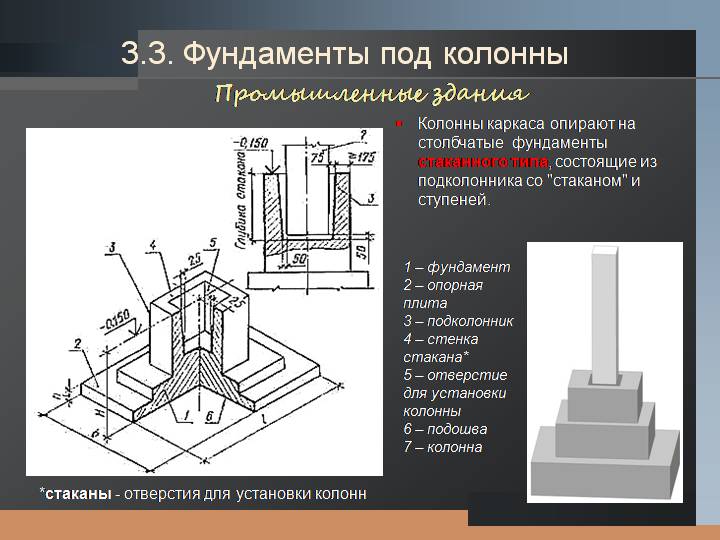
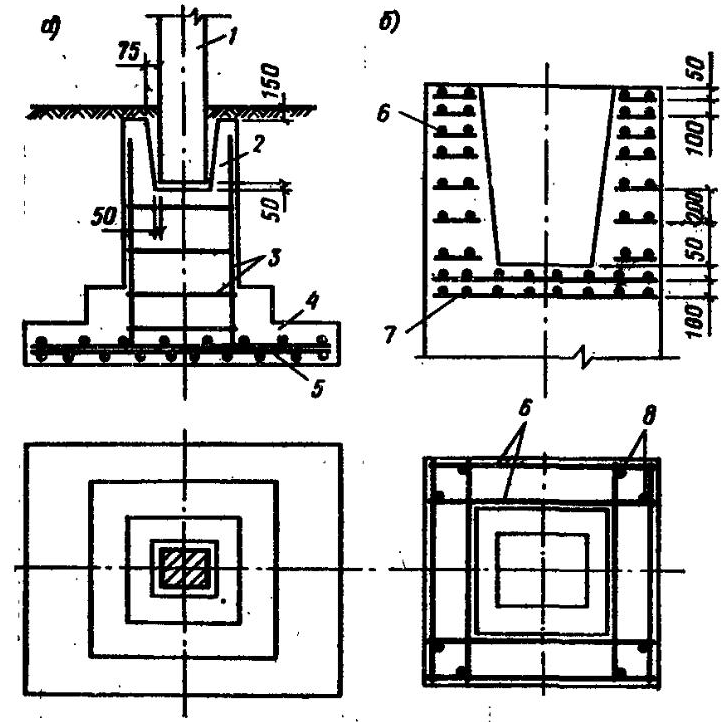
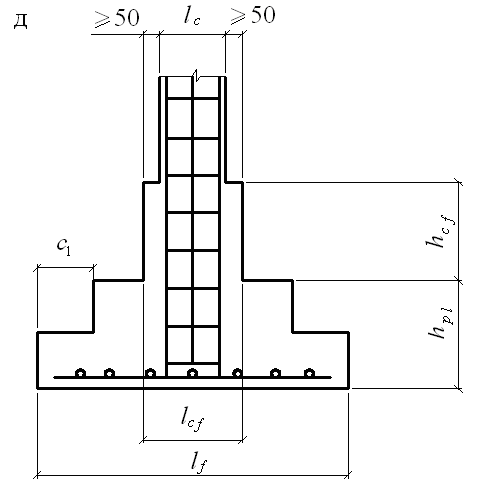
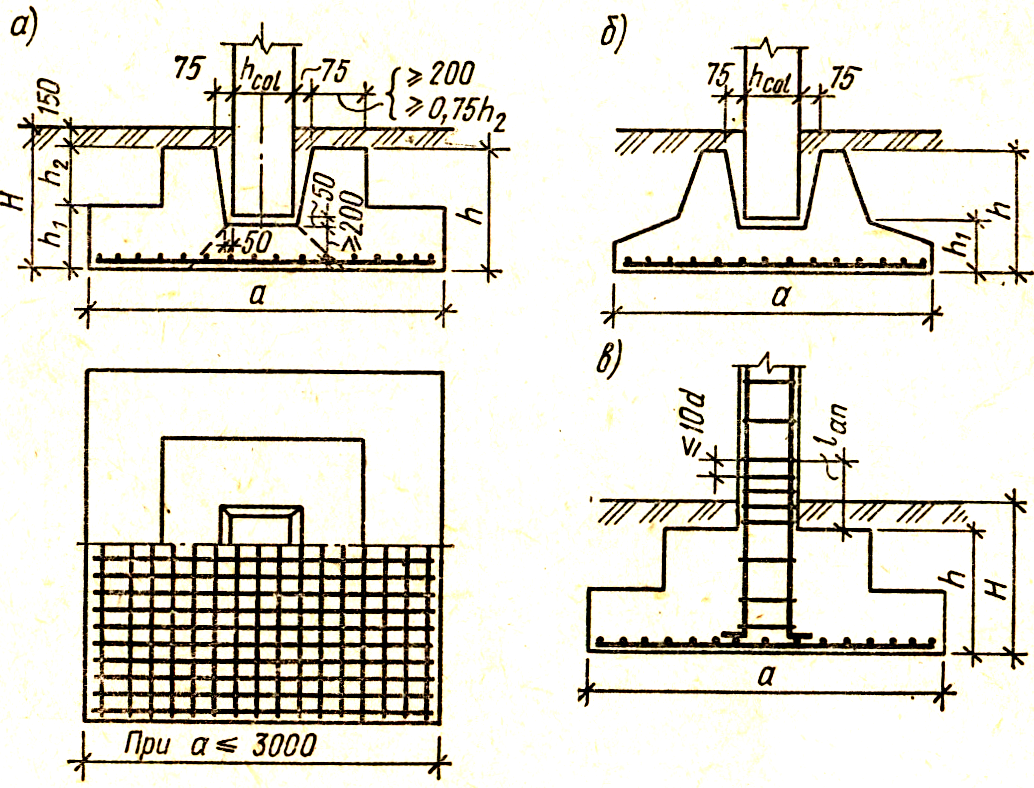
Concrete works
After verifying that the installation is correct
formwork and reinforcement make foundations concreting.
Concrete transport
carried out by a concrete mixer with unloading into rotary bunkers or
receiving funnel of the concrete pump.
The scope of work on concreting
foundations include:
reception and supply of concrete mix;
laying and compacting concrete mix.
Concrete supply in the structure
is provided in two versions:
vehicle crane SMK-10 v
rotary bunkers;
concrete pump SB-126A (with
concrete mix mobility from 4 to 16 cm).
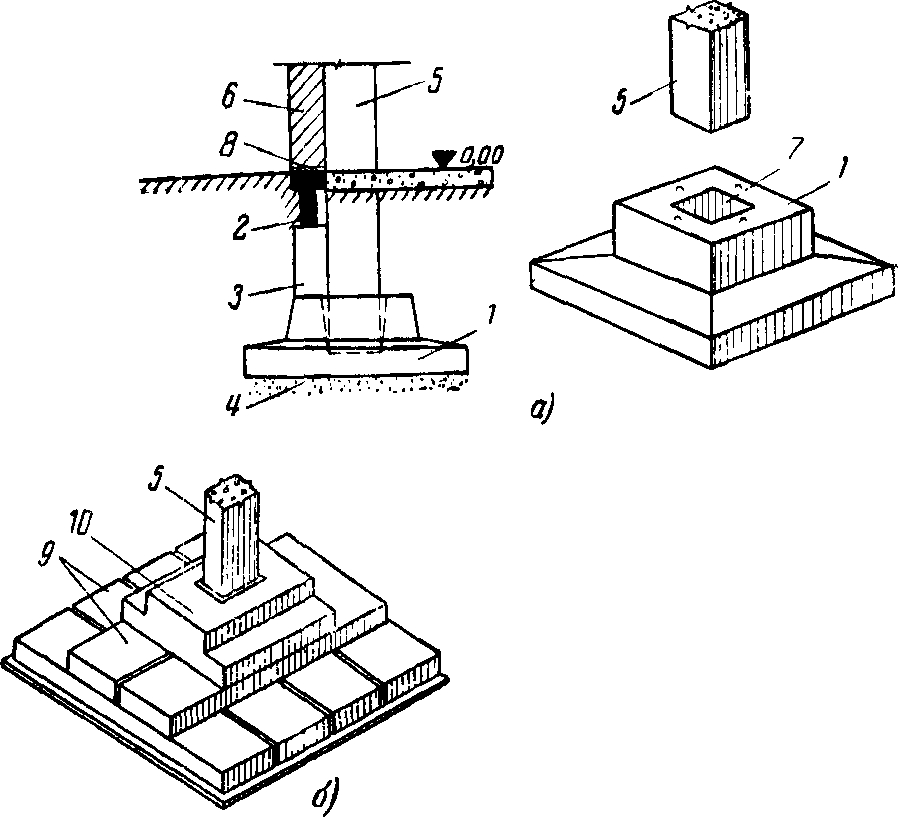
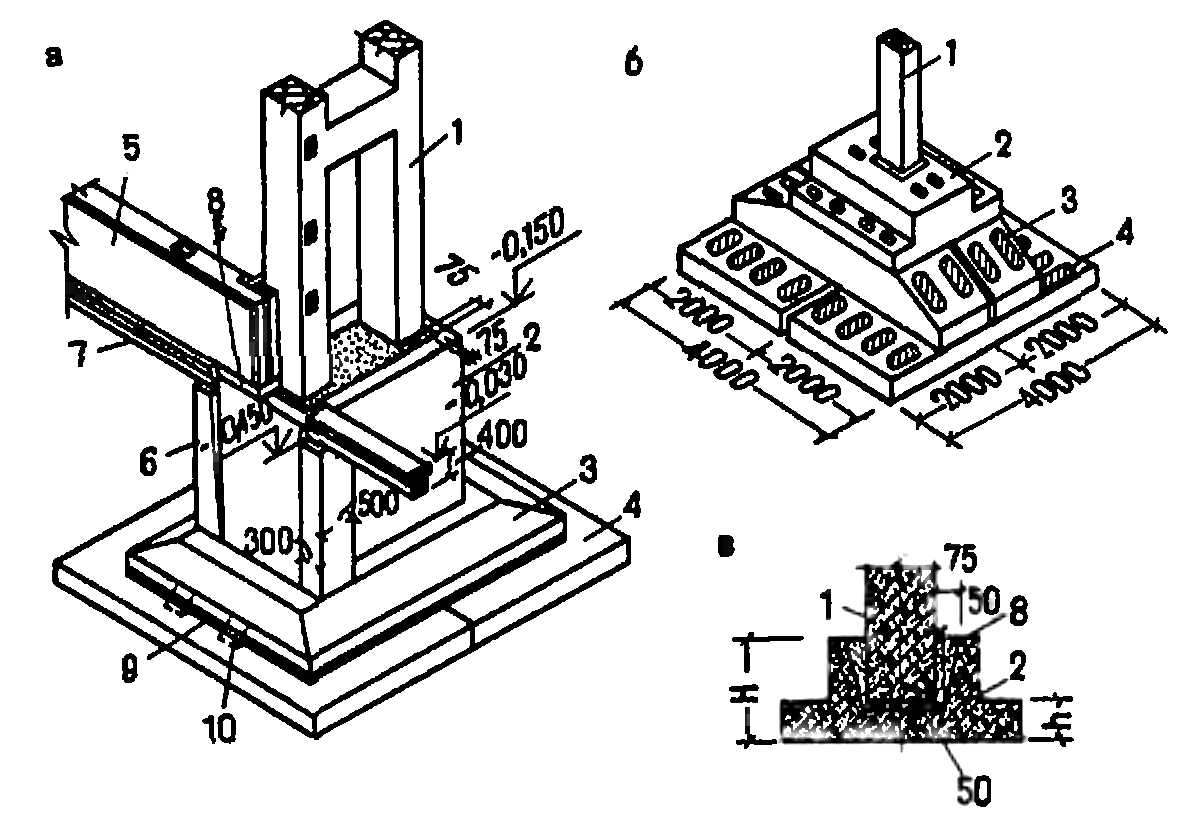
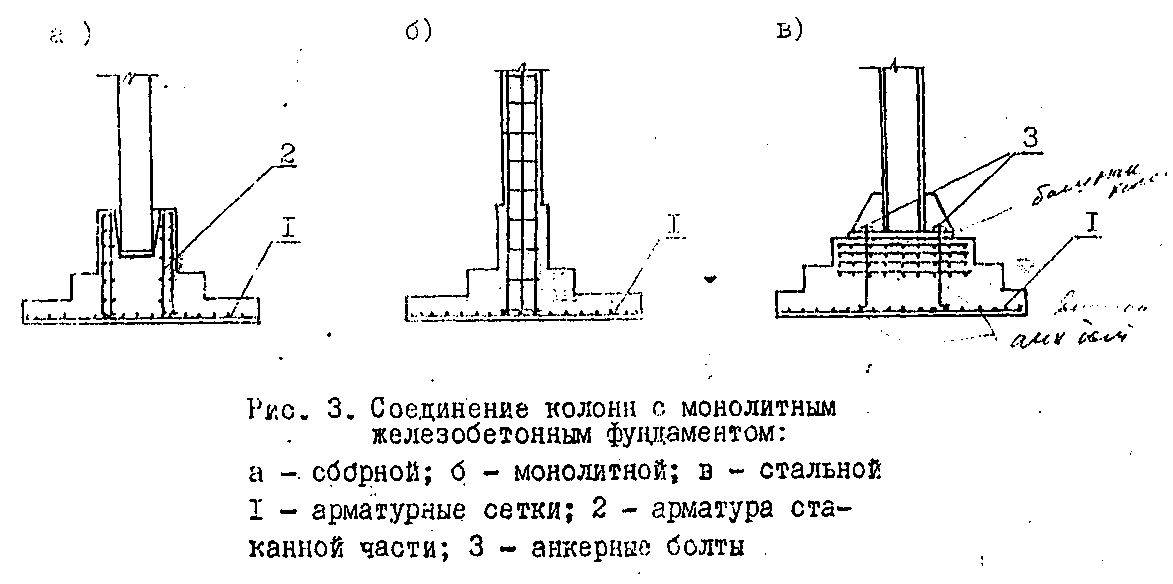
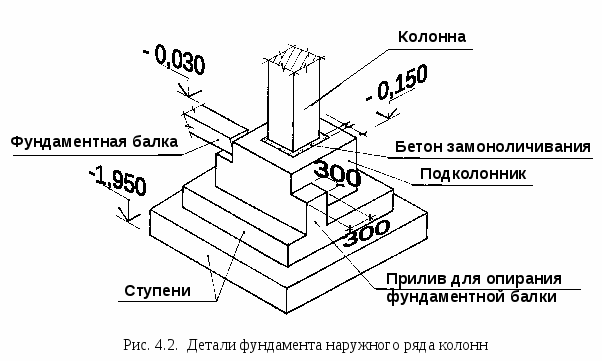
Foundations concreting
is carried out in two stages: at the first stage, the foundation shoe is concreted and
sub-column to the bottom of the liner; at the second stage, the upper part is concreted
the sub-column after installing the liner.
The concrete mix is laid
horizontal layers 30 - 40 cm thick.
Each layer of poured concrete
carefully compacted with a deep vibrator. When compacting concrete mix, the end
the working part of the vibrator should be immersed in a previously laid layer of concrete on
depth 5 - 10 cm. The vibrator ball should not exceed 1.5 radius
his actions.
Overlapping the previous concrete layer
the next one must be performed before the start of the setting of concrete in the previous
layer.
Concrete formwork in the corners and near the walls
the mixture is additionally compacted by bayonetting with manual metal shurovki.
Foundations are concreted with
mounted scaffolds.
When concreting monolithic
foundations with concrete pump SB-126A operating range of the distribution boom
allows you to lay the concrete mix in one row from two points.
Concrete care measures in
period of curing, the procedure and timing of their implementation, control over the implementation
these measures must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 3.03.01-87
“Load bearing building envelopes. Work rules ".
The aging period and the frequency of watering are prescribed by the construction laboratory.
3.
REQUIREMENTS FOR QUALITY AND ACCEPTANCE OF WORKS
Maximum position deviation
formwork elements, reinforcement and made monolithic foundations in relation to
alignment axes or reference marks during acceptance should not exceed the values
specified in SNiP
3.03.01-87.
Technical criteria and means
control of operations and processes are given in table. 1.
Table 1
|
Name |
Item |
Tool |
Periodicity |
Responsible |
Technical |
|
Mounting |
Bias |
Ruler |
V |
Master |
Permissible |
|
Deviation |
Plumb line, |
V |
Also |
Permissible |
|
|
Mounting |
Deviation |
Ruler |
During |
Also |
Permitted |
|
Bias |
Also |
Also |
Also |
Permissible |
|
|
Deviation |
Geodesic |
Also |
Also |
Permissible |
|
|
Styling |
Thickness |
Visually |
Also |
Also |
Thickness |
|
Sealing |
Also |
Also |
Also |
Step |
|
|
Mobility |
Cone |
For |
Construction |
Mobility |
|
|
Composition |
By |
Also |
Also |
Experienced |
|
|
Stripping |
Examination |
Visually |
After |
Manufacturer |
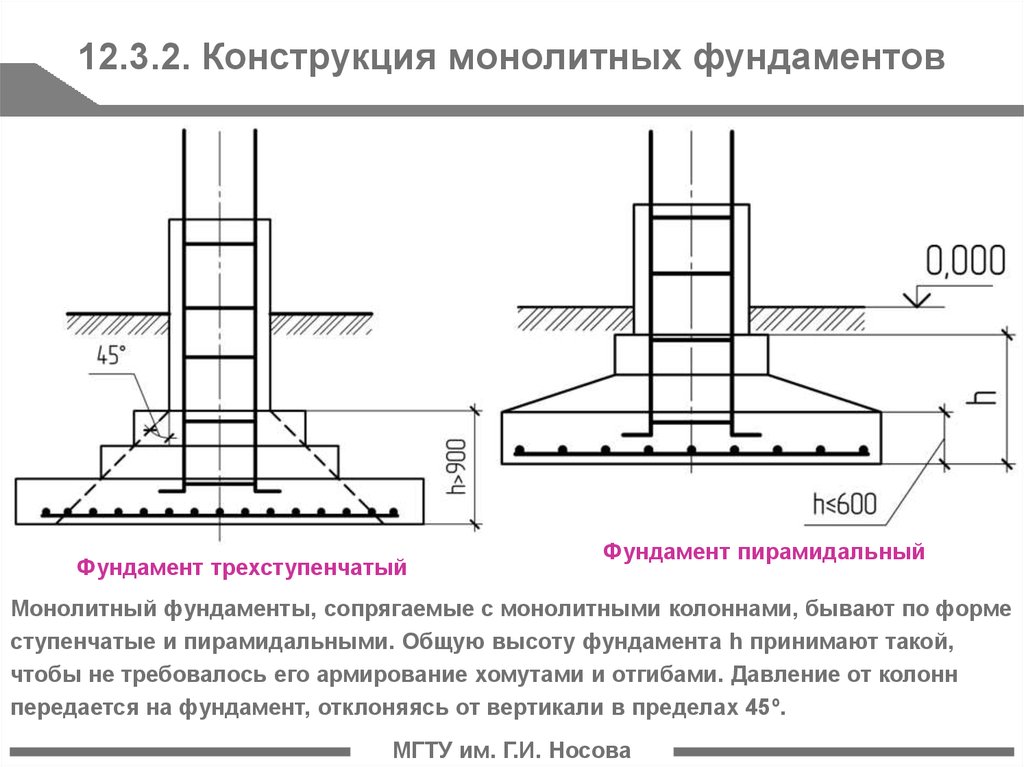
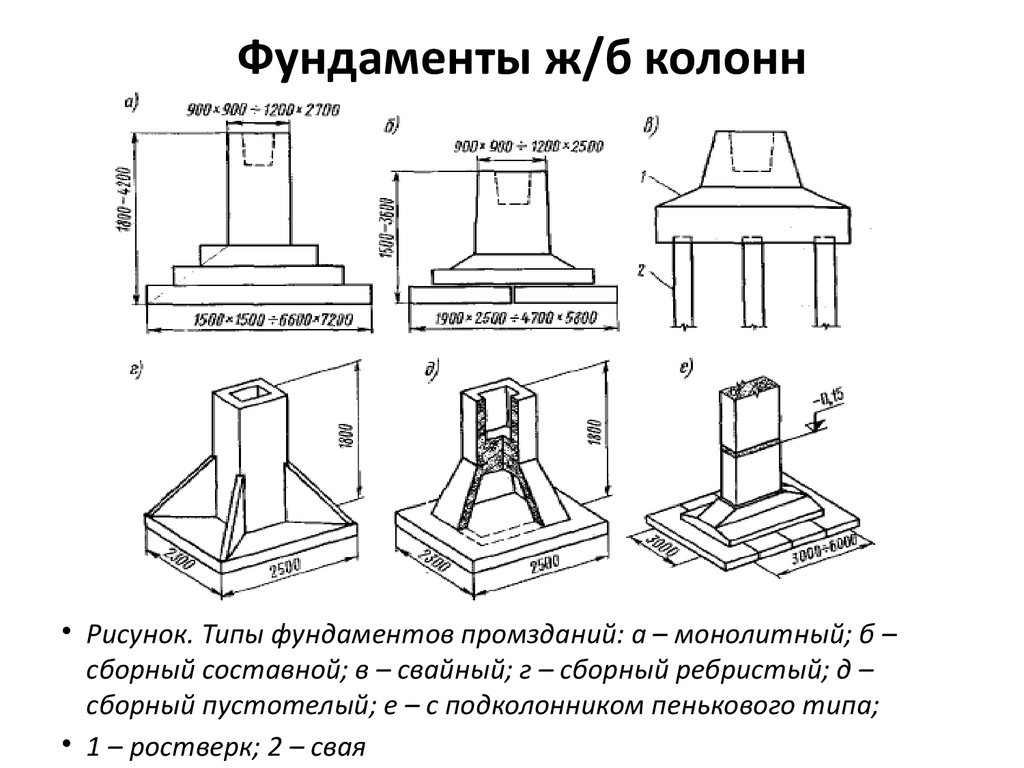
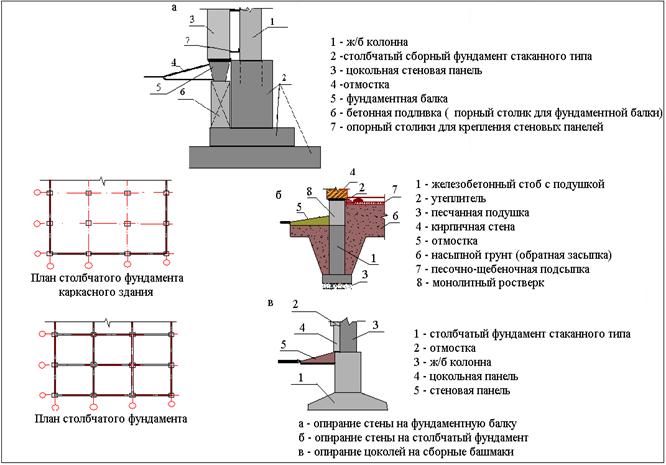
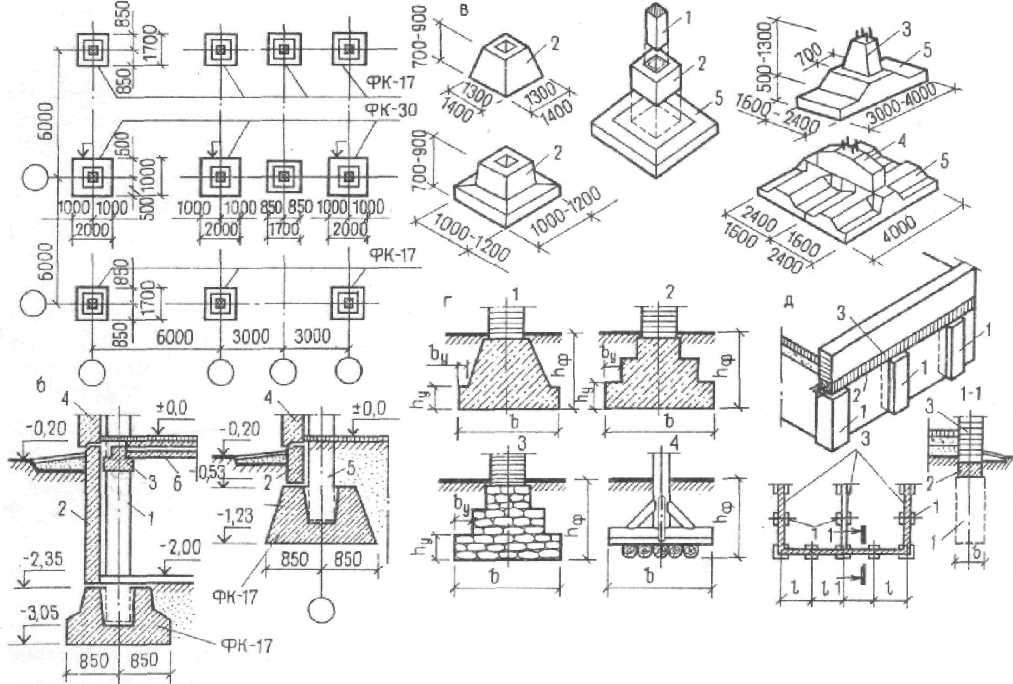
What types of foundations are made for walls
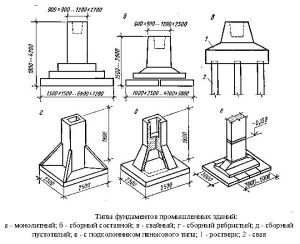 Types of foundations being built
Types of foundations being built
Pile, columnar and strip foundations are mounted under the load-bearing walls of industrial buildings.
Pile foundations are performed on loose soils, which lie at a considerable depth. Piles are divided into different types depending on their purpose. They are made of wood, steel, concrete and reinforced concrete. Distinguish between solid and prefabricated reinforced concrete piles.
Prefabricated piles are widely used in construction. They are produced in two types: cylindrical tubular and square solid.
Concrete piles are generally manufactured in one piece with varying depths, loads and cross-sections. Metal piles are made from pipes, channels and I-beams. Such piles are rarely used when arranging a foundation for walls due to their susceptibility to corrosion, as well as due to a shortage of steel. Wooden piles are produced from larch, pine. A yoke (steel ring) is put on the upper edge of the column, and a metal shoe is put on the lower edge. This is necessary in order to protect the pile from grinding during driving.
Columnar bases for load-bearing walls of industrial buildings are performed with dense bases and low loads. Below the basement walls, the pillars are located at the point of joining, intersection and in the corners, as well as at various intervals at a distance of less than 3–6 m. Separately installed columns are connected to each other by beams that take the load from the walls.
Tape bases are mounted under self-supporting or load-bearing walls made of bricks and blocks. Such bases are solid and prefabricated. Prefabricated bases are more popular. Such bases are arranged from concrete and reinforced concrete blocks.
Tape bases are made of the following components:
- block-pillows of the F brand;
- rectangular wall blocks of the SP brand.
Wall blocks have the following dimensions:
- height - 0.6 m;
- length - 2.4 m;
- thickness - 0.3-0.6 m.
Also, blocks of additional SPD brands are produced, the dimensions of which differ only in length (they have it 0.8 m). They are used to tie blocks at the base.
Wall blocks are made solid, with blind holes located at the bottom. They are made of concrete grade M150.
Installation of a monolithic grillage
 To pour concrete mortar, it is necessary to mount high-quality formwork
To pour concrete mortar, it is necessary to mount high-quality formwork
To pour concrete mortar, it is necessary to mount high-quality formwork. Start with the lower retaining shields.To do this, it is necessary to cut boards equal to the step between the foundation columns. For their fastening, it is recommended to drive the retaining stakes into the ground. The formwork boards are laid on the stakes flush with the upper edge of the pillars.
The side formwork panels are fixed at the edges and securely fixed. The side formwork strips can be covered with roofing material.
The next step is to reinforce the entire structure. Here, an armored belt made of horizontal rods with a cross section of 12-16 mm and longitudinal elements with a cross section of 6-8 mm is used as standard.
It is important in the places of the pillars to tie the reinforcement with the rods protruding from the columns
Filling the grillage solution must be carried out in one stage. Therefore, it is better to order a construction mixer or concrete mixer of the required volume. When pouring concrete, it is necessary to ram the mortar every 30 cm.The total thickness (height) of the grillage, as a rule, does not exceed 60 cm.
After 7-10 days, subject to good dry weather, the concrete is considered completely solidified. Now you can remove the formwork and let the foundation settle. All surfaces of the grillage are also covered with waterproofing materials.
After the structure has completely dried, it is necessary to backfill the pit with compaction of soil around the columns. The pit is filled up flush with the mark of the above-ground part of the foundation columns. To decorate the pillars and reduce heat loss, you can use decorative siding of the pillars or lay natural stone.
List of machines and equipment
Table 1
Name of machines, mechanisms and equipment
Type, brand
Technical specifications
Appointment
Number per link (brigade), pcs.
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
Automobile crane
KS-35715
Telescopic boom length 8 - 18 m. Lifting capacity
16 t
Supply of reinforcement, formwork, concrete mix
1
2
Concrete pump
SB-170-1 (SB-170-1A)
Distribution boom delivery range - 19 m.
Capacity up to 65 m3 / h
Concrete supply
1
3
Concrete mixer truck
SB-92V-2
The geometric volume of the drum is 6.1 m3. Output
ready mix not less than 4.5 m3
Concrete transport
1
4
Welding transformer
TD-500 4-V-2
Supply voltage 200/380 V. Rated power
32 kW. Weight 210 kg
Welding works
1
5
Compressor
SO-45B
Compressed air supply
1
Pouring with concrete
 Concrete pouring process
Concrete pouring process
Given the large volume of concrete, such a foundation should be poured in portions of 300-400 cm in height with an interval of subsequent pouring of no more than 2-3 hours. Each portion of the filling is shaken well with a vibrator.
For this type of foundation, concrete of a high strength class M300 is used, with a water resistance coefficient greater than W8, frost resistance from F200 and a mobility index of P3.
With a significant size of the foundation, pouring is done with an auto mixer, with a small one - with a concrete mixer.
Monolithic tape
 Filling the formwork with concrete
Filling the formwork with concrete
The first step is to calculate the amount of concrete that will be required to fill such a foundation. Concrete grade should be from M200 to M400. The best quality is prefabricated concrete.
If the foundation is relatively small, then the concrete mixture is prepared independently, using high-quality cement and fine sand. When building such foundations, you can get by with a concrete mixer and pour concrete by hand.
The poured concrete is leveled, and its upper part must be strictly at the zero horizontal mark. Before starting the laying of floors or walls of a building, the concrete must gain its original strength. To do this, it is covered with a film to retain moisture and kept for several weeks.
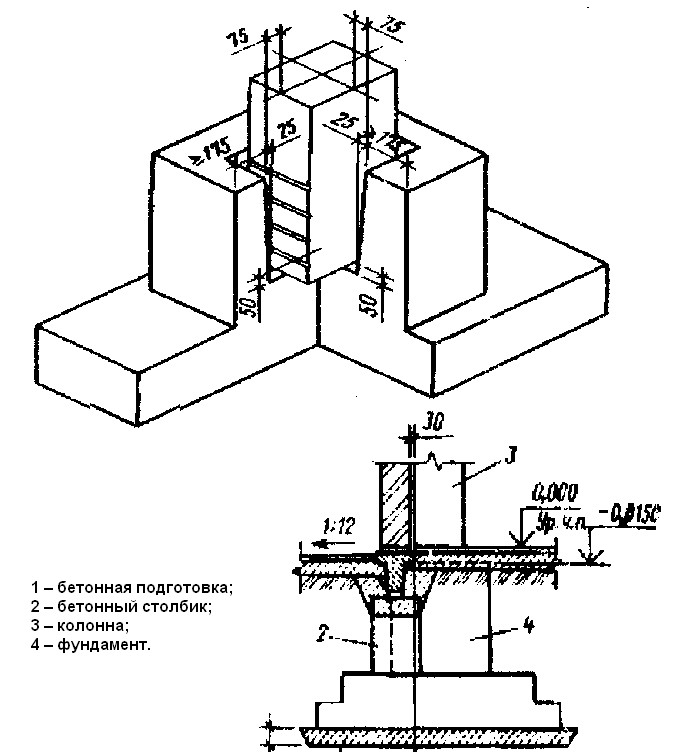
Formwork works
2.5. Formwork on
the construction site must come in a complete set, suitable for installation and operation,
without finishing touches and corrections.
2.6. Received
on the construction site, the formwork elements are placed in the area of operation of the assembly
crane.All formwork elements must be stored in a position suitable for
transport, sorted by brands and sizes. Store items
formwork is necessary under a canopy in conditions that exclude their damage. Shields
stacked in stacks no more than 1 - 1.2 m high on wooden pads;
fights of 5 - 10 tiers with a total height of no more than 1 m with the installation of wooden
gaskets between them; other elements depending on dimensions and weight
put in boxes.
2.7.
Small-panel formwork consists of the following components:
linear shields
made of a bent profile (channel), the deck in the shields is made of
film faced plywood 12 mm thick;
load-bearing elements
- contractions are designed to absorb the loads acting on the formwork, and
also for combining individual panels into panels or blocks. They are made from
bent profile (channel);
corner shields -
serve to combine flat panels into closed contours;
mounting corner
- serves to connect boards and panels into closed formwork contours;
tension hook -
used for attaching fights to shields;
bracket -
serves as the basis for the working floor.
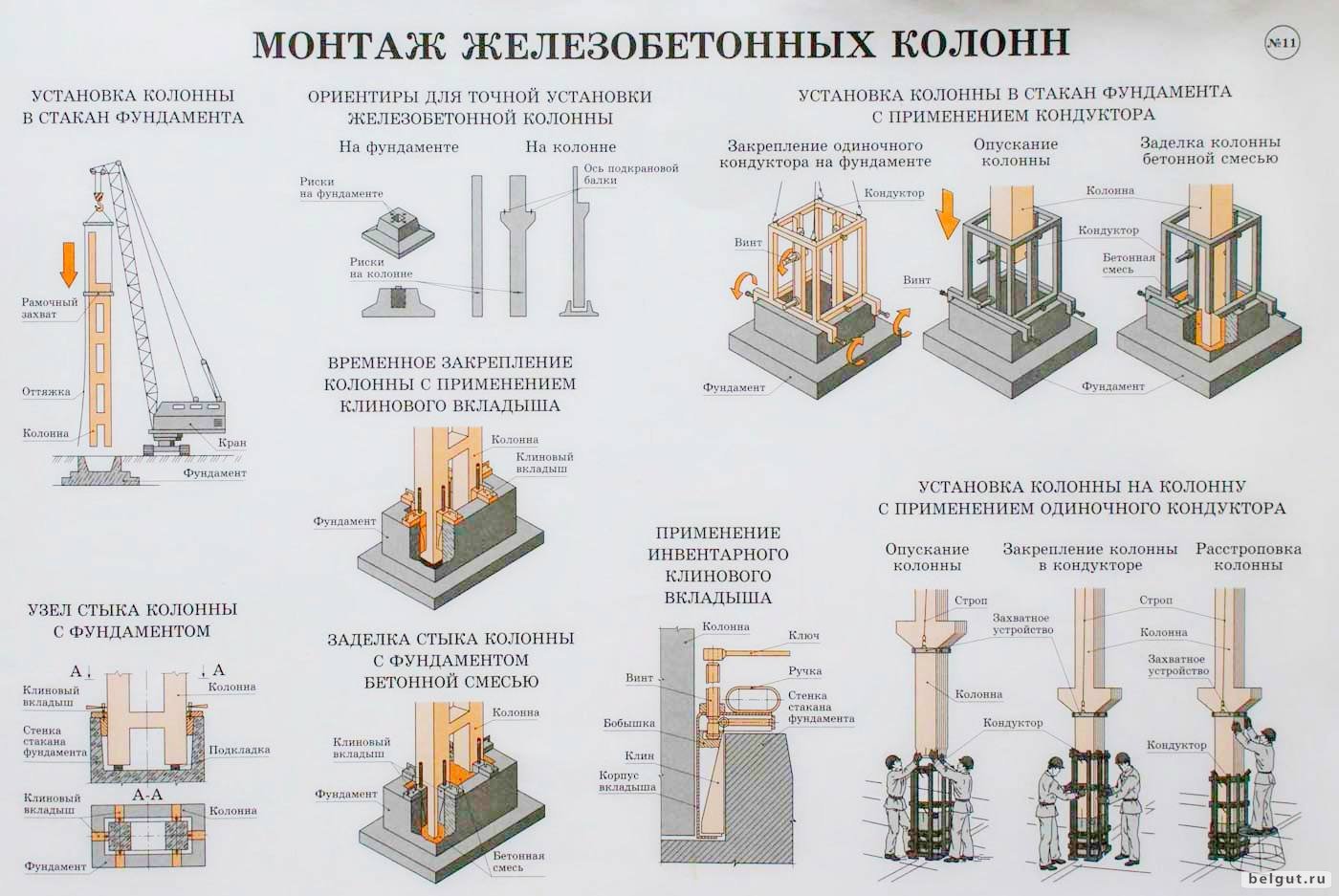
2.8. Installation and
dismantling of the formwork is carried out using a KS-35715 or KS-45719 truck crane,
KS-4572A.
2.9. Before the beginning
the installation of the formwork, the pre-assembly of the panels in the panel is carried out in the next
sequences:
on the site
warehousing collect a box of contractions;
hang on fights
shields;
on the edge of the shields
the panels are painted with risks indicating the position of the axes.
2.10. Device
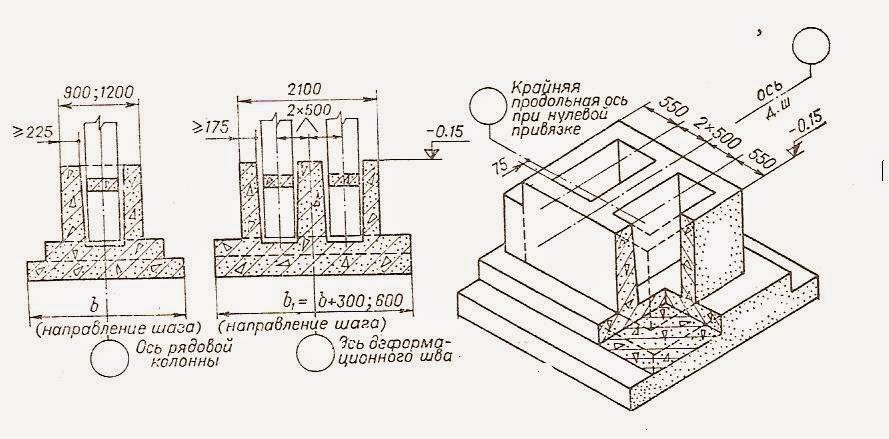
formwork of foundations is carried out in the following order:
establish and
fix the enlarged formwork panels of the lower step of the shoe;
establish
the assembled box is strictly along the axes and the formwork of the lower step is fixed
metal pins to the base;
applied to the ribs
enlarged panels of the box risks fixing the position of the box of the second stage
foundation;
stepping back from
marks for a distance equal to the thickness of the boards, set in advance
assembled box of the second stage;
finally
install the second stage box;
in the same
the sequences set the box of the third stage;
applied to the ribs
enlarged panels of the upper box, risks fixing the position of the box
podkolon;
establish
column box;
establish and
fix the liner formwork.
Mounted
the formwork is accepted according to the act by the foreman or foreman.
2.11. Per
the condition of the formwork must be continuously monitored during
concreting. In case of unforeseen deformations of individual formwork elements
or impermissible opening of the slots, additional fasteners should be installed and
fix deformed places.
2.12. Dismantling
formwork is allowed to be made only after the concrete has reached the required
according to SNiP
3.03.01-87 strength and with the permission of the manufacturer of the work.
2.13. During
tearing off the formwork, the surface of the concrete structure should not be damaged.
Dismantling of the formwork is carried out in the reverse order of installation.
2.14. After
removal of the formwork is necessary:
to produce
visual inspection of the formwork;
clear from
adhered concrete, all formwork elements;
lubricate
decks, check and lubricate screw connections.
2.15. Schemes
formwork production are given in Fig. -.
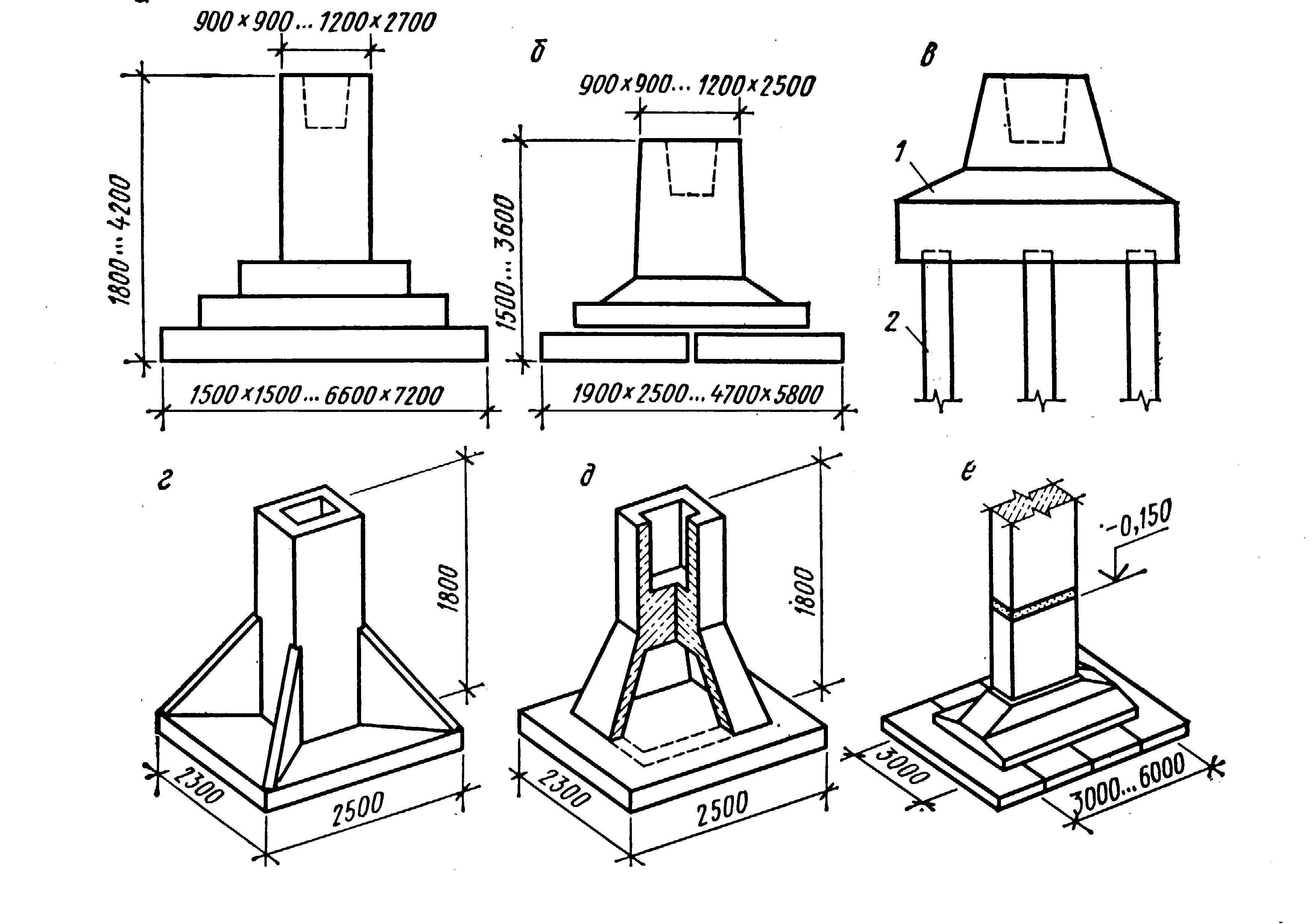
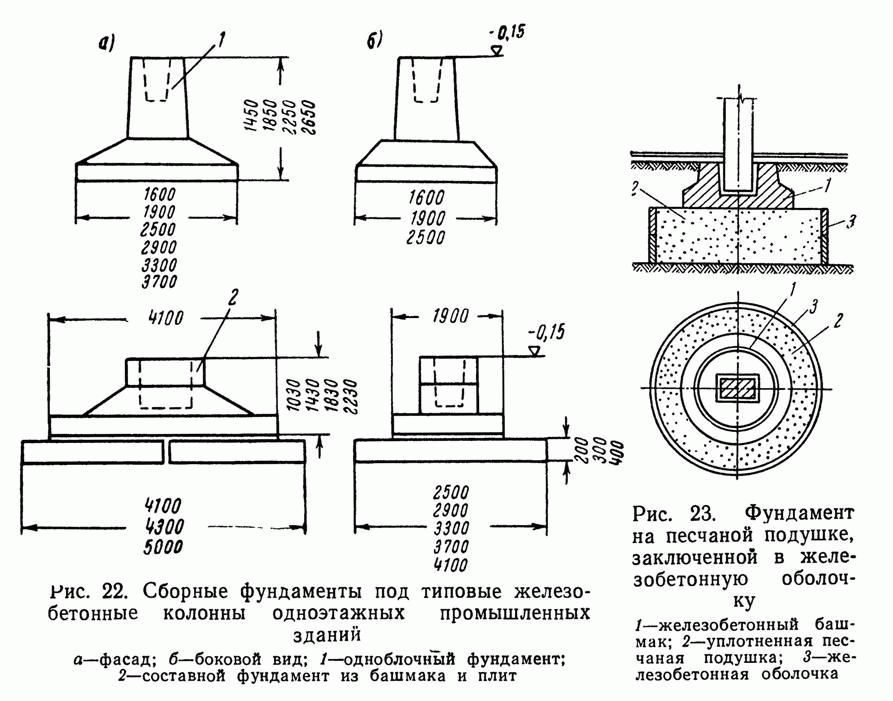
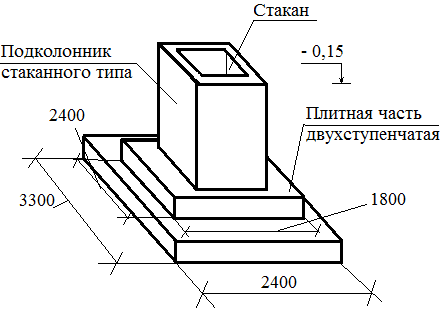
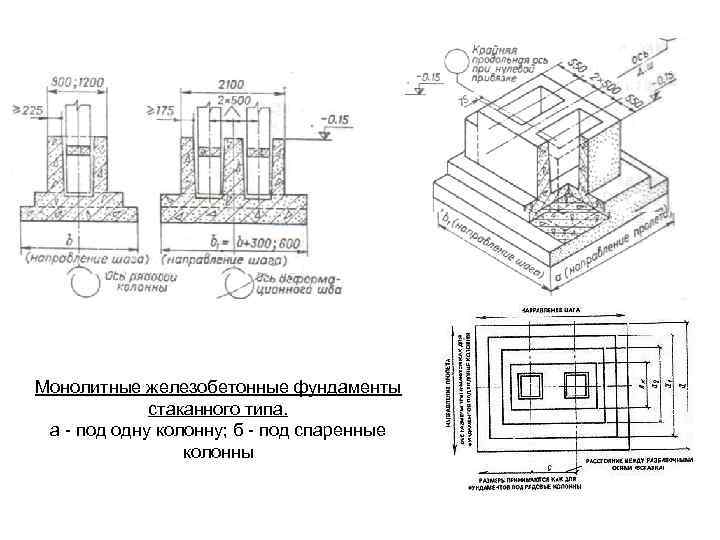
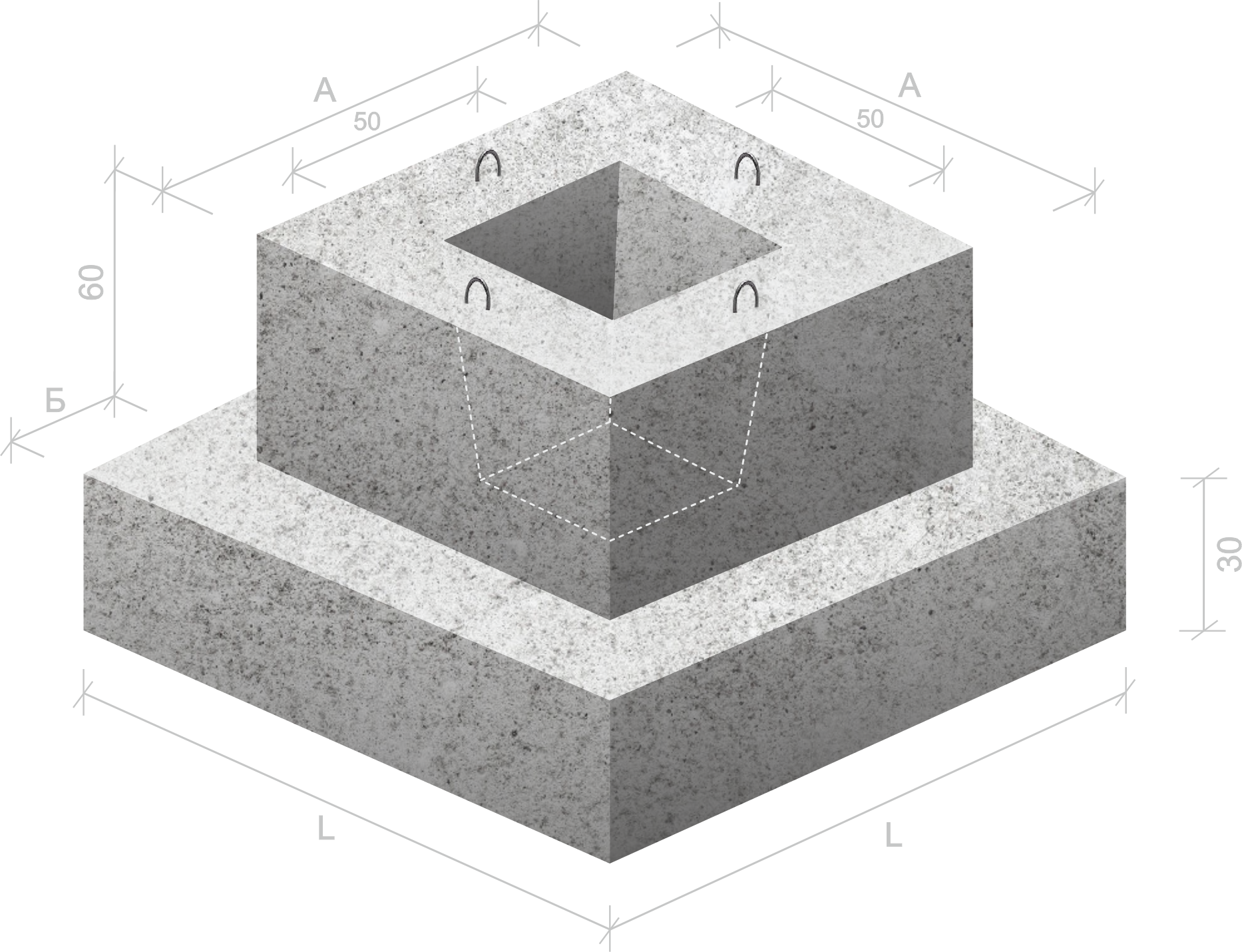
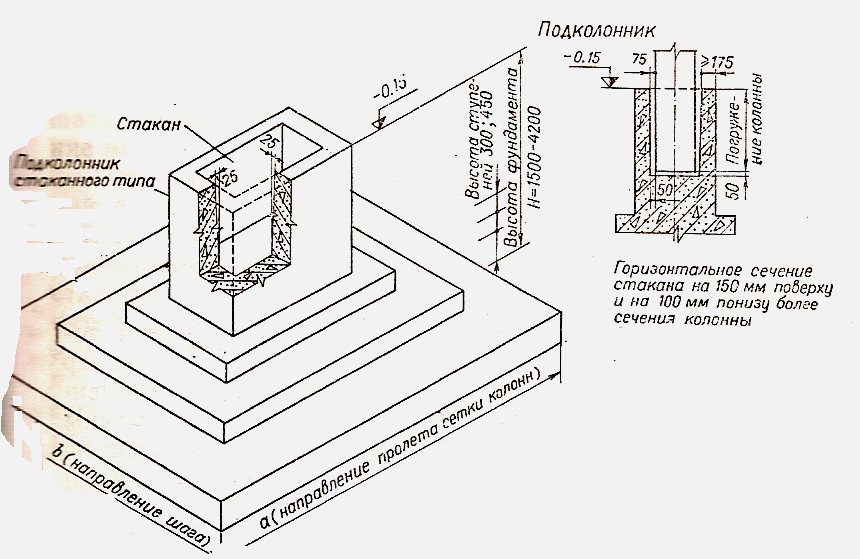
Glass-type foundation: technical requirements in accordance with GOST 23972-80
State standard of the union of the usr reinforced concrete foundations for parabolic trays technical conditions gost 23972-80
- Concrete grade not less than М200 В2;
- Installation of structures only after reaching the required concrete strength;
- The level of water absorption is not more than 5%, the indicator can be achieved with the help of waterproofing;
- Rigid reinforcement in all belts;
- The thickness of the concrete layer around the reinforcement is at least 3 cm;
- The thickness of cracks in concrete is not more than 0.1 mm;
- Complete removal of mounting loops using a grinder, removal by the impact method is strictly prohibited;
- There should be no naked reinforcement at the base.
The foundation of the glass type is quite expensive to install, because it uses powerful thick reinforcement, formwork and a complex waterproofing system. Now, according to GOST, you can buy several glass bases in size:
| Nomenclature | Dimensions, mm (LxHxW) | Weight, kg |
| 1F 12.12.1 | 1 200x1 200x650 | 1 475 |
| 1F 9.9.1 | 990x900x650 | 900 |
| 2F 15.15.1 | 1 500x1 500x650 | 2 025 |
| 1F 8.6.5 | 800x550x600 | 475 |
Manufacturing of glass-type foundations and basic requirements for them
When installing such bases, it must be remembered that the strength of the product can be achieved only through the use of high-quality building materials and good reinforcement. Therefore, the reinforced concrete foundation has a long service life.
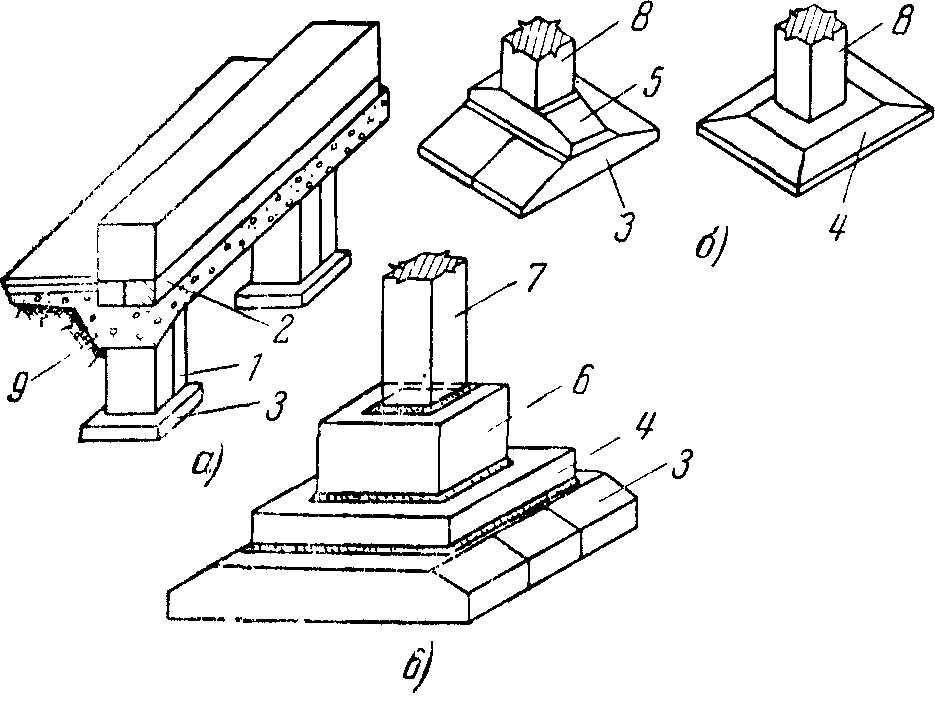
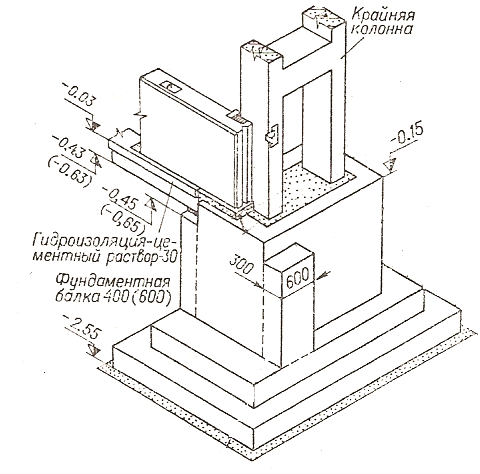
Installation of the column in the foundation glass.
This type of foundation is rarely used in general private construction, because it is distinguished by its high cost and the need to use mechanized equipment. It is forbidden to put the base on heaving and subsiding soils. The technology provides for the installation of reinforced concrete supports and racks in a finished glass, in which then fixation takes place.
Foundation requirements:
- Concrete must comply with M200 and have a B2 waterproof rating;
- The transportation of racks should be carried out to the construction site only after the base has gained the necessary margin of safety;
- It is imperative to reinforce the base. The thickness of the concrete layer around the reinforcement must be at least 30 mm;
- Naked fittings are a factory defect; it is strictly forbidden to use such products in construction;
- If there are cracks in the concrete with a thickness of more than 0.1 mm, then this is also a marriage;
- All production hinges in blocks must be carefully dismantled; it is strictly forbidden to hammer them into concrete.
When you need to use a glass foundation
- In the construction of industrial and private buildings of general purpose, in the supporting structure of which concrete supports and racks are used;
- When erecting power plants, as well as in the nuclear industry, when installing reinforced racks for engine rooms and condensation rooms;
- When carrying out restoration and restoration work on racks and columns in office buildings;
- If the project provides for the use of racks as the only possible supporting structure of the building.
Advantages of glass foundations
- High strength and quality of factory blocks, because during their production, quality control and testing for strength and rupture of all bearing elements are carried out;
- This is the optimal foundation for the construction of industrial buildings, where there are local loads per unit area of the foundation;
- Simple installation technology;
- Saving time and effort on the construction of the foundation.
You also need to take into account the need to transport individual racks and columns directly from the manufacturer, and, given their size, sometimes you have to think over special routes.
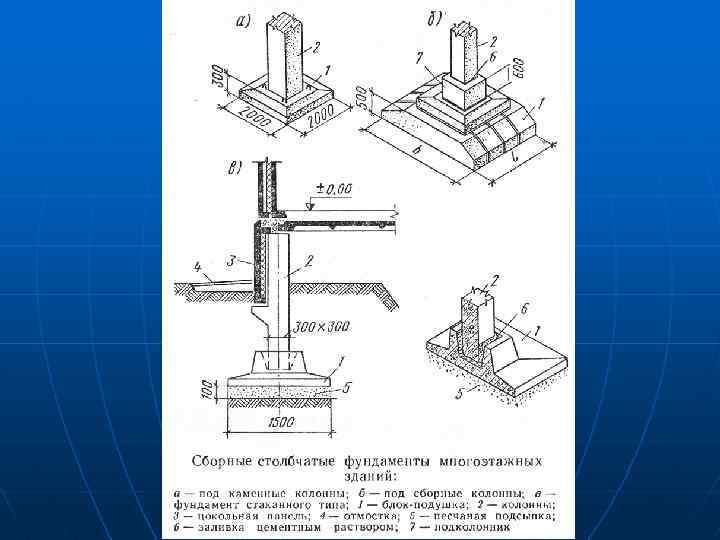
Installation of glass foundation
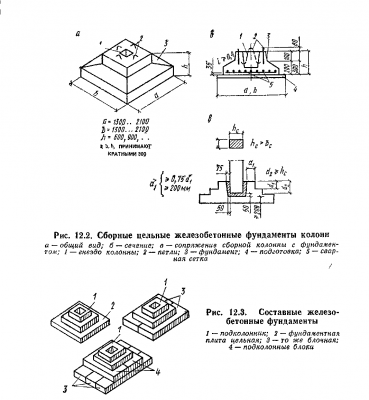 Installation of prefabricated foundations of columns weighing from 5 to 30 tons is usually carried out by jib cranes.
Installation of prefabricated foundations of columns weighing from 5 to 30 tons is usually carried out by jib cranes.
Given the key features of the foundations under consideration, installation is carried out only under the direct supervision of specialists. Only they are able to control the entire process of installing supports and the correctness of their reinforcement. During the installation process, reinforced concrete products go through several stages:
- Surface preparation. It is carefully leveled, because displacement of reinforced concrete beams in glass-type foundations is highly undesirable;
- Preparation of grooves. They are dug to a specific depth, then they are strengthened with gravel, carefully rammed;
- Reinforced concrete foundation construction.At this stage, soil compaction is also used, as well as the installation of blocks.
The key task facing glass-type foundations is to ensure an even distribution of loads over the entire soil surface. Accordingly, glass bases can be used only on such soil that is capable of withstanding heavy loads and not sagging over time.
Reinforcement
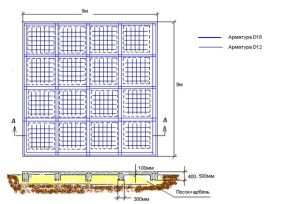 The length of the reinforcement in running meters is calculated in advance with a small margin. Ribbed reinforcement with a diameter of 14-16mm is suitable. The rods are laid crosswise on laid bricks with a mesh size of 20 cm.
The length of the reinforcement in running meters is calculated in advance with a small margin. Ribbed reinforcement with a diameter of 14-16mm is suitable. The rods are laid crosswise on laid bricks with a mesh size of 20 cm.
As a result, two grids are obtained - one at the bottom, 5 cm from the surface of the sand cushion, and the second - on top, 5 cm from the surface of the foundation slab. The reinforcement joints are fastened with a knitting wire or welded.
Monolithic tape
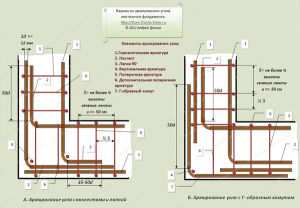 Incorrect and correct reinforcement of the obtuse angle of the strip foundation
Incorrect and correct reinforcement of the obtuse angle of the strip foundation
For the manufacture of a reinforcing frame, you will need reinforcement 8 and 12 mm. Of eight millimeter ribbed reinforcement, identical rectangles are made, the ends of which are welded or fastened with knitting wire.
Then take 5 pieces of reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm, the length of which should be equal to the length of the side of the house. If the foundation is long, then the rebar of the desired length can be obtained by tying or welding several pieces of rebar. The spacing of the intermediate bundle should be 20-25cm.
Four pieces of such reinforcement are passed through the prepared rectangles and tied to the corners. The fifth rod is tied to the top of the rectangle.
Then pins are driven into the walls of the trench and the reinforcing frame itself is attached to them.
Pile-tape monolithic
 Reinforcement strip foundation schematic
Reinforcement strip foundation schematic
The device and installation of the strip part of such a foundation resembles the reinforcement of a strip foundation. The difference is the binding of the parts of the reinforcing frame to the column head. The grillage is fastened by tying the column head.
If the grillage is not recessed, then the reinforcing frame is placed on the column and tied with reinforcement, which is located on top of its head. Often, the frame for the grillage is made of prefabricated elements of the channel and pipes.
The frame for the reinforced concrete pile itself is made, depending on the configuration, often from the same material as the grillage, and installed in the formwork strictly vertically.
Main characteristics, application and advantages
Consider the main types of monolithic reinforced concrete foundations, as well as their application and advantages in the construction of buildings and houses. What are the characteristics of reinforced concrete foundations of monolithic types?
Monolithic slab
 Monolithic base example
Monolithic base example
It is one of the most common and reliable. One of the advantages is that it does not need to be placed at the depth of soil freezing, which in turn reduces the cost of building materials.
Such a foundation provides reliability in case of sudden temperature changes, is a solid foundation when building it on soft soils. It is also called floating. A slab monolithic foundation is a solid reinforced concrete slab that is buried in the ground.
A slab of such a foundation can also serve as a rough floor of a future house. It is so reliable that skyscrapers are even built on it. A monolithic slab foundation is also used for the construction of houses, baths, industrial structures, both on soft and hard soils.
Monolithic tape
 Recessed strip foundation
Recessed strip foundation
It is a reinforced concrete strip that is located around the entire perimeter of the building and inside it. Such a foundation can withstand loads well in any climatic conditions. There is a buried, shallow and not buried - grillage.
Shallow-buried is suitable for buildings of small houses and structures, buried - for constructions of 1-2-storey buildings.
Monolithic tape is used in the construction of houses with an inclined plane of the site, it is an ideal option for the construction of buildings from aerated concrete, foam blocks, as it evenly distributes the vertical load on the piles and soil.
Columnar monolithic
This type of foundation consists of pillars, the heads of which are interconnected along the perimeter of the building and at the intersection of partitions inside it. The grillage, connecting the columns, creates a single monolithic structure. This foundation combines all the advantages of pile and tape. It is used for the construction of medium and light types of structures.
Excavation
 The scale of excavation is determined by the type of foundation, namely the depth of its grounding
The scale of excavation is determined by the type of foundation, namely the depth of its grounding
Having previously calculated the thickness of the foundation, which depends on the weight of the future building, the characteristics of the soil, the presence of groundwater, they begin to dig a pit. In the construction of small foundations, the soil is extracted manually; for the construction of large residential and industrial structures, construction equipment is used for digging a foundation pit.
The depth of the pit depends on the thickness of the slab itself, the characteristics of the soil, and the accounting for the supplied communications. For a small house, a sufficient depth of no more than 0.5 m.
Monolithic tape
 Excavation at the foundation construction site
Excavation at the foundation construction site
After marking, trenching is carried out to a depth higher than the design one by 20-25 cm to make a base from crushed stone and sand.
If formwork is used for pouring concrete, then the width of the trench should be increased by half a meter. Excavation of soil during the construction of trenches can be performed both with an excavator and manually.
The latter type is more common among developers, as it has certain advantages. This is a decrease in the volume of excavated soil, and then the walls are smoother, and this, in turn, leads to significant savings in cement when pouring a concrete mixture without using formwork.
To increase the support area of the future foundation, the bottom of the trench should be expanded in the form of a cone or rectangle.
Monolithic columnar
 Excavation work for a columnar foundation
Excavation work for a columnar foundation
When marking trenches for the grillage, it is necessary to correctly outline the places where the foundation columns will be installed. The distance between them should be from 1.5 to 2.5 m.
Excavation work during the construction of this type of foundation foundation consists in digging holes in the trench itself, in which columns will be placed, which perform the main bearing functions.
When using bored piles, wells are made using a drill. The depth of the well should be 300-400mm below the freezing of the soil and another 200-300mm for placing the sand cushion.
Application and types of block pillows
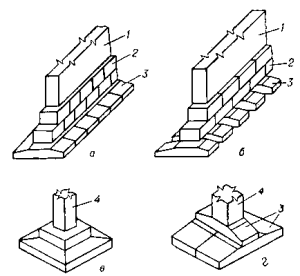 Schematic representation of the components of the foundation
Schematic representation of the components of the foundation
Block cushions are used to increase the size of the sole of the base. Have the following dimensions:
- length - 1.2-2.4 m;
- thickness - 0.3-0.4 m;
- width - 1-2.4 m.
Block pillows with a thickness of 1-1.6 m, in addition to standard sizes, can be made of shorter length, that is, additional ones. They are made of concrete of the M150 and M200 grades. Hot-rolled steel is used as a working material for reinforcement. To protect against additional loads, block cushions are placed on a flat surface or a preparation made of sand.
Bases of block cushions are intermittent and solid. In free-standing bases, such cushions are laid with the formation of a gap, the size of which varies from 20 cm to 90 cm. Such a design makes it possible to reduce the consumption of building materials, reduce the load and make it possible to fully use the bearing capacity of the soil.
During the construction of industrial buildings on subsiding soils, a reinforced seam is arranged under the base cushions, the thickness of which varies from 3 cm to 5 cm, and a reinforced belt with a thickness of 10 cm to 15 cm is mounted on top of it.This allows you to reduce the load, increase the rigidity of the base, and prevent the occurrence of cracks in case of uneven shrinkage of the structure.
The foundations of large buildings made of massive reinforced concrete components are made of wall panels and cushion panels. Wall panels are installed on top of cushion panels. They come with through holes, ribbed and solid. The assembled panels are fastened between adjacent ones, by welding the embedded metal components. These pillows are stacked in the form of intermittent or continuous strips. They are solid and ribbed.
Monolithic strip foundations are mainly made of reinforced concrete. They equip themselves inside the formwork, in which the reinforcement is mounted (if we are talking about reinforced concrete foundations), and they lay the concrete mixture.
Pile foundations have a number of advantages: they practically do not shrink, reduce the time spent on earthworks, and also reduce construction costs. Any structure with the use of piles can stand for more than 100 years.