Video
Video instruction for calculating the depth for the foundation.
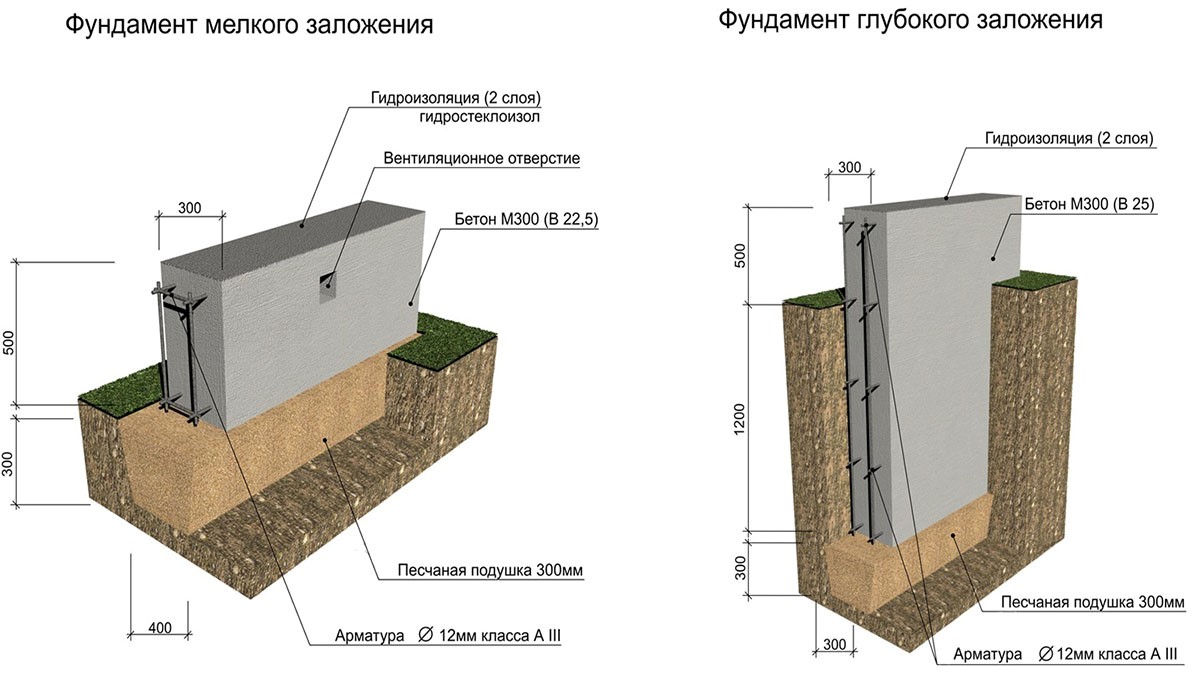
Shallow (MZF)
The main feature of such foundations is that the depth of any shallow foundation does not reach the depth of soil freezing. The choice of this type is explained by a number of advantages:
- MLF will cost less than a buried analogue.
- It is possible to equip the basement (which in the previous case will not work).
- Possibility of construction on heaving soils. To do this, you need to correctly make the foundation cushion, as well as reinforce the structure with reinforcement.
- Due to the minimum area of contact with the ground, shear forces act on the base to a minimum.
MLF is built in the following cases:
- When erecting light buildings without a basement and basement room.
- In the presence of a high level of groundwater (but more than 1 meter from the surface).
- If the ground is strong enough.
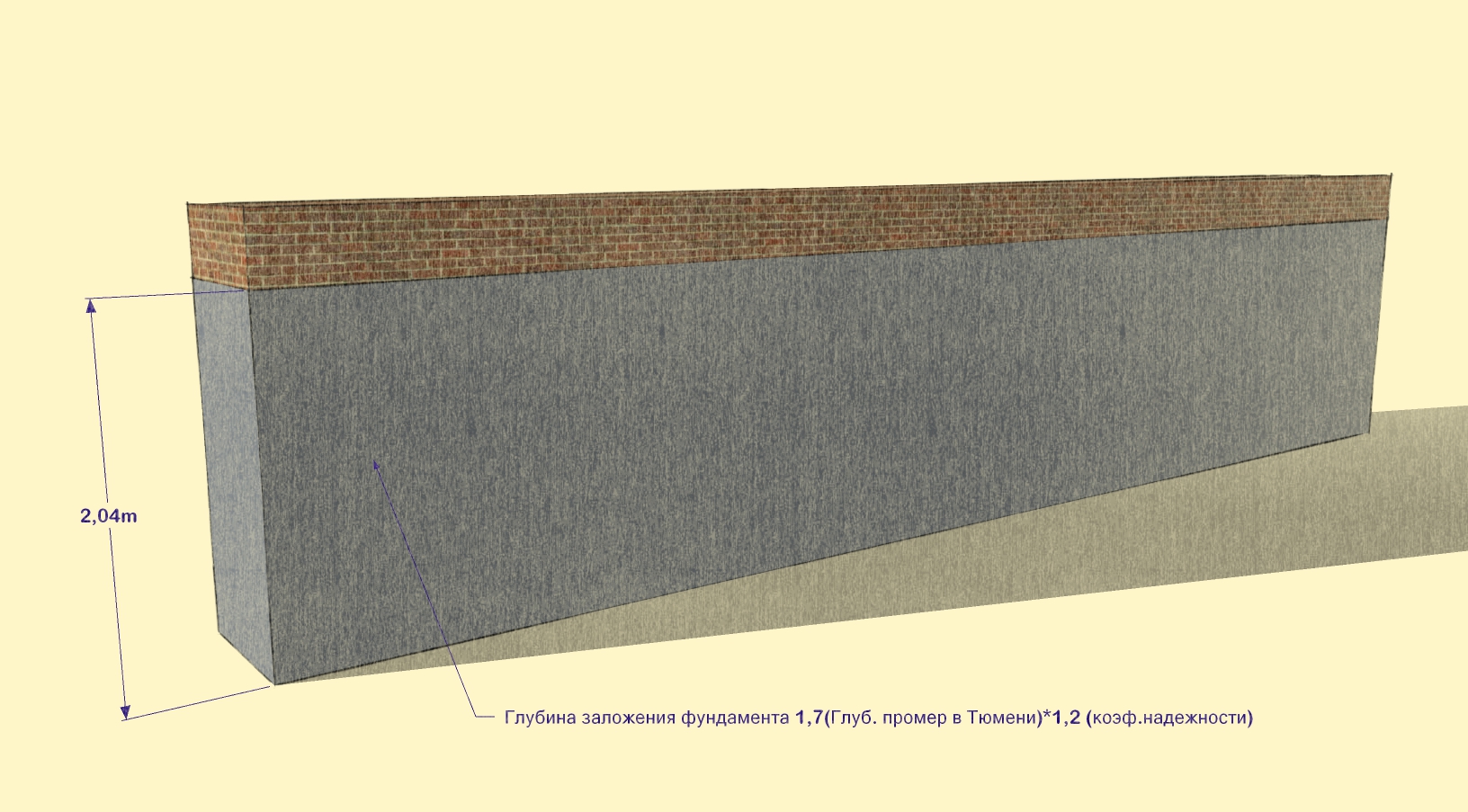
The minimum foundation depth may vary. Depending, for example, on the level of freezing, it looks like this:
- With a freezing depth of up to 3 meters - 0.5 - 0.75 m;
- If the soil freezes to a great depth, the foundation can be laid a meter below the soil level.
The main indicator is influenced by more than one factor. Therefore, it is impossible to determine the specific depth of the foundation for, for example, a one-story house. However, if you calculate everything correctly, such a foundation will last a very long time.
Recessed
Despite the high costs, such foundations are quite common.
The minimum depth of the foundation of such a foundation falls below the level of freezing of the soil (as a rule, by 30 - 40 centimeters). But not only this factor is decisive. So, the depth of the foundation for a dimensional concrete two-story house will be greater than for a brick building on one floor. Other factors must also be taken into account (for example, type of soil, level, groundwater).
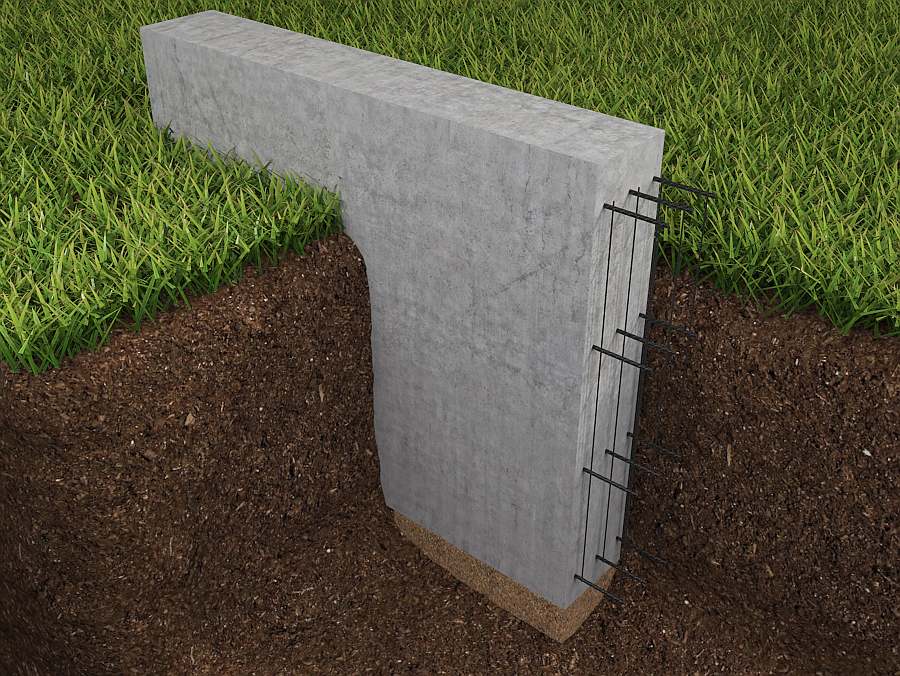
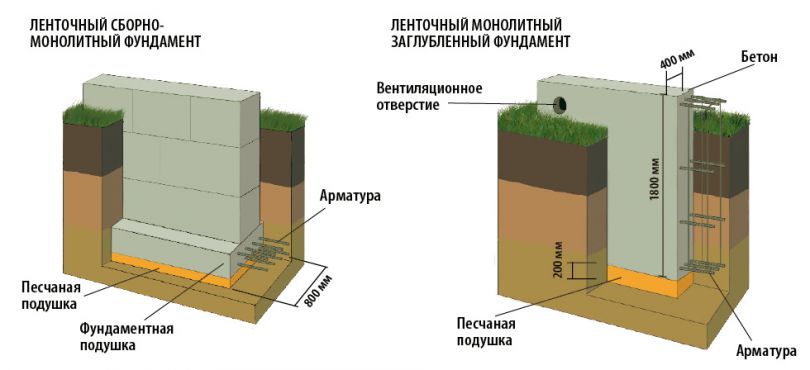
The bases of deep laying, as a rule, are made of tape. It seems not surprising, because tapes are built most often. But there is a good reason here. The fact is that for deep foundations it is necessary to excavate the soil to a great depth. And, of course, it is easier and more economical to dig a trench than a foundation pit.
Ground and depth
Starting to determine the optimal depth of the strip foundation, first of all, you should pay attention to the quality of the soil. In many ways, it is this characteristic that determines whether it is generally possible to erect a foundation of this type in this place, and if so, how deep
The depth varies depending on the type of soil as follows:
- • rocky rock is particularly stable and durable, because of this, the construction of a strip foundation is possible simply on its surface, without any deepening;
- • silty soils are not suitable for the construction of a strip foundation, since their strength is too low, and it is extremely difficult to predict their behavior during freezing and flooding;
- • Soil with a high content of peat before erecting the foundation for the house requires the creation of drainages and cushions of sand and gravel, the thickness of which should be at least half a meter. Taking this into account, it is easier to erect a pile-strip foundation on such a soil, the depth of which is made equal to the depth of a strong layer on which the piles will rest;
- • Sandy soil is more stable if it is made up of large particles.Construction on fine sandy soil is impossible, but on medium and coarse sand it requires a foundation depth of half a meter to 80 centimeters;
- • coarse-grained soil is a very reliable type and in terms of its qualities is in second place after rocky soil. On such a surface, a shallow foundation can be erected without fear. In the same case, if a significant admixture of fine sand and clay is found in this soil, during the construction of a strip foundation, the depth of the foundation should be about half a meter;
- • clay soil requires deepening the base of the building at least 25 centimeters lower than the level of maximum soil freezing.
Considering all of the above, before starting the construction of the foundation, it is required to correctly determine the soil on which the structure will stand. Without this, it will not be possible to carry out a competent calculation of the depth of the strip foundation.
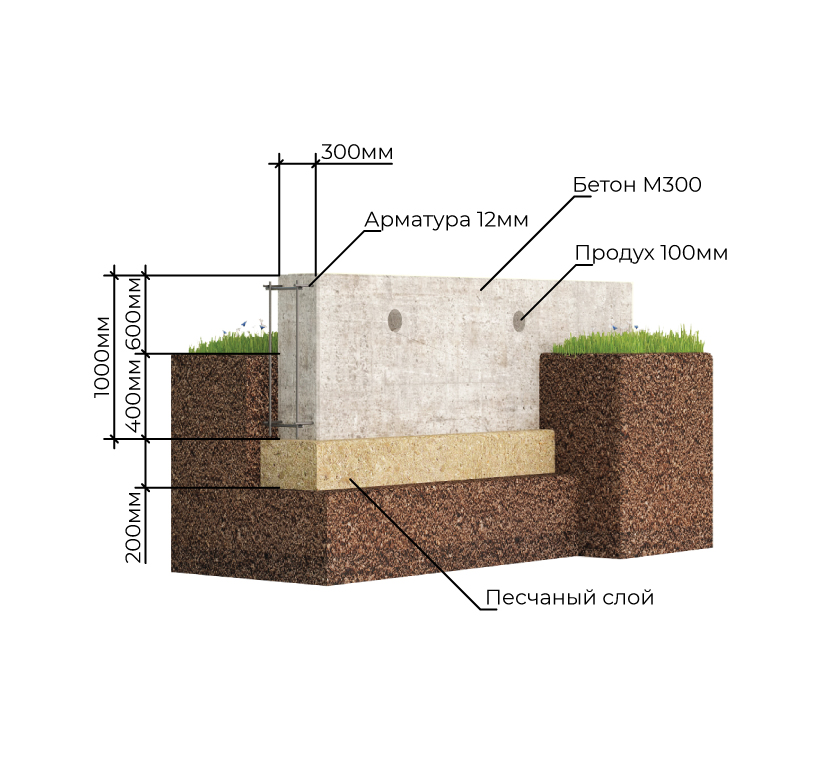
What is its device
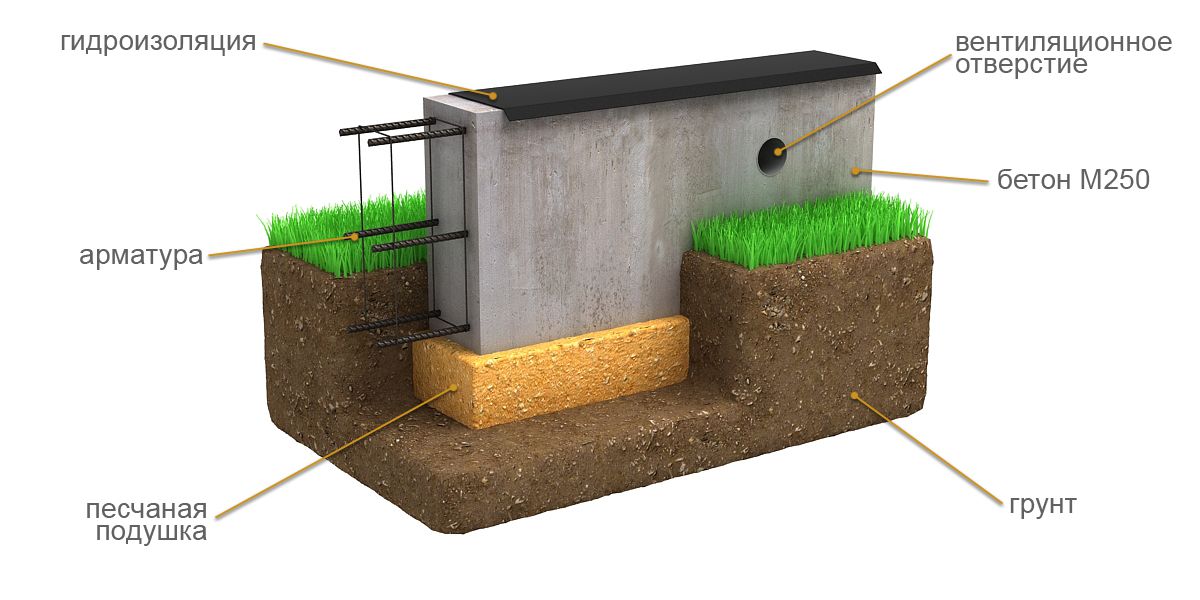
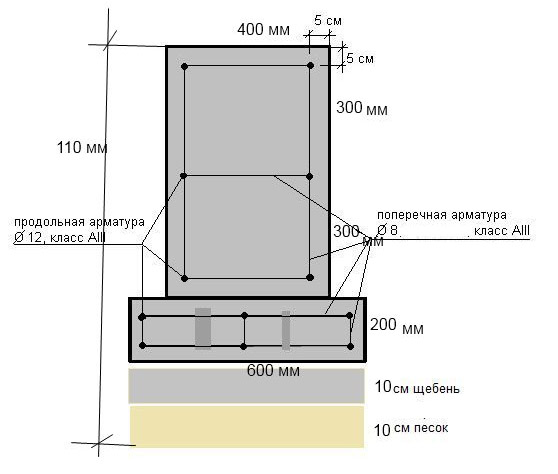
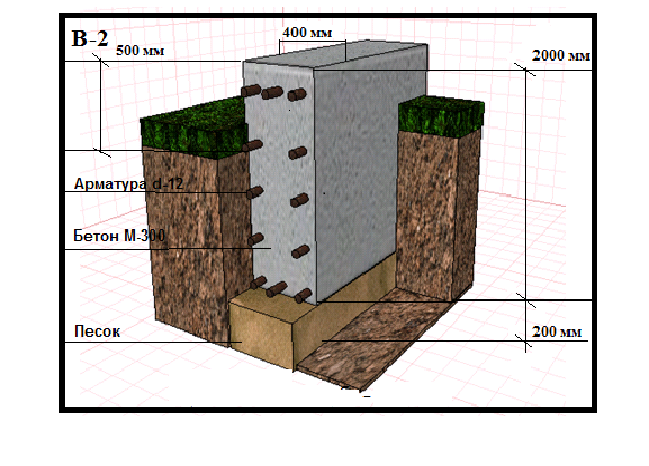
The strip foundation is an extension of the load-bearing walls, immersed in the ground. During construction, a trench or foundation pit is first dug, on the bottom of which a layer of sand cushion is poured. Then the formwork is installed, the reinforcing cage is assembled and the concrete is poured.
This is a schematic and abbreviated description of the technology for creating a monolithic tape; in practice, the number of stages can be increased.
To create prefabricated foundation views, the sequence changes - after a layer of sand cushion, a concrete base is installed (or poured), on the surface of which a tape of bricks or block elements is built.
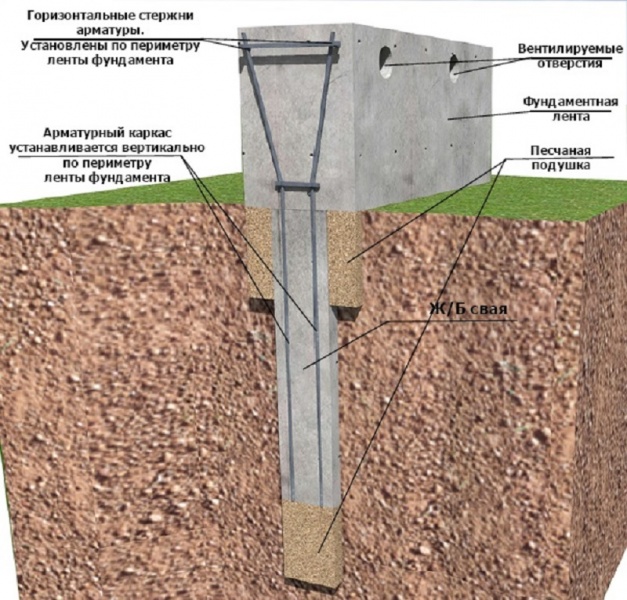
There are combined base options, such as pile-tape. They consist of an ordinary tape, to which piles are attached as additional supports, reaching up to dense layers of soil.
Redistribution of loads allows you to build houses on problem soils, loose or weakly bearing.
His photo in section:

Foundation depth - determining factors
 How deep should the foundation be laid
How deep should the foundation be laid
When determining the type of future foundation, and deciding on the deepening of the supporting structure, take into account the conditions in which the building will be used.
It is important to pay attention to the following points:
- geological aspects;
- the impact of climatic factors on the depth of the foundation;
- the influence of the structural features of the building on the level of the foundation.
Before starting the calculations and choosing the type of foundation, it is necessary:
- perform soil analysis activities at the construction site;
- study the landscape, as well as thoroughly clear the construction site;
- develop a building plan and calculate the mass of building structures.
At the stage of collecting information about the features of the construction site, a number of factors should be analyzed:
- the nature of the soil at different depths;
- the average statistical amount of precipitation throughout the year;
- level location of aquifers;
- the depth of freezing of the soil;
- fluctuations in height and features of the relief at the construction site.
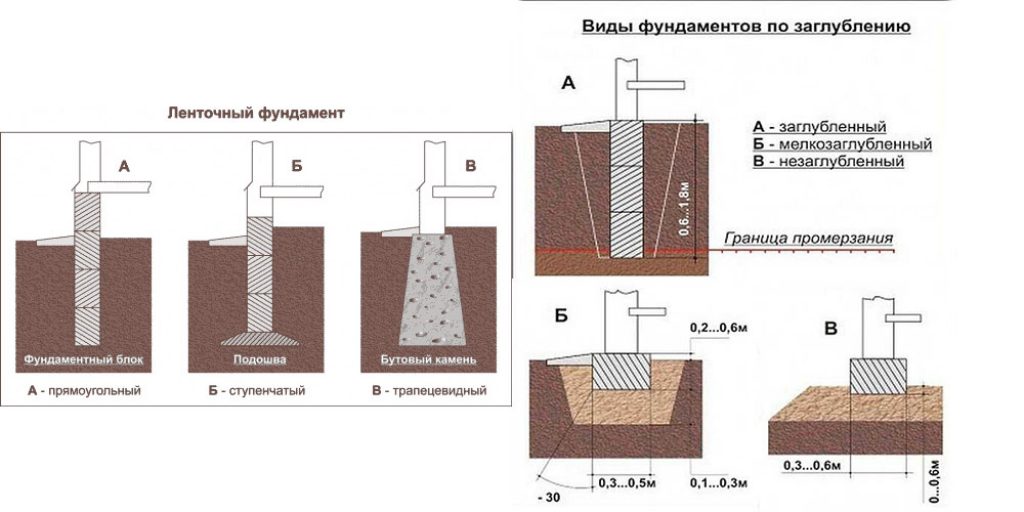
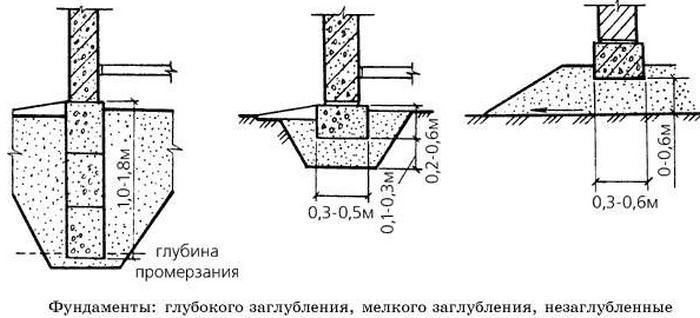
 Types of foundations by the method of deepening
Types of foundations by the method of deepening
The decision on the type of foundation and the level of its laying is made taking into account the following points:
- building features incorporated in the project;
- the mass of the building;
- the presence of a basement room;
- the level of the location of underground utilities.
The average temperature in this area throughout the year and climatic conditions also affect the size of the pit under the base.
Determining what determines the depth of the laying of support structures, you should pay attention to climatic factors:
- for buildings planned for construction in southern latitudes, it is necessary to ensure a minimum displacement of the trench base from the soil level by 0.6 m;
- when performing construction activities in a cold climate, the level of deepening of the foundation sole into the soil can reach 1.5 m.
For each type of soil, the freezing level is different:
- highly weathered soils, which include sandy loam, loamy and clayey soils, freeze to a level of 0.5-1 m;
- medium-loamy sandy soils containing inclusions of clay particles and sandy fraction freeze to a depth of 0.6–2 m;
- soils not prone to heaving, containing sandy particles, sandy loam, loam and clay inclusions, have an increased level of freezing up to 1–3 m.
 The factor of the depth of freezing of the earth when laying the foundation
The factor of the depth of freezing of the earth when laying the foundation
The tendency of the soil to frost heaving is influenced by the following factors:
- moisture concentration in the soil;
- the level of the location of groundwater during freezing.
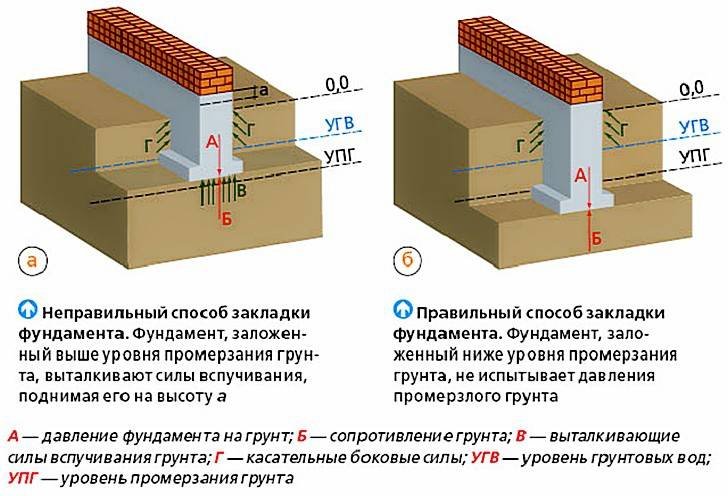
An error in performing calculations can lead to deformation of the base.
As a result of this, negative aspects are possible:
- shrinkage of the structure;
- the appearance of cracks on the walls;
- violation of the overall stability of the building.
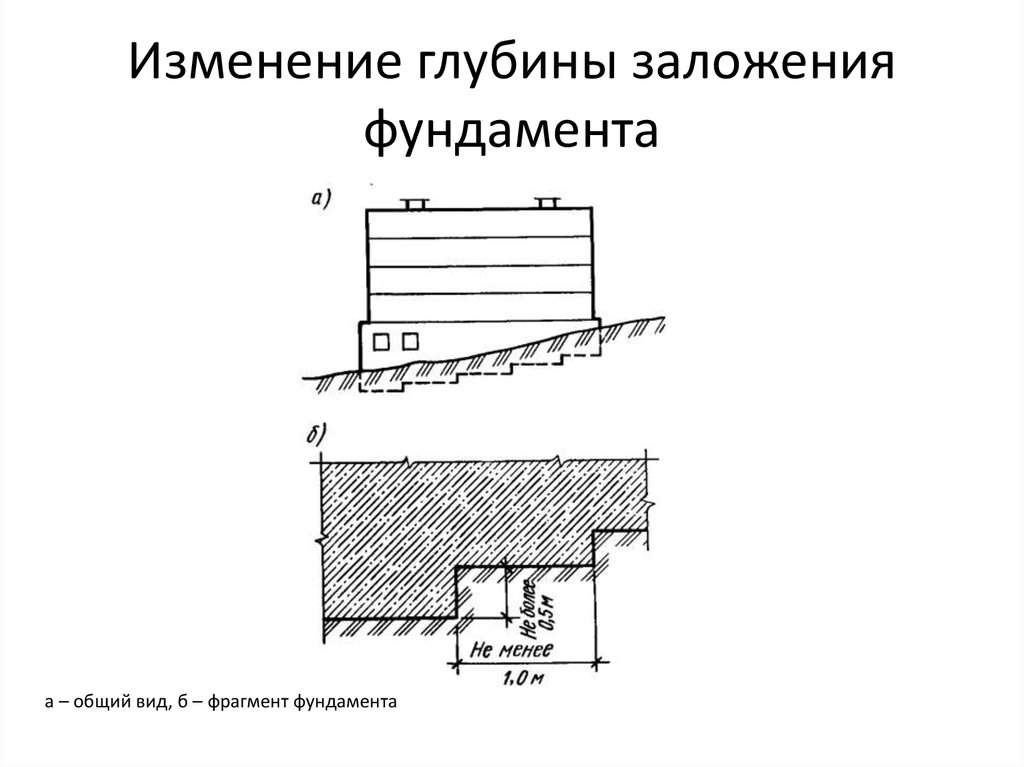
Along with the nature of the soil and the level of freezing, an important factor is the terrain. The building codes contain requirements for leveling the site before construction begins. However, for areas located on sloping terrain, as well as on rocky soil, it is not always possible to level the building area. In this situation, the minimum level of the foundation is determined by the lowest point of the inclined platform. For such conditions, preference is given to a pile base, as well as a screw base, which is also not afraid of height differences.
After analyzing the natural factors, building features and determining the nature of the soil, it is necessary to decide on the design of the foundation for the future home.
 Factors affecting the foundation of the building
Factors affecting the foundation of the building
The following options are possible:
- shallow or deeply buried strip foundation;
- columnar base in the form of piles or reinforced concrete columns;
- slab construction of the base of the structure.
Where deep foundation is applied
The excellent load-bearing characteristics of the foundation have made it the de facto basic type for high-rise brick and precast concrete buildings. At the same time, when carrying out survey work, it is inappropriate to focus on deep burial in places with an elevated groundwater level. In such cases, all efforts can be reduced to zero, there will be no firm support on the ground.
Deep reinforced concrete foundations are expensive structures, the construction of which requires a fairly large financial and time costs.
It is rational to build deep foundations in soil conditions, in which the depth of soil freezing does not exceed 2.5 meters, and the groundwater level is less than the GPG.
| Expert advice! When laying foundations to a depth of more than 2-2.5 meters, the labor intensity and cost of earthworks associated with digging trenches and pits, and the amount of required consumables, increase dramatically. |
In such cases, it would be more rational to use pile foundations based on bored or driven reinforced concrete piles, the bearing capacity of which will not be less, and the total cost will be an order of magnitude lower.
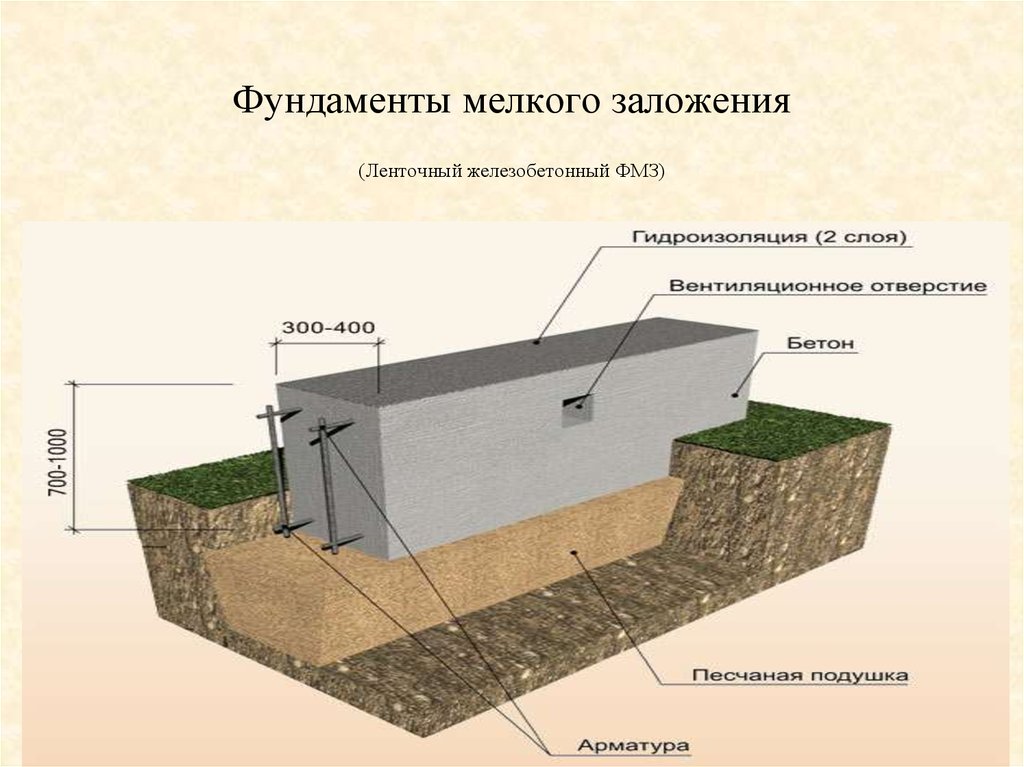
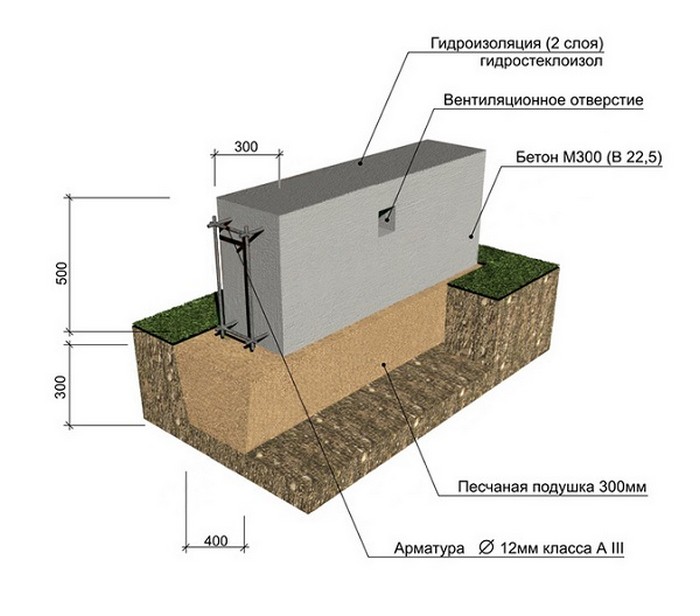
Shallow foundations
This type of foundation is suitable for the following applications:
- building a light house without a basement or basement;
- high level of groundwater location (but more than 1 meter from the earth's surface);
- sufficiently good strength characteristics of the base soil.
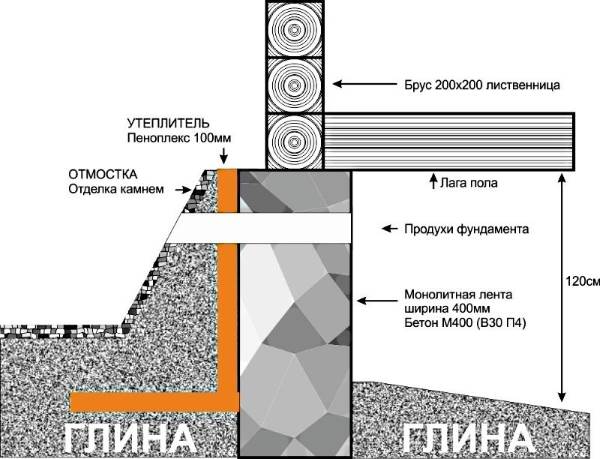
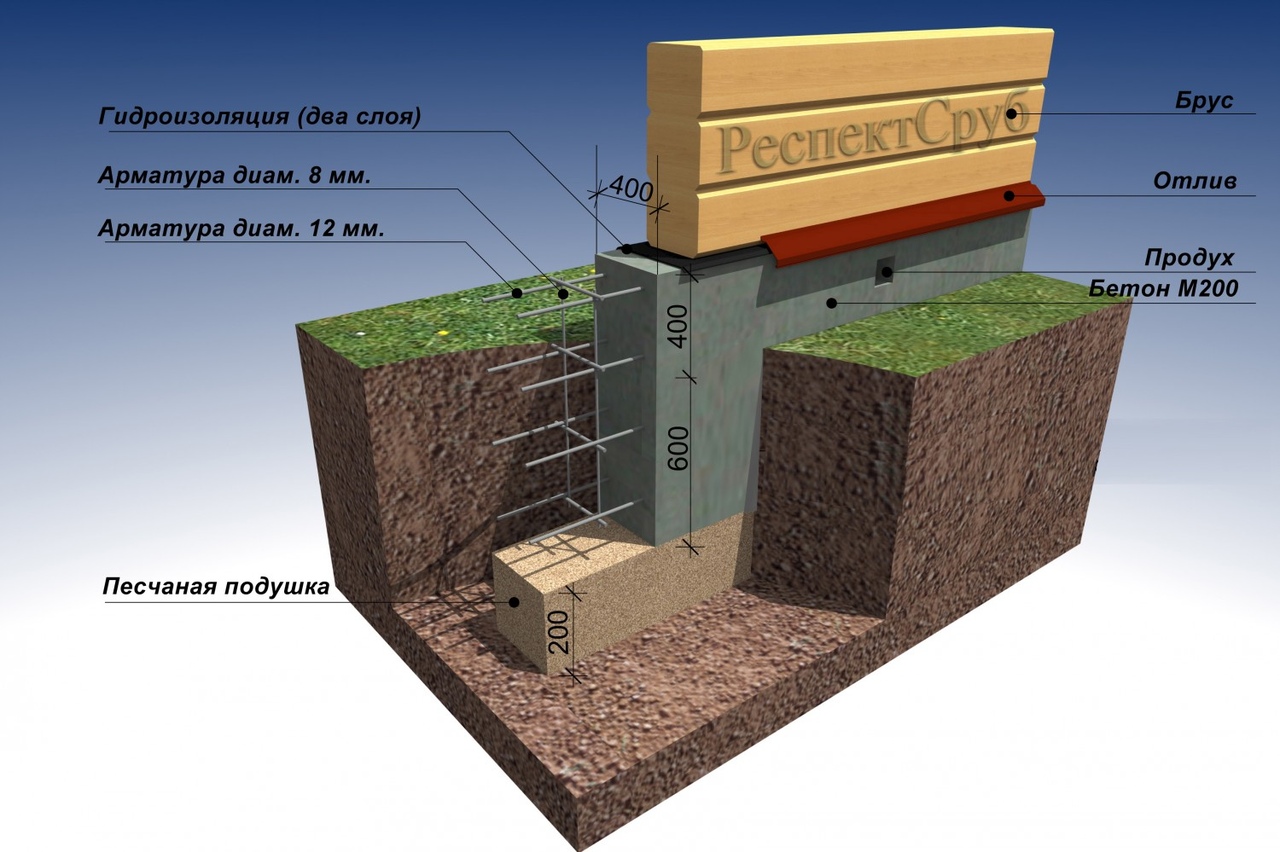
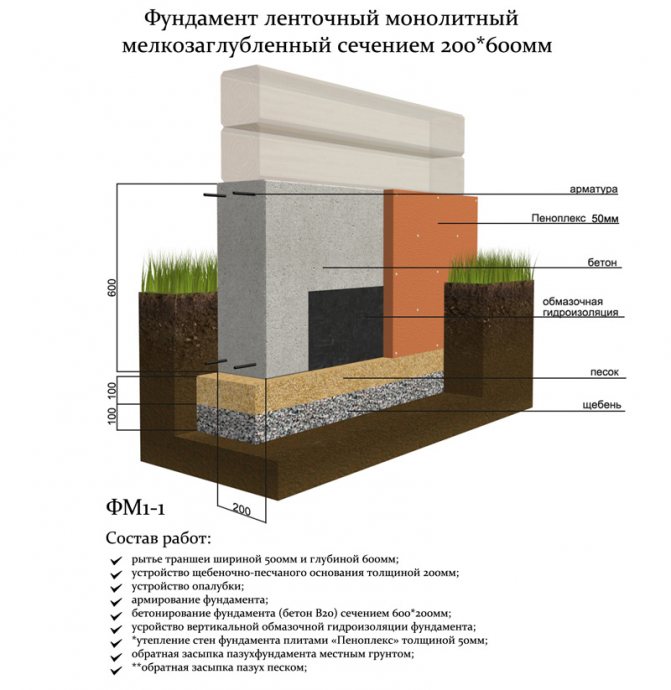
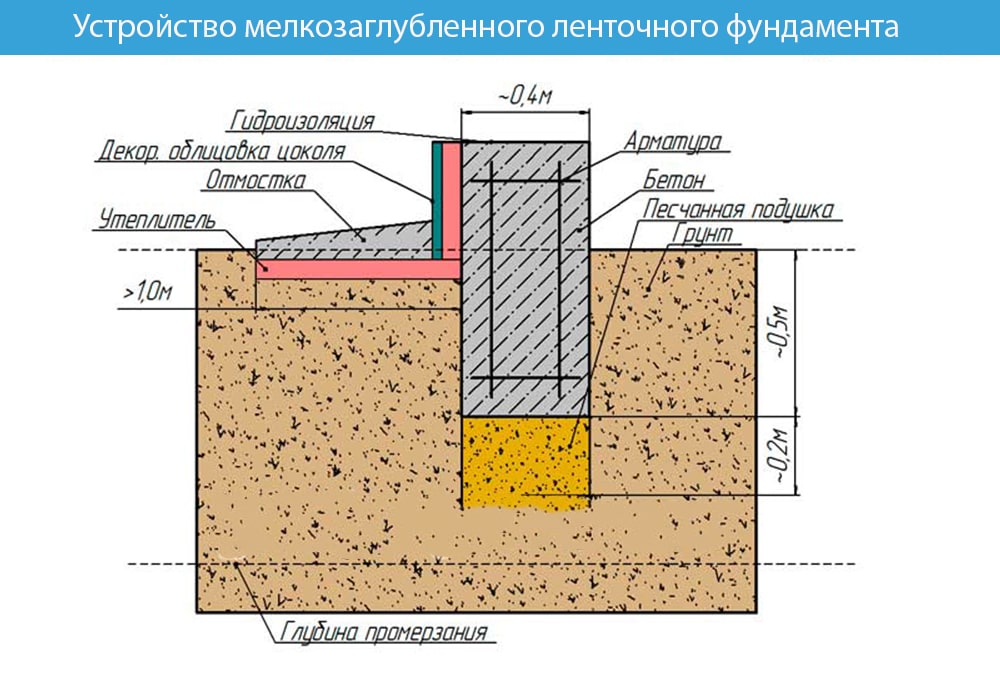
Scheme of insulated shallow strip foundation
When building such a foundation, you do not have to dig deep into the ground, which allows you to reduce labor and time costs. The minimum depth of laying a shallow foundation for conventionally non-porous soils (sandy, coarse-grained) may be as follows:
- at a freezing depth of up to 3 m - 0.5 m;
- up to 3 m - 0.75 m;
- more than 3 m - 1.0 m.
To prevent damage to the structure by frost heaving forces and water, the following measures must be taken:
- Waterproofing.Like any other foundation, a shallow one requires reliable protection from moisture. The blind area protects the structure from rain and melt water. Bituminous mastic is applied to the vertical part of the foundation along the entire height or rolled waterproofing materials (linokrom, waterproofing) are glued.
- Insulation of the foundation in height and the device of a warm blind area. Extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex) can be used as a heat-insulating material. The thickness of the insulation is selected by heat engineering calculation. For most regions of the country, you will need to install 100 mm of foam. Mineral wool should not be used as thermal insulation. Insulation is laid outside along the entire height and under a concrete or asphalt blind area.
- Sand pillow. It prevents frost heaving. It is laid from sand of medium or coarse fraction with layer-by-layer compaction. The thickness of the pillow depends on the actual strength characteristics of the soil, on average it is 30-50 cm.
- Drainage of ground and rainwater from the structure. This function is taken over by drainage and storm water drainage. Even with a sufficiently low level of groundwater location, these measures are necessary, since during the period of rains or melting snow, the soil is highly saturated with moisture. If we allow the simultaneous impact of water and low temperatures on the foundation, the consequences can be irreversible. The most common type of drainage is wall drainage. The perforated pipe is laid in a layer of gravel wrapped in geotextile. The maximum distance from the drainage pipe to the foundation is 1 meter. The depth of the foundation is 30-50 cm below the base of the foundation.
In the case of shallow foundation slabs, an insulated Swedish slab (USHP) will be a modern solution. This is the base that houses the underfloor heating system and some utilities. For production, a permanent formwork made of expanded polystyrene is used, which subsequently plays the role of a heater.
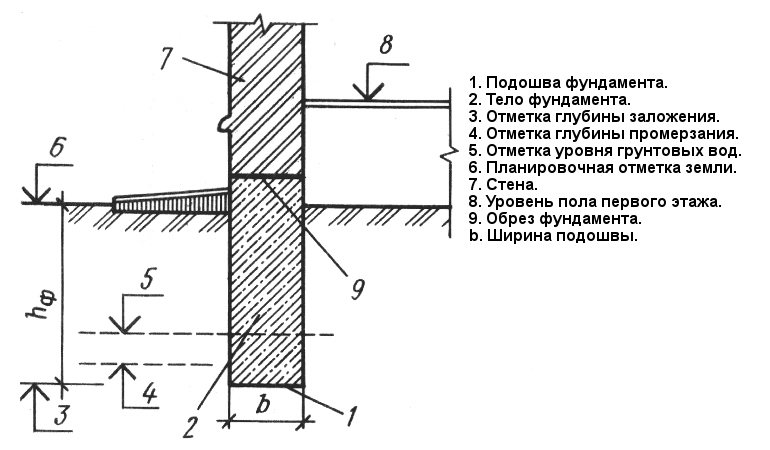
The depth of the foundation is one of the decisive factors affecting the durability and reliability of the foundation
It is important to take into account all the requirements, and if it is impossible to fulfill them, take the necessary measures to protect the structure
Good publicity
Video description
What are the features of concrete driven piles? We will talk about the pile foundation in our video: Since this technology is relatively new and not all construction companies can boast that they have mastered it perfectly, there are still cases when, some time after construction, the house sags somewhat under some piles. But foreign experience shows that such incidents occur only when the technology is not followed, and if the installation of the pile foundation is done according to all the rules, then it will become a reliable support for the house. In addition, piles make it possible to erect buildings even on soils with a high degree of mobility.

Sectional pile foundation
The depth of the strip foundation
As a rule, ground waters (their level) are always subject to compulsory research during geotechnical surveys. Of course, it is obvious that the depth of the foundation should be at least half a meter above the water table. There are cases when the foundation is laid below their level, but this is very rare and at the same time expensive, since in such cases special drainage and forced pumping of water are required.

Also, another factor affecting the depth of the laying is whether the building will have a basement floor or not. If a basement is provided, in this case the base of the base is arranged below the floor of the basement, but do not forget that it must be above the groundwater level.
During the construction of the foundation, as well as during its preliminary design, as a rule, in all cases, a drainage cushion is created under its supporting surface, which has a thickness of no more than 20 cm, while non-porous materials are used for it. The most optimal option is a sand-gravel mixture or sand with coarse grains. Thanks to this filling, the load on the soil will become more uniform, and it also has the ability to quickly remove excess moisture from the soil under the foundation.
Note that in different regions, depending on the properties of the soil, there may be completely different depths of the foundation. For example, if the foundation is deeply buried, in this case tangential lateral forces can even lead to the destruction of the structure. In order to avoid such processes and to significantly reduce the effect of lateral heaving forces, it is necessary to use high quality reinforced concrete reinforcement.