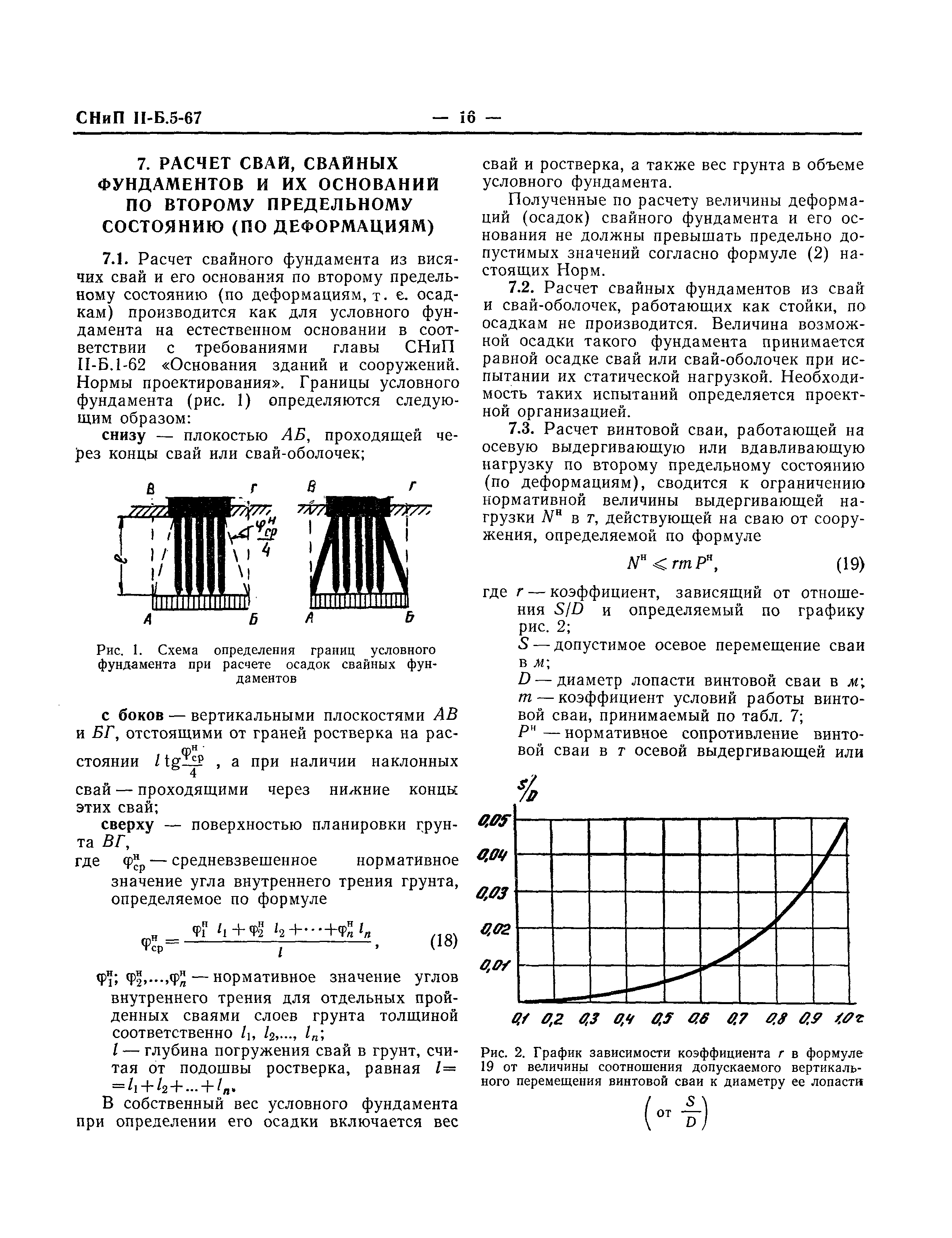
Preparing for calculation
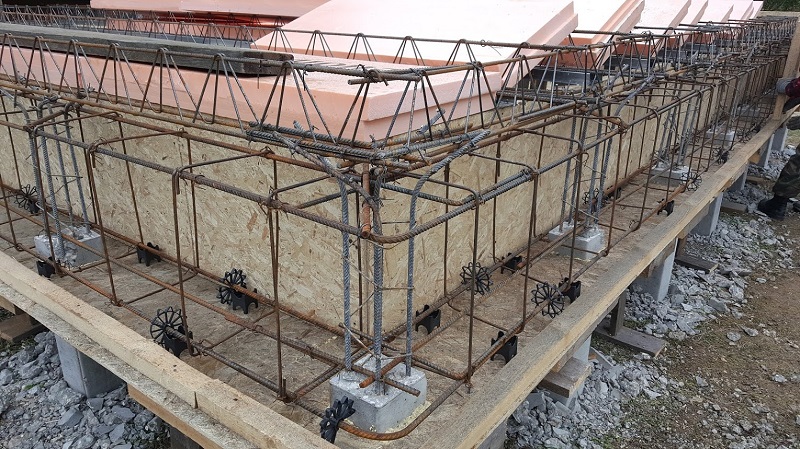
Construction of bored piles
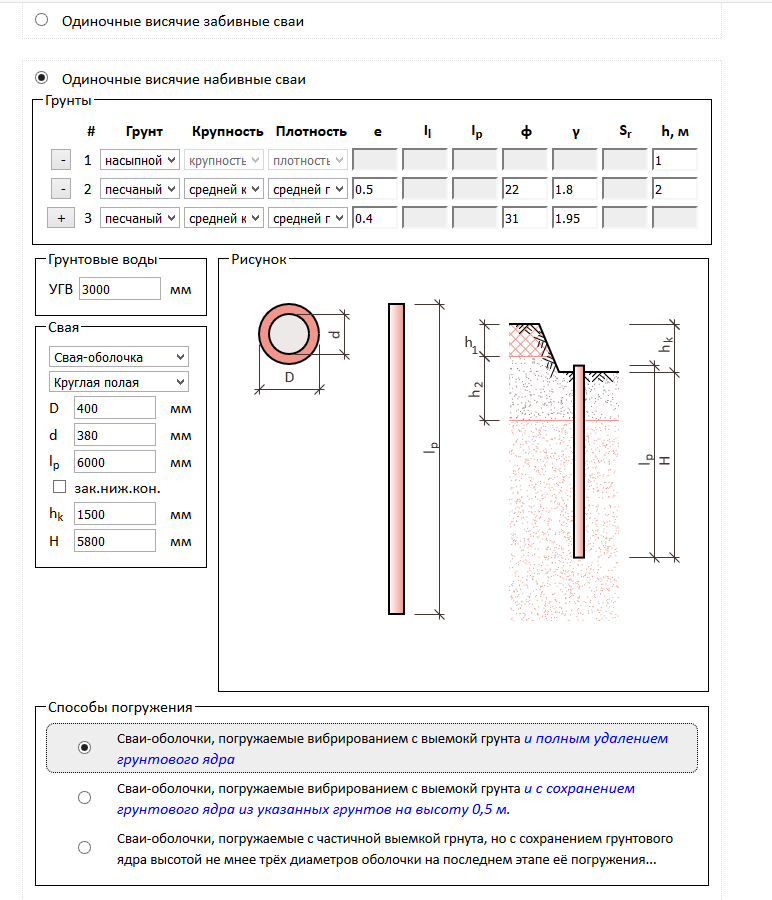
The initial data that will be needed to calculate the bearing capacity of a bored pile is obtained as a result of conducting geological surveys and calculating the total estimated load of the building. These are compulsory stages of the calculation, the implementation of which is justified by the theory of calculating the strength characteristics of bored foundations.
Indicators such as the depth of freezing, the level of occurrence of groundwater, the type of soil and its mechanical characteristics are very important for obtaining an accurate result. Information on the depth of soil freezing is in SNiP 2.02.01-83 *, the data are divided by climatic regions, presented cartographically and in the form of tables.
The calculation of the mass of the building is carried out taking into account the climatic region, the location of the building relative to the rumba of the winds, the average amount of precipitation in winter, the mass of building structures and equipment. This indicator is most significant in the design of the foundation - the data for this part of the calculation, as well as the diagram and calculation formulas can be found in SNiP 2.01.07-85.
Carrying out geology
Pit for geological surveys
Conducting geological surveys is a responsible event, and in the mass flow-line construction this is done by geologists. In individual housing construction, an independent assessment of the condition of soils is often carried out. Without experience in conducting surveys of this level, it is very difficult to assess the real state of affairs. The work of a competent specialist for the most part consists in a visual assessment of the state of strata.
To begin with, they arrange shufras on the site - vertical excavations of soil of a rectangular or circular section, a depth of two meters and a width sufficient for a visual inspection of the base of the pit walls. The purpose of the pits is to open the soil in order to access the strata hidden under the top layer of the soil. Geologists measure the depth of the seams, take a soil sample from the middle of each layer, and then observe the accumulation of water at the bottom of the face. Instead of pits, round wells can be arranged, from which a core is taken out with the help of a special device or local samples are taken.
All the data obtained are entered into a summary table. In addition, a profile of the soil section is drawn up, which makes it possible to predict the state of the soil at the points where drilling was not carried out. When self-assessing the foundations, one should be guided by the information provided in SNiP 2.02.01-83 * and GOST 25100-2011, where in the relevant sections the classification of soils with descriptions, methods of visual determination of soil types and characteristics in accordance with the types are presented.
Characteristic Advantages and Disadvantages of Driven Pile Installation
This type of foundation for a structure has beneficial and indisputable differences from other bases in terms of parameters: This is how round-shaped driven piles look like
- no need to carry out a large amount of earthwork, while easy to install;
- foundation piles can be driven into any fragile soil, except for greasy rocks;
- the material for the manufacture of piles can be selected based on the budget of the construction site, the parameters of the building and the type of soil;
- holds a large mass of a structure well, is used in the construction of high-rise buildings with a large number of floors;
- the service life of this foundation is 100 years;
- the possibility of increasing strength by arranging a strip foundation from piles;
- the pile foundation for a brick house is not afraid of temperature extremes, moisture-resistant, non-combustible and resistant to environmental influences;
- easy to transport and store RC piles.
But like any material and method of arranging foundations for a house, this type of foundation has a number of disadvantages that are worth talking about:
- First of all, you will have to plan the basement floor and provide for ways to arrange it.
- If planting and swelling soils prevail on the site, then the pile-driven foundation may not be stable enough.
- If the soil on your site is the same as described above, then you should not despair and buy another land - there is a way out of this situation. The pile-driven foundation can be strengthened, for example, by installing a monolithic slab on the supports, or by equipping the pile-strip foundation.
Important! If you decide on the arrangement of the grillage, then there should be a gap between the soil and the tape, which, after installation, is filled with fine crushed stone, or sand. This is done so that during winter heaving the soil could not affect the grillage tape.
Of course, this type of foundation has drawbacks, but there are few of them and at the same time they can always be bypassed and a way to eliminate them can be found. There is one more important point - before buying material, for the manufacture of a pile-driven foundation, you need to carefully study the documents in which you should contain information about the manufacturer of the piles, the material used in their manufacture, the date of production, the batch number. In addition, the seller must provide you with a certificate of conformity for this product.
If there are no documents, then you should refuse to purchase.
Examine the material carefully; the surface of the piles should be even and smooth without visible damage and unwanted inclusions. For example, microcracks can be detected by wetting one side.
When dry, darkened stripes will appear on the surface - this indicates that the material is of inadequate quality. It is also worth considering the types of piles, since they can be made of different materials.
In addition, the seller must provide you with a certificate of conformity for this product. If there are no documents, then you should refuse to purchase.
Examine the material carefully; the surface of the piles should be even and smooth without visible damage and unwanted inclusions. For example, microcracks can be detected by wetting one side.
When dry, darkened stripes will appear on the surface - this indicates that the material is of inadequate quality. It is also worth considering the types of piles, since they can be made from different materials.
Why you need to use the calculation of the pile foundation
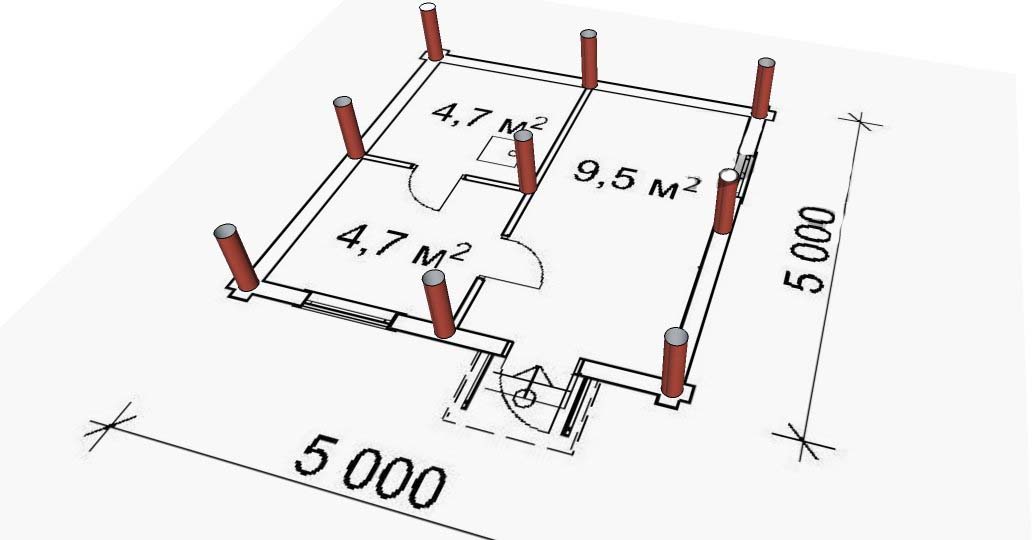
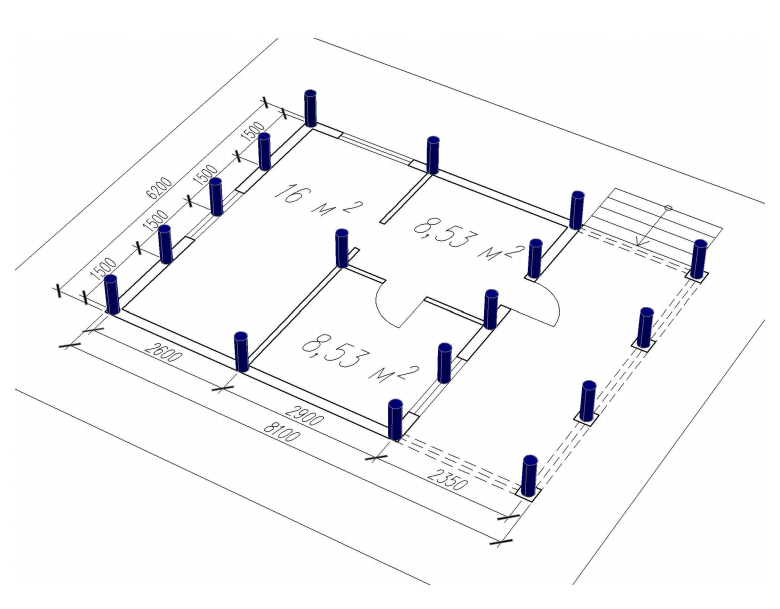
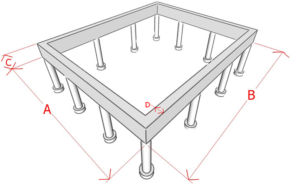 Sketch indicating the parameters required for the calculation
Sketch indicating the parameters required for the calculation
Considering that the piles in the foundations are the usual pivot points, which are responsible for the uniform transfer of the entire volume of loads from the side of the building and the soil through the sole to solid soil layers, they are selected only after calculating the grillage. For example, the maximum permissible dimensions, thickness, design, and other parameters.
Also, the choice of the diameter of the piles used in construction is influenced by factors related to the type of soil, which are also taken into account in the calculations. The calculation of the pile foundation is needed for some conveniences:
- It will turn out to make an extended project of the pile foundation, taking into account the locations of the supports, as well as the distance between them.
- You can significantly save on the amount of building materials used by choosing the optimal type of support.
- The calculation provides for the selection of the optimal support in terms of diameter, its length and dimensions, as well as the selection of the type of sole.
You can also immediately determine whether screw piles are suitable for a given type of construction or whether you need to use ram or other types of piles.
Calculation example
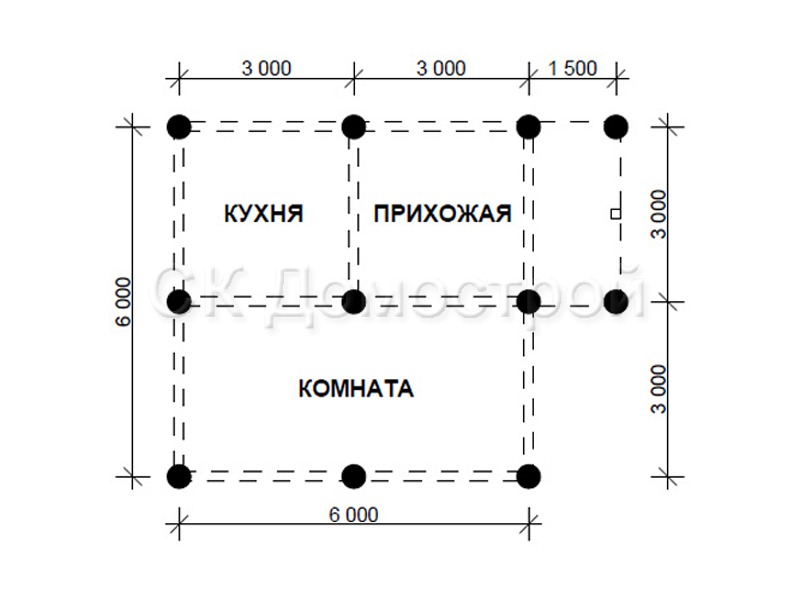
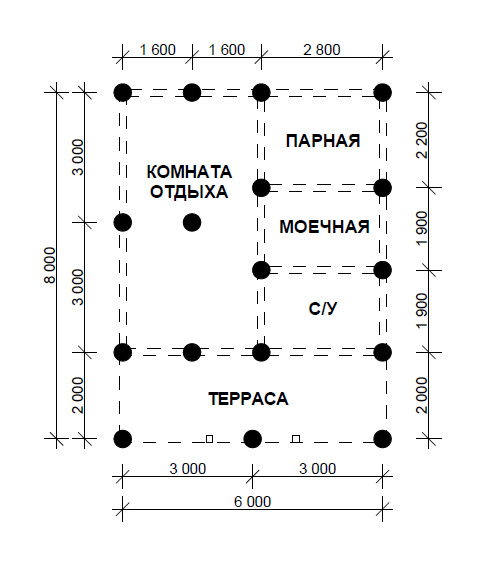
To get a better understanding of how calculations are performed, consider the calculation example.Here we consider a one-story brick building with a hip roof made of metal tiles. The building is supposed to have two floors. Both are made of reinforced concrete with a thickness of 220 mm. The dimensions of the house in terms of 6 by 9 meters. The wall thickness is 380 mm. Floor height - 3.15 m (from floor to ceiling - 2.8 m), total length of internal partitions - 10 m. There are no internal walls. A hard-plastic sandy loam was found on the site, the porosity of which is 0.5. The depth of this sandy loam is 3.1 m. From here, according to the tables, we find: R = 46 tons / sq. M., Fin = 1.2 tons / sq. M. (for calculations, the average depth is taken equal to 1 m). The snow load is taken according to the values of Moscow.
We collect loads in the form of a table. At the same time, do not forget about the reliability factors.
| Load type | Payment |
|---|---|
| Brick walls | perimeter of walls = 6 + 6 + 9 + 9 = 30 m; wall area = 30 m * 3m = 90 m2; wall mass = (90 m2 * 684) * 1.2 = 73872 kg |
| Partitions made of drywall, not insulated with a height of 2.8 m | 10m * 2.8 * 27.2kg * 1.2 = 913.92kg |
| Overlap made of reinforced concrete slabs 220 mm thick, 2 pcs. | 2pcs * 6m * 9m * 500 kg / m2 * 1.3 = 70200 kg |
| Roof | 6 m * 9 m * 60 kg * 1.2 / cos30ᵒ (roof slope) = 4470 kg |
| Load from furniture and people on 2 floors | 2 * 6m * 9m * 150kg * 1.2 = 19440 kg |
| Snow | 6m * 9m * 180kg * 1.4 / cos30 ° = 15640 kg |
| TOTAL: | 184535.92 kg ≈ 184536 kg |
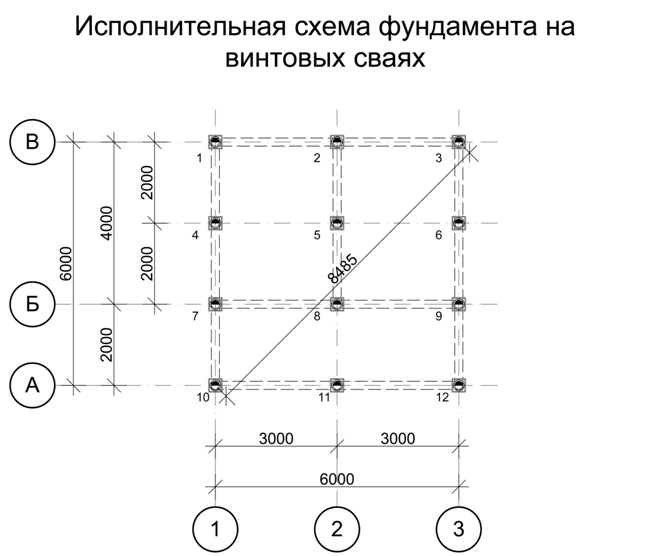
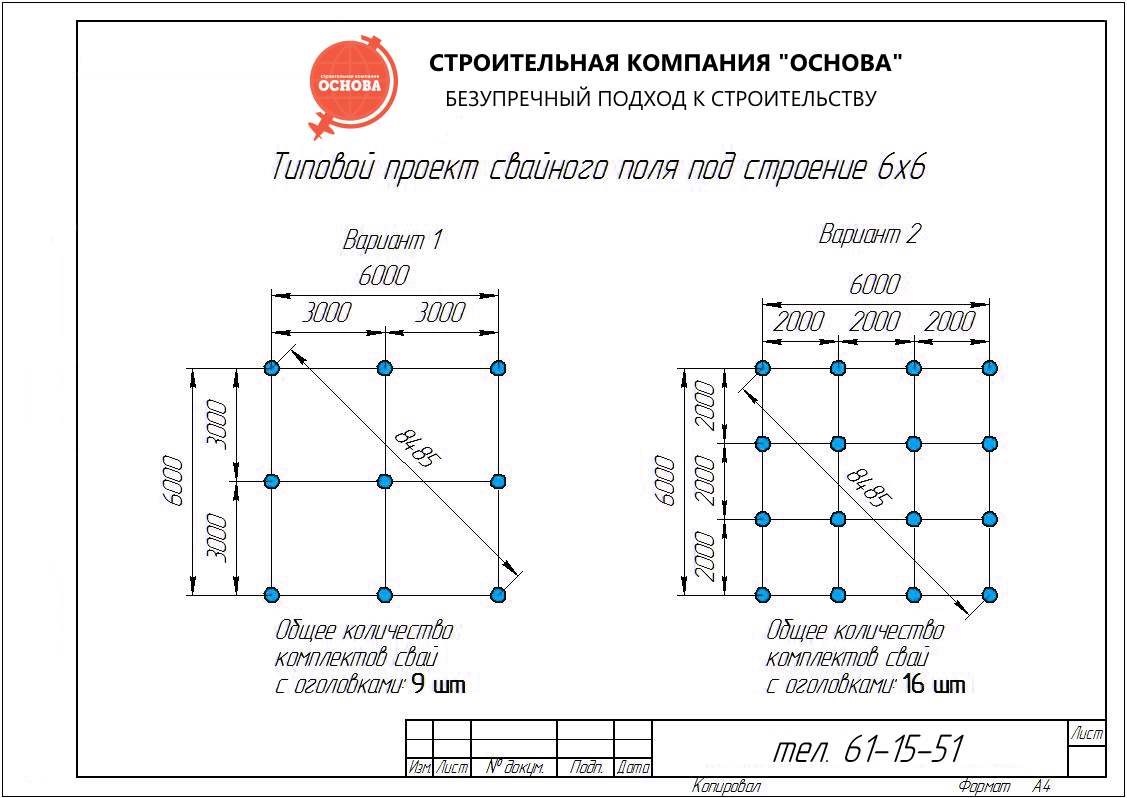
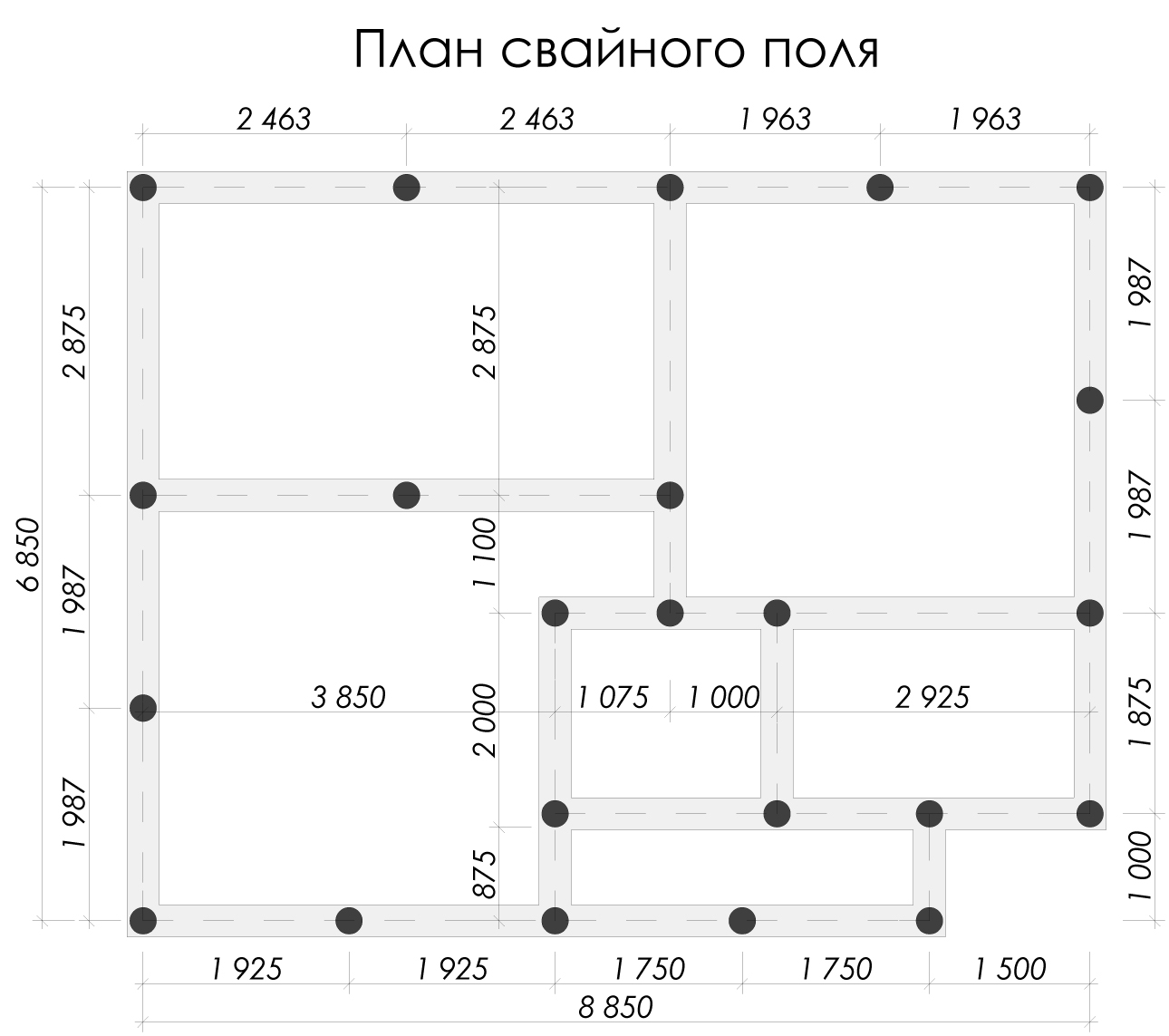
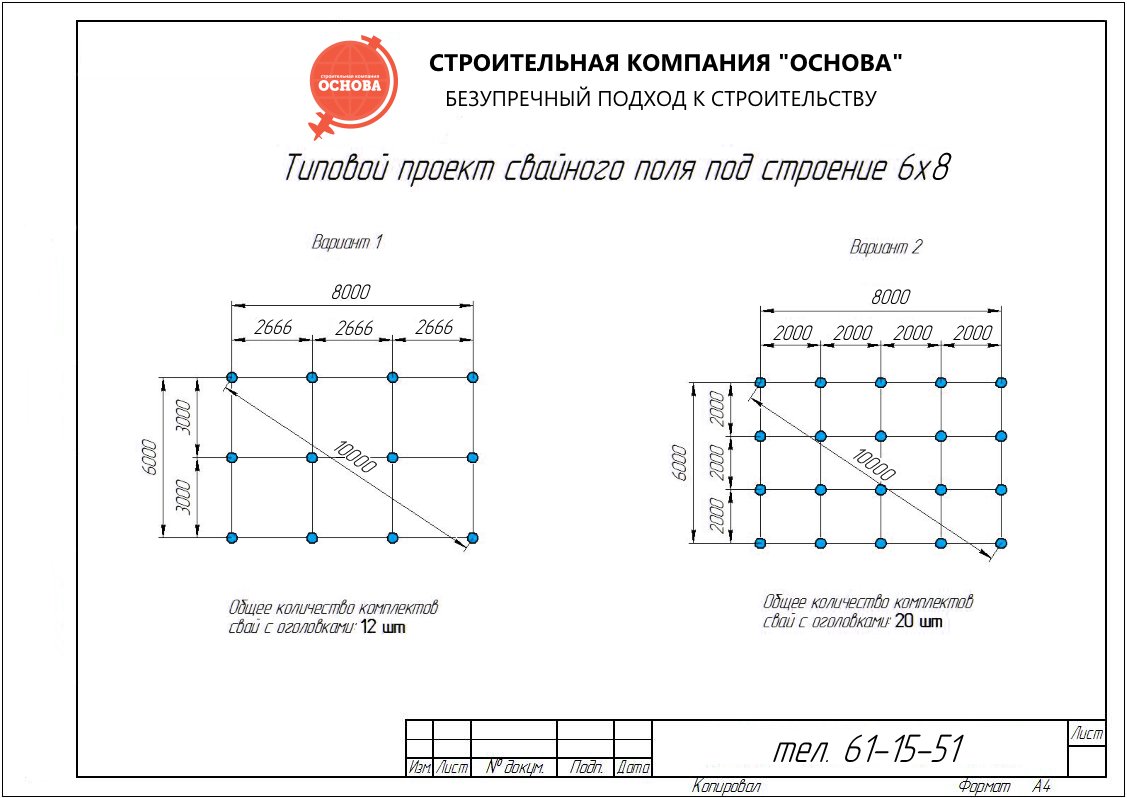
We pre-assign a grillage 40 cm wide, 50 cm high. The pile length is 3000 mm, section D = 500 mm. We use an approximate pile pitch of 1500 mm. To calculate the total number of supports, you need to divide 30 m (grillage length) by 1.5 m (pile pitch) and add 1 pc. If necessary, the value is rounded down to a whole number. We get 21 pieces.
The area of one pile = 3.14 * 0.52 / 4 = 0.196 sq.m., perimeter = 2 * 3.14 * 0.5 = 3.14 m.
Let's find the mass of the grillage: 0.4 m • 0.5 m • 30 m • 2500 kg / cubic meter • 1.3 = 19500 kg.
Let's find the mass of piles: 21 • 3 m • 0.196 sq.m. • 2500 kg / cubic meter. • 1.3 = 40131 kg.
Let's find the mass of the entire building: the sum from the table + the mass of the piles + the mass of the grillage = 244167 kg or 244 tons.
The calculation requires a load per meter of grillage = Q = 244 t / 30 m = 8.1 t / m.
Calculation of piles. Example
We find the permissible loading on each element according to the formula indicated earlier: P = (0.7 • 46 tons / sq. M. • 0.196 sq. M.) + (3.14 m • 0.8 • 1.2 tons / sq. m. • 3 m) = 15.35 t. The pile pitch is taken equal to P / Q = 15.35 / 8.1 = 1.89 m. Round up to 1.9 m. If the step turns out to be too large or small, you need to check several more options, while changing the length and diameter of the foundations.
For frames, rods D = 14 mm and clamps D = 8 mm are used.
Calculation of the grillage. Example
It is necessary to calculate the mass of the building, excluding the piles. Hence M = 204 tons. The width of the tape is taken equal to M / (L • R) = 204 / (30 • 75) = 0.09 m. Such a grillage cannot be used. The overhangs of the walls of a brick building from the foundation should not exceed 4 cm. The width is assigned structurally 400 mm. The height remains at 500 mm.
Reinforcement of the pile foundation grillage:
- Working 0.1% * 0.4 * 0.5 = 0.0002 sq.m. = 2 sq. Cm. Here, 4 rods with a diameter of 8 mm will be enough, but according to regulatory requirements, we use the minimum possible diameter of 12 mm;
- Horizontal clamps - 6 mm;
- Vertical clamps - 6 mm.
The calculations will take a certain period of time. But with their help, you can save money and time during the construction process.
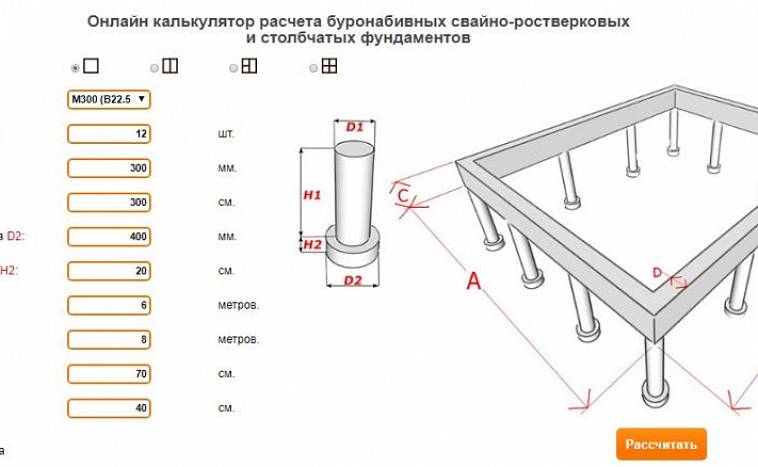
You can also calculate the foundation using an online calculator. Just click on the Calculation of a Columnar Foundation link and follow the instructions.
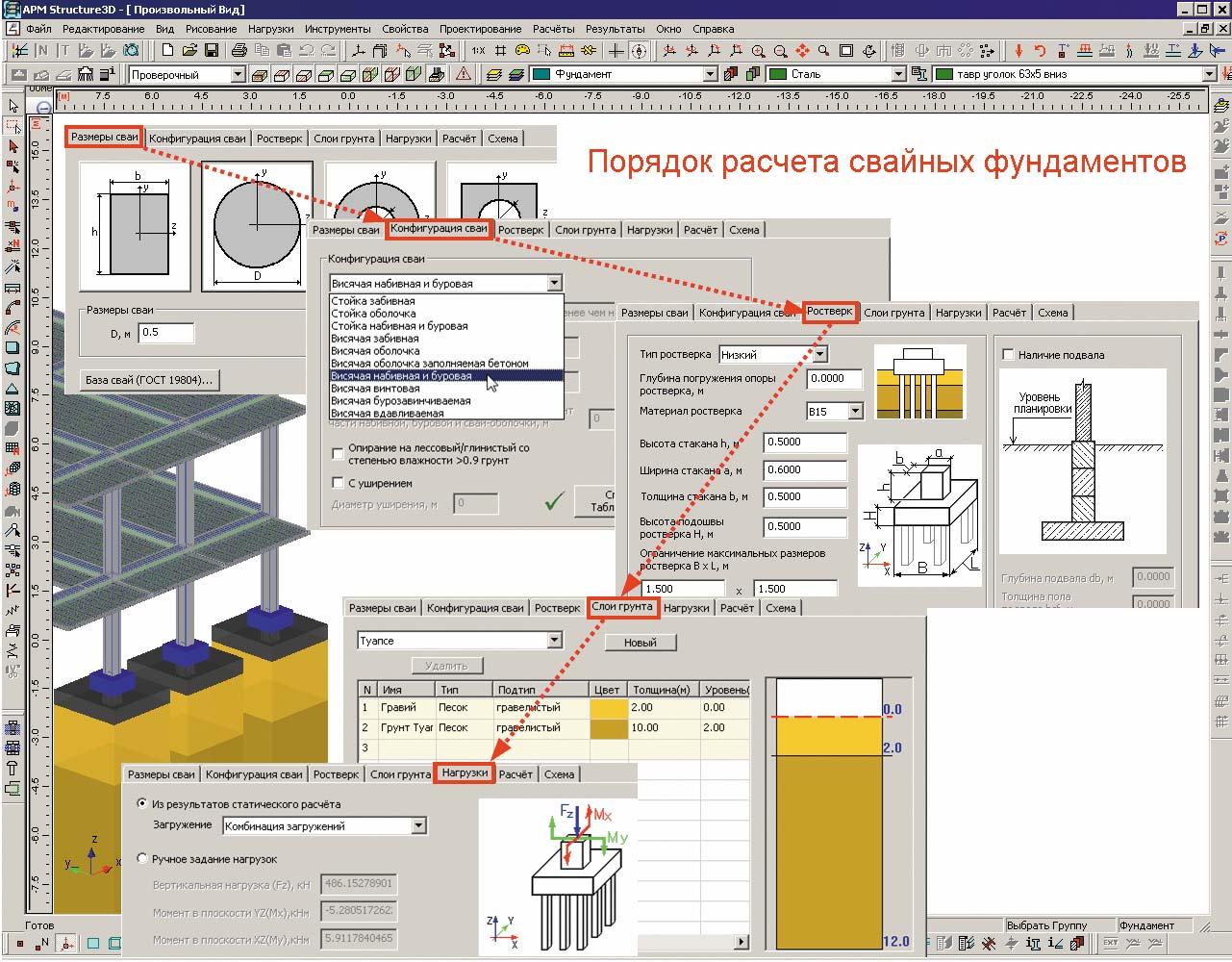
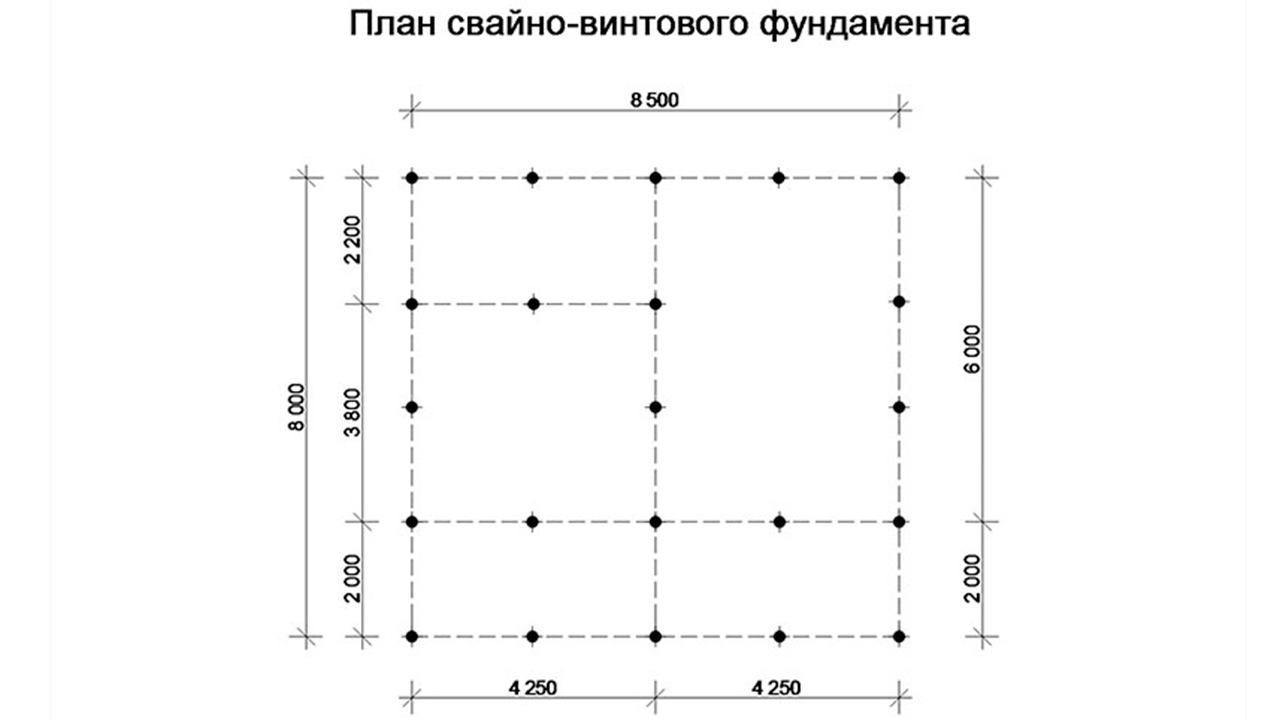
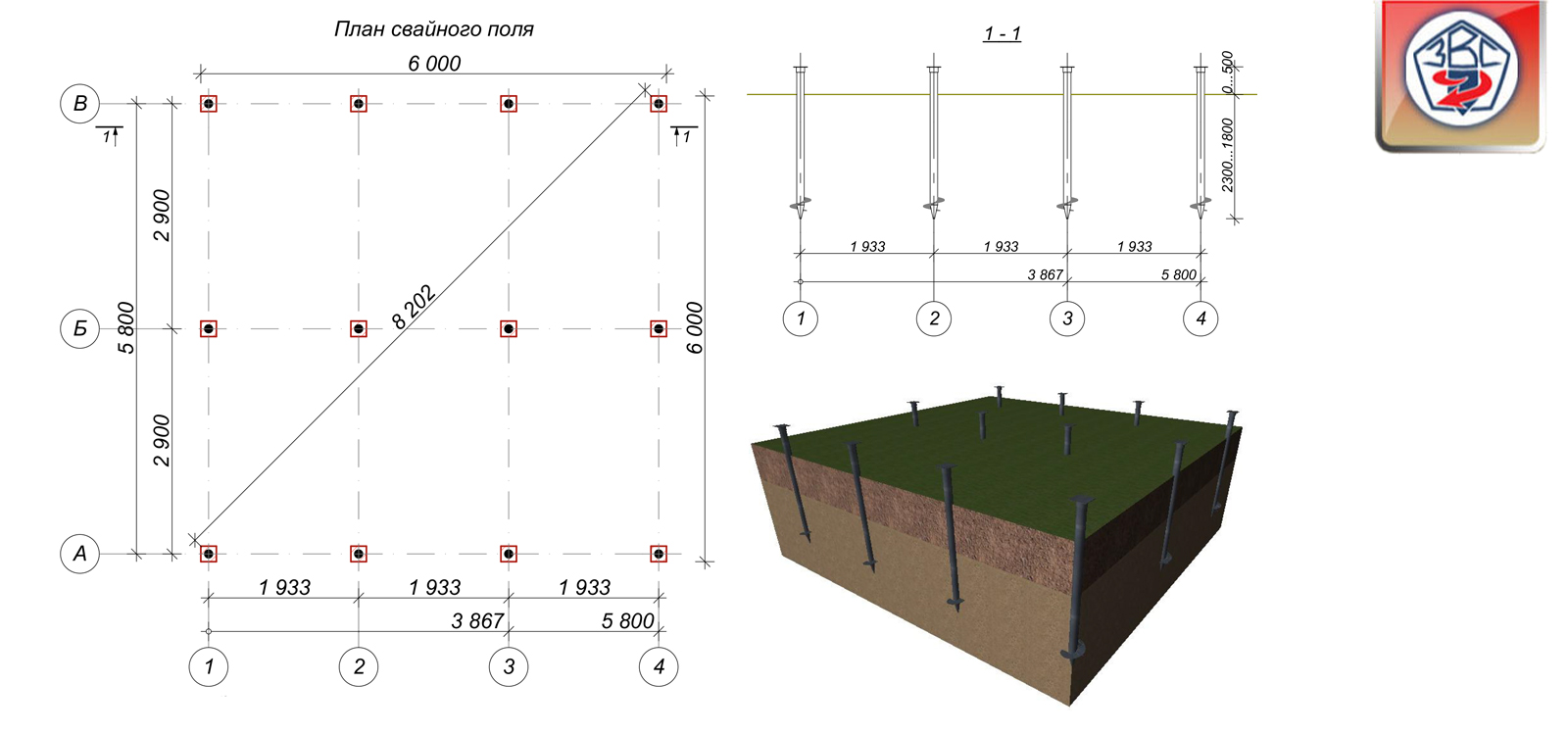
How to calculate the number of piles for a foundation
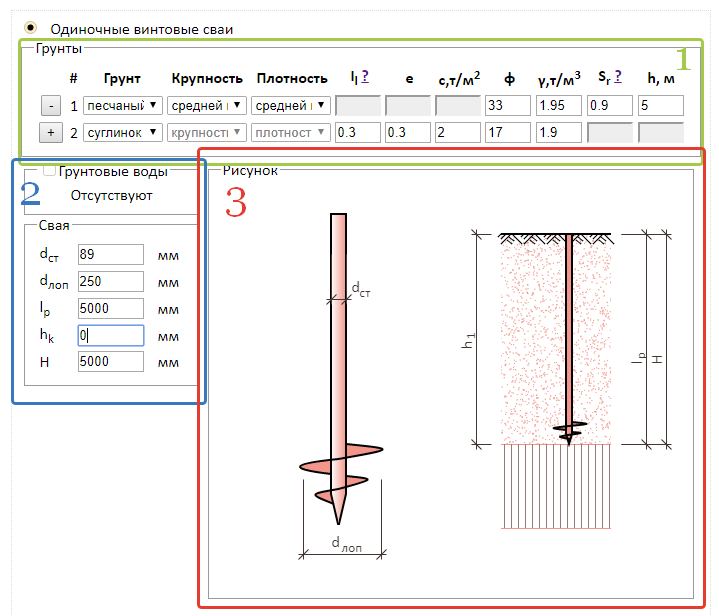
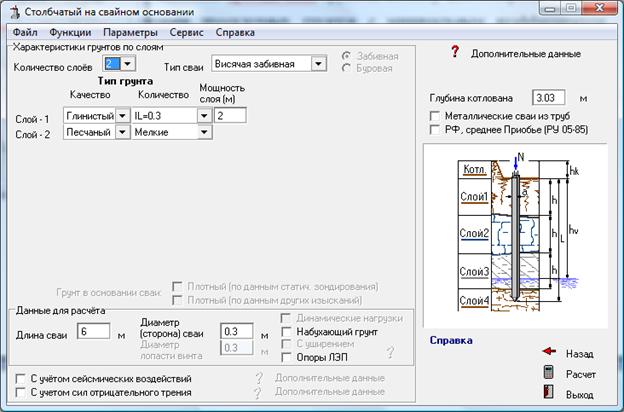
The correct calculation of the number of piles used requires preliminary geodetic exploration. First of all, it is necessary to calculate the level of soil freezing in winter, given that this indicator differs in different regions. For a solid installation of the pile, its lower end must be below this level.
And also it is necessary to find out the degree of density of the soil layers. The higher the density, the shallower the pile depth should be laid at the design stage. For example, for semi-rocky and large-block rocks, it will be minimal (but not less than 0.5 meters), and for sandy and clayey soils, it will have to go deeper to the maximum.
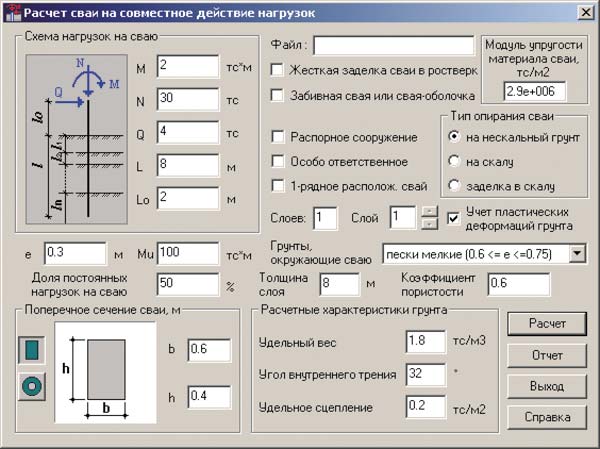
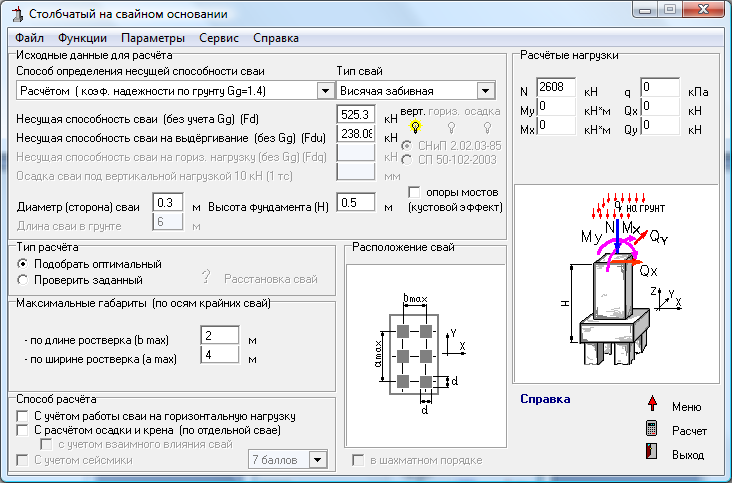
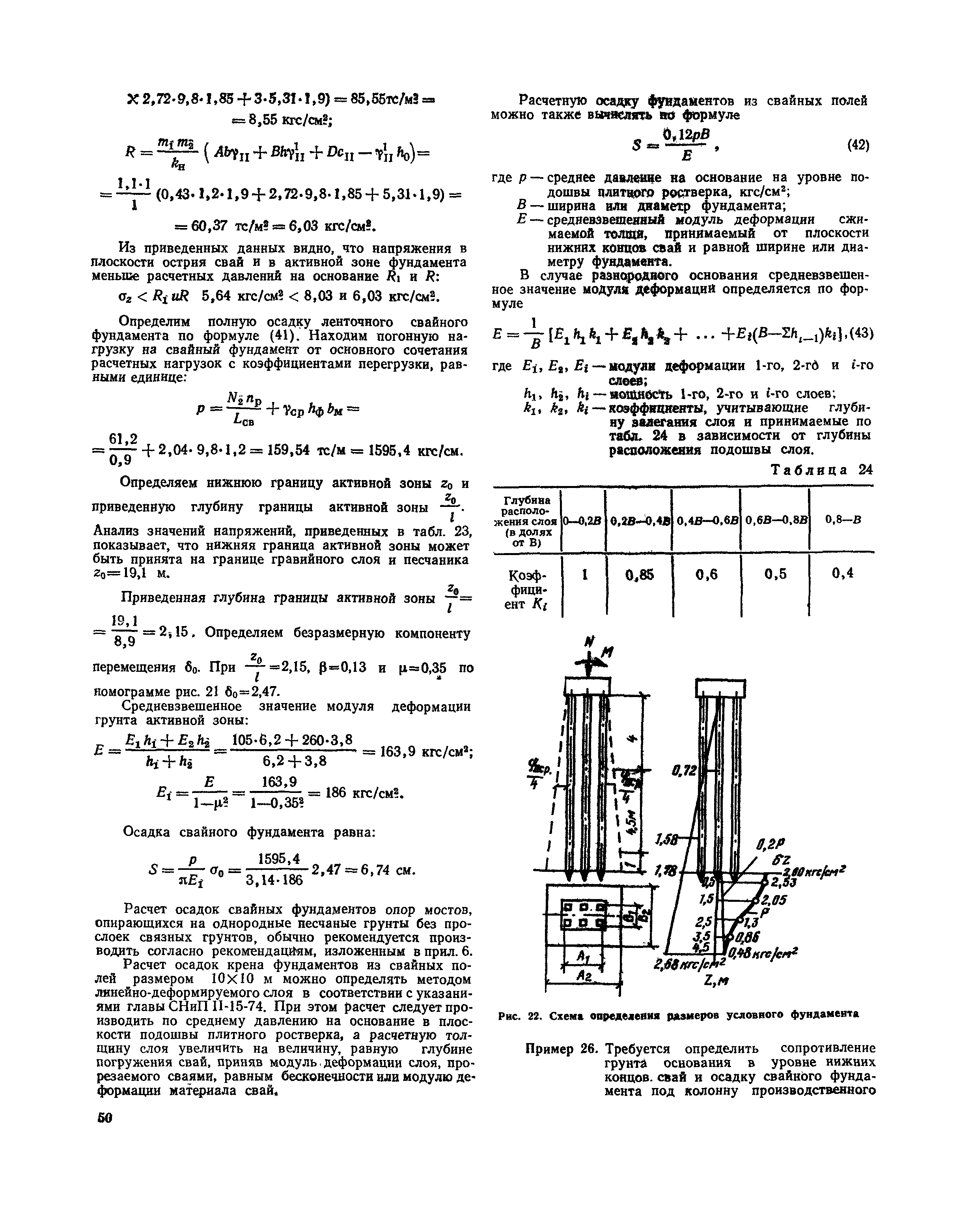
1. Calculation of the potential ultimate load on piles
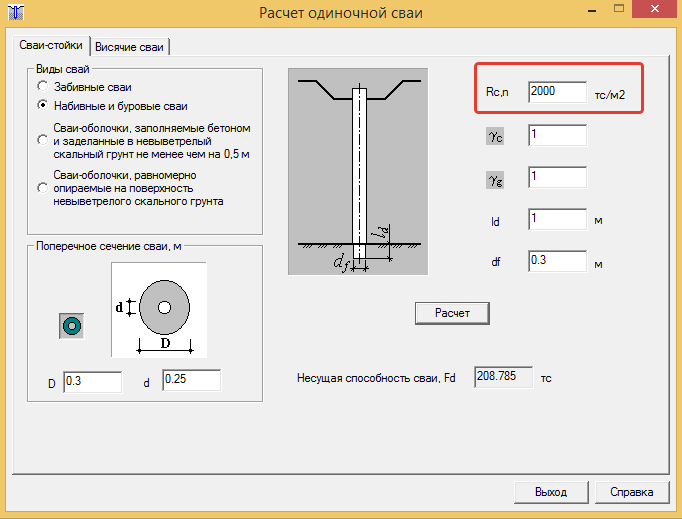
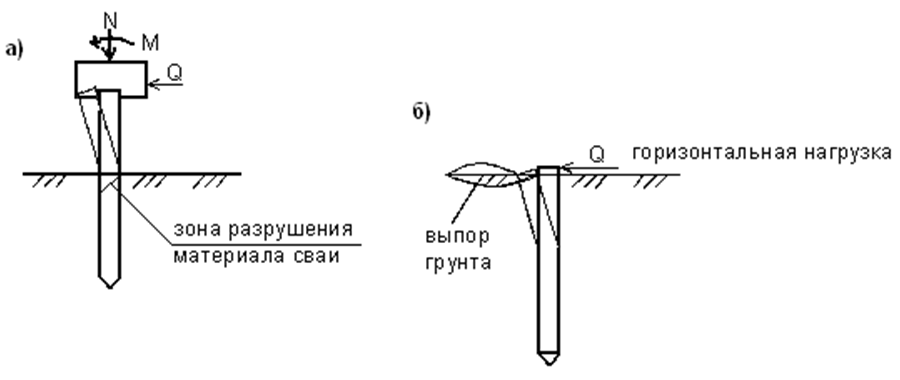
Before calculating the number of piles for a foundation, you should find out the bearing capacity of an individual pile.The general view of the formula is as follows:
In this case, W is the required actual bearing force, Q is the calculated value of the bearing force, calculated for an individual pile according to the material, dimensions and characteristics of the soil; k is an additional "safety factor" that expands the operational reserve of the foundation.
2. Calculation of the design load on the piles
Next, we need to find the Q parameter, without which the calculation of the pile foundation is impossible. The design load is determined by the formula:
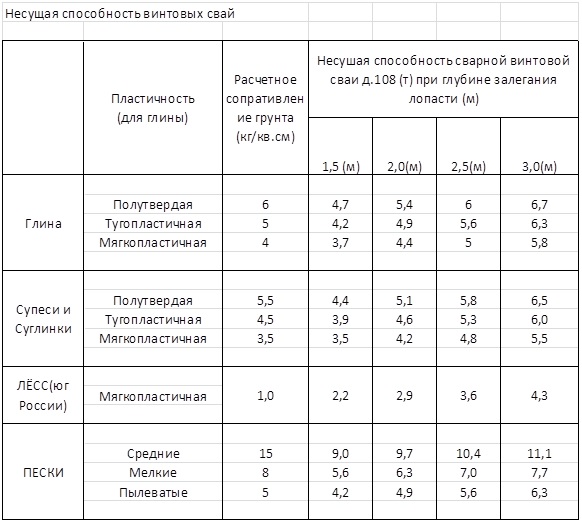
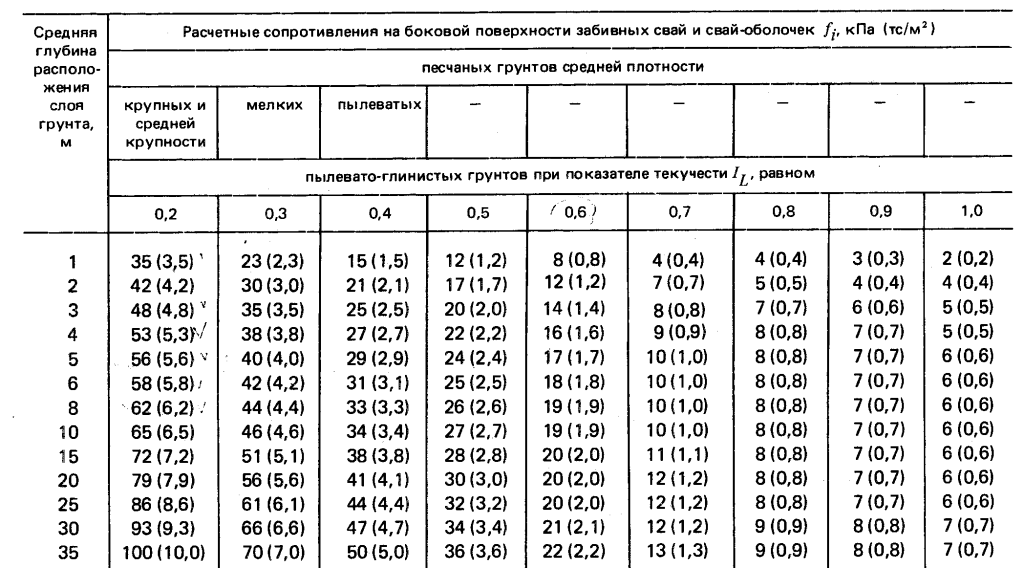
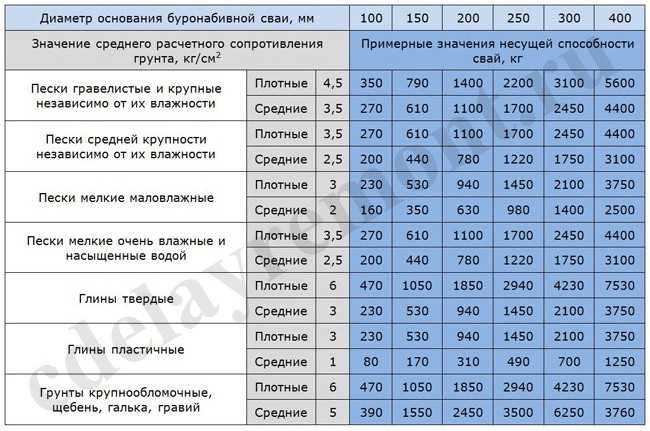
Where S is equal to the cross-sectional area of the pile blades, and Ro is an indicator of soil resistance at the depth of placement of the blades. Soil resistance can be taken from a ready-made table:
table 2
As for the "safety factor" of the conditional foundation, its value can vary within 1.2-1.7. It is logical that the lower the coefficient, the lower the cost of the foundation at the design stage, since it will not be necessary to use a large number of piles to achieve a given value of the bearing force. To reduce the coefficient, a high-quality and reliable soil analysis should be carried out at the construction site, involving specialists.
3. Calculation of the load from the building structure
At the final stage of the design of the pile foundation, the number of piles is calculated. To do this, you will need to sum up all the elements of the building structure: from the main walls and floors, to the rafter system and the roof. It is quite difficult to accurately calculate all the components, so we recommend using one of the specialized calculators. And also, operational loads are entered into the calculation calculator, including interior items, furniture, household appliances and even people living in the house.
4. Counting the required number of piles
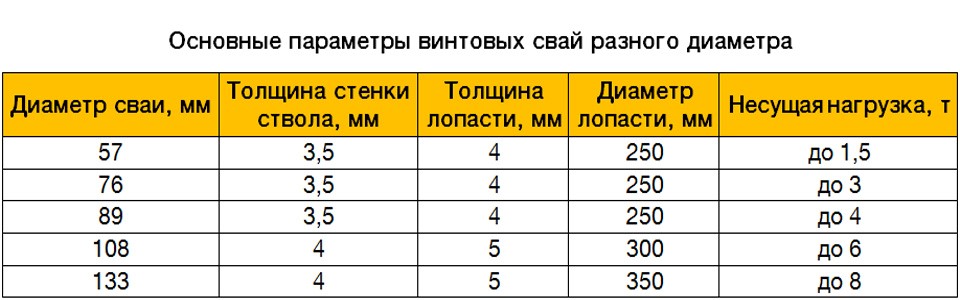
Before calculating the number of piles involved, we need to obtain at the previous stages two values: the total mass of the building (M) and the bearing capacity of the pile (W) multiplied by the "safety factor". The value of the bearing capacity can be taken from Table 1. So, if the mass is 58 tons, and the corrected bearing capacity of the SVS-108 pile is 3.9 tons, then:
As the calculation example showed, for a house weighing 58 tons, 15 SVS-180 piles will be required. It should be noted that this value is approximate and does not take into account the rules for the exact distribution of piles according to SNiP:
- The former should be installed at the intersection points of the supporting structures;
- The rest are mounted evenly between the designated corners;
- The minimum distance between individual piles is 3 meters;
5. Depth of installation of piles and distance between them
The base value of the pile installation depth is calculated based on the depth of soil freezing in a particular region, plus 25 centimeters. And also, before calculating the pile foundation, you need to find out:
- The level of pile strength in terms of material and construction;
- The bearing capacity of the soil;
- Calculate the settlement of the pile foundation, which occurs over time under the load of the building;
- Additional parameters (temperature regime throughout the year, amount of precipitation, wind loads, etc.).
How not to be mistaken in the absence of experience
With soil group
Pile foundations are a good choice for clayey soils
The basis in calculating and determining the feasibility of erecting a pile, as, indeed, any other foundation, is the identification of the type of soil.
Soils can be conditionally divided into several groups:
- Stony (rocky) soil in itself can represent a reliable foundation for building a house, therefore it makes no sense to build a pile foundation on it;
- On sandy soils (as well as on "gristly" - a mixture of sand, gravel, clay), there is also no special need to install piles - it is best to arrange shallow strip foundations on them, of course, below the freezing depth;
- On loams and sandy loams, evenly folded, it is quite possible to build a house on a strip foundation;
- Peat bogs allow only light slab structures to be erected. Watch the video on how not to be mistaken with the type of foundation.
With the number of piles
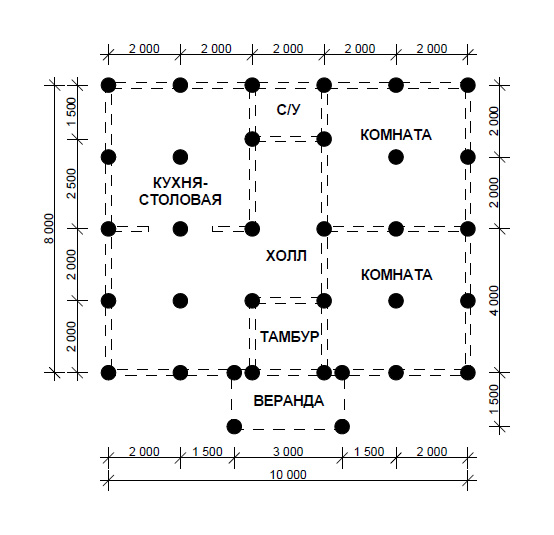
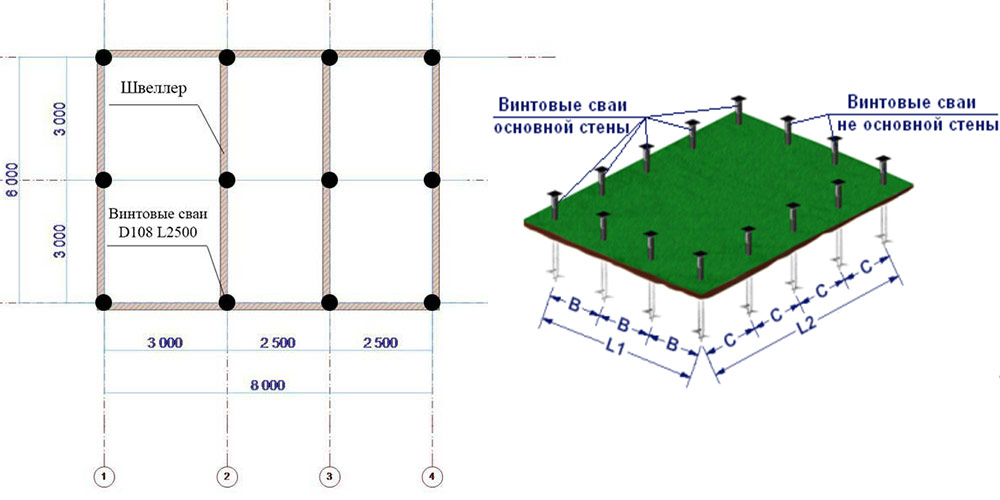
To use the rather complex calculations described above, simple rules have been developed for selecting the number of piles in accordance with the distribution of control points along the perimeter of the structure:
- Under frame-panel and wooden houses, the interval between piles should not exceed 3 m;
- For lightweight concrete structures, the distance between buried supports should be taken no more than 2m.
The following example is the simplest and most understandable.
A house plan is drawn on a sheet of paper to scale. At the corners and intersections of the walls, points are outlined at which the piles should be installed first of all. Further, the rules for placing supports, described just above, are applied depending on the material from which the building is being erected. Watch the video on how to calculate the number of piles.
No matter what materials the house is built from, no matter what size and design features it has, the calculation of the pile foundation as the supporting structure of the entire structure can be called the main nuance of successful construction.
Determine the size of the piles
 If, while drilling a well, a peat or floating soil is found, then you need to go deeper
If, while drilling a well, a peat or floating soil is found, then you need to go deeper
For construction sites with stable, dense soil, supports with a length of 2.5 m are suitable.On an area with difficult terrain, it is imperative to take into account the height differences. On uneven areas, we use piles of different lengths, which depend on the height of the terrain.
When carrying out construction on unstable soils, the length of the pile should reach a layer of dense soil. Finding the location of stable ground using test drilling. We introduce a drill into the ground, take it out at small intervals and look at the type of soil on the knife.
If a peat bog, quicksand, wet earth is found, we drill to a sandy or clay layer. After finding lumps of sand and clay on the drill, we measure the depth of the well with the help of a stone lowered on a rope.
Pile pull-out tests
To determine the pull-out loads, static tests of screw piles are carried out. In the presence of sandy layers of soil, measurements are carried out after 3 days, and for clayey - only after 6 days. For bored piles, test work should be performed only after the concrete has gained strength, determined from the data taken from samples created during the laying of the support.
Indentation tests
 Static test of screw piles
Static test of screw piles
The list of basic tests for indentation of supports under a house includes the following steps:
- Uniform load.
- Differentiated load.
- Differentiated load based on hysteresis.
The magnitude of the load is determined by the need to determine the specified level of measurement accuracy. Usually, for a uniform load, it is 0.07-0.1 of the total calculated, and for a differentiated one - 0.2-0.4 for the initial stage and 0.07-0.1 for subsequent ones.
The transition between the degrees of loading is carried out only after determining the exit to a complete stop of shrinkage. The criterion is the absence of changes during the last 2 hours of observation. An exception to this rule is sandy and clayey soils, where accelerated testing becomes necessary. In this case, the conclusion about the stabilization of the pile is accepted within an hour if there are no displacements less than 0.1 mm.
At each stage of loading, the readings of the measuring instruments about the vertical displacement of the pile are recorded. The sampling intervals are 15 to 30 minutes. The total number of intervals must be at least three. If an odd number of steps is selected, then the load on the first one is taken equal to the value of all subsequent ones.After that, the time dependence on the vertical displacement is plotted, and then compared with the standard value of SP 22.13330.2011. The limit is considered to be such a value that corresponds to 0.1 of the standard load.
Watch the video on how to perform an indentation test on supports.
Pull-out tests
Tests for pulling out screw piles under a house with a diameter of 108 mm are determined by soil parameters, as well as the magnitude of the expected loads. They include the following types of loading:
- Increasing step load while waiting for a steady state to be reached in the pile position.
- Pulsating step action with increasing load in several stages: 1.25, 2.5 or 5 ms. The bottom line is to carry out loading at each stage from zero to maximum, and then it is completely removed without waiting for a steady state. Changing the steps is carried out only after the vertical displacement of the support has stabilized in comparison with the previous one.
- Alternating load. The support is acted upon by repeated loading of the same magnitude for pulling and indentation, which change their sign when passing through the unloaded point.
- Continuously increasing load - a constant pulling force acts on the pile. When the loading value changes, complete stabilization is not expected, since it is quite enough to reach a certain conditional value. The limiting value of the load is considered when the movement of the support upward does not exceed 0.1 of the value of its diameter. For variable loads and pulsating, the change in position should not be more than 0.05 of the pile diameter.
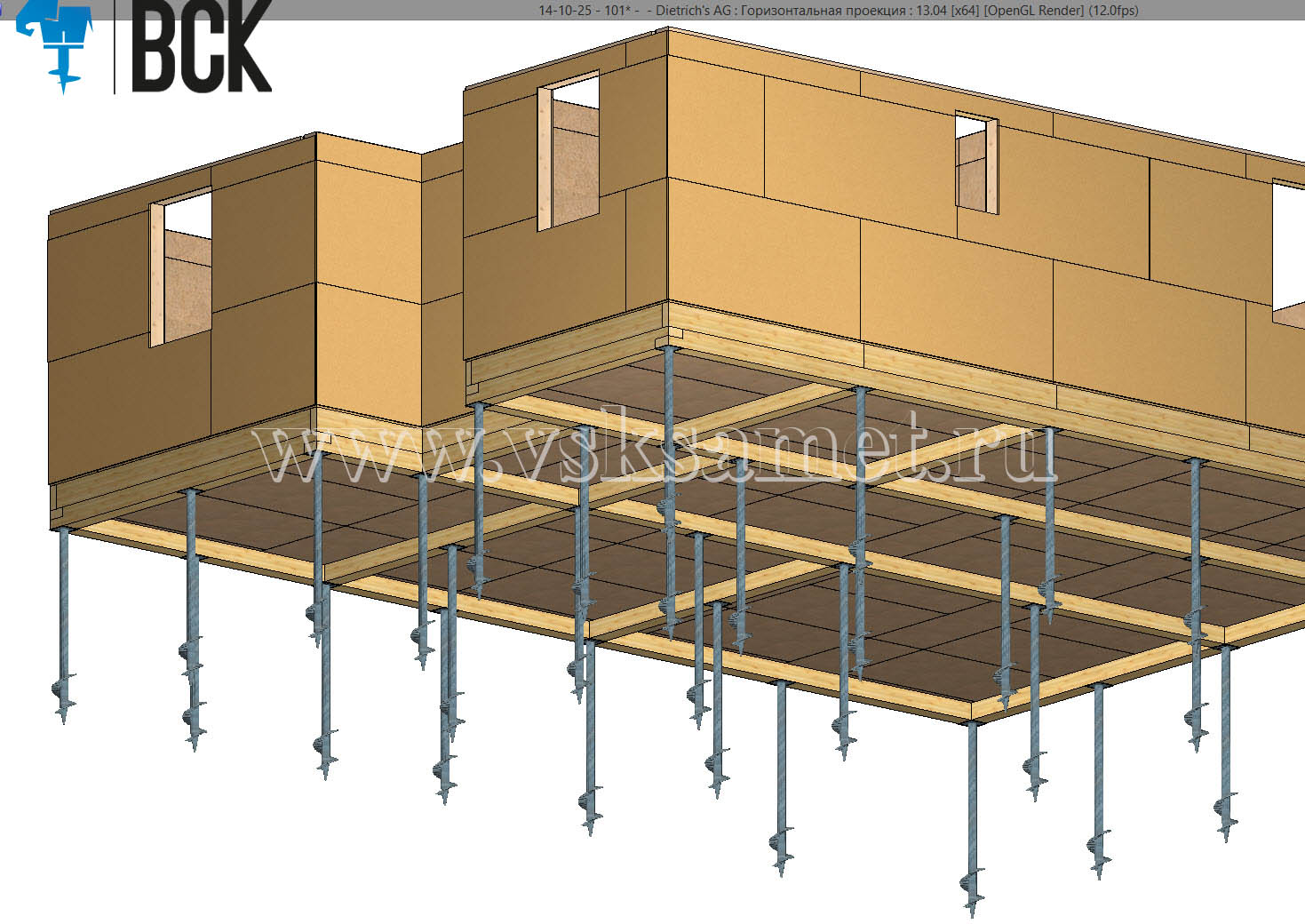
Bored pile structures
When creating a pile foundation of this type, pile structures from monolithic concrete are made and applied.
When creating a pile foundation of this type, pile structures from monolithic concrete, combined, prefabricated (from reinforced concrete) are made and used. The latter are often made with a widening of the heel - the option is shown for construction in problem soils, where the main composition is clay and loam. The broadening of the heel makes it possible to enhance the bearing capacity of the pile element, but this technique is not used in rocky soils.
When determining the types of bored piles, it is necessary to be guided by GOST 19804.2-79; GOST 10060.0-95. The most used are bored, bore-section, bore-tangent piles. Drilling foundations also include downhole structures: wells filled with crushed stone filling with layer-by-layer compaction, supports with a widened heel, for the manufacture of which blasting operations are used and hollow supports made by using a core.
Bored piles
These are structures, including reinforced concrete ones, which are widespread due to the simplicity of arrangement.
These are structures, including reinforced concrete ones, which have become widespread due to the simplicity of arrangement, the possibility of using them to strengthen the existing foundation and the construction of foundations in a limited space. The advantage is the minimum dynamic load on neighboring buildings, the absence of destructive effects on the routes, underground communications. In addition, the technology for manufacturing the foundation allows the object to operate in a normal mode during restoration work.
Wells are carried out by means of drilling tools, when the required depth is reached, the drill is removed and the well is reinforced with a pre-fabricated frame, after which it is filled with a mixture of concrete. The production of bored piles can be carried out using the following technologies:
- With the use of a casing;
- Using a clay talker;
- Through the use of a through-feed auger;
- Using a double rotator;
- By compaction of the soil.
Drilling piles advantages:
- Possibility of manufacturing at the building site;
- Long service life;
- Relative cheapness of the project;
- High bearing capacity of the foundation;
- Thickness variability;
- Minimum requirements for the use of heavy equipment (sometimes you can do without it altogether);
- Wide range of applications.
However, there are also disadvantages:
- Compared to strip and slab foundations, the bearing capacity is low;
- Increased labor costs;
- The complexity of the manufacture of piles on water-saturated soils.
Boring piles
Cutting elements are mounted with a step "to zero", that is, they represent a solid wall of structural bodies
These are structures, the installation technology of which repeats the bored pile elements. The difference is that the bore-section elements are mounted with a step "to zero", that is, they represent a solid wall of structural bodies, which serves to equip a full-fledged support of the soil. They are used for the construction of underground parking lots, tunnels, crossings. Construction according to SNiP 2.02.01-83 of this type is permitted at shallow depths - no more than 30 meters.
Tangent piles
A foundation of this type is used in the case of vertical and horizontal load on the elements from the nearest buildings.
A foundation of this type is used in the case of vertical and horizontal load on the elements from the nearest buildings, groundwater. As a rule, this method is used in construction in a confined space, as well as for fencing very deep pits, for cutting embankments in soils with solid coarse-grained inclusions.
The advantages of the technology are the following indicators:
- The ability to carry out work in a dense building;
- There is no need to arrange additional drainage, drainage;
- It is not difficult to make bore tangent piles both in terms of labor costs and promptly in time.
How to calculate the number of piles for a foundation
The correct calculation of the number of piles used requires preliminary geodetic exploration. First of all, it is necessary to calculate the level of soil freezing in winter, given that this indicator differs in different regions. For a solid installation of the pile, its lower end must be below this level.
And also it is necessary to find out the degree of density of the soil layers. The higher the density, the shallower the pile depth should be laid at the design stage. For example, for semi-rocky and large-block rocks, it will be minimal (but not less than 0.5 meters), and for sandy and clayey soils, it will have to go deeper to the maximum.
1. Calculation of the potential ultimate load on piles
Before calculating the number of piles for a foundation, you should find out the bearing capacity of an individual pile. The general view of the formula is as follows:
In this case, W is the required actual bearing force, Q is the calculated value of the bearing force, calculated for an individual pile according to the material, dimensions and characteristics of the soil; k is an additional "safety factor" that expands the operational reserve of the foundation.
2. Calculation of the design load on the piles
Next, we need to find the Q parameter, without which the calculation of the pile foundation is impossible. The design load is determined by the formula:
Where S is equal to the cross-sectional area of the pile blades, and Ro is an indicator of soil resistance at the depth of placement of the blades. Soil resistance can be taken from a ready-made table:
table 2
As for the "safety factor" of the conditional foundation, its value can vary within 1.2-1.7. It is logical that the lower the coefficient, the lower the cost of the foundation at the design stage, since it will not be necessary to use a large number of piles to achieve a given value of the bearing force.To reduce the coefficient, a high-quality and reliable soil analysis should be carried out at the construction site, involving specialists.
3. Calculation of the load from the building structure
At the final stage of the design of the pile foundation, the number of piles is calculated. To do this, you will need to sum up all the elements of the building structure: from the main walls and floors, to the rafter system and the roof. It is quite difficult to accurately calculate all the components, so we recommend using one of the specialized calculators. And also, operational loads are entered into the calculation calculator, including interior items, furniture, household appliances and even people living in the house.
4. Counting the required number of piles
Before calculating the number of piles involved, we need to obtain at the previous stages two values: the total mass of the building (M) and the bearing capacity of the pile (W) multiplied by the "safety factor". The value of the bearing capacity can be taken from Table 1. So, if the mass is 58 tons, and the corrected bearing capacity of the SVS-108 pile is 3.9 tons, then:
As the calculation example showed, for a house weighing 58 tons, 15 SVS-180 piles will be required. It should be noted that this value is approximate and does not take into account the rules for the exact distribution of piles according to SNiP:
- The former should be installed at the intersection points of the supporting structures;
- The rest are mounted evenly between the designated corners;
- The minimum distance between individual piles is 3 meters;
5. Depth of installation of piles and distance between them
The base value of the pile installation depth is calculated based on the depth of soil freezing in a particular region, plus 25 centimeters. And also, before calculating the pile foundation, you need to find out:
- The level of pile strength in terms of material and construction;
- The bearing capacity of the soil;
- Calculate the settlement of the pile foundation, which occurs over time under the load of the building;
- Additional parameters (temperature regime throughout the year, amount of precipitation, wind loads, etc.).