Phased execution of work
The foundation is a slab on piles, the construction technology of which requires a phased implementation of work, is created by sequentially creating a pile field and pouring a concrete slab. Consider the creation of an SPF on bored piles, one of the most difficult and time-consuming options.
Procedure:
Preparation
Preparatory work begins with freeing the site from plants, foreign objects, dismantling unnecessary structures and improvement elements. Then the surface is leveled (leveling). If the project provides for the creation of a recessed insulated slab, then a pit of appropriate dimensions should be dug under it.
The next step is to mark the pile field. For this, stretched cords and pegs are used. The boundaries of the site are indicated, according to the scheme, pegs are driven in along the axes of future wells. In the process of marking, it is necessary to constantly monitor the correct installation of the stakes, check the parallelism of the lines and the accuracy of right angles.
Pile making
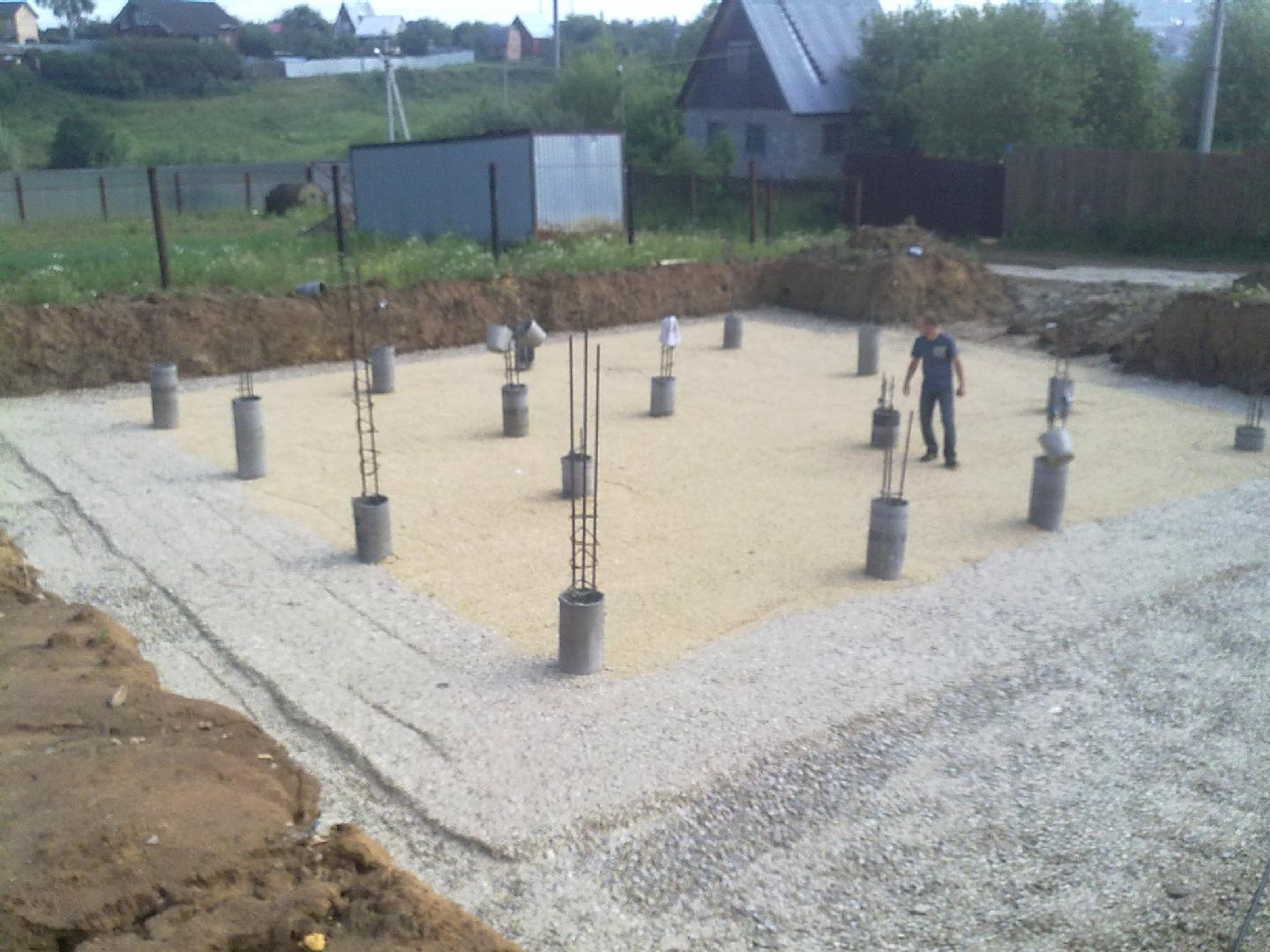
After the end of the marking, they start drilling wells. They have a certain depth and diameter, which provide the design parameters of the piles. A sleeve (casing pipe, permanent formwork) is lowered into the finished well - a pipe made of plastic or a rolled strip of roofing material. The sleeve will provide the necessary concrete hardening mode and prevent the premature release of water from the solution into the ground. In addition, the sleeve will subsequently serve as a waterproofing shell for the pile, preventing capillary impregnation of concrete with soil moisture.
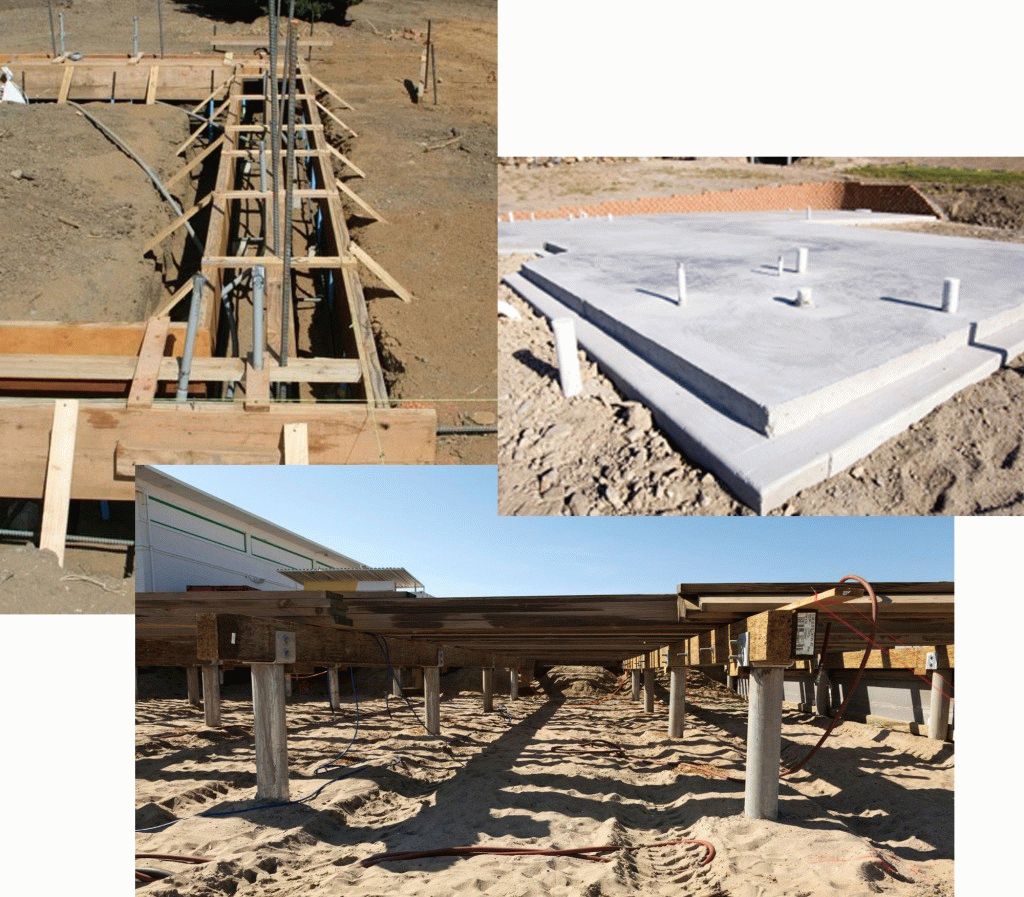
The next step is to make a reinforcing cage. For it, use metal or fiberglass reinforcement, assembled in a spatial lattice. Its dimensions in the section are 5 cm less than the diameter of the sleeve, and its height exceeds the depth of the well for subsequent integration with the plate armature belt. The finished frame is lowered into the well and the position is fixed in a stationary state.
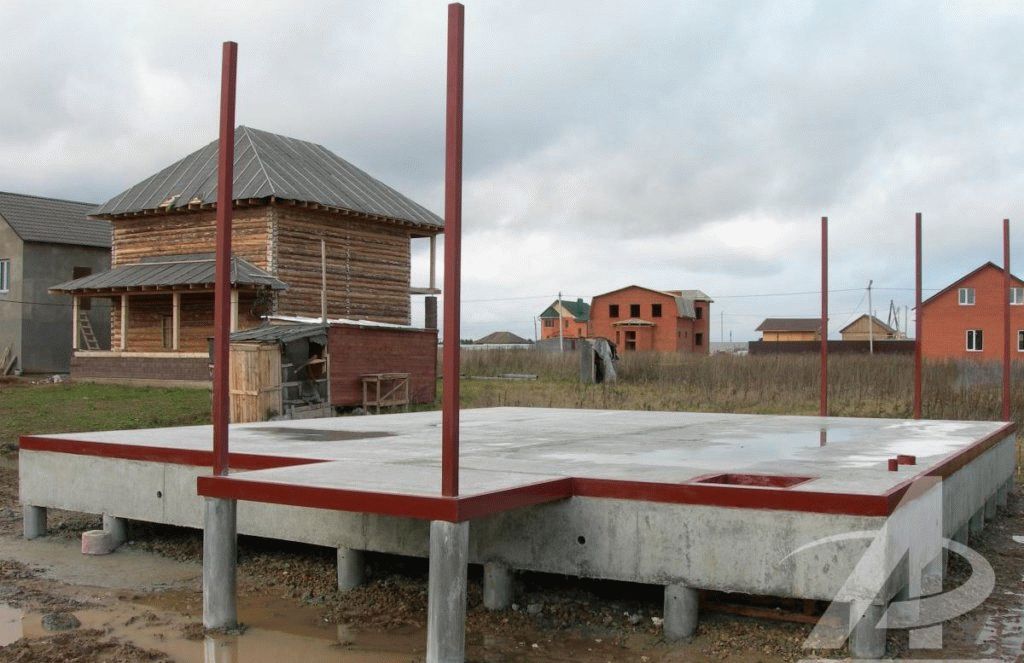
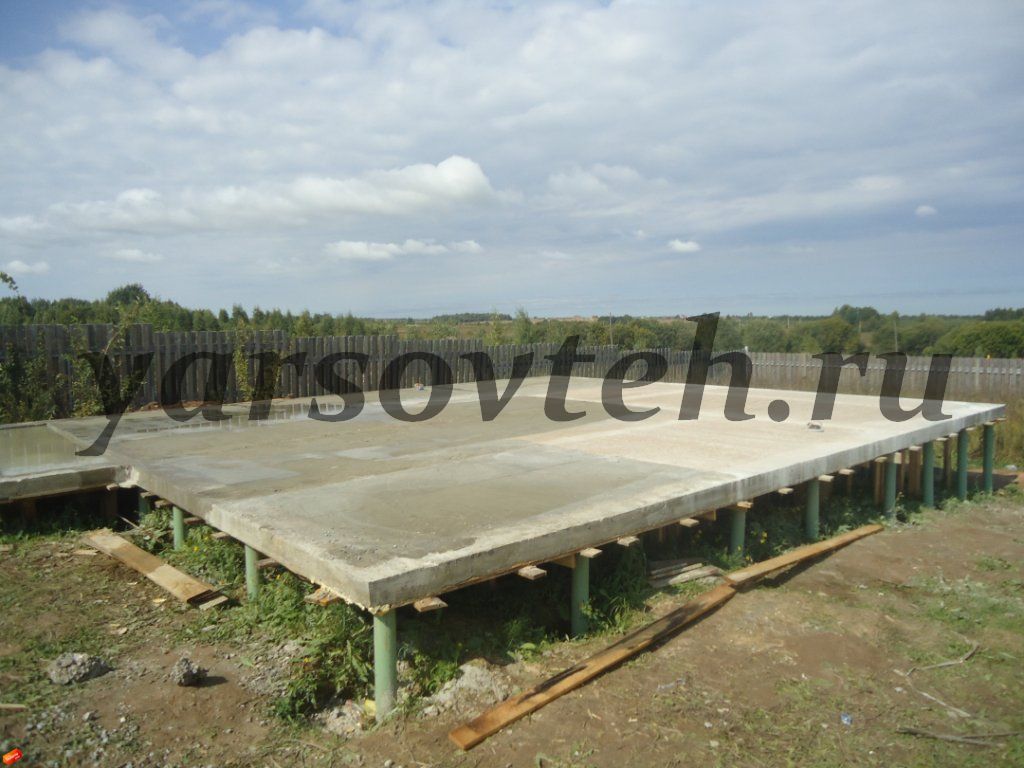
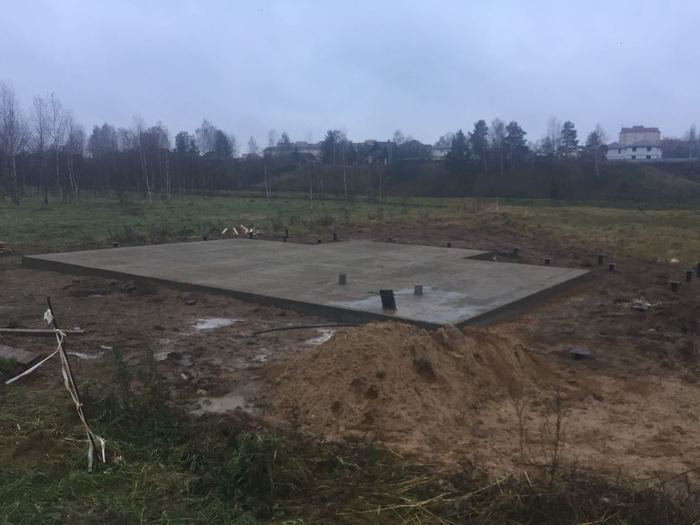
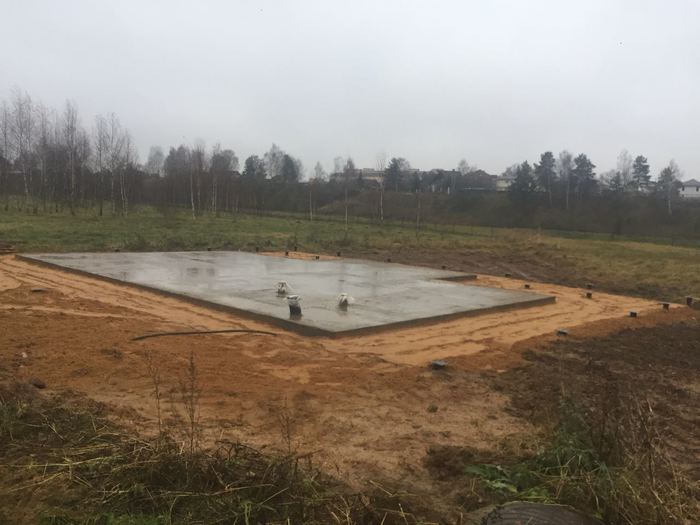
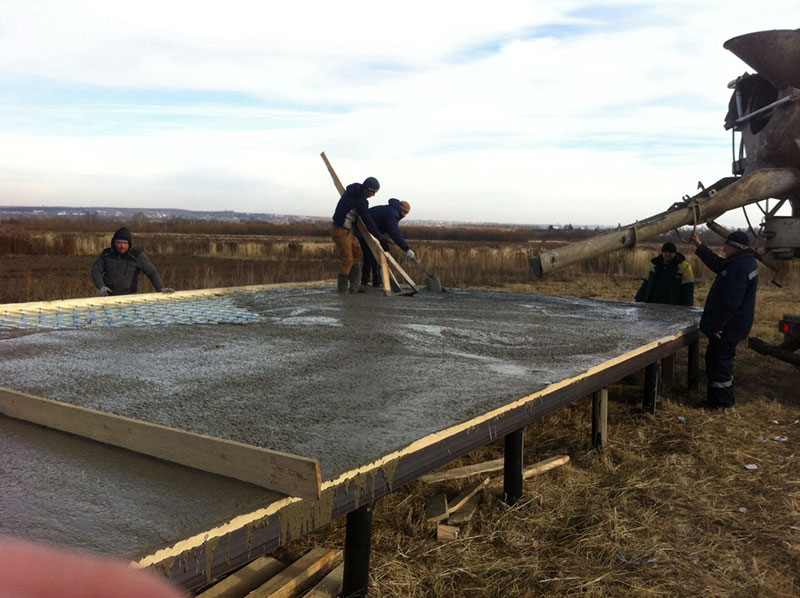
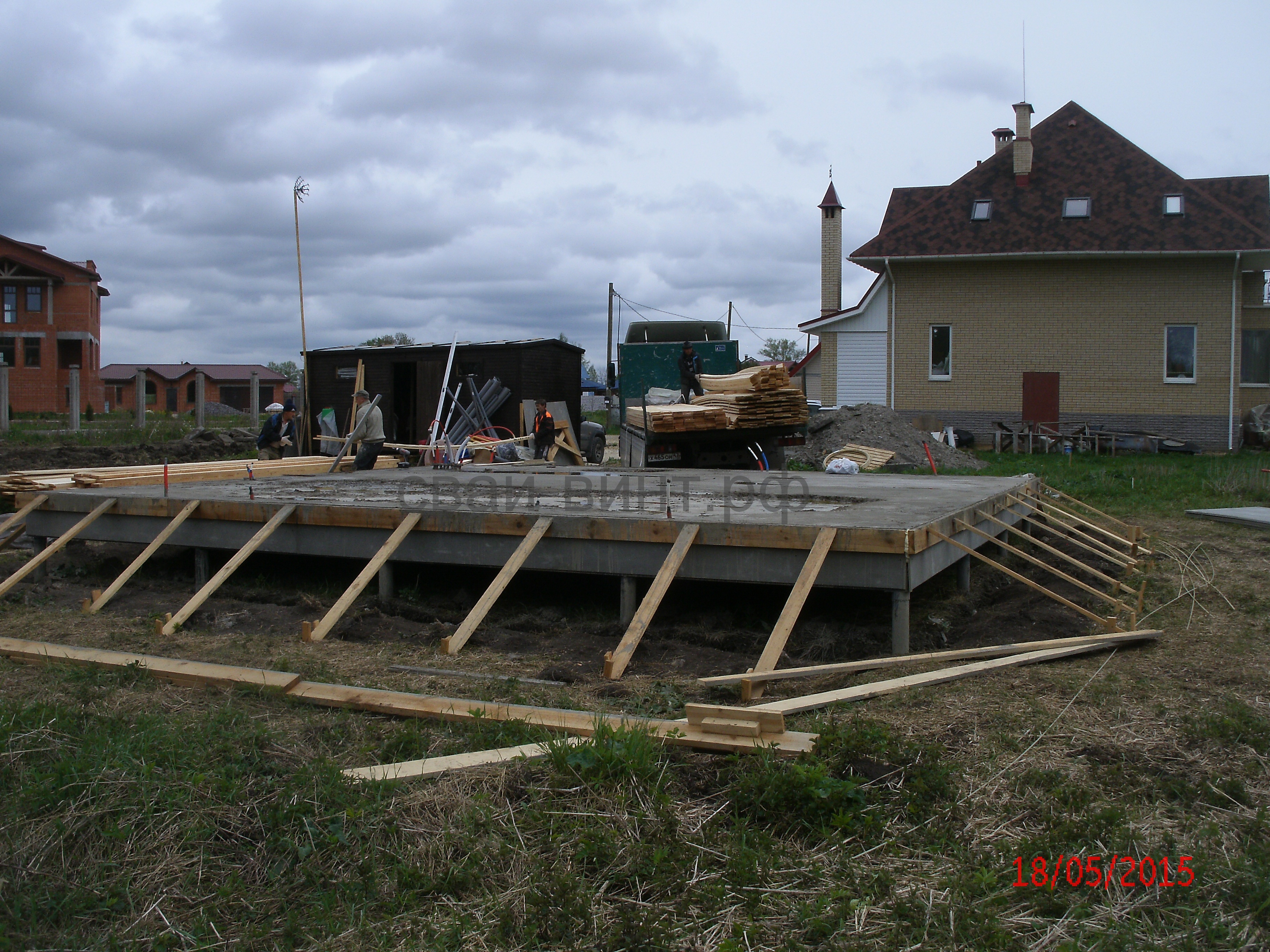
After all the wells are prepared, concrete is poured. For it, use the material of the M400 brand. You can make it directly on the site, but, to speed up the work and get the highest quality concrete, it is better to order the finished material with delivery directly to the construction site. Filling is carried out with simultaneous bayonetting to remove air bubbles and seal the pile shaft. After filling the sleeve, the top is covered with burlap and kept for the required time (2-3 weeks) to gain structural strength. The forced pause is usually spent on creating the formwork for the slab.
Pouring a monolithic slab
The concrete slab is poured using different pile connection techniques. Technologies can be applied:
- full integration of piles and slabs with a common armature belt;
- pouring the slab along the pile heads;
- making a "hanging" slab with an air gap between the soil surface and the underside of the slab.
Of these options, the most successful is the pouring of the slab along the pile heads. The reasons for this are:
- the absence of a rigid mechanical connection allows you to get some mobility of the foundation elements, which is useful in earthquake-prone areas;
- the presence of a seam between the concrete of the piles and the slab contributes to the waterproofing cut-off of capillary moisture.
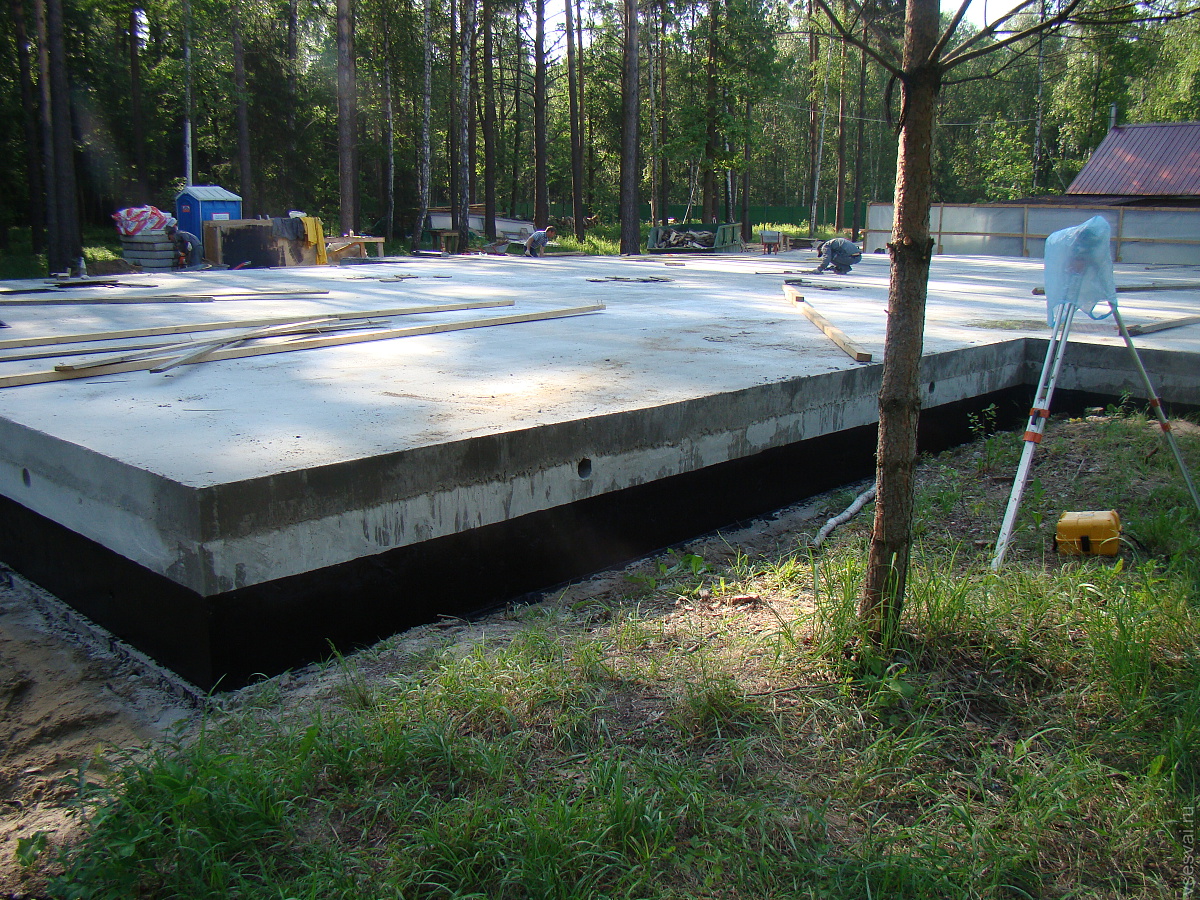
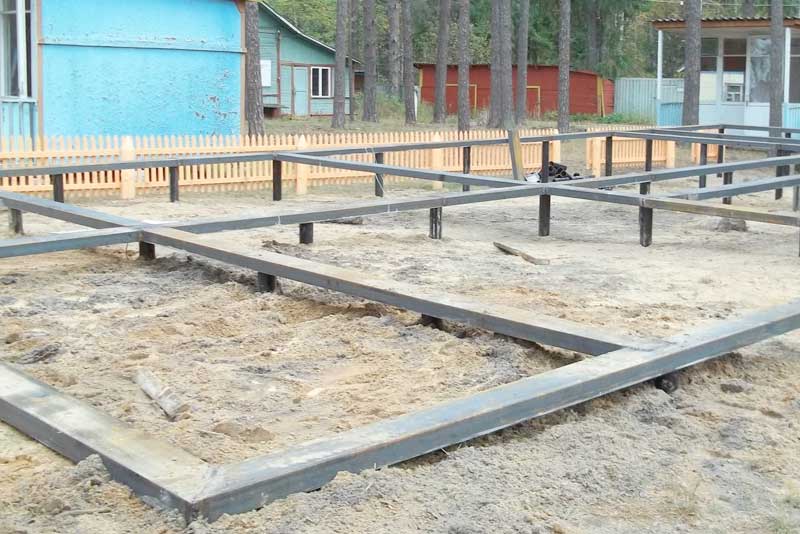
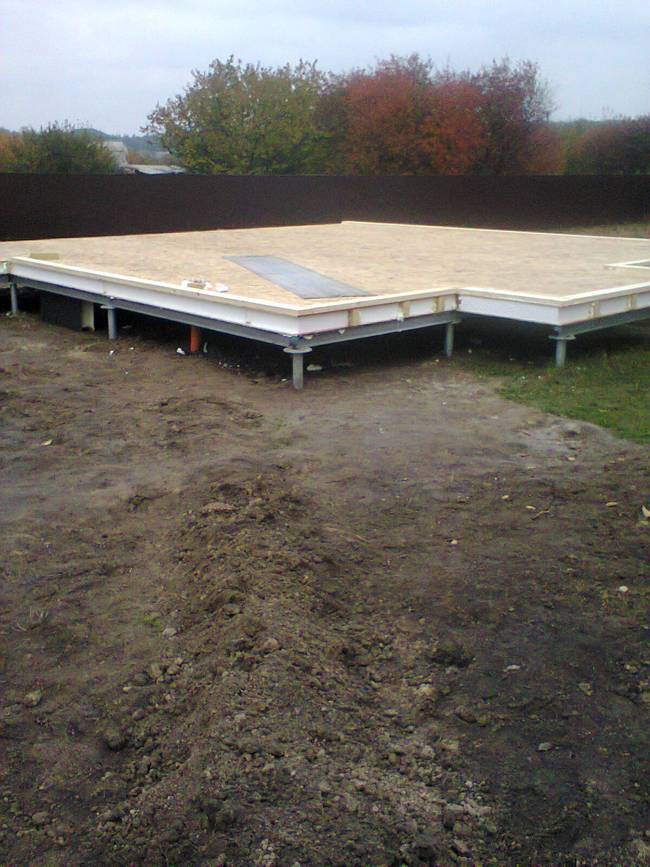
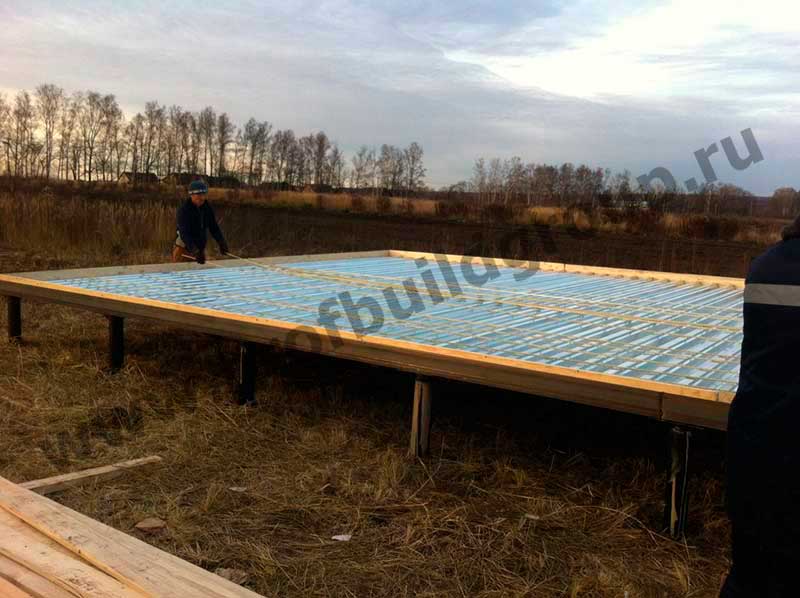
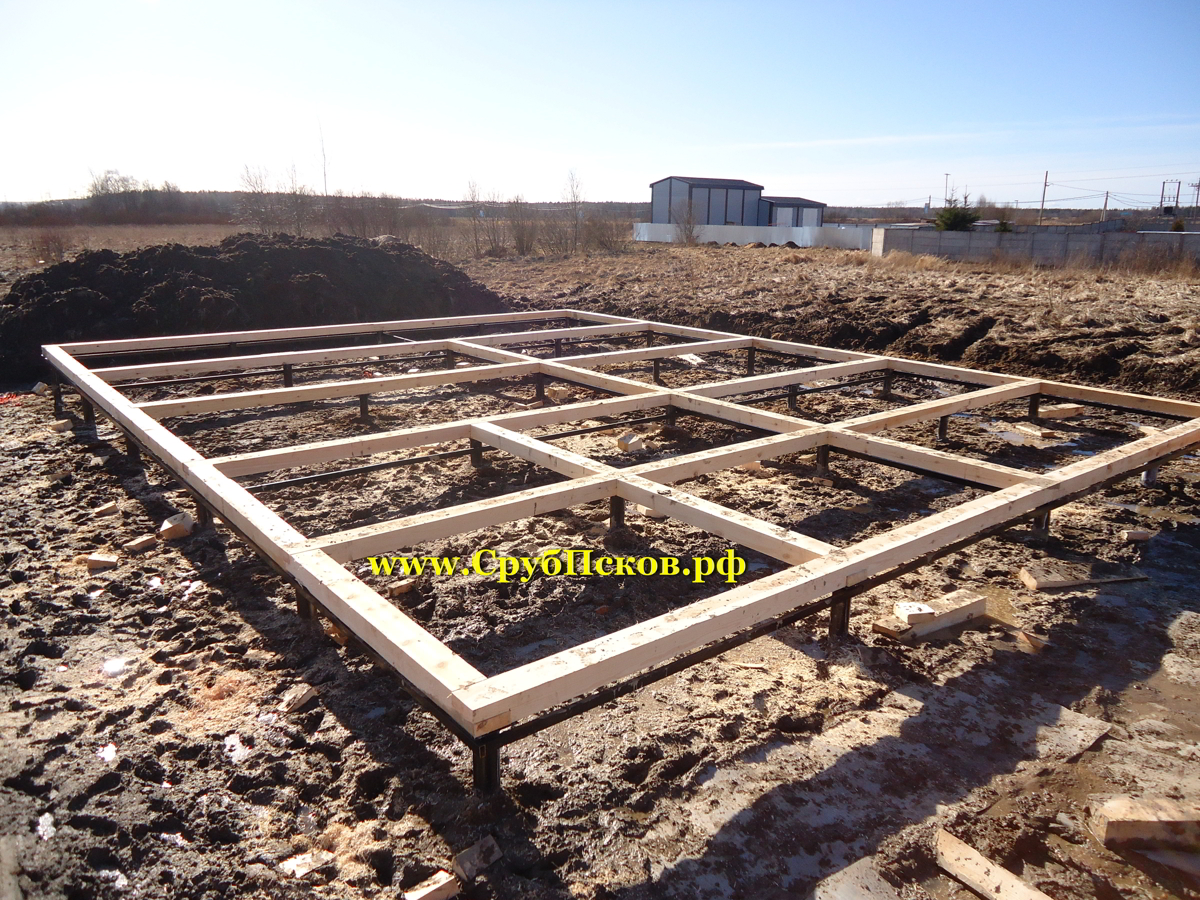
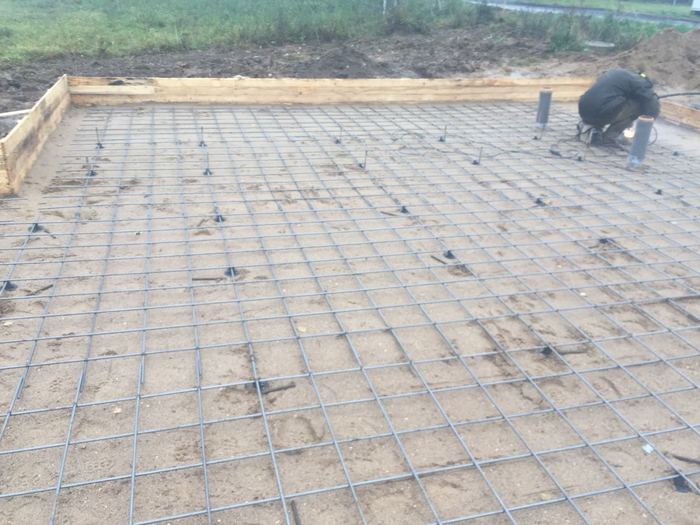
Before pouring concrete, it is necessary to carry out the entire complex of preliminary work - pour a sand cushion, lay a layer of heat insulator, assemble the formwork, tie the reinforcement cage.
A sand cushion 15-20 cm thick is carefully rammed and leveled horizontally.A layer of geotextile is laid on top of it, on which a heat insulator (foam for the foundation) is laid. After that, they proceed to the assembly of the formwork.
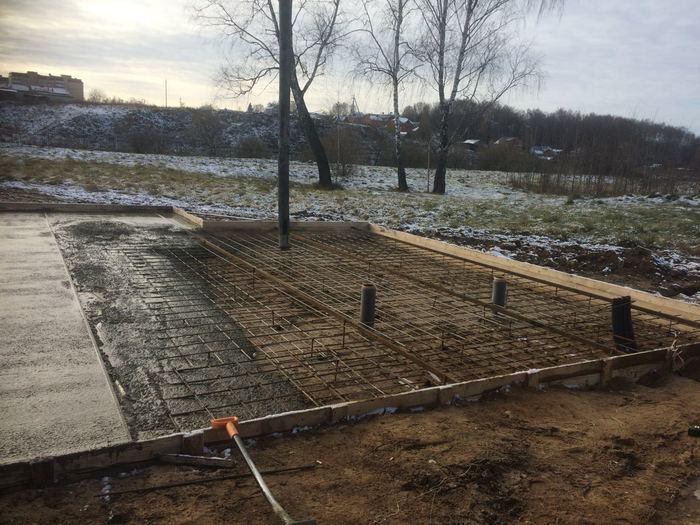
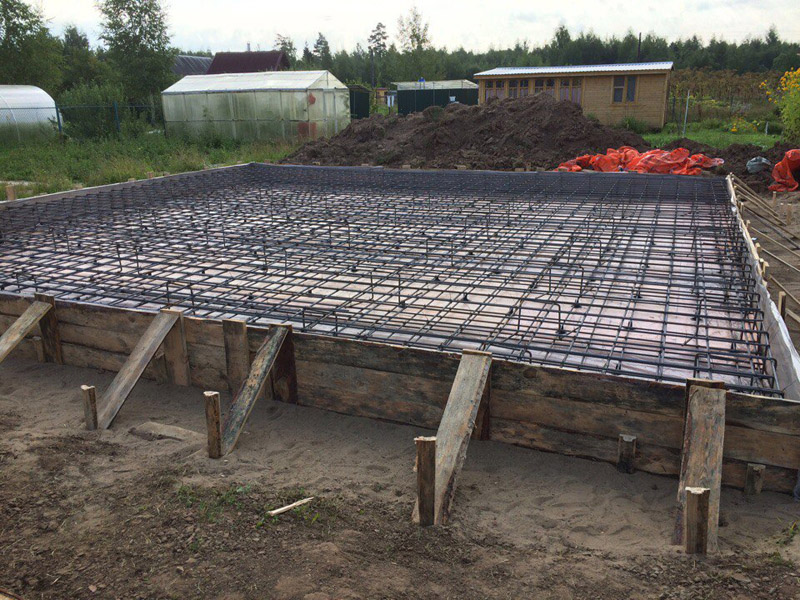
The mold for casting is assembled from boards, the height of which is 10-15 cm more than the thickness of the board. If you plan to manufacture a "hanging" slab, the design of the formwork becomes more complicated, since it must withstand the weight of concrete and reinforcement. Edged boards with a thickness of 25-40 mm are used for assembly. The assembly is carried out with the maximum density, without gaps and gaps.
The reinforcement belt is tied from metal corrugated rods. Annealed steel wire 1mm thick is used for the connection. The frame height should be 5 cm less than the slab thickness.
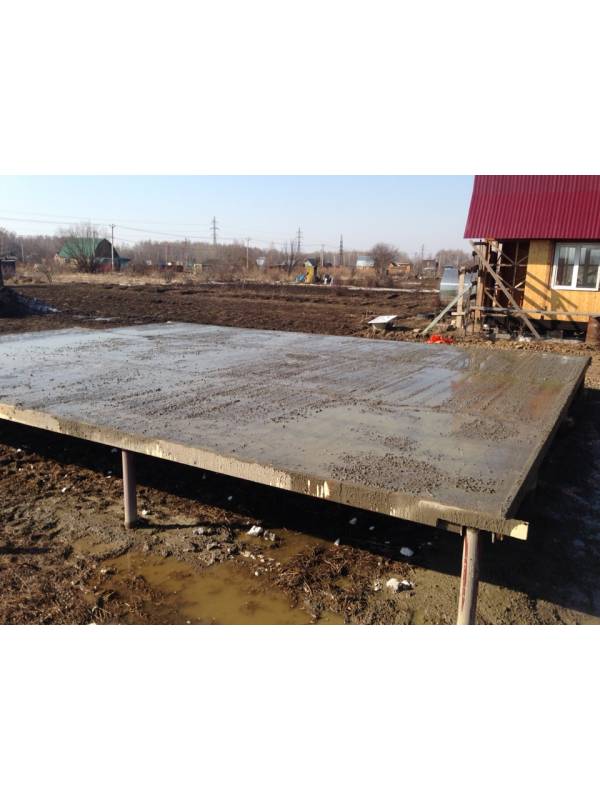
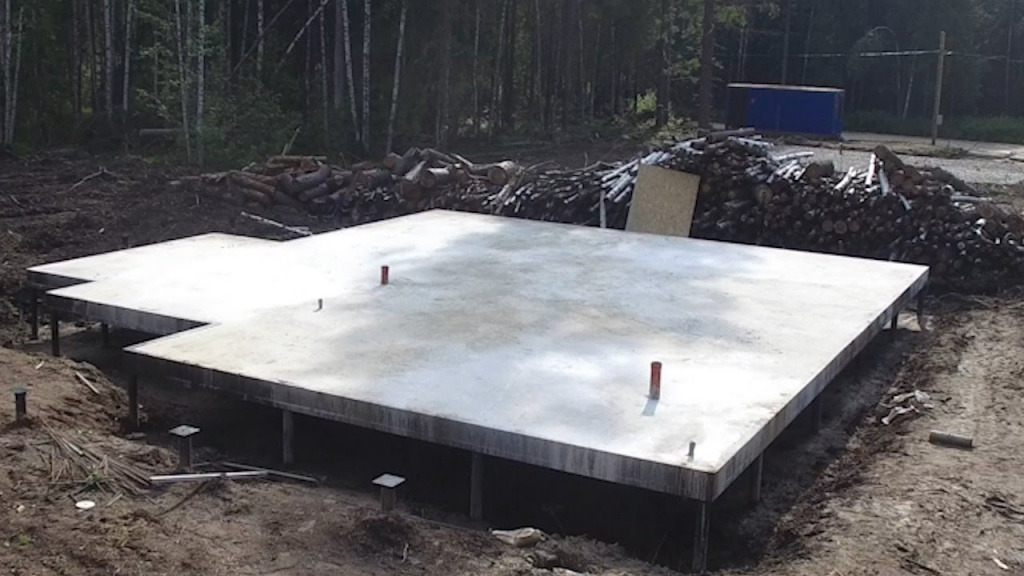
Pouring concrete should be done simultaneously. Interruptions of more than 1 day are unacceptable, since during this time the concrete will begin to set and the monolithic structure of the casting will not work. The fully poured and glued plate is covered with plastic or burlap from the sun. For the first 10 days, concrete is poured several times a day with water from a hose. The formwork can be removed after 2 weeks, and the construction work can be continued after 28 days.
Fields of application of SPF
- weak or loose soils;
- areas with a high level of groundwater occurrence;
- the presence of seasonal flooding;
- wetlands;
- peat bogs;
- high level of frost heaving.
These conditions require the use of reliable supporting structures - piles. They transfer the load from the weight of the house to dense soil layers located at great depths. The slab is an additional element that evenly distributes the load between all piles and absorbs vibration waves. As a rule, SPF is used for high-rise buildings. They place a significant load on the supporting structure and vibrate strongly during operation. A powerful slab on a pile foundation, which is an enlarged version of the grillage, connects all the piles into a single support system and absorbs parasitic vibrations from the structures of the house.
This is interesting: Types of paints for wooden floors - we state in all details
Payment
The procedure for calculating the SPF is complicated; for an unprepared person, this procedure is an insurmountable task. The pile-slab foundation, the structure of which consists of two nodes, requires a parallel calculation of the bearing capacity of the underground and aboveground parts of the foundation. It is necessary to determine:
- pile field configuration;
- type of piles;
- number of vertical supports;

- the scheme of their placement;
- depth and method of diving.
The calculation of the slab is no less complicated, in which the following parameters should be determined:
- the degree of settlement of both the slab itself and the entire base as a whole;
- roll level of the plane;
- the configuration of the slab, taking into account the uneven arrangement of the piles.
In addition, the base load is calculated based on the weight of the building. It consists of two quantities - building structures and a payload, which consists of the weight of finishing materials, furniture, people, and other objects and materials. To this are added the snow load on the roof in winter, the degree of wind exposure and other external factors. It is especially difficult to calculate a slab-pile foundation for a high-rise building experiencing increased external loads in combination with operational influences.
To perform a correct and correct calculation, it is required to attract a competent and experienced designer specializing in foundations of this type. Attempts to independently resolve the issue are doomed to failure, since, in addition to mathematical formulas, geological exploration data, the values of seasonal fluctuations in the level of groundwater, the depth of soil freezing and other special indicators will be required. Alternatively, online calculators can be used, of which there are quite a few online.
How to make a monolithic grillage on piles?
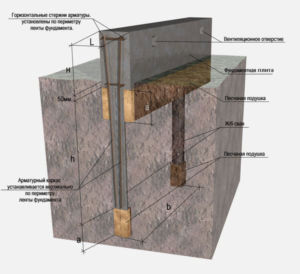 Diagram of a pile-based flare-up device
Diagram of a pile-based flare-up device
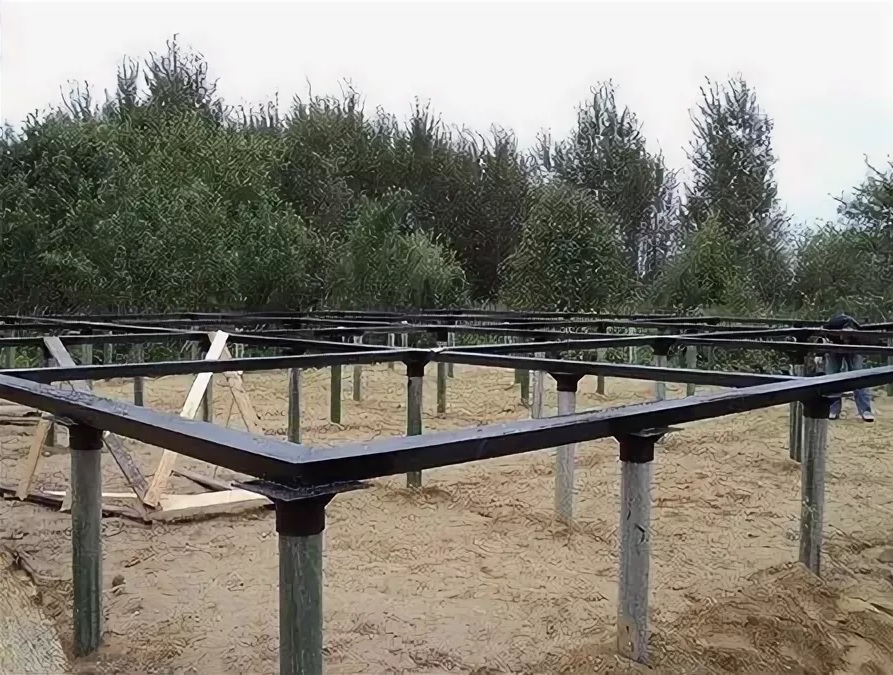
It is quite simple to build such a foundation with your own hands, this is the key advantage of pile-grillage foundations. This can be done as follows:
- develop a draft design of the future house, calculate the load from the side of the structure itself and the monolithic slab. Based on the data obtained, calculate the number and step of installing reinforced concrete piles, make a project for the future foundation;
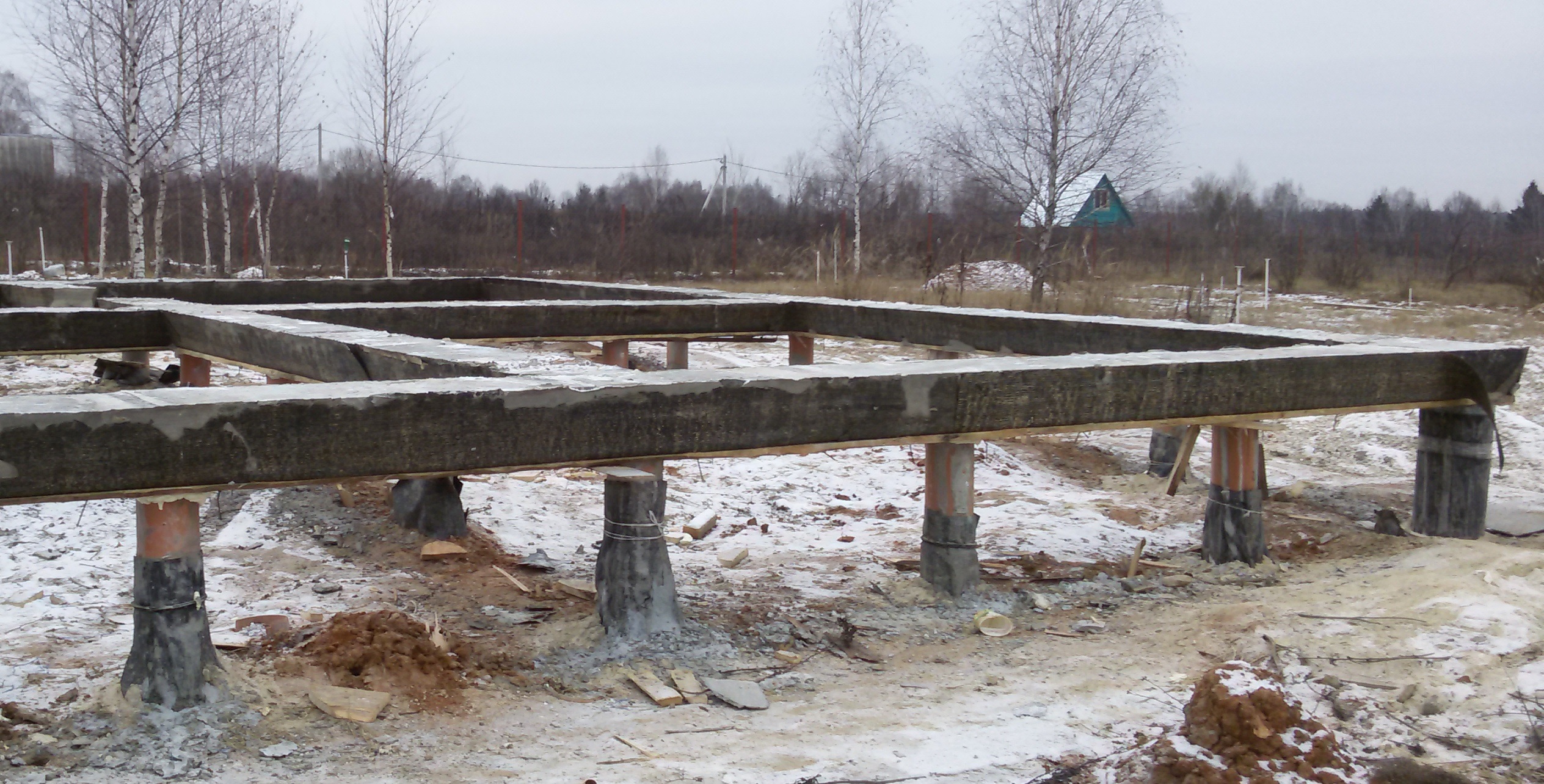
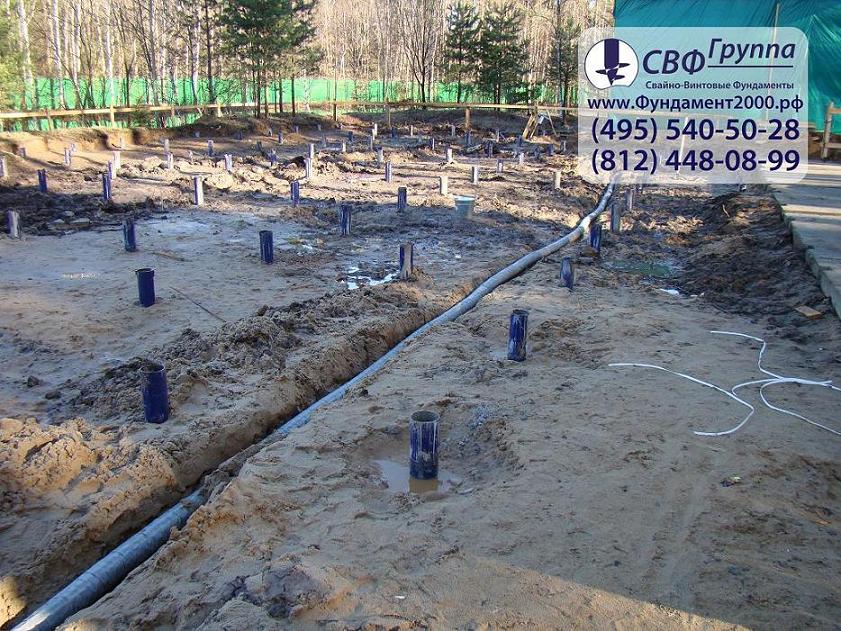
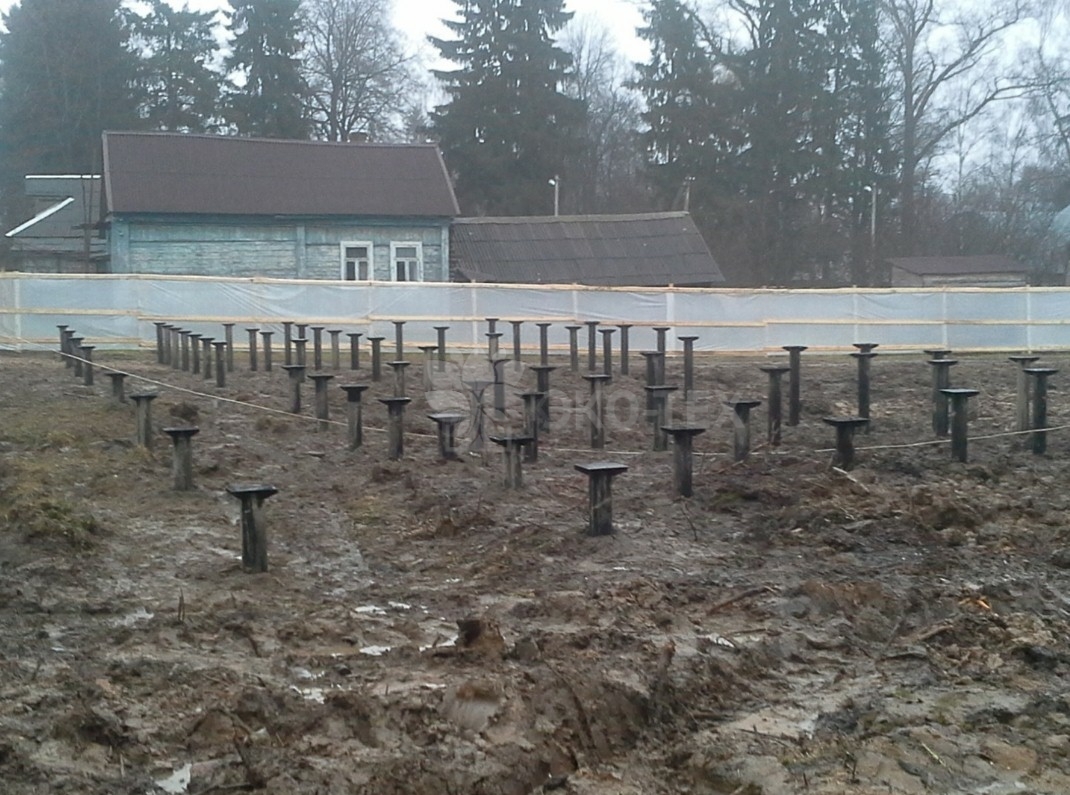
- according to the finished drawings, drill or dig wells to a given design depth. If the choice is settled on factory products with tips, they can be installed using a hammer;
- as soon as all screw piles are installed at the specified depth, they must be leveled horizontally and, if necessary, cut with a grinder. It is recommended to install the supports strictly vertically; deviation from the vertical is allowed no more than 2-3 degrees;
- then they begin to make the formwork. It can be made fixed from expanded polystyrene plates or removable from wood. The choice of the type and design of the formwork depends on the financial capabilities of the developer. All cracks and joints must be closed so that the concrete does not leak out, it is also recommended to strengthen the bottom of the formwork during pouring with concrete, so that it does not crumble from the mass of concrete;
- inside the formwork, install a reinforcing cage, calculated according to the principle as for a conventional monolithic slab, with the exception that the vertical rods will then be connected to the reinforcement of the supporting elements themselves;
- if a shallow or buried monolithic grillage is erected, then you must first dig a trench and install the formwork in it;
Next, the piles are poured with concrete, then a few days later - the grillage itself. The approximate time at which the concrete will pick up the given grade strength, depending on climatic conditions, is up to a month.
Overlapping on screw piles for a log house
The environmental aspect plays an important role in the choice of materials for the construction of a residential building or a bathhouse on piles. If the foundation of the house is made of screw piles, the upper part of the building is very often erected from wooden materials. Wood belongs to the classic, environmentally friendly, building materials that have been used for centuries for the construction of baths, residential buildings and outbuildings. How to properly arrange overlapping in a log house on screw piles? Let's try to figure out the technology of overlapping in a wooden building on pile-screw supports.
The technology of erecting a floor for a log house on screw supports
After screwing the required number of piles (screw) provided for by the project into the ground, the supports should be cut to one level, filled with concrete mixture and the heads should be strengthened on each screw support. The heads are strengthened by welding.
 Log house on screw piles
Log house on screw piles
Then you can start laying the lower crown, for which a wooden beam or a rounded log can be used. The cuts for fixing wooden parts are made strictly above the heads of the pile support elements.
There is another way, when the screw piles are connected by a grillage belt made of metal. Metal pins are welded along the entire perimeter of the grillage, which, during installation, must coincide with the drilled holes in the wooden parts of the lower trim of the building
In this case, it is very important not to loosen the support ring with too many drilled holes. Waterproofing between metal and wood parts must be done very carefully.
The connecting pins themselves need to be treated against corrosion (they are thickly covered with bitumen).
After that, they begin to lay a log from a bar, then a wooden floor is erected, which is at the same time a floor.
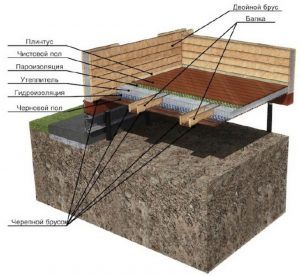
Floor "pie" (building overlapping on screw piles)
Considering that the building on screw piles has an unprotected space from below, is freely blown by the wind, it is necessary to properly arrange the overlap of the lower floor. To begin with, a supporting frame made of wood is laid, which is combined with a subfloor of wooden planks. Watch the video on how to make the ceiling on screw piles correctly.
A layer of foil insulation will protect the first floor from heat escaping. Then the main heat-insulating layer is laid, which is covered with roll film materials for isolation from moisture and steam. The completion of the puff "pie" of the floor, combined with the floor, are the boards of the finishing coating.
The following materials are used for the floor insulation device:
- Sheets of polystyrene - sheets of material are laid on the subfloor. It should be noted that with insufficient insulation from moisture and low temperatures, the foam easily collapses, breaking up into small segments. In general, sheet polystyrene, as insulation, does an excellent job.
- Mineral wool - insulation is offered for sale in the form of separate mats or in rolls. Mineral wool can be slag, glass or stone - all types are perfect for insulating the ceiling of buildings on screw piles. Protect the material from moisture.
- Penoplex, expanded polystyrene - materials ideally protect building structures from freezing and high humidity. Insulation of floors of buildings on screw piles with expanded polystyrene or expanded polystyrene is the most reliable method of all available today.
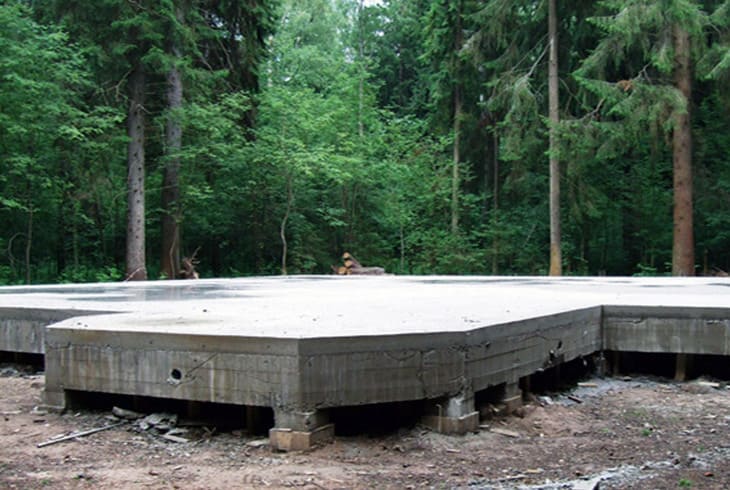
A pile foundation with a monolithic slab is one of the popular foundation options
A reliable foundation on single supports is gradually gaining popularity among private developers, as it has several main advantages over other options. It is faster to build a pile foundation, you do not need to carry out voluminous earthworks, you can cover a much larger area and build a cottage with an impressive area - all this indirectly leads to significant savings in money, both in the construction of the foundation and in the construction of the entire private house.
The monolithic grillage connecting the protruding parts of the supports also has several advantages that affect the durability of the building and its structural strength:
- A full-fledged slab of small thickness initially serves as a rough floor and does not require the creation of an additional floor;
- The load from the weight of the building and the reverse pushing force from the ground are evenly distributed over the entire area, loading even those piles that stand on a more durable
- basis. Thus, the pressure on each individual element is reduced and the structure does not collapse;
- The ability to create several options for the location of the base in relation to the soil surface - high, at ground level, slightly recessed. Each of the methods is applied based on the characteristics of the site and after processing the geological exploration data;
- External finishing of the foundation may not require additional external insulation, since the closure of the space creates a kind of air barrier that reduces heat transfer between the house and the environment. Even without external decor, it is enough to insulate the pile base with a monolithic slab from the inside of the house in order to obtain a normal microclimate inside the premises;
- Construction can be carried out at different times of the year. InnovaStroy specialists use concrete with special additives to expand the temperature range of application - the base can be poured even in winter or autumn;
- Full reinforcement of a monolithic slab, as a rule, is associated with reinforcement inside the piles - this makes the foundation completely unified and increases its resistance to external factors.Properties such as tipping and pushing out of the soil, typical of sloped sites, will not affect the condition of your suburban residence.
Types and purposes
Overlap - a structure that divides the building vertically (usually the overlap is arranged above the technical underground and between floors). Floor slabs perceive loads from the weight of building elements, furniture, people in the house, and then transfer these loads to the walls of the building.
 Basement construction
Basement construction
Overlappings are usually subdivided according to their location:
- Underfloor (basement) - these structures serve to protect the building from the outside environment (when constructing a house on screw foundations), as well as to separate it from the basement, basement or technical underground.
- Interfloor - these overlaps are arranged between the floors of a building during the construction of an object of several floors.
- Attic - necessary in the construction of buildings with attics and attic, their purpose is to separate living quarters from attic.
In this article, we will try to find out how to properly arrange a basement overlap on a pile-screw foundation (screw piles).
Monolithic slab - "floating foundation" for peatlands
 The main difference between a monolithic slab and other types of foundations is that when the soil moves (buckling), the foundation moves along with the constructed objects, which eliminates the occurrence of distortions and uneven settlement of the building. When moving in a horizontal plane, the slab with buildings smoothly moves (floats), without causing destruction of the buildings erected on it.
The main difference between a monolithic slab and other types of foundations is that when the soil moves (buckling), the foundation moves along with the constructed objects, which eliminates the occurrence of distortions and uneven settlement of the building. When moving in a horizontal plane, the slab with buildings smoothly moves (floats), without causing destruction of the buildings erected on it.
This type of foundation is suitable for light buildings (buildings made of wood or low-rise foam concrete blocks), in which case a monolithic slab can be erected without additional stiffening ribs.
The most important requirement for a monolithic slab to create a reliable foundation for the building is to create a perfectly flat area for the slab device. To do this, it is necessary to plan an area with a restless relief, having previously removed all vegetation.

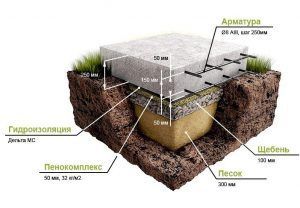
If the site for the installation of a monolithic slab has a slope, even the smallest, the constructed building can slide off the foundation when the soil vibrates. The cleared areas for the construction of a monolithic slab are covered with construction waste, rubble. The backfill layer requires natural shrinkage, if it is not possible to wait for about a year, artificial compaction of the bulk layer is used by rolling with mechanical rollers.
For the compacted layer of crushed stone, it is necessary to perform concrete preparation, for which a removable formwork is made that exceeds the dimensions of the foundation slab. A thin layer of concrete is poured into the installed formwork, which should gain strength within several days.
A solidified, durable layer of concrete pouring is laid with a layer of insulation up to 10 cm thick, for this they use Penoplex or expanded polystyrene. Geotextile is spread over the layer of insulation, the edges of which are welded with an overlap (two strips should have an overlap strip of at least 10 cm). Geotextile is a protective layer that protects the concrete screed from destruction.
A layer of waterproofing is laid over the geotextile, using diffusion film membranes to protect against groundwater. The diffusion film strips are edge sealed with two parallel seams with an air pocket between them.
 The next layer is geotextile, along which a thick polyethylene film is laid. If the film consists of stripes, they are glued together with double-sided tape.
The next layer is geotextile, along which a thick polyethylene film is laid. If the film consists of stripes, they are glued together with double-sided tape.
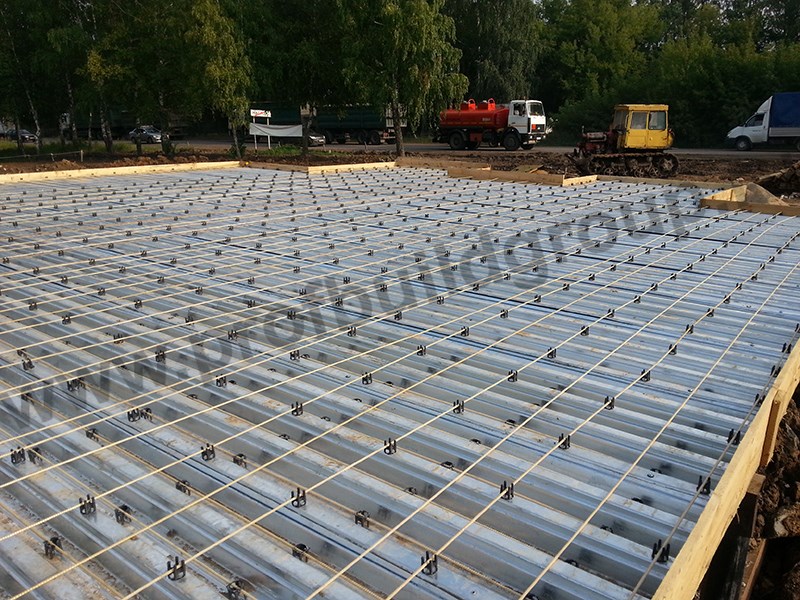
After laying the insulating layers, the formwork is set to the size of the required monolithic slab. On the formwork, the level of the required concrete fill can be marked. A special frame made of reinforcing mesh from a reinforcing bar with a diameter of 12 to 16 mm is laid in the formwork.
The laid concrete mixture must be tamped with a special vibrator - mixing the concrete mixture allows you to remove air bubbles that could have formed during the concrete pouring. The top of the slab is smoothed with a vibrating screed, achieving a perfectly flat surface.
 The concrete, which has gained strength, is protected from the effects of soil moisture with the help of a coating waterproofing.
The concrete, which has gained strength, is protected from the effects of soil moisture with the help of a coating waterproofing.
The monolithic slab works ideally on peat soils, ensuring the stability and durability of the constructed buildings. However, the work on the device is very laborious, and the cost of materials is very high. Foundations on the peat bog can be made using a different technology - with the strengthening of the base of the site with the help of screw piles.
Excavation of peat soil
 There is another technology for constructing foundations in wet peatlands - excavation. Using this technology, peat is removed from the building site, if only the thickness of the peat layer is insignificant, after which foundation structures are erected on dense soils. Determining the thickness of a peat bog is a very serious operation, in which it is necessary to punch several pits in the area in different places, with a depth of 1 to 2 meters. This allows you to better verify the length and thickness of the peat layer.
There is another technology for constructing foundations in wet peatlands - excavation. Using this technology, peat is removed from the building site, if only the thickness of the peat layer is insignificant, after which foundation structures are erected on dense soils. Determining the thickness of a peat bog is a very serious operation, in which it is necessary to punch several pits in the area in different places, with a depth of 1 to 2 meters. This allows you to better verify the length and thickness of the peat layer.
The extraction of peat is carried out by mechanized equipment with the subsequent planning of the site.
There are many ways to build foundations on soft and wet soils containing peat - it is always worth choosing the most suitable one for each specific case.
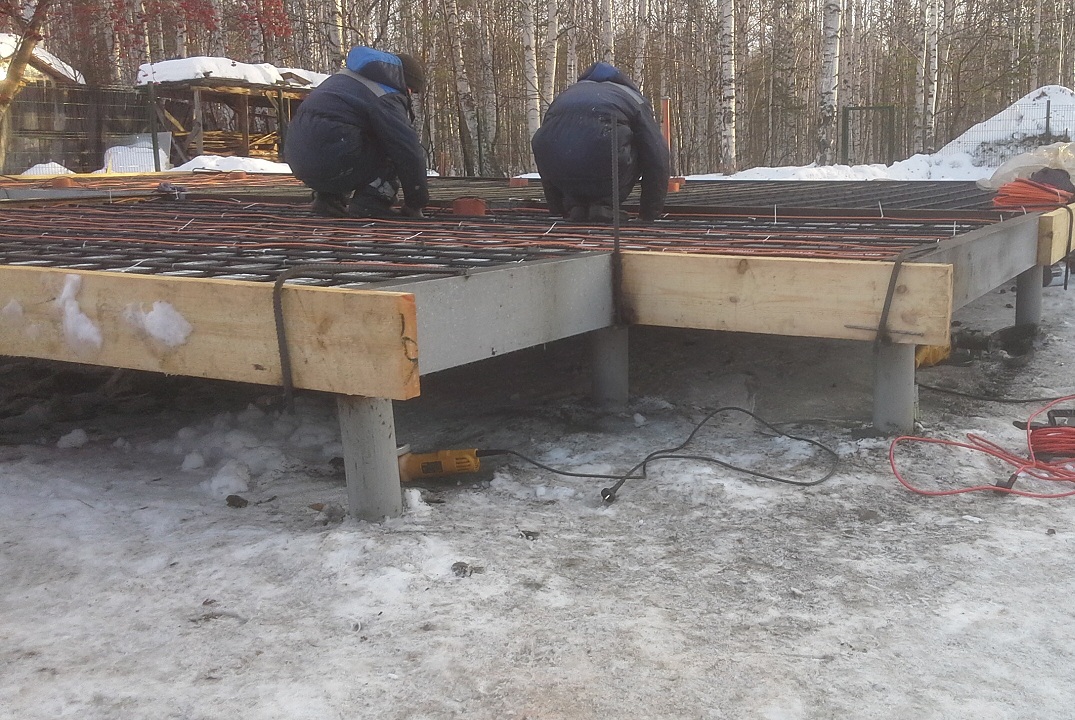
Reinforcement of a monolithic slab on piles
 Reinforcement of the support and foundation monolith
Reinforcement of the support and foundation monolith
The peculiarity of the reinforcement of a monolithic foundation is that it is necessary to connect the reinforcement cage of the bearing supports and the grillage into a single structure. For reinforcement, it is necessary to create two independent reinforcement belts, one on top and one on the bottom. In each section, at least two longitudinal reinforcement must be used. For reinforcement, spiral-type rods with a diameter of up to 14 mm are used, and for vertical rods - up to 9 mm smooth.
Transverse reinforcement has nothing to do with loads, it knits the entire structure into a single frame
The reinforcement cage is completely immersed in the concrete solution, during installation it is important to always leave the upper ends of the rods - they are then connected to the reinforcement of the bearing supports
Before pouring a monolithic slab, a flexible connection is made at the points of contact between the formwork and the internal frame of the slab. If steel bearing supports are used, then the heads are welded to the lower reinforcement chord. At the same time, the lower edge of the belt should be buried in concrete to a thickness of up to 5 cm in order to protect the metal from corrosion. The frame for the slab is considered complete, the distance between the belts is up to 10 cm, and between the vertical rods - up to 50 cm.
Piles also need additional reinforcement, especially if they are reinforced concrete or steel structures. Wooden and steel supports are not reinforced, they are connected with reinforcement or wire rod to each other. For a reliable connection of the grillage and supports, the heads are welded with wire rod or rods to the bottom layer of the slab reinforcement. The width of the grillage should be slightly larger than the outer dimensions of the sections for better reinforcement of the structures.












































