Filling technologies
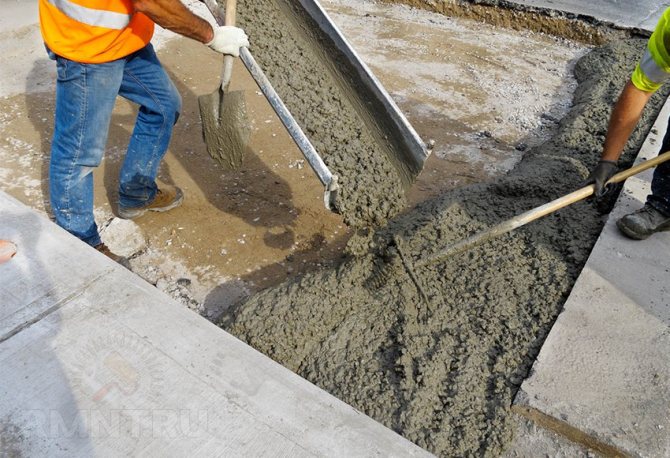
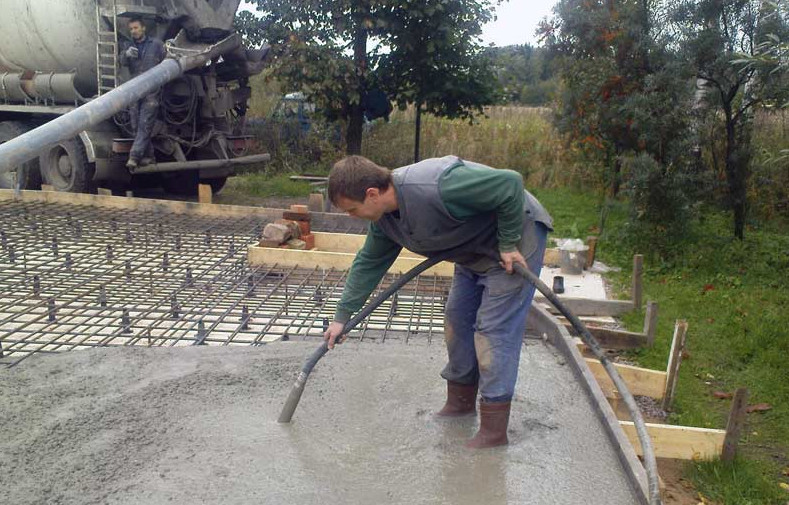
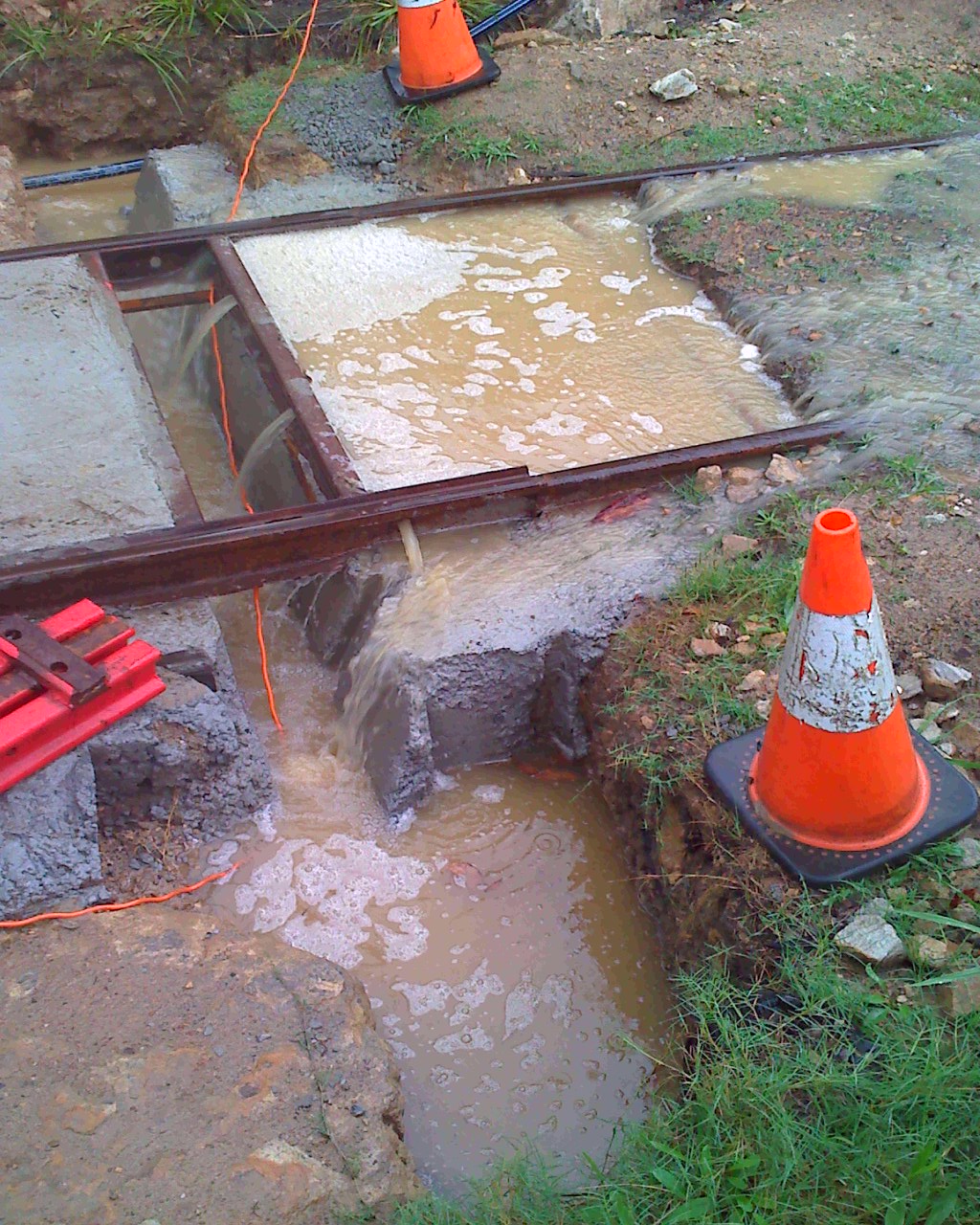
Before pouring concrete into water, it is necessary to choose the right technology that would meet the requirements and conditions of work, would allow achieving the required strength and reliability characteristics. In industry and private construction, different technologies are used, which is explained by differences in the scale of work and the conditions for their implementation.

Rising tube technology
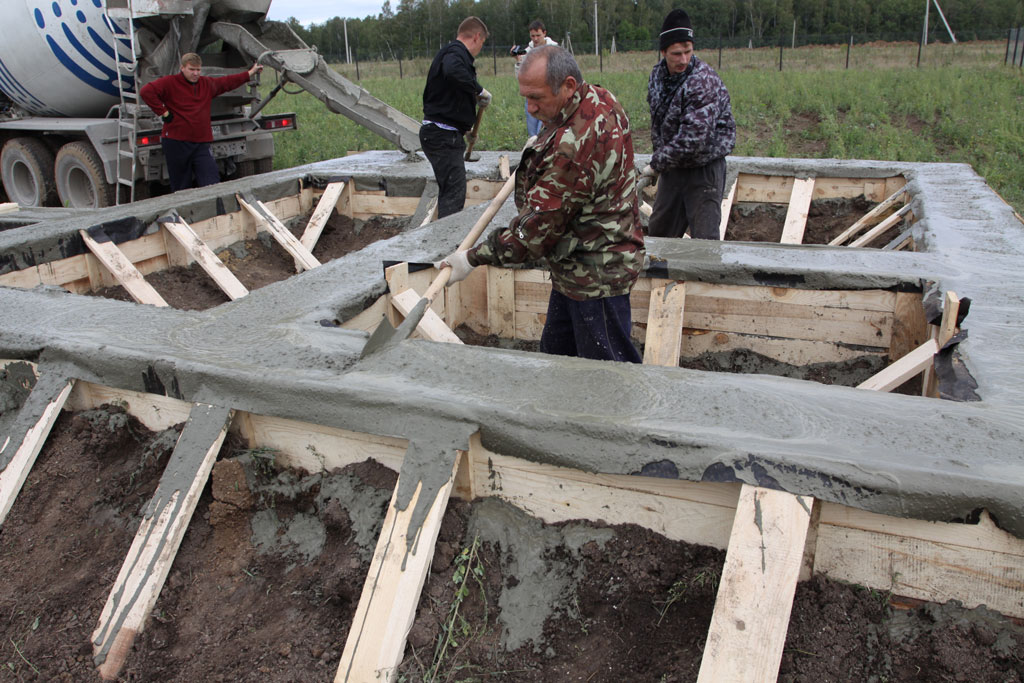
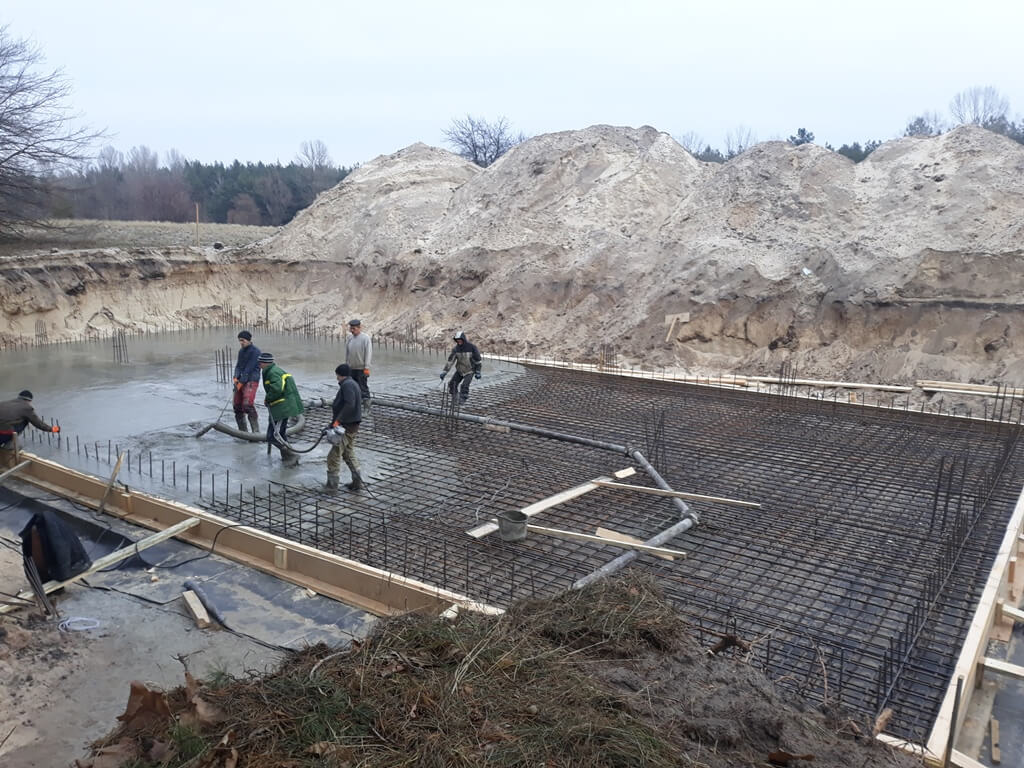
To implement this technology, you will need: two types of concrete solution, a platform made of piles, any device for lifting a load (it can be a winch or a hoist, a small floating crane, etc.), a traverse, pipes, a hopper, formwork (will help to fence off a closed the space of the working object from the reservoir).
Thanks to this method, it is possible to create strong and reliable concrete structures at relatively shallow depths. On the surface of the reservoir, directly above the structure to be poured, on piles (driven into the bottom), a working platform is built. A traverse is installed on it, a pipe is suspended from it for supply with a cross section of at least 20 centimeters. The pipes are lifted and lowered using a winch or hoist.
It is best if the slurry is supplied using a concrete pump and the pipe is lowered / lifted by a floating crane - this can achieve greater productivity and better quality. The number of loading pipes depends on the filling volume.
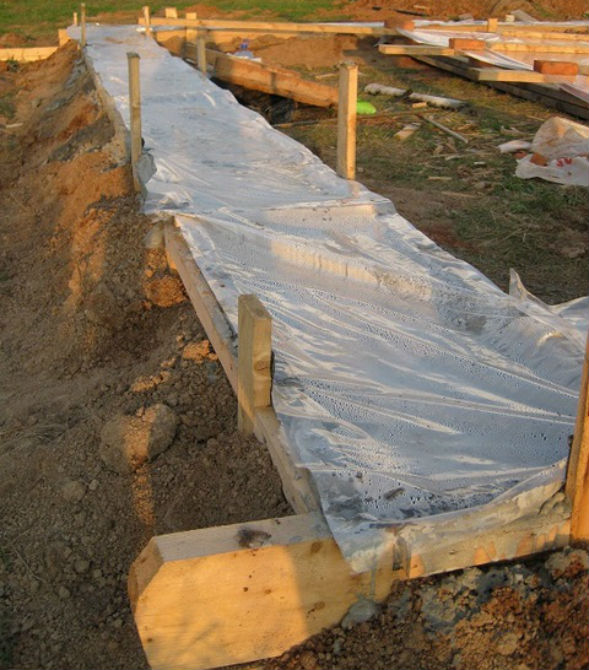
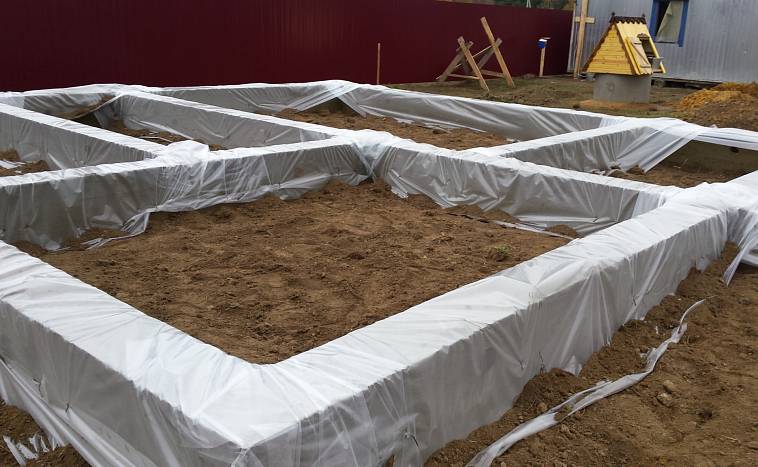
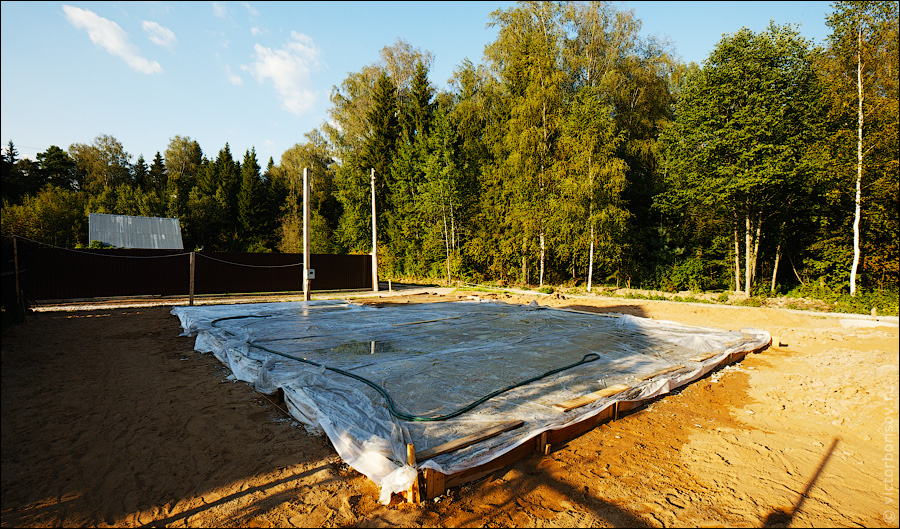
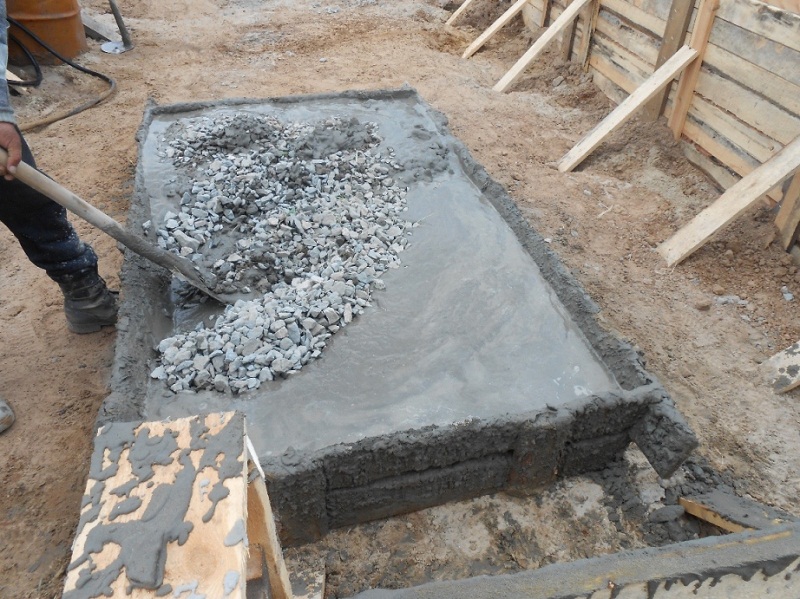
Before pouring, the bottom of the structure is covered with a tarpaulin or canvas (any dense fabric), making an overlap on the formwork, then the surface is leveled with stone and crushed stone (this is done to avoid concrete leakage through relief drops). For pouring, saturated and unsaturated concrete is used: the formwork is strengthened along the perimeter first, the core of the structure is made the second. Both solutions are kept in air before pouring.
The process of pouring concrete into water:
- The pipe (or pipes) are lowered to the bottom
- Concrete is fed into the pipe until its internal space is completely filled.
- The pipe is lifted with a lifting device, during which the solution is discharged to the bottom
- Layer-by-layer pouring is done until the work is completed.
The work must be done quickly - so that each lower layer does not have time to turn to stone and remains semi-liquid. The method of concreting with pipes is relevant only where there are no strong currents and there are no noticeable waves in water bodies.
Caisson method
To implement this method, you will need: concrete solution in bags (for making the base), just a solution for pouring, special formwork (caisson), filling pipes (always with valves), a concrete pump, a small floating crane, anchors with cables. Usually this method is chosen for deep-water concreting at a depth of 30-50 meters, as well as where there are large waves, underwater currents.
The method requires the construction of a sufficiently strong formwork - if the volume of work is small, it is made of a welded metal structure, which is lowered to the bottom by a floating crane (this is the caisson).
If you plan to pour concrete on a large structure:
- Digging a pit or trench using dredgers at the bottom of a reservoir with a size that matches the design
- Filling the pit with bags of concrete
- Driving steel piles into the bottom clearly along the entire perimeter of the base of the structure - you need to do so that they are with a slight slope (it turns out that the piles are fanned out) to the outside of the structure (to make slopes)
- So that the slope is not violated, the piles are anchored and ropes to the bottom.
- Inside, the surface between the piles is evenly sewn up with steel sheets at least 10 millimeters thick or boards at least 50 millimeters thick
- The outer surface between the piles is reinforced with belts made of metal rods, channels or corners

The solution is supplied to the pipes under the action of excessive pressure - after all, there are two valves at the ends of the pipe, the supply is made by a concrete pump. The rest of the steps are similar to the pile concreting process.
Why wet the foundation
Replenishment of moisture required to complete the processes of crystallization of cement is a prerequisite for obtaining high-quality concrete. But not the only thing, since it is also necessary to water the concrete after pouring to compensate for its shrinkage.
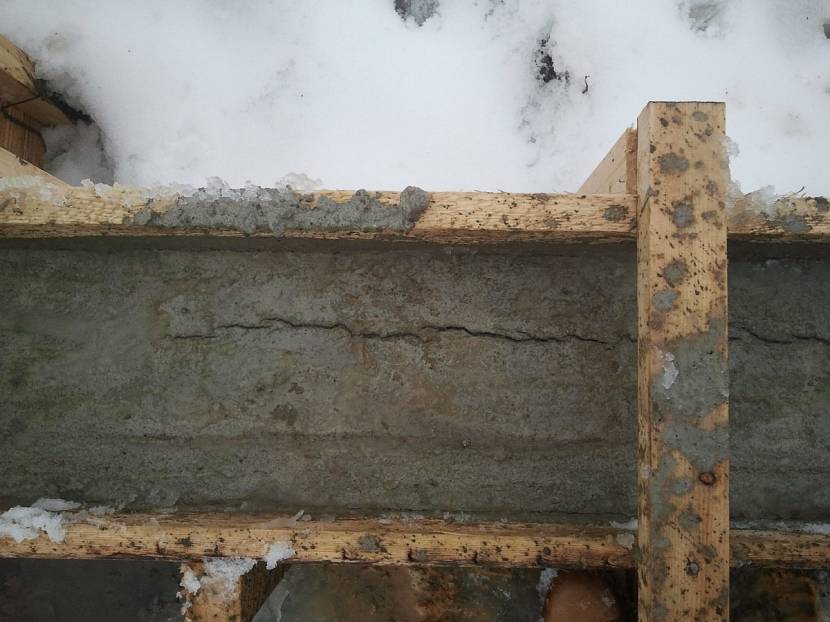
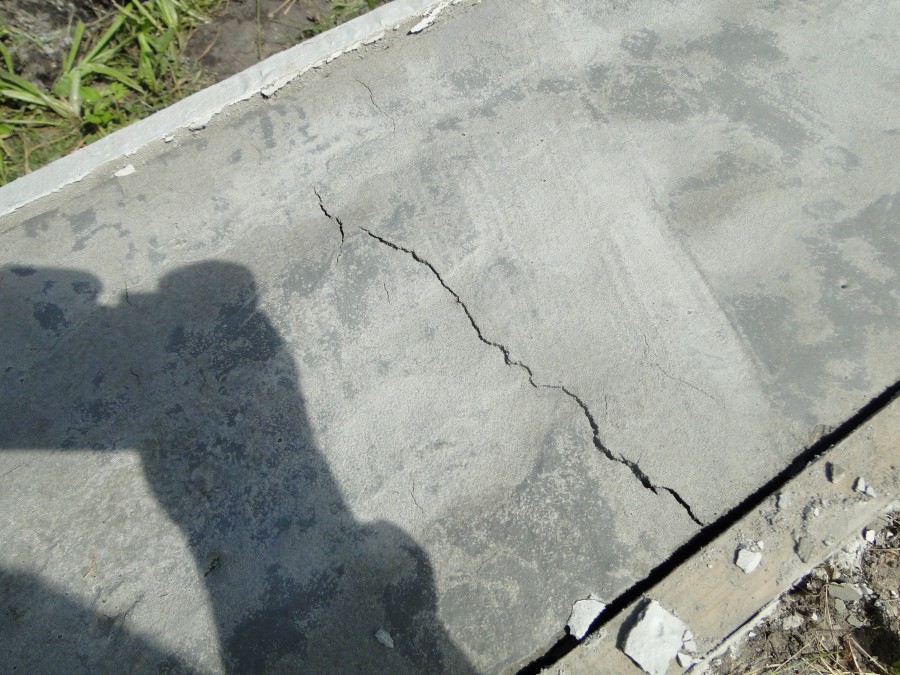
The solution, evaporating moisture, decreases in volume. With a lack of water, this occurs with the formation of cracks, the depth and number of which largely depend on climatic factors.

Shrinkage crack in a concrete foundation Source.
These cracks are infiltrated by rainwater, which, when frozen in the winter months, expands and tears apart the concrete from the inside. The crack grows larger with each subsequent freeze, and gradually the foundation collapses.
The need for moisturizing
Waterproofing scheme for a foundation made of in-situ concrete.
Many novice builders, having independently made the pouring of some object with concrete, mistakenly consider the work on this finished. And they are deeply mistaken, since it takes quite a long time from pouring to the final gaining of concrete strength. Typically after 2-3 weeks, depending on ambient temperature and weather conditions, the poured concrete is strong enough to withstand significant pressure on its surface. Those. if we are talking about a poured foundation, then after this period of time you can drive out the walls of the house. According to the laying technology, the standard length of time for concrete to gain strength is 28 days, although concrete gaining strength can last for years.
It is imperative to take into account the fact that, hardening, concrete has the unpleasant property of changing its volume. For a concrete structure to be of high quality, concrete must gain strength. He collects it by evaporation of moisture, and evaporation should occur evenly from the entire volume of concrete masonry. But in high temperatures or strong winds, the outer layer of the concrete structure gives off moisture faster than the middle. When it dries, a sludge appears, and it will be the larger, the faster the drying process takes place.
Scheme of a concrete floor on the ground.
After the concrete structure has completely hardened, these little scoundrels will definitely show their evil character, helping adverse conditions to destroy the integrity of the concrete. They are especially zealous in winter, when moisture collected in the cracks freezes and simply tears the structure, weakening it and significantly reducing its service life. This is most noticeable when such a nuisance happens to the concrete foundation of a building. It gives slack, as a result of which, far from small cracks may appear along the facade of the building, which, if you do not strengthen the foundation, will only increase over time.
But that's not all. If the top ball of concrete is too dry, a process called cement hydration stops. As a result, concrete gains strength too slowly. Simply put, the strength of the ready-mixed concrete will not correspond to the planned grade, it will be much lower.
To avoid this trouble, it is necessary to regularly wet the concrete until it hardens completely.
It is important to understand that no matter how much we water the concrete, we do not make it stronger, but simply do not allow it to become more fragile. If the concrete structure during its hardening is sufficiently wet, then the settling of concrete will occur rather slowly, respectively, the stress on the surface of the concrete structure will be rather weak
In other words, if the surface of a concrete structure is wet all the time until its full strength gain, then the probability of the appearance of temperature-sedimentary cracks on its surface will approach zero.
Winter care
All construction and repair work that involves the use of concrete mix is not recommended in cold weather, i.e. in winter. Construction in the cold season will require additional financial costs.
If the air temperature drops below 0 ° C for a short period of time, and then rises above + 5 ° C, frost is not critical. In order for the structure to harden correctly, special antifreeze modifiers are added to the solution. They keep the mixture from freezing. If not used, it is recommended to warm up the solution before pouring and wrap it up.
Special heaters can be used on large construction sites in winter. At home, their use will be costly. Caring for concrete in winter means warming it up. Heating is necessary in order to keep the thermal energy of hydration in the solution.
Maintenance of concrete structures
The main goals of surface care after the foundation is poured:
- reduction of plastic shrinkage;
- increased strength;
- drying out prevention;
- neutralization of the influence of temperature drops;
- increased service life;
- prevention of the influence of chemical and mechanical forces.

To understand how much concrete to water, you need to know about the existing rules. The methods of leaving after pouring the foundation are influenced by:
- type of cement;
- type of construction;
- climatic conditions, etc.
The period of care is influenced by the speed of hardening of the cement in the mixture:
- cement structures that harden gradually need to be moistened for 4 weeks;
- Portland cement structures - from 2 to 3 weeks;
- on fast-hardening cement - 8 days.
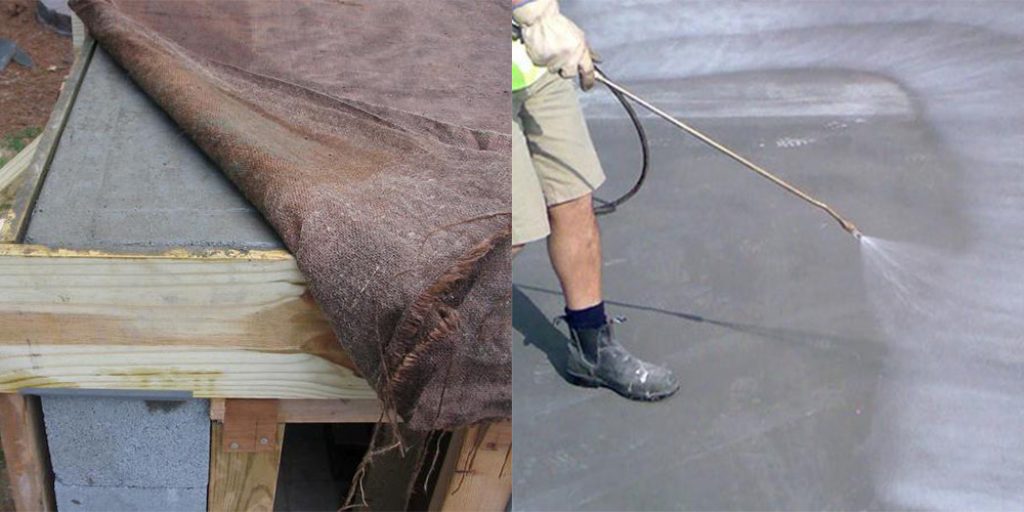
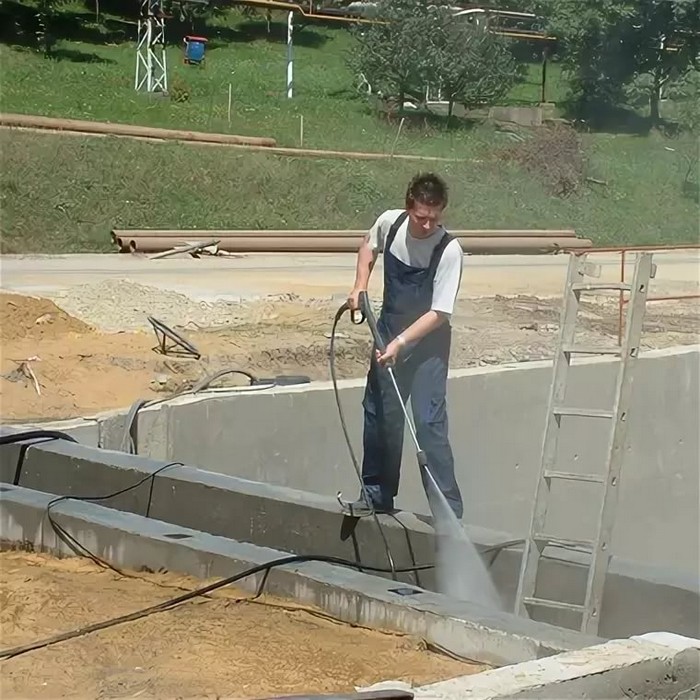
In hot and dry weather, a longer maintenance period is required. For slower evaporation of moisture and in order to protect against overheating after pouring, it is recommended to cover the foundation with moistened sawdust, matting, roofing material.
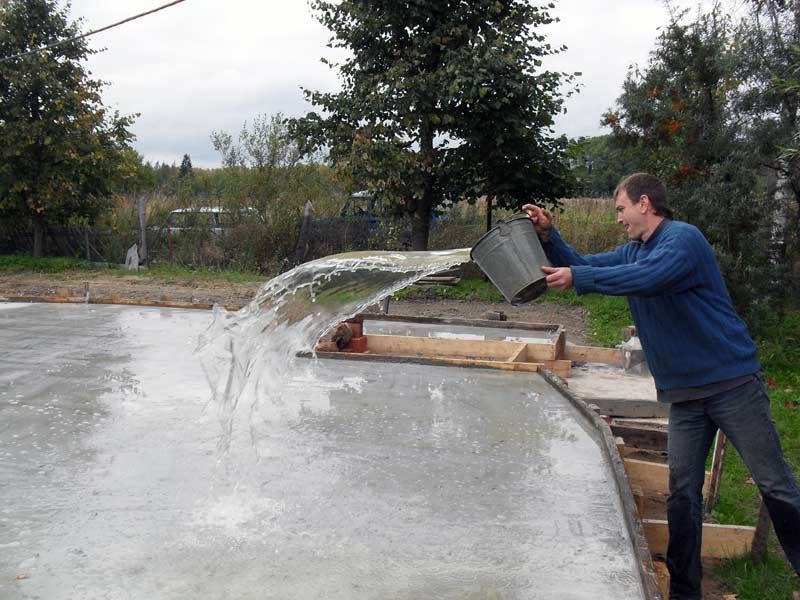
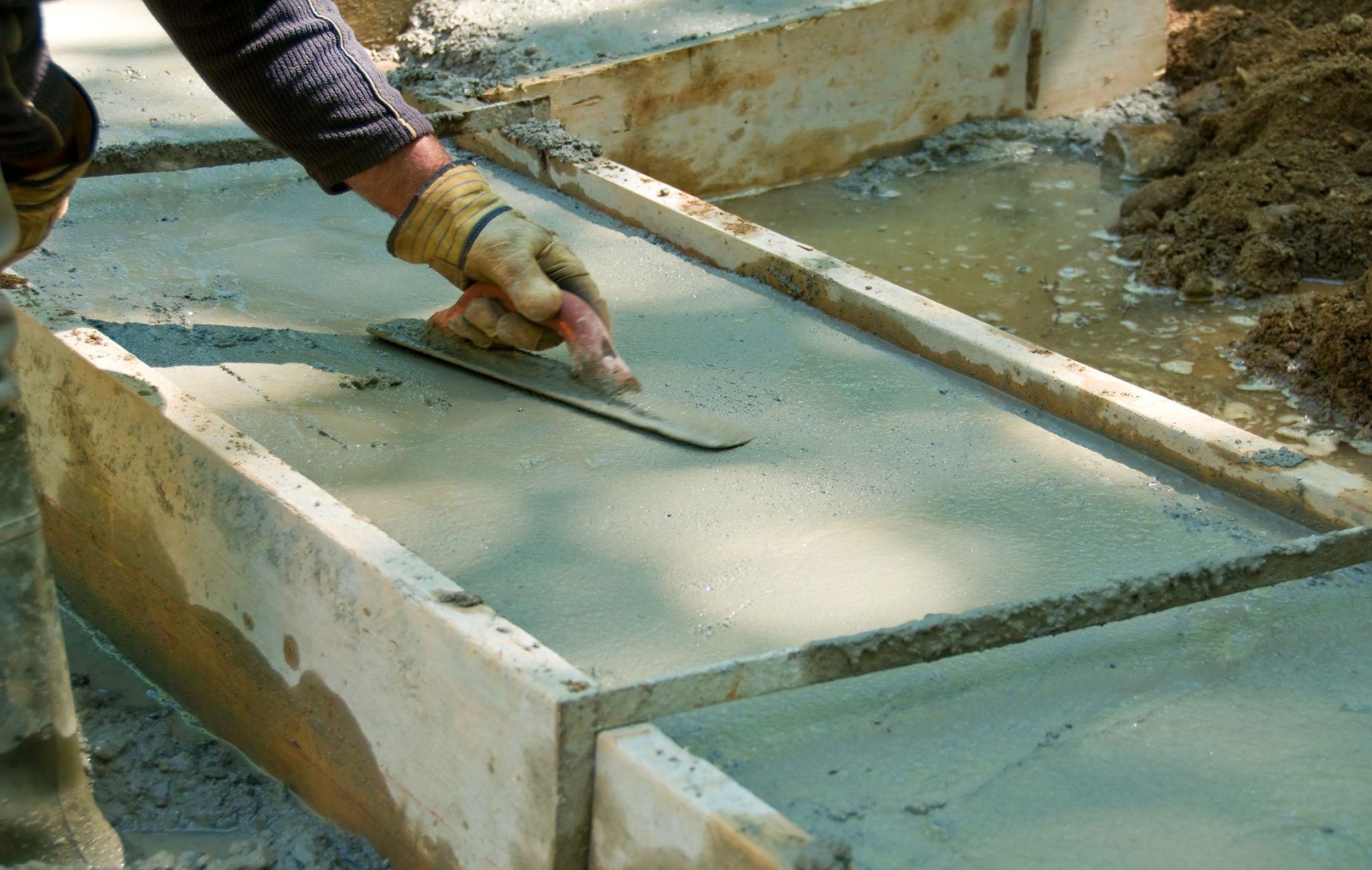
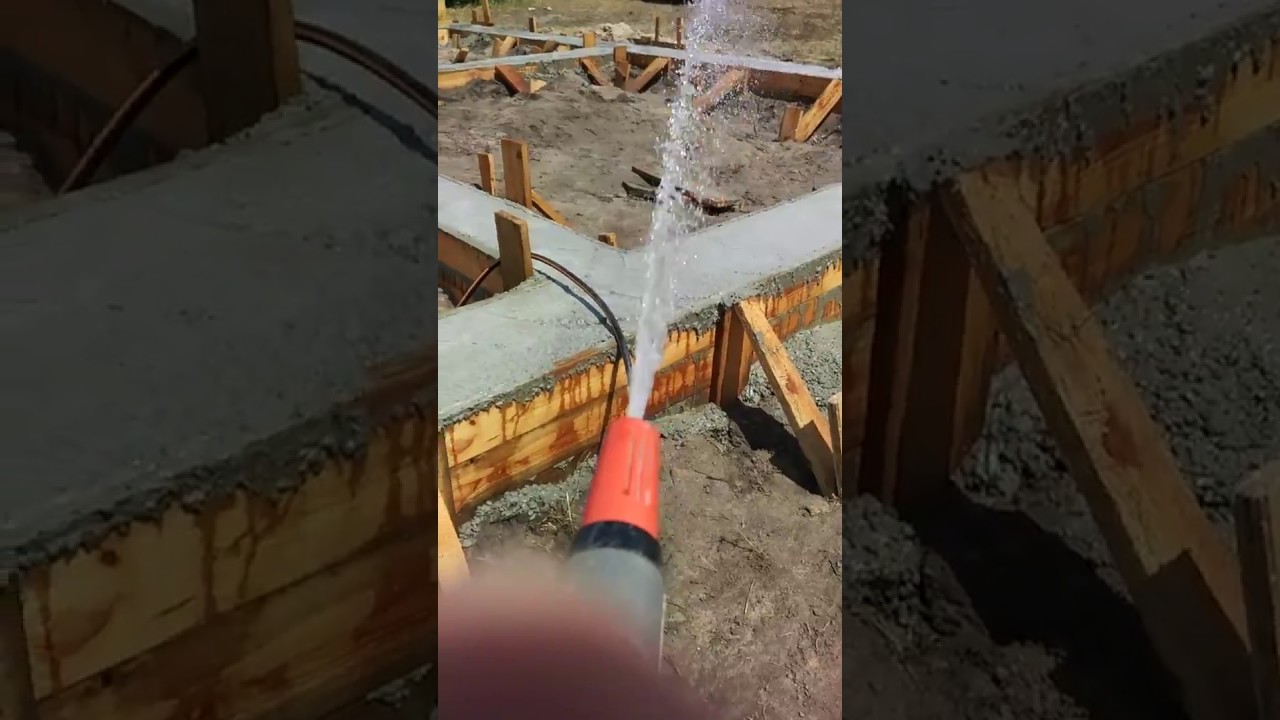
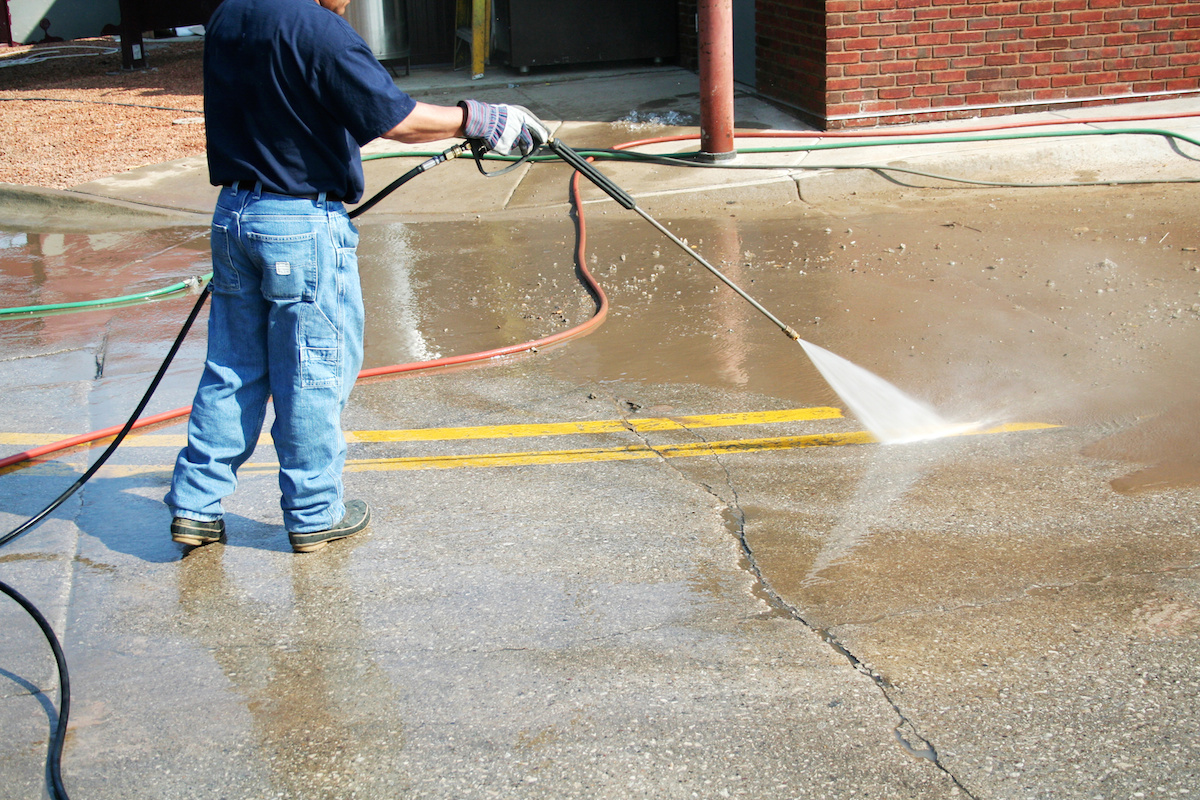
In hot weather or strong winds, it is recommended to start irrigating the surface 2-3 hours after the end of the work. Not everyone understands how to water properly.
If you use a jet with a strong pressure for humidification, the plane that did not have time to harden may deform. It is recommended to use a spray to simulate rain over the surface.
Watering should be carried out during the day so that the structure is constantly wet
You can understand how often you need to irrigate the surface by paying attention to the temperature and humidity of the air.

It matters how much time should elapse between waterings. In extreme heat, the breaks between humidification should not be more than 2 hours, in other cases - every 3 hours during the day, up to 3 times at night. Hissing during irrigation indicates insufficient water supply.
Requirements for irrigation water:
- must be clean flowing;
- it should not contain impurities that can have an aggressive effect on the surface;
- you can not use the groundwater located close to the surface;
- a pH level of 7 is recommended (tolerance is 1);
- must not contain pesticides or organic deposits;
- should not be in large amounts of calcium, magnesium, sodium.
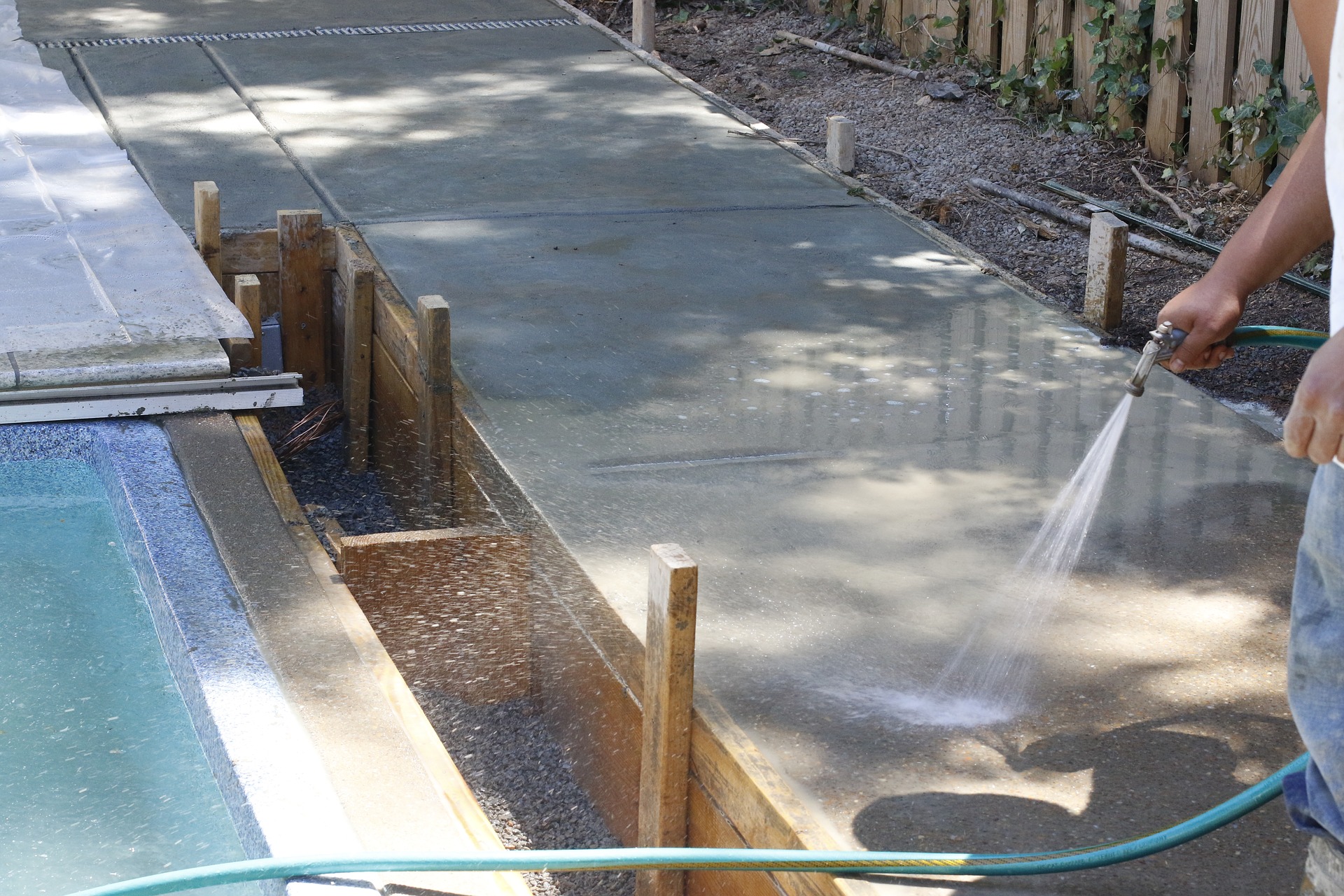
On the foundation, which is in the formwork, moisture remains longer, therefore, irrigation is allowed less often. After removing the formwork, it is necessary to start watering, paying more attention to the edges of the structure, since they are more exposed to the influence of wind and temperature, therefore, moisture loss occurs faster.
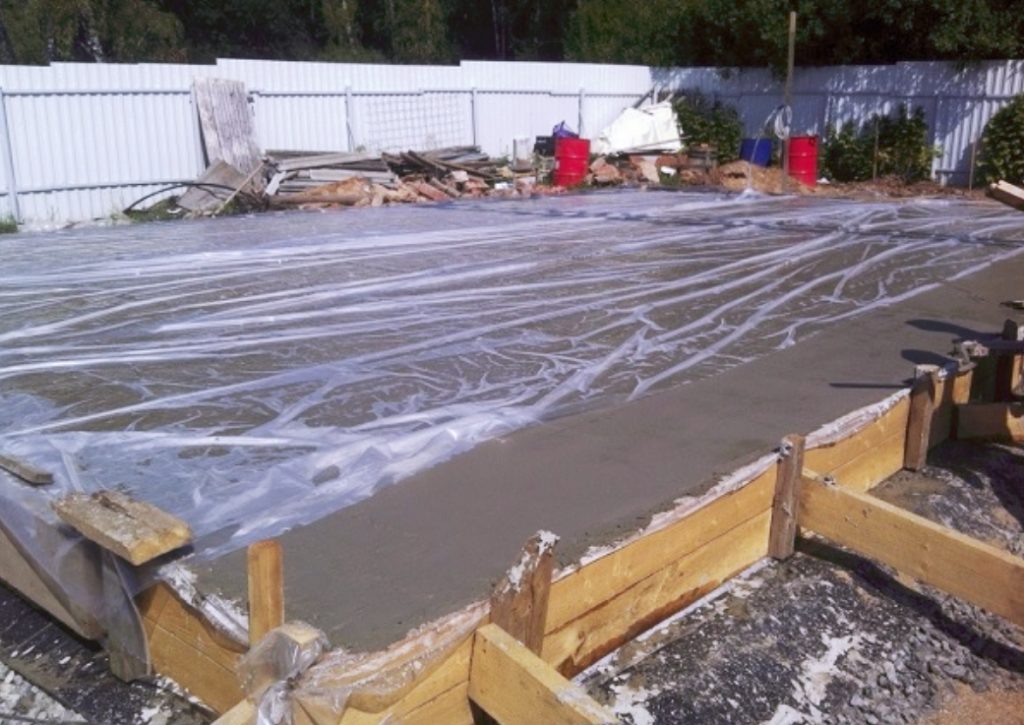
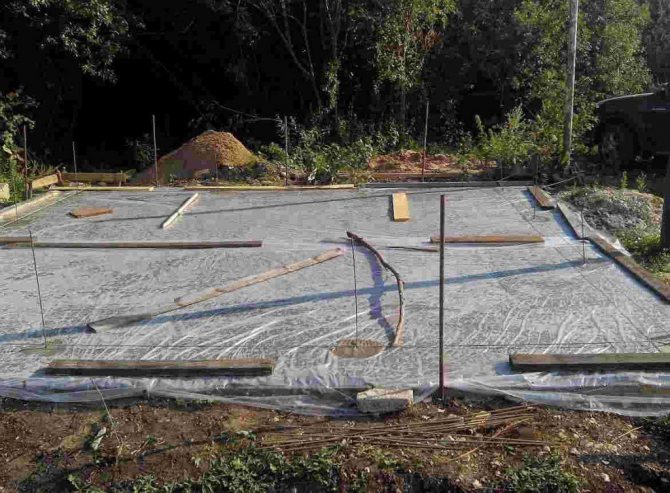
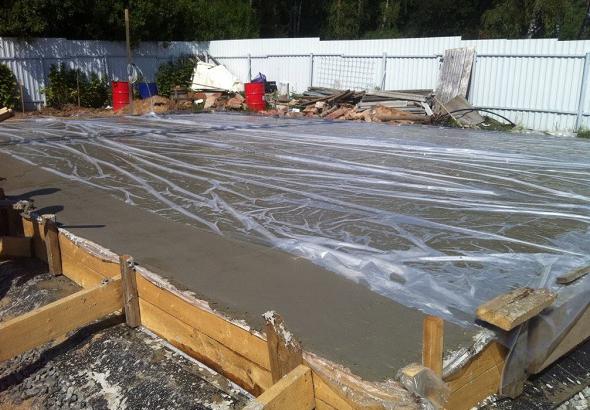
Sometimes, to preserve moisture, the surface is covered with a polyethylene film.In the process of evaporation, water droplets end up on the inner side of the film, part of the moisture returns to the foundation. This technique allows you to reduce the number of irrigations, but is not able to replace them completely.

Concrete watering frequency
Periodic moistening during the day and night helps maintain a sufficient moisture level in the concrete.
The frequency of the procedure depends from weather conditions and features of cement:
- When the air temperature exceeds + 15 ° C, concrete is watered from the second day after pouring it. You need to moisturize for 7-15 days.
- Upon reaching an average temperature of + 10 ° C, watered for up to 1.5 weeks.
- In the first days, water it 4-5 times a day, and after 5 days - several times, if it is not hot outside.
- In hot and windy weather, the intervals between watering should be at least 1.5-2 hours, and in a cloudy period - with a frequency of 3 hours.
- Slag or pozzolanic Portland cement, you need to moisten it 5-7 times a day for 2-3 weeks.
- Alumina cement requires moisture for 7 days.
Less water evaporates from the concrete in the formwork. After its removal, the stripped surface of the foundation also needs watering.
Why wetting concrete foundations plays an important role
 The process of wetting the concrete foundation
The process of wetting the concrete foundation
- Water is involved in all physical and chemical processes, therefore it is quickly neutralized. But concrete does not have time to gain the necessary strength and it is necessary to compensate for the loss of moisture;
- Moisture condenses faster from the open surface of concrete, therefore, exchange processes there are weaker. As a result, an unstable solid surface is formed, which immediately collapses under load. And under it is a liquid layer of concrete, which simply did not have time to gain its strength;
- When concrete hardens, it decreases in volume, therefore, to compensate for losses, it is necessary to use water to activate metabolic processes inside the structure. But here you need to strictly dose the amount of water, taking into account the temperature conditions and climate;
- The key factor is climate. If the air is hot enough, then the moisture evaporates much faster than necessary. As a result, little moisture remains in the concrete, it is not enough for metabolic processes and a clean cement structure is formed. It is not able to withstand even minor loads, it is loose and porous. And if you add wind to this, then the foundation will quickly erode and a large number of cracks will appear.
 Cracks in concrete
Cracks in concrete
It is these microcracks that are especially dangerous. They destroy concrete, because through them rainwater, as well as dust and dirt, gets inside. As a result, the outer surface remains intact, while the concrete collapses inside. Cracks are especially dangerous in winter with sudden temperature changes.
Due to the ingress of moisture, water is converted into ice, which expands and enlarges the crack, after which the concrete fragment swells and breaks off. In fact, this is a chain reaction that as a result completely destroys the foundation.
Moisture plays another important role. Concrete is formed by hydration, where water is the key ingredient. If the top layer of concrete is overdried (it lacks the required amount of water), then the concrete will gain strength too slowly or this process will be stopped altogether.
If the concrete is poured with water, then it will also become too elastic, and if using capillary wetting, then the effect will be maximum. Accordingly, if the outer surface of the concrete is constantly wet, then the possibility of temperature-sedimentary cracks will be minimized, especially after using thermal films.
Why wet concrete
During the drying process, the cement decreases in volume, giving shrinkage. When the concrete mass has an increased thickness, it dries unevenly.Then the inner layer retains moisture, maintaining the same volume, and the surface dries up, decreasing in volume.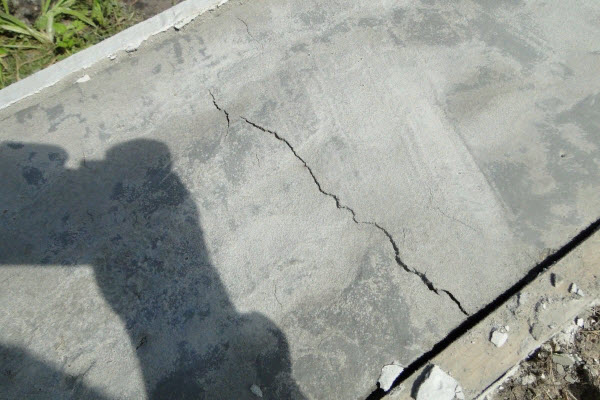
As a result, the gaps between these areas suffer from surface tension, the concrete crust tends to compress, decrease, but this is not enough to close a larger depth layer. This leads to cracks.
In the process of bonding sand and gravel, a sufficient volume of water is required for the cement to react with the liquid. When the surface dries out unevenly, and there is not enough water, some areas remain unused to the end. Loss of water must be replenished by moistening the concrete.
How often do you need to water the foundation with water
After pouring, the concrete should be cared for continuously for two weeks. It follows from this that when caring for it, it needs to be watered every 1-2 hours, depending on how much moisture evaporates during the specified period. If, when watering, it begins to hiss, then this indicates an insufficient amount of water in it.
We recommend watching a video in which the specialist talks in detail about the full cycle of care for the poured base.
The first watering is carried out after 10-12 hours, after pouring. If the air temperature is about 15 ° C, then the humidification is repeated every 3 hours. At night, water the foundation 1-2 times within seven days.
In order not to constantly water the surface with water after pouring, it is not necessary to remove the formwork. Concrete, being in it, will better retain moisture.
If the formwork is removed, then special attention must be paid to the edges of the building structure. It loses moisture several times faster than the concrete surface, as it is blown by winds from both sides simultaneously
If it is not properly moistened, then not only cracks on the verge will appear, but even chips.
You can also surface with plastic wrap. Moisture, in this case, evaporating from the solution, will collect in the form of condensate from the inner side of the film and will partially return to the solution. Of course, this trick reduces the number of watering concrete with water, but it does not completely replace it, it is still necessary to water it, but not so often.
Watch the video on how to properly water the base after concreting.
Why water the concrete?
In the process of concrete hardening, special attention should be paid to moisturizing the composition. Why do you need to water concrete? There are a number of factors that prove this need.
- Water is the main element of the cement slurry. It participates in physical and chemical processes, as a result of which it is quickly neutralized. For optimal hardening of the concrete mixture, a certain amount of moisture is required, which must be compensated for.
- The solidification of cement is not uniform. The upper layers are characterized by weak exchange processes and, as a result, the unstable hardened surface deforms quickly when the concrete layer inside is still liquid. In order for the structure to gain strength, it is necessary to provide optimally the same conditions.
- During hardening, the base decreases in volume. Loss can be replenished using a dosed amount of liquid.
- Climatic conditions are a factor that has a direct impact on the formation of a solid structure. Hot air promotes rapid evaporation of water, so the foundation needs constant watering. Windy weather removes moisture particles from the cement, which provokes the appearance of numerous cracks in the surface.

Microcracks are one of the risks in the formation of the base. Through them, rainwater, dirt and dust get into the product. As a result, the surface remains intact, and the inner part of the structure is deformed.
The formation of cracks and cracks in the foundation occurs in winter with strong temperature drops.When moisture gets inside, it transforms into ice, which has the properties of expanding and increasing the size of the crack. Swelling of the base occurs, and after the foundation of destruction, it passes to the main structure. Water is involved in hydration processes. The optimum moisture level contributes to the gaining of strength characteristics.
Why do you need to care for the concrete mix?
The strength of the concrete mixture after hardening is in direct proportion to how optimal it will be to create conditions for hydration. Neglecting this, you can get various defects that appear as cracks or other damage. Maintaining the foundation is important and requires some effort. Otherwise, the strength of the concrete will decrease and the threat of destruction will hang over it. It is necessary to carry out a whole range of measures that are aimed at providing suitable conditions for obtaining strength.
The main goals pursued at the stage of caring for the solidified concrete solution after the foundation is poured are as follows:
- minimization of plastic shrinkage;
- ensuring strength;
- neutralization of the effects of temperature changes;
- prevention of excessive and premature drying out;
- ensuring durability;
- prevention of exposure to mechanical as well as chemical forces.
Care rules
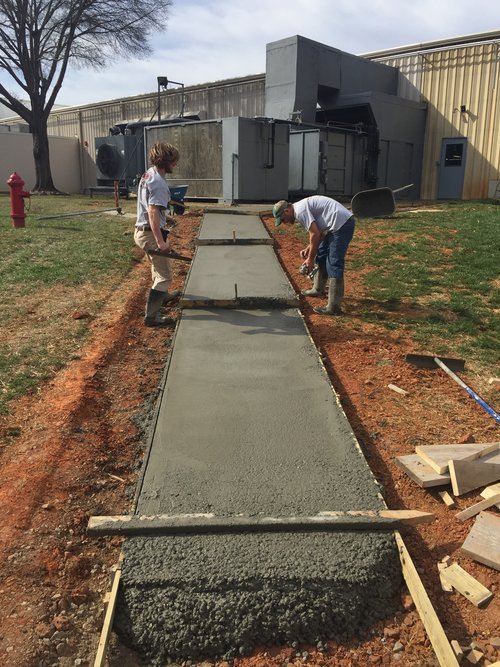
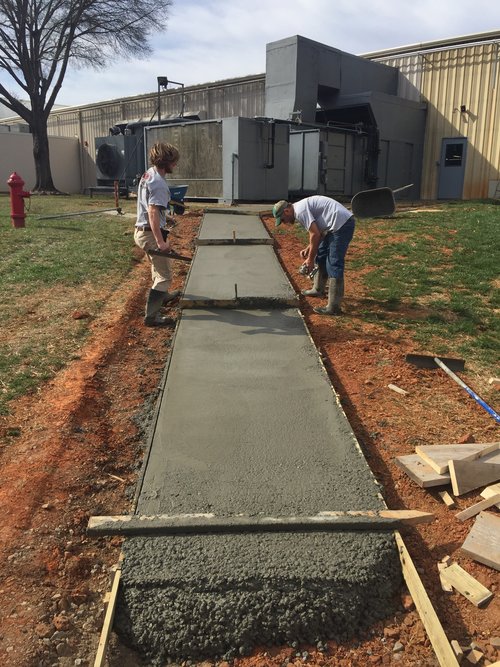
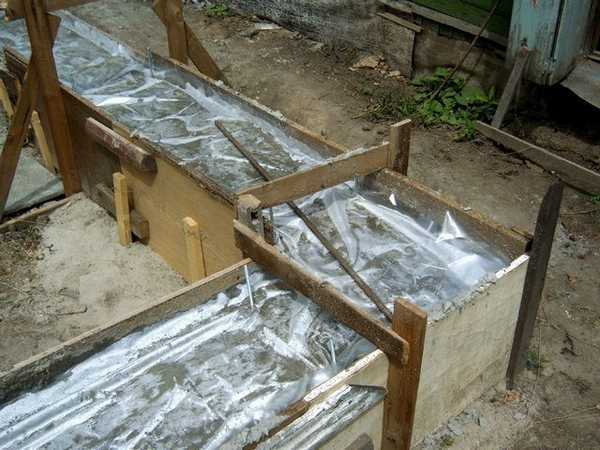
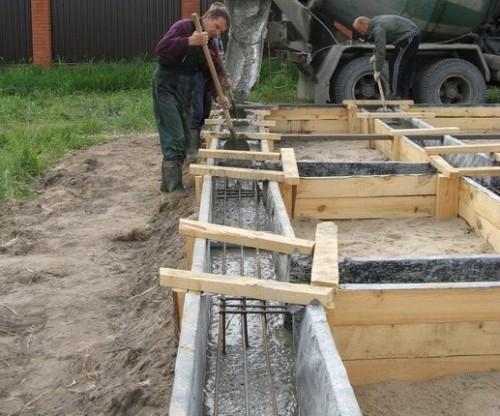
Post-pouring foundation maintenance is being completed after at least 65% strength has been achieved or after the formwork has been completed, for which there is a technical justification. First of all, after concreting, it is necessary to examine the formwork itself for damage that can cause the mixture to flow out and, accordingly, deformation of the base. If breakdowns were found, they should be immediately eliminated before the concrete has time to set. The mixture has an approximate setting time of up to two hours.
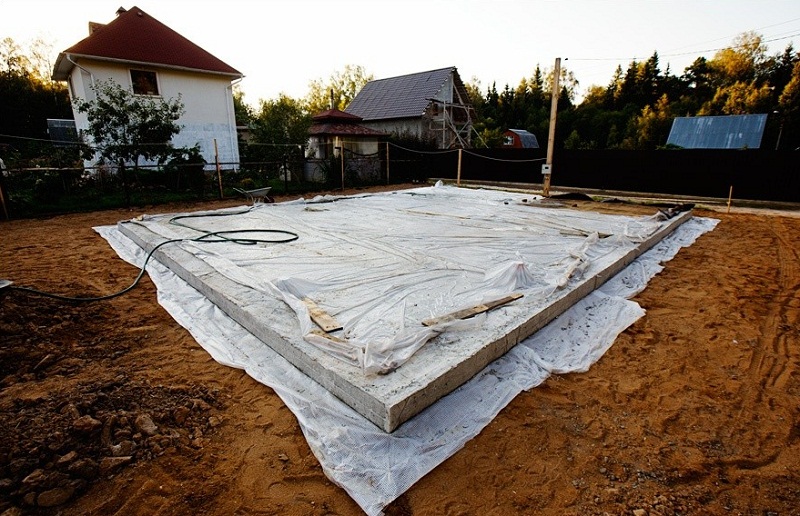
At the time when the foundation solidifies, it should not shake or be subjected to any other type of mechanical stress. It is recommended to cover the structure with polyethylene foil after pouring. This will help avoid the likelihood of erosion.

Maintaining optimal humidity and temperature conditions is an important stage in the care of the concrete mixture. The mixture must be kept at a humidity of 90-100%.
It should be noted that early dehydration does not have the best effect on the concrete mix. Basically, this phenomenon is observed in the case of leakage of the water component from the solution, which occurs as a result of damage to the formwork. As a result, various troubles are possible, which are expressed in a decrease in strength and even sand separation. Shrinkage cracks appear, which leads to a sharp decrease in the volume of the mixture in open areas. This is due to rapid weathering.

Surface cracks, which are formed in the first place, quickly propagate deeper. This poses an even greater threat to the entire structure. Therefore, it is recommended to extend the drying period until the substrate has reached the required strength level.
In windy weather, concrete dries out many times faster, this must be taken into account. The drying rate is also affected by the level of humidity, as well as the temperature regime. After 8 hours, it is necessary to regularly moisten the foundation. This uses diffuse watering. In addition, it is possible to protect the hardened concrete mixture with a layer of sawdust. You can also cover the structure with tarps or burlap. The materials used for protection are constantly wetted to create a wet compress conditions.
It is important to remember that measures to moisten the concrete mixture are carried out only if the average daily temperature is above +5 degrees. If there is a possibility of frost, the foundation is covered with mineral wool, rags or other heat-insulating materials.
In the absence of the possibility of constant moistening, the concrete is covered with a polymer film. It is necessary that the thickness of this material be above 200 microns. The main thing that needs to be achieved is to minimize the number of joints. They are glued with tape or using a special tape.
To prevent the still fresh concrete from being damaged by groundwater, everything possible must be done so that it is not washed out. As the mixture gets stronger, it will be more difficult to blur it. Typically, the required strength is reached 3-4 days after pouring. Concrete maintenance, ENiR notes this, is completed after stripping.
The composition of the mixture
The components of the mixture are:
- cement (after mixing, it connects concrete elements);
- water;
- aggregate (sand, crushed stone or gravel).
It is possible to improve the operational and technical parameters of the structure with the help of special additives (mineral or organic).
Beginners do not always understand for what purpose it is necessary to water the concrete after pouring, because they do not know the features of this material. The main active components are water and binder, which envelop the filler (which is passive in the mixture).
Fillers take up to 85% of the total volume. Their properties affect the physical and mechanical properties of concrete. The proportion of water in the mixture is about 7% of the volume, cement - 13%.
The top layer loses moisture more quickly (compared to the bottom layer and the middle), so cracks can occur in the concrete. When the surface is overdried, the strength of the product decreases, the design will not be able to meet the required brand.

Concreting in dry hot climates
Concrete does not like not only frost, but also heat. When the air temperature rises to +35 and above, and the humidity is at 50%, the water evaporates too quickly, which provokes a violation of the water-cement balance. Hydration slows down or stops altogether, and therefore the concrete must be protected from moisture loss too quickly.
Chilled (or diluted with ice) water is used to lower the temperature of the mixture. This eliminates the rapid evaporation of water during the laying of the mixture.
After a certain time, the mixture heats up, therefore it is important to ensure the tightness of the formwork (so that water does not evaporate through the cracks). Formwork can also absorb moisture, and therefore, to limit the adhesion of concrete and construction material, it is treated with special compounds before pouring.

The hardening concrete is protected from direct ultraviolet rays - the surface is covered with a tarpaulin (burlap), the surface is wetted every 3-4 hours. Moistening may be needed for all 28 days of curing with a monolith.
Often this method is used to protect concrete from heat: an airtight PVC film with a thickness of at least 0.2 mm is created above the surface.
Concrete prepared according to the recipe is able to set, harden and acquire all design characteristics at an ambient temperature of +20 degrees and a humidity of about 100%. In the case of work in frost or heat, you must take care of heating or cooling measures that will guarantee the strength and durability of the finished structure.
When is waterproofing indispensable?
Waterproofing is necessary only when a recessed base is created in order to have a basement with a normal microclimate. Moreover, the degree of soil moisture in this case depends only on how serious and thorough waterproofing measures should be. But basement waterproofing is needed in any version, and from all sides, even if at the time of construction no prerequisites for this are visible. After all, no one knows how in a few years the bed of the underground surface current will change, or how much the climate will change in terms of annual precipitation.
Basement waterproofing at moderate soil moisture
 Diagram of the device for vertical and horizontal waterproofing of the basement floor
Diagram of the device for vertical and horizontal waterproofing of the basement floor
Even in a situation where the groundwater is far from the surface and the region does not differ in the fallout of a large amount of atmospheric moisture, all basement surfaces should be delimited by a hydro-barrier. That is, you need horizontal and vertical moisture insulation of the foundation and the concrete slab, which serves as the base of the floor in the basement. Moreover, it is desirable that the waterproofing layer is continuous.
In the situation under consideration, the base of the building is usually poured or laid out of reinforced concrete blocks first, and then the foundation of the floor is made in the basement. For vertical moisture protection, it is enough to use coating materials such as bituminous mastic or hydrophobic plaster. If the foundation is made of blocks, masonry joints are first processed, and then one or two layers of waterproofing compound are applied continuously. With a monolith it is easier - the coating is continuous and that's it.
Before pouring the foundation, a horizontal waterproofing layer is made, which is designed to protect the sole of the base. A pillow is being prepared (gravel below, sand or fine gravel on top) and laid in two or three layers of roll waterproofing material.
Basement waterproofing at high soil moisture
 Blind area device with a surface water drain and drainage system
Blind area device with a surface water drain and drainage system
To begin with, it is worth finding out the source of waterlogging, for which you should consult with specialists. If the moisture is of atmospheric origin, first of all, it is worth taking care of its removal from the building. It is an efficient storm drain and a wide blind area. You can make a clay castle around the foundation. When the soil is moistened with groundwater, care should be taken to arrange a drainage system.
Subject to the implementation of the above measures, the waterproofing measures are the same as in the previous case, only more reliable moisture protection means are selected. When waterproofing the soles of the base, roll materials are supplemented with layer-by-layer coating with bitumen mastic. For vertical waterproofing, two-layer waterproofing is applied over the foundation wall treated with primers. For the base of the floor, a two-layer roll waterproofing with preliminary surface treatment with bitumen is also suitable.
Measures for severe waterlogging
Unfavorable hydrological conditions are usually associated with ground moisture, but can be seasonally supplemented by heavy rainfall or snowmelt. This refers to soils that are prone to waterlogging, as well as areas where the subterranean upper waterway is close to the surface.
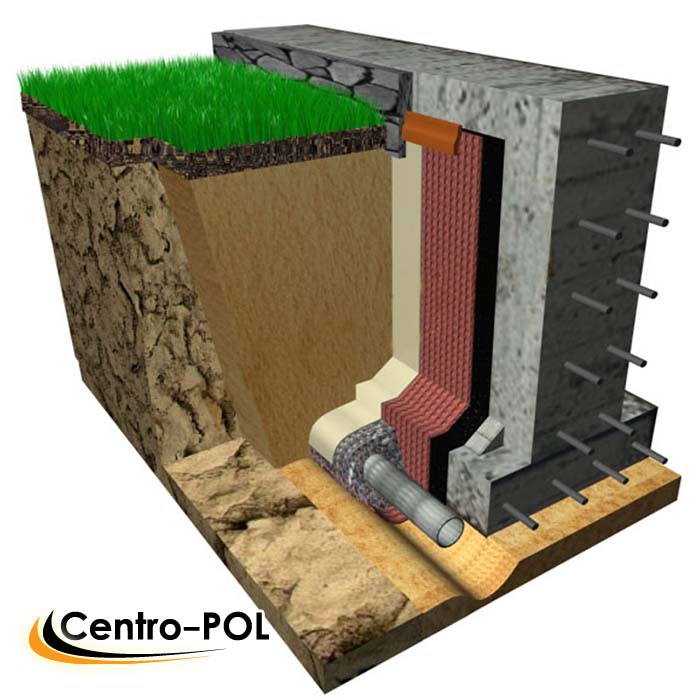 Diagram of a waterproofing device with a drainage system for removing moisture
Diagram of a waterproofing device with a drainage system for removing moisture
In such a situation, no basement waterproofing will help if you do not make full-fledged effective drainage around the foundation. A drainage system is formed below the base of the base to prevent groundwater from reaching horizontal and vertical concrete structures. It is imperative to make a powerful (at least half a meter) earthen castle, especially when there is additional waterlogging due to atmospheric moisture. Of course, - blind area and storm sewer.
Usually, in such a situation, a horizontal reinforced concrete slab is first created, slightly protruding beyond the outer perimeter of the base of the building, and only then the foundation structure is formed. It is better to waterproof the slab in two stages:
the first layer before pouring the rough concrete;
second layer before finishing screed.
The choice of material is made taking into account the complexity of hydrological conditions. It can be multilayer roll-on hydro-barriers based on bitumen.
Vertical waterproofing of a concrete structure can be done as follows. Two layers of waterproofing and a waterproof membrane on top of it.You can apply treatment with liquid rubber or special impregnations, which make the concrete structure impervious to moisture.

















































