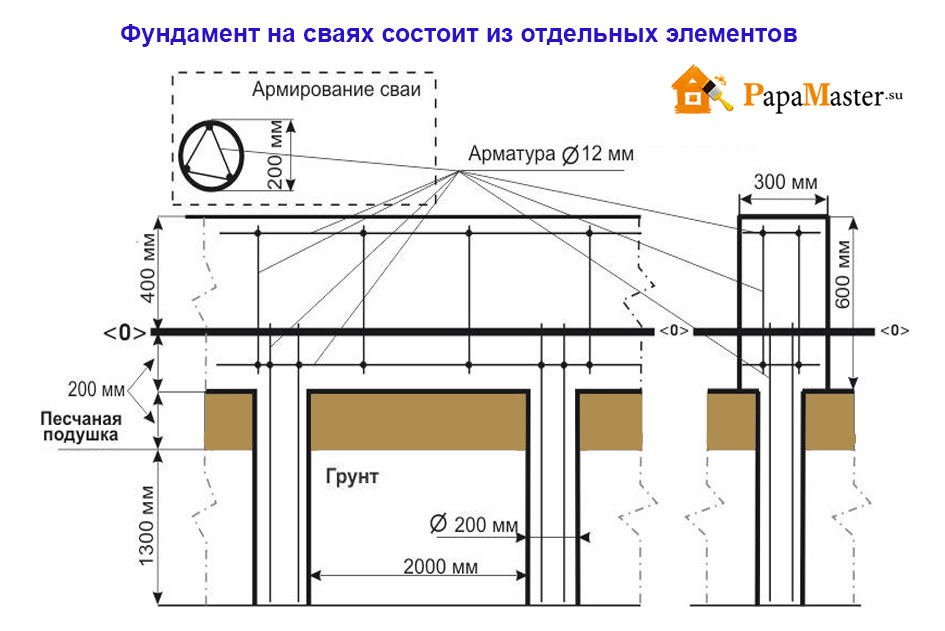
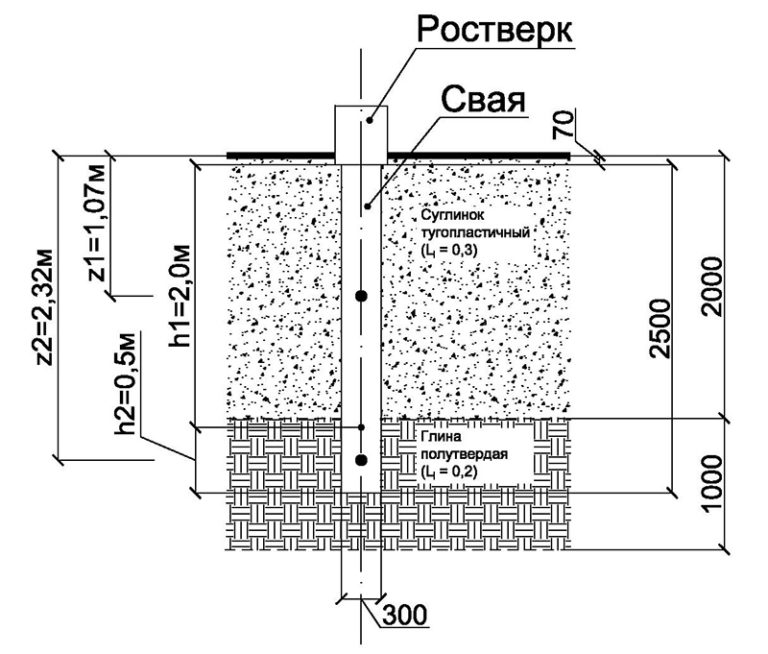
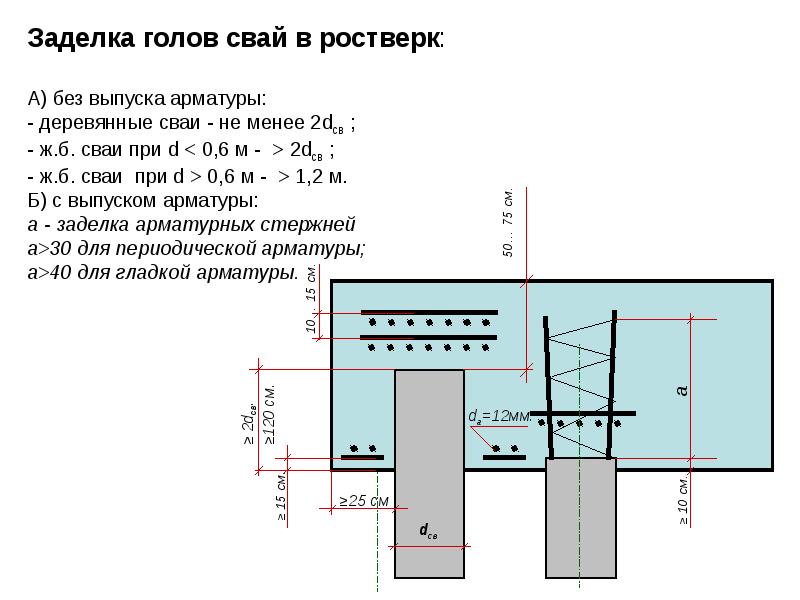
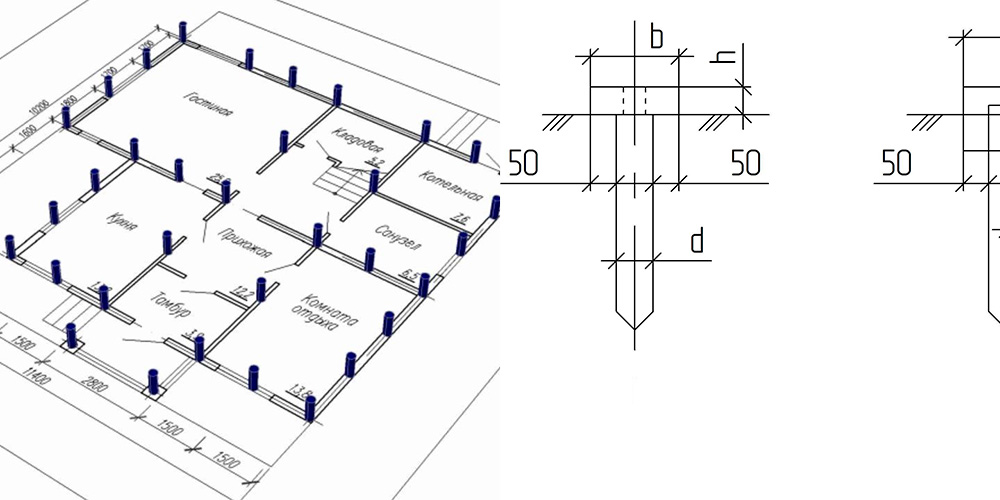
Characteristic Advantages and Disadvantages of Driven Pile Installation
This type of foundation for a structure has beneficial and indisputable differences from other bases in terms of parameters: This is what round driven piles look like.
This is what round driven piles look like.
- no need to carry out a large amount of earthwork, while easy to install;
- foundation piles can be driven into any fragile soil, except for greasy rocks;
- the material for the manufacture of piles can be selected based on the budget of the construction site, the parameters of the building and the type of soil;
- holds a large mass of a structure well, is used in the construction of high-rise buildings with a large number of floors;
- the service life of this foundation is 100 years;
- the possibility of increasing strength by arranging a strip foundation from piles;
- the pile foundation for a brick house is not afraid of temperature extremes, moisture-resistant, non-combustible and resistant to environmental influences;
- easy to transport and store RC piles.
But like any material and method of arranging foundations for a house, this type of foundation has a number of disadvantages that are worth talking about:
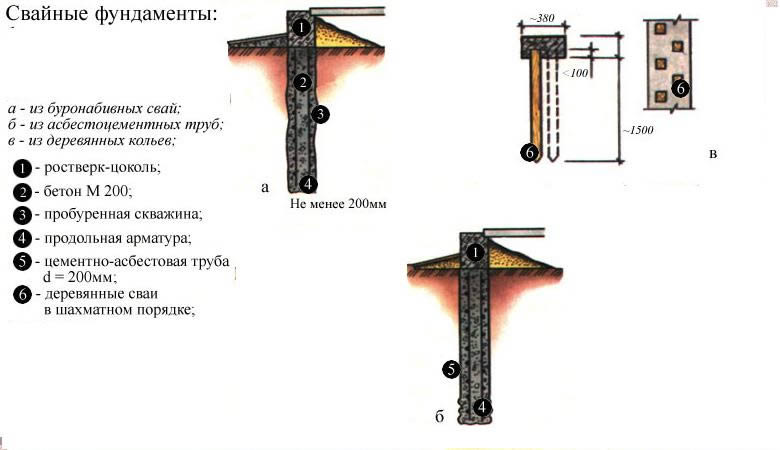
- First of all, you will have to plan the basement floor and provide for ways to arrange it.
- If planting and swelling soils prevail on the site, then the pile-driven foundation may not be stable enough.
- If the soil on your site is the same as described above, then you should not despair and buy another land - there is a way out of this situation. The pile-driven foundation can be strengthened, for example, by installing a monolithic slab on the supports, or by equipping the pile-strip foundation.
Important! If you decide on the arrangement of the grillage, then there should be a gap between the soil and the tape, which, after installation, is filled with fine crushed stone, or sand. This is done so that during winter heaving the soil could not affect the grillage tape.
Of course, this type of foundation has drawbacks, but there are few of them and at the same time they can always be bypassed and a way to eliminate them can be found. There is one more important point - before buying material, for the manufacture of a pile-driven foundation, you need to carefully study the documents in which you should contain information about the manufacturer of the piles, the material used in their manufacture, the date of production, the batch number. In addition, the seller must provide you with a certificate of conformity for this product.
If there are no documents, then you should refuse to purchase.
Examine the material carefully; the surface of the piles should be even and smooth without visible damage and unwanted inclusions. For example, microcracks can be detected by wetting one side.
When dry, darkened stripes will appear on the surface - this indicates that the material is of inadequate quality. It is also worth considering the types of piles, since they can be made of different materials.
In addition, the seller must provide you with a certificate of conformity for this product. If there are no documents, then you should refuse to purchase.
Examine the material carefully; the surface of the piles should be even and smooth without visible damage and unwanted inclusions. For example, microcracks can be detected by wetting one side.
When dry, darkened stripes will appear on the surface - this indicates that the material is of inadequate quality. It is also worth considering the types of piles, since they can be made from different materials.
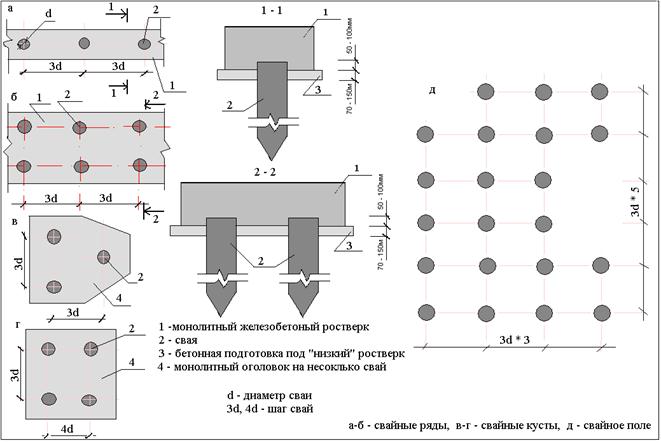
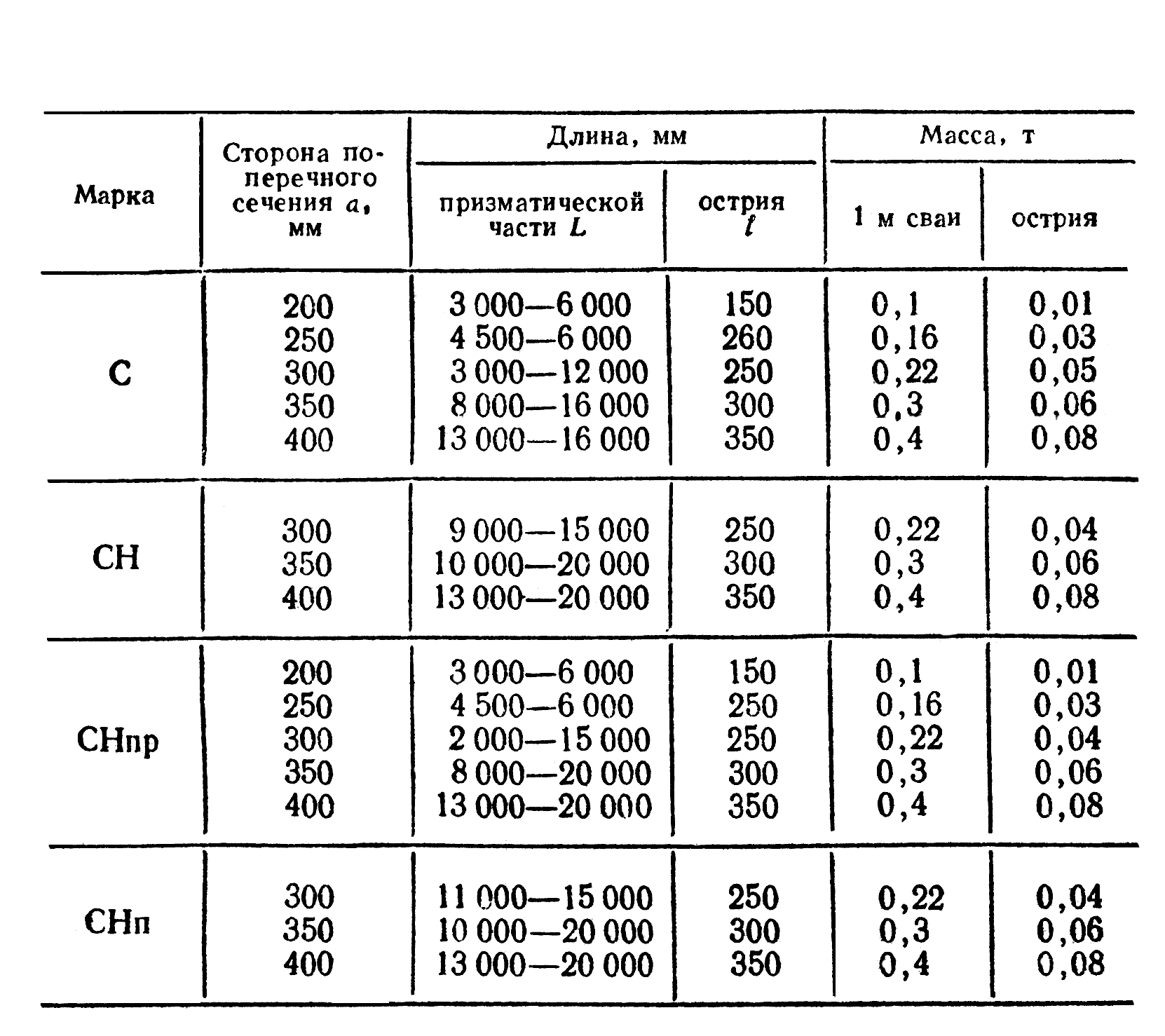
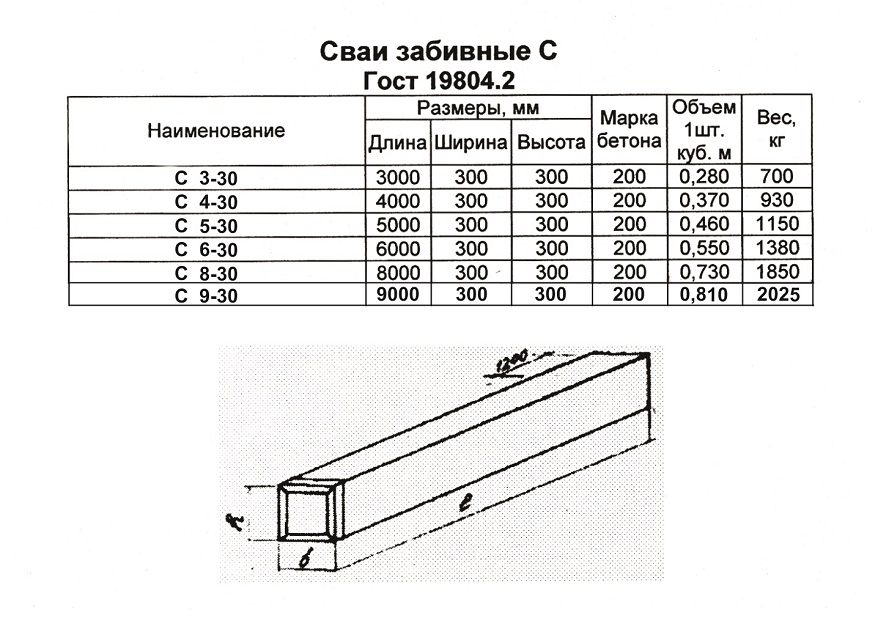
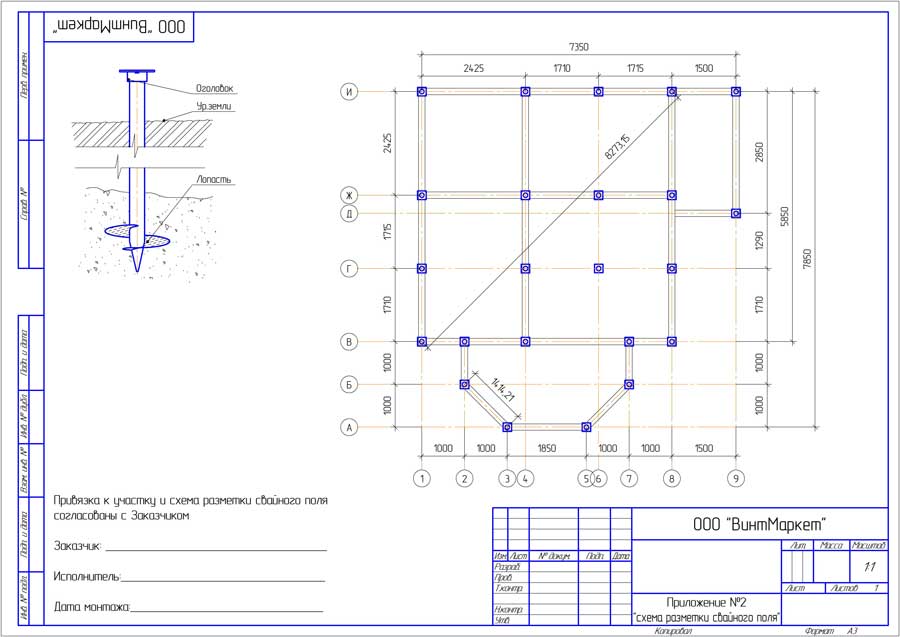
Support dimensions
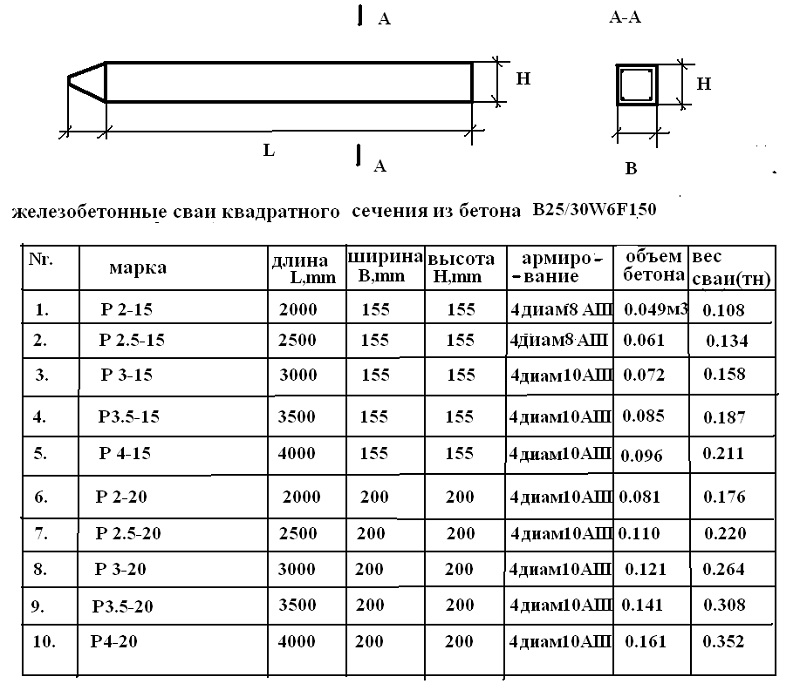
The manufacture of screw piles in the factory is regulated by the provisions of GOST, created on the basis of numerous laboratory tests, calculations and practical observations. First of all, the standards determine the steel grades acceptable for the production of supports, their length and diameter. The durability of their operation and bearing capacity completely depend on these parameters.
The standard dimensions of screw piles, according to GOST, are:
Diameter
- 57 mm;
- 76 mm;
- 89 mm;
- 108 mm;
- 133 mm;
- 159 mm.
In length, they can be from 1.6 to 12 m.
Specifications
The key parameter for determining the bearing capacity is the size of screw piles, first of all, their diameter. The length of the support can be adjusted by cutting directly on the construction site. Thus, the cross-sectional diameter is the main parameter of the pile, from which they are repelled when designing the bearing foundation for the future building. Knowing the bearing capacity of the screw piles, the architect-designer will be able to calculate the minimum allowable cross-section of the support and the distance between them.
 Types of pile supports
Types of pile supports
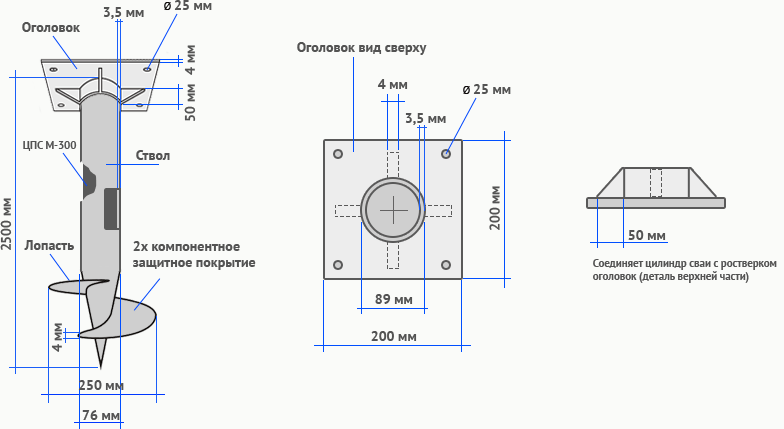
57 mm
The bearing capacity of screw piles of this type, taken as an average value, is 0.8 tons. Such supports are widely used for the construction of wooden, frame and other lightweight low-rise buildings on subsiding and heaving soils.
Also, 57-mm piles can be used if it is necessary to erect a building on a site with a significant slope. As a rule, the deepening of racks of this diameter is done manually using a svaykroot lever.
89 mm
Screw piles of this diameter can withstand, provided they are installed on solid ground, up to one and a half tons of external loads. The field of application of supports of such a section is log, timber or aerated concrete structures in 1 - 2 floors, erected on bulk soils, swampy soils or in areas with a high level of groundwater. The deepening process takes place, depending on the strength of the soil, either manually or using technology.
108 mm
The bearing capacity of 108-mm screw piles reaches 3 - 3.5 tons. Due to this, they can take much higher loads: on such a foundation, one-story brick or reinforced concrete structures, hangars with metal frames, storage rooms, etc. can be built. It is very difficult to mount such foundation structures without the use of specialized equipment, especially if the sinking depth is 5-10 meters.
 Screw posts of various diameters
Screw posts of various diameters
133 mm
This type of pile has the highest bearing capacity, exceeding 6 tons per one support. They can be used for the construction of massive mansions, cottages and country houses made of brick, stone or monolithic reinforced concrete. The deepening of supports with such a diameter to any significant depth without special equipment is impossible due to the large mass of the pile and the increased resistance of the soil.
The video shows how you can independently make lightweight screw piles for the fence using improvised materials and tools. However, supports of such a design are quite suitable for the construction of light outbuildings: a bathhouse, a barn and a garage.
With the help of screw piles, you can create an inexpensive and, most importantly, a strong and durable base for low-rise buildings of almost any type. It is only necessary to correctly calculate the total weight of the future structure and, in accordance with this, choose the correct type of support.
Calculation types
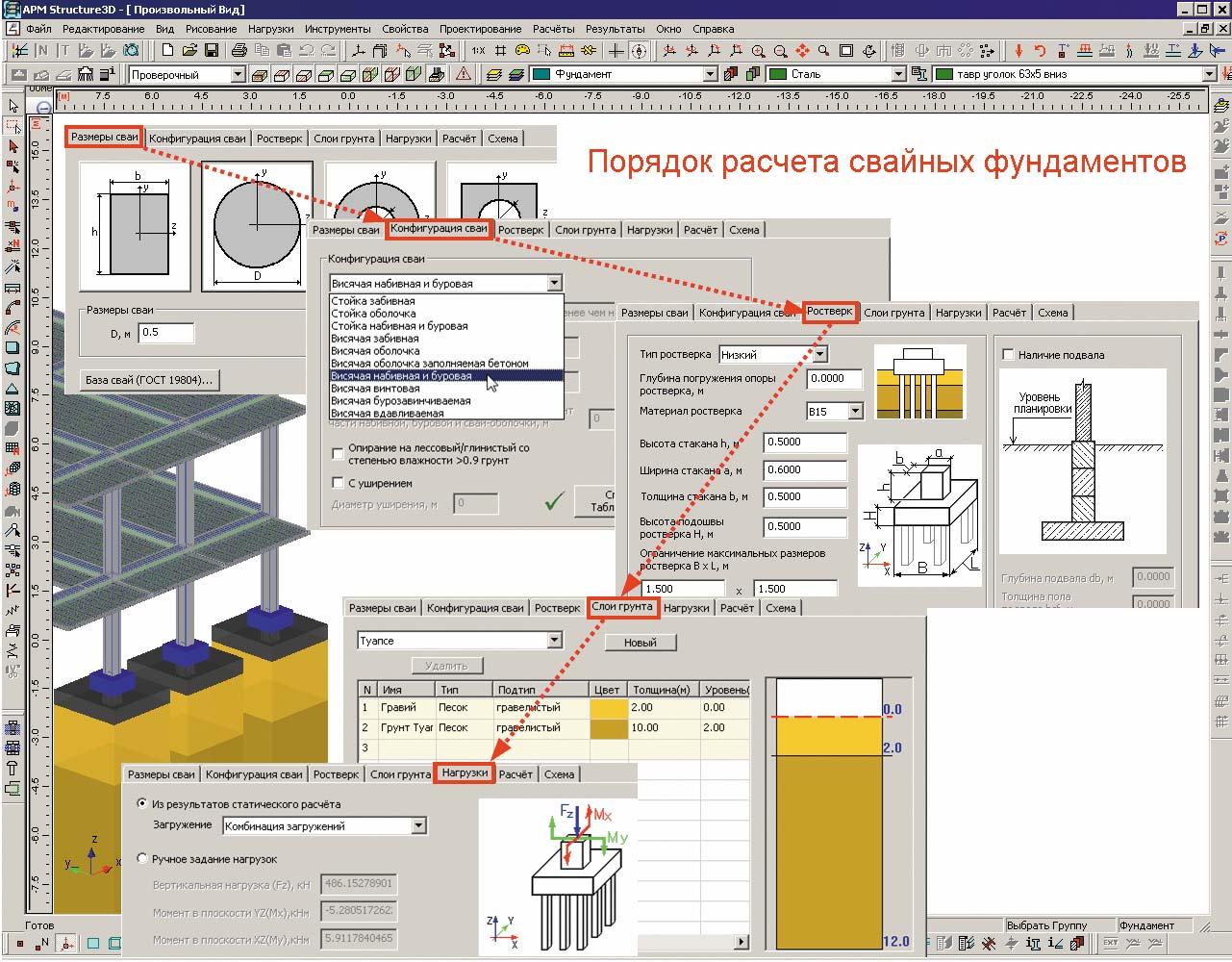
SP 24.13330.2011 indicates that the calculation of the foundations is carried out according to critical states, divided into two groups.
 Pile installation process
Pile installation process
According to the limiting states of the first group, both stability and bearing capacity are calculated, and the strength characteristics of materials are taken into account.The second group concerns the settlement of piles under the influence of vertically applied loads, various displacements of the base in the horizontal plane together with soil layers, the formation of cracks of considerable depth in the body of the structure of reinforced concrete foundations.
The permissible settlement of the underground base of the building, according to SNiP 2.02.03-85, must be calculated according to the second group of states.
The most important nuance of calculations is the obligatory acceptance of a safety margin. The final value is taken by calculation for various alternative options and comparison of the data obtained.
In SP 24.13330.2011, the required design values and constants are presented, the loads on the base and their possible combinations are specified.
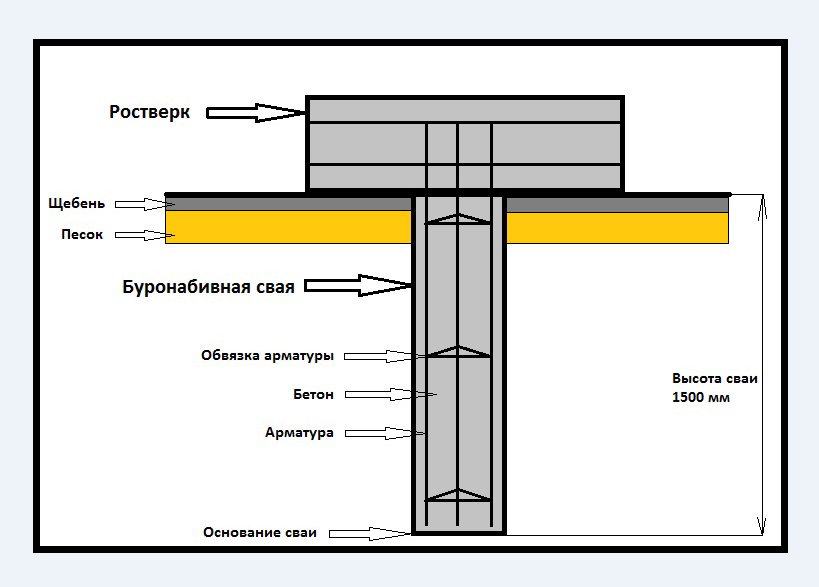
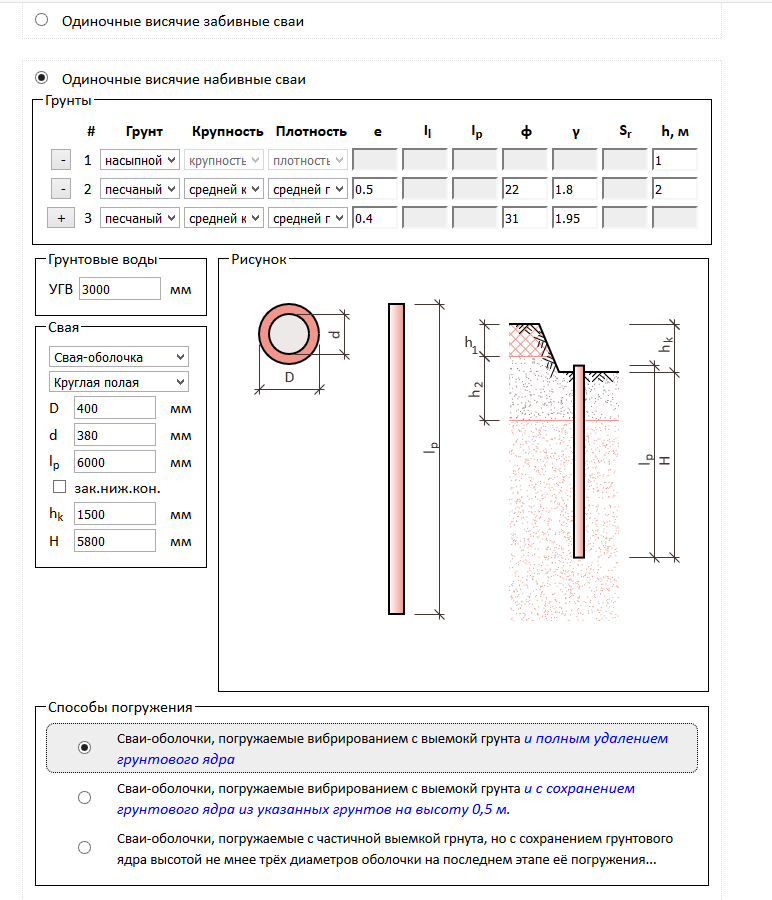
3.2. Determination of the bearing capacity of the pile.
Definition
bearing capacity of the pile on the ground.
Load bearing capacity Fd hanging drill pile on the ground is determined by
formula
where is the coefficient of conditions
pile work;
= 1.0 - coefficient
working conditions of the soil under the end of the pile, taking into account the way it
diving;
R = 2185 kPa - calculated
soil resistance under the end of the pile, taken along;
A = p × 1.02 / 4 = 0.785 m2 -
pile bearing area, taken for drill piles;
u = p × 1.0 = 3.14 m - the outer perimeter of the cross section
piles, m;
= 0.8 - coefficient
working conditions of the soil on the lateral surface of the pile, taking into account the method
immersion of piles, taken by;
- estimated
resistance i-th layer of soil along the lateral surface of the pile, kPa,
taken by;
- thickness ith
soil layer in contact with the lateral surface, m.
3.3 Calculation
multi-row pile foundation according to group I limit states by the method
displacement
For the convenience of calculations, we carry out the calculation in relation to
one row of piles (this technique is possible only if the arrangement of the piles is identical
in each row).
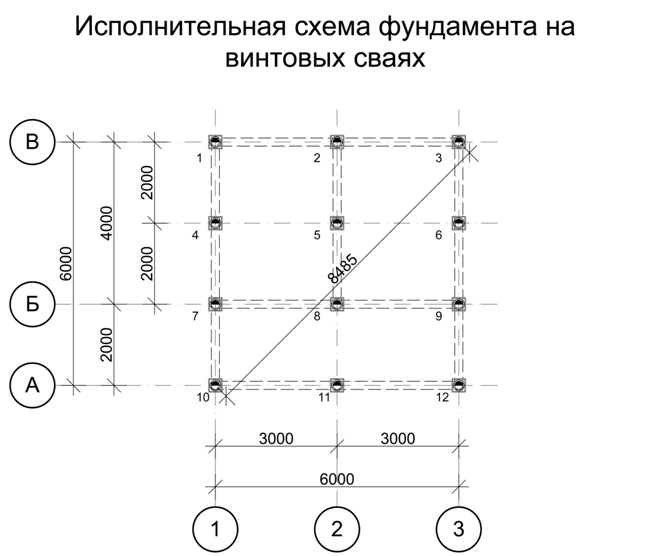
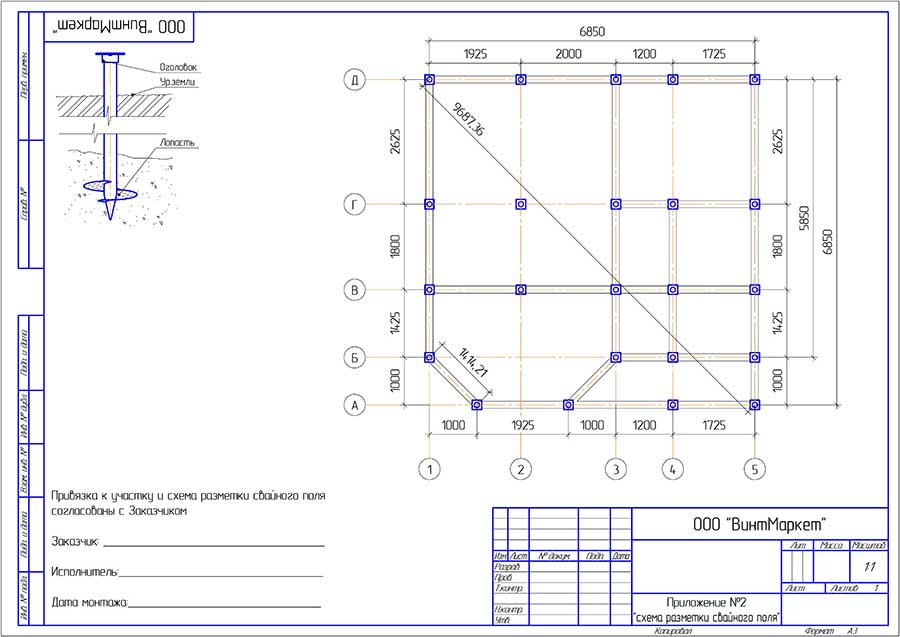
The diagram for calculating the efforts in piles is shown in the figure.
Design efforts per design series,
make up:
;
;
.
The calculated pile width is determined by the formula:
, where:
—
d - pile diameter;
—
TOf - coefficient taking into account the cross-sectional shape
piles, with a circular cross-section TOf = 0,9;
;
Calculated modulus of elasticity of concrete for B35:
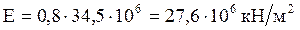 ;
;
Bending and compression stiffness of piles:

We determine the depth by the formula,
within which the action of resistance (passive pressure) of the soil is taken into account:
.
Within hk
= 5 m is greenish-gray ribbon clay. By
we take the value K = 5880 kN / m4.
We determine the value of the coefficient by the formula
deformations:
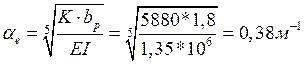
We calculate the reduced depth of the pile in
soil
- length
pile section in the ground;
Since, the values are determined by the following formulas
 kN / m;
kN / m;
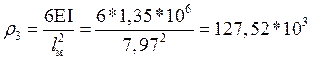 kN / m;
kN / m;
kN / m;
having previously calculated the bending length of the piles using the formula:
- free length of piles, m;
–
coefficient taken from certain tables.
Next, we find the compression length of the piles resting on the soil
solid consistency, and its characteristics according to the formulas:
kN / m.
We determine the coefficients of the canonical equations and
other quantities included in the system
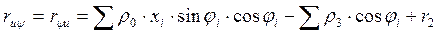
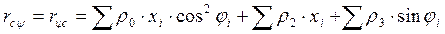
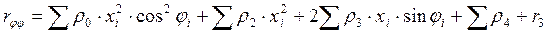
Members taking into account the effect of the resistance of the soil surrounding
foundation slab by the coefficients of the canonical equations:
since grillage is
high.
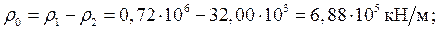
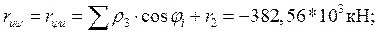

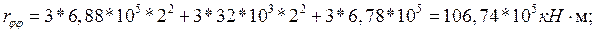
Horizontal movement of the plate:;
Vertical movement of the plate:;
Slab rotation: where
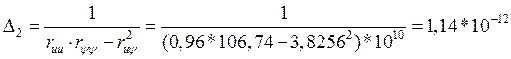 ;
;
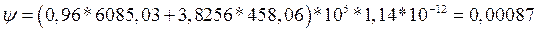
Determine the forces acting from the plate
grillage on the head of each pile in the calculation row according to the formulas:
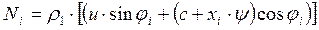 ;
;
;
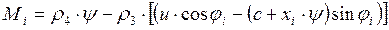 .
.
Determining longitudinal forces
;
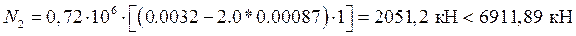
Determining lateral forces
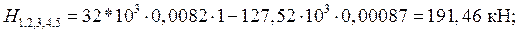
Determine the moment:

We check the following formulas:
1) ;
2) 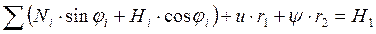 ;
;
3) 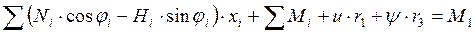 .
.
1) 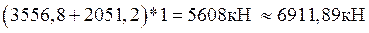 –
–
check completed;
2) –
check completed;
3)
3.4 Calculation
multi-row pile foundation according to the II group of limit states by the method
displacement
Calculation according to the II group of limit states
determine the horizontal displacement of the top of the support, the settlement of the pile foundation and
compare their calculated values with the maximum permissible according to the norms. Payment
is carried out on the calculated loads obtained by multiplying the standard loads
overload factor γfII = 1,0.
Horizontal offset of the top of the support height h, cm, is determined from
formulas:
 , where:
, where:
—
u and ψ are the values defined above;
—
δx
- horizontal displacement of the top of the support as a result of deformation of its body
(we take it equal to 0);
—
LR –
the length of the smallest span adjacent to the support, but not less than 25 m.
Multiplying by 1 / γfI, where γfI = 1,2,
transition from values u and ψ,
determined in the calculation for group I limit states, to the values u
and ψparticipating in the calculation for group II
limit states.
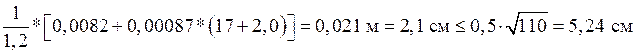 - check completed
- check completed
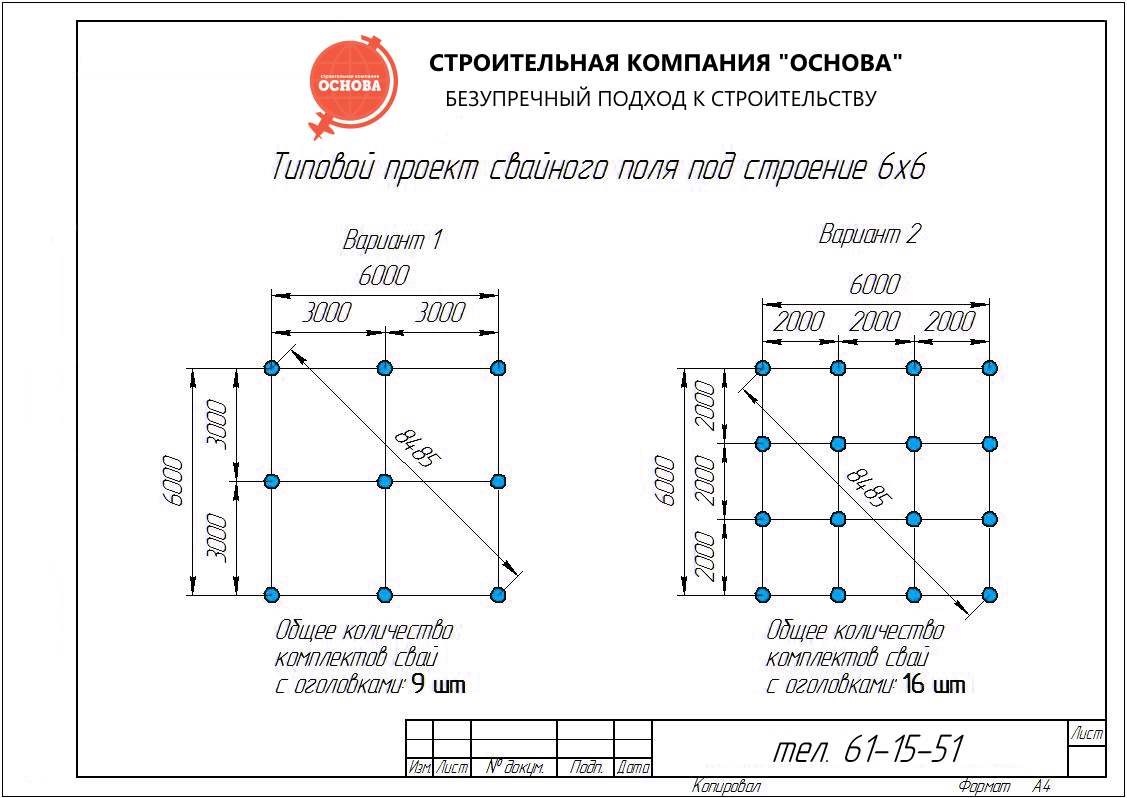
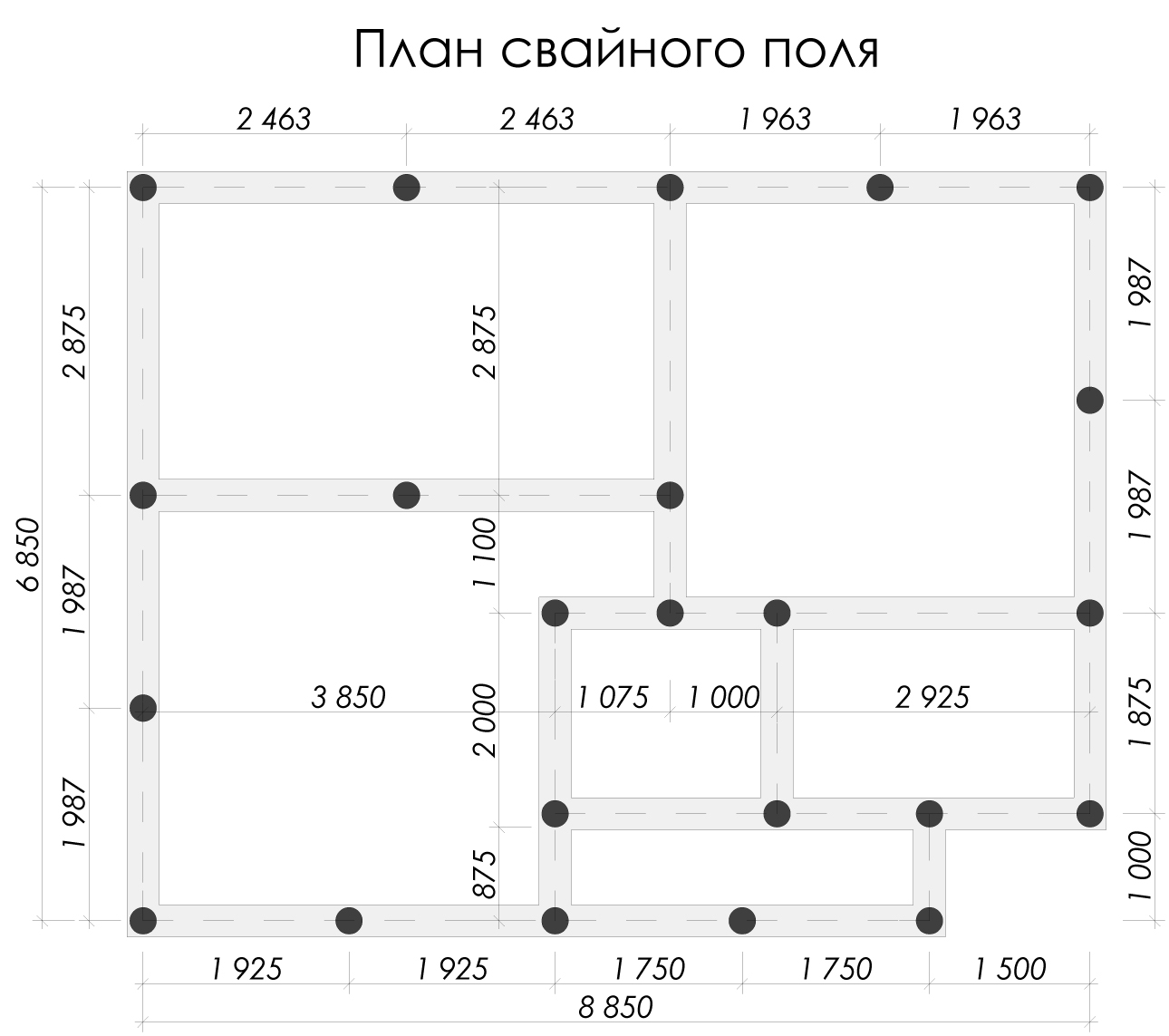
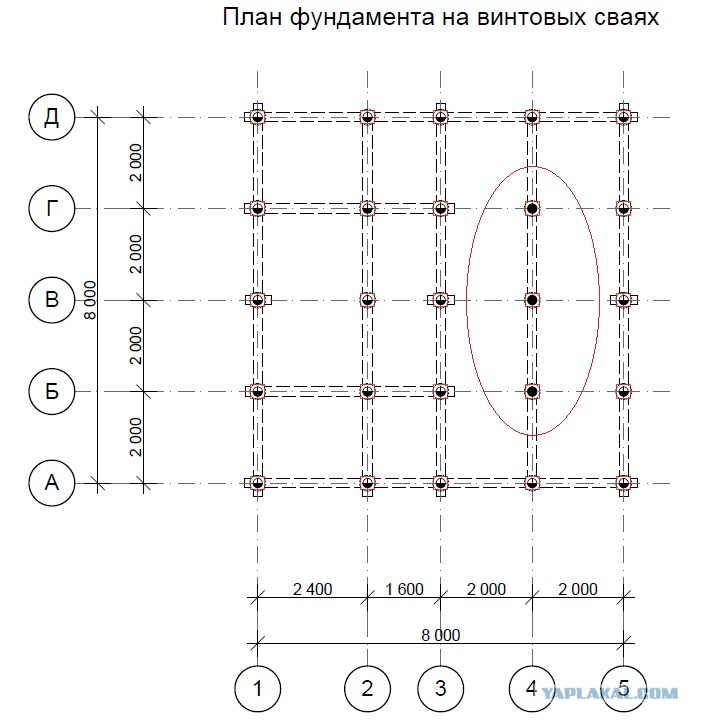
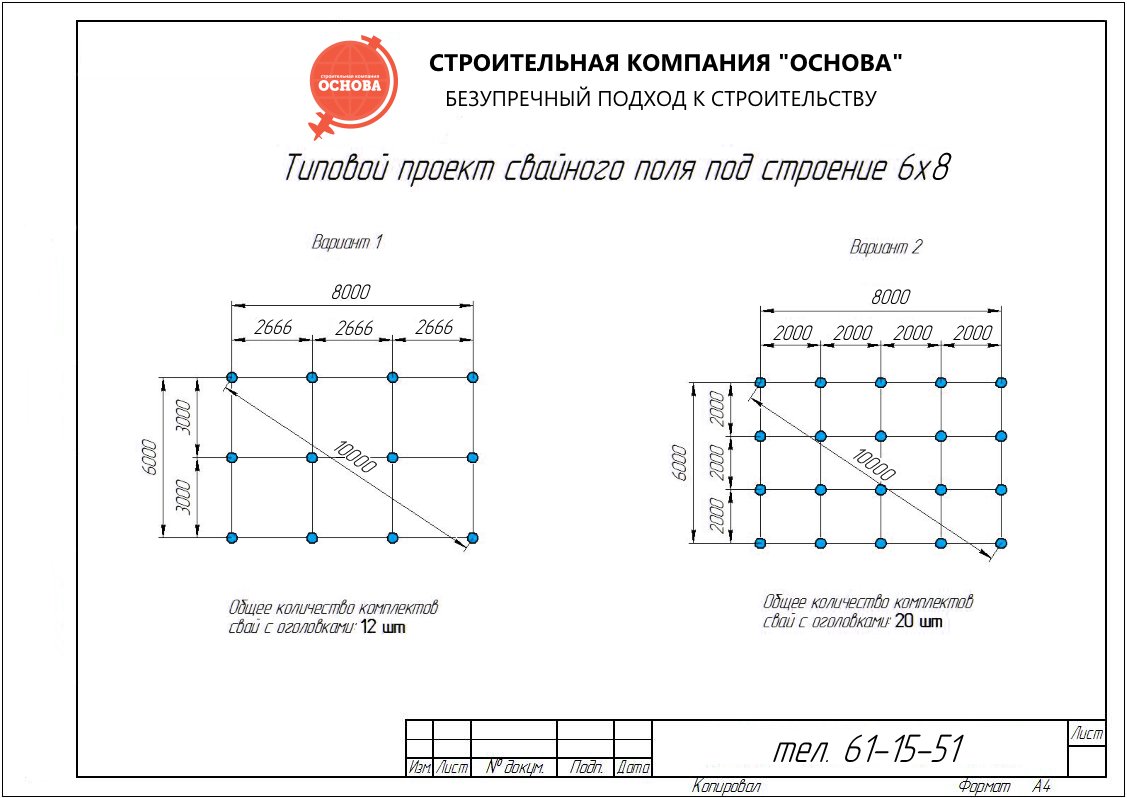
Selection of the optimal number of supports according to the parameters of the permissible section
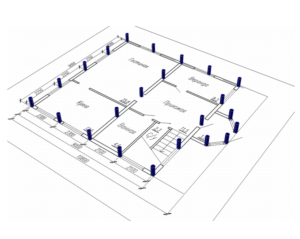 Conditional calculation of the number of piles in the foundation
Conditional calculation of the number of piles in the foundation
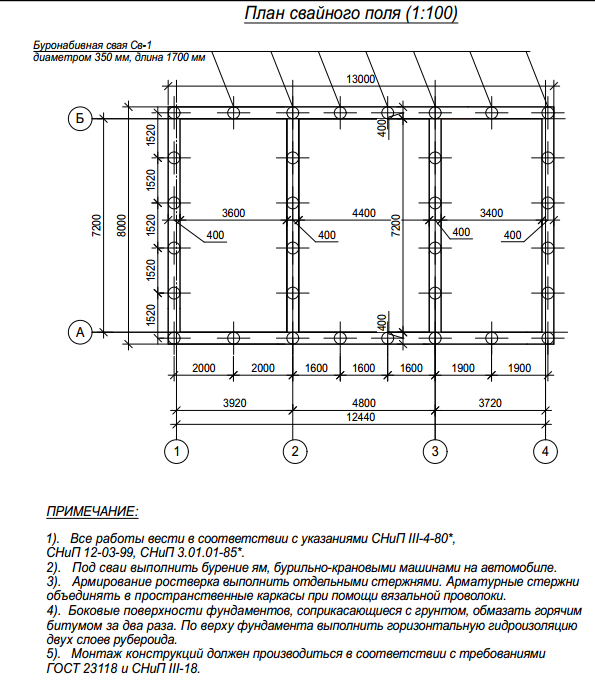
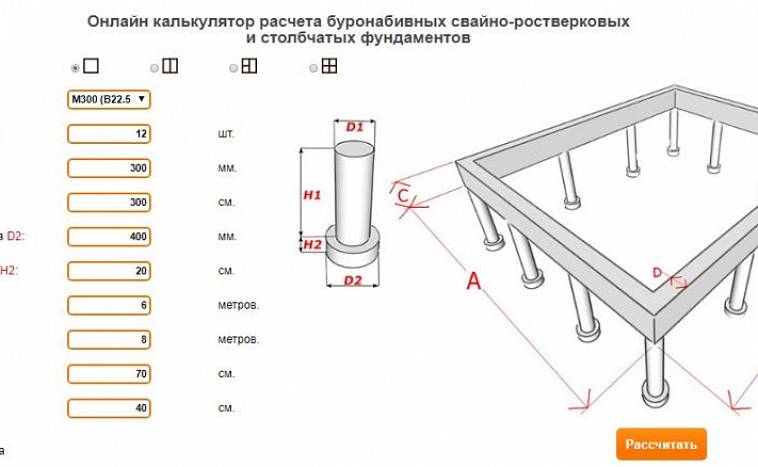
The minimum number of supports for foundations with a low grillage can be calculated using the formula:
n = KN 'I Y k\ F d
Where k - coefficient is 1.4; N 'I - vertical load on the foundation from the side of the building; Fd - bearing capacity of the support; Y k - the coefficient of reliability is 1.4.
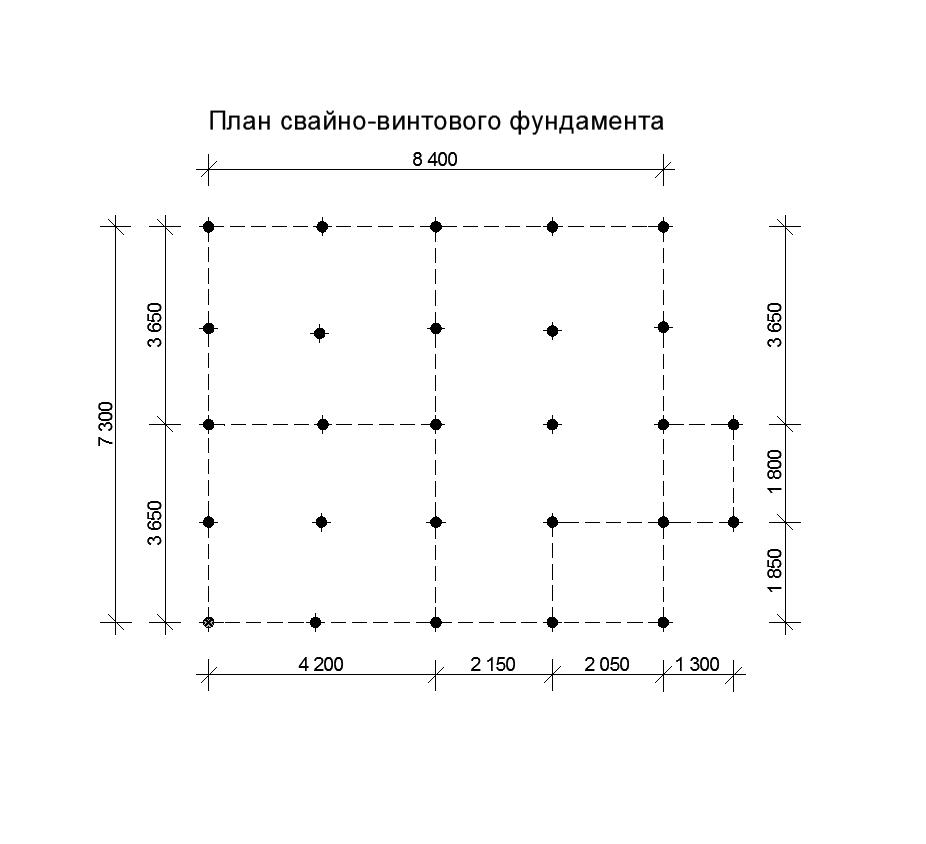
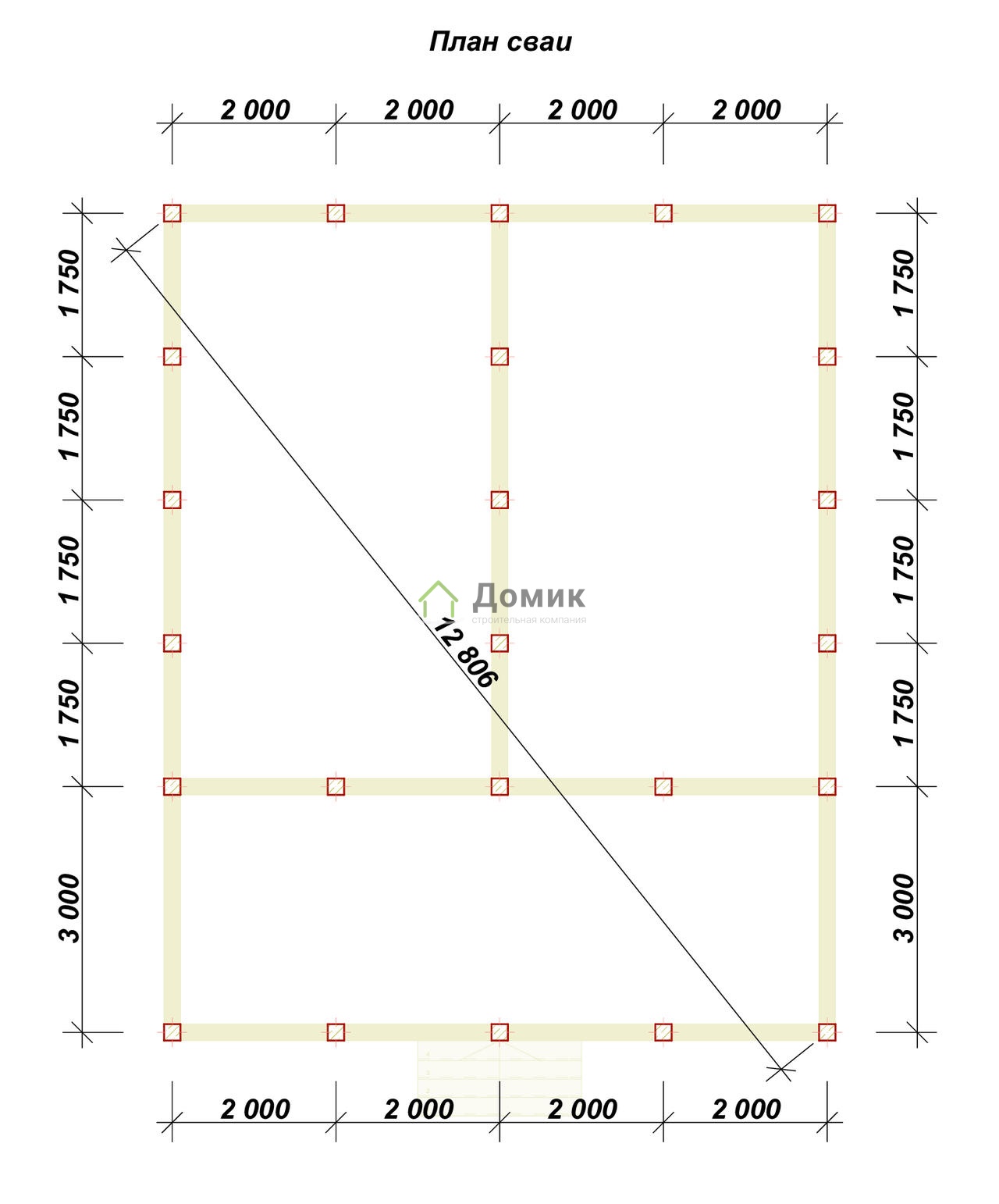
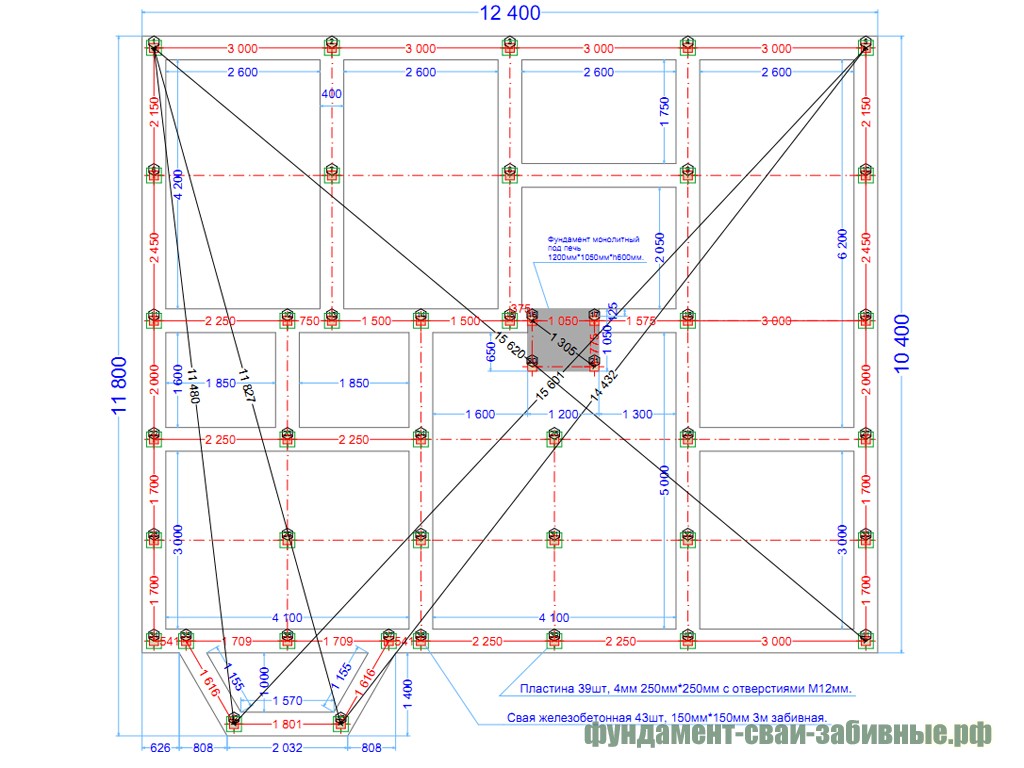
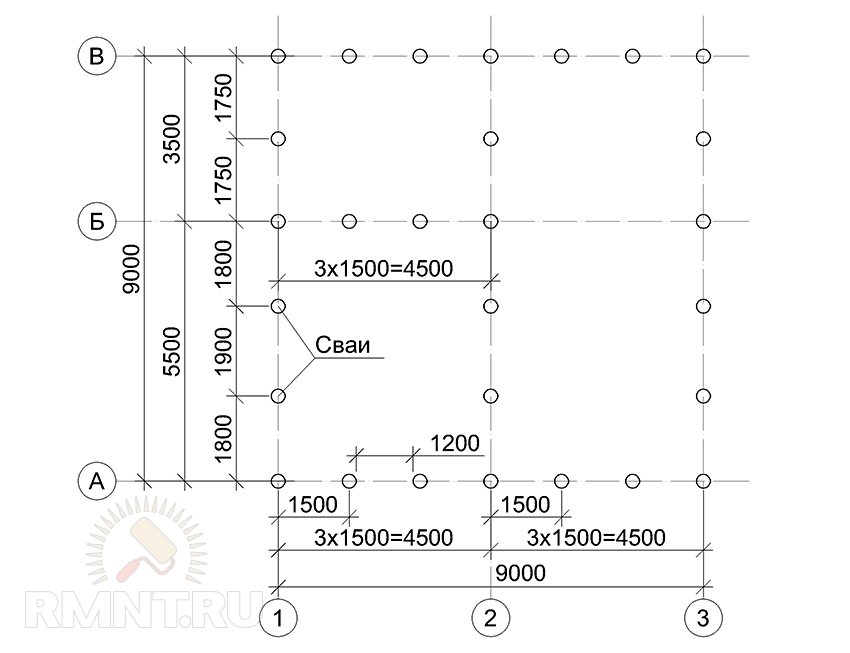
After calculating the minimum required number of supports, you can start making a draft design of the future foundation. The distance between the supports is taken up to 1.5 meters, they must be installed at the intersection corners of the bearing walls and at the points of the highest load on the ground. The volume of building materials is calculated individually based on local conditions and characteristics of the supports.
The preliminary distribution of piles over the minimum area of the lower edge of the grillage is calculated as follows:
A min = (bo + 2c) (ao + 2c)
Here the parameters a, b are the width and length of the support, and c is the width of the trim, of that part of the support that is cut off when the foundation is aligned along the horizontal plane.
In some cases, it is advisable to combine several types of piles at once or to increase the volume of the base by means of a pile field. It is recommended to arrange it in cases where there is a significant load from the building on a unit of soil area. As a rule, such fields are mounted in concrete glasses, the volume of necessary building materials is calculated separately, as well as the grade of concrete. It is also highly recommended here to calculate the permissible load on building materials.
The calculation of the foundation settlement according to the second group is carried out in the same way as the calculation of the foundation settlement of a shallow foundation. Settlement is determined by the diameter and area of the pile foot, as well as their number and the choice of acceptable material during stretching. Moreover, if hanging supports are designed, then the deformation is not calculated.
How not to be mistaken in the absence of experience
With soil group
 Pile foundations are a good choice for clayey soils
Pile foundations are a good choice for clayey soils
The basis in calculating and determining the feasibility of erecting a pile, as, indeed, any other foundation, is the identification of the type of soil.
Soils can be conditionally divided into several groups:
- Stony (rocky) soil in itself can represent a reliable foundation for building a house, therefore it makes no sense to build a pile foundation on it;
- On sandy soils (as well as on "gristly" - a mixture of sand, gravel, clay), there is also no special need to install piles - it is best to arrange shallow strip foundations on them, of course, below the freezing depth;
- On loams and sandy loams, evenly folded, it is quite possible to build a house on a strip foundation;
- Peat bogs allow only light slab structures to be erected. Watch the video on how not to be mistaken with the type of foundation.
With the number of piles
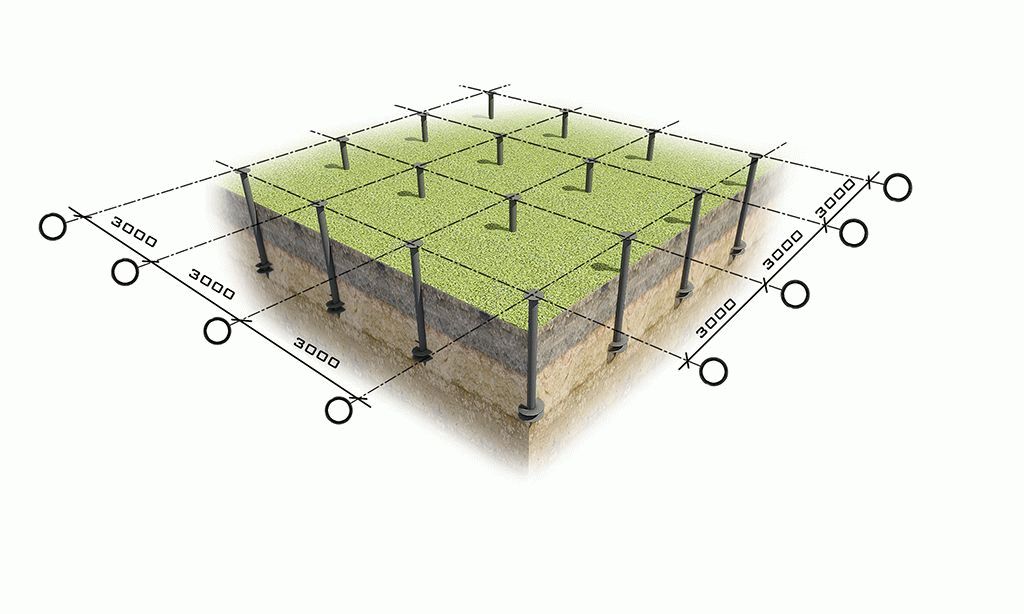
To use the rather complex calculations described above, simple rules have been developed for selecting the number of piles in accordance with the distribution of control points along the perimeter of the structure:
- Under frame-panel and wooden houses, the interval between piles should not exceed 3 m;
- For lightweight concrete structures, the distance between buried supports should be taken no more than 2m.
The simplest and most understandable is the following example.
A house plan is drawn on a sheet of paper to scale. At the corners and intersections of the walls, points are outlined at which the piles should be installed first of all. Further, the rules for placing supports, described just above, are applied depending on the material from which the building is being erected. Watch the video on how to calculate the number of piles.
No matter what materials the house is built from, no matter what size and design features it has, the calculation of the pile foundation as the supporting structure of the entire structure can be called the main nuance of successful construction.