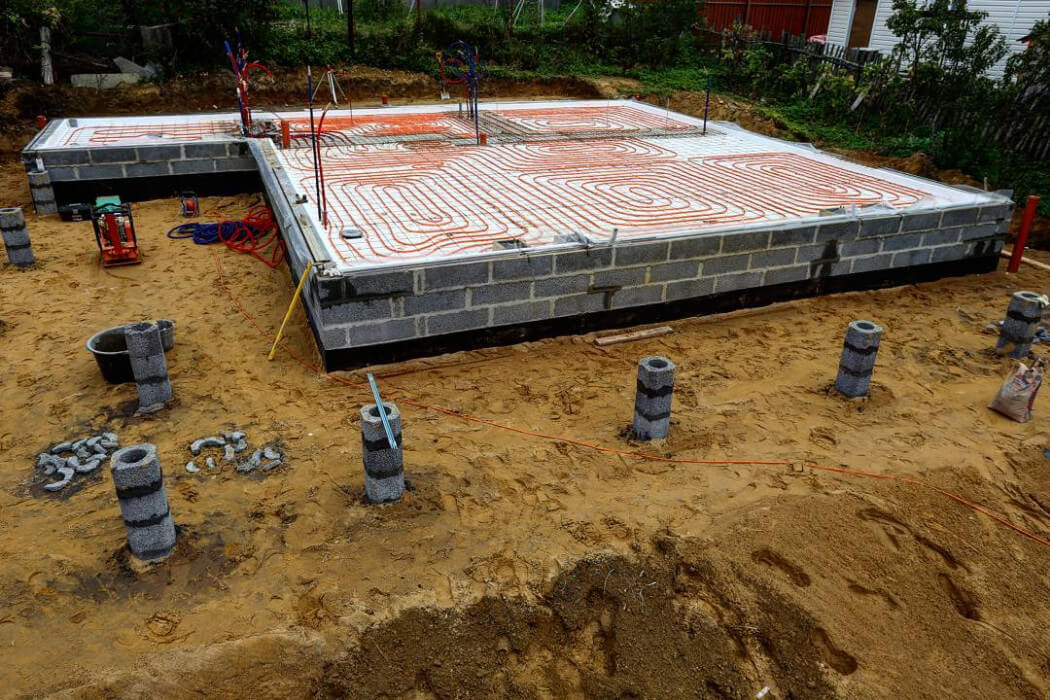
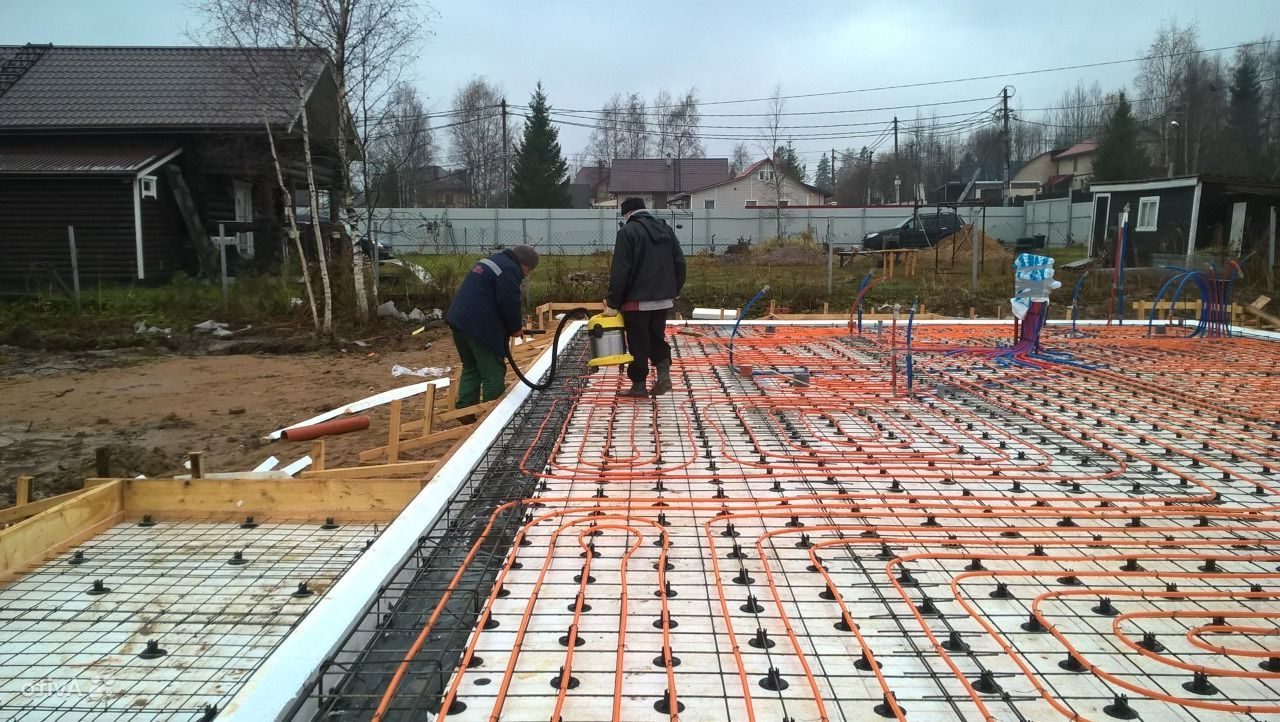
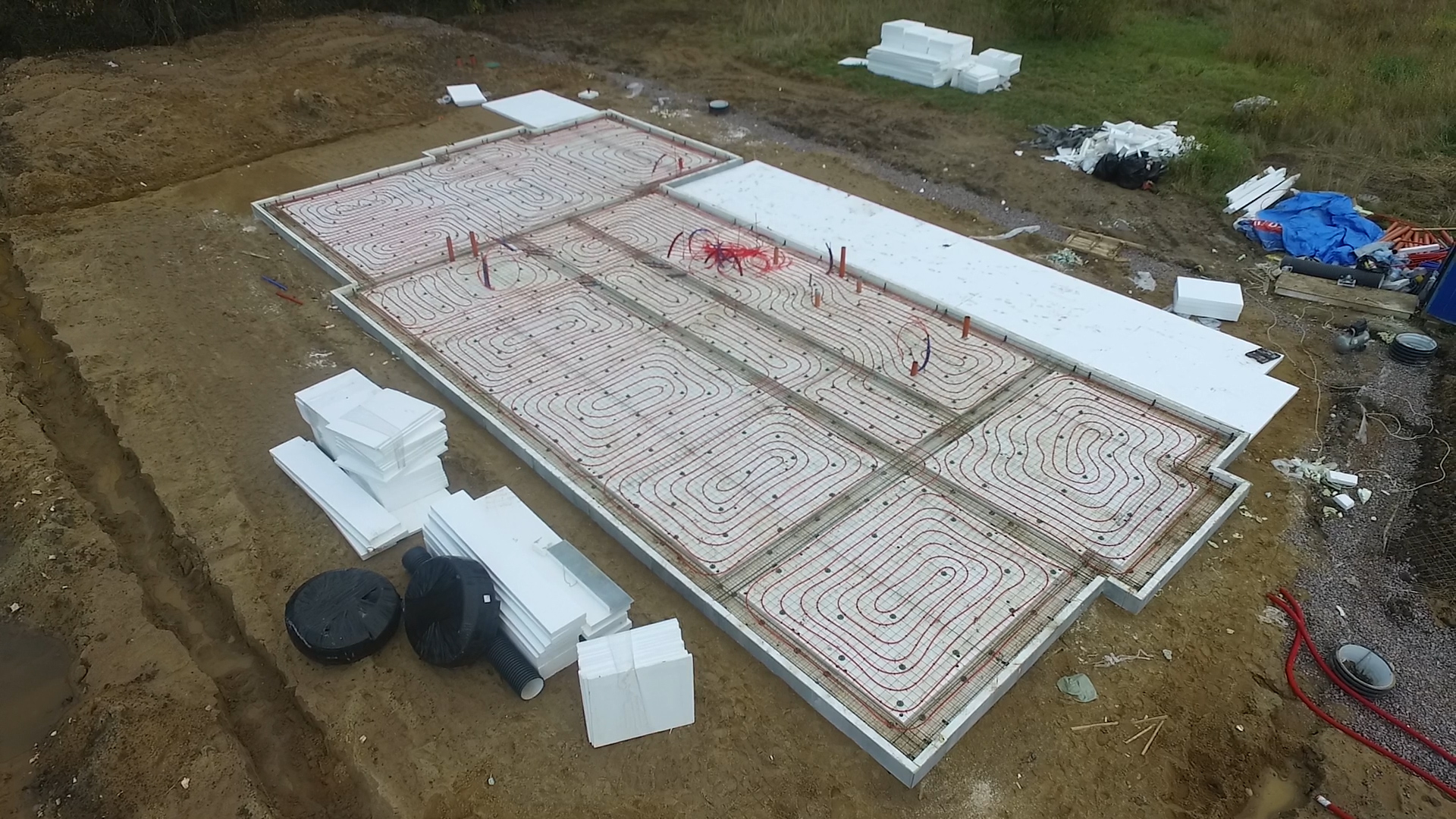
Reinforcement, pipe installation and concrete pouring
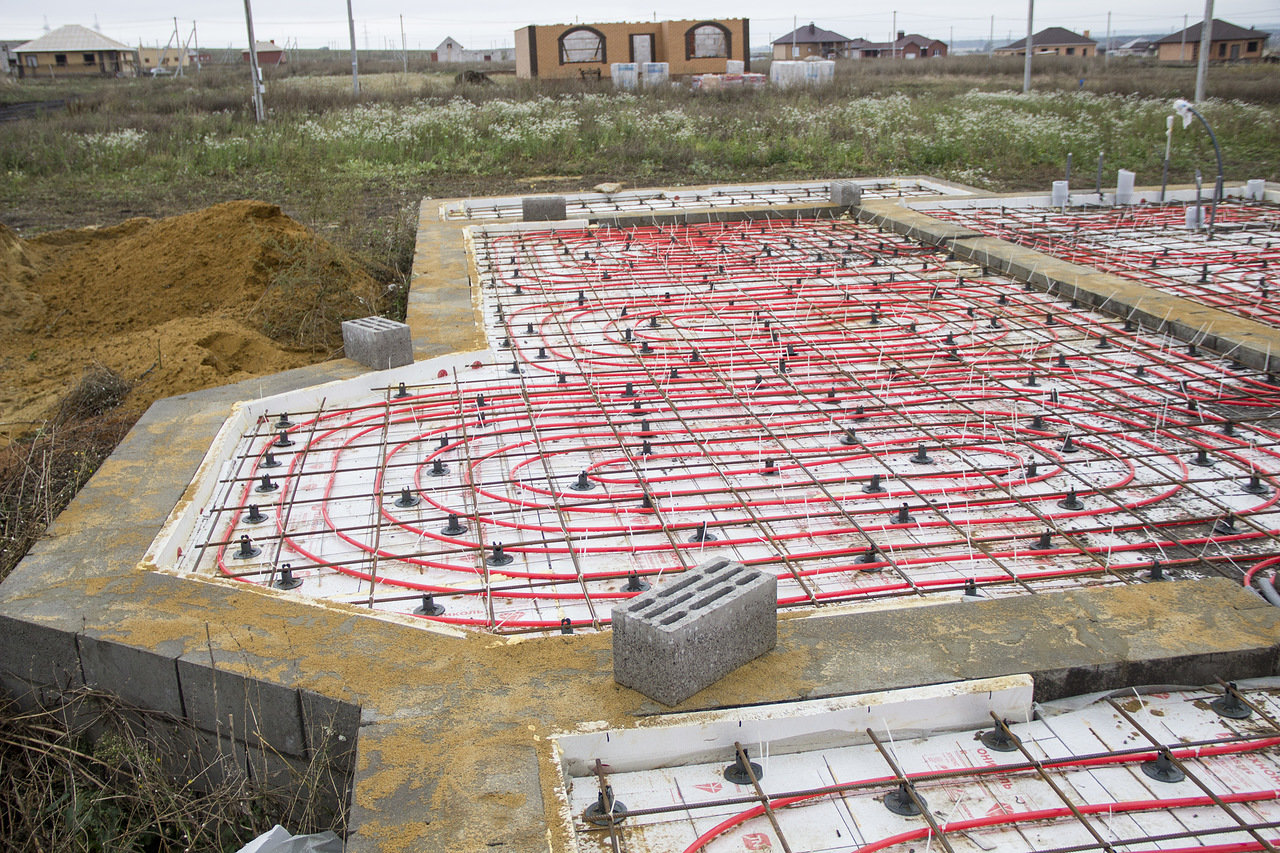
Lay ready-made or self-knitted reinforcing meshes with a mesh size of no more than 150 mm on the surface of the insulation (for more details on reinforcement, see here).
 Mount the pipes of the underfloor heating water on top of the mesh, tying them to the fittings.
Mount the pipes of the underfloor heating water on top of the mesh, tying them to the fittings.
The length of the pipeline in each individual circuit should not exceed 90 meters with a diameter of 14 mm and 120 meters with a diameter of 16mm. Therefore, when installing pipes, you will get several heating circuits, depending on the total area of the house.
Reinforcement.
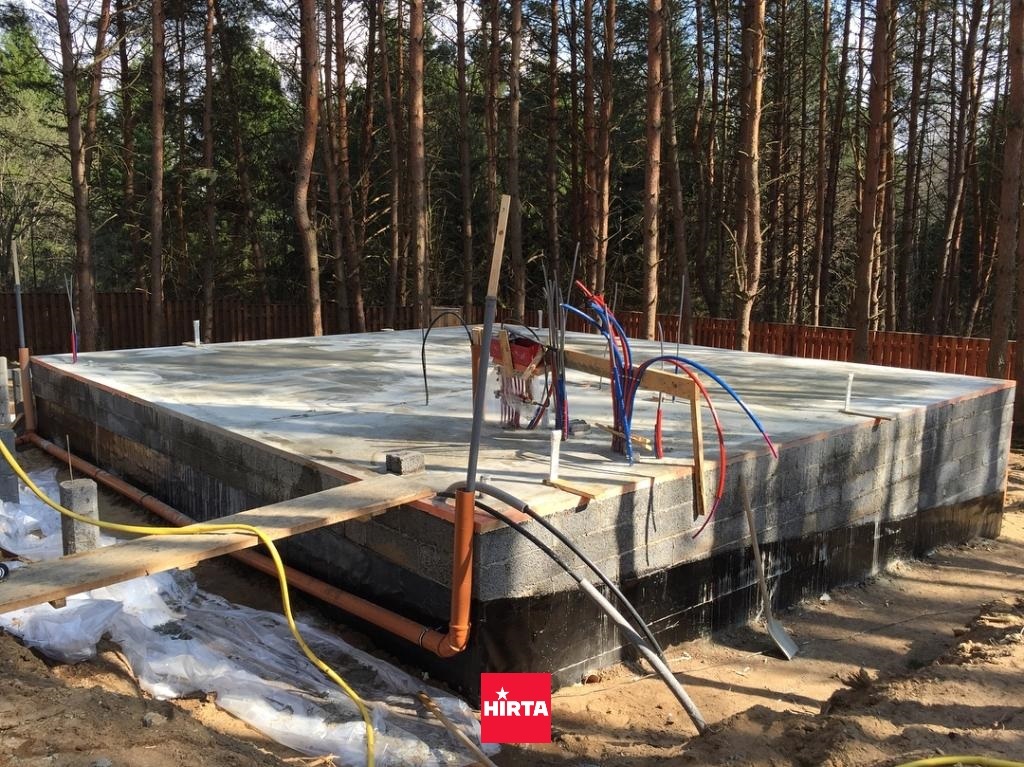
The concrete mixture must be poured in one working shift, without making technological breaks. To do this, it is recommended to use the services of a centralized delivery of prefabricated concrete. The poured mixture must be well compacted using a submersible vibrator or vibrating screed.
 Pouring concrete.
Pouring concrete.
Warm blind area device
The base of the blind area is a layer of rubble and sand, covered with geotextiles. On top of it, insulation slabs, a reinforcing mesh are laid and a layer of concrete is poured. The width of the blind area is at least one meter. When placing concrete, the slope of the surface should be observed to the side of the house.
 Insulation of the blind area.
Insulation of the blind area.
In more detail, the technology for arranging the insulated Finnish foundation step by step can be seen in the following video.
How the UVF works
So, for the correct laying of the UFF, you need to go through a number of complex works, the quality of the foundation being erected depends on the correctness of their implementation. For this purpose:
- It is necessary to decide on a place suitable for building.
- When choosing a location, all the features of the landscape are taken into account.
- The markup should be done with a margin of about 0.5 m.
- The fertile soil layer must be completely removed.
- Then, a trench is dug at a depth equal to the level of the bed and the most optimal height of the backfill layer.
- Further drainage is installed.
- Waterproofing is installed under the pillow and reinforced.
- The formwork is being installed.
- A communications system is being installed.
 UVF device
UVF device
This is a rather complex and responsible process that requires an increased concentration of attention, and therefore, the help of specialists is sometimes simply necessary.
Budget options for mounting the base
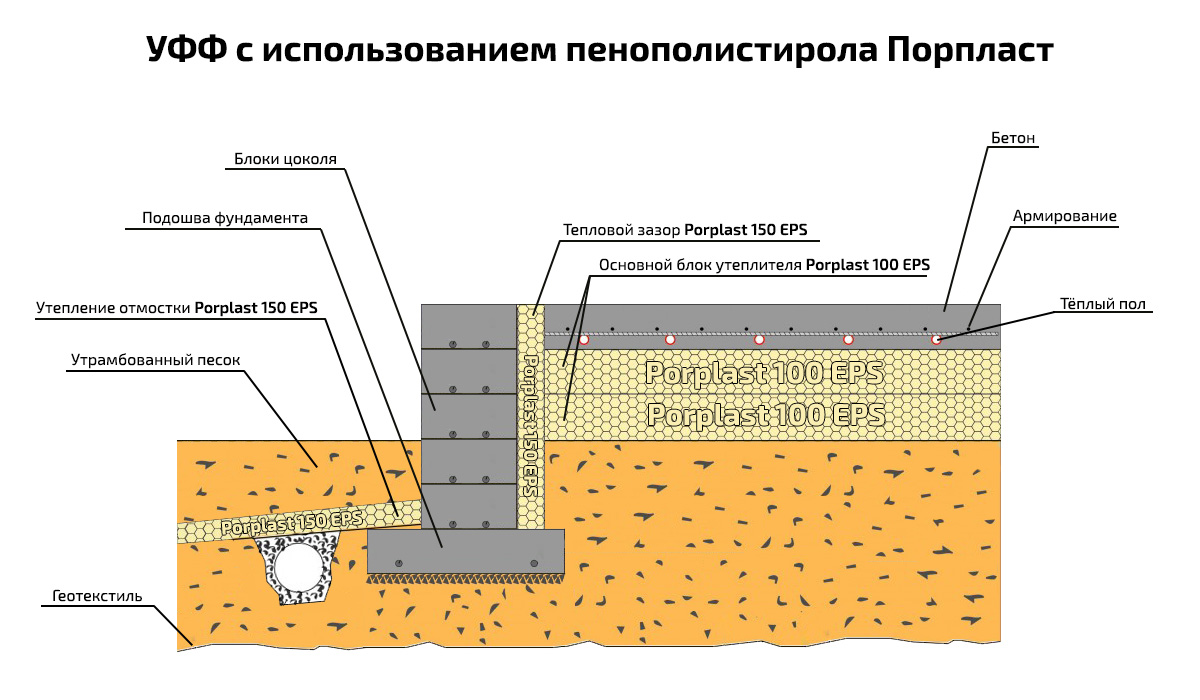
 The design of the insulated shallow slab
The design of the insulated shallow slab
Of the whole variety of types of foundations for Finnish houses, the following representatives should be distinguished:
- Insulated shallow concrete slab. Around the perimeter of the area of the future building, soil is dug to a depth of 50 to 60 cm. 30 cm of sand and gravel mixture is poured into the resulting depressions with high-quality compaction of each of the layers. Extruded polystyrene foam is laid on top of the resulting substrate and a waterproofing membrane is placed. Further, concrete is laid with additional reinforcement in a thickness of 30 cm. As a result, a small concrete slab is obtained, protruding 10-15 cm above the ground surface. Subsequently, a plinth made of brick or concrete components is arranged on the resulting base to a height of 40-50 cm ... The presented type of foundation takes a middle place in terms of pricing, however, it is one of the most versatile and durable types of foundation that can withstand any house made using Finnish technology, be it glued beams or a wooden frame.
- Pile grillage foundation. Along the perimeter of the base, taking into account the connecting beams under the grillage, piles are driven in by means of a small installation. Such work can be easily handled by using the services of a small pit-drill. The number of piles is pre-determined according to the future load. Due to the fairly light equipment and the piles used, this foundation is accessible on any type of soil and is convenient in arrangement. Each of the placed piles is cleaned and connected with a welding machine to the grillage reinforcement. Watch a video on how to build a house using Finnish technology on a pile foundation.
Bored pile foundation. Being a type of the previous foundation, the presented type is distinguished by the construction technology, which consists in drilling holes, reinforcing them and pouring concrete. All other processes, in particular the construction of the grillage, are identical to the method described above.
The described pile foundation construction methods are easily carried out independently or with the use of a small number of serviced equipment and personnel, which greatly reduces the cost of its arrangement.