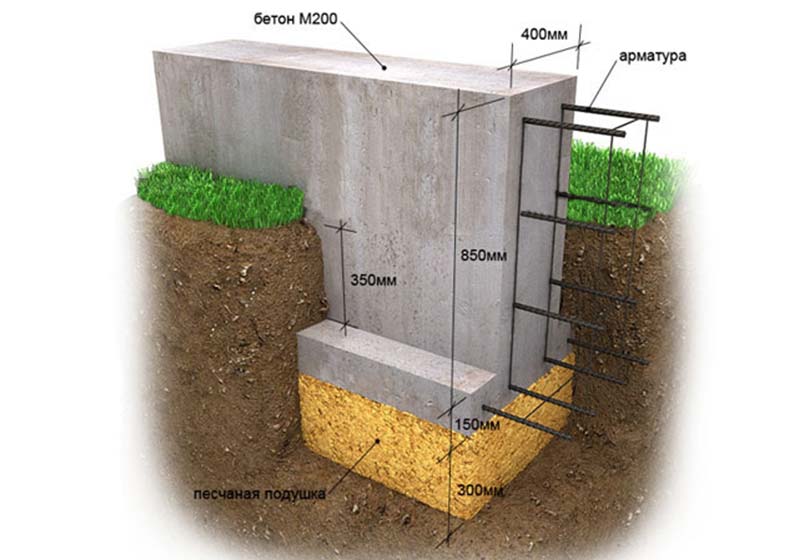
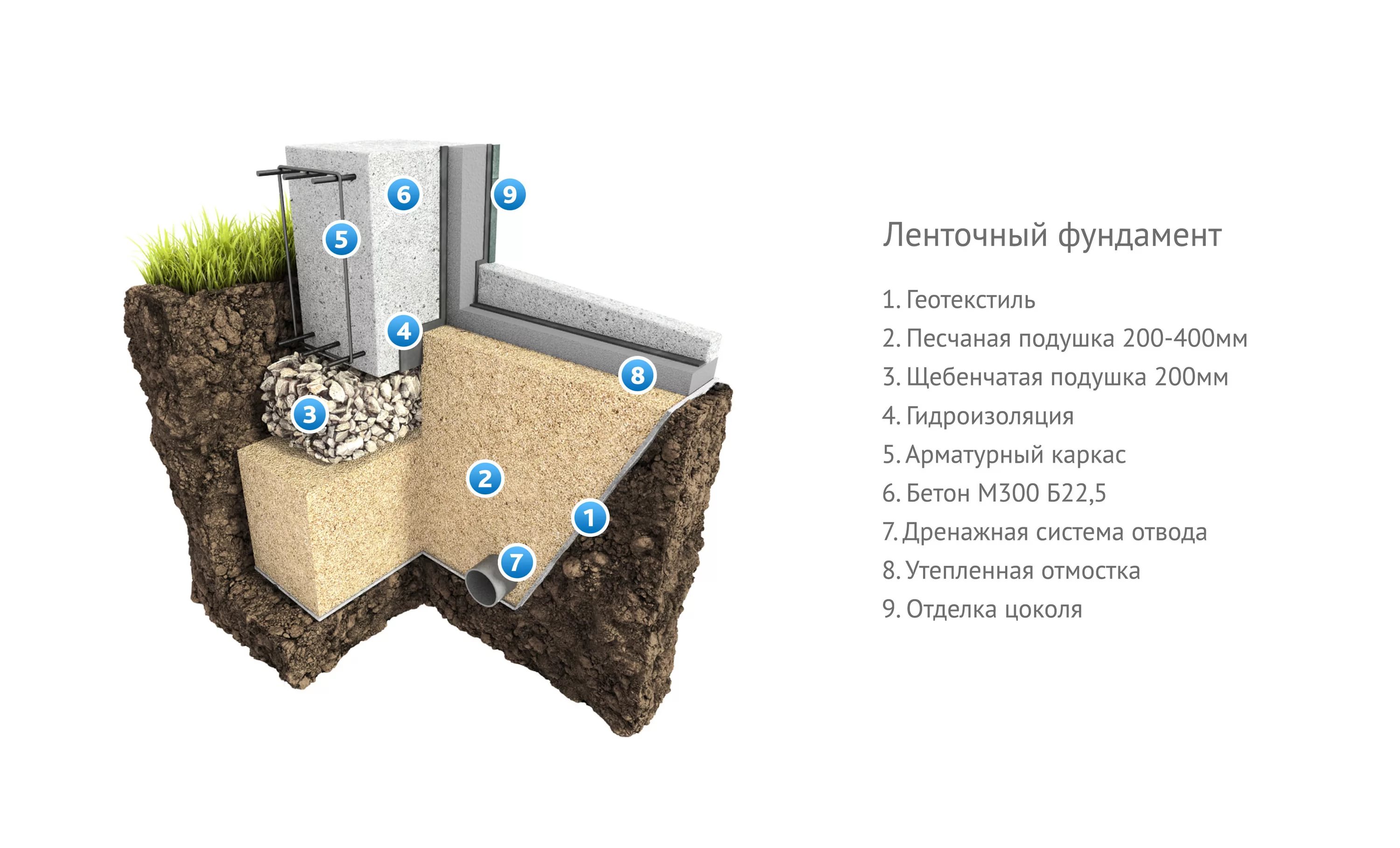
Features of the technology of building a foundation, depending on the type of soil
With the help of the correct type of foundation and adherence to the technology for building the base, you can create a solid support for construction on any kind of sandy soils.
Dusty and fine-grained
To build a house on dusty and fine sand, due to the extreme instability of the layers, it is necessary to create the most solid foundation. In such cases, the construction of a slab foundation is permissible. To do this, remove the fertile soil layer and cast a concrete slab, the scale of which is slightly larger than the area of the planned building. The structure does not collapse under the influence of seasonal changes in the soil, since this type of foundation is able to move with the ground, therefore it is called a floating foundation.
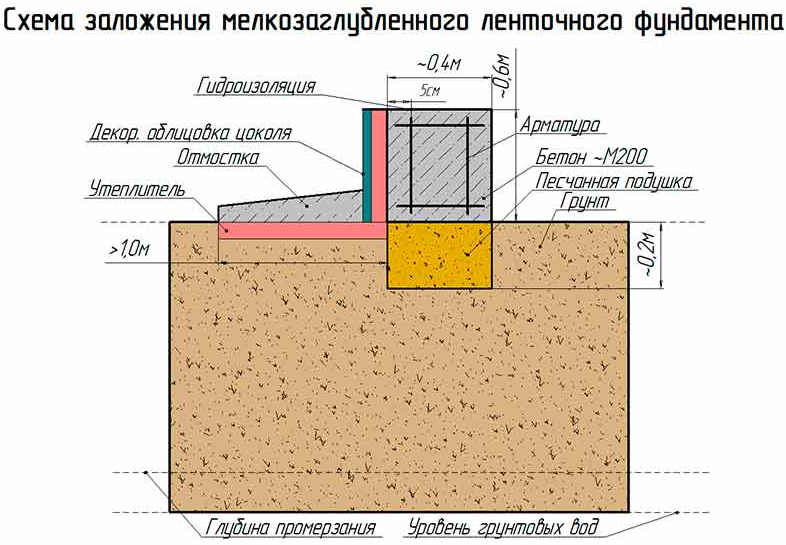
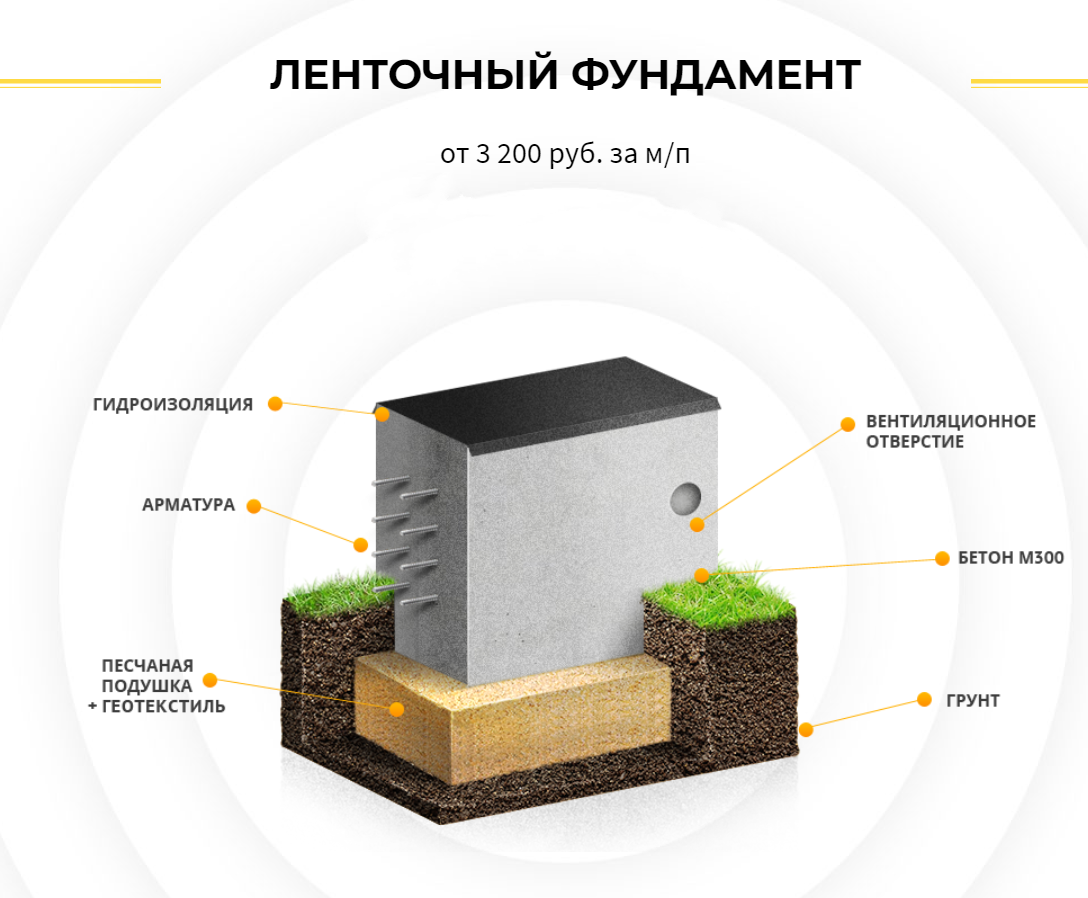
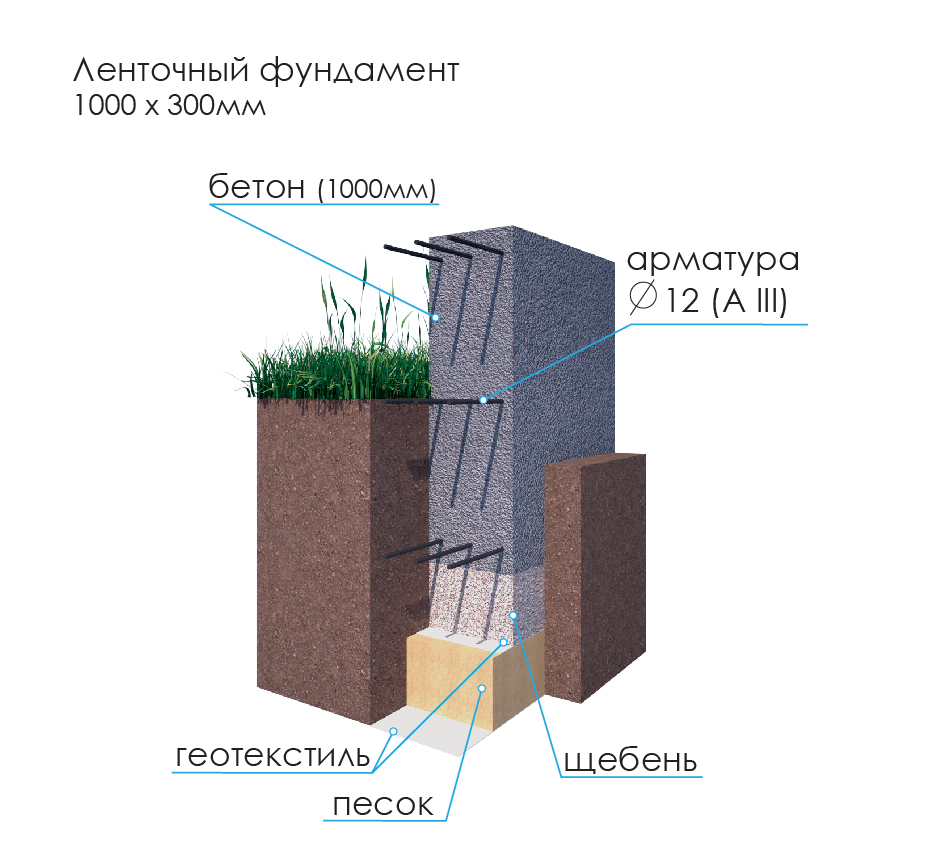
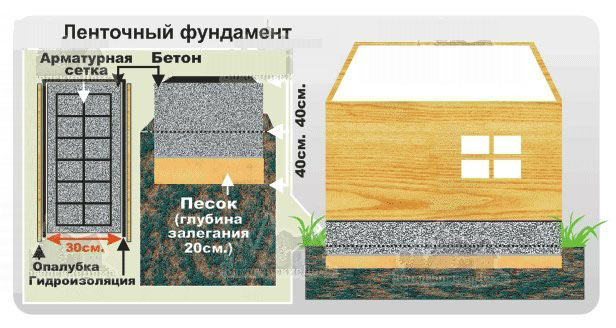
Another more common way to create a solid foundation for a building on silty and fine sandy soil is to use a monolithic strip foundation of a shallow type. It is recommended to make it trapezoidal with lines expanding downward. This contributes to a significant reduction in the influence of frost heaving on the base of the house.
Before pouring the foundation tape, the trench is equipped with a waterproofing layer. When laying the sole structure under a structure on fine sand and silty soils, drainage is especially important. Closed systems, which are equipped on the basis of drainage pipes, are recommended as effective methods.
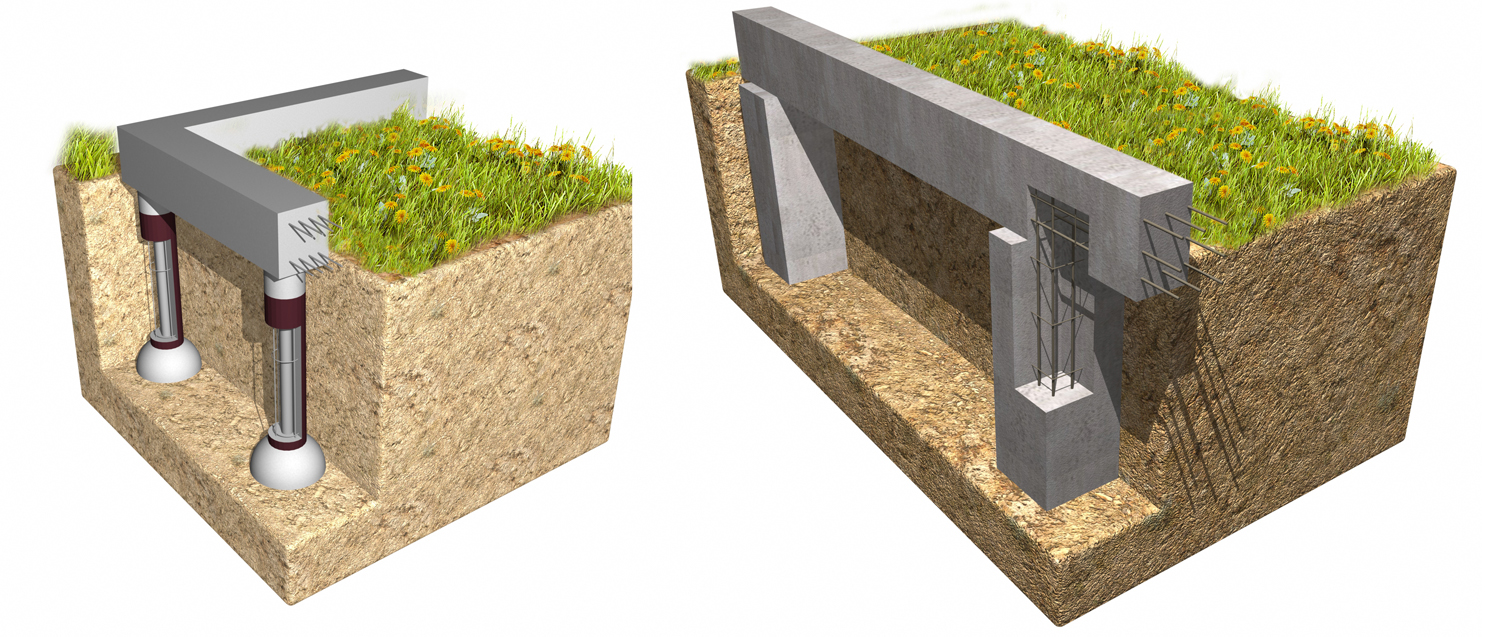
When working on the construction of the base of the base for heavy buildings on fine and dusty sand, it is worth using the pile-tape option for arranging the foundation:
- carry out the markup, dig a pit, install the formwork;
- at the intersections of the tape, wells are drilled to a depth of stable soil layers;
- pipes based on asbestos cement are installed in the wells, the structures are leveled qualitatively, and reinforced with spacers;
- the pipes are poured with concrete solution by 1/3, slightly raised to form a thickening at the bottom. Next, the pipes are filled with a solution, having previously lowered the fittings into them.
Formwork and reinforcement for pile-strip foundations
Piles can be poured without installing pipes, if the environment is not very wet and the wells are not filled with water:
- the lower part of the well is expanded with a special plow;
- reinforcing material is lowered into the well and poured with a solution;
- after the pile structures have solidified, they begin to pour the tape into the formwork.
Experts note that after pouring the foundation on fine-grained and dusty sand, the structure must stand for six months before continuing construction work.
Large and gravelly
Since coarse sandy soils have a reliable level of bearing capacity, any types of foundation structures are relevant here:
- if it is planned to build a house without a basement, the tape version of the shallow type is most often used;
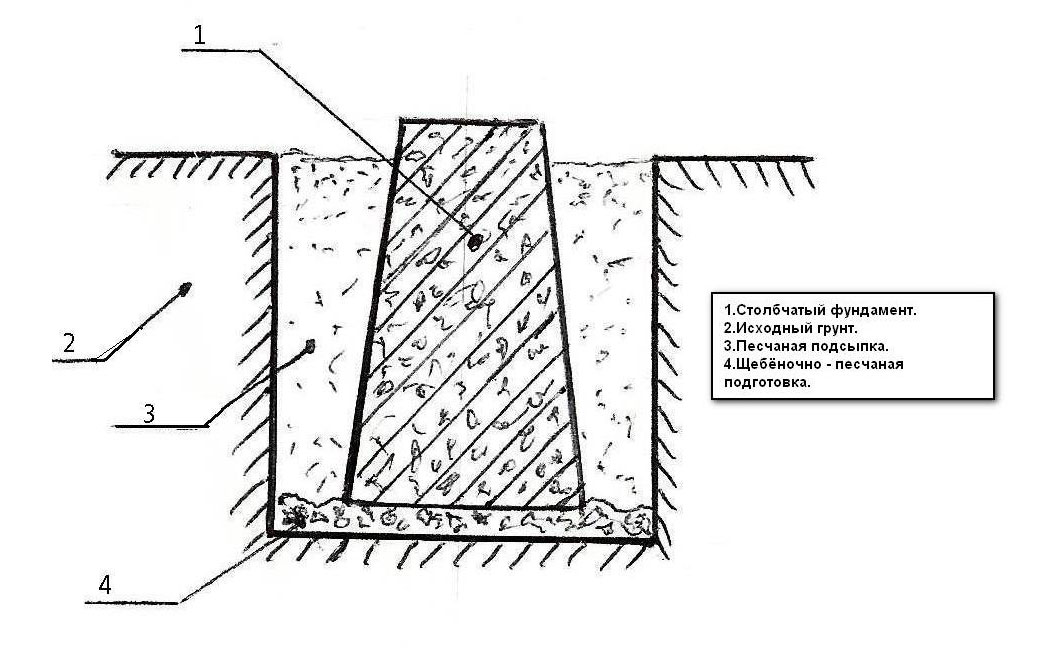
- a columnar base is suitable for a structure made of light materials in the form of frame structures, wooden houses or panel structures;
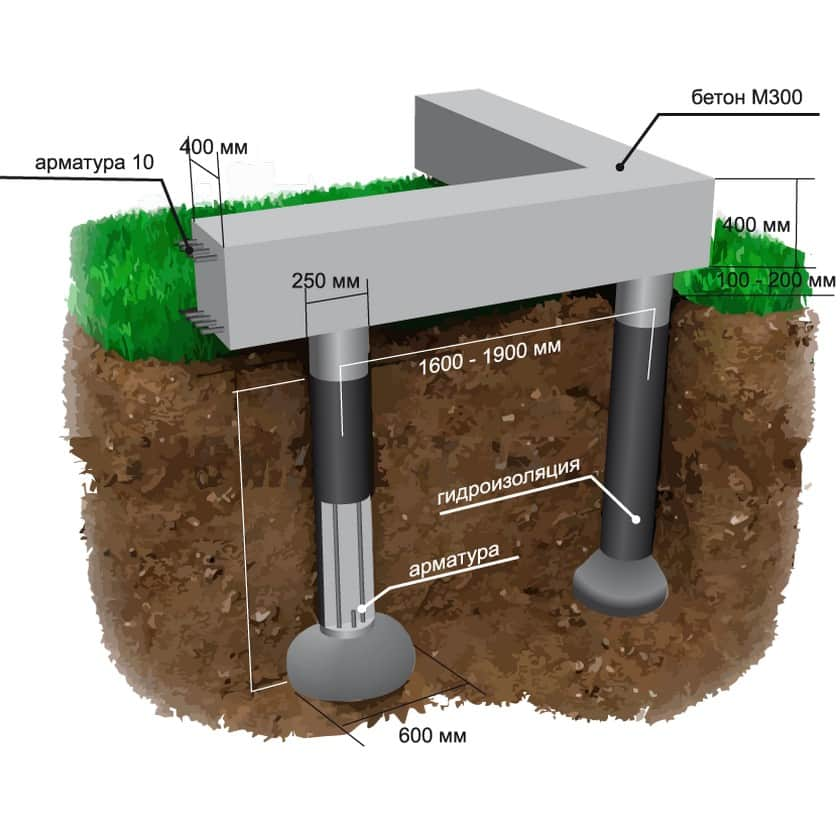
- for massive buildings with a basement, a strip foundation of a strongly recessed type is performed.
Column foundation for a frame house
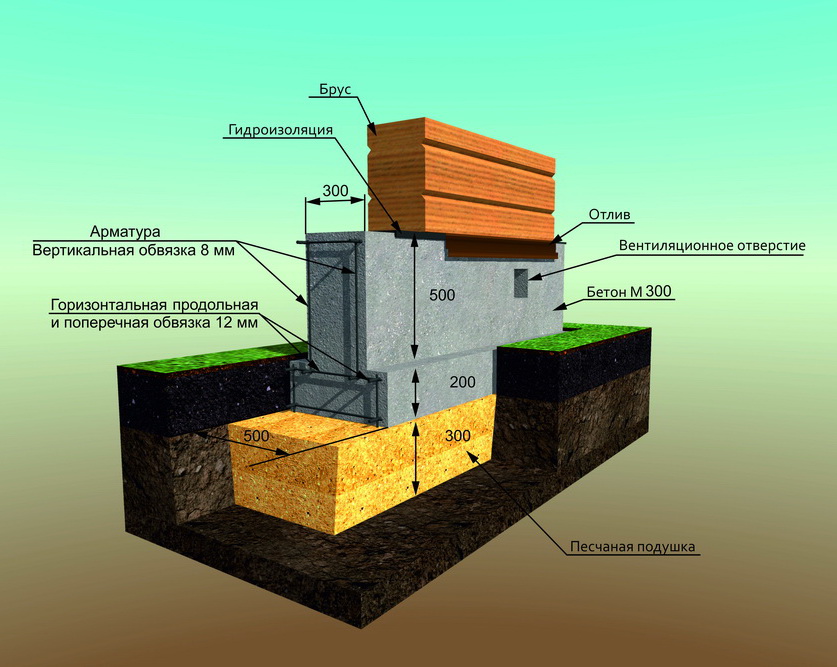
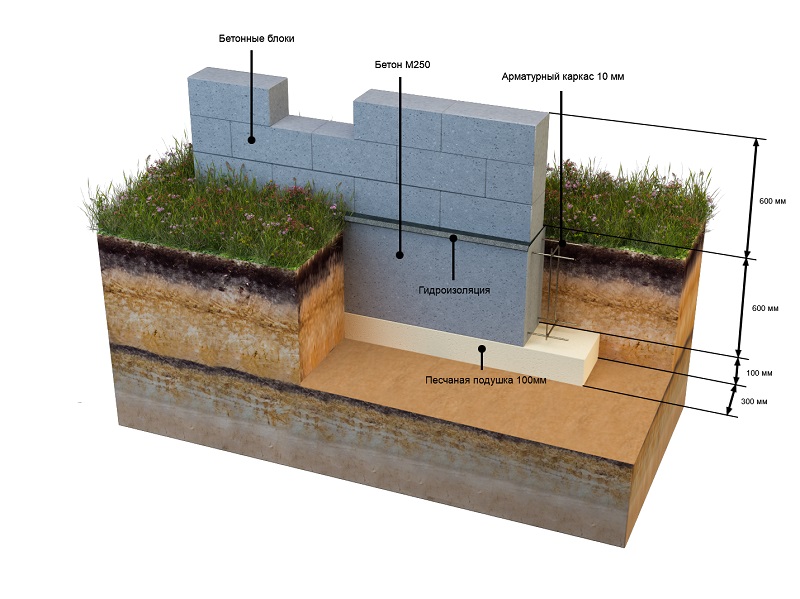
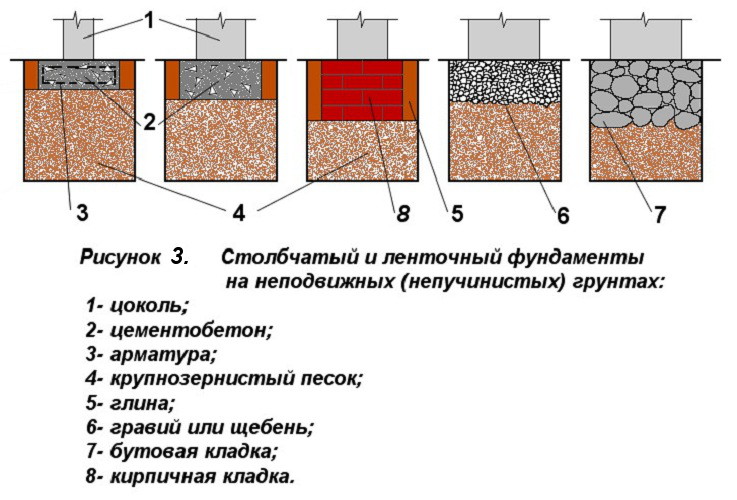
When laying a columnar or strip version of the base of the base, foundation blocks or ceramic bricks are also used.
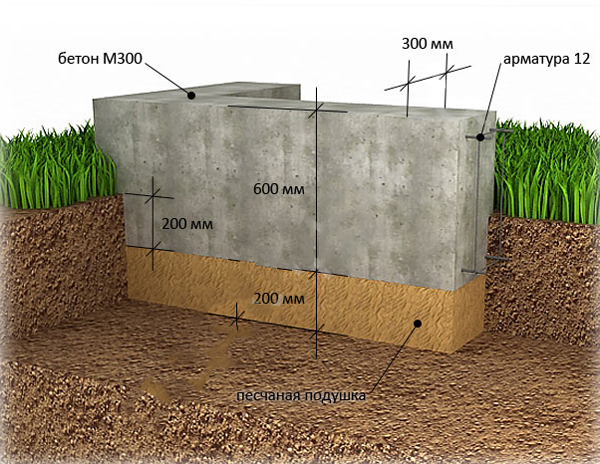
On a shallow strip base on coarse sand, you can put a building made of foam blocks or wood, a frame / panel view of a structure, or a small brick house. At the same time, the depth of laying the sole varies in the range of 40-70 cm.
Do-it-yourself technology for pouring a monolithic shallow tape:
- Site preparation. Having removed the fertile layer of earth, the surface will be leveled.
- Markup. The work is carried out on the basis of the house project.
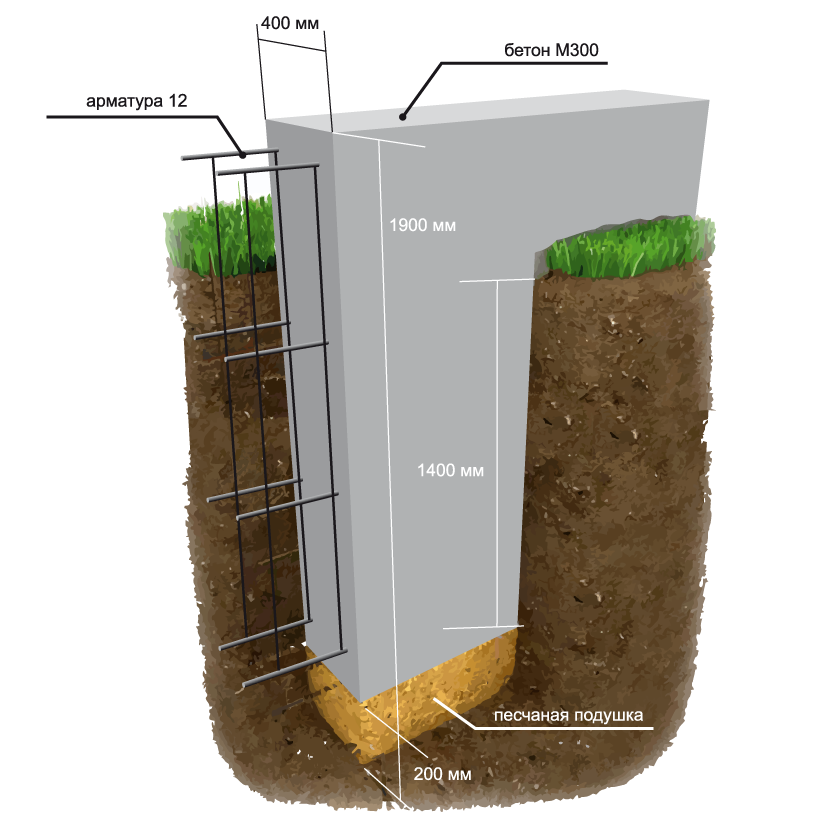
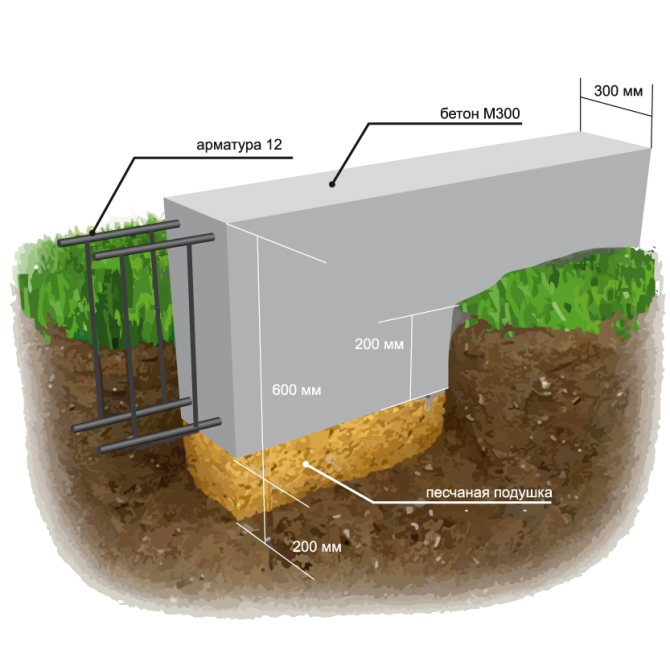
- Trench preparation. Dig a trench 60-80 cm deep. The width of the recess is equal to the thickness of the planned walls plus 20 cm, that is, 5 cm on both sides of the wall for the stability of the structure and 5 cm for the formwork.
- Filling the formwork with concrete mortar.
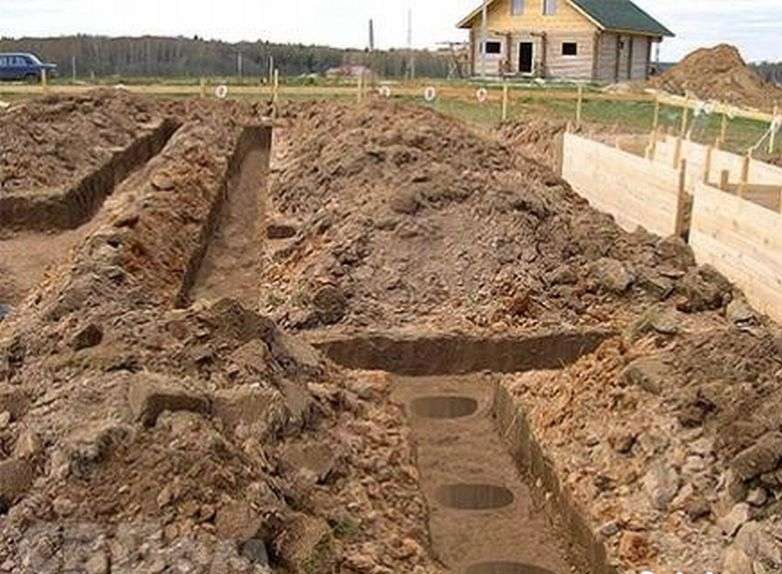
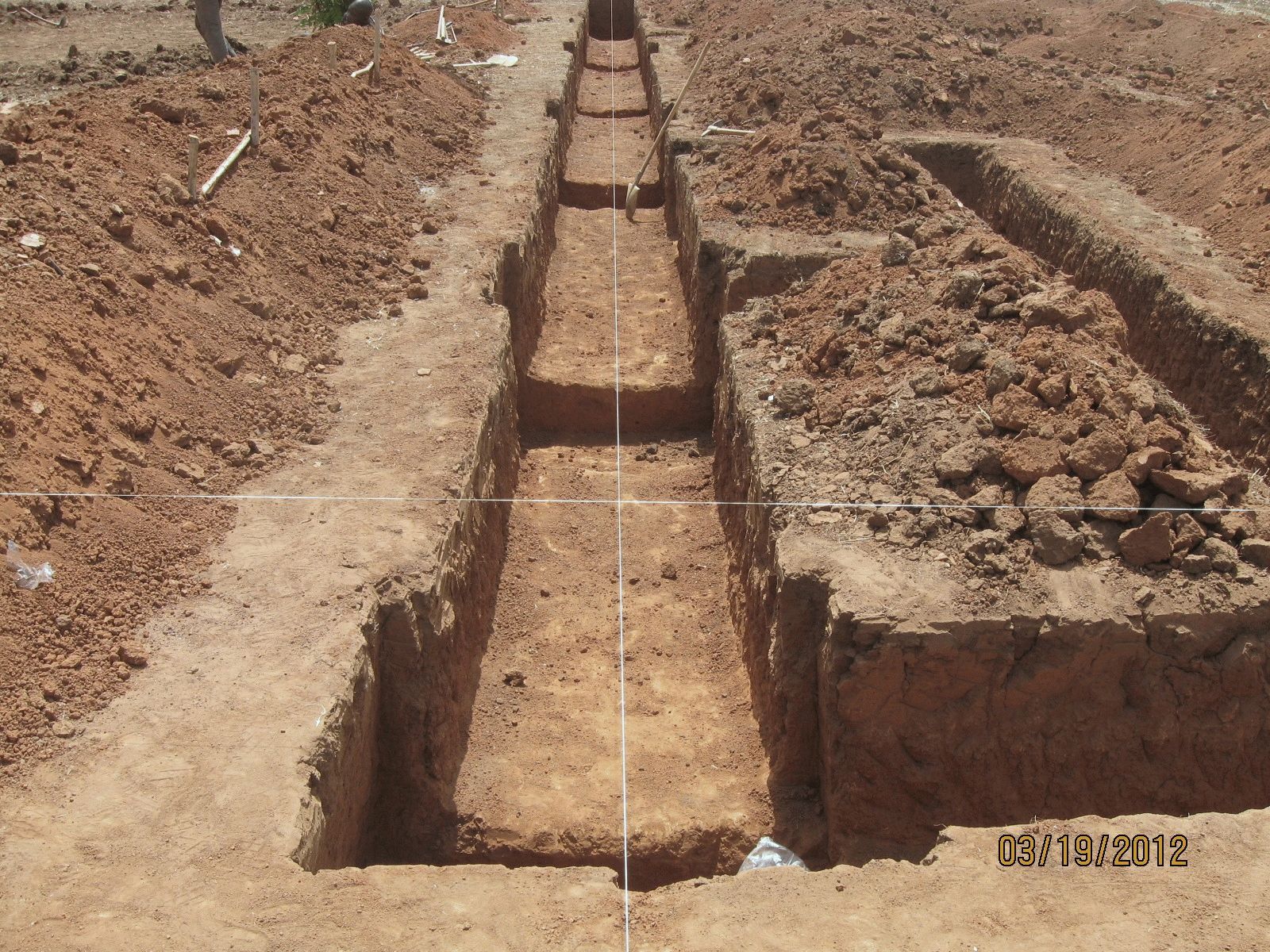
Foundation trenches
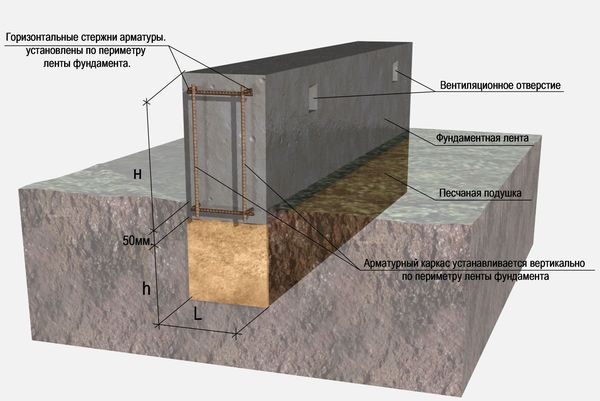
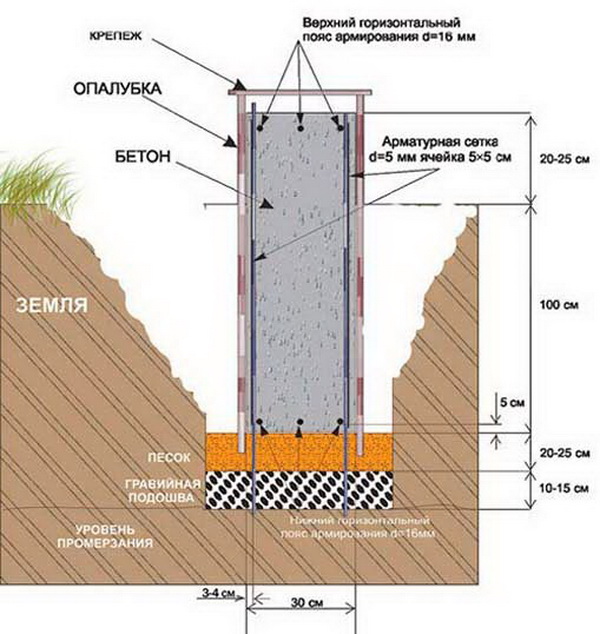
For formwork, plywood sheets, edged boards, profiled sheets are used, the inner surface is lined with polyethylene, reinforcing materials are used to strengthen the composition.
When constructing massive buildings or houses with a residential basement or basement, a deep foundation tape is laid. Moreover, the sole under the brick house is installed 20 cm below the level of soil freezing. The deeply buried strip foundation is provided with a waterproofing layer on all sides, including the lower surface. Quality drainage is also required.
Causes of deformations of the building foundation and their prevention
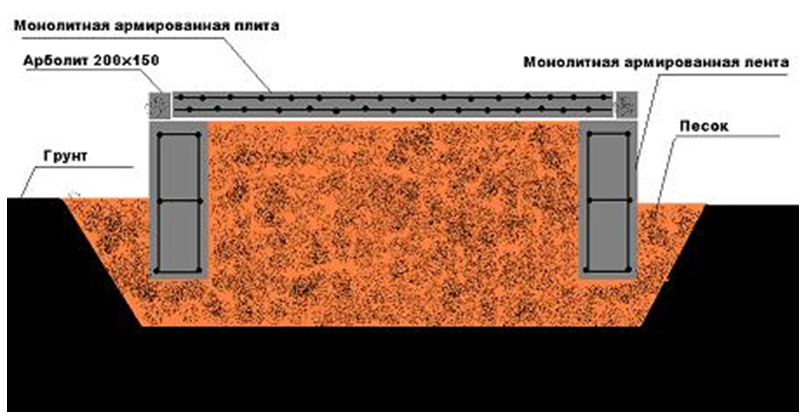
Scheme of a shallow strip foundation on clay.
Clays, consisting of very small particles, can accumulate moisture in their composition and be washed away by groundwater. As a result, clayey soils are subsiding, plastic and highly loamy. Loamy with a lower bearing capacity than clays are also loams - sands with an admixture of clay.
Those who are going to lay the foundation with their own hands on such soils should have an idea of the most common causes of damage to the foundations of buildings:
- subsidence of the base - gradual immersion in the soil. It is quite rare in low-rise buildings. In addition, the supporting area of the strip foundation, as a rule, significantly exceeds the calculated area;
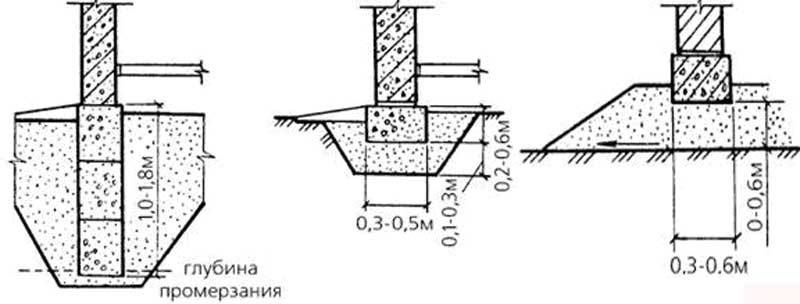
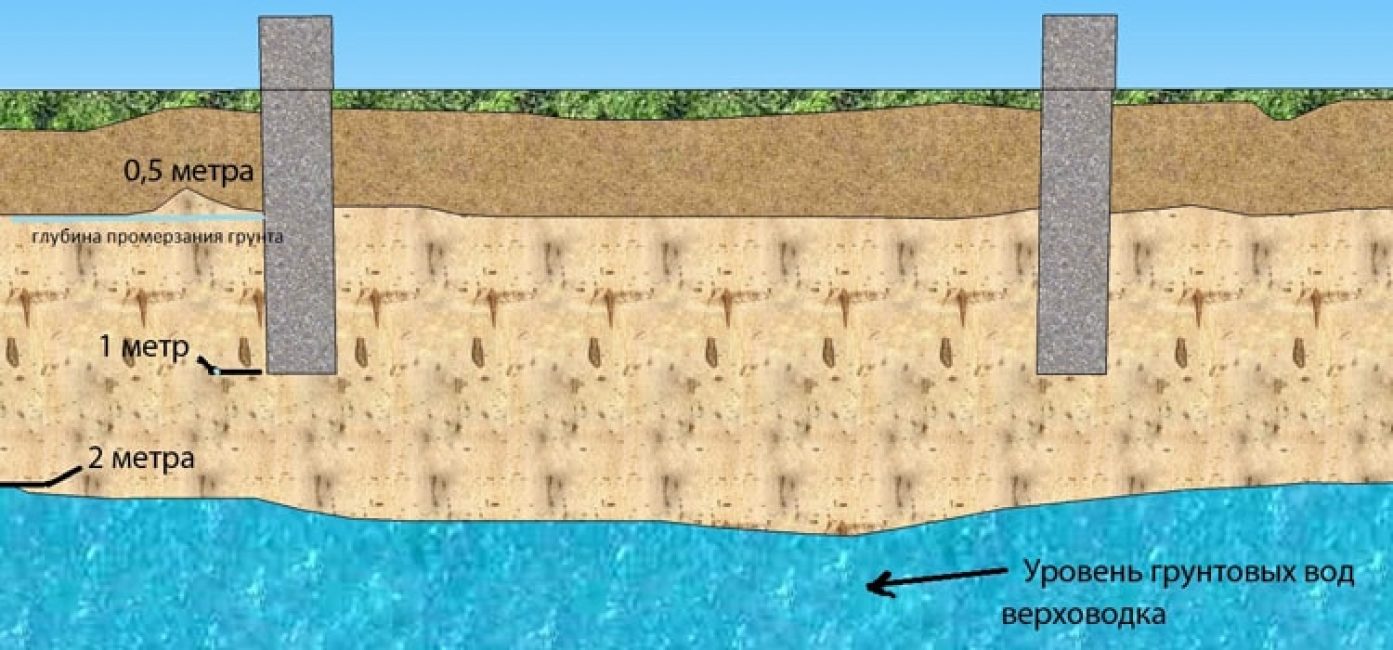
- bulging in the case of laying the foundation above the soil freezing line can manifest itself in heaving soils containing loam or moisture-saturated clays. When freezing, they increase in volume. Acting on the base from the bottom up, their pressure can exceed the weight of the building itself. When the soil freezes to a depth of one meter, this effect can cause a displacement of up to 15 cm;
- lateral impacts that do not disappear, even if the sole of the base is located lower than the freezing depth of the soil. They are able to tear the top of the foundation from its bottom or even pull it out along with the frozen soil. It follows that the opinion that the deeper the foundation, the better, is erroneous;
- lateral shift.
Damage to the foundation can be prevented in the following ways:
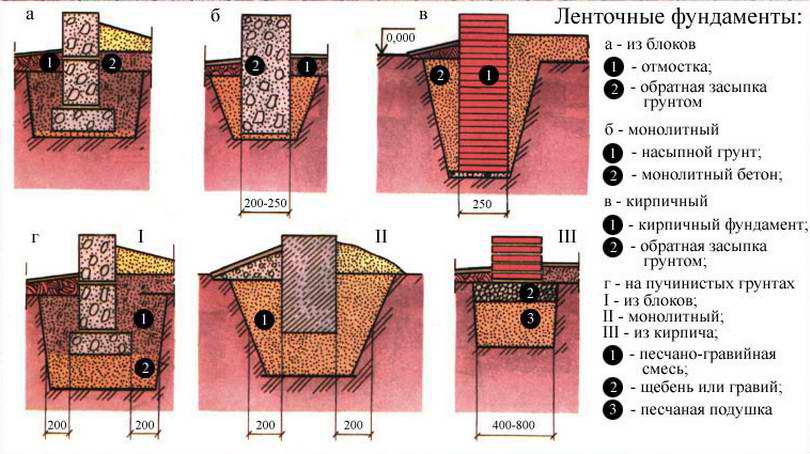
Figure 1 - Options for the construction of a strip base: 1 - Monolithic, 2 - Precast-monolithic, 3 - Precast from reinforced concrete blocks connected by an upper and lower reinforcing belt, 4 - Precast from reinforced concrete blocks connected by an upper reinforcing belt.
- inside the body of the foundation, along its entire volume, a reinforcing metal frame should be laid, which rigidly binds its upper and lower parts;
- the sole of the base should be wider than the top and the sides should be carefully aligned. It is advisable to cover the side surfaces with a sliding layer - polyethylene film or machine oil. This will significantly reduce the lateral impact of the soil on the foundation;
- the action of the lateral forces of heaving of the soil can be weakened by using a shallow foundation, since in this case its lateral surface decreases.
- lateral shear can occur when erecting a building on a steep slope. In these conditions, strip bases are more reliable rigidly connected by reinforcement in the longitudinal and transverse directions;
- the depth to which the soil can freeze can be reduced by insulating the soil layer around the foundation with foam, expanded clay or slag.
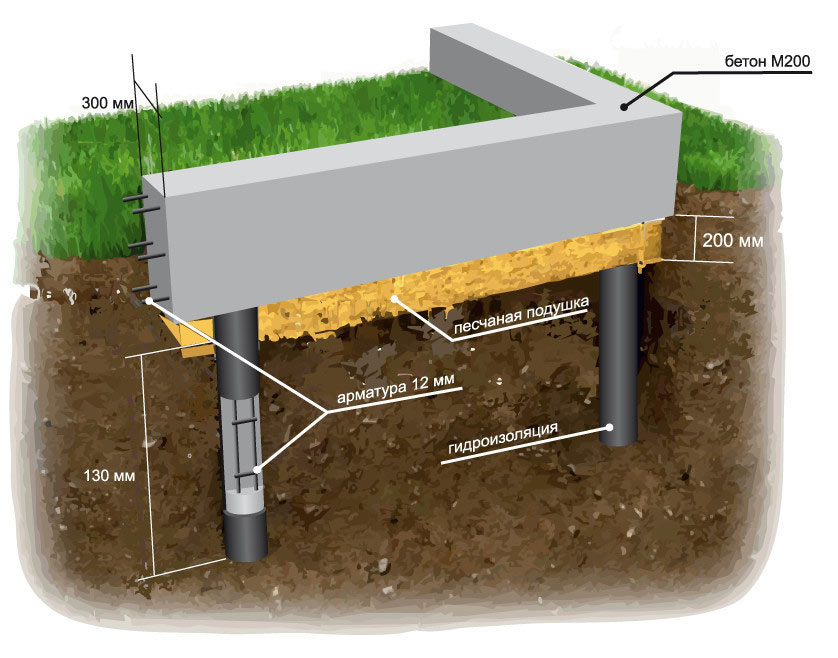
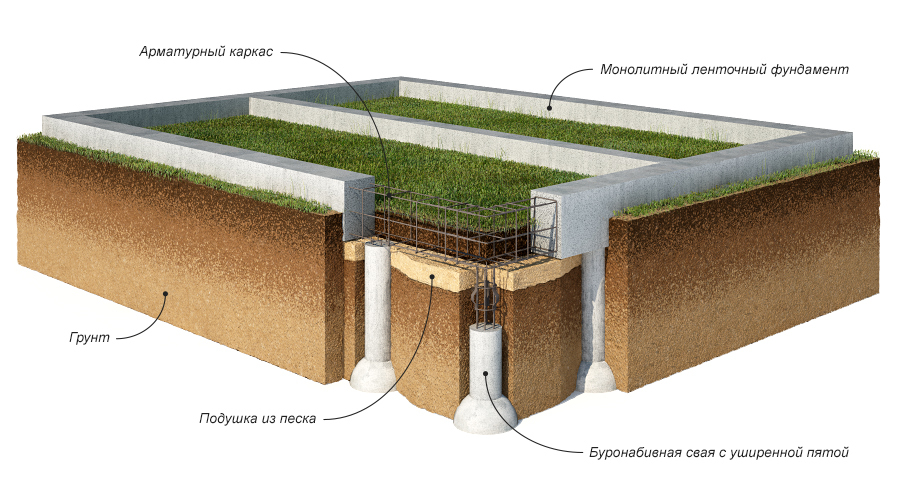
Construction of a pile foundation
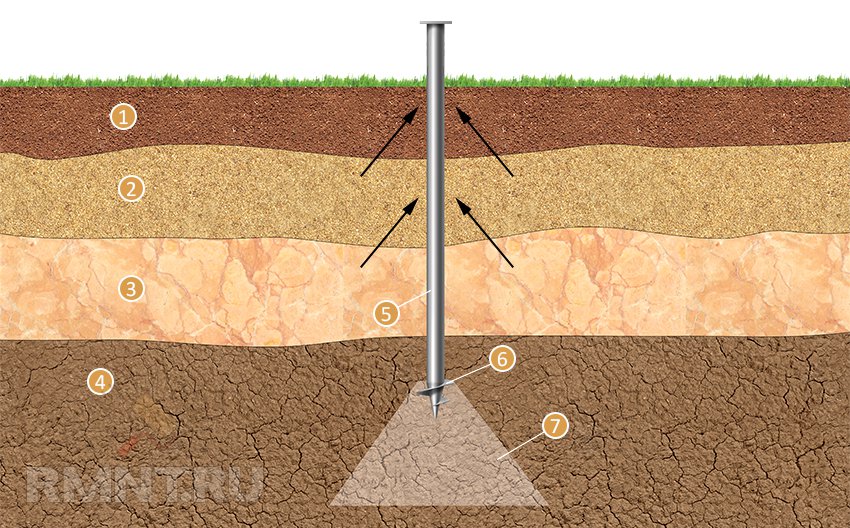
A pile foundation is often required for building on fine-grained sand.Depending on the terrain, the complexity of the construction site, screw piles and bored piles are used. The design will turn out to be reliable, the piles are brought to a level just below the soil freezing zone.
Screw piles - hollow pipes with a screw at the end. After drawing up a plan, calculating, checking the loads, the number of piles is selected. They are screwed into the ground, the base of the house is placed on them.
The type of base is reliable, the load is calculated with a margin of 20-30%. The arrangement is carried out so that the lower parts of the pillars are below the soil freezing limit.
Installation of piles into the soil will take a little time, especially with special equipment. The construction price is lower than analogs.
The downside is the impossibility of erecting a too massive, heavy building.
 Bored pile foundation
Bored pile foundation
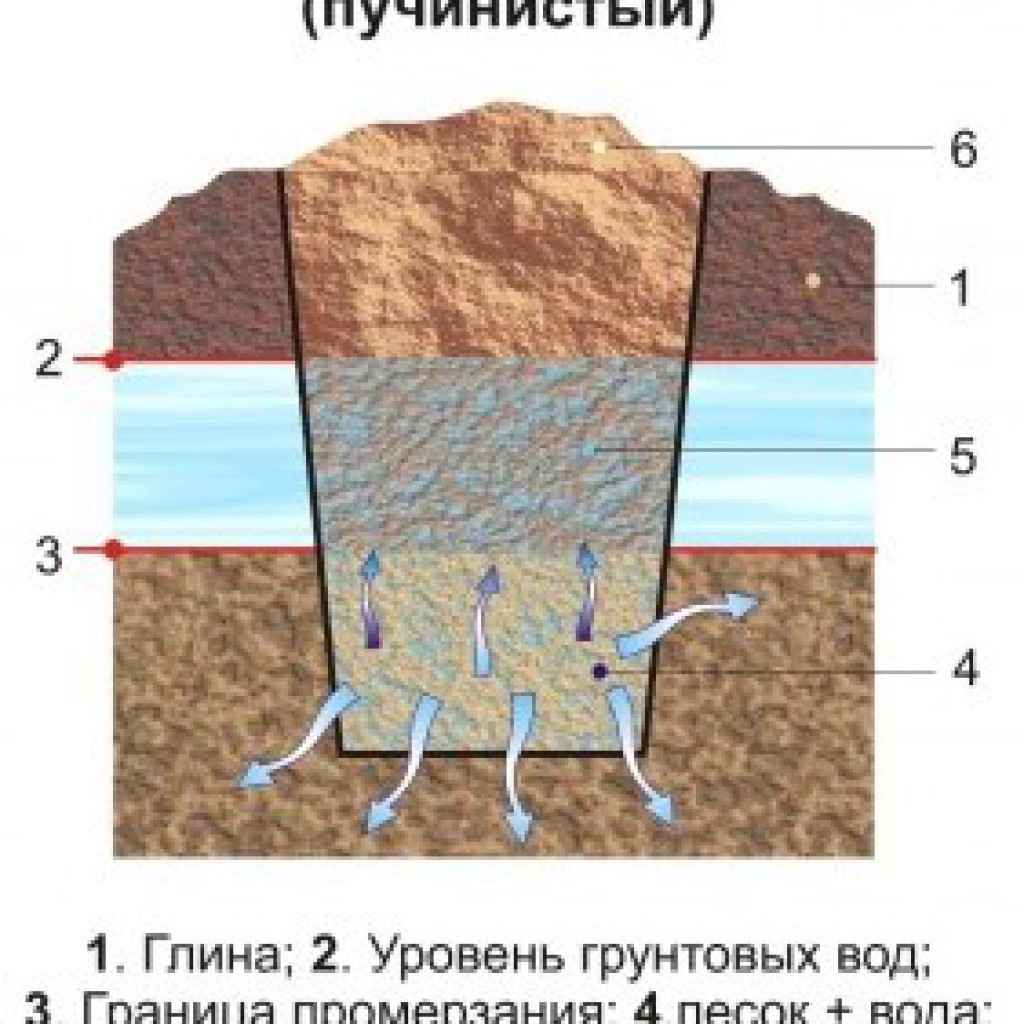
Frosty swelling of clays
Permafrost science is a branch of engineering geology and a very serious science, which, among other things, develops special methods for studying the characteristics of frozen soils and methods of high-quality construction on these extremely difficult soils.
Wet clay freezes in a rather complicated way. Clay does not freeze all at once with the entire massif, since it has pores, although you will not notice this visually. First, water in large pores becomes ice and cements soil particles, as a result of which weak clay turns into rocky soil, which can only be mined with a pickaxe, or even explosives. The increase in volume when freezing is about 9%. It is clear that in the spring this rock will turn into mud.
But the matter does not end with the freezing of water in the pores of the soil, since during the long winter there is a process of constant increase in the moisture content of the clay, due to the suction of groundwater from the lower horizon. And if the groundwater level is high and this water is nearby, the frozen soil can absorb it so much that it forms whole layers of ice, while increasing its volume so much that it easily and simply lifts the house, swells road clothes made of asphalt concrete, deforms the railway tracks and the runway of the airfield and so on. Tens of centimeters of heaving in winter is not uncommon.
And in spring, the result of this phenomenon, called frost heaving, is evident - the liquid thawed soil becomes mud, the asphalt is destroyed, there are pits and potholes on the road, the buildings sagged, and the foundation cracked. And repairs often won't help.
Another "interesting" phenomenon is that the frozen water-saturated soil tends to freeze up with the foundation, including the pile, as with any underground structure. The pressure from the frozen ground, which arises in this case, is so great that it breaks the piles. These forces act tangentially on the vertical surfaces of the foundation walls, both destroying and pushing structures out of the ground. One of the effective means to prevent all this is to arrange vertical waterproofing of the foundation using roll materials, this will significantly reduce adhesion and make the frozen soil "slide" over the surface, while the tangential heaving forces will be largely leveled.
But professional builders and road builders do not just have a bunch of troubles from the process of frost heaving, but quite effectively fight it. The methods are different, sometimes with the use of chemistry. But on your site, the best method of dealing with the depths is a simple tool - drainage. If it was possible to drain water by arranging an effective drainage system, then swelling will either not occur, or will be much weaker.
But before you fight, you need to get to know the enemy by sight. To build a capital house on clay soil, geological studies and design calculations are needed. Contacting a design organization in this case will be a practical solution, and construction in compliance with technologies, and according to a project carried out by specialists, will save you from unpleasant surprises in the future.
In the case when a bathhouse, a garage or a small house is being built, it is possible to make a high-quality foundation on clay soil on your own, having studied the issue technically and guided by building codes.
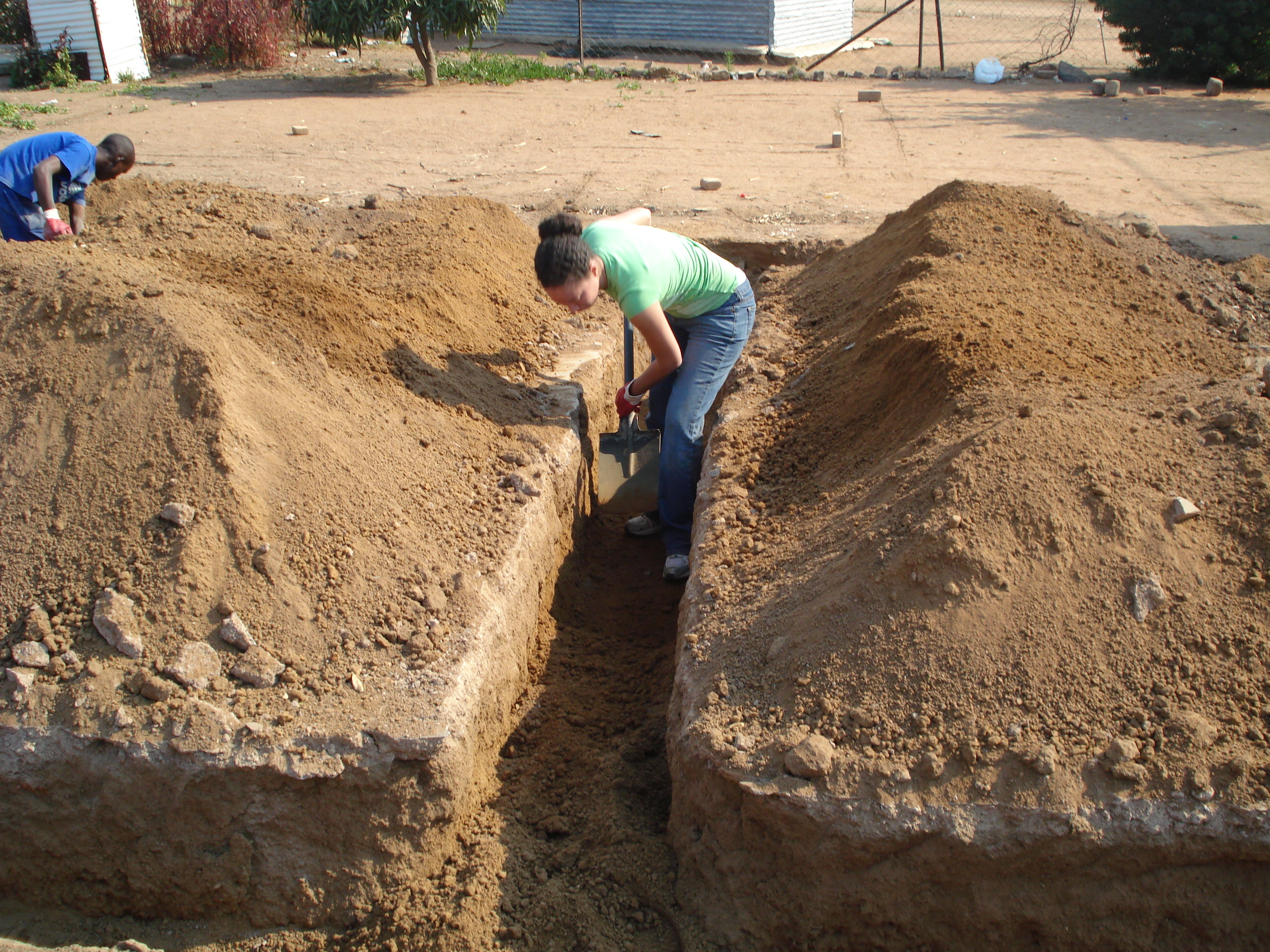
Preparations for strip foundations and manual soil finishing
The construction of the strip foundation begins with the preparation of the territory. This is a geodetic stakeout. This process consists of several stages:
- Cleaning the territory. It is necessary to remove everything that will interfere with construction.
- Finding the main landmarks. In geodesy, these are axes or lines, which will serve as a reference point for the structure being erected.
- Performing geodetic work - the correct calculation of the angles. Each angle should be 90 degrees. Accurate observance of this indicator will avoid distortion of the building, which can reduce its operational characteristics.
- Completion of geodetic work - marking with construction cords and pegs - they are just baited immediately, and not driven into the ground. After completing the marking, it is necessary to check everything again and only then firmly fix the pegs and start excavating the soil under the strip foundation.
Choosing the type of foundation on clay
The choice of the type of foundation on clay depends both on the depth of freezing and on the height of the passage of groundwater.
Shallow strip foundation on clay
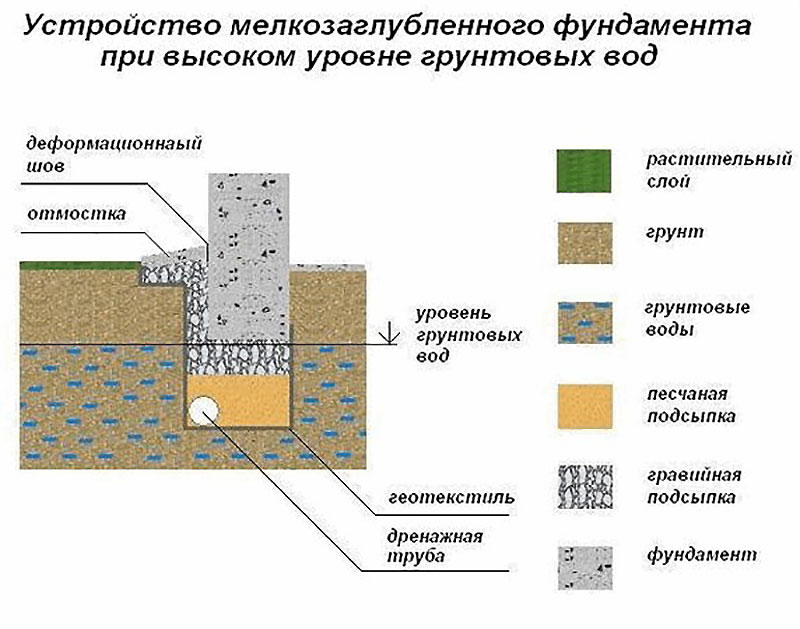
If the groundwater level is much lower than the freezing depth, then it is possible to choose for a small structure MZLF - a shallow monolithic tape. However, there are several features:
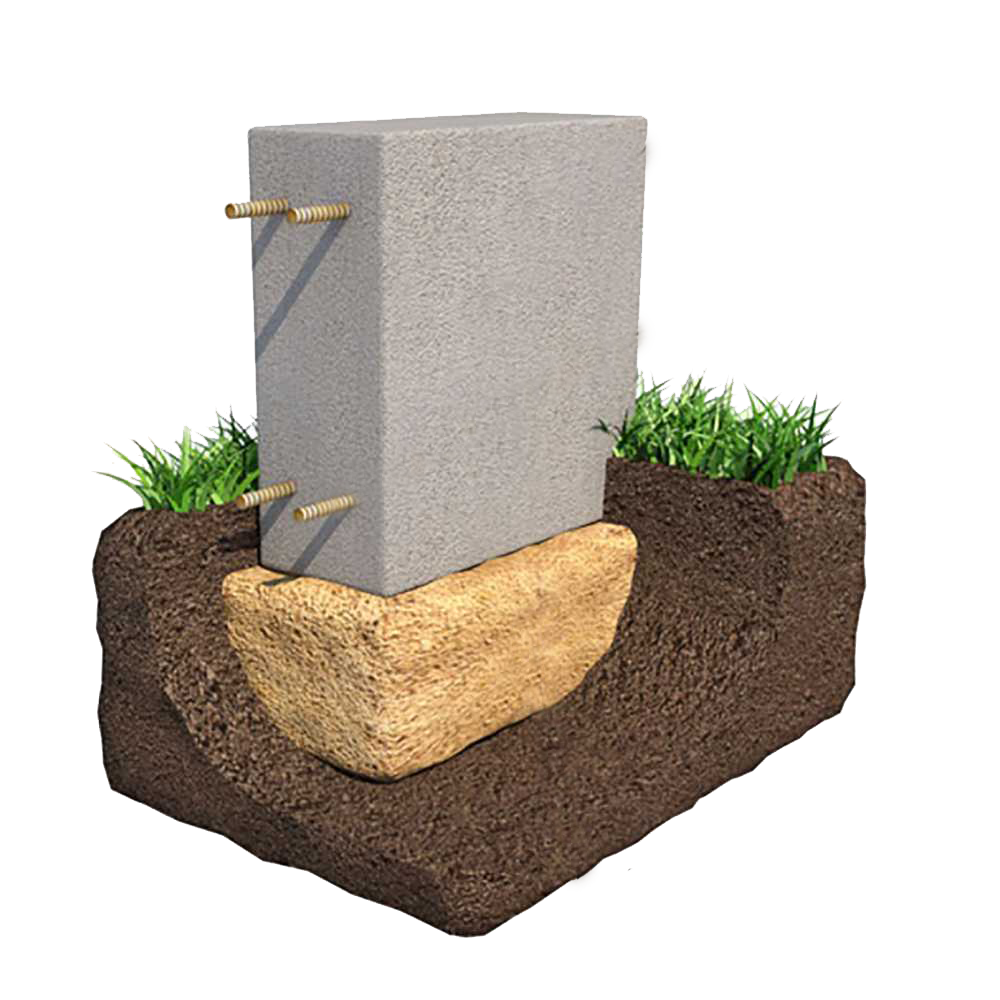
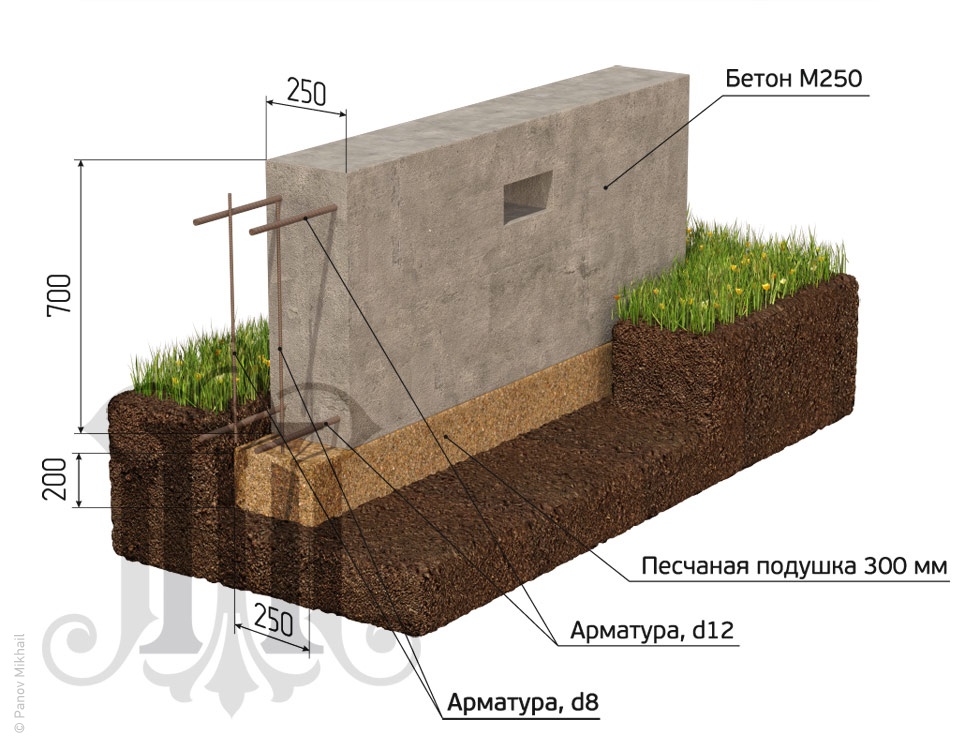
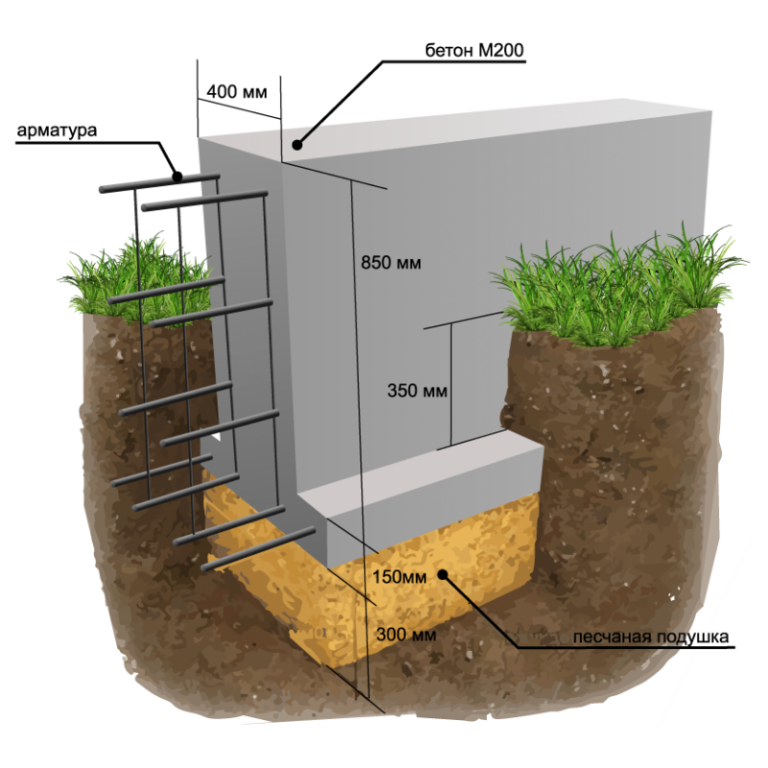
The section of the tape must be taken in the form of a trapezoid resting on a wide base, or make a T-shaped widening of the sole of the tape. These measures will lead to an increase in the area of the base of the foundation, and as a consequence - to a decrease in the specific force on the foundation from the ground.

A pillow is needed under the foundation - at least 40 cm of coarse sand, compacted in layers, in layers of up to 10 cm. The pillow can be made of crushed stone or sand gravel mixture. The main thing is that this base will be drainage, that is, it will divert water from the foundation. Another function of the cushion is that it is a shock absorber.

External vertical waterproofing of the foundation is mandatory, and it must be performed using roll-up waterproofing materials of high strength. By creating a sliding surface, waterproofing will weaken the adhesion of the frozen soil to the foundation walls, and will not allow clay to stick to the foundation. As a result, the frozen clay, which has increased its volume, will move by its mass separately from the foundation wall, without causing its shift, uplift and destruction. Insulating the foundation is also a rational measure. Of course, if a basement with heating is being built, insulation is done in any case.

The blind area around the building, which has an insulating layer as part of the "cake", significantly reduces the effect of frost heaving forces on the foundation.

Monolithic floating slab on clay
The second case is when groundwater flows close to the surface, it is more difficult. In this case, it is possible to choose a base in the form of a reinforced monolithic floating slab.

This foundation will remove the problem of the influence of heaving and seasonal movements on the building, since by its design it is designed not to fight the foundation soil, but to move along with it, like a boat on the surface of the water. Therefore, this base is called "floating". One serious disadvantage is that this foundation is the most expensive.

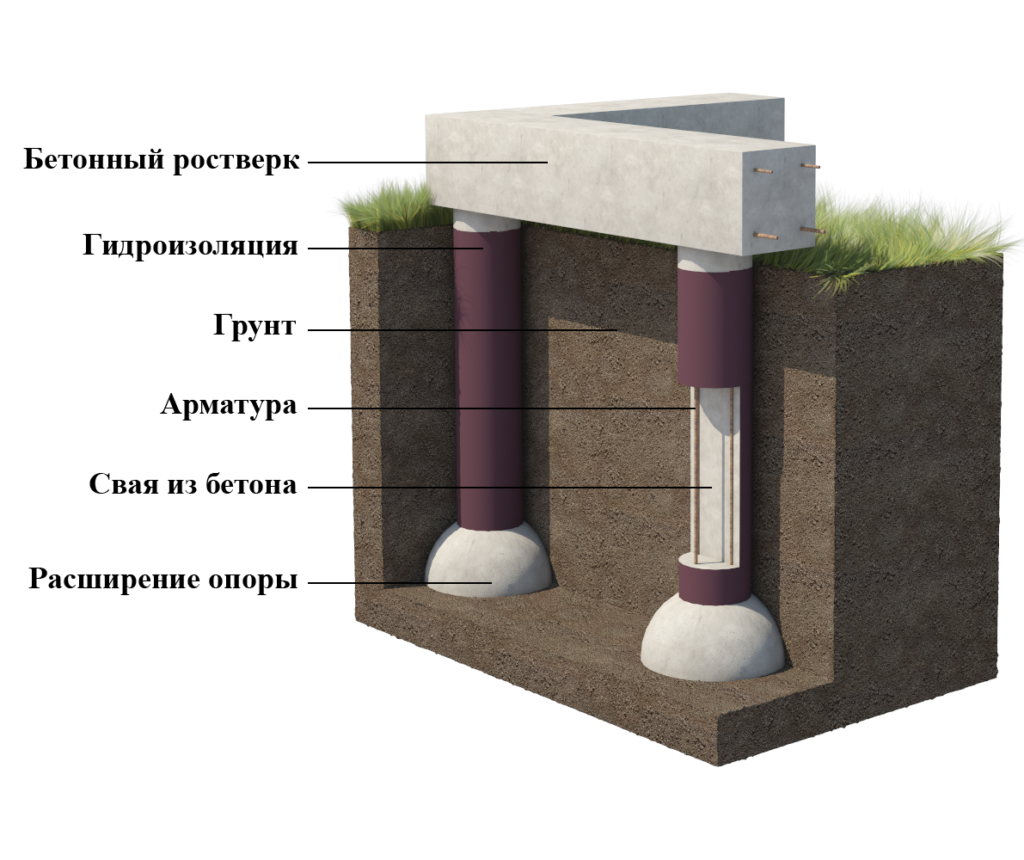
Pile foundation with widening on clay
Another possible type of foundation is a pile foundation with widening. Bored piles are buried to a considerable depth, below the freezing of the soil, and, in addition, they are not made with a constant cross-section, but with a "heel". The widening at the end of the pile does not allow the forces of frost heaving to push it out of the ground. One of the technologies for the installation of piles with widening - the TISE technology is used by many private builders.

The pile-screw foundation has also earned the respect of private builders.The technology of the device of a reliable base with relatively low material costs and time is becoming more and more popular. Piles made of steel seamless pipes with a specific wall thickness, which have undergone anti-corrosion treatment both inside and outside the pipe, have helical blades at the ends. These blades make it possible not only to drill a pile into the ground, even frozen ground, but also perform the task of widening the pile base. The internal cavities of screw piles are filled with concrete to prevent metal corrosion.

One of the effective measures to combat heaving remains drainage and dewatering at the site - that is, the device of a drainage system.