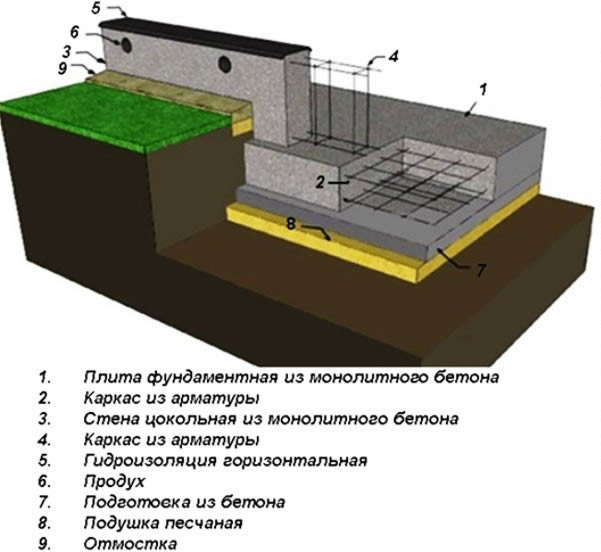
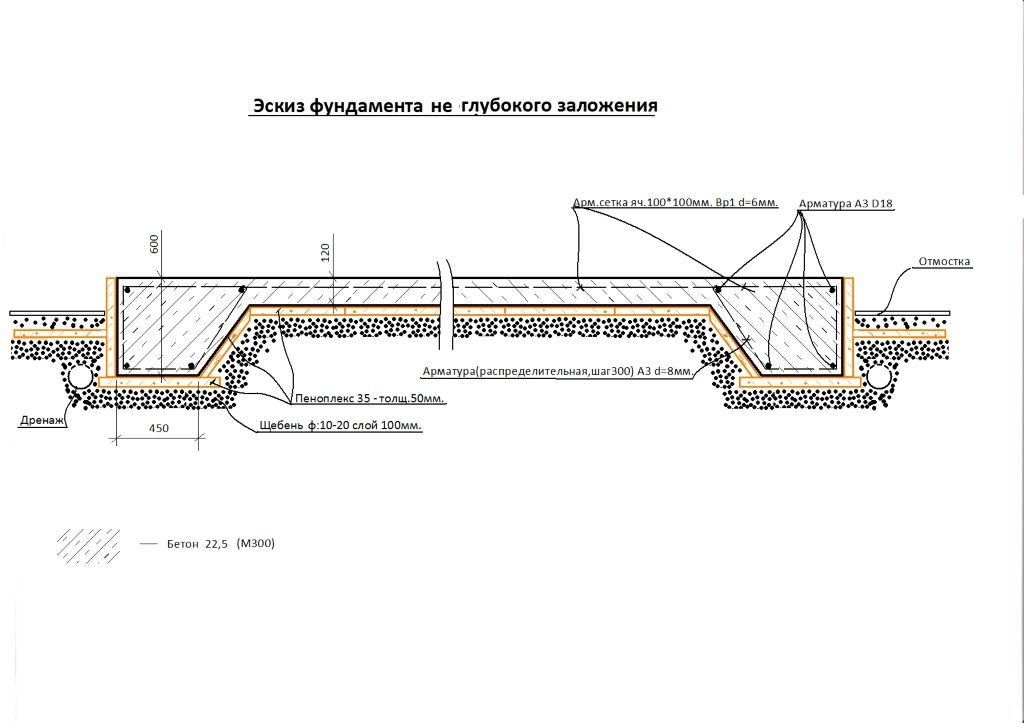
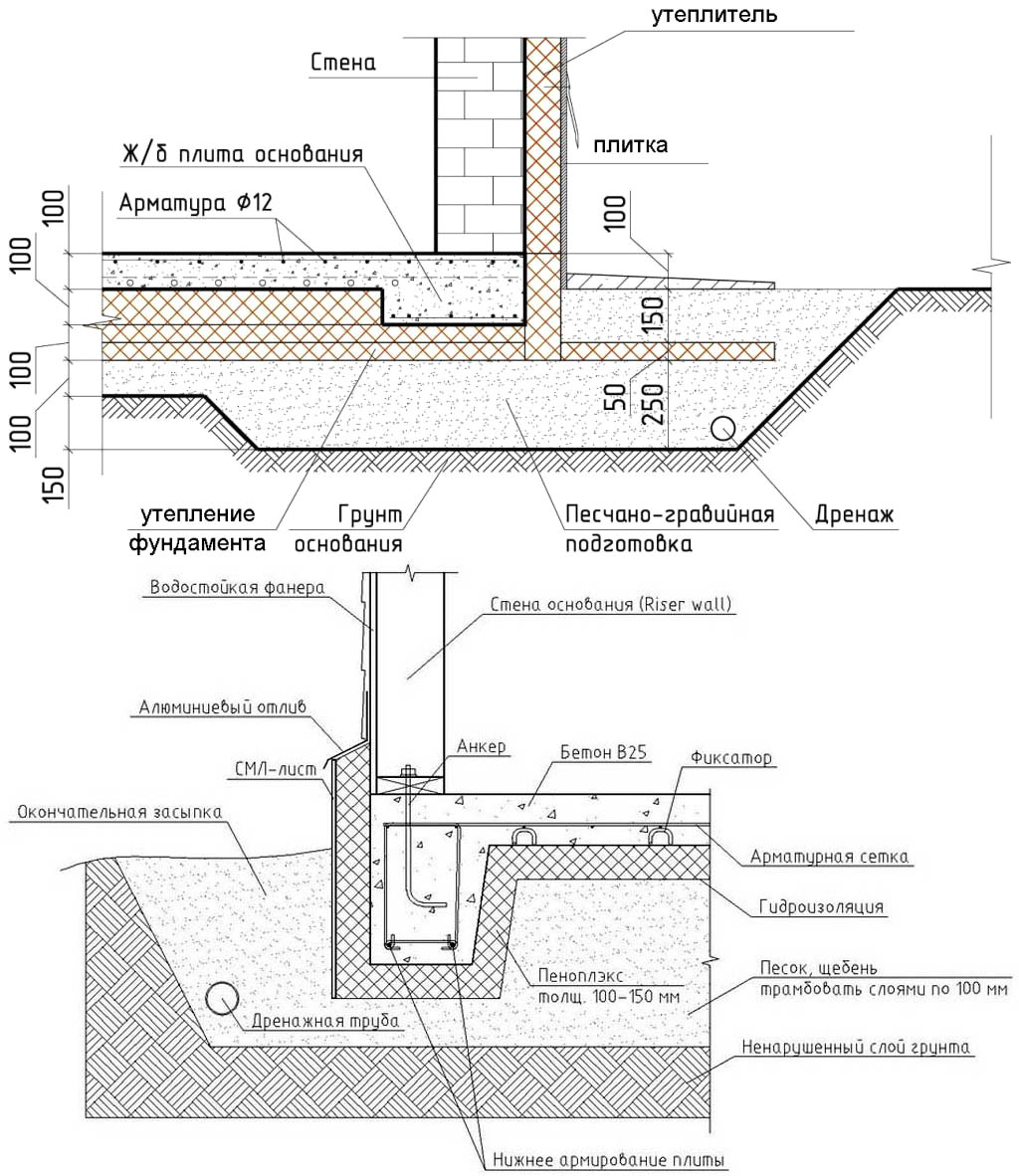
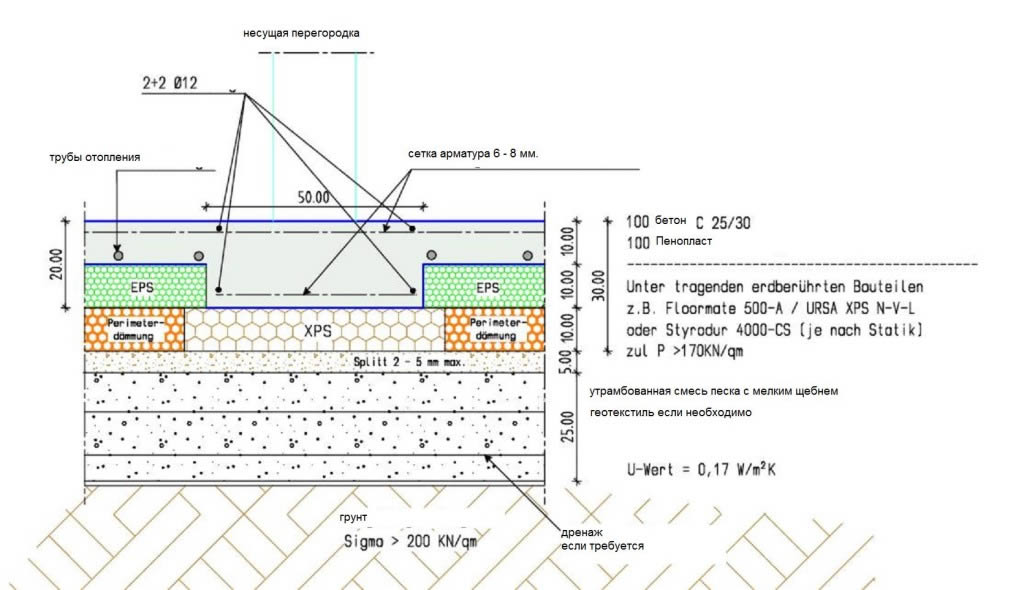
An example of self-calculation of the width of the strip foundation
To better understand how to calculate the width of a monolithic tape, you need to consider this with an example. Initially, you need to systematize the initial data necessary for the calculation.
- the size of the house in the plan is 10 mx 10 m. The building area is 100 m 2;
- inside the house there is a load-bearing wall in the middle;
- brick walls, 1 brick thick - 250 mm and 2.7 m high. Specific weight of brickwork - 1600 kg / m 3;
- slate roof - 40 kg / m 2;
- floor from reinforced concrete slabs - 500 kg / m 2;
- depth of soil freezing - 700 mm;
- groundwater level - 2.2 m;
- soil base - dry loam of medium density with a design resistance of 2 kg / cm 2;
- snow load - 50 kg / m 2;
- payload - 20 kg / m 2.
Determination of the total load from the house on the strip monolithic foundation
Based on the available initial data, the total load on the foundation is calculated. The dimensions of the monolithic tape are also determined. It is necessary for developers to make a calculation in the following order:
Roof
Gable slate roof. Taking into account the slope of the roof and its overhangs, a coefficient of 1.1 is applied. The load from the roof will be: 100 m 2 x 1.1 x 40 kg / m 2 = 4000 kg.
Brick walls
To determine the load from the walls, knowing their thickness, you need to calculate their length. The length of the walls along the perimeter will be: (10 x 4) - (0.25 x 4) = 39 m. The deduction of twice the thickness of the brickwork is made because the axes of the house plan are drawn in the middle of the thickness of the walls. The length of the internal load-bearing wall will be 10 - 0.25 = 9.75 m. The total length of the load-bearing walls will be equal to 48.75 running meters.
The volume of brickwork will be: 48.75 x 0.25 x 2.7 = 32.9 m 3. The total load from the brick walls is 32.9 x 1600 = 52 670 kg.
Reinforced concrete slab overlap
The one-storey house has floors on two levels. This is the overlap of the basement and the ceiling in the house. The overlap area is: 100 x 2 = 200 m 2. Accordingly, the load from the floor slabs will be equal to: 200 m 2 x 500 kg / m 2 = 100,000 kg.
Snow load
To calculate the snow load, take the total area of the roof of the house - 100 x 1.1 = 110 m 2. The snow load will be: 110 m 2 x 50 kg / m 2 = 5,500 kg.
Payload
The rate of this load is calculated on the basis of the average values of the weight of technical equipment, internal communications, interior decoration, furniture, and others. The specific weight of the payload ranges from 18 to 22 kg / m 2.
The payload is calculated on the basis of an average of 20 kg / m 2. The weight will be: 100 m 2 x 20 kg / m 2 = 2000 kg.
In total, the total load on the foundation will be equal to: 4,000 + 52670 + 100,000 +2,000 = 159,000 kg.
Calculation of the width of a monolithic tape
According to the above formula, the minimum footprint of the foundation is determined:
(1.2 x 159,000 kg): 2 kg / cm 2 = 95,400 cm 2. That is, the minimum allowable footprint of the base of the house will be 10 m 2.
The total supporting area of brick walls is determined by the product of the length in terms of load-bearing walls by their thickness: 48.75 mx 0.25 m = 12.18 m 2.
As a result, it can be seen that the calculated reference area is less than the minimum reference area of the walls. Therefore, the width of the strip footing should be 250 mm + 100 mm = 350 mm.
The need for materials for the device of a monolithic tape
Considering the thickness of the soil freezing (0.7 m) and the depth of the groundwater level (2.2 m), the monolithic tape is made shallowly buried - 1 m.
For pouring the formwork, concrete M 300 is used. The volume of the need for concrete solution is: 0.35 mx 1 mx 48.75 m = 17 m 3.. Taking into account unforeseen losses, the need for concrete will be 17.3 m 3.
The reinforcement cage consists of 4 longitudinal reinforcing bars of a periodic profile with a diameter of 12 mm. Since the transverse rods of the frame are made from the same rods, the total need for reinforcement will be: 50 mx 4 = 200 m.
From all of the above, we can conclude that calculating the width, height and length of the strip foundation for your home is quite within the power of people who are in the slightest degree versed in the construction business.
Foundation calculation
This procedure, as a rule, does not cause serious complications if approached with the proper level of responsibility. It involves the collection of load data and the study of the bearing layers of the soil. The thickness of the foundation for a two-story house will be determined depending on the ratio of these two components.
The video explains in detail how to calculate the base yourself.
The first step is to conduct a thorough study of the working area. The depth of the foundation for a two-story house made of foam blocks should be 35–55 cm higher than the average freezing depth.
Formwork and reinforcement
Such data are acceptable only if the living space is heated in the winter season. Otherwise, it is necessary to adhere to the set freezing temperature for a particular region.
The relative value of the width of the tape will be 25 cm. This value is approximate and will change during the calculation.
The next step is to calculate the pressure on the strip foundation for a two-story house. It is advisable to use the table below to determine the appropriate value.
| Construction type | Density (kg / m2) |
|---|---|
| Walls | |
| Brickwork (half brick) | 210–240 |
| Foam concrete houses | 170–180 |
| Log houses (d = 240 mm) | 130–145 |
| Houses from a bar (150 mm) | 11–125 |
| Overlap elements | |
| Attic (wooden beams) | 10–120 |
| Hollow concrete slabs | 30–380 |
| Reinforced concrete floors | 450–520 |
| Roof | |
| Metal tile, profiled sheet | 25–35 |
| Two-layer roofing material | 35–45 |
| Slate (comb height - 4 cm) | 50 |
| Snow load for the central regions of Russia | 100–120 |
The next step is to calculate the total weight of the strip slab. To do this, you must first calculate its volume, which is calculated using the product of length - L, width - A and height - B.
The resulting value is multiplied by the specific gravity of reinforced concrete, which is 2500 kg / m3. The end result is total weight. To calculate the total load - M - on the supporting soil layer, it is enough to add this value with the weight of the building.
Now it becomes necessary to set the optimal value of the base sole width - O. It is derived by the following formula: O = 1.3 * M / (L * R). A value of 1.3 serves as an indicator of the bearing capacity, and R is the density of the soil layer, which is indicated in the table below.
| Soil type | R |
|---|---|
| Clay with pebbles | 4,2–4,5 |
| Pise | 4 |
| Coarse sand | 6 |
| Medium-grained sand | 5 |
| Fine-grained sand | 4 |
| Sandy loam | 3,2–3,5 |
| Loam | 3,2–3,5 |
| Clay | 6 |
If the width of the tape is less than the approximate value, the final width will be the declared 20 cm. If, according to the results of the calculations, this value has exceeded the initial figure by more than 4–6 cm, it is necessary to re-calculate the base mass with a new value of the width of the tape.
What parameters affect the calculation of the slab.
The thickness of the foundation slab for the aerated concrete house. A diagram showing the thickness of all layers of the slab foundation.
- the material of the future building, it can be wood, brick or aerated concrete;
- the distance between the reinforcement layers. This is a calculated parameter, depending on the depth of the groundwater, the structure of the soil and the method of making the slab;
- estimated concrete thickness. It must be remembered that concrete must completely close the reinforcement on all planes, without exception, it is advisable to give a reserve thickness of at least 5-7 cm along the formwork;
- thickness, type and dimensions of the reinforcement mesh.
As a rule, for soft and light building materials, such as aerated concrete, it is enough just to sum up all these indicators and then the thickness of the slab is obtained. The optimal thickness of the slab is 20-30 cm, but the end result is also determined by the composition of the soil and the uniformity of all soil rocks. Sometimes a layer-by-layer stacking parameter is also added to such indicators if the soils are heterogeneous.
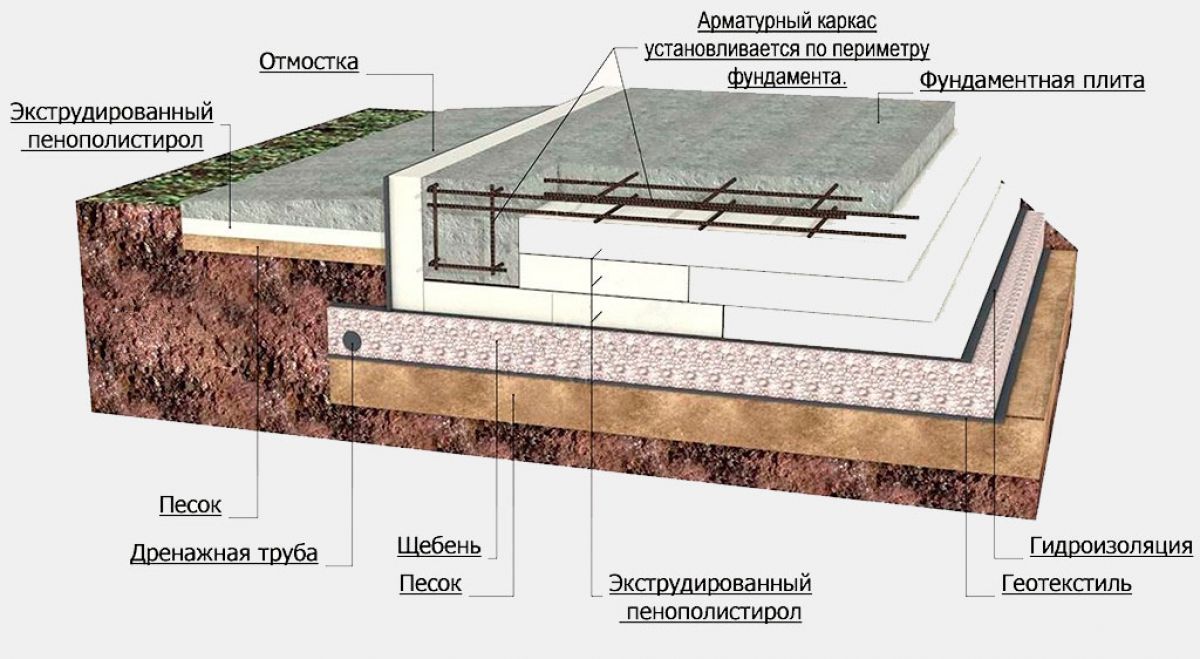
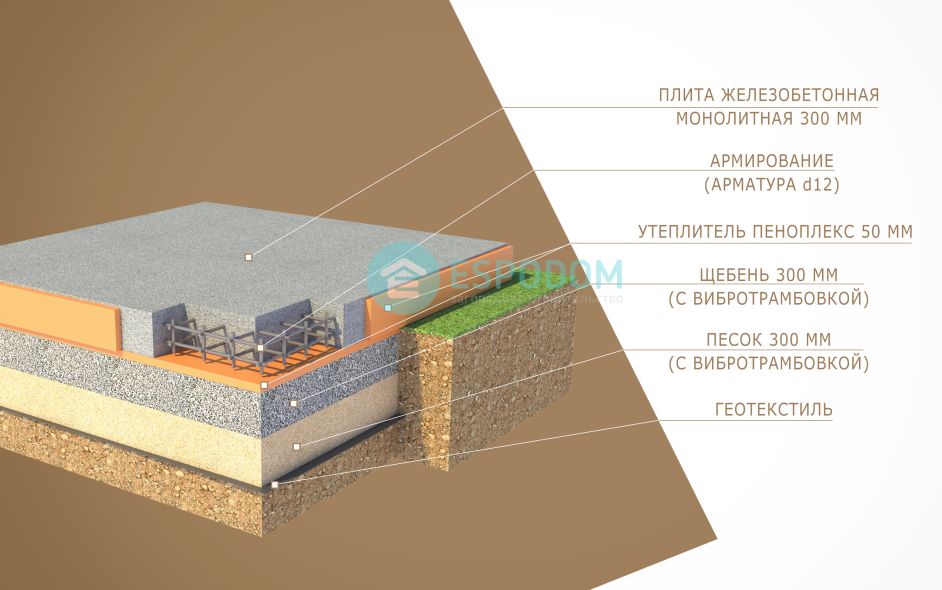
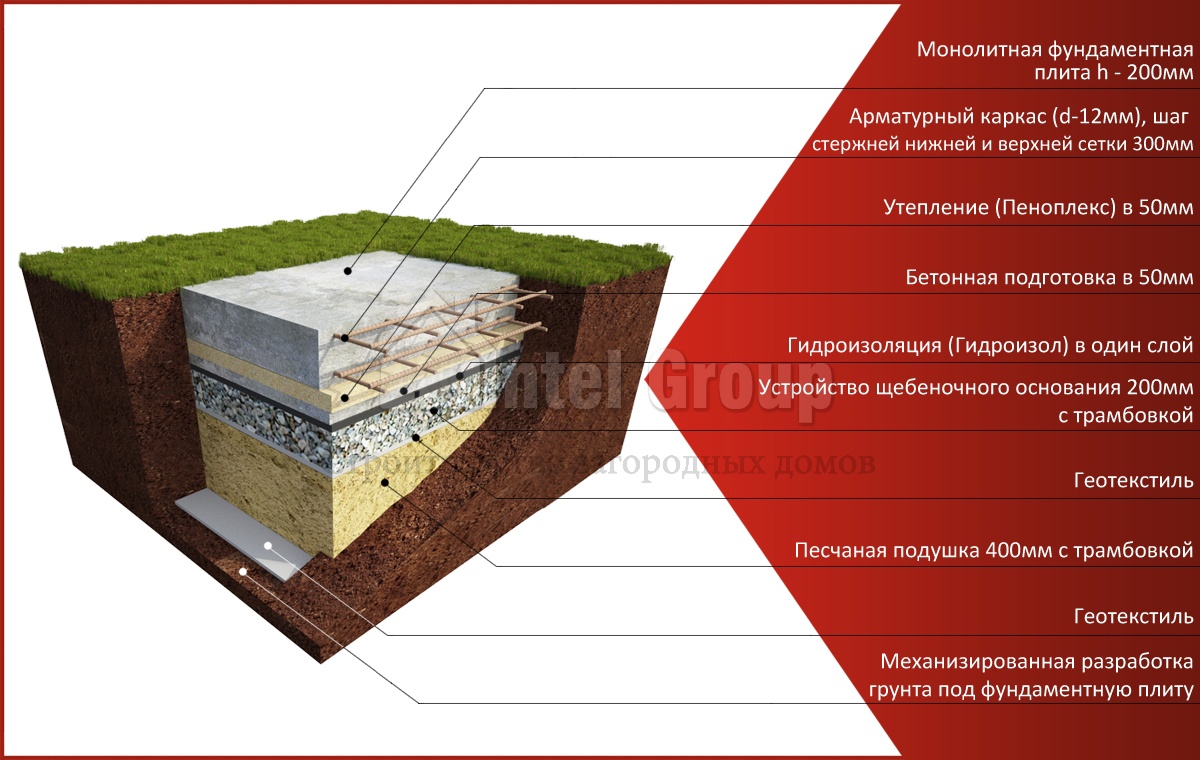
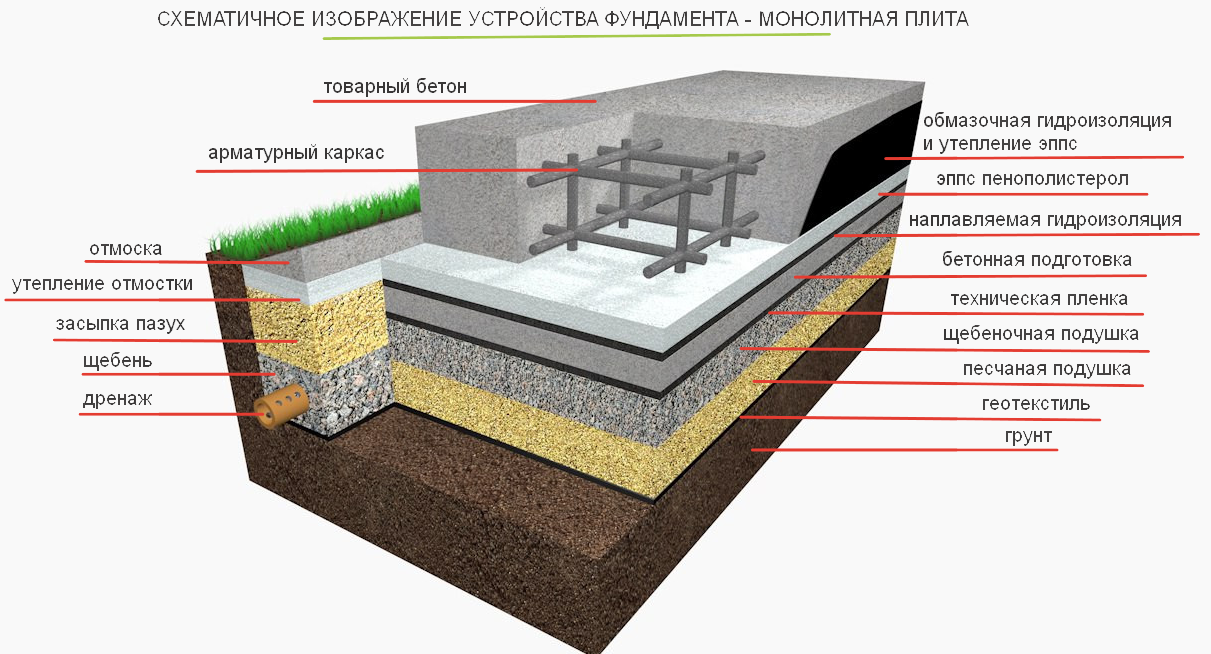
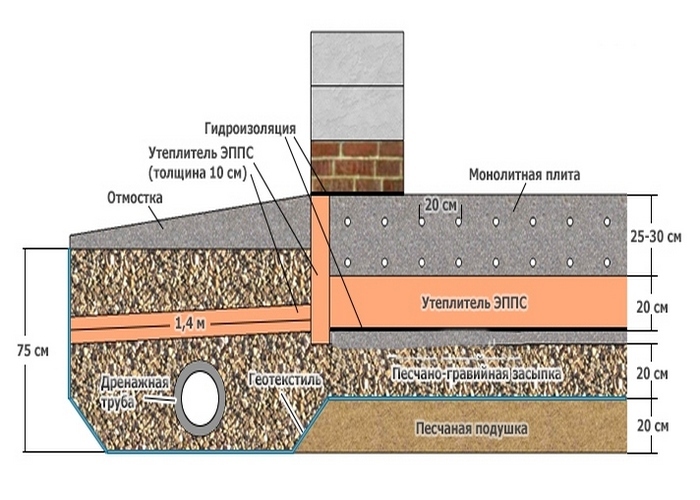
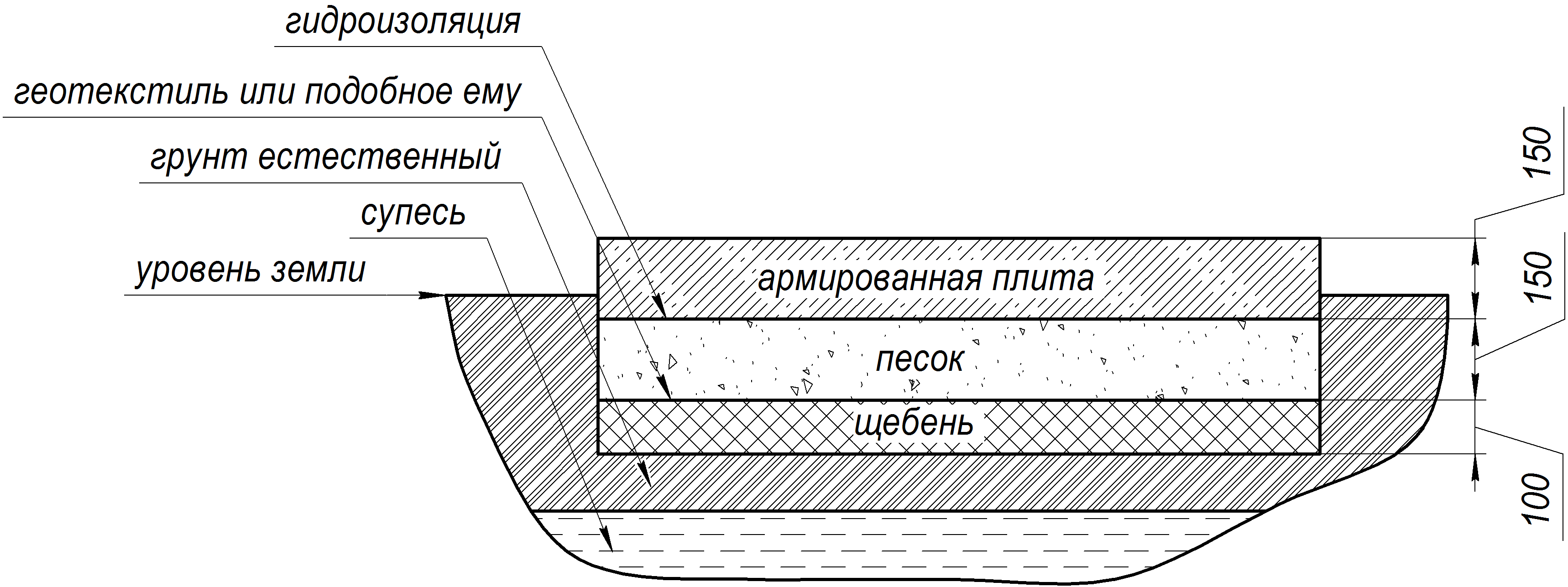
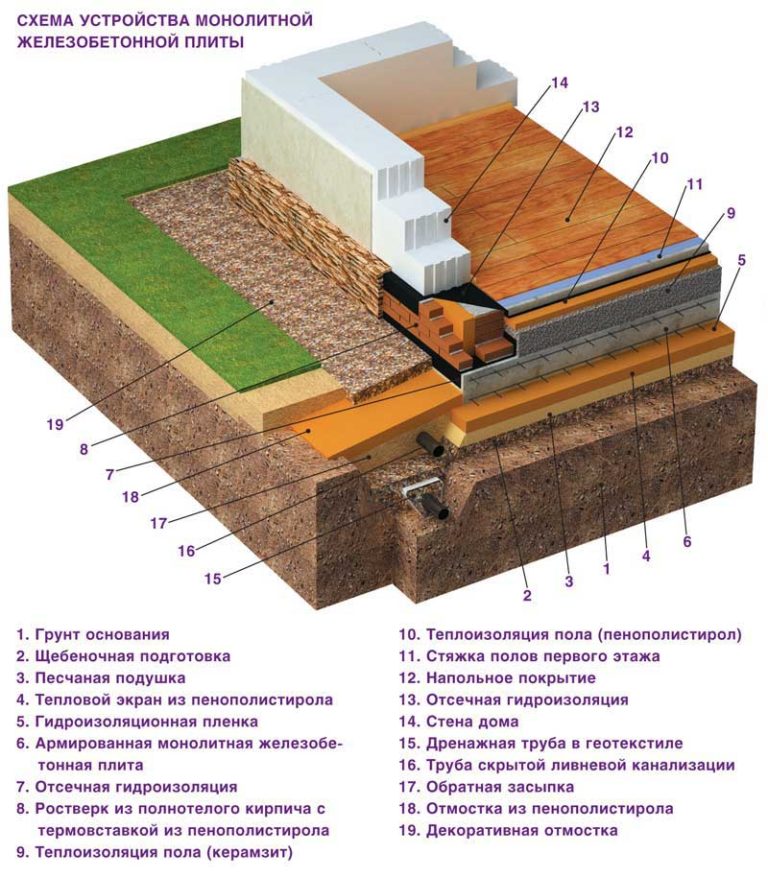
In addition to the dimensions of the slab base itself, there is also the thickness of the drainage layer, sand cushion and waterproofing layer.You also need to remember that to equip such a foundation, you need to remove the top fertile soil layer and dig a pit to a depth of at least 0.5 m.This depth of the bottom of the pit is determined by the need to lay crushed stone 0.2 m thick and sand 0.3 m thick.
As a result, it turns out that the estimated thickness of the slab foundation is approximately 0.6 m in total.But even this value is not considered standard, because there is also a factor of soil subsidence due to the mass of the building, there are soil characteristics and the height of the soil horizon. It is also worth considering the mass of concrete, which will also affect the thickness of the structure as a whole.
For example, the foundation for a brick house should be 5 cm thicker than for aerated concrete. The presence of additional floors is also taken into account, since each adds its own load to the base, and it will evenly increase in thickness.
So, the higher and larger the building, the thicker the foundation slab, and if the house is made of aerated concrete, then the slab will be even thicker. A standard two-story house made of aerated concrete will be built on a slab with a thickness of 35 cm, sometimes even more, if the house has a complex structure and an extensive system of load-bearing walls and partitions.
Cheaper alternatives to UWB
1. Slab-pile foundation (PSF) on TISE piles. Cheaper and more reliable.
Alexander is engaged in such foundations. He published a book and has a YouTube channel.
Don't expect drastic cost reductions. But it will come out cheaper due to less insulation and concrete.
TISE piles with plank strapping and wooden flooring.
This is a real alternative in which the following are crossed out:
- cubic meters of concrete
- fittings
- preparation of the base (excavation, crushed stone, sand, tamping)
- drainage
- blind area
Drainage and blind area still have to be done. You can postpone them for a year or two. This will alleviate the financial burden on the construction site. Plus, both the first and second in this foundation are simpler, which means a little cheaper.
True, with such a foundation, only a wooden house: a frame frame or a self-supporting insulated wire.
Instructions
You should start laying a monolithic foundation with a marking, and the base should be perfectly flat. For this:
Remove the top layer of soil with the material at hand, level the base with a level.
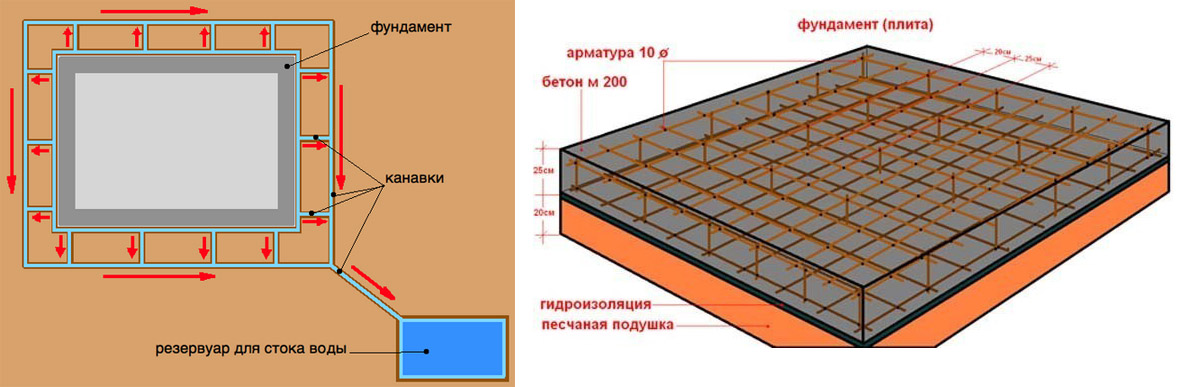
We fill up the drainage cushion under the future monolith: sand and crushed stone with a total height of about 12 cm.Crushed stone should be tamped separately, and then sand. Water the pillow evenly.
At this stage, you can carry out the necessary communications, sewerage.
Now you can proceed to the slab screed: processing with concrete and bitumen resin.
Treat the slab with a waterproofing layer of any material suitable for these works. Seams are soldered with a lamp or burner
Please note: the layer should hang from the monolith by 50-70 cm, this is how the second goal is pursued: protection of the sides of the foundation.
This is an optional but desirable action: insulate the base of the monolithic foundation. Durable foam materials can be used.
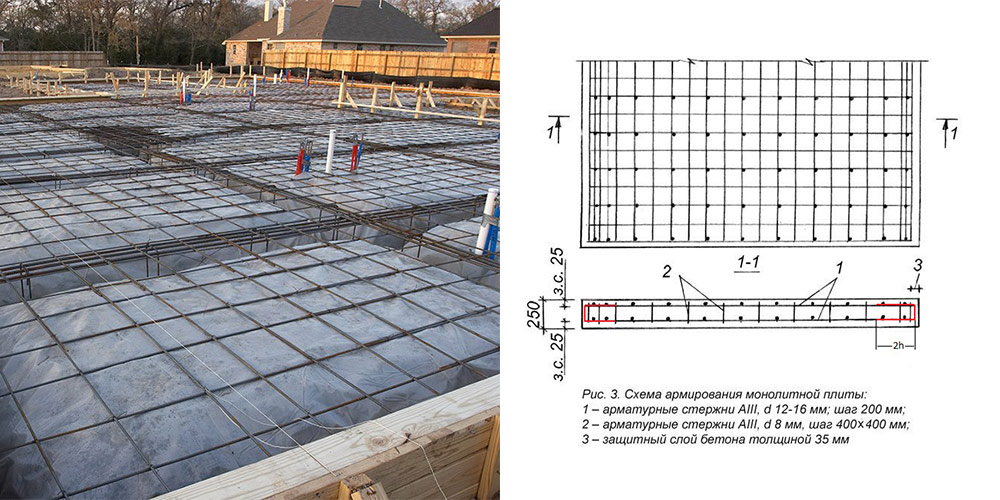
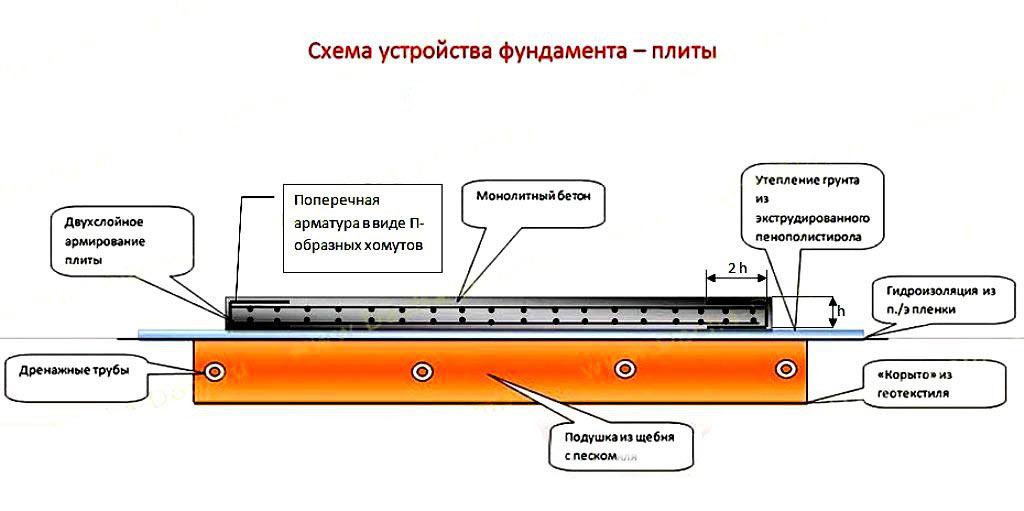
Now you need to equip the formwork: reinforcing pins with a diameter of about 15 mm are installed in it, and a mesh mesh with a mesh size of about 20 mm
The lower edge of the net should be lowered from the stove by about 5 cm, and the upper edge should be raised by the same distance.
The preparatory work is over, the monolith can be poured with concrete.
After complete drying, the formwork is removed, and for waterproofing purposes it is covered with a protective layer.
Of course, the arrangement of a monolithic foundation is the most difficult in comparison with other types, and non-observance of the order and sequence can lead to disastrous results. But if you do everything correctly, following our advice, then you will never have other problems with skewing windows and doors.
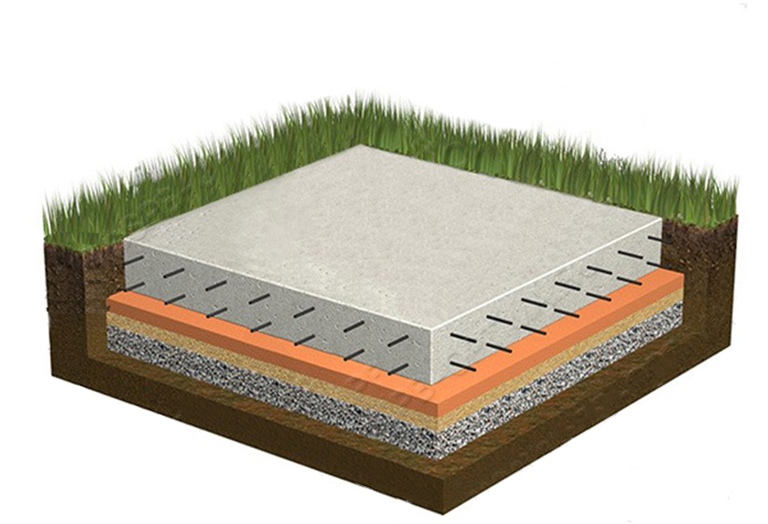
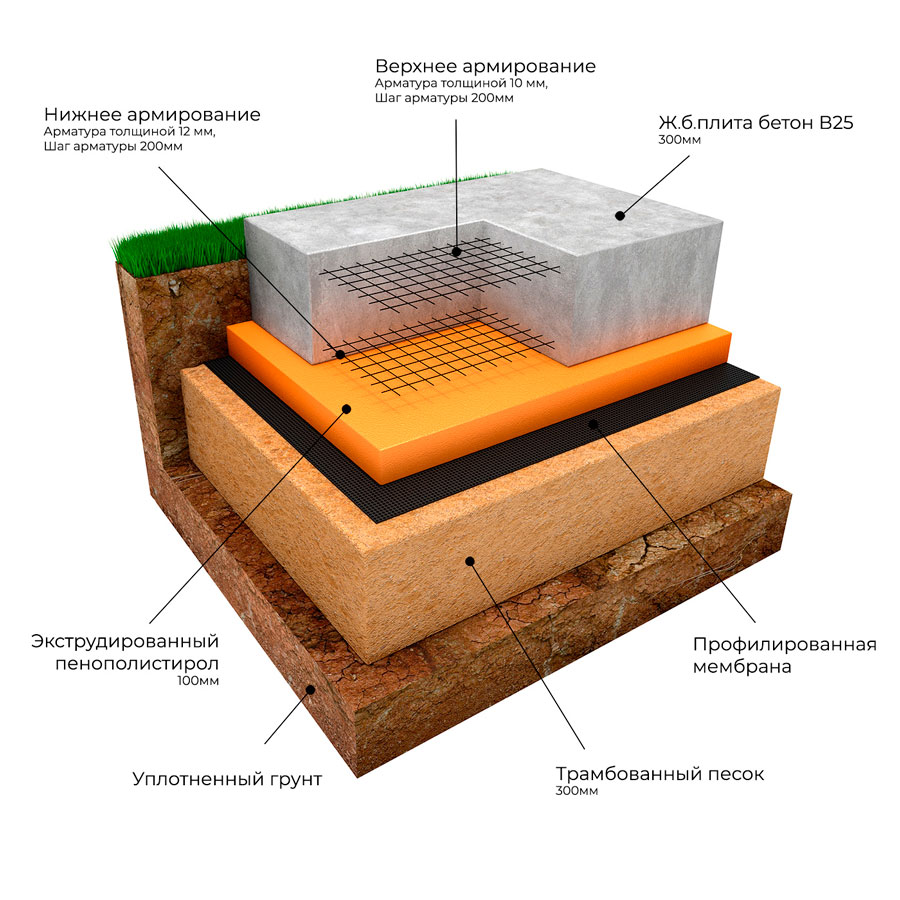
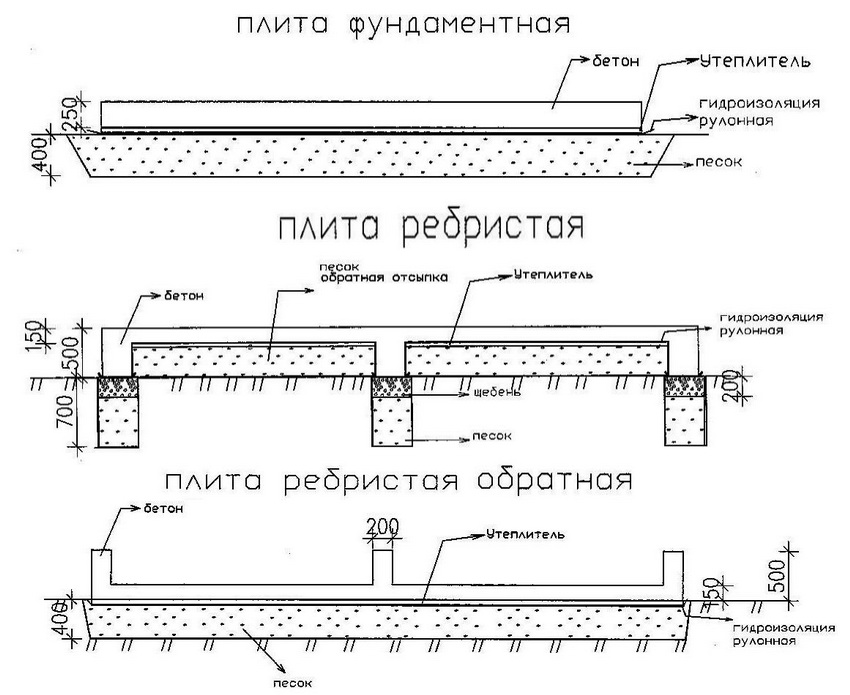
How thick should a monolithic foundation slab be?
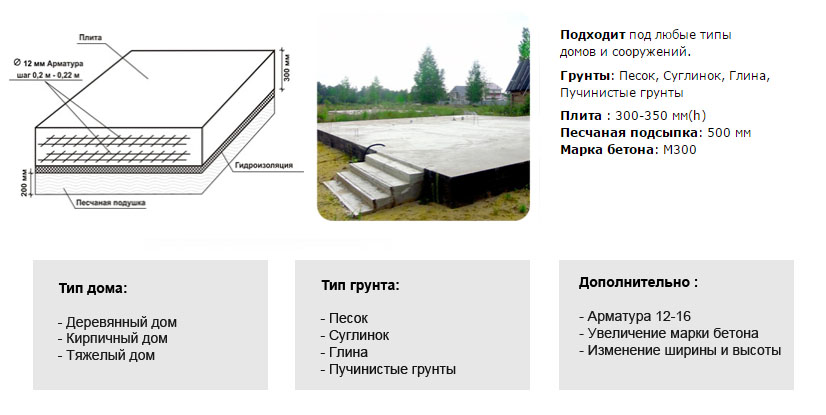
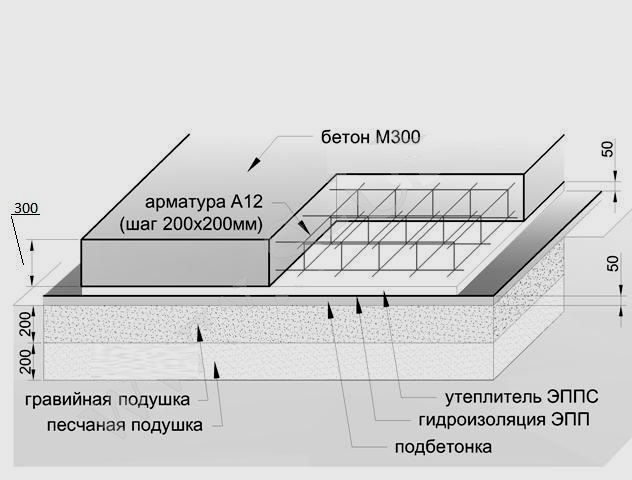
The slab foundation is considered the most reliable and is chosen when building houses on unstable and flooded soils. This type has a minimal impact on the ground and ensures an even distribution of all weight loads. The pouring technology itself is simple, the main emphasis is on calculating the parameters of the slab, namely: the depth of laying, the height of the cushion, the grade and thickness of concrete, the section of the reinforcement, the need for insulation. The range varies from 15 to 35 cm, if the calculated value is different, then other options for the foundations are considered.

The thickness of the foundation slab for an aerated concrete private cottage.
Features of the slab foundation.
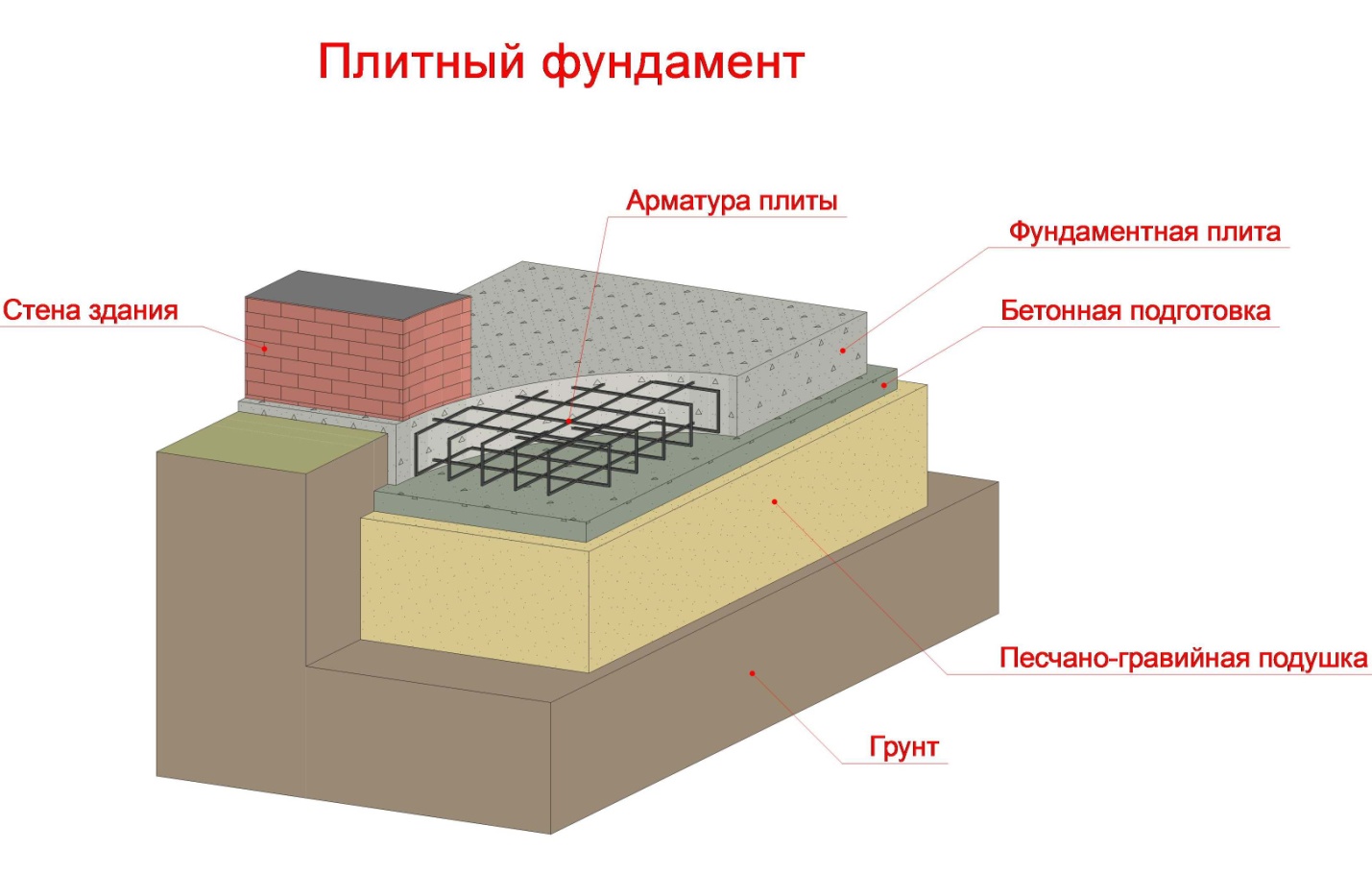
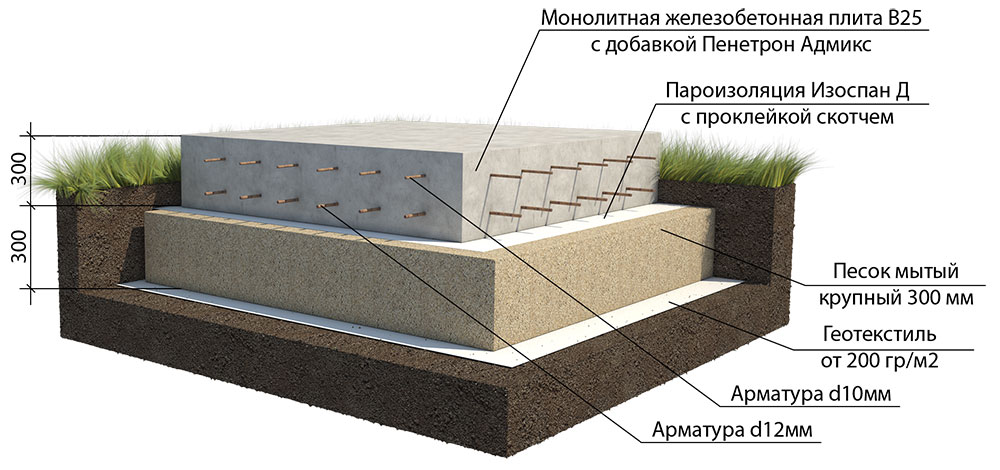
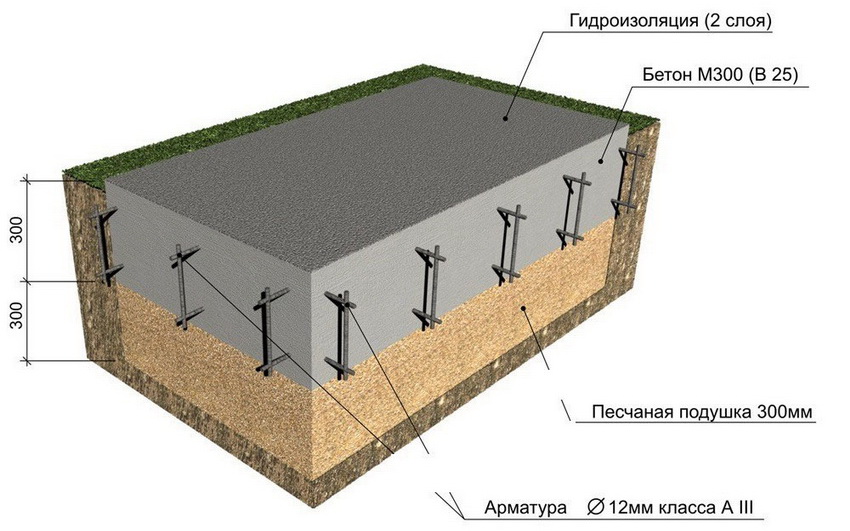
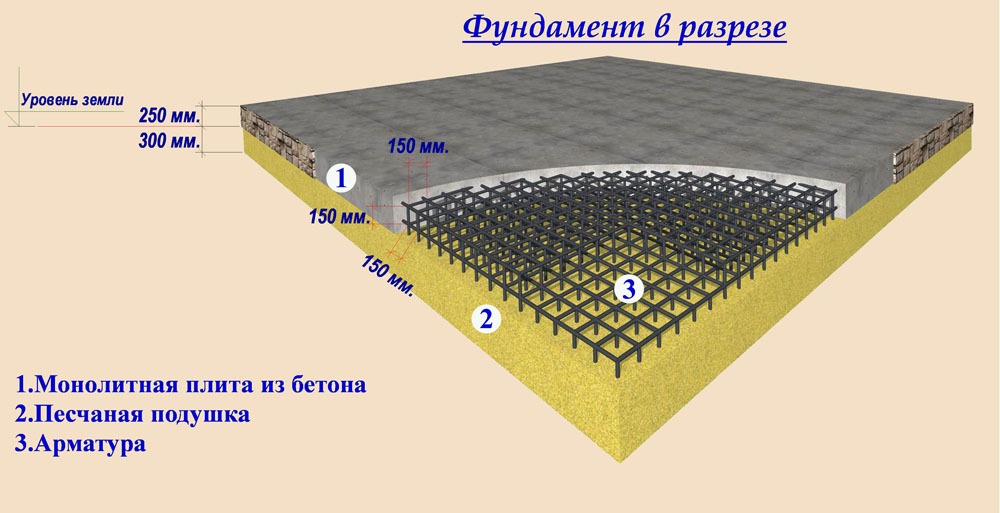
It is a concrete monolith with two rows of mesh made of reinforcement, placed on top of a compacted sand cushion, in especially difficult cases - reinforced with stiffening ribs from below. The cost of its construction depends on the depth of the foundation: on stable soils, it is practically equal to the ground and requires minimal investment and effort. On floating soils or, if necessary, the organization of the basement space on the slab foundation leaves up to 1/3 of the general construction budget, since the laying is carried out below the freezing level.
For stable soils.
For very heaving.
The thickness of the slab for a wooden house depends on the number of storeys; when using well-dried materials, their specific weight does not exceed 600 kg / m 3, which is 2.5-3 less than that of a brick. As a consequence, the recommended value is 30 cm.
The thickness of the foundation slab for a one-story aerated concrete cottage.
An example of calculating the main parameters of a foundation slab
Sketch of the optimal thickness of the foundation slab
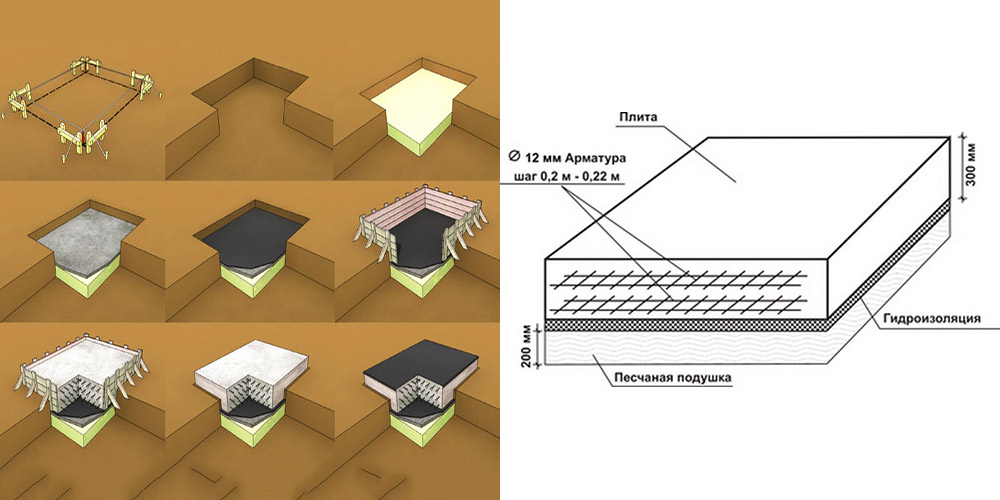
In order to correctly understand the calculation of the parameters of the slab foundation, as well as to clearly calculate the required amount of concrete, it is worth using the following example:
- A typical building made of aerated concrete with an area of 100 m² (10x10) is taken and a slab foundation is selected for it on rocks with a thickness of 0.25 m of a shallow type.
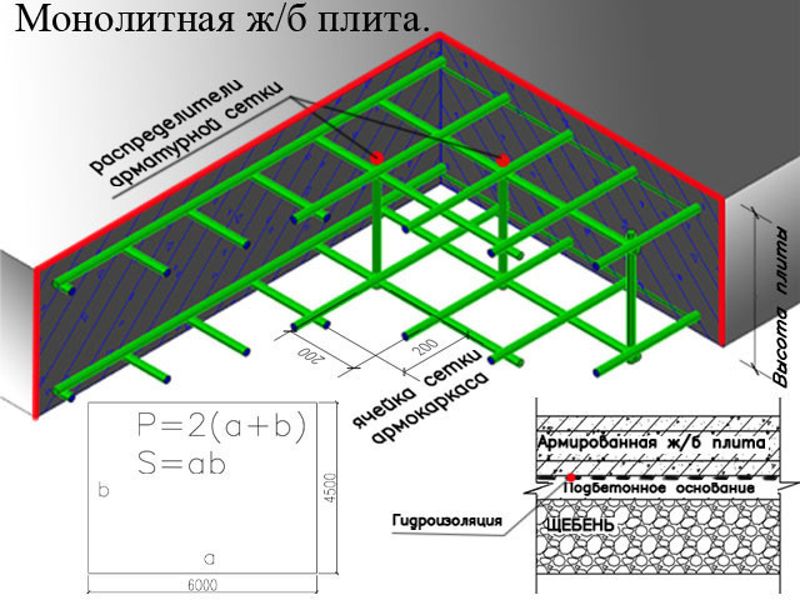
- The volume of the slab in such cases is 25 m³. This is the total amount of concrete required to fill such a structure. Here the volume of the reinforcement mesh is taken as zero, so as not to complicate the calculations. In practice, such calculations are also carried out, but for large structures.
- Installation of stiffeners, which are used to improve the reliability of the structure. The stiffener spacing is 3 m, thus creating squares.
- The length of the stiffeners will correspond to the length of the foundation, and the height is the thickness of the slab.
So, for pouring a slab foundation with an area of 100 m², you need to use 25 m³ of concrete. Also, a certain amount of reinforcement, waterproofing and sand with crushed stone for the pillow will go here. In general, I would like to note that any developer can calculate the thickness of the slab on their own, it is enough to have minimal mathematical knowledge.
But, if you immediately make a calculation of the foundation slab, then you can generally control the costs of building materials, and monitor unscrupulous builders, as well as clearly determine the size of a house made of aerated concrete or brick. You can also calculate the required amount of materials on our online calculator.
Types and structure of slab foundation
A slab foundation is understood as a base made in the form of a flat slab of concrete and reinforcement. There are two types of structures (with subspecies), differing in bearing capacity. They are shown in the table.
Table - Classification of slab bases with their characteristics
| № | Monolithic | Made |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | one-piece reinforced concrete structure that occupies the entire area under the structure under construction | created from ready-made standardized factory products |
| 2 | is divided into the following types: simple slabs, Swedish insulated (USHP), reinforced | they are laid on a flat, pre-compacted surface using special equipment |
| 3 | for simple ones - the lower plane is even | such structures are unstable to soil movements, even small |
| 4 | for reinforced ones - it contains stiffeners located in the calculated order, and Swedish plates are a type of reinforced type | suitable as a support for wooden structures on stable soils (non-porous, stony) |
 With soil movements, the entire erected building moves, which minimizes the possibility of deformation of its individual parts. Therefore, slab bases are called floating and are used in the following cases:
With soil movements, the entire erected building moves, which minimizes the possibility of deformation of its individual parts. Therefore, slab bases are called floating and are used in the following cases:
- with weak soils;
- when groundwater flows close to the surface;
- if the erected structure is subject to heavy loads.
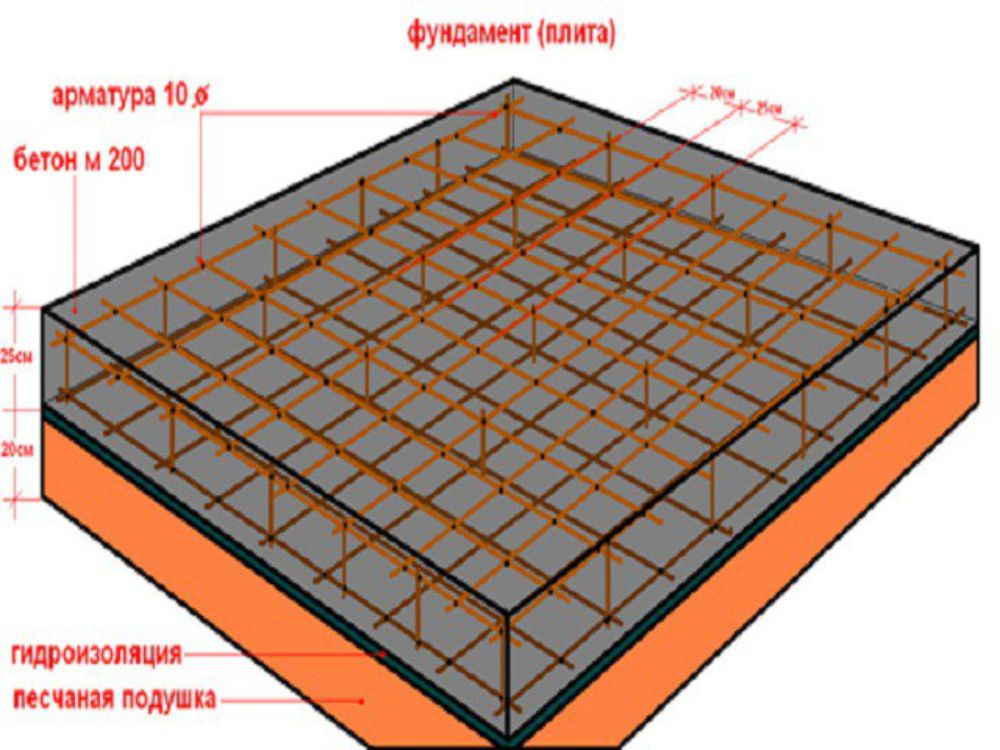
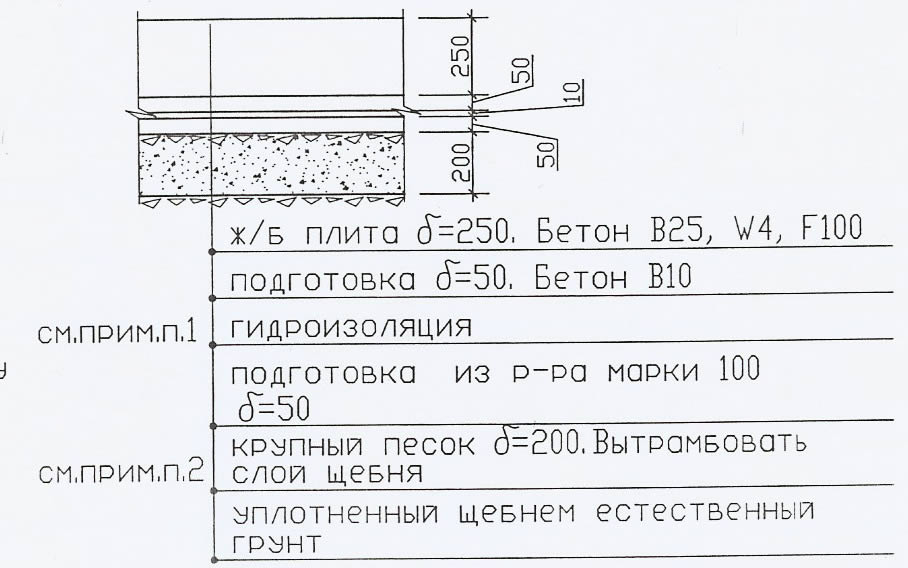
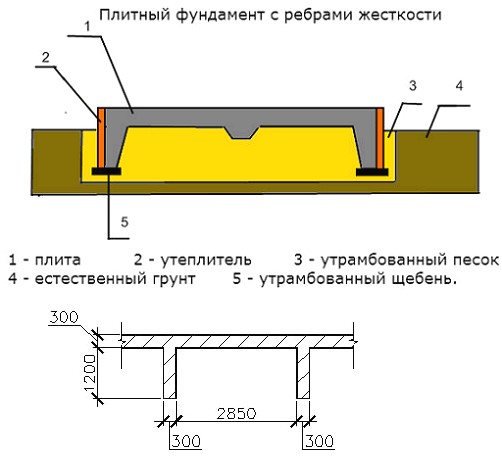
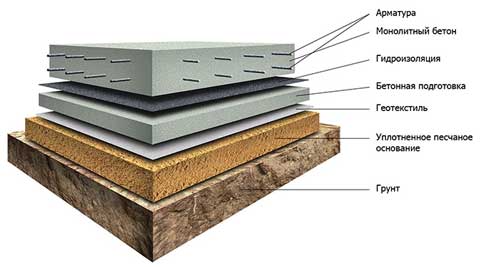
The thickness of a monolithic slab foundation consists of several parts:
- cushions, the height of which is calculated according to the geological characteristics of the soil;
- reinforced concrete layer, its parameters are calculated based on the existing loading effects.
The use of a slab base for a house requires calculating the thickness of the foundation and the amount of working material.
Slab foundation for aerated concrete house
 Arrangement of a slab base for a house made of aerated concrete
Arrangement of a slab base for a house made of aerated concrete
When building a house from aerated concrete, they adhere to the same requirements at the research stage. The water level, the presence of heaving and the quality of the soil are determined.
For the construction of an aerated concrete structure on soils with a low bearing capacity and with a strong saturation with moisture, the only rational solution would be to construct a monolith. These can be solid monolithic structures or a lattice type of base.
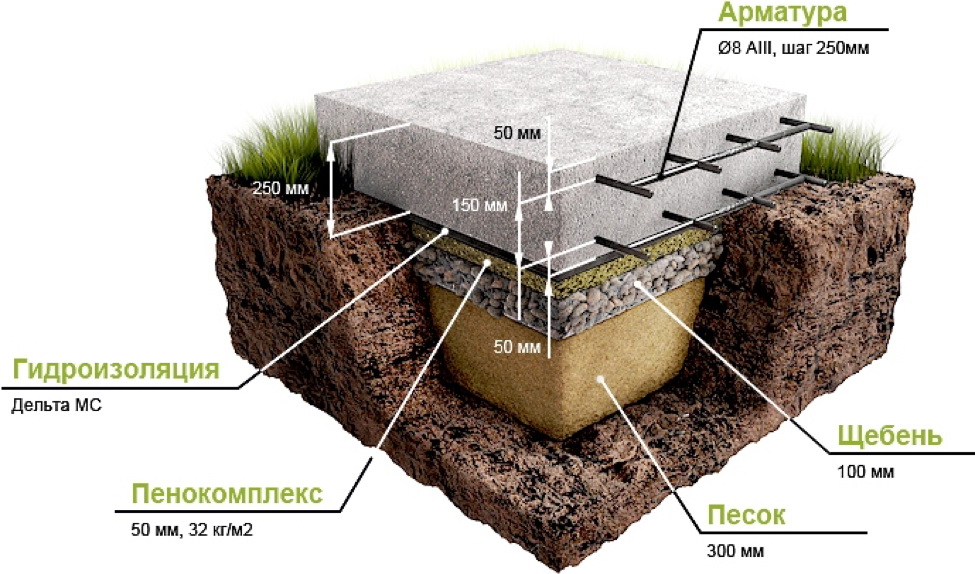
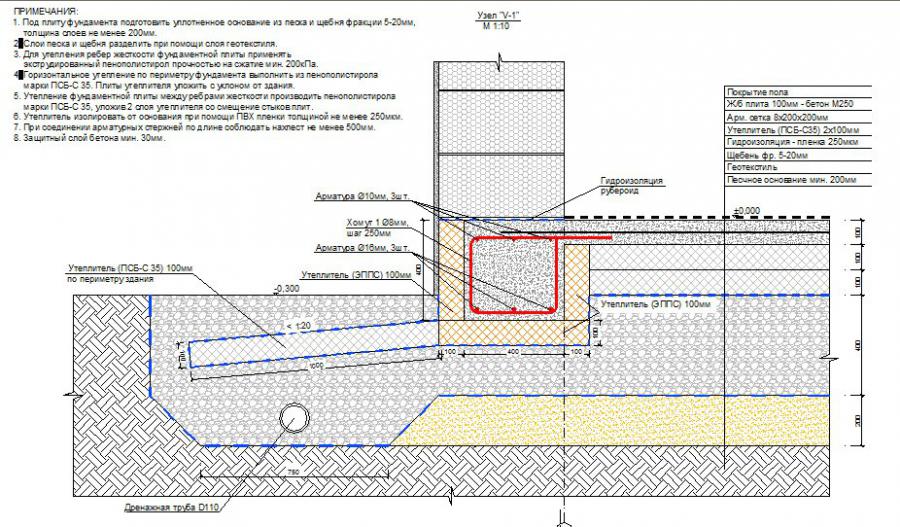
The main difference from the foundation for a garage is that the base for the house requires mandatory thermal insulation. The stage of warming can be divided into two: the laying of extruded polystyrene foam and the device of "warm floors".
Taking into account the differences from the device of the garage base, the steps for preparing a slab for a house made of aerated concrete (dimensions 7x8 m) can be summarized as follows:
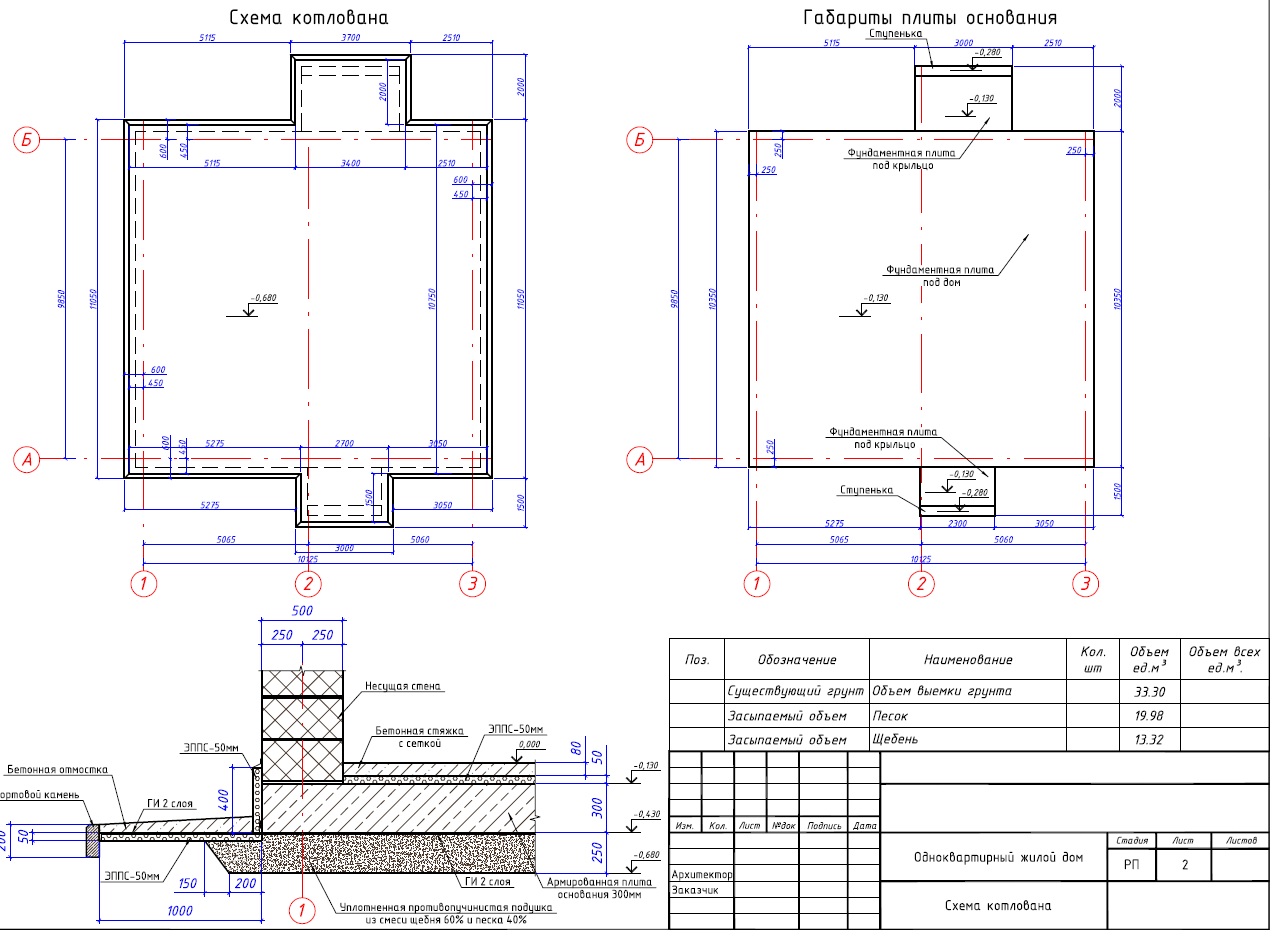
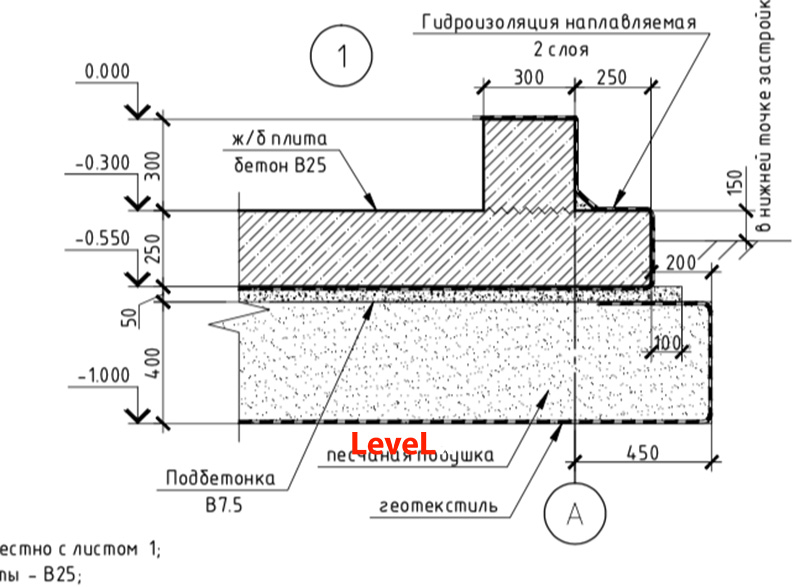
- Preparation of a pit (depth 75 cm) with additional protrusions along the perimeter (by an amount equal to the freezing depth).
- Laying of communications.
- Sand cushion device (thickness - 20cm.)
- Geotextile laying. Its task is to prevent siltation of the drainage system and sand erosion.
- Drainage system layout (only if the water level is high).
- Backfilling of a mixture of gravel with sand - up to 20 cm, tamping and checking for horizontalness.
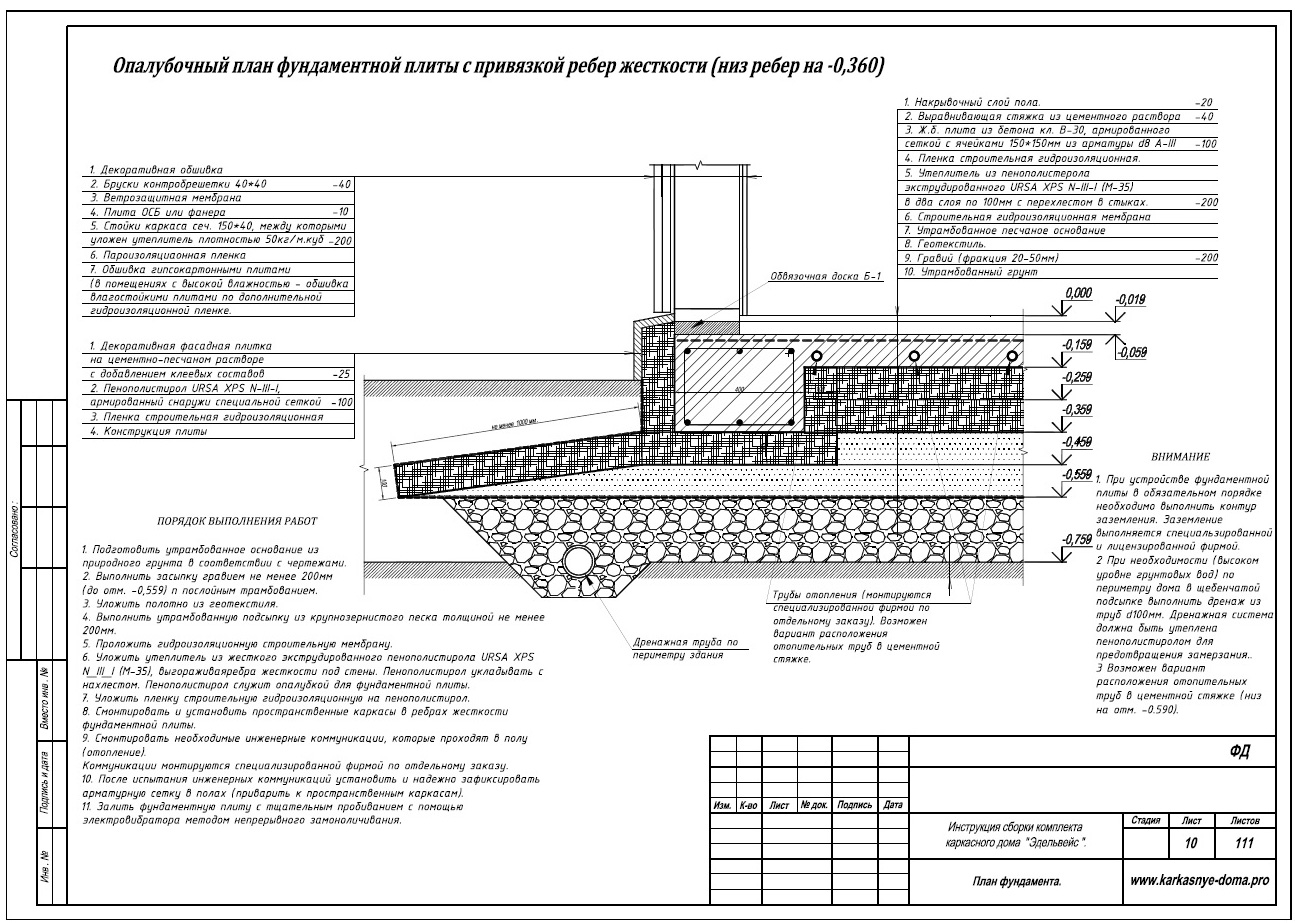
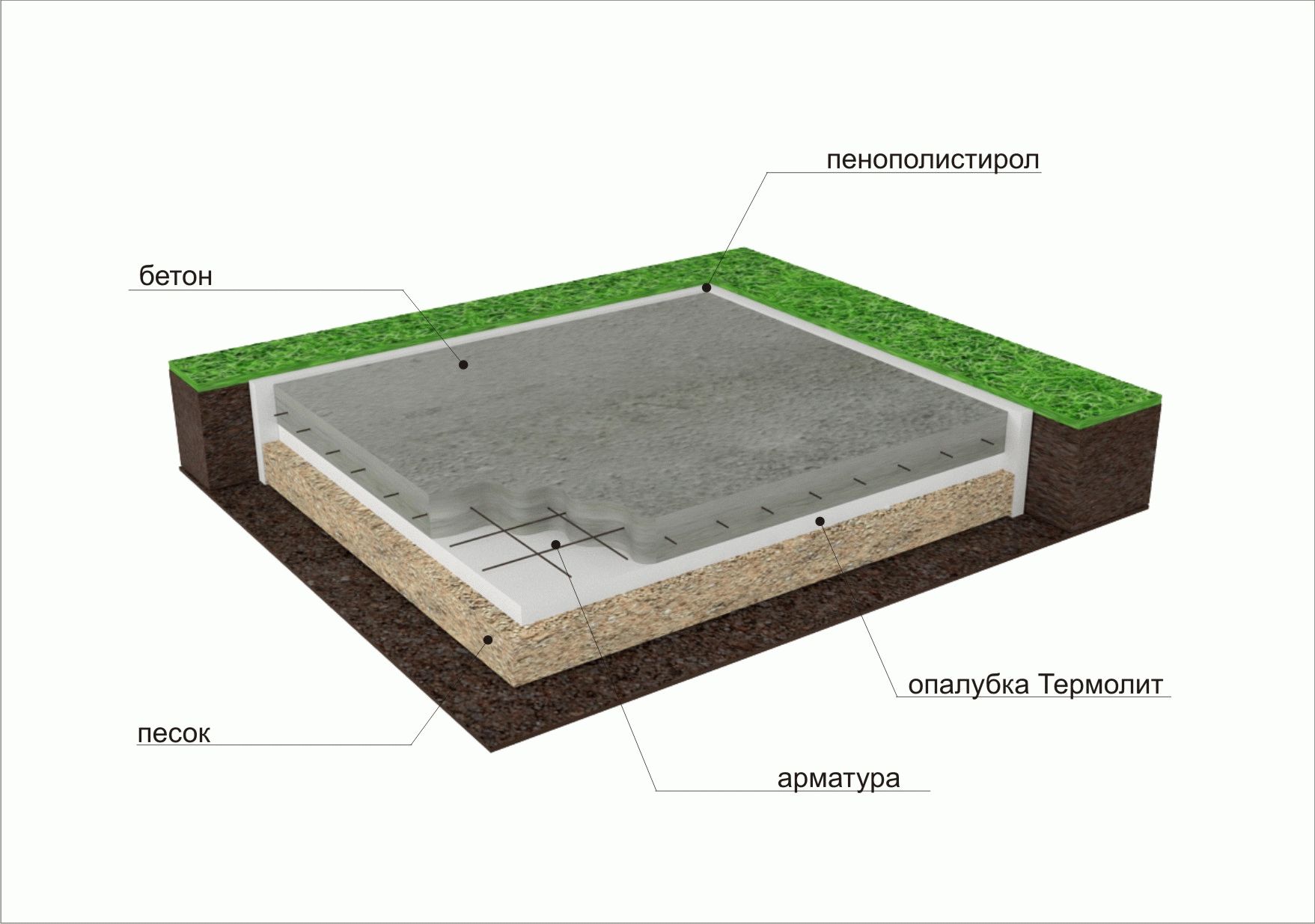
- Installation of formwork (removable or not). If fixed formwork is installed, it will additionally insulate the foundation and play the role of a mold for pouring concrete.
- Thermal insulation from extruded polystyrene foam (horizontal) with a slight angle of inclination.
- Laying waterproofing: dense polyethylene, polymer-bitumen materials and others.
- However, when choosing roll materials as a heater, a thin layer of "lean" concrete (grade M100) is poured.
- Laying insulation on the upper part of the base. The same sheets of expanded polystyrene with a layer of 20 cm.
- Bandaging a two-level frame made of reinforcement and laying pipes for a "warm floor".
- Pouring concrete mortar.
- Providing care for the finished substrate (see above).
It should be remembered that aerated concrete is a rather fragile material, and the walls of a house made of it can undergo serious deformations.
Therefore, at the stage of designing a residential building made of aerated concrete, special attention should be paid to the choice and calculation of the foundation
We calculate the slab foundation
The most important point in the calculation is to determine the thickness of the building base plate. The complete and most accurate calculation is performed by a professional builder with an appropriate level of knowledge and design experience. But this takes time, money and a professional. For a private non-professional developer with a slight excess of material consumption and less accuracy, a simpler calculation of the foundation slab may be sufficient.
For example, you have fine sands with medium density. They withstand a specific foundation pressure of 0.35 kg / cm2.
2. We calculate the total mass of the future home
- Knowing the dimensions of the house, the location of windows, doors, openings, the material of the walls, floors, their configuration and the thickness of the structures and, taking into account the specific gravity of the materials, we determine the weight of individual parts of the building.
- Summing up the found values, we get the total mass of the building.
- Having the area of the building, we calculate its snow load associated with the angle of inclination of the roof and the region of construction.
3. We calculate the specific pressure of the building on the ground
The calculated total mass of the building is divided by the area of the monolithic foundation slab. We get the specific pressure of the building on the ground (without the weight of the foundation). Determine the required weight of the slab.
4. We calculate the optimal volume and thickness of the foundation
We divide the mass of the slab by the density of reinforced concrete, which is approximately 2500 kg / cubic meter. m. Divide the volume by the area of the slab, we get its thickness.
5. Round off the resulting thickness
We round the resulting thickness to larger and smaller values, multiples of the size of the building step of 50 mm. We choose a suitable value and, taking it into account, we recalculate the mass of the foundation slab. Adding the resulting mass with the mass of the house, we calculate the specific pressure on the ground.
Then we compare the obtained figures with the tabular characteristics of the site soil. Spread should be less than ± 25%.
What you need to know when determining the size of the foundation
To choose the required optimal size of the foundation, ensuring the reliability of the entire structure, you need to know:
- soil composition at the site;
- the height of the groundwater;
- the depth of soil freezing in a given region;
- the weight of the building itself, i.e. loads on the foundation from the weight of walls, floors, and roofs.
The overhang of the walls above the foundation by a width of 10-13 cm is allowed, but no more. This is due to the fact that reinforced concrete has a high strength, much higher than the strength of wall materials, therefore it can withstand the load from a wider wall, and a narrow foundation can reduce the consumption of concrete and reinforcement.
Determining the bottom of the foundation
The calculation of the width of the foundation is determined depending on the width of its base, which is calculated based on the loads pressing on the foundation. The foundation, in turn, exerts pressure on the ground.
As a result, in order to correctly calculate the size of the foundation, it is necessary to know the properties of the soil at the construction site.
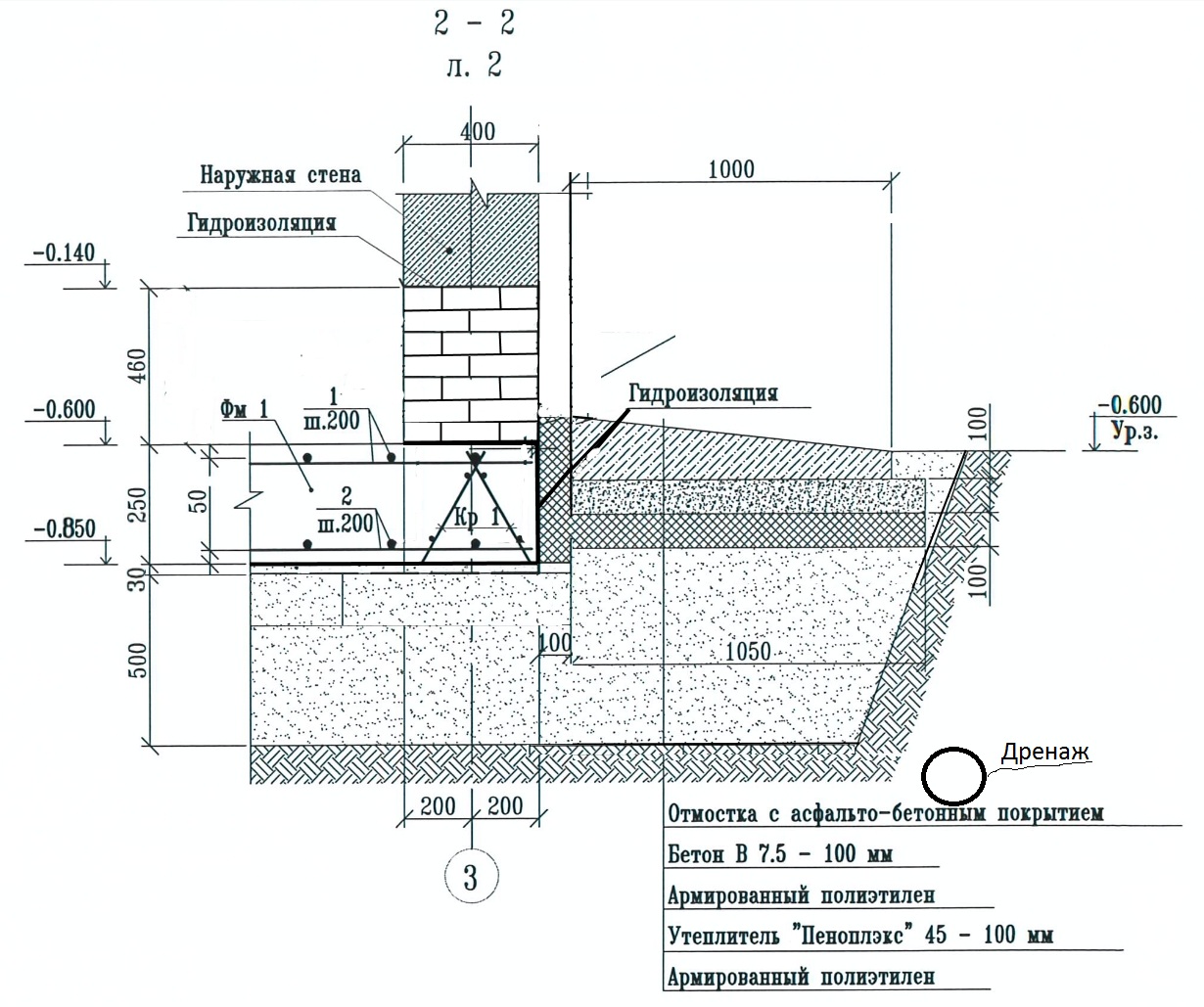
If the soil on the site is heaving, and the house is supposed to be built from bricks or concrete blocks, then the best option for choosing a foundation would be deepened. And since foundations of this type are arranged below the level of soil freezing, the height of the strip foundation for the house will be within 1–2.5 m to ground level.
Laying the foundation on heaving soil
For small buildings - a bathhouse, a garage or a country house, a shallow foundation with a height from base to top within 60-80 cm is quite suitable.In this case, there will be 40-50 cm of foundation height in the ground, the rest will protrude above the soil level and be the basement of the building. Despite the low height, the strength of the foundation will be guaranteed by the properties of concrete and reinforcing cage.
Before calculating the width of the strip foundation, it is necessary to calculate the loads that can be easily determined knowing the dimensions of all wall structures, roofs and the specific gravity of the materials used. To these loads is added the weight of people and everything that will be in the house - furniture, household equipment and others.
The dimensions of the strip footing are calculated in such a way that the load on the base does not exceed the permissible loads on the ground at the given construction site.
When calculating the strip foundation, we find out the height and width, after which we determine:
- the amount of concrete required for pouring,
- number of fittings,
- material for formwork.
As you can see, the dimensions of the foundation allow you to learn a lot for the device of a reliable foundation.
The first step is to determine the depth of the buried tape foundation. To do this, you need to know the depth of soil freezing in your region in the winter. All this can be found in construction guides.
The depth of soil freezing in different regions
When making a calculation, first set the preliminary dimensions of the foundation (width of the sole, height), focusing on the design features of the house. If the bearing capacity of the soil is greater than the pressure of the building on the ground, then the selected dimensions are left unchanged, otherwise, the dimensions are selected so that the calculated soil resistance is not less than the specific pressure of the building weight.
And if, among other things, there is reason to believe that the site has a high level of groundwater, then the calculation of the foundation and the assessment of the soil is best ordered from specialists so as not to risk the money invested in the construction. Because heaving soils can change their properties over time under the influence of some factors, such as, for example, a change in the level of groundwater.
You can independently find out the height of the strip foundation above the ground using the online calculator, where the program itself will calculate both the area of the base of the foundation, its height, and the thickness of the sand cushion based on data about your soil.