Material advantages
 Foam concrete is a product obtained from the composition of sand, water, cement foam and plasticizers, which has a porous structure
Foam concrete is a product obtained from the composition of sand, water, cement foam and plasticizers, which has a porous structure
Foam concrete is a product obtained from the composition of sand, water, cement foam and plasticizers, which has a porous structure. The variety of the size range of block elements allows you to build any structure quite quickly and without special financial costs.
The density of foam concrete is three times lower than the density of brick, which means that the weight is also much less. At the same time, other indicators, such as: heat, waterproofing, strength - remain at the level of the most durable and expensive materials. However, given the fragility of foam concrete, it is not worth building multi-storey structures, it is recommended to carry out one- or two-story buildings, it is possible with an attic.
Foam concrete blocks are often compared to aerated concrete, but the latter reacts much more to moisture. Therefore, if your site is located in an area where the soils are oversaturated with water, the construction of a foam concrete structure on screw piles is an ideal option for building a practical and very warm house.
Aerated concrete house foundation
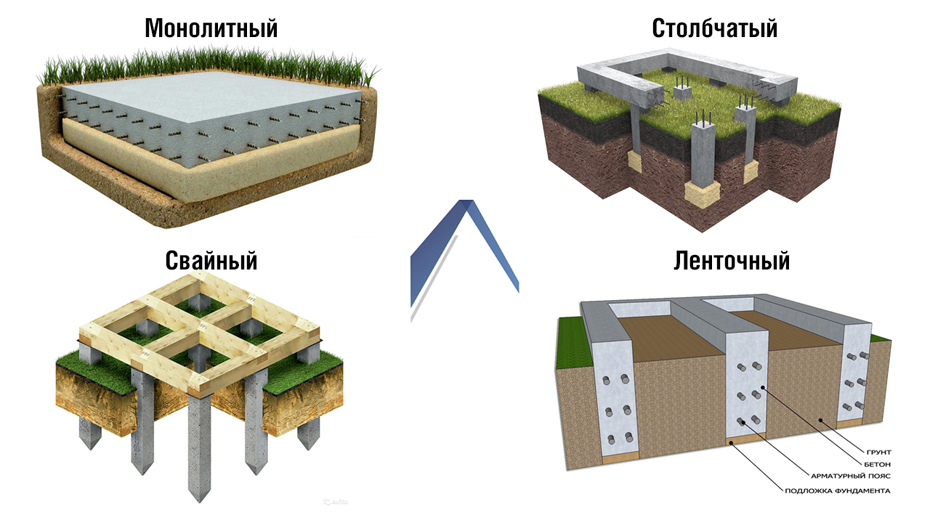
When choosing a foundation for a house made of aerated concrete, four main types are considered:
Monolithic
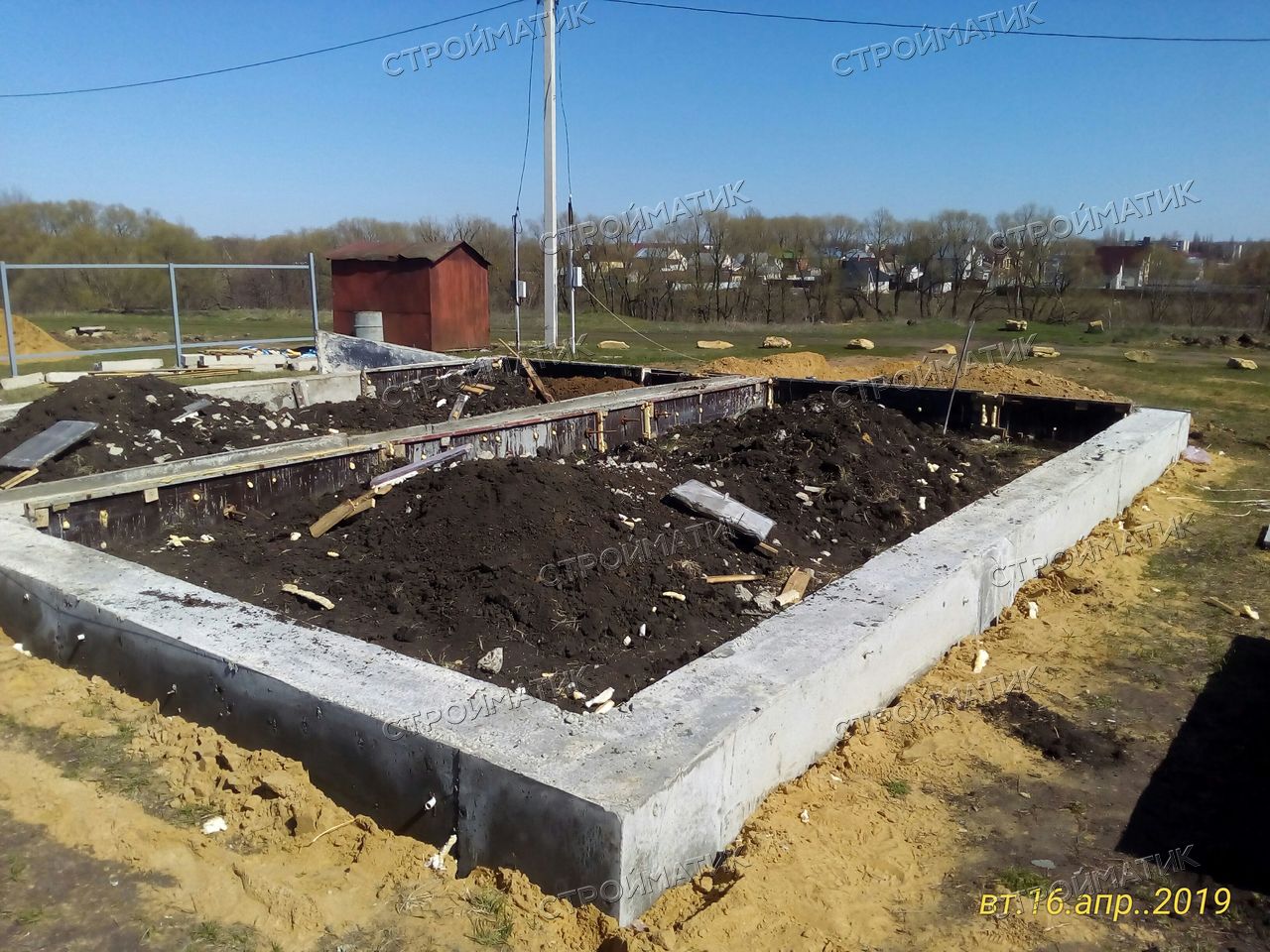
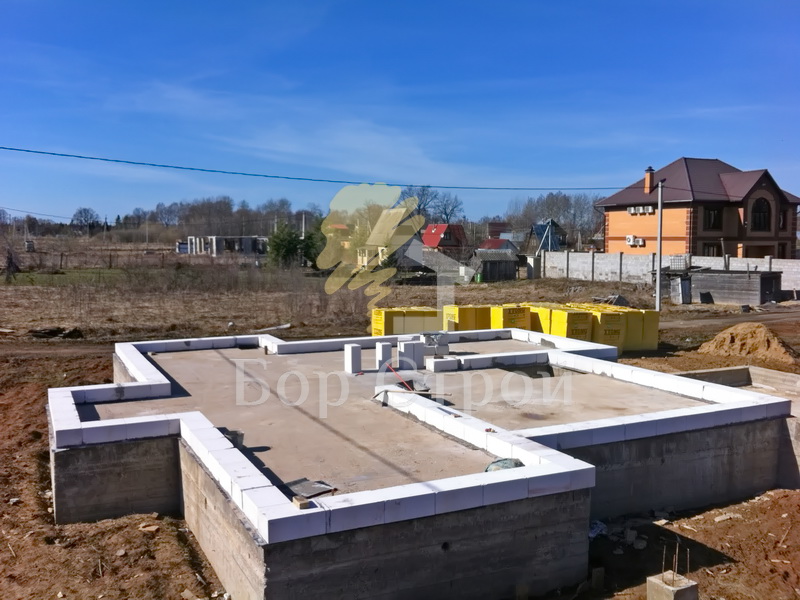
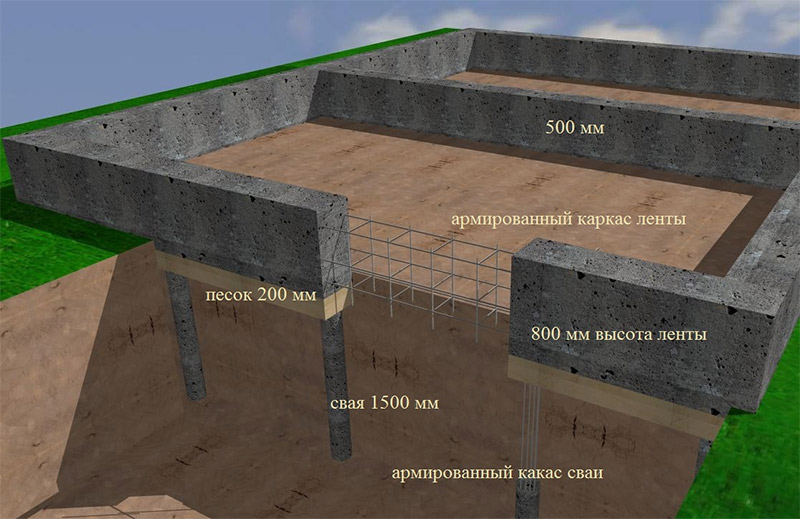
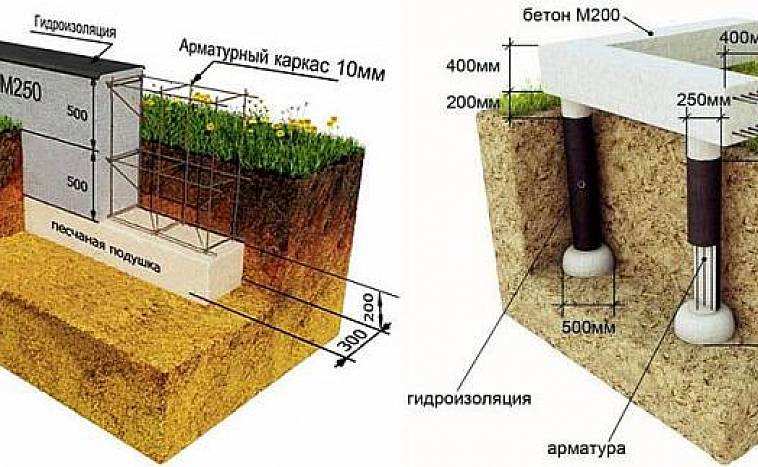
This is a durable and reliable type of base. For its construction, several layers of reinforcing mesh are formed and poured with concrete. This option is maximally resistant to various weather conditions and soil movement. This eliminates the possibility of deformation of the building and the appearance of cracks. A monolithic foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is suitable for heavy structures and complex structures. It is built on almost all types of soil and can withstand even the most severe climates. The disadvantage is the relatively high price, it is the most expensive but also the most reliable type of foundation.
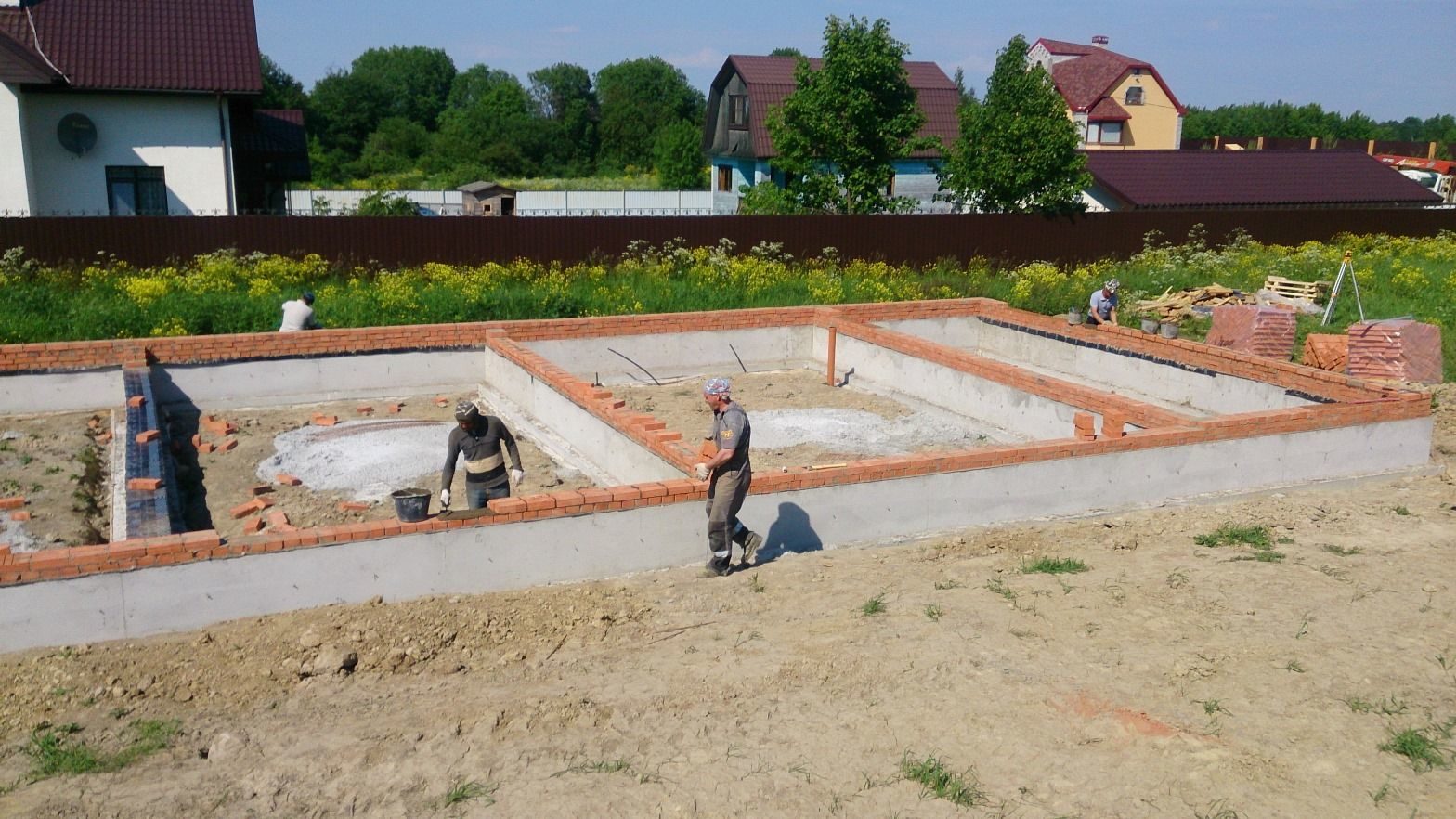
Tape
One of the most demanded and economical options for the construction of various structures. Depending on the type of soil, the level of groundwater and the expected load from the building, one of several subspecies of this foundation is selected. They are divided according to the degree of immersion in the soil into: shallow and buried. Both options have high levels of stability and reliability. The installation price and construction speed are lower than that of a monolithic one due to the smaller amount of required materials.
Columnar
It is possible to install a columnar foundation for an aerated concrete house in Moscow and the Moscow region, provided there is stable soil and no slope. If the criteria for the construction site are met and the basements are not planned, then this option will be very profitable and economical. When installed, the pillars are installed vertically at the corners of the building, at intersections of walls and in areas of maximum load. The entire structure is combined with each other to evenly distribute the load.
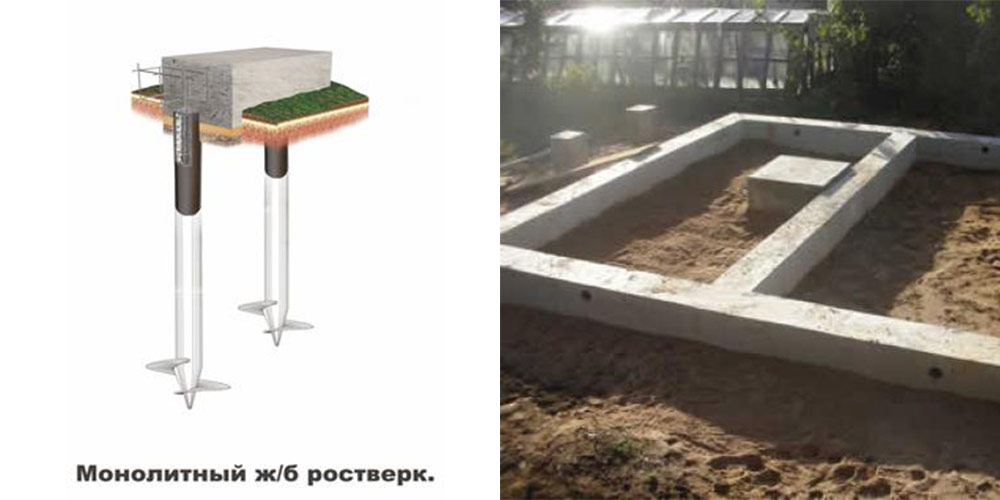
Pile
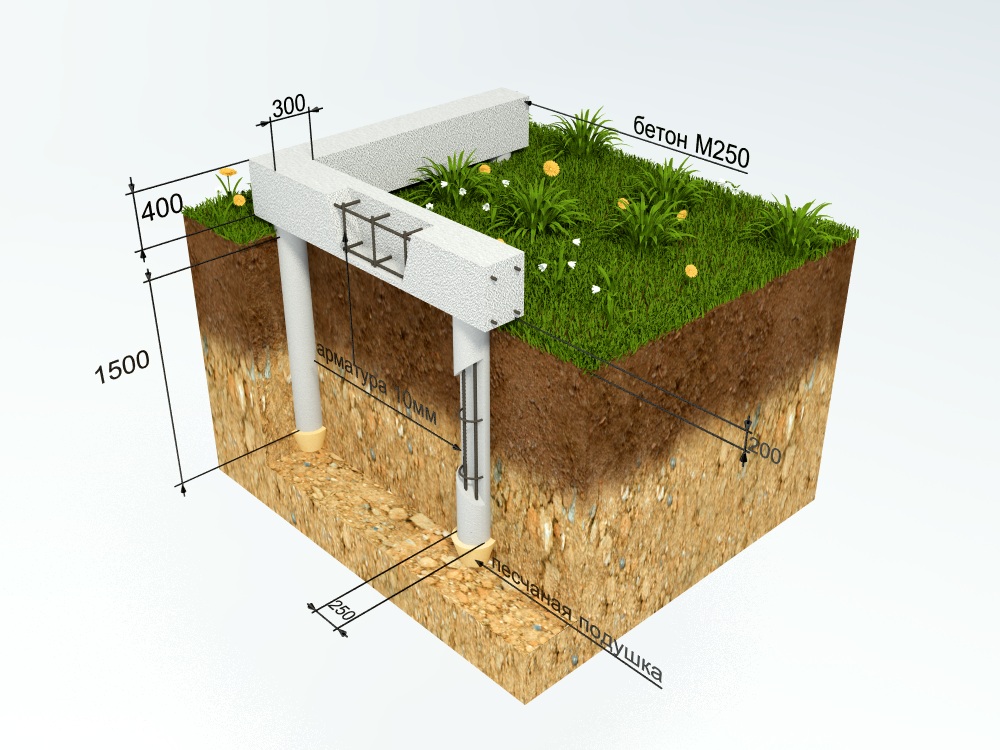
This foundation for a private house made of aerated concrete is best suited in case of unstable soil, difficult terrain or high groundwater levels. Depending on the specific case, bored or driven piles are used. To strengthen the base structure and distribute the entire load, a monolithic grillage is used.
Regardless of the chosen base option, when building a house from gas blocks, it is mandatory to install waterproofing and additional insulation of the basement. This will reduce the effect of moisture and prolong the durability of the structure.
We fill the foundations in Moscow and the Moscow region and guarantee the quality and reliability of the erected structures.To do this, our staff employs highly qualified designers and builders with extensive construction experience. We use only high quality materials and specials. technique. In our work, we use modern methods and technologies for the construction of foundations and apply an individual approach to each order.
On our website you can use aerated concrete house foundation calculator to roughly calculate the cost of our services. Our specialists will answer all your questions by phone free of charge.
We provide a free service of a specialist visit to the construction site. There he will be able to make a more accurate calculation, taking into account all the features of the site and the requirements for construction.
All the details and features of the order are specified in the contract. After signing it, we strictly adhere to all points. The price also remains fixed and cannot be changed.
Our professionalism and well-coordinated work at all stages of construction guarantees the timely delivery of the facility on a turnkey basis.
Nuances of choice
To make the right choice, you should take into account all aspects that can affect the operation of the base for foam blocks. The main selection criterion is the characteristics of the soil: its strength and the level of groundwater at the construction site.
Soil characteristics
 The denser the soil, the more stable it is.
The denser the soil, the more stable it is.
Before choosing this or that base option, it is necessary to determine the type of soil prevailing on the site. The strength and bearing capacity of the soil directly depends on its composition. All types of soil are divided into several groups, each of which has its own characteristics.
- Rocky or clastic. It belongs to the most durable types of soils, practically not prone to settling and heaving. On such soils, you can use absolutely any type of load-bearing base. The most preferred option is a shallow strip foundation base. The device of a shallow strip foundation for a house made of foam blocks saves money, effort and time, while at the same time providing the necessary strength. A slab foundation for a house made of foam blocks is recommended for use with a small building mass.
- Sandy. More than half of such soils are coarse or medium-sized sand. The main plus of sandy soils is that they do not accumulate moisture in themselves - it seeps through them freely into the lower layers. On such soils, a variety of types of bases can also be used - tape, columnar, slab, etc.
- Sandy loam and loam. These soil types are dominated by a mixture of sand and clay in varying proportions. In the first case, most of it is sand, and in the second, clay. These soils are not particularly durable due to the fact that clay tends to accumulate water. With the onset of cold weather, it turns into ice and increases in volume, which leads to the effect of frost heaving: the earth begins to bulge out in the form of mounds. As a result, foundation structures can be deformed or even partially destroyed.
- Clay soils can be composed almost entirely of clay with small inclusions of sandstone and stones. Such soils are even more prone to frost heaving, therefore, the choice of load-bearing bases in this case must be approached with the utmost responsibility.
Ground water
 High groundwater threatens future problems
High groundwater threatens future problems
Groundwater height is another criterion that must be considered when choosing a supporting base. The higher the level of their occurrence, the greater the likelihood of destruction of the foundation in winter due to heaving of the soil.
In addition, subsoil water can be a problem when trying to construct buried strip foundations for arranging a basement or basement floor.All work in this case becomes much more complicated: it will be necessary to make multi-layer waterproofing of the basement walls, as well as to think over an effective drainage system around the building. The easiest way to avoid all possible problems is to put the house on buried piles.
Building dimensions
 Another factor that directly affects the calculation of the foundation is the size of the building and its number of storeys. It is quite natural that for a house with 2 floors and dimensions of 10 x 10 m, a more solid foundation will be needed than for a garage or other ancillary structure.
Another factor that directly affects the calculation of the foundation is the size of the building and its number of storeys. It is quite natural that for a house with 2 floors and dimensions of 10 x 10 m, a more solid foundation will be needed than for a garage or other ancillary structure.
In this case, you need to calculate the approximate mass of the building so that the load on the base is evenly distributed. Otherwise, uneven subsidence of the foundation, its deformation and destruction is possible.
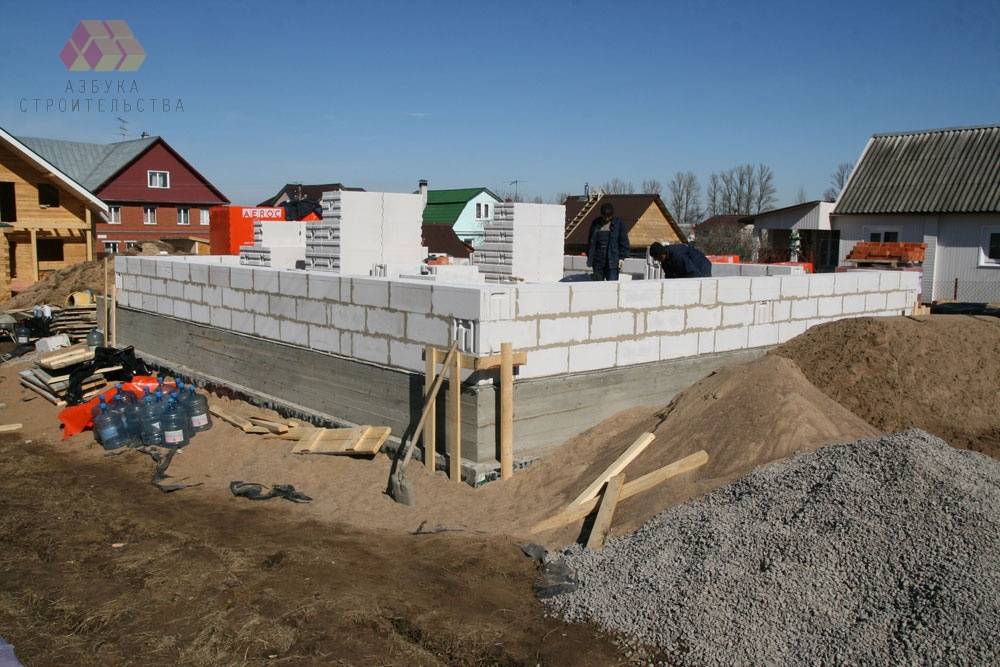
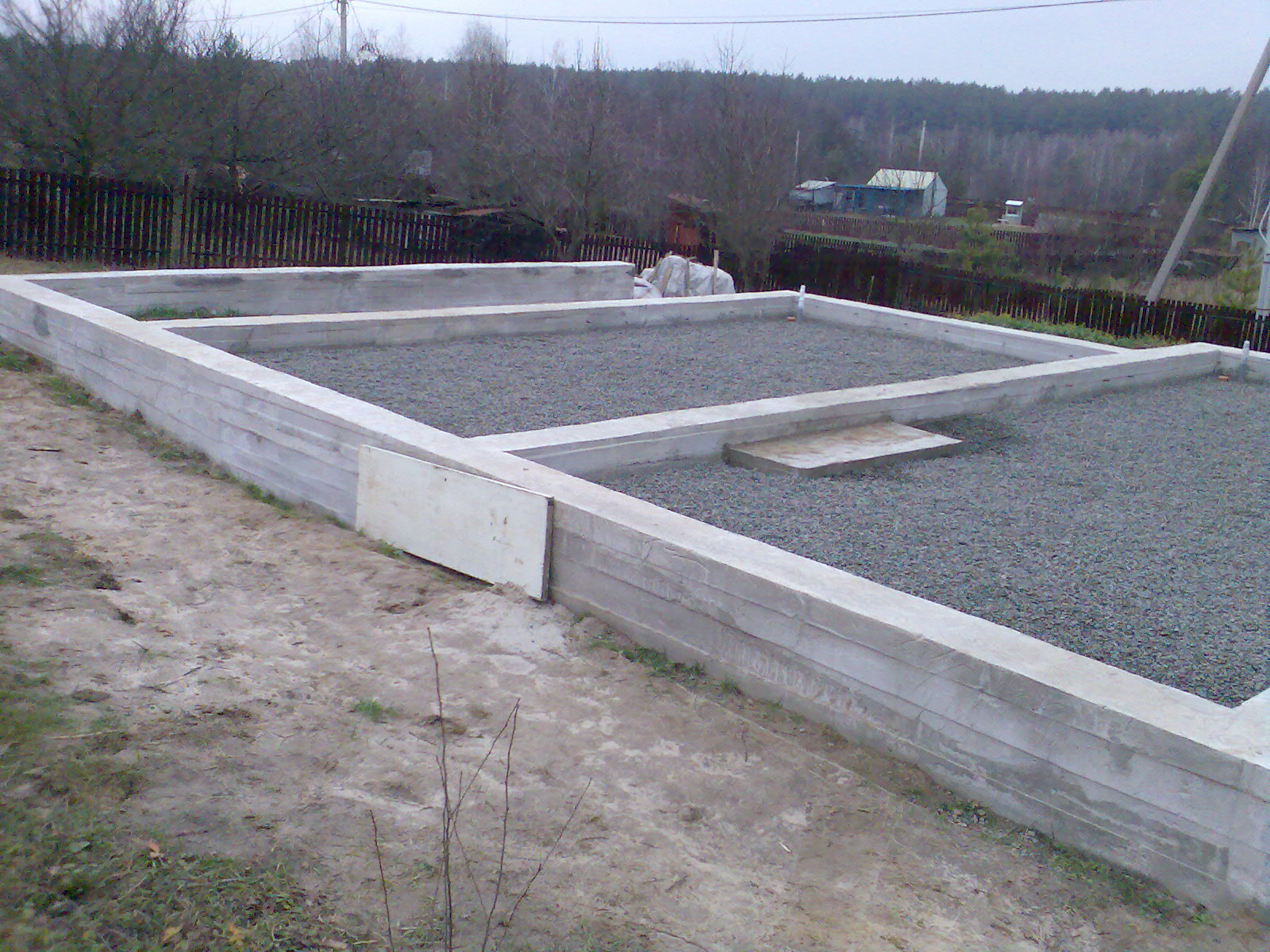
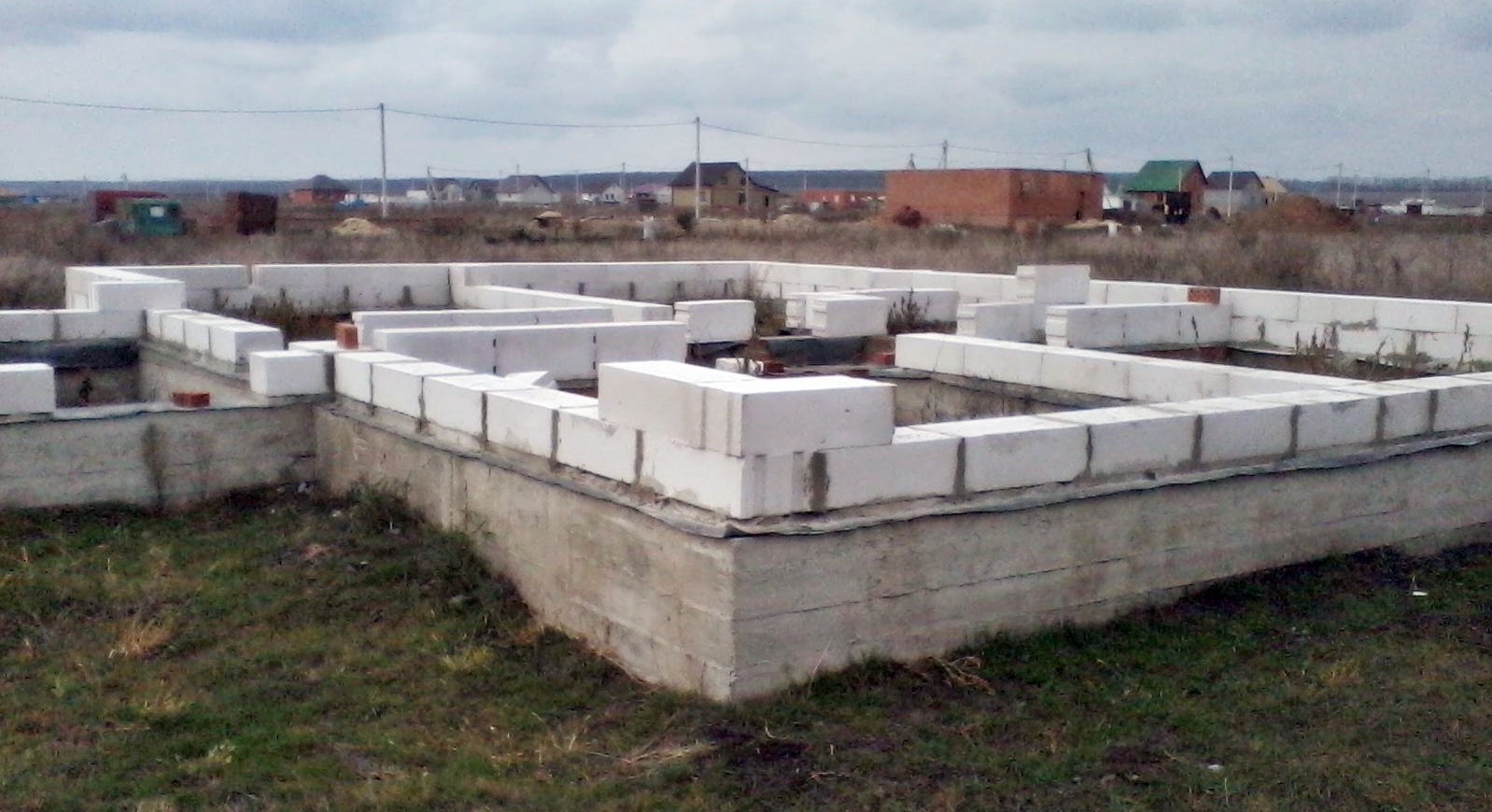
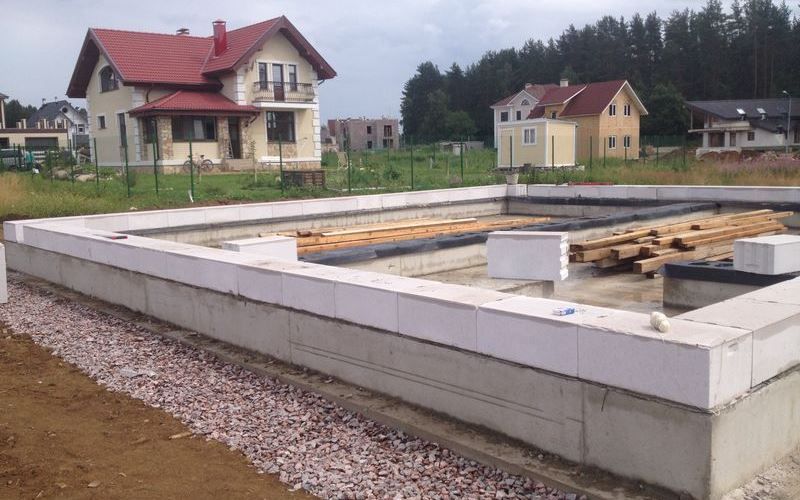
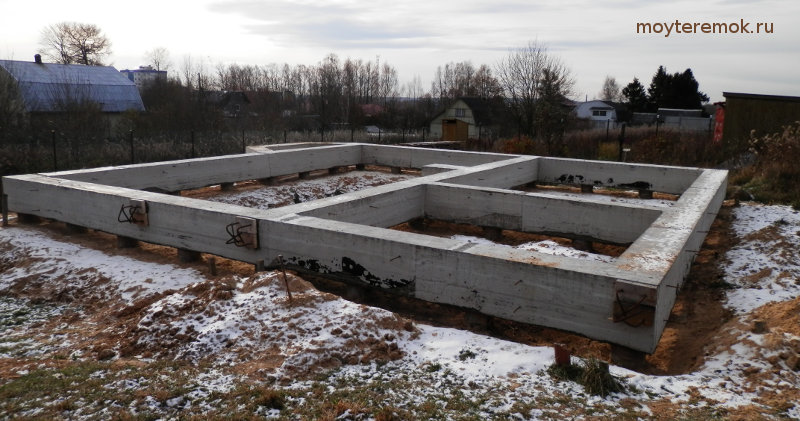
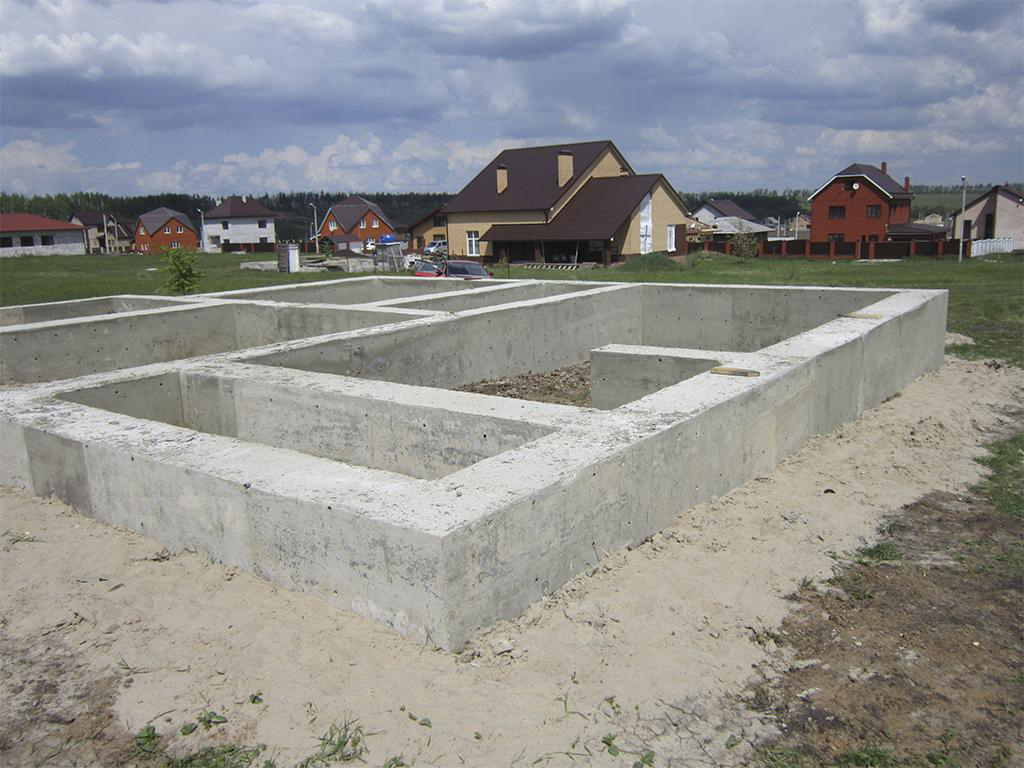
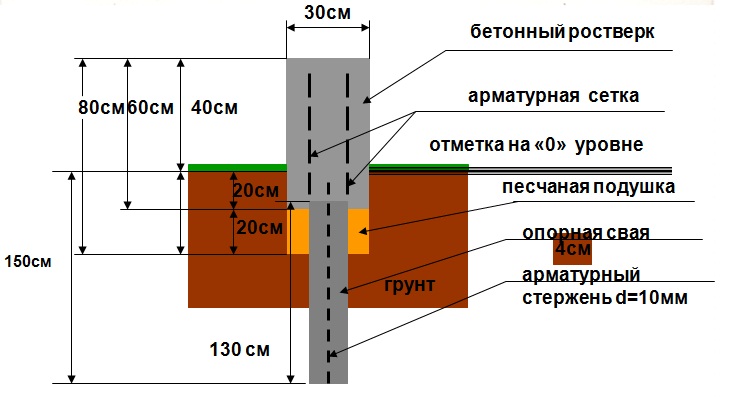
The main types of aerated concrete foundations from foam blocks
 Monolithic tape construction
Monolithic tape construction
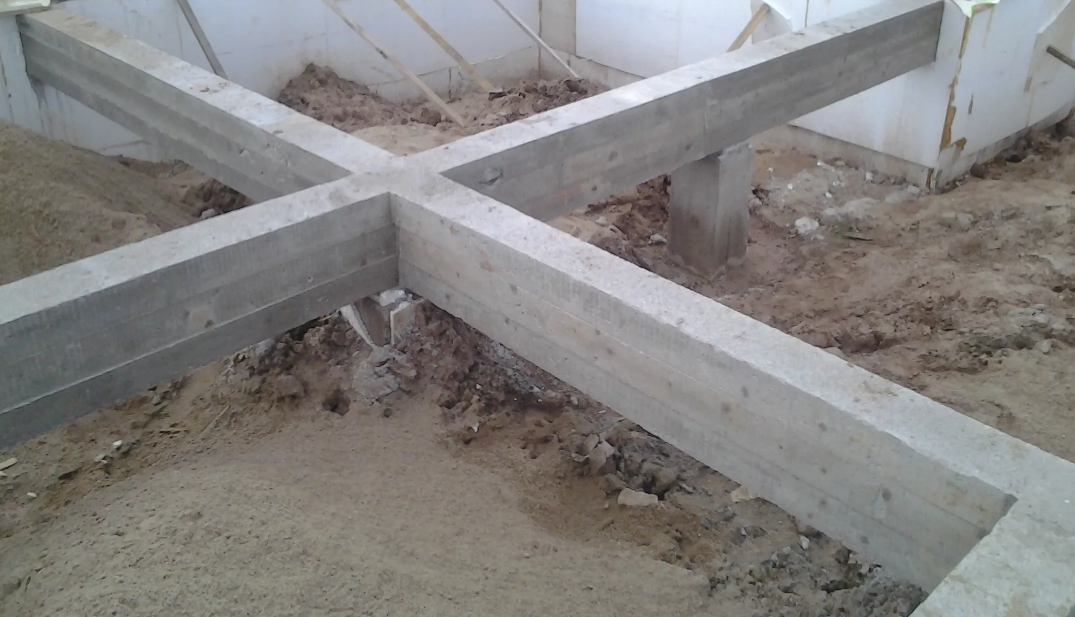
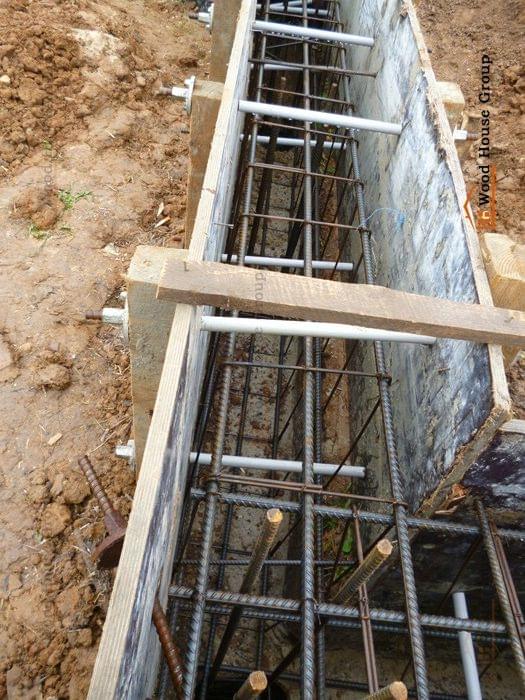
Considering that aerated concrete blocks do not differ in strength, the scope of use of such products is limited. Therefore, all foundations from foam blocks must have powerful reinforcement, and in several directions at once.
Without reinforcement, the base may not withstand even small movements and will slowly collapse. Given this factor, several types of foundations can be noted, during the construction of which it is advisable to use aerated concrete foam blocks.
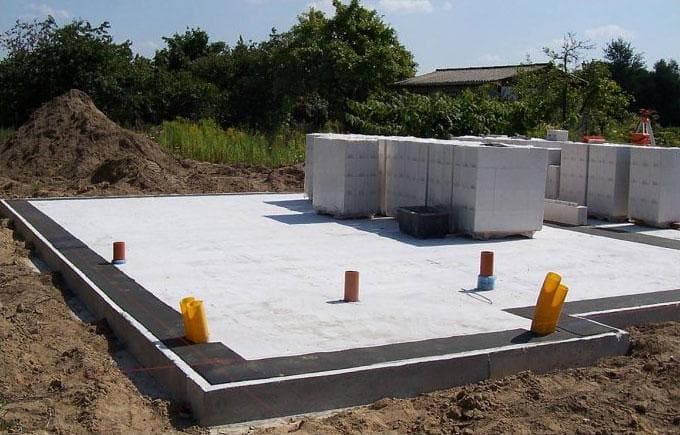
- Slab shallow foundations. They are used for the construction of wooden buildings or structures made of foam blocks on soils with high groundwater levels. In such cases, the reinforcement is able to neutralize the effect of small point deformations on the masonry.
- Monolithic tape structures. They can also be built from foam blocks, but the type of soil and the depth of soil freezing play an important role here. They are of various types, for their construction it is not necessary to carry out large-scale earthworks, but at the same time there are difficulties in protecting the structure from external influences.
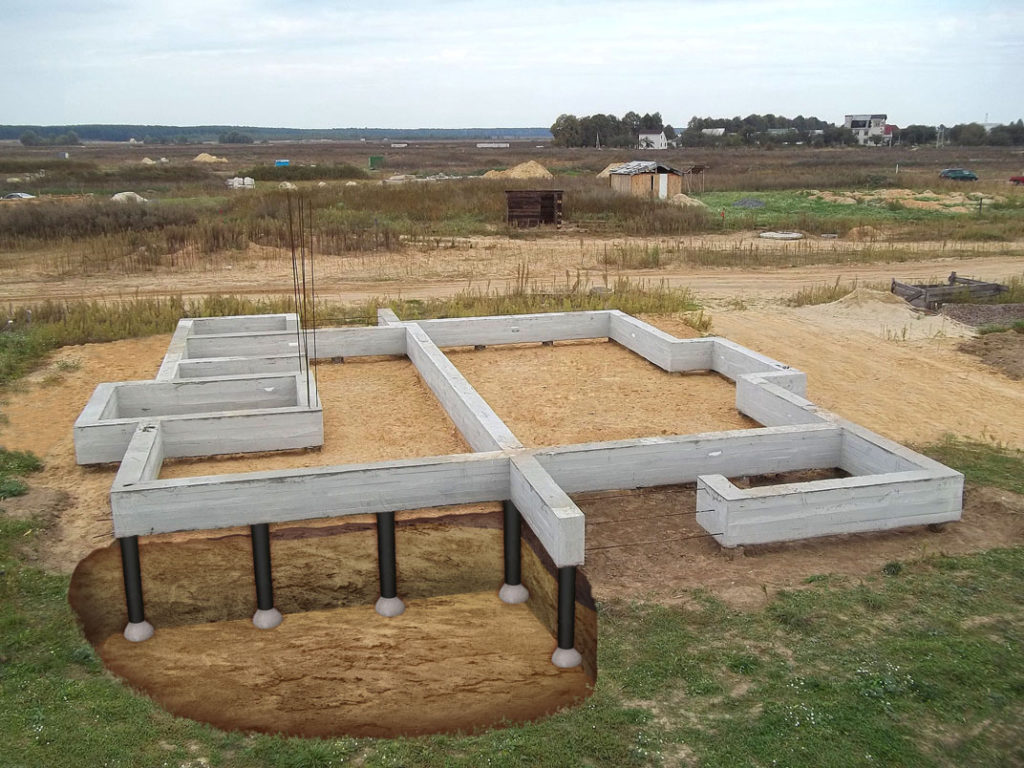
- Columnar foundation made of aerated concrete with grillage. It is this technology that is used in summer cottage construction, because it is cheap, and the pillars of foam blocks are able to withstand minor soil movements and the presence of a good reinforced grillage. As a material for the grillage, a tape structure made of foam blocks, which then becomes a load-bearing base for the walls, as well as wooden beams, are excellent. Therefore, the pile construction is especially popular in small construction.
Calculating the number of screw piles using a calculator
Pile calculator
Side A
Less than 3m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 m9 m10 m11 m12 m13 m14 m15 m
Side B
Less than 3m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 m9 m10 m11 m12 m13 m14 m15 m
Building type
GazeboOutdoorGarageAttachmentBathHouse
Number of storeys
11.52
Building material
FrameCylindrical wood d = 150 Cylindrical wood d = 200 Cylindrical wood d = 250 Bar wood 100x100 Bar wood 150x150 Bar wood 200x200 Gas concrete Foam concrete
Soil selection
Sand Loam Peat, thickness 1.5 meters Peat, thickness 3 meters Peat, thickness 5 meters Peat, thickness 7 meters Peat, thickness 9 meters Peat, thickness 10.5 meters
Number of corners of the house
456789101112131415
Planned height above ground
less than 50 cm more than 50 cm
Stove in the house
No Yes
Number of piles:
Pile diameter:
Pile length:
- Indicate the length of the sides of your structure.
- Indicate the type of building - a gazebo, a bathhouse, a house, a garage, a household structure, etc.
- Indicate the number of floors, if necessary. Note: A house with an attic will be considered a 1.5-storey structure.
- Select the building material for your structure.
- Indicate the type of soil on the site.
- Indicate the number of corners of the planned house.
- Indicate the height of the basement floor from the proposed options.
- Check if you are going to install a fireplace / stove.
- Click on the "Calculate" button.
Of course, this calculation is preliminary, it will serve as a guideline when planning a budget and further ordering.
Examples of calculating the depth of immersion of piles
The immersion depth is calculated empirically. But the depth of the dense soil layers is difficult to calculate, since it is a random variable. Therefore, the only correct option is to drill a test well or immerse an experimental pile, which makes it possible to find out the depth of occurrence of hard soil rocks. This is required by SNiP, and other methods do not provide reliable information.
The depth determined by the trial method is one of the indicators that are used in subsequent calculations. Calculations of the foundation of the pile-grillage type also imply the determination of the number of piles per structure. It is obtained by dividing the estimated weight of the house by the bearing capacity 1 of the support. So, if the conditional mass of the house is 10 tons, and the bearing capacity of the piles is 1 ton, then 10 piles are needed.
The pile distribution scheme depends on the project of the house - its configuration. The most critical areas in the foundation are the corners of the structure. In the design process, they first place a pile at each corner, determine the point of abutment to the load-bearing walls and other loaded nodes. Further, the rest of the supports are evenly distributed for adequate perception and distribution of the load.
Experienced designers advise to provide a certain margin of safety for the foundation so that it can withstand additional loads from operation, extensions.

Pile foundation: screw supports
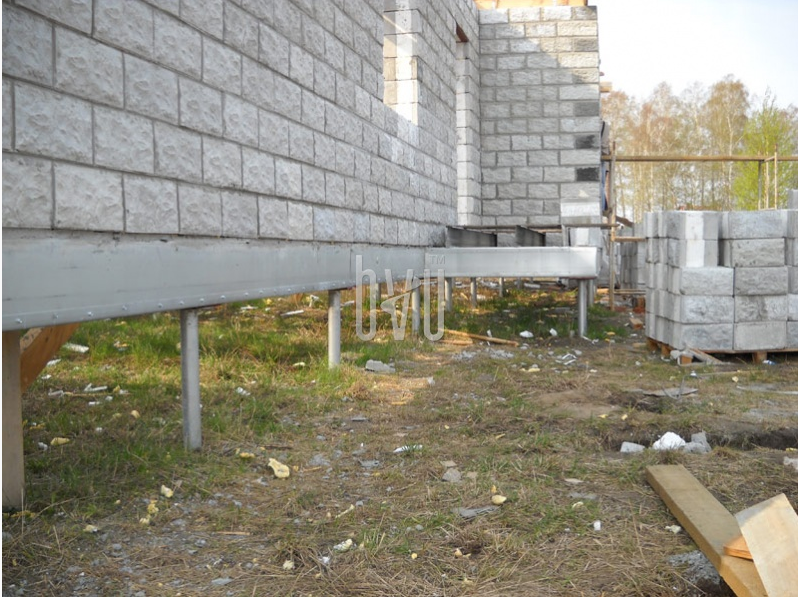
 Due to the ease of construction, a block house on screw piles can be built in a couple of weeks
Due to the ease of construction, a block house on screw piles can be built in a couple of weeks
Consider the option of erecting a residential building made of foam concrete on screw pile supports. For the construction of a foundation of this type, specialized equipment and tools are not required; 3 workers are quite capable of performing the work.
The screw supports represent a metal hollow rod with a pointed end. At the bottom of the supporting elements, blades are welded, which, when the pile rotates, help it sink into the ground. There are two types of blades: welded and cast.
Cast structures have a higher strength and reliability, in the places of the welded seam, especially with insufficient insulation, there is the development of foci of corrosion, which significantly weaken the support, and eventually render it completely unusable.
The rotation is carried out clockwise until the pile stops completely, the work is performed by 2 workers who immerse the pile using a special device. There is a special hole at the upper end of the screw supports, it is through it that a rotary mechanism is passed, which helps the piles to sink into the soil. Private developers often use scrap that is passed through a hole in the pile. Sections of pipes are put on scrap, when exposed to them, the support is screwed in.
We recommend watching a video on how to independently install the supports.
Before starting the immersion of the screw elements, it is worth treating them with special protective compounds against corrosion.
The thing is that the pile coating is injured, passing through the soil. Scratches form on the metal surface, which serve as open gates for corrosion, piles are destroyed especially quickly in wet soil (for example, clay), so additional processing of the elements will never be superfluous.
Grillage device
The screwing of individual pile foundation rods is provided along the perimeter of the building, as well as under the internal load-bearing walls and partitions. The distance between the supports is usually 1.2 to 1.5 meters.
When all the piles are screwed into the ground, you can start trimming the protruding parts of the supports
It is very important to maintain a uniform level of foundation posts that rise above the ground. When trimming, try to remove that part of the trunk in which there was an eye for screwing elements into the ground
After cutting the piles, the hollow part of the pipes is filled with concrete mortar, after which it is covered with a metal head. The headrest is welded to the pile support rod, reliably blocking access to moisture and atmospheric precipitation.
Watch a video on how to build a grillage with your own hands without the help of professionals.
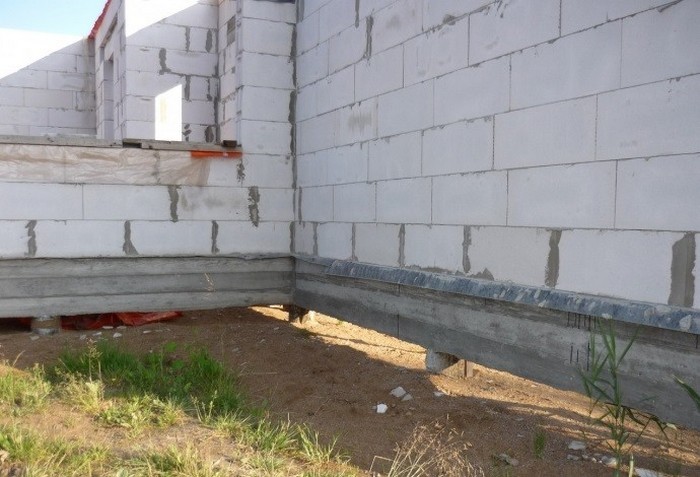
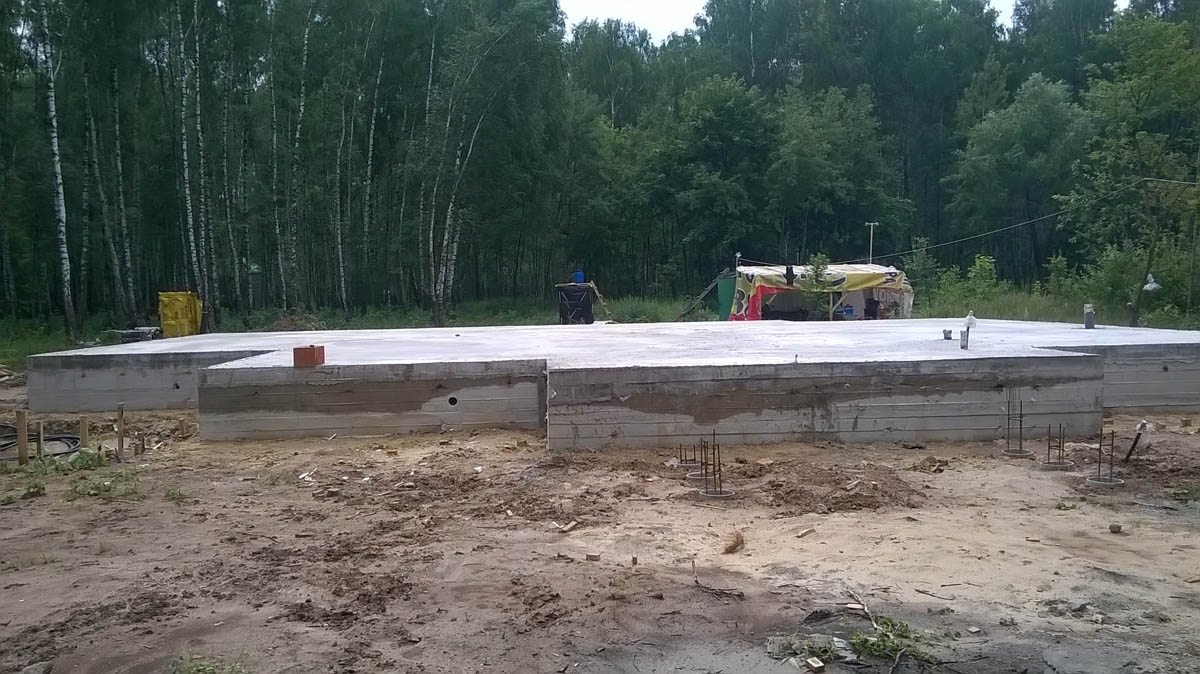
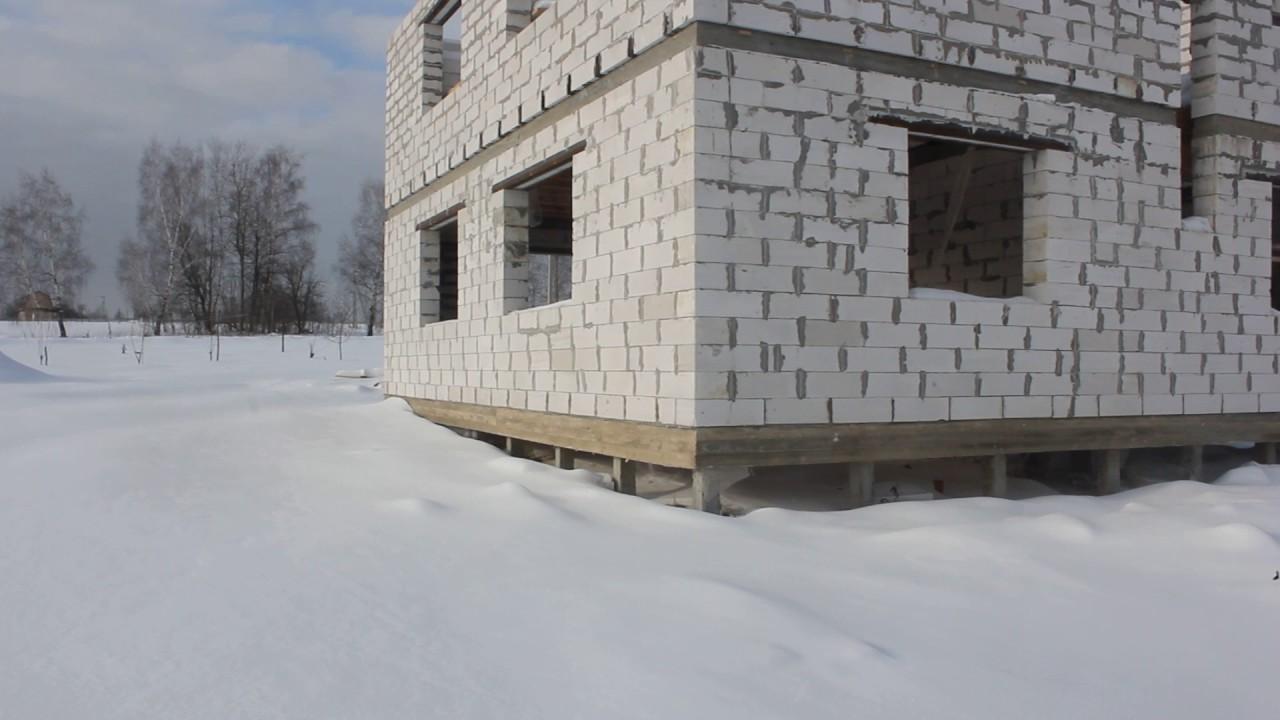
The foundation grillage is made of wood, monolith or rolled metal (beams, channel bars), for a foam block house built on clay soil, the ideal grillage is obtained from a channel laid on the heads in a position with shelves down.
The upper platform of rolled metal has a flat surface on which it is easy to lay waterproofing and the first row of foam blocks. The quality of the walls of the dwelling, the stability of the structure and its strength depend on how smoothly the first row of block masonry is laid.
Base and blind area
A house on stilts usually requires a basement cladding, which will protect the space under the house from winds, precipitation and low temperatures. An equipped plinth helps to keep warm on the first floor of a foam block house, improves the appearance of the building itself and serves to reliably protect the structure from adverse factors.
The pile foundation for a block house can be hidden behind a brick or monolithic reinforced concrete block. The space between the piles can be closed with siding, matching the color to the style of the exterior facade of the building. There are many options for installing a basement, you can always find the most acceptable option for each building.
The blind area is usually performed with a slope from the wall, which helps to protect the foundations and basements from precipitation. The insulated blind area helps to retain heat, a device of this design is especially important in the presence of a basement or technical underground.
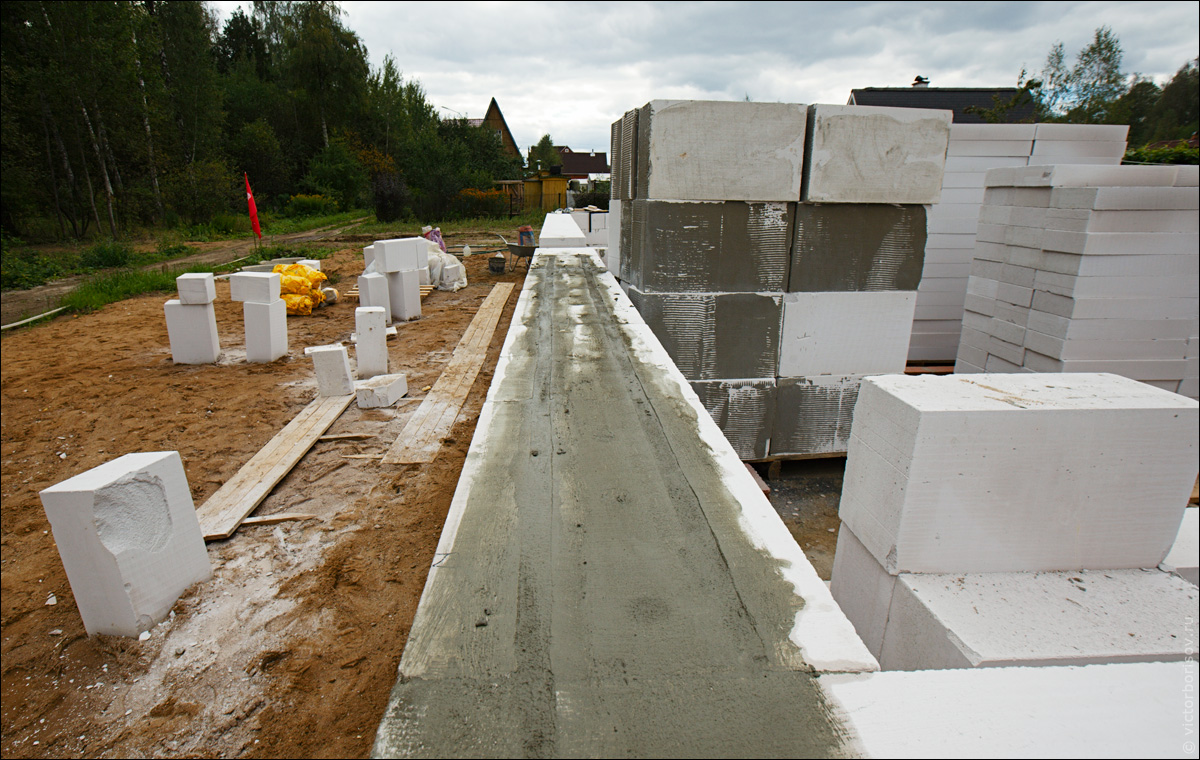
Foam blocks
Foam concrete is a relatively new building masonry material. Foam blocks are made from it for the construction of walls. Foam concrete blocks (PB) have gained great popularity due to their quality characteristics.
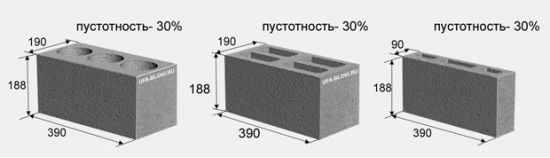 Sizes of foam blocks
Sizes of foam blocks
PB are manufactured at the factory using special equipment. Foamed cement-sand mortar is treated with hot steam under high pressure. The resulting mass is poured into molds, which are sent to the drying chamber for 2 hours. Then the process of final solidification of the foamed mass takes place in the open air.
For the construction of external walls of buildings, PB of standard dimensions are used 390x188x190 mm. Blocks 90 mm thick are used for masonry partitions. There are varieties of foam blocks with lateral locking systems - "thorn-groove". Sometimes the horizontal surfaces of the masonry elements are also made in the form of locks, which provide an almost seamless PB connection.
 Cutting the block with a saw
Cutting the block with a saw
In terms of their quality characteristics, foam concrete blocks surpass many of their counterparts. Foam concrete blocks are used for laying external fences of multi-storey buildings, where the structural function of the building is performed by the frame of the structure (columns + floors). The porous structure of the material gives the blocks high thermal insulation qualities. In winter, the wall masonry does not let the cold through, and in hot weather it keeps the interior cool.
The main disadvantage of the material is its low bearing capacity, therefore, as external enclosing structures, foam block masonry is made in houses with a height of no more than 2 floors.
What types of foundations are suitable for a foam block garage
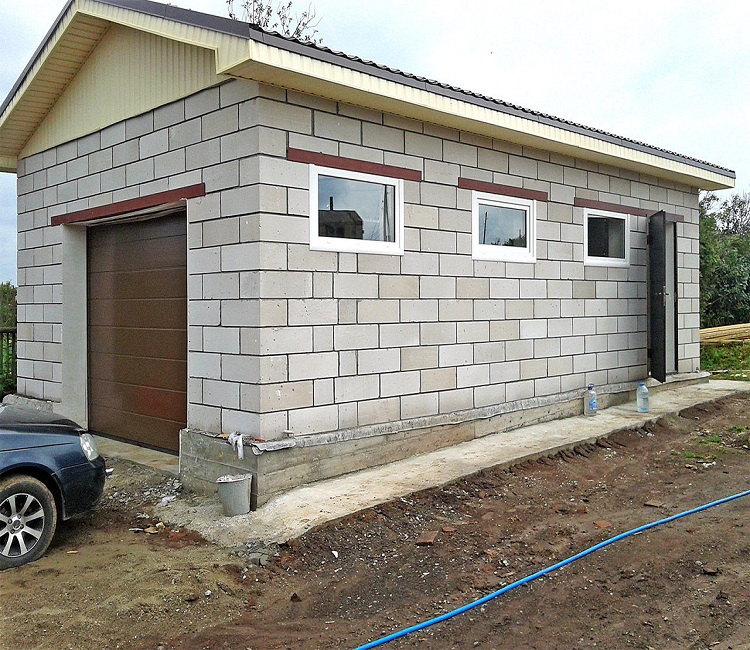 You should get such a nice design at the end of the construction.
You should get such a nice design at the end of the construction.
The foam block is a lightweight building material, the weight of which directly depends on the density. For the construction of garage walls, structural and heat-insulating blocks with a density of 600-800 kg / m3 with a size of 200x300x600 mm are mainly used. Such a building stone weighs 19-22 kg, and 1 m3 of blocks - within 460 kg.
Thus, a low weight load will be applied to the foundation and bases with a high load-bearing capacity are not required. For the construction of a garage from foam blocks, the following types of foundations are suitable:
- shallow belt (MZL);
- plate (if there will be heavy large-sized equipment in the garage);
- screw;
- pile.
When choosing the type of base, in addition to the weight load of the structure, several more parameters are taken into account:
- type of soil;
- soil freezing point (TPG);
- groundwater level (GWL).
Foundation on screw piles
 The installation of such a foundation can be handled without special equipment.
The installation of such a foundation can be handled without special equipment.
On mobile soils with a predominance of sand or sandy loam, it is optimal to build a foundation on screw piles. These supports are immersed below the TPG by 20-30 cm, due to which the pile is firmly held in the ground and does not react to its natural or seasonal (freeze-thaw periods) movements.
For the installation of the foundation on screw piles, the help of expensive equipment is not necessary: a drill, a pile driver, specialized installations. Craftsmen have long developed a technology for installing metal supports with their own hands. For this purpose, a scrap or metal pipe is used, which is inserted into the technological holes under the head. The pile is screwed in by the efforts of several people. The number of supports is calculated based on the requirement: the distance between them should be no more than 3 meters.
Advantages of a foundation on screw piles for a garage from a foam block:
- Lack of labor-intensive and time-consuming earthworks.
- Installation speed.
- Possibility of installation at high ground level.
- Ventilation of the lower floor.
- The possibility of installing hollow concrete slabs on piles, which is optimal for a garage with a car). In this case, the distance between the supports is reduced to 2 m.
Disadvantages:
- The need for a ramp to enter the garage, since the building will be raised above ground level.
- In the absence of the possibility of installing reinforced concrete slabs, the lower floor is made of wood, which is fraught with other disadvantages and operational difficulties.
Pile
Pile is in many ways similar to the foundation on screw piles
A pile foundation has the same pros and cons as a screw foundation. The difference lies only in the material from which the supports are made, and the method of their installation.
For the construction of a pile foundation, the following can be used:
- narrow and long concrete blocks;
- metal or asbestos-cement pipes with concrete poured into them;
- pillars, hand-made with formwork and concrete.
The supports are immersed in the ground below the TPG by 20-30 cm. They are fixed in a vertical position using backfilling and concreting.
Platen
 If you plan to keep trucks in the garage, we recommend opting for a slab foundation.
If you plan to keep trucks in the garage, we recommend opting for a slab foundation.
A slab foundation for a garage made of foam blocks can be arranged in two cases:
- if there will be trucks in the building;
- if there is heaving soil on the construction site and in the region there are harsh climatic conditions.
In the first case, the slab is deepened by analogy with the MZL: by 30-40 cm. In the second, a USHP (insulated Swedish slab) is arranged, which is at the same time a "floating" foundation that compensates for all ground movements.
Insulation is necessary to create favorable conditions for the operation of the garage and its durability in cold climates. Often, such a decision is made when building a garage next to a house, since the presence of a UWB reduces heat loss.
Types of foundations
Foundations are divided into several main types:
- Tape.
- Columnar.
- Plate.
- Pile-screw.
Each type of foundation has its own characteristics, strengths and weaknesses. Since we are talking about a foundation for a foam block bath, some too strong foundation is not required, and the choice of material for construction will not be difficult, any type will do.
An overview of types
- Belt - a base consisting of a continuous concrete strip along the entire perimeter of the building and internal load-bearing walls. The most common type of foundation, tested in thousands of buildings. Possesses high bearing capacity, rather high material consumption.
- Columnar consists of a system of pillars or piles located at the nodal points of the future building - at the corners, at the junctions or intersections of load-bearing walls and piers. Most often, such a foundation is buried in the ground to a depth of 0.5 - 1 m below the depth of soil freezing. When building a bath, you can do with simpler methods - use pillars from separate blocks on a sand bed, without deepening. For a serious mistake of such foundations, see the video below.
- Screw piles. Such a foundation is most beneficial in areas with difficult terrain, with a slope or folds. Screw piles are screwed into the ground to solid layers, from above they are cut off or built up until a single plane is obtained on which the grillage supporting the walls is mounted. They allow you to do without leveling the relief of the site, which requires technology and is not always possible.
- Plate. This is a monolithic concrete slab laid under the entire building. Such a foundation is also called “floating”, since the slab does not sink into the ground and moves with the building when the soil moves, for example, seasonal when snow melts, etc. It is used on soft soils, capable of carrying significant loads. The high material consumption, and, as a consequence, the high price of such a foundation is compensated by the fact that the foundation itself is the floor of the basement floor.
Useful video
The video below shows how a foundation made of screw piles will help to erect a structure with relatively low (compared to concrete) costs on relief terrain, slopes and even over water:
The following video shows a serious mistake made when erecting columnar foundations: