Types of strapping
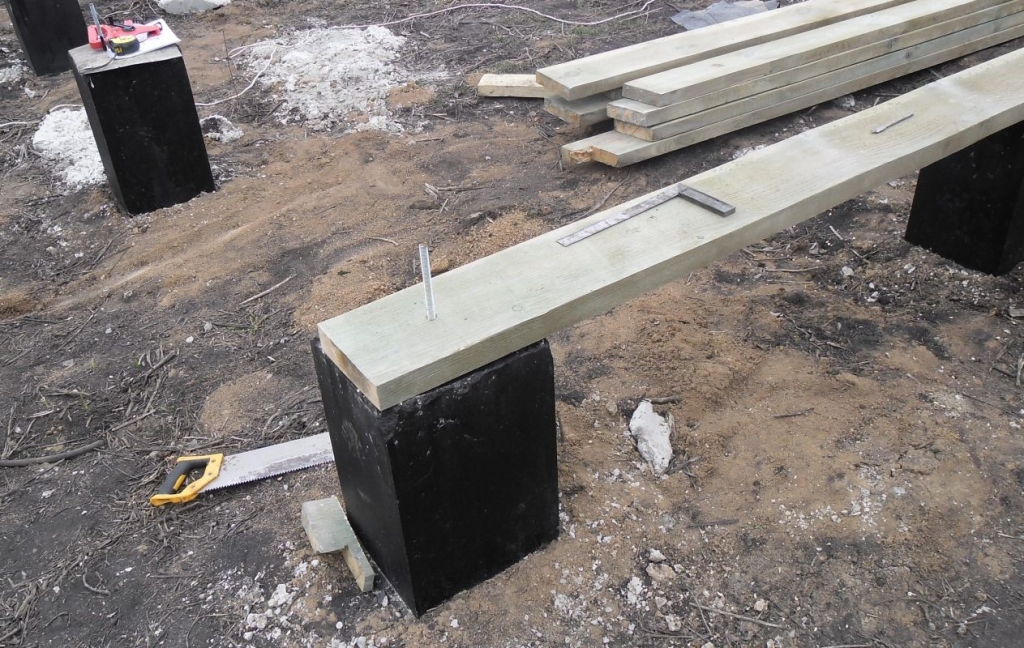
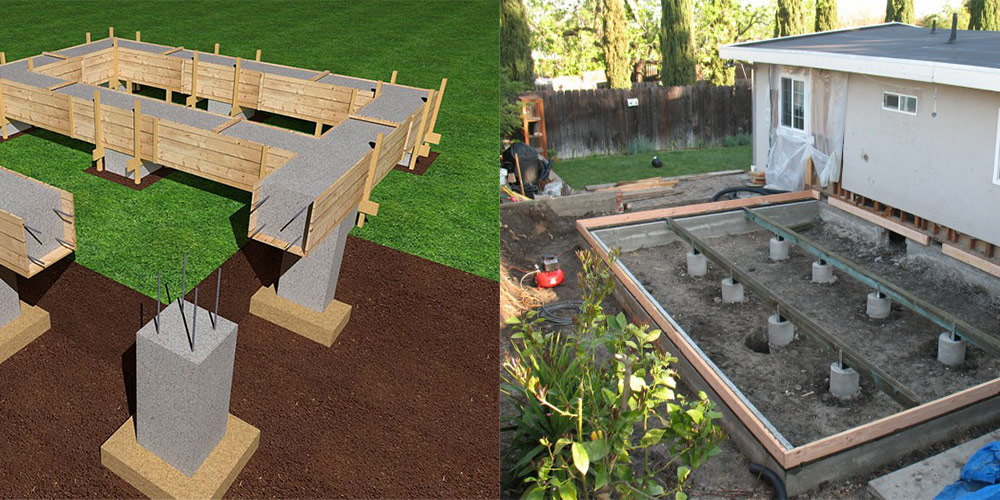
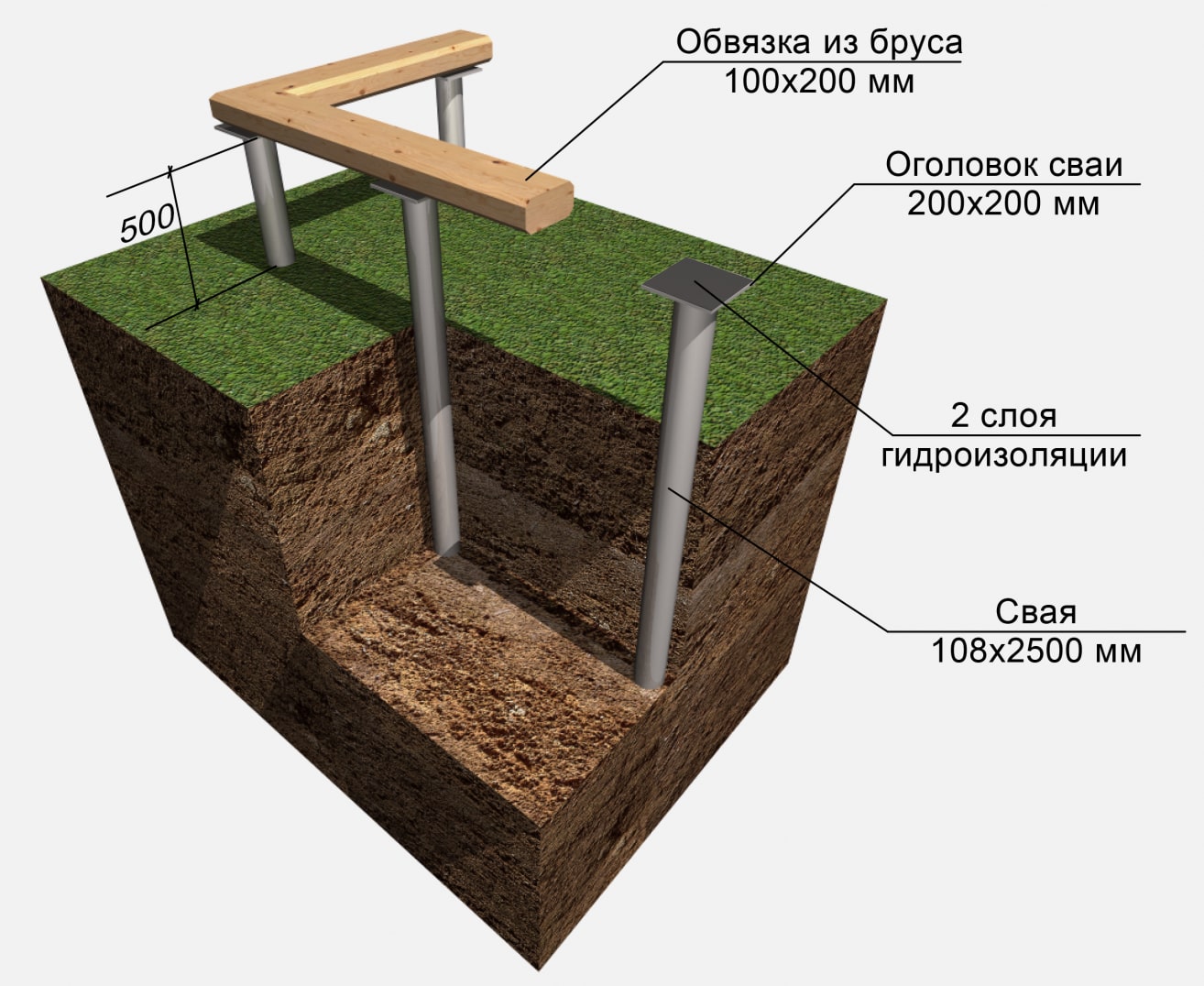
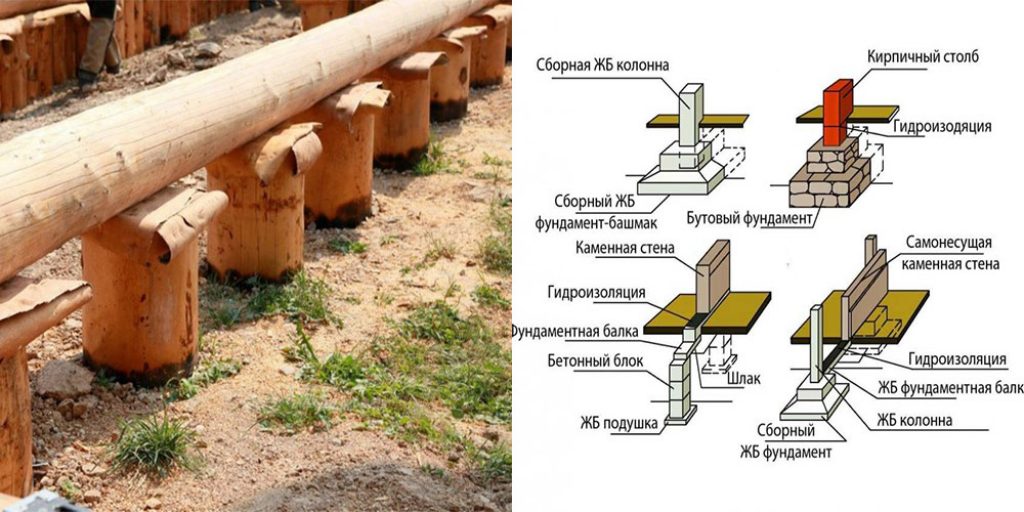
The tops of the pillars are connected by strapping into a single support system. The type of strapping depends on the material of the structures of the building itself. For wooden, panel board and frame structures, the strapping is made from a bar. When forming the support pillars, a vertical metal stud with a threaded end is laid in the upper part. The harness is fastened by screwing a nut onto a metal stud threaded through a hole in the bar.
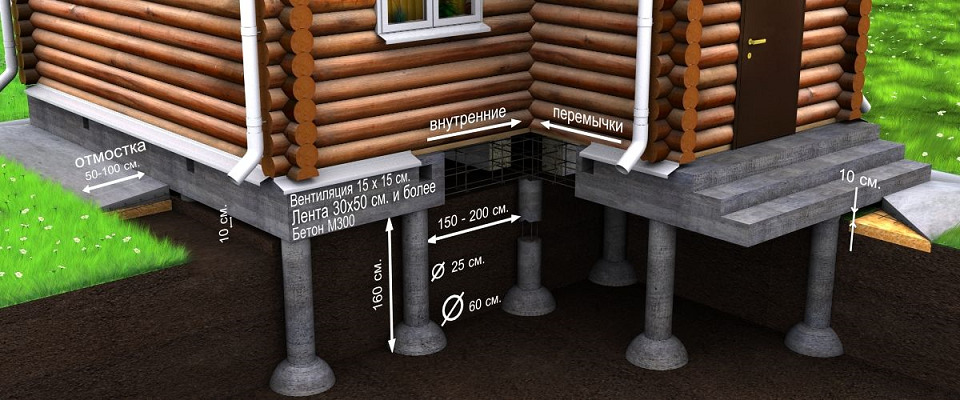
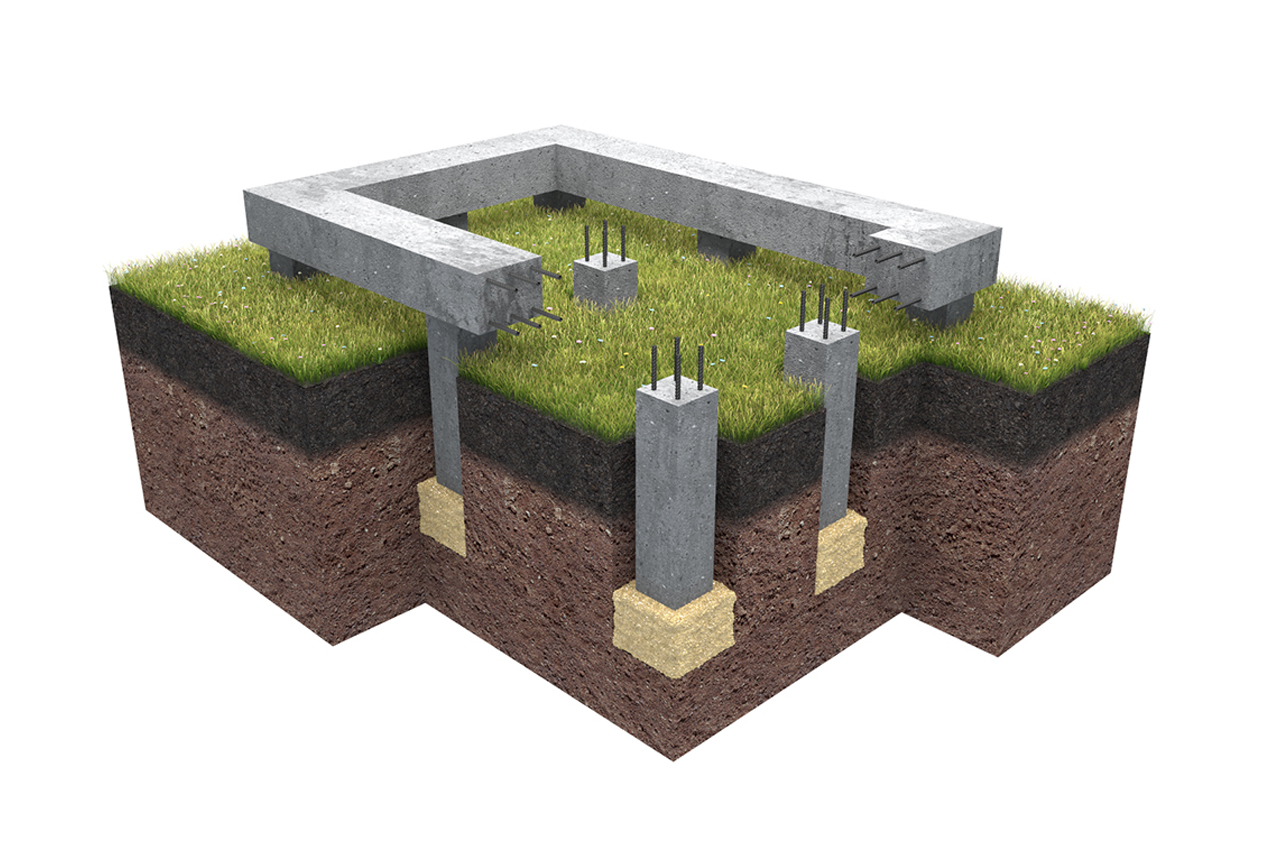
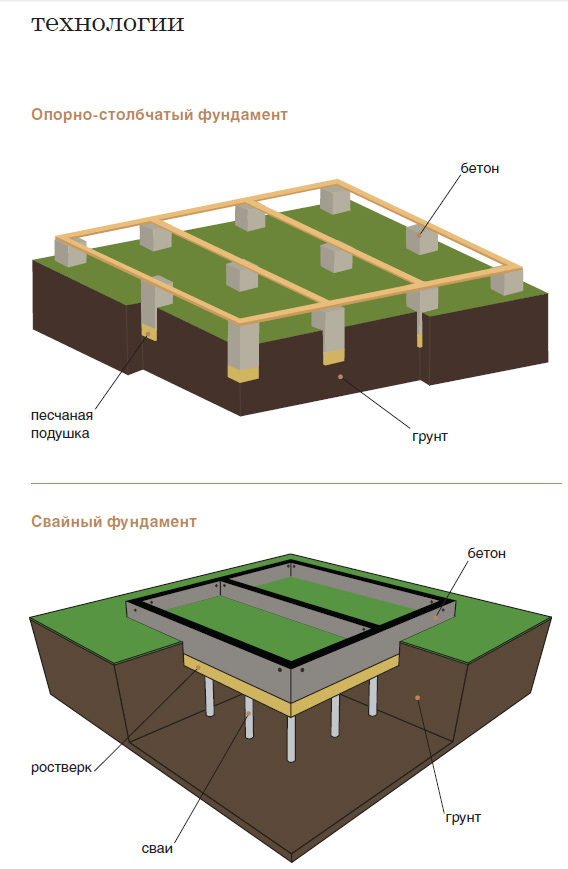
Under heavy walls, a strapping made of monolithic reinforced concrete is brought in, as a rule, resting on pillars of the same material. The strapping and the posts are prepared immediately at the same time in a single formwork. When forming columnar foundations from prefabricated reinforced concrete blocks, the strapping is arranged from reinforced concrete beams (randbeams) resting on pillars.
We recommend watching a video on how to properly mount the strapping in order to avoid the main drawback of the grillage - cracks.
Embedded parts are attached to the heads of the columnar foundations. A channel or building corner is welded to them. As a result, a grillage from a metal profile is obtained, which has high strength and reliability.
Columnar foundation straps are very sensitive to the displacement of each columnar support. As a result of pushing the support up by the frozen soil, and when the pillar falls down, the geometry of the structure of the piping structures may be violated. This can cause cracks to form in the load-bearing walls. This is the main disadvantage of the tie-downs of columnar foundations.
Depth of laying
According to the depth of the foundation, the foundations are divided into two types:
- Shallow;
- Deeply buried.
Shallow columnar foundation
For light small buildings, a shallow columnar foundation is laid. A shallow base is considered to be the pillars laid at a shallow depth (0.5-0.7 m) in the zone of soil freezing.
Shallow foundation design
In order to prevent the supports from being pushed out of the soil under the influence of expanded frozen soils, a number of measures are taken. This is the insulation of the blind area and the enclosing structures of the basement. The lateral surfaces of the foundation are covered with materials that significantly reduce the lateral frictional forces of the soil.
The erection of monolithic reinforced concrete supports, unlike other types of pillars, incurs additional costs for the manufacture and installation of reinforcing cages, preparation and placement of concrete mixture, as well as for the assembly and disassembly of the formwork.
The disadvantage of a shallow foundation is its sensitivity to the effects of heaving of frozen soils. Buildings on such bases require additional costs for insulating the blind area and basement.
The advantages of such foundations undoubtedly include the cost-effectiveness of their construction in comparison with a deep-buried foundation.
Deeply buried columnar foundation
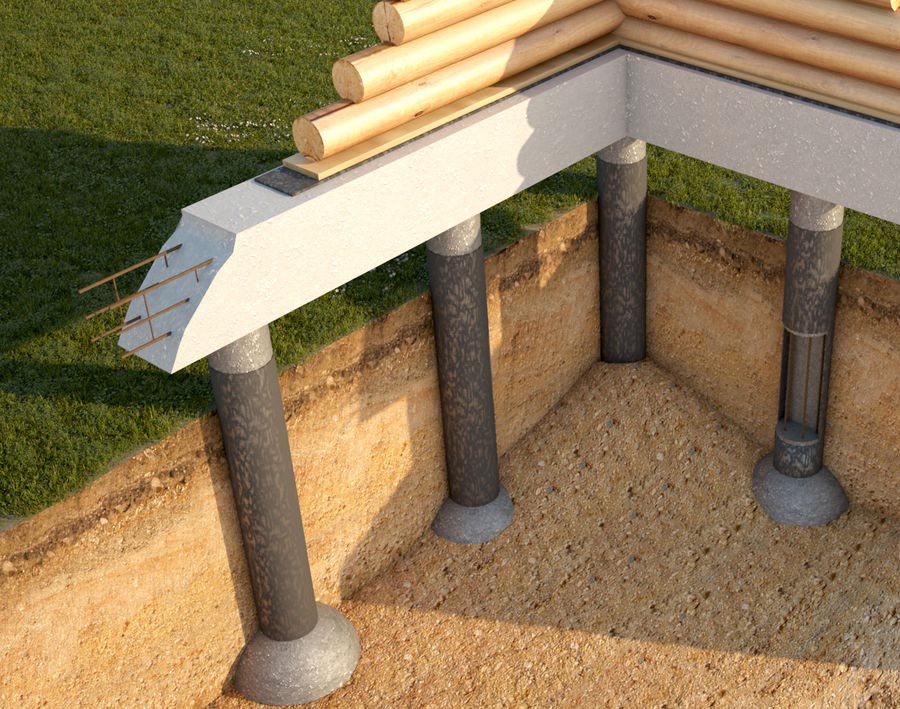
Deep supports are located below the soil freezing zone. For the installation of supports, reinforced concrete pillars, metal and asbestos-cement pipes are used. At the bottom of the pit, a sand cushion or concrete preparation is made. At great depths, the formwork for monolithic pillars is made extended towards the base. The conical shape of the support shaft increases the resistance to being pushed out by swollen soils.
Pillars with a section of 400 x 400 mm
On the basis of some pillars, concrete preparation or masonry is made of stone, brick in the form of ledges, which gives the same effect as the shape of a cone.
The dimensions of the minimum section of the foundation pillars are determined by their material:
- Reinforced concrete - 400 x 400 mm;
- Rubble concrete - 400 x 400 mm;
- Natural stone - 600 x 600 mm;
- Slabs - 400 x 400 mm;
- Brickwork - 380 x 380 mm.
The disadvantages of deep columnar supports include the complexity and laboriousness of performing earthworks for arranging pits for formwork. The advantage of erecting such supports is the saving of material resources and labor costs compared to other types of foundations.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pile and support foundations
Each solution was designed from the ground up to be used in a specific situation.
- Monolithic foundations - when erecting heavy multi-storey buildings;
- Tape bases - an intermediate option when building on moving soils;
- Supporting-columnar bases - for the independent construction of small residential complexes.
In view of this, some of the disadvantages present of the support-column base may be considered insignificant in the construction of target buildings.
The list of disadvantages includes:
- Small carrying capacity. Supporting foundations are not able to withstand heavy multi-storey structures;
- The fragility of the structure. Initially, the support structure was intended for construction in frozen soils. The use in moving soils or self-loosening of the soil reduces the stability of the structure pillars.
- In the future, it is impossible to create a cellar or basement. The distance between the pillars does not allow digging a wide enough room that can serve as an underground extension.
If you build a building taking into account these restrictions, then in return you can use all the advantages to the maximum:
- High speed of creation of the base;
- The ability to make the foundation yourself, without using additional equipment;
- Cost of work. Except for the lack of additional equipment, the cost of materials is half that of the construction of a strip base. The price ratio between columnar and monolithic foundation is 1:10;
- Lack of additional training. When erecting buildings on a supporting base, it is not necessary to carry out additional heat and waterproofing.
- The ability to use for the construction of buildings on frozen soils.
- The service life of the foundation, if properly used, is 80-100 years.
The support-columnar base is easy to repair. And even in case of big problems with the foundation, its restoration will not take much time and resources.
Payment
You still need to start laying the foundation by making calculations. And it is better to act according to the following (albeit very approximate) method:
- To begin with, according to the design documentation, you will need to determine the weight loads from the structures of the future building.
- Further, according to the Russian maps of zoning of climatic loads, it is necessary to find the necessary indicators for snow and wind.
- After that, it is necessary to independently determine the operating loads. They depend on many factors: the number of tenants, as well as guests who will come to the tenants; home equipment with household and other appliances; the residence of pets (and which ones) and the presence of an aquarium; number of plumbing fixtures, etc.
- Then, according to the relevant documents (SNiP 2.02.01-83 "Foundations of buildings and structures", SNiP 2.08.01-85 "Constructions of residential buildings", SNiP II-B.1-62 and other SNiPs), it will be necessary to calculate the total weight of the house. The essence of the operation is to reduce absolutely all loads to the weight imposed on the foundation.
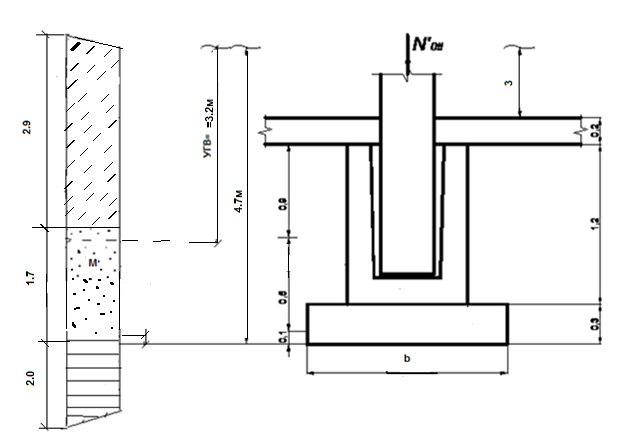
- Then it will be necessary to determine the RPG - the estimated depth of soil freezing at the construction site. Here you need to focus on the maximum value of this parameter on the map for a given area. And it would be better to consult on this issue with specialists - geologists and builders.
- At this stage, you can proceed directly to calculating the size and nature of the pillars' deepening:
- for deepening up to 1 m, it is necessary to take the standard indicators of the bearing capacity of the soil 1.7 kg x sq cm or 17 tf x sq m;
- for deepening more than 1 m, you will have to take other indicators - 2 kg x sq cm and 20 tf x sq m;
- on dense soils (dry loams and clay, gravelly or stony), freezing by more than one and a half meters, the value obtained as a result of the above calculations must be multiplied by a factor of 1.15;
- Further, for the pillar, according to the size of its heel, the support area is calculated. The limiting value for concrete pillars in hand-drilled wells is 0.28 sq. M.
- Then the value of the bearing capacity of the soil must be multiplied by the size of the supporting area. As a result, the load on one pole will become known.
- After that, the total weight of the building must be divided by the bearing capacity of the pillar in order to calculate the number of pillars for a particular foundation.
- From the obtained number of pillars, then it is necessary to subtract the number of corners formed by the load-bearing walls, as well as the number of overlaps of the load-bearing walls.
- The total value of the length of the perimeter of the building and the internal load-bearing walls must be divided by the value obtained as a result of actions in clause 10. As a result, the pitch of the position of the pillars will be obtained (the value should be within 1.5-2.5 m).
- Next, you should calculate the weight of the foundation together with the rundown or with the grillage, depending on the type chosen for the design (if additional structures are generally provided for by the sketch). In this case, you need to proceed from the standard density:
- reinforced concrete (27 tf / m3);
- wood (8.7 tf / cubic meter);
- or brick (4 kg per brick with mortar).
- Then the weight of the foundation will need to be added to the total weight of the building.
- The next stage of calculations is the distribution of pillars. Each corner and crosshairs should be identified by a pillar, and the rest of the pillars should be evenly "placed" across the entire area under the foundation. In the most loaded spans (this is where the stove or, for example, a bathtub will be located), the pillars will have to be combined in two.
At this point, the calculations can be considered complete and proceed to other activities.
Columnar foundation construction
Column foundation made of concrete blocks
Due to the variety of structural materials, poles can be manufactured using several technologies:
- masonry - brick 38 x 38 cm, block 40 x 40 cm, rubble (usually 60 x 60 cm) without reinforcement;
- monolithic - concrete (20 cm side or column diameter), reinforced concrete (30 - 40 cm diameter or side) or rubble concrete.
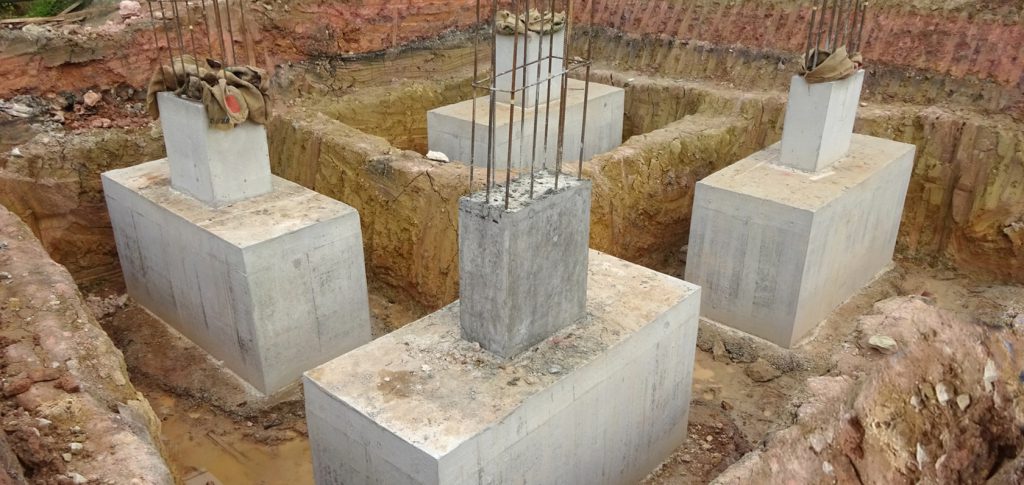
When choosing a concrete structure of pillars, it is necessary to take into account that the upper 0.5 m are made of concrete with the reinforcement of the head of the pillar with a frame of 8 - 14 mm vertical rods bent at right angles for connection with the grillage. For monolithic pillars, panel or tubular formwork is used. In the first case, shields are mounted on the broadening, propped against the walls of the pit. In the second, asbestos-cement or polyethylene pipes of large diameter are put on the reinforcement cage, providing a protective layer of 2 - 4 cm.
Column foundation made of fired clay bricks
Without waterproofing, concrete structures operating in the soil have a resource of 30-50 years (brick, reinforced concrete, respectively). Therefore, it is not recommended to pour concrete into holes drilled in the ground, which is related to the technology of hanging piles.
Reinforced concrete columnar foundation
The only option to reduce the construction budget and labor costs in the manufacture of a columnar foundation using the pile technology in the above way (for example, the TISE option) is to add penetrating additives to the concrete (Admix mixture from the Penetron manufacturer). In this case, the structure of the structural material acquires water-repellent properties throughout the entire depth. However, the insulation of the blind area and drainage at the level of the soles of the pillars are necessary for the underground structure without fail.
Thus, a columnar foundation with a metal grillage is the best option for a log house, half-timbered frame, "frame".When using a low monolithic grillage on reinforced concrete pillars with widening of the sole, a two-story brick cottage with an attic can be supported on it. If necessary, a cellar can be made inside the lattice grillage.
Good publicity
Features of the construction of a columnar foundation
In detail:
- A cut of the fertile (green) soil layer is required for the following reason - moisture is required for the growth of greenery. Plants will actively pull it out of the ground and atmosphere, accumulating it in themselves and in the soil. Moisture under the floor for a house made of timber is detrimental to any construction material, therefore, it is better to exclude the possibility of its formation in advance. The thickness of the cut layer is up to 30 cm.
- On the leveled area, markings are applied under the pits. They are guided by the following calculation: the distance between the pillars of the columnar foundation is equal to 1 m of the length of the wall of the object. For work, use wooden stakes and a string stretched between them.
Installation methods further differ due to differences in foundation types from each other.
Column foundation
Pits are made with the help of a garden drill. They must be wide enough to accommodate posts, masonry or block structures. The depth of the columnar foundation should exceed the level of freezing of the soil + 30 cm for adding sand and gravel - an amortization cushion. A pit more than 1 m deep must be reinforced along the walls so that the soil does not crumble inward. To do this, you can use polystyrene foam plates, which will play the role of insulation.
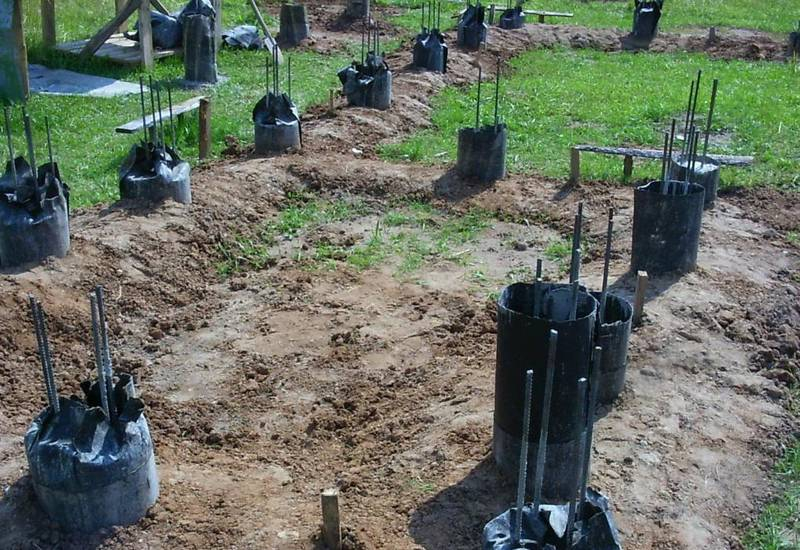
Ready pits for pouring are reinforced with a steel bar - 3-4 pcs. just dig into the ground inside the pit. If a prefabricated columnar foundation with a reinforced concrete grillage is provided, the ends of the reinforcement protrude from the foundation by 25–30 cm. A stud extending from the middle of the column is sufficient to adhere the foundation to the embedded crown - the reinforcement is not visible in this case.
Bricklaying or the installation of ready-made poles is a simple task
It is only important to check the height of the pillars at the building level. Pouring with concrete is carried out slowly, using a vibrator for work, eliminating voids in the thickness of the mortar
If the weather is sultry, then the finished structures are spilled with cold water until white foam (milk) appears on the surface. Foam speaks of complete concrete subsidence.
Installation of a support-column foundation
Differs in the design of a concrete "shoe" - a support for brickwork or a monolithic pillar. Procedure:
- After removing the top layer of soil, it is required to prepare a pit. The depth of the columnar foundation is different, there are: not buried, buried and slightly buried options. The average value - from 0.7 to 1 m - is typical for the climate of central Russia.
- On a leveled and tamped surface, areas are marked for the installation of "shoes". It can be one brick masonry, monolithic pouring 10-15 cm thick or ready-made concrete slabs - see the photo above.
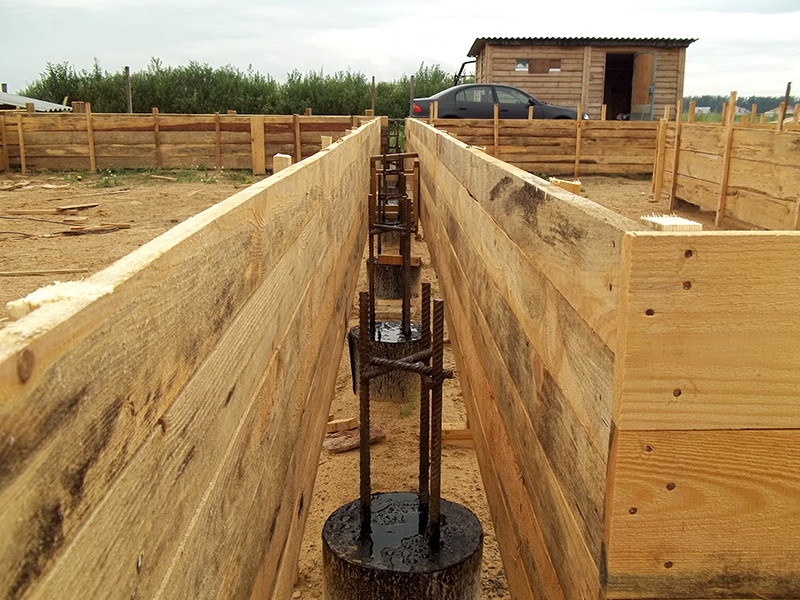
- After installing the stands, the pillars are assembled or poured. In the latter case, formwork from boards is built and reinforced. Work is carried out in calm weather - concrete is less enriched with air, as a result, there are fewer voids. It is impossible to remove the formwork before the end of the curing of the concrete.
When the pillars are ready, they are waterproofed. The pit is covered with layers of sand and gravel 15 cm thick. The remaining space is covered with excavated soil. The ends of the pillars protrude from the ground by at least 30 cm.
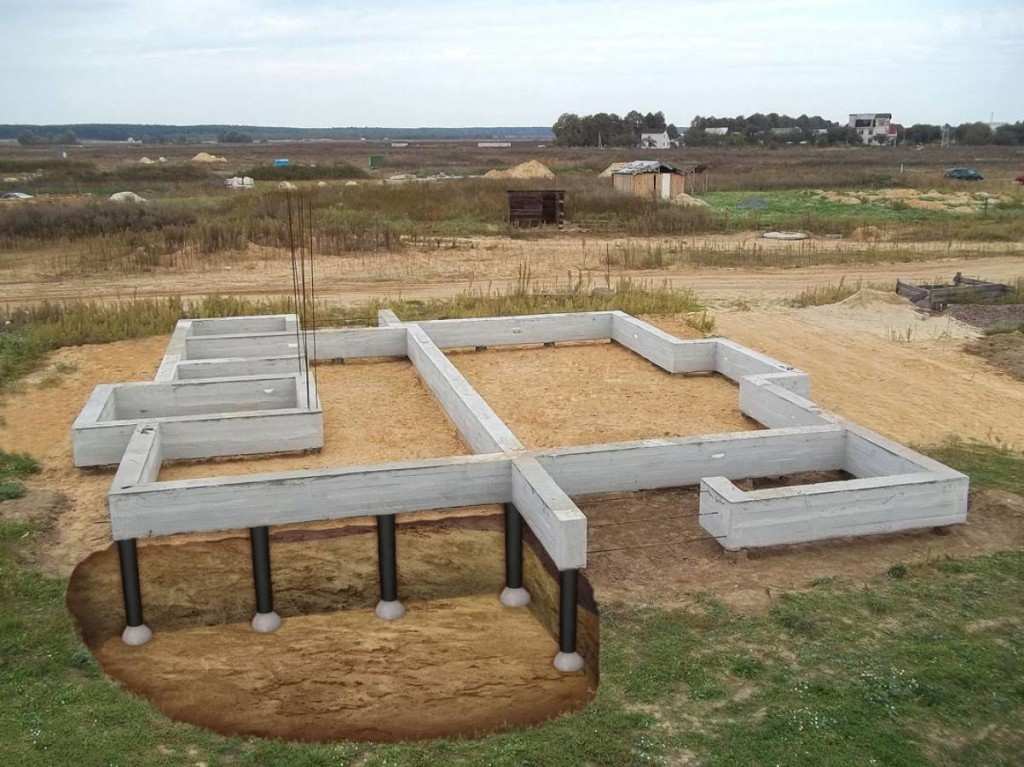
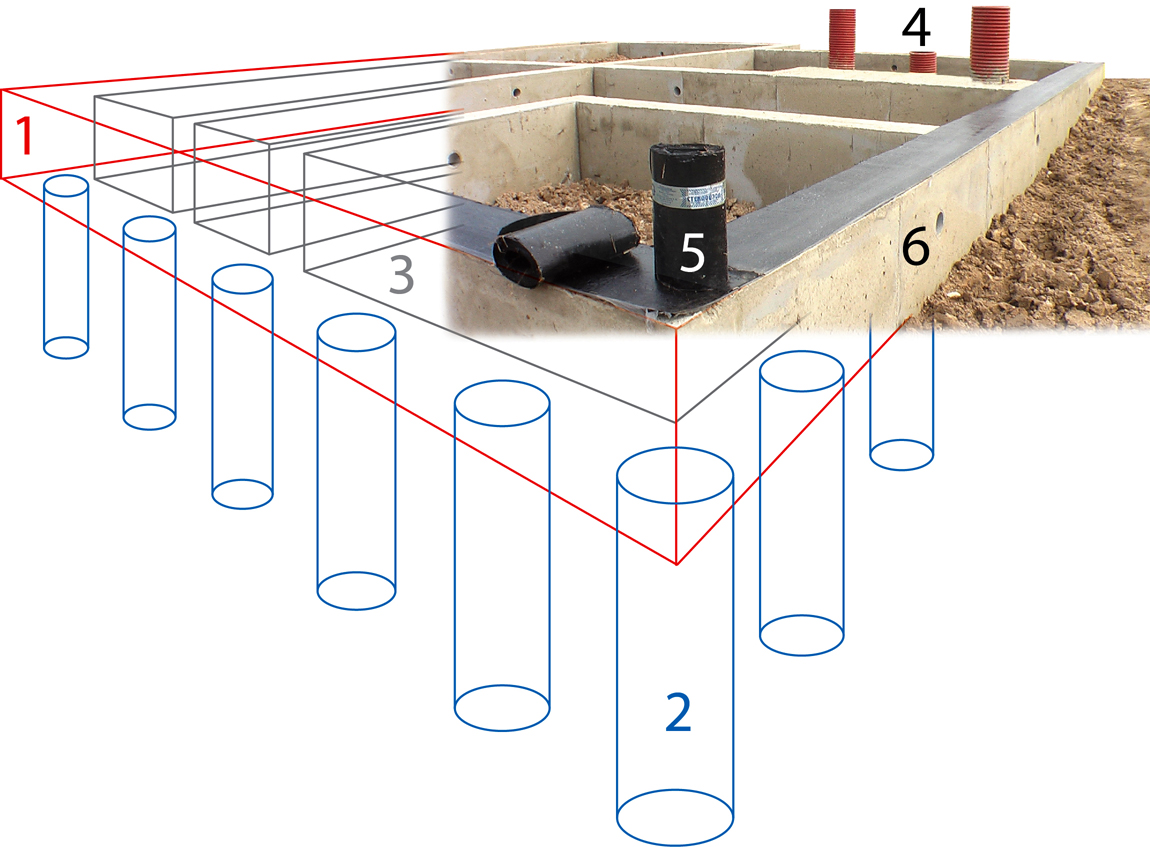
The device of a columnar foundation with a grillage
This columnar foundation resembles a monolithic tape. The work is carried out in two stages:
The device of a columnar foundation with a grillage
- First, holes are dug under the pillars. The dimensions of the columnar foundation and the installation description are similar to the arrangement of a simple columnar foundation.
- Then a wooden formwork is made for pouring a concrete grillage.It is pre-reinforced with a large amount of special wire. You cannot weld the rods together. High temperatures will affect the strength of the knots. Therefore, the reinforcement is knitted by hand. For the correct choice of a rod and a knitting pattern, it is recommended to refer to GOST standards or special literature.
- Pouring is carried out slowly using a vibratory rammer. You can also use a rebar, piercing the concrete and expelling air, but the quality of the automatic assistance is better.
Installation work
The process begins with the installation of markings on the territory
The process begins with the installation of markings on the territory. This is a fairly responsible process, which must have correct calculations and accurate markings. The main rule for laying is vertical design, taking into account the straight line of the pillars. To achieve maximum results, you should use ropes and sand, which outline the lines of the structure. It is also worth considering the distance from one pipe to another, which should be about 2 meters.
Next, drilling of wells for pipes begins. If finances allow you to hire a drill. Then use the service, but if this is not possible, then you can do them yourself. The size of the hole width should exceed the pipe diameter by 10 cm. It should be noted that the length depends on the type of base. When building a bath, the pipe is installed directly into the hole, and if it is a more complex structure, then a pillow should be made under it. All these nuances must be taken into account before creating wells.
Formation of the foundation
Form a pile foundation on asbestos-cement pipes according to the following algorithm:
- Drill, using a garden drill or special equipment, holes that exceed the pile length by 0.2 m and the diameter by 0.1 m.
- Expand the bottom of the canal using a manual or automated device.
- Fill the cavity with sand, forming a pillow with a thickness of 0.2–0.3 m, spill with water.
- Cover the top of the channel with plastic wrap or roofing felt to provide waterproofing.
- Lower hollow piles into the prepared well, fix them around the perimeter with reinforcement or wooden planks.
- Pour sand around the protruding part of the support to keep the column in place.
- Assemble the reinforcement cage using 4 solid steel bars 1–1.2 cm in diameter and securing them with reinforcement bars.
- Place the assembled reinforcement in the asbestos-cement channel, and keep it stationary when pouring with spacers.
- Install, if necessary, together with the reinforcement anchor rods to fix the elements of the lower trim.
-
Prepare the concrete mortar by mixing cement, sand and gravel in a 1: 2: 2 ratio, add water to ensure the required consistency.
- Fill the internal cavities of the piles with pre-prepared concrete.
- Make sure the concrete is able to achieve operational strength within four weeks.
- Check the horizontal position of the upper parts of the support columns by preliminary marking with a building level.
- Waterproof the protruding part of the support with roofing felt, cover with sand and tamp.
- Make a strapping of reinforced concrete or beams, guided by the recommendations of the project of the building to be erected.
When performing work, pay attention to the following points:
- control of the verticality of the wells during drilling is provided with the help of a level that allows you to determine the correct location of the tool after plunging several revolutions;
- roofing material, rolled up during work along the perimeter of the upper part of the canal, will help prevent soil shedding into the well;
- on soil containing inclusions of fine gravel, there is no need to equip a pillow;
- processing before immersion of its underground part with bitumen mastic will provide reliable waterproofing of the supports;
- You can remove air bubbles from a concrete support using a vibrator for concrete or a metal bar.
After completing the construction of the pile foundation, begin to erect the walls of the building.
Pillar base variations
What will be the columnar foundation, they decide, relying on the amount of finance and the ability to independently engage in construction.
Block supports
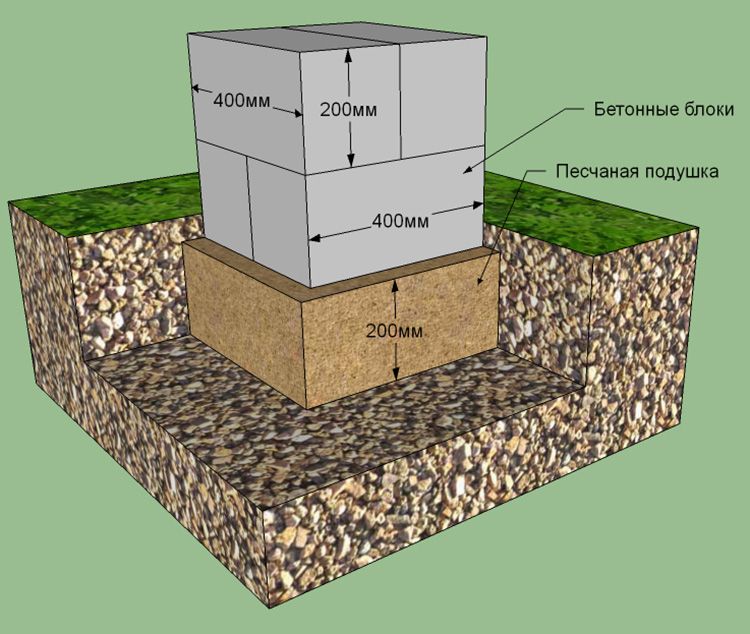
The columnar foundation can be made of concrete or reinforced concrete blocks, made separately and mounted directly when arranging the supporting structure for the building.
Each pillar of the structure can be assembled from separate blocks - a very reliable material
The GOST indicates that the blocks that will be used for the construction of the foundation must be made of concrete of a grade not lower than M-100. As for the size of the blocks, private developers are used to taking raw materials with parameters 20 * 20 * 40 cm and weighing 32 kg. Foundation blocks made of expanded clay concrete, a material that is resistant to thermal effects, are considered relatively light.
Most often, light small blocks are taken for the independent construction of a columnar foundation, since it will be possible to build supports from large raw materials only with the use of technology
The best depth for anchoring a pillar of blocks in the ground is from 50 cm to 1 meter. If the type of soil and the weight of the building dictate different requirements, then it is wiser to build not a block foundation, but a base of asbestos-cement pipes filled with concrete. It is too difficult to lay blocks deeper than 1 meter.
Brick pillars
Having thought of building a pillar foundation made of bricks, it is necessary to purchase only red solid ceramic building materials. This material meets all the necessary requirements: it is waterproof, extremely durable and frost-resistant.
For the construction of the foundation, it is customary to use a red solid ceramic brick, because it is the most durable
Bricks can be used to construct both shallow and buried columnar foundations. The depth of the first version of the base varies between 40 and 70 cm. And the buried foundation is always installed below the freezing level of the soil by 30-50 cm.
To make the foundation reliable, brick supports of a columnar foundation must be created in 2 bricks
The main pillars of the foundation (supports standing in the corners of the external walls and at the intersection of internal partitions) are usually made in 2 or 2.5 bricks. In other cases, the pillars are allowed to be made in one and a half bricks and placed at a distance of one and a half or two meters from each other.
"Legs" made of wood
A base made of wooden "legs" is the most economical option. Logs suitable for the foundation are easy to cut and process on their own.
Wooden pillars are intended only for the lightest temporary structures, as they can break under excessive pressure
The best raw materials for creating wooden poles are pine, oak or larch wood. "Rods" are cut from the butt of a log with a diameter of 2 to 40 cm. When they are placed in the pits, the pillars of wood are fixed on the sides with bricks, stones or compacted rubble.
Sometimes wooden supports are fixed in place with concrete mortar. In this case, the pillars are immersed in liquid concrete by 10 cm. Another good fixer for wood supports can be a cross made of two plates 0.8 meters long, arranged in a crosswise position.
To securely fix the pillar in the ground, use a crosspiece and jibs
Wooden supports are supposed to be protected from rotting in a special way. First, they are covered with clay so that a layer 1 cm thick is formed, then they are fired with hot coals. The last task is performed slowly, making sure that literally 1.5 cm of wood is charred. The fired pillars are treated with heated bitumen or tar and dried.
Under the outer walls, wooden supports are immersed in the ground to a depth of 70 to 120 cm.And the pillars to support the partitions inside the house are placed at a depth of 50 cm.
The main pillars of the wooden foundation are supposed to be immersed to a depth of 70-120 cm
Monolith
Buildings with 2 or 3 floors are preferable to build on a columnar monolithic foundation. Such a foundation will not subside even under significant pressure.
A monolithic foundation is considered the most popular structure compared to other columnar foundations.
The monolithic base of pillars is made of concrete, reinforced with metal rods and poured into special forms - pipes or formwork. This foundation turns out to be unusually durable, since it is completely devoid of seams.
Shallow base
This is the most popular type of columnar foundation, since a minimum of money and effort is spent on its construction.
This is the most popular type of columnar foundation, since a minimum of money and effort is spent on its construction, and the scope of use is quite wide. Such structures are suitable as a basis for a wooden bathhouse and a frame house.
Usually the pillar is made of pipes, inside which the frame is installed and concrete is poured. Since the main load is taken up by the concrete filling, the material of the pipe does not matter much. It acts more as a permanent formwork. Usually plastic or asbestos sewer pipes are used.
The choice of pipe diameter depends on the purpose of the building. For light arbors, a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm is sufficient, and for log buildings, a pipe with a cross section of 250-300 mm is suitable. The volume of concrete is calculated taking into account that for every 10 m of a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm, 0.1 cubic meter of concrete is required, and for a product with a diameter of 200 mm, 0.5 cubic meters are consumed, for a pipe with a cross section of 300 mm, 1 cubic meter of concrete solution is required.
The order of work is as follows:
- After preparing the site and performing the breakdown, using a hand drill, holes are made in the ground to install the poles. It should be remembered that the depth of the pit should be 200 mm more than the length of the post for making a sand cushion.
- After completing the pit, sand is poured onto the bottom, poured with water and rammed. To protect the concrete mixture from moisture loss, layers of roofing material are laid on top of the sand cushion.
- Further, pipe sections are lowered into the pits, which should have a 10-centimeter headroom. The pipes are leveled and fixed in the well with wooden blocks.
- After that, a little concrete-gravel mixture is poured into the pipe. Immediately after this, the pipe is lifted and fixed in this position until the mixture completely solidifies at the bottom of the pit. Thus, we will get a solid foundation that will well resist the forces of heaving of the soil.
- When the concrete hardens, the pipe is wrapped with roofing felt to perform waterproofing.
- The well is backfilled with sand with layer-by-layer water pouring and ramming. During these works, the position of the pipe must be checked using a level.
- Then reinforcement is installed inside the pipe and concrete is poured.
- Further work can be done in 28 days. At the same time, the foundation is isolated from the main part of the structure using a bituminous or polymer solution.