Block features
The prefabricated strip foundation from FBS blocks for the house has a number of features. Before starting construction, it is necessary to take into account all the advantages and disadvantages of the material and select the most durable type of blocks.
Why block base?
Such a foundation can be erected in 5-6 days; it takes several months to lay a pile or monolithic foundation. The walls are erected immediately after the plinth is laid: FBS blocks do not gain strength, unlike monolithic slabs. Additional details are not used during the construction process, formwork installation and reinforcement are optional. The block foundation is laid independently, the help of experienced builders is not required.
What are FBS blocks
The base of the plinth is made up of building foundation blocks. These are concrete structures made using a special technology. The material used in the process is durable reinforced concrete. Foundation blocks evenly distribute the load over the entire area. Before starting construction work, you need to calculate the approximate size of the building being erected.
Standard characteristics for foundation blocks:
- height - no more than 58 cm;
- width - 60, 50, 40 and 30 cm;
- length - 238, 118 and 78 cm.
In the lateral parts of the blocks, special holes are made at the plant, which are poured with cement during construction.
Positive sides
FBS blocks used in the construction of the foundation have a number of advantages in comparison with other materials.
These include:
- soundproofing;
- thermal conductivity;
- lack of negative impact of external factors;
- ease of installation;
- wide range of;
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- long service life;
- high strength and reliability;
- low cost (in comparison with other materials).
Construction work is carried out regardless of the type of soil. Buildings can be erected in earthquake-prone regions.
Cons of blocks
The FBS strip foundation has a number of disadvantages
Stacking resembles the assembly of a constructor, so it is important to pay attention to linking the blocks to each other. Monolithic masonry forms a flat surface, so the structure does not require additional reinforcement, unlike a block foundation
If the base is laid out from large blocks, then special equipment may be needed.
Base types
Before starting construction, you need to decide on the type of foundation.
There are several main types:
- Pile. Suitable for the construction of structures (baths, garages) on soils with a high level of acidity and groundwater (deep bedding).
- Linear. One- or two-story residential buildings are built on a linear foundation.
Fundamental building blocks (by design) are:
- Empty. Low-strength material used for the construction of fences. Low weight provides a void inside the block.
- Monolithic. Reinforced concrete structure is provided with grooves, it is used for the installation of communication systems.
- Solid. The blocks are connected to each other in advance, forming a square. To increase strength, the structure is additionally reinforced.
A selection of blocks by size allows you to calculate in advance the parameters of the structure being erected and make an estimate.
How to choose block sizes
When buying FBS, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Manufacturer. The quality of the material directly depends on the manufacturer. You need to purchase FBS made at the factory. Plates made by handicraft have lower compression grades.Before buying, you need to study reviews about a particular material.
- Accuracy of geometry. FBS with precise geometry is faster and easier to install. Much depends on the technology of making the plates. If concrete is poured into special forms, then the block turns out to be even. When using the technology of immediate stripping, the slabs will have a trapezoidal section. They provide a large support area, so this type of material is used in the construction of buildings in earthquake-prone areas.
- Places of communication. They are determined in advance. In order not to drill holes in solid slabs, you need to purchase special FBS.
For the construction of residential buildings, it is preferable to use slabs with a length of 238 cm. The use of such FBS will reduce the number of vertically located joints.
Device and types
In depth, strip foundations are shallow and deep. Shallow ones can be used on calm, non-powdery soils with good bearing capacity for buildings with a small mass - made of wood and erected using frame technology.
In this case, the tape should go 10-15 cm into a solid layer, which is located under the fertile one. At the same time, according to the standards, it cannot be less than 60 cm.
Types of strip foundations by depth
Deep-laid monolithic strip foundations are made for heavy, massive houses. In the general case, they are lowered 10-15 cm below the level of soil freezing for a given region. In this case, the sole must be supported by a layer with good load-bearing capacity. If this is not the case, you have to go deeper below. For example, if the level of freezing of soils is 1.2 m, and the fertile layer ends at 1.4 m, then you have to drop below 1.4 m.
With or without formwork
In general, the technology for erecting a monolithic strip foundation provides for the installation of formwork. These are panel structures that shape the concrete and prevent it from spreading. It is clear that the formwork is an additional cost for materials, as well as additional time for its assembly and installation.

Formwork - a structure made of boards or plywood, which gives the foundation a shape
Sometimes, in order to save money, on good soils, a foundation pit is dug exactly along the markings - to the required width and depth. And concrete is poured into these pits without formwork. Such technology cannot guarantee the required degree of reliability; the result cannot be predicted. The fact is that concrete needs a certain amount of water to gain normal strength. Without formwork, water, although a little, is absorbed into the soil, which can affect the quality of the concrete stone itself. In the worst case, it can crumble.
They get out of the situation by spreading plastic wrap in the trench. But then they walk on it - you need to do the reinforcement. Both rods and boots damage the film more than once. As a result, moisture still goes away.

A foundation without formwork is a risky undertaking
In some cases, such foundations can be defended for a number of years without problems. But sooner or later, cracks appear or concrete begins to crumble. The second difficulty in working with such a foundation is its far from ideal geometry. In order to reduce heat loss, the foundation is insulated, most often with foam plates or extruded polystyrene foam. Try sticking them on an uneven surface. The same situation with vapor barrier: it is very difficult (almost impossible) to stick the film on uneven, porous concrete with interspersed soil. Whether this approach is justified or not is up to you, but such a foundation can only be recommended for a fence or a shed.
Determination of the load of the structure on the foundation
The load of the structure on the foundation is the total weight of the following components:
- The building's constituent parts are slabs, load-bearing walls, roofing elements, insulating and finishing materials.
- Operational components include communication systems, ventilation, heating mains, pipelines and items located inside the building.
- Base strip weight.
- In case of snowfall, the weight of the snow cover that will lie on the roof is taken into account.
Having calculated the total weight, the area of the strip base is determined. If the calculated load exceeds the permissible value of the resistance of this type of soil, then the area of the lower plane of the foundation must be increased.
Belt device design
 The design of the strip foundation can be different
The design of the strip foundation can be different
Often you have heard or read the title of a video with such a concept as a monolithic or prefabricated structure. What it is now we will try to describe to you. These are such types of strip foundations, based on the structure of the device. So, monolithic schemes are a single element that is erected on the site of a construction site. The prefabricated one is made at the factory, and at the site it is assembled and assembled with the help of technology. Let us now discuss in detail the types of devices for these foundations.
The device and features of a monolithic base
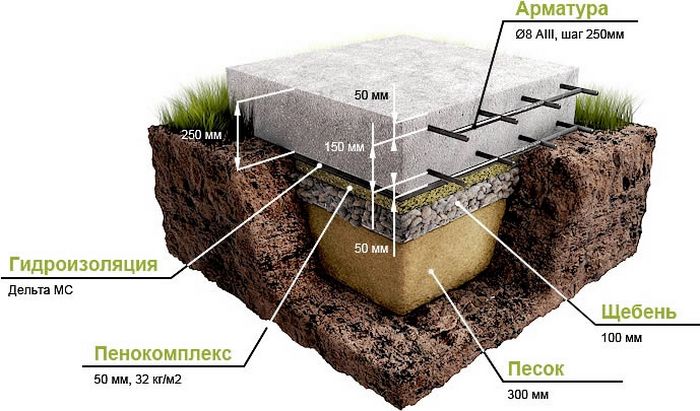 To erect a device from a monolith, it is necessary to use a concrete solution and reinforcement
To erect a device from a monolith, it is necessary to use a concrete solution and reinforcement
To erect a device from a monolith, it is necessary to use a concrete solution and reinforcement. A mandatory requirement for construction is the presence of formwork and a foundation pit, which is the basis for the installation of this fixed structure.
To obtain a durable monolith, it is poured with a concrete mixture and compacted well. The following qualities distinguish them from all other types of bases:
- Durability;
- Stability throughout the entire operational period;
- Perfect compatibility with all types of buildings.
Such foundations are a continuous strip of reinforced concrete, which is located along the entire perimeter of the structure. Their ability lies in optimal erection on unstable soil. However, this construction technology is only appropriate for the construction of small wooden buildings. It is also worth highlighting their disadvantages:
- Large weight;
- Influence of base shrinkage on calculations.
Prefabricated structures and other types
 The technology for erecting a prefabricated foundation provides for the presence of reinforced concrete or reinforced concrete blocks
The technology for erecting a prefabricated foundation provides for the presence of reinforced concrete or reinforced concrete blocks
The technology for erecting a prefabricated foundation provides for the presence of reinforced concrete or reinforced concrete blocks, which are fixed with wire or a special solution. By giving preference to this type of foundation, you will save time, but spend more money.
The scope of these structures is low-rise buildings. The constituent bases are manufactured on site. With minimal pressure, you don't need to lay the sand cushion. Since the structure has a higher strength, its walls may be smaller than those of the building itself.
Their advantages over the rest should be highlighted:
- Ease of assembly of the structure;
- A little waste of time on work
- The ability to load them at the end of construction.
There is also such a list of shortcomings in relation to these species:
- Massiveness;
- Low level of practicality;
- Due to the numerous joints, liquid may leak;
- High price;
- The need for equipment during construction;
- Strength index is 25% lower than that of a monolithic base;
- Low rigidity;
- Impossibility of reinforcement reinforcement.
It is possible to reduce the financial costs of such construction if the technology of intermittent foundations is used, when the blocks are laid with a running start. This method will save you up to 25% of the estimated costs.
To date, video amateurs also demonstrate such types of strip foundations such as brick and rubble. Based on their recommendations, we can draw a conclusion on the structure of the base.So a brick foundation takes a lot of physical effort, but in terms of strength it loses to both types, which are described above. Rubble, however, is very durable and has a high resistance to moisture, but it is very expensive. And the device takes a long time due to the selection of stones. Therefore, we recommend that you use either a composite or a monolithic foundation.
Monolithic foundation technology
The technology of reinforcing the angle of abutment of the strip foundation.
tape consists of the following main stages.
It provides for the clearing of plots for the construction site, the supply of building materials. A breakdown of the house is carried out, in which the location of the main components of the structure is fixed with pegs and lacing. If the area is flat, measurements are simple. If the terrain on the site is difficult, then it would be wise to use the rail and level. A mandatory check of the angles is necessary, since they must be 90 °. Next, the marks of the bottom of the trench are checked using a theodolite. The perimeter of the construction site must be made 3-4 m wider than the size of the building.
Digging a trench
The trench is dug with an excavator or manually. Then the bottom of the trench must be cleaned and leveled. Then the pit is fenced off. After that, a sand and gravel pillow of 12-20 cm is laid at the bottom of the trench. A plastic film is laid on the pillow so that the water that comes out of the concrete does not flow into the ground.
Formwork device
The installation of the formwork for is carried out from a planed board, the thickness of which should be 4-5 cm. After it is cleaned of debris and abundantly wetted with water. A prerequisite is the rigidity of fixing with spacers to the walls of the trench in order to avoid bulging of the walls. The formwork is then raised 300 mm above ground level. After pouring the monolith, the upper part of the foundation is covered with a waterproofing ball to protect the walls of the building from moisture penetration into them.
Installation of fittings
During the installation of the formwork, the reinforcement previously assembled into frames is laid along the entire perimeter. The frame consists of two rows of vertical reinforcement, fastened with horizontal reinforcement, the amount will depend on the depth of the foundation. should be from 10 to 25 cm.
Placement of concrete in the formwork
The concrete mixture is laid in stages, with balls of 20 cm. To eliminate voids in the mass of concrete, each ball must be rammed using a wood rammer. The best and most reliable way to do this is to use a concrete vibrator.
Waterproofing ball device
After 10 days after placing the concrete mix, the formwork can be dismantled. To ensure waterproofing, bituminous mastic is used, which is applied to the outer walls and a waterproofing film is glued. To ensure more reliable moisture resistance of the structure, the soils adjacent to the foundation are treated with binding polymer mixtures.
Backfill
After installing the waterproofing, backfilling is carried out. It is performed using sand in a layer-by-layer method. These operations are carried out manually so as not to damage the waterproofing. This phase ends.
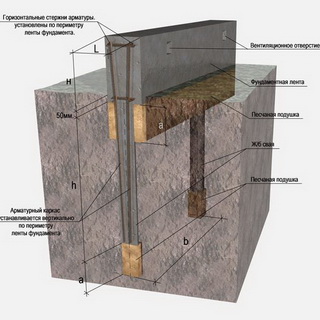
Work technology
 Prefabricated foundation device diagram
Prefabricated foundation device diagram
The technological process of assembling a prefabricated strip foundation consists in the phased implementation of all stages of construction, from marking and ending with the care of the finished strip foundation structure.
Preparatory stage
At the initial stage of the foundation arrangement, it is necessary to prepare the construction site: to clear the area and carry out the necessary markings according to the executive working scheme of the foundations. With the help of a rope and pegs, the linear dimensions of the foundations are fixed directly to the ground
Pay attention to the correct marking angles.A control check for the correct layout is a check of the diagonals of the linear configuration of the foundation: all diagonals of rectangular sections must have the same value
Excavation
Excavation work consists in preparing a trench for laying prefabricated elements. For a large volume of excavation, it is best to use construction earthmoving equipment - an excavator.
 FBS blocks stacking scheme
FBS blocks stacking scheme
With small volumes of land and a shallow foundation depth, you can prepare a trench yourself with your own hands. The working width of the trench is slightly larger than the calculated width of the foundation blocks. This distinction is necessary for the convenience of performing installation and waterproofing works. The bottom of the trench is cleaned and leveled to the building level.
Preparation of the base
On the prepared cleaned bottom, it is necessary to lay a sand preparation with a thickness of 50 - 100 mm. The filled-in sand is leveled and compacted with manual or electro-vibration rammers. After that, the sand cushion is spilled with water. A waterproofing layer made of rolled roofing material is laid on the finished sandy floor. The waterproofing is filled with a cement-sand mortar, after drying, the base is considered ready for installation of foundation blocks.
Assembly of prefabricated elements
For the correct laying of prefabricated blocks, it is necessary to transfer the center lines of the diagram or drawing of the building to the edge and bottom of the trench. Beacons are placed along these lines, along which corner foundation elements will be laid.
 Laying of foundation elements
Laying of foundation elements
With the help of lifting construction equipment, prefabricated foundation elements are laid on the concrete mixture and the horizontalness is checked by the building level. The grooves of the blocks are filled with cement mortar.
The final stage of the foundation assembly
After finishing the laying of the foundation blocks, it is recommended to carefully fill the joints between the blocks with cement mortar, and after they have completely dried, it is necessary to perform a protective coating or adhesive waterproofing of the side surface of the strip foundation. Such an insulating coating will reliably protect the foundation structure from capillary and atmospheric moisture. Correctly executed waterproofing creates a comfortable microclimate for living in the house.
Video example of stacking FBS blocks:
For the laying of utilities, it is necessary to provide for the mounting holes in the foundation strip in advance. The device of such holes will allow you to easily lay all the necessary pipelines and cable products into the basement of the foundation for further wiring throughout the house.
House foundation device: basic requirements and foundation depth
What are the basic requirements for the foundation of a house when constructing buildings?
The foundations of buildings must meet the following basic requirements: have sufficient strength, stability and frost resistance, withstand well the influence of groundwater, match the service life of the building in terms of durability and, of course
Another important requirement for the foundation of the house is its efficiency. The cost of building a foundation is about 10% of the cost of building an entire house
Labor intensity reaches 15%. The mass of the foundation is up to 20% of the total mass of the structure.
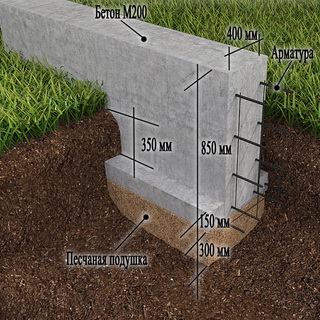
What is the structure of the foundation for the foundation and how to prepare it?

Before proceeding with the development of trenches for the foundation, it is necessary to perform the following work: draw up a project of the house, including an estimate and the procedure for the production of work; mark the site for construction; determine the type of soil, the level of groundwater and the depth of freezing. If necessary, drain the area, compact the soil, drain melt and rainwater. Immediately before the start of construction, the contours of the foundation are marked with twine.Trenches are torn off immediately before the start of the foundation construction, so that the earth does not crumble while drying out, and precipitation does not flood them with water. If necessary, the walls of the trenches are reinforced with formwork and temporary spacers are installed. After marking, they begin excavation work. The profile of the trenches depends on their depth and the soil in which they break off. If the depth of the trenches does not exceed 1 m, their walls can be made vertical.
What should be the depth of the foundation of a building under construction?

The depth of the foundation of the house depends on the type of soil, the level of groundwater, the depth of freezing. For example, for dry soils, the depth of laying should be at least 0.5 m, and for wet fine sandy and clayey soils - not less than the freezing depth. As a rule, it is recommended to lay foundations below the freezing depth. It is much more difficult to erect foundations in heaving soils, especially when they are deeply frozen. In all cases, for the construction of such foundations, it is necessary to use water and frost-resistant materials, including high-strength concrete. In gravelly, large and medium-sized sands, as well as in coarse-grained soils, the depth of the foundation does not depend on the depth of freezing. But still, it should be at least 0.5 m from the planning mark.
Does the reliability and stability of the foundation depend on the depth of its foundation?


Indeed, the vertical forces of frost heaving cease to act on the base of the foundation laid below the freezing depth. But the tangential forces of frost heaving acting on the side surfaces can pull out and tear off the foundation along with the frozen soil. This is especially dangerous in cases where the foundation is made of bricks or small blocks and a light structure is installed on it.
How are communications laid across the foundation?


If you are going to leave communication holes in the foundation, temporary plugs must be installed in the formwork, which are removed after the concrete has hardened. According to the technology of the foundation, after laying the pipes, the gap in the holes around them should be sealed with tow and coated with clay mixed with broken glass (against rodents). In some cases, communications are laid even before the construction of the foundation.
Varieties
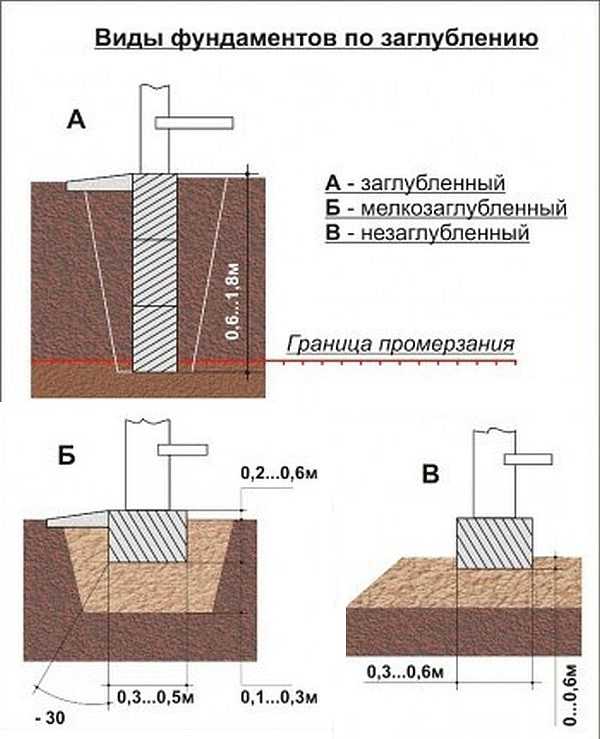
The strip foundation is referred to as monolithic structures. There are three types of it: not buried, shallow and buried.
A shallow strip foundation (Fig. A) is arranged in non-porous and slightly heaving soils with low shrinkage and horizontal movement: that is, on rocky, clastic, stony, gravelly, medium and coarse-grained soils. They also include clay soils without impurities or with a different content of sand and stones, which are not affected by moisture in a year-round mode and are constantly in a dry state. Usually, an unburied strip foundation is laid for light buildings or one-story houses made of stone, concrete and bricks with a low roof. It is not recommended to erect tall buildings on such a foundation in order to avoid their collapse or overturning.
A shallow strip foundation (Fig. B) is used in the construction of small stone, frame, panel board and wooden houses on non-porous and slightly porous soils with a foundation to a depth of 0.2–0.7 m. a layer of freezing soil in order to make the base heavier. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to erect superstructures in the form of an additional floor or an attic from light building materials.
The deepened strip foundation (Fig. C) is used for the construction of all types of buildings on non-heaving, slightly heaving and heaving soils, including houses with several floors, thick walls, heavy floors, a basement or basements.Such a foundation is laid below the freezing depth by 0.15–0.2 m and is classified as material intensive.
Varieties of strip foundations:
- a - not deepened;
- b - shallow;
- in - buried,
- where 1 - soil; 2 - blind area; 3 - foundation.
It is more expedient to carry out work on the construction of the foundation in late spring or early summer, when the earth has dried up. During this period, the soil is still quite loose and excavation is much easier than in other seasons. Based on the desire to save money, many developers try to do most of the work on their own, including earthwork.
Depending on the characteristics of the soil and the level of deepening of the strip foundation, preliminary work is performed: for non-deepened - a building spot is prepared; for shallow ones - they dig trenches around the perimeter of the house; for buried ones - trenches or foundation pits. If necessary, sand bedding, heat and waterproofing are placed on the bottom. In the future, the following types of work are performed:
- installation of a reinforcing cage (reinforcement);
- markup;
- assembly of formwork;
- pouring the foundation;
- stripping;
- waterproofing device;
- backfilling of the sinuses of the trenches.
Markup
It is advisable to install the formwork after the completion of all work on the reinforcement of the foundation and on the laying of connecting elements with future walls. This will facilitate the observance of the required depths of the reinforcement into the monolith and the connection of the ends of the reinforcement to each other.
Before the start of the formwork, markings are made according to the external dimensions of the foundation, its thickness at each location, including partitions, and height above ground level so that in the future it is possible to assemble an accurate, durable and reliable form for pouring concrete mixture. In this case, the deviation of the vertical should not exceed 5 mm per 1 m of height, the displacement of the axes of the formwork - 10 mm, the horizontal - 3 mm. The markings for all types of strip foundations are made in the same way.
To mark the outer dimensions of the foundation, first, two pegs are driven in along the line of one of the sides with an indent of 50–70 cm from the walls perpendicular to it (Fig. A). A string is pulled along them (Fig. B) and tied at the appropriate foundation height above ground level, adjusting the horizontal with the help of a hydro level (Fig. C). The same operation is performed on the opposite side of the foundation, defining the horizontal line along the first two pegs (Fig. D). At the end of this stage, mark the remaining perpendicular sides (Fig. E). In a similar way, the internal marking is carried out along the width of the external and internal walls (Fig. E).
The sequence of marking for the installation of formwork:
- a - fixing the first pegs;
- b - the tension of the twine along them;
- c - determination of the horizontal of the future foundation;
- d - tension of the twine for the opposite side in a similar way; d - marking of perpendicular sides;
- e - markings along the width of the external and internal walls.
The formwork can be installed immediately after marking the perimeter of the foundation and continue simultaneously with marking the internal dimensions, in this case, you should use two methods.
The first one can achieve the convenience of leveling the concrete mixture along the edge of the board (Fig. A). For this, the installation of the formwork is carried out by combining its upper edge with a stretched string, and leveling the lower one with the ground level or slightly deepening, which is often difficult, especially on hard clay, rocky and rocky soils. The opposite side of the formwork can be positioned at any height.
The second method is more versatile and simple both in installation and in the use of shields of different sizes. In this case, the bottom of the formwork is set according to the relief of the earth, and the concrete mixture is poured along a stretched string (Fig. B), for which the corresponding slots are made in the walls of the formwork.
Leveling the horizontal of the concrete mix according to:
- a - the edge of the board;
- b - twine.
Materials (edit)
For the construction of the strip foundation, different materials are used:
- Concrete.
- Brick.
- The stone is rubble.
Most often, the option of pouring concrete into the formwork is used, where a reinforcing frame made of metal reinforcement was installed. The prefabricated version also belongs to concrete structures, the elements of which are manufactured at the factory. This technology is easier and faster to install. But to install the foundation blocks, a crane will be required, for the services of which you will have to pay, which will increase the construction budget.
Brick strip foundations are rarely used today.
But if it is chosen, then when buying, you need to pay attention to the technical characteristics of the brick itself, namely, strength and frost resistance. As for rubble stone, it is recommended to use solid rocks for the construction of a large stone house.
The complexity of the construction of a strip foundation made of stone lies in the fact that the stones will have to be adjusted to each other both in size and along the mating planes. It takes a lot of time, and the experience of such a construction will not hurt. Therefore, if there is no experience, then it is better to abandon this type in favor of a concrete structure.
Materials for strip foundation
Commonly used are rubble concrete, reinforced concrete, brick, and block.
Reclaimed concrete strip foundations.
Diagram of the device of wooden formwork.
Presented by a mixture of sand-cement mortar and large stone. The result is a solid foundation. With a sufficient supply of large stone and if the site is represented by light soils, then this is the most suitable option. If the soil is clayey, it is better to refuse to use this material, since there is a risk of cracks or complete destruction of the foundation made of rubble concrete. The width of the foundation should be between 20 and 100 cm. This figure will depend on the loads acting on the building. Such foundations require a sand or gravel cushion with a thickness of at least 10 cm to level the soil surfaces and make it easier to lay the concrete mixture.
They are represented by a mixture of cement, sand and crushed stone, reinforced with metal meshes or reinforcement rods. It is a widely used material for foundations. It is cheap, durable, and makes it possible to create monolithic structures of complex configurations. If the site is represented by sandy soils, this material will be optimal. The width of such foundations is chosen depending on the thickness of the walls.
Suitable for aboveground and underground parts of foundations. Do not forget that the brick easily absorbs moisture and in this state it can easily be destroyed even by light frosts, therefore it is necessary to provide protection from moisture with the help of waterproofing. High groundwater levels and large depths preclude application.
Foundation slab and block.
For prefabricated foundations, a foundation slab of the type FL 12.12, FL 14.12 is used. and a foundation block, the length of which is 90, 120 or 240 cm of the FBS type. This reinforced concrete product is manufactured in the factory. They have high strength, reliability and are suitable for all types of soil and structures.
